Abstract
In the present paper, strong deflection gravitational lensing is studied in a conformal gravity black hole. With the help of geometric optics limits, we have formulated the light cone conditions for the photons coupled to the Weyl tensor in a conformal gravity black hole. It is explicitly found that strong deflection gravitational lensing depends on the coupling with the Weyl tensor, the polarization directions, and the black hole configuration parameters. We have applied the results of the strong deflection gravitational lensing to the supermassive black holes and and studied the possibility of encountering quantum improvement. It is not practicable to recognize similar black holes through the strong deflection gravitational lensing observables in the near future, except for the possible size of the black hole’s shadow. We also notice that by directly adopting the constraint of the measured shadow of , the quantum effect demands immense care.
1. Introduction
Conformal (Weyl) gravity is a curious gravitational theory in four dimensions defined through the action provided by the Weyl tensor square, where . The Weyl’s transformation of the metric () is a specific symmetry of that action. This theory has appeared periodically for many causes. It was studied as a desirable UV culmination of gravity [1,2,3] and also for the useful setting up of supergravity theories [4,5] as a result of twistor string theory [6]. Recently, conformal (Weyl) gravity, formulated by Weyl’s pure square action, has been considered a good substitute for Einstein’s gravity. From the symmetry of conformal gravity and the equation of motion, the conformal solution to Einstein field equations emerges naturally as a solution to conformal gravity. Basically, depending on the state of the Neumann boundary, gravity may agree with Einstein’s solution [7,8]. Moreover, in contrast to Einstein’s gravity, conformal gravity has been proven to be repetitive in terms of four dimensions [9], resulting in exciting forms of quantum gravity [10]. Another interesting feature of conformal gravity arises from cosmology. Though Einstein’s gravity can fully explain the physics at a solar system scale, there are some unresolved issues when considering large scales, which include incompatibility detection of galactic curves and accelerating space. As a result, anonymous organizations that are “dark matter and dark energy” should be introduced to address these problems of non-compliance. Therefore, one may think of the possibilities for changing the state of gravity for the explanation of physics at larger scales while preserving the right character at the solar system scale. Moreover, conformal gravity allows for more solutions than Einstein’s, which can yield effective energy in tandem with this visual object, making it an attractive gravitational view [3,11,12,13,14]. Conformal gravity as well as Einstein’s gravity can share similar solutions of spacetime, and a black hole’s thermodynamic quantities, such as the mass and entropy, depend on the action instead of the line element.
The difference in action can be explained by how the thermodynamics of black holes for two different magnetic fields can vary. The thermodynamical phase structure of this conformal gravity in 4D (A)dS black hole spacetime was examined [15,16,17,18]. The formation of a conformal gravity contains two types of equations for statistics. One is a zero-order phase transformation, while the other is a Hawking Page-like transformation. Now, we give a brief review of gravitational lensing, which occurs due to the bending of light rays when they pass nearby the massive object [19] and the object produces a noticeable deviation, termed a gravitational lens. Now, this strong deflection (SD) lensing phenomenon has been proven to be a major tool for detecting the existence of gravitational waves and black holes in the cosmos [20]. In 1959, for the first time, it was predicted by Darwin [21] that the light emitted by a large deviation could prevent many loops before its escape when light rays pass too close to astrophysical structures such as black holes, and reliable images appear on all sides of the object. In addition, the information contained in the photographs involved can be useful in the study of the properties of massive objects in the cosmos. This research could play a significant role in studying other theories of gravity in its strongest deviation field [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Eiroa [33] explored the physical profiles of photons in Born–Infeld electrodynamics and pointed out that the geodesics method depends on the Born–Infeld combination. The nature of gravity is widely discussed in many theories of gravity [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42], and it has been proven to be a major aspect of celestial bodies. It is known that the dynamic force of gravity depends on the formation of the curvature of the background, the powerful features of photons, and the interaction of light with various other fields. Actually, light is considered to be a type of electric wave. The distribution of photons will be altered due to the coupling between the electromagnetic tensors and the curvature, resulting in some incidents of SD gravitational lensing.
Drummond [43] found that the effective action of photons is achieved by single-loop vacuum polarization when a similar kind of coupling is applied in quantum electrodynamics (QED). By considering the effective field theory, the coupling of the electromagnetic field and the Riemann curvature tensors is considered to be quantum, and hence all the combined terms remain small. Thus, the combined terms must have values of the second order of the Compton wavelength of the electron . Turner [44] found more interesting results than the electromagnetic variation by rethinking the Drummond model [43] with the coupling combination. Ni [45,46] presented a generalized electrical model and proved that the electrical power with the Riemann curvature tensor is often combined at the intervals of integration. Ni’s electric model [45,46] has been discussed extensively [47,48,49,50,51,52,53]. Such kinds of model have been thoroughly studied for the specific selection of constants in [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] for the cause of further physical attraction. Ritz and Ward [62] showed that the electric power of Weyl’s adjustment and the global relationship with the average payout of U(1) has a changing holographic conduction after the (A)dS space period. The value of the critical temperature and the order of the phase are altered in the origination of holographic superconductors [63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70]. The powerful evolution and the Hawking radiations for electromagnetism have dependence on the integration parameter of the field [71,72,73,74,75].
The authors of [76,77] measured the weak as well as SD gravitational lensing that removes the gravity of photons attached to the Weyl tensor and found the SD angle, the angular separation, and the brightness variation among the relativistic picture outcomes. Moreover, the time delay among such types of interlinked images was also found in [78,79]. Among these, gravitational lensing in the weak or strong gravity regime of a black hole has gained a lot of attention since it can reveal a black hole’s features [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95]. For instance, Horvath et al. studied gravitational lensing in the Kehagias–Sfetsos spacetime emerging in the framework of Hořava–Lifshitz gravity [80]. Eiroa and Sendra studied gravitational lensing by braneworld black holes with no matter or mass [81]. Moreover, Izmailov et al. investigated light deflection in modified gravity in the weak and strong field regimes [82]. Weak and strong deflection gravitational lensing by the hairy black holes in Einstein-scalar Gauss–Bonnet gravity with five types of coupling functions (quadratic, cubic, quartic, inverse-polynomial, and logarithmic), which can evade the no-hair theorem, were studied by Gao and Xie [83]. Cheng and Xie [84] showed that the black bounce traversable wormhole is indistinguishable from a Schwarzschild black hole and is loosely tested by the Event Horizon Telescope in strong deflection gravitational lensing. In addition, Zhang and Xie studied weak and strong deflection gravitational lensing with a black bounce Reissner–Nordström spacetime and obtained their lensing observables [85].
Li [96,97] proposed the old photon tests integrated with the Weyl tensor for the solar system. Pang [98] explored the gravitational lensing of massless and giant particles in a Reissner–Nordström (RN) black hole. Tsukamoto [99] calculated the SD angle in the static, spherically symmetric, and asymptotically flat spacetime. Eiroa [32] investigated the SD gravitational lensing phenomenon by taking an RN black hole as a lens and worked on the positions and magnifications of these relativistic images. Zakharov [100] explored the direct measurements of a black hole’s charge with future astrometrical missions. Moreover, weak and SD gravitational lensing by a charged Horndeski [101] and renormalization group-improved Schwarzschild black hole [102] were investigated. The phenomenon of SD gravitational lensing was investigated through several black holes, including braneworld black holes [103], a charged Galileon black hole [104], and a modified Hayward black hole [105]. More work concerning SD gravitational lensing has been performed for different black hole spacetimes, such as a Kerr black hole [106], a regular phantom black hole [107], a Kiselev black hole [108], and a charged Kiselev black hole [109]. All the considered black holes for SD gravitational lensing are asymptotically flat. It would be interesting to study the SD gravitational lensing for a non-asymptotically flat black hole, such as a conformal gravity black hole, which is non-asymptotically flat due to terms proportional to r and .
Aside from the requirement for dark matter in galaxies, the standard Newton–Einstein theory also calls for more dark matter in clusters of galaxies than is contained within the individual galaxies within the cluster. This fact is also qualitatively consistent with the conformal theory, because the linear potential term leads to larger and larger deviations from the standard theory at larger and larger distance scales. Galactic gravitational lensing provides an actual possible comparative test of the relative merits of the conformal theory and the standard dark matter scenario, which might even be demonstrated to be conclusive once a detailed picture of gravitational lensing is calculated in a fourth-order theory, such as the Weyl theory of gravity. Thus far, all considered black holes for SD gravitational lensing have been asymptotically flat. It would be interesting to study SD gravitational lensing for a non-asymptotically flat black hole, such as a conformal gravity black hole, which is non-asymptotically flat due to a term proportional to r [110].
In this work, the SD gravitational lensing phenomenon is explored for the photons coupled to the Weyl tensor in a conformal gravity black hole. In addition, we study the consequences of coupling on the motion of the photon sphere, the SD angle, and the SD gravitational lensing observables for and . This paper is ordered as follows. In Section 2, the equations of motion are investigated for the photons coupled to the Weyl tensor in conformal gravity. In Section 3 and Section 4, the photon sphere equation, the SD angle, and the SD gravitational lensing observables for and are probed. In the last section, we give our outcomes.
2. Conformal Gravity Black Hole
The electromagnetic field action for the photons coupled to the Weyl tensor [62,76,78,97,106,108,109] is given by
where denotes the electromagnetic field tensor, represents the gauge potential, and is a coupling parameter. Other terms such as R and represent the Ricci scalar and the Weyl tensor, respectively. For any n dimensional spacetime, [76] is defined as follows:
The simplest form of the four-dimensional conformal gravity black hole [111,112,113] is defined by
with
and . The four integral constants , , d, and can be defined under the given constraint [113]
which implies
If we take and , then the solution reduces to the Schwarzschild (A)dS black hole. The last term of Equation (4) contains , which corresponds to the“cosmological constant” that comes from the integral rather than the action. The electromagnetic field action in Equation (1) with ( gives the following corrected Maxwell equation [76]:
which means that the photons’ propagation will change via the Weyl tensor, and the wavelength of the coupled photons is greater than the electron Compton wavelength, but it is smaller than the traditional curvature scale (i.e., ). This signifies that both the electromagnetic and gravitational fields may be neglected by the typical curvature scale for the coupled photon propagation. Now, by using the geometric optics approximations [43,114,115,116,117,118,119], we can easily find the electromagnetic field tensor [76]:
The term and the quantity are the slowly varying amplitude and rapidly varying parameter, respectively. Here, defines the polarization vector satisfying the condition , and represents the wave vector (i.e., ). The derivative term can be omitted. Now, by solving Equations (7) and (8), we can find the equation of motion for the photons coupled to :
Now, we introduce the field of tetrads (vierbeins) as follows [76]:
and
In Equation (10), defines the Minkowski metric, and are called vierbeins. The vierbeins in the form of an antisymmetric combination may be expressed as [43,114,115,116] . The complete Weyl tensor can be rewritten as follows [76]:
where
Here, we introduce the three combinations of momentum components [43,114,115,116] (i.e., , , and ). After a tedious calculation, Equation (9) provides the precise light cone conditions [76]:
with
Here, we have
and
3. Equation of the Photon Sphere
The effective metric (i.e., ) in a conformal gravity black hole is defined as follows [76,120]:
and
By using the symmetry of the black hole, we can obtain the geodesic constants of motion [76]:
The parameter E stands for the energy, and L stands for the angular momentum per unit mass, while is called the affine parameter. Moreover, it is found that the photons obtain various trajectories with various polarizations, and hence every side of the bodies has two sets of relativistic images, since the observer as well as the source are placed in the required equatorial plane (i.e., ). With Equation (23), and using the condition , we see that Equation (9) for the photons in the conformal gravity BH can be further rewritten as follows:
Now, by studying the photon sphere equation [22,121,122], it is easy to find the impact parameter and the equation of the photon sphere [76] in this scenario:
and
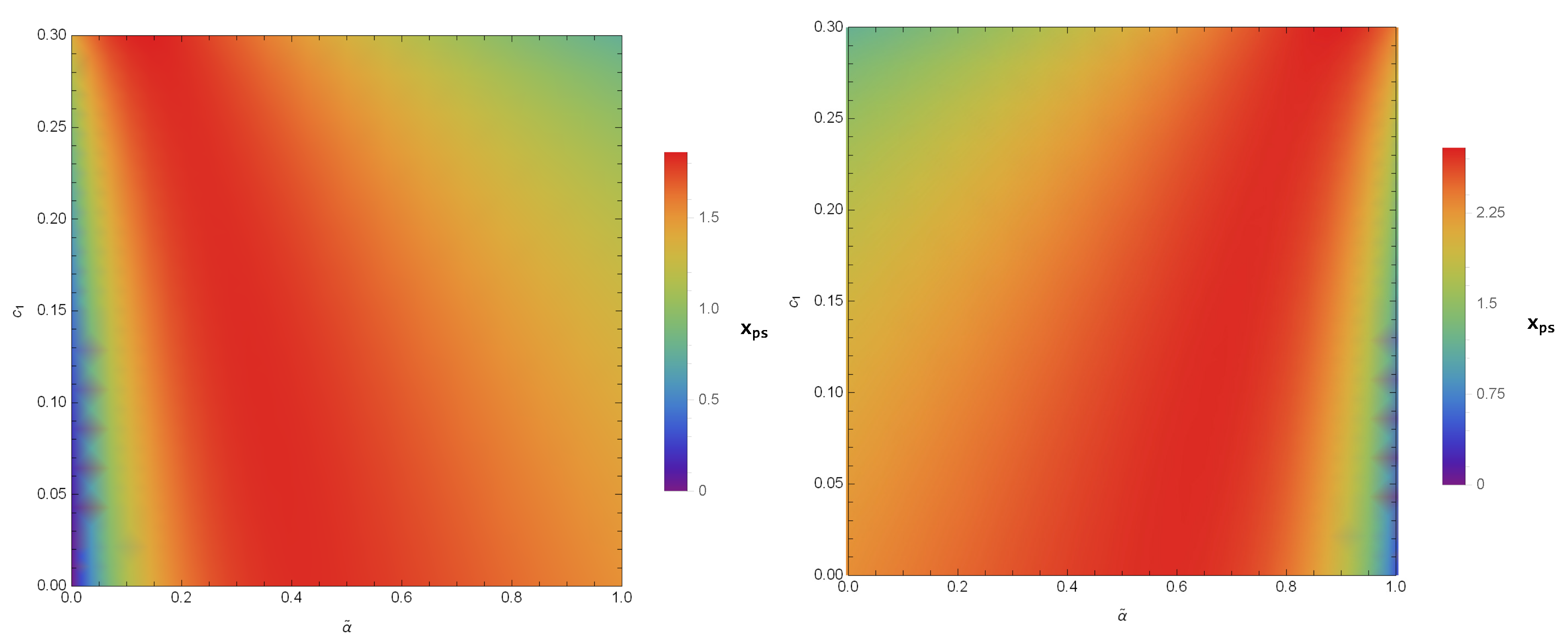
Here, the sign represents the radial derivatives. Here, the photon sphere is described as the innermost circulating orbit for the photons. If we find the solution to Equation (26), then the radius of the photon sphere appears as its largest root. We study the radius with (coupling parameter) and (black hole parameter) for the PPL and PPM cases (see Figure 1). This shows that when increases with , the radius becomes for PPL and for PPM. It is easy to find that is a constant with the length-squared dimension, and in order to be consistent with the observation, we have to constrain [96]. If we take the the BHs in the galactic center as having a mass [123] and having a mass [124], then the dimensionless coupling constant . The same procedure was adopted in [107] to discuss the strong gravitational lensing for photons coupled to the Weyl tensor in a regular phantom BH.
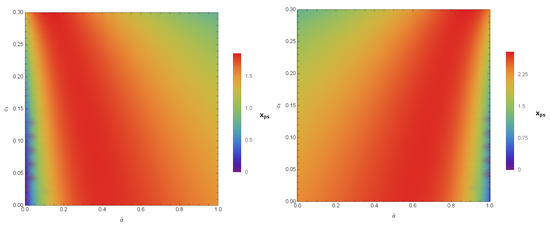
Figure 1.
Color-indexed variations of the radius () with and (left) for PPL and (right) for PPM. Here, we set , , and .
4. Strong Deflection Angle
In this part, we study the SD angle as the null geodesic (i.e., the photons coming from infinity) become limited. Hence, the SD angle can be defined as [125]
and
The variable stands for the closest approach distance. We see that as , the SD angle diverges while the photons are caught from the black hole, which assures that certain light rays cause a complete loop about the heavy objects before arriving at the observer. Furthermore, as changes into 2 for a specific value of , the SD angle increases, but the distance decreases. Hence, the physical characteristics of the SD angle are perfectly various. By adopting the Bozza technique [27], Equation (28) further reduces to
where
The function deviates as , but the function is regular for each value of and z. Now, we separate the integral in Equation (29) into two particular parts (, the divergent part, and , the regular part) as follows:
and
The function is described as follows:
with
When is nonzero , the dominant order of the divergence in assumes the form of but is integrated to give limited consequences. As vanishes , the aforementioned result becomes , which causes the integral to appear to be divergent. In this situation, every photon () is caught from the central body and cannot be brought back up. However, the SD angle diverges logarithmically for the photons [27]:
Here, we have
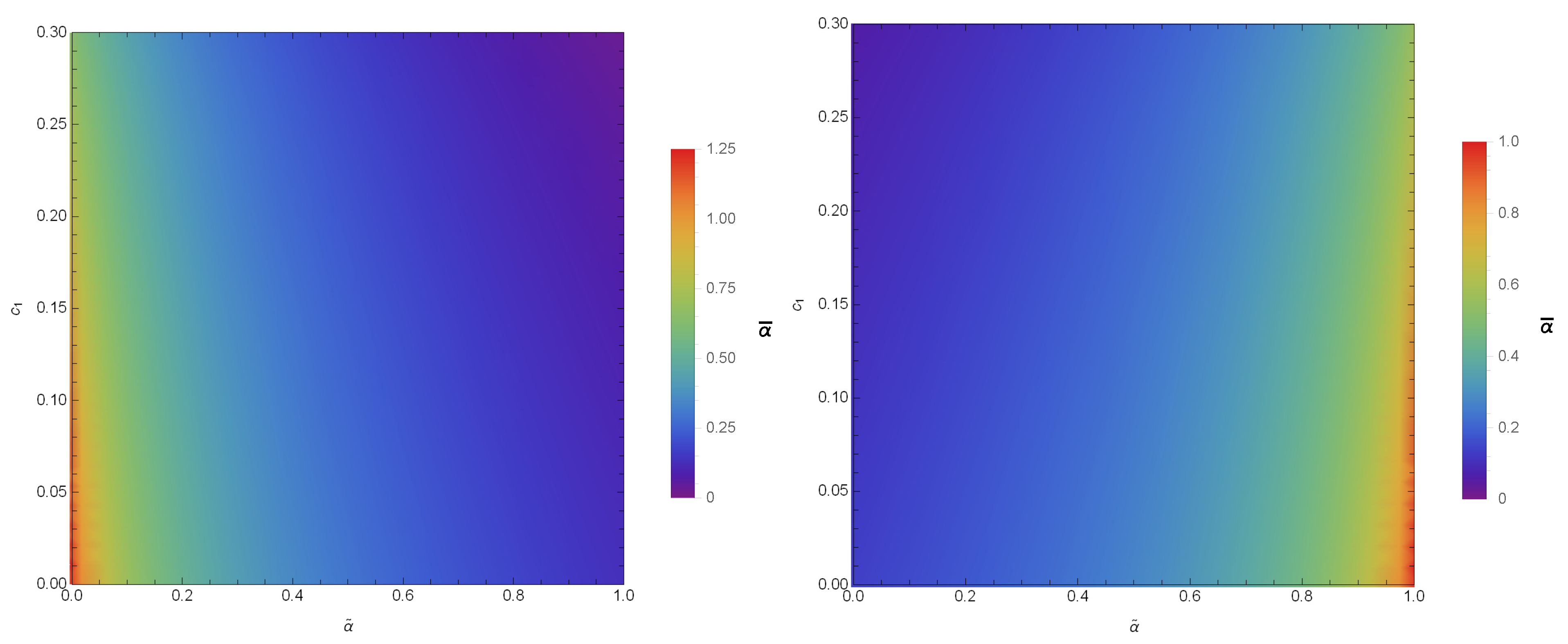
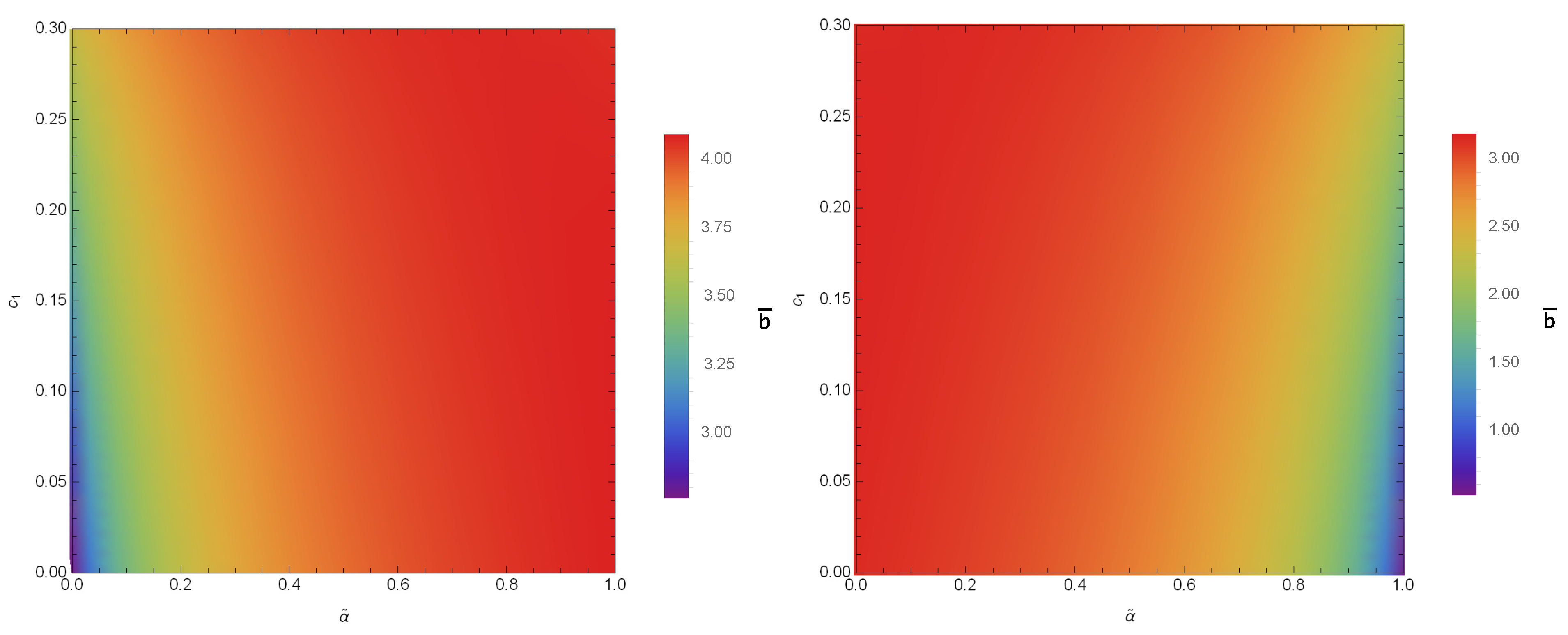
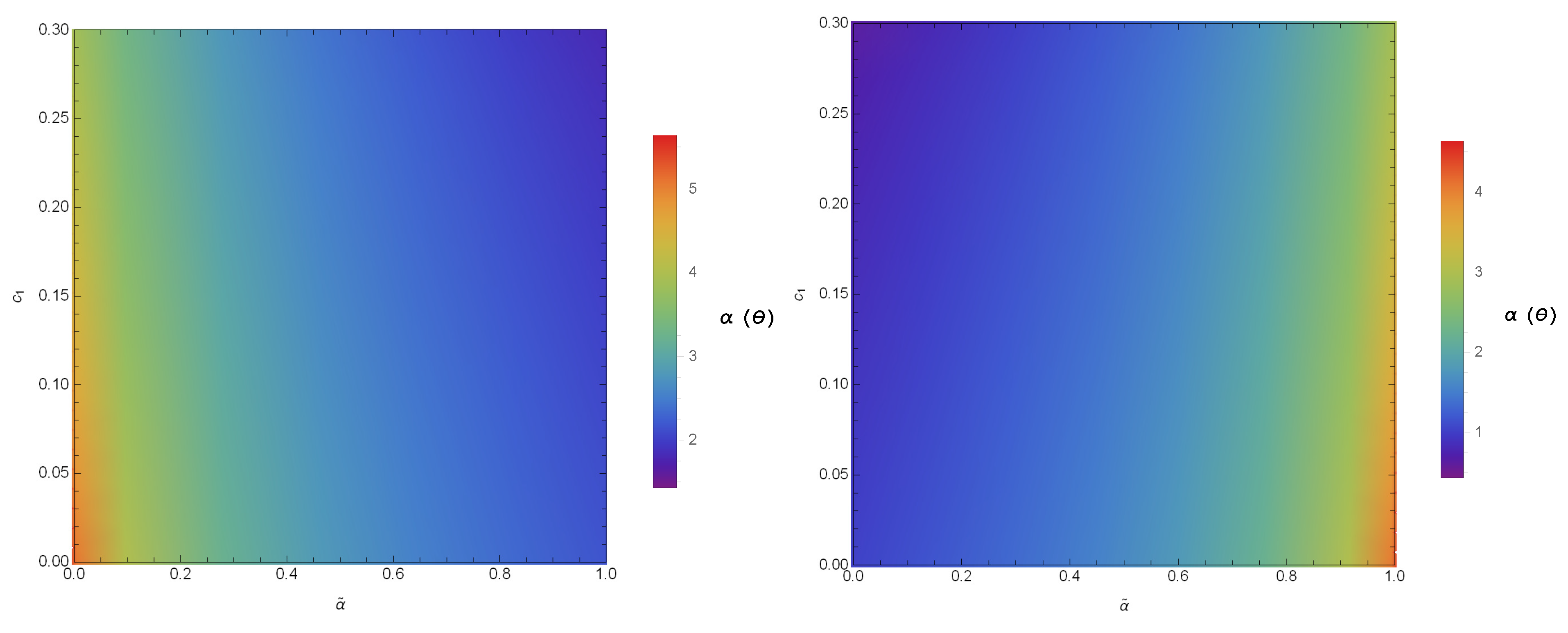
Here, stands for the distance between the observer and the gravitational lens. From Equations (21) and (22), the numerical characteristic of in conformal gravity is studied. The variations of the quantities with bars ( and ) for different values of and are given in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The coefficients and not only depend on the parameters of the black hole but also on the coupling parameter and the polarization directions of the photons. Hence, with the increase in and in the constant , the coefficients and have values and for PPL and and for PPM. Since, the coefficients are the functions of , the alike features may be observed in the SD angle. We study the variations of calculated at , presented in Figure 4, where it is noted that the SD angle () has the values for PPL and for PPM.
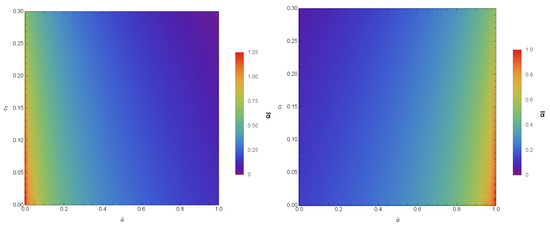
Figure 2.
Color-indexed variations of the coefficient () with and (left) for PPL and (right) for PPM. Here, we set , , and .
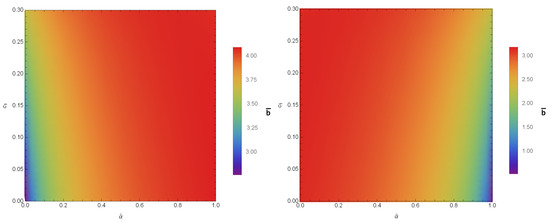
Figure 3.
Color-indexed variations of the coefficient () with and (left) for PPL and (right) for PPM. Here, we set , , and .
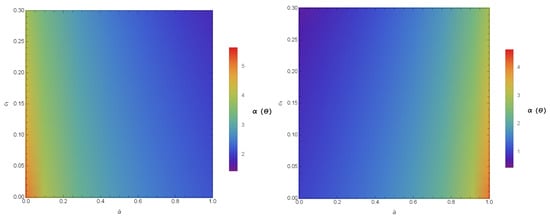
Figure 4.
Color-indexed variations of the SD angle () with and (left) for PPL and (right) for PPM. Here, we set , , and .
5. Strong Deflection Gravitational Lensing Observables for and
To probe the polarization consequences for the photons in conformal gravity, we deal with the lens equation [28,126,127]:
The variable represents the angle in the direction of the source, which is analogous to the optical axis, while stands for the observer lens distance and stands for the source lens distance. The angular separation s between the relativistic image and the lens yields the following result [28,126,127]:
where
The position of the relativistic image analogous to the SD angle for any number n is . The term (at ) yields the impact parameter associated with an asymptotic position of the set of the images :
Furthermore, to evaluate the coefficients (, ) from Equation (37), we deal with the perfect situation [27,28,126,127], and hence we obtain the following relations:
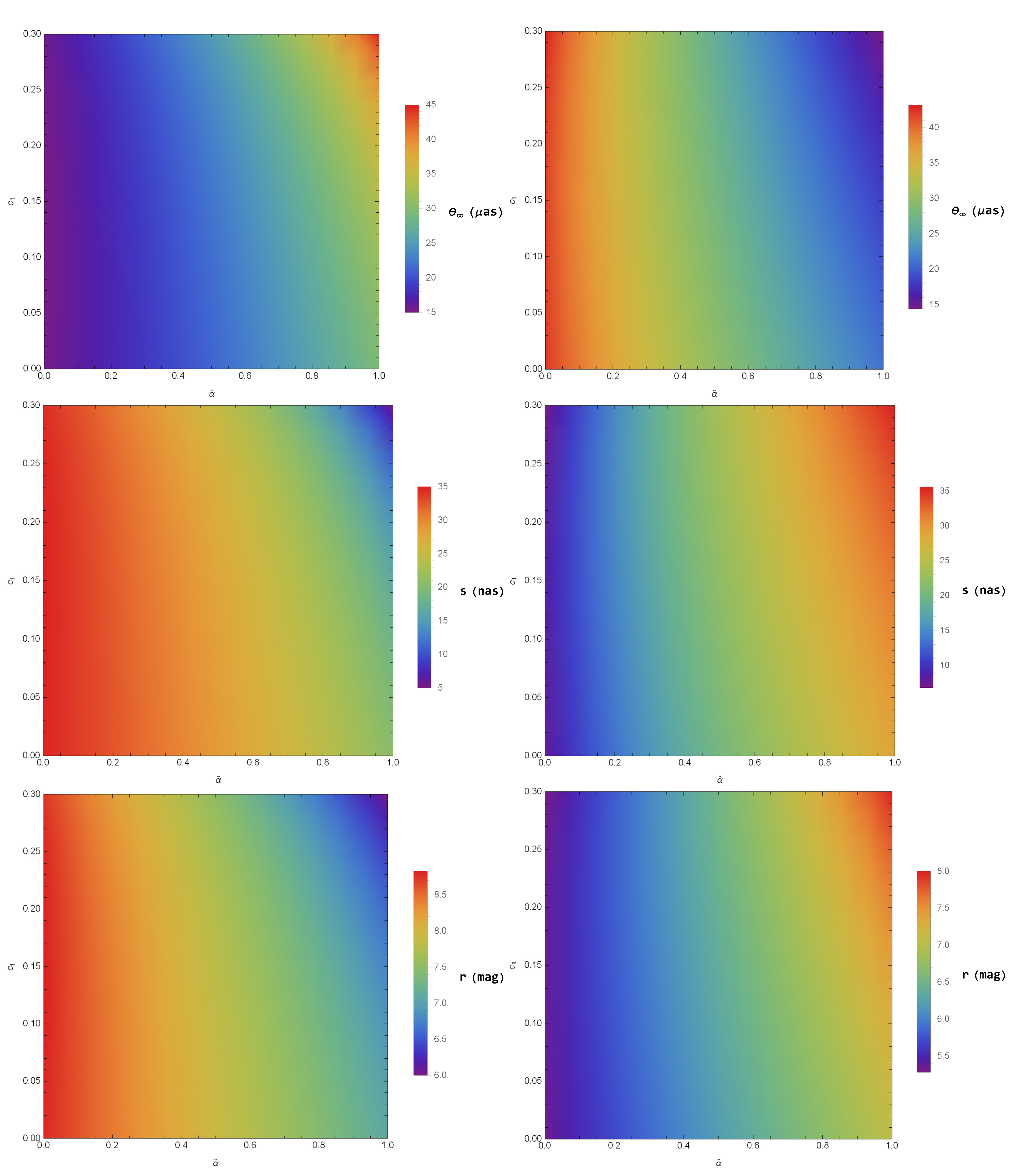
Here, the variable s stands for the angular separation, obtained by separating the outermost image () and the innermost images (). The variable r stands for the relative magnitudes, and the quantity stands for the flux ratio of the outermost image () and the innermost images (). With the help of these observables (, s, and r), it is easy to evaluate the minimum impact parameter and the coefficients (, ) of the SD angle in the conformal gravity black hole. We consider to be a lens having a mass and [123]. From this assumption, it is easy to estimate the values of the observables (, s, and r) for the SD gravitational lensing phenomenon. In general relativity, is supposed to be a Schwarzschild black hole, and hence the values of the observables (, s, and r) for the Schwarzschild black hole are , , and . The color-indexed values of the observables (, s, and r) for the conformal gravity black hole are given in Figure 5, corresponding to the Schwarzschild black hole. Specifically, the observable varied, ranging from to for PPL and to for PPM, whereas it had the theoretically lower limits (i.e., when and ) of and for PPL and PPM, respectively. Based on the results presented in Figure 5, the value of the observable s (angular separation) ranged from about 5 nanoarcseconds to about 35 for PPL, whereas the angular separation s ranged from about to about 36 for PPM. In Figure 5, the observable r (relative magnitudes) had values ranging from to for PPL and from to for PPM. Similarly, these observables (, s, and r) can easily be found by using the same technique for the case of having a mass and distance [124]. From Equations (42–44), we have the following relations for :
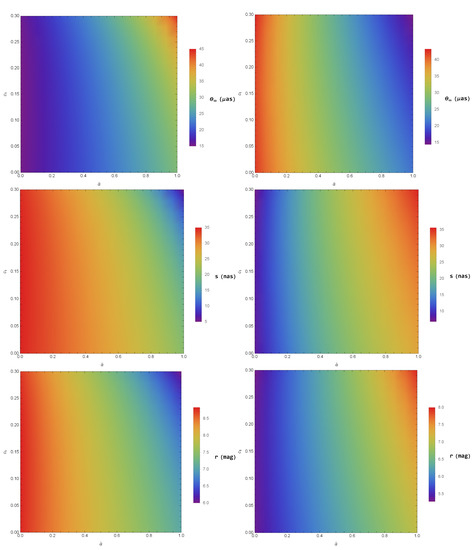
Figure 5.
Color-indexed variations of the observables (, s, and r) in the SD gravitational lensing in the conformal gravity BH from that of a Schwarzschild one for (left) for PPL and (right) for PPM with and .
We assume to be a Schwarzschild black hole. Then, the values of the observables and s for are and , whereas the observable remains unchanged and obtains the same value as it attained in the case of . The pattern of the observables (, s, and r) will be same in Figure 5, but their values will be changed for . We observed that the values of the observables and s for the conformal gravity black hole reached for PPL, for PPM as well as for PPL and for PPM, respectively. However, the observable r remained unchanged. It is viable to observe the quantum correction by calculating the variation of the shadow and the variations combined by the relativistic images, which are unworkable due to the lack of adequate angular separation. We have to assert repeatedly that being very accurate is a prerequisite when the calculation via EHT [128] is accurately practiced to constrain the conformal gravity BH considered here, as the models for measuring the properties of the shadow of [124] obtain two essential factors: the rotation of the black hole and the GRMHD of the plasma about it, neither of which are studied in the present work. However, when placed on the calculated diameter of the shadow of [128], we can measure the tentative and rough bounds on and as and in the given domain . According to Figure 5, for , these are natural signs for the case of the quantum effect but not legitimate constraints on it. We would like to mention that is a multiple of .
6. Conclusions
The SD gravitational lensing phenomenon and the dynamical equations of motion for photons were studied with the background of a conformal gravity black hole. We found that the black hole parameter , the polarization directions, and the coupling parameter are influential for the improvement of photons in the conformal gravity black hole. We observed that the parameters played a significant role in expounding the photon sphere radius, the SD coefficients, the SD angle, and the other SD lensing observables. The altered light cone conditions recommend that the photons move along the null geodesics. We found that the photon sphere was described as the innermost circulating orbit for the photons, but the photon sphere radius was the largest root of Equation (26). In Figure 1, we presented the radius () for the cases of PPL and PPM. This explains that with an increase in the coupling parameter and the constant , the radius () becomes and for PPL and PPM, respectively. The color-indexed deviations of the coefficients for the specific values of the constant were presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3. We identified that the SD coefficients and had the values for PPL and for PPM, whereas for PPL and for PPM. The variation in the SD angle ( for PPL and for PPM) was figured out to be , as can be seen in Figure 4. By taking and as two lenses, it is concluded that the present technology can only calculate the supposed size of the shadows of black holes and their variations from those of the Schwarzschild type. On behalf of the calculated diameter of for ’s shadow [128], we can have rough and tentative limits for the coupling parameter and the constant () as and in the given domain . According to Figure 5 (for ), these are natural signs for the case of quantum effects but not legitimate conditions for it.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A. and A.Ö.; methodology, A.M.; software, M.Z.; validation, G.A. and A.Ö.; formal analysis, A.M.; investigation, A.M. and M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, A.Ö.; writing—review and editing, G.A.; supervision, G.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data used in this research is available from the corresponding author and will be provided on request.
Acknowledgments
A.Ö. would like to acknowledge the contribution of the COST Action CA18108-Quantum gravity phenomenology in the multi-messenger approach (QG-MM).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adler, S.L. Einstein gravity as a symmetry-breaking effect in quantum field theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1982, 54, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooft, G.t. A class of elementary particle models without any adjustable real parameters. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1104.4543. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim, P.D. Making the case for conformal gravity. Found. Phys. 2012, 42, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergshoeff, E.; de Roo, M.; Wit, B.d. Extended conformal supergravity. Nucl. Phys. B 1981, 182, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, B.; van Holten, J.W.; Proeyen, A.V. Structure of N = 2 supergravity. Nucl. Phys. B 1981, 184, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovits, N.; Witten, E. Conformal supergravity in twistor-string theory. J. High Energy Phys. 2004, 0408, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldacena, J. Einstein Gravity from Conformal Gravity. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1105.5632. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiou, G.; Olea, R. From conformal to Einstein gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 086008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, P.D. Comprehensive solution to the cosmological constant, zero-point energy, and quantum gravity problems. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2011, 43, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelle, K.S. Renormalization of higher-derivative quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 16, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, P.D.; Kazanas, D. Exact vacuum solution to conformal Weyl gravity and galactic rotation curves. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, P.D. Alternatives to dark matter and dark energy. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2006, 56, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, P.D.; Brien, J.G.O. Impact of a global quadratic potential on galactic rotation curves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 121101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnozzi, S.; Roy, R.; Tsai, Y.D.; Visinelli, L.; Afrin, M.; Allahyari, A.; Bambhaniya, P.; Dey, D.; Ghosh, S.G.; Joshi, P.S.; et al. Horizon-scale tests of gravity theories and fundamental physics from the Event Horizon Telescope image of Sagittarius A*. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.07787. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Pang, Y.; Pope, C.N.; Vazquez-Poritz, J.F. AdS and Lifshitz black holes in conformal and Einstein-Weyl gravities. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 044011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, L. Critical phenomena of static charged AdS black holes in conformal gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 736, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L. Black hole thermodynamics and heat engines in conformal gravity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2017, 26, 1750151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yung, M.H. On the thermodynamic phase structure of conformal gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 783, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. Lens-Like Action of a Star by the Deviation of Light in the Gravitational Field. Science 1936, 84, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin, C. The gravity field of a particle. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1959, 249, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Virbhadra, K.S.; Ellis, G.F.R. Schwarzschild black hole lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 084003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virbhadra, K.S.; Keeton, C.R. Time delay and magnification centroid due to gravitational lensing by black holes and naked singularities. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 124014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virbhadra, K.S. Relativistic images of Schwarzschild black hole lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 083004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frittelly, S.; Kling, T.P.; Newman, E.T. Spacetime perspective of Schwarzschild lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 61, 064021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, V.; Capozziello, S.; Lovane, G.; Scarpetta, G. Strong field limit of black hole gravitational lensing. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2001, 33, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, V. Gravitational lensing in the strong field limit. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, V. Quasiequatorial gravitational lensing by spinning black holes in the strong field limit. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Fu, C.E.; Yang, K.J. Strong field limit analysis of gravitational lensing in Kerr-Taub-NUT spacetime. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 10, 053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.W.; Liu, Y.X. Equatorial and quasiequatorial gravitational lensingby a Kerr black hole pierced by a cosmic string. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 064044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraniotis, G.V. Precise analytic treatment of Kerr and Kerr-(anti) de Sitter black holes as gravitational lenses. Class. Quant. Grav. 2011, 28, 085021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiroa, E.F.; Romero, G.E.; Torres, D.F. Reissner-Nordström black hole lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 024010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiroa, E.F. Gravitational lensing by Einstein-Born-Infeld black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Strong field gravitational lensing in the deformed Hořava-Lifshitz black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 024036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Strong gravitational lensing in a squashed Kaluza-Klein black hole spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 124017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Geodetic precession and strong gravitational lensing in dynamical Chern–Simons-modified gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2010, 27, 225006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Liu, Y.; Jing, J.L. Strong gravitational lensing in a squashed Kaluza-Klein Godel black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.K.; Kang, S.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Strong gravitational lensing in a noncommutative black-hole spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 084005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Strong gravitational lensing by a rotating non-Kerr compact object. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 124029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Q.; Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Strong gravitational lensing of quasi-Kerr compact object with arbitrary quadrupole moments. J. High Energy Phys. 2012, 8, 097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.Y.; Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L.J. Strong gravitational lensing in a rotating Kaluza-Klein black hole with squashed horizons. J. High Energy Phys. 2014, 089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.J.; Jing, J.L.; Chen, S.B. Strong gravitational lensing for black holes with scalar charge in massive gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 064054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, I.T.; Hathrell, S.J. QED vacuum polarization in a background gravitational field and its effect on the velocity of photons. Phys. Rev. D 1980, 22, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.S.; Widrow, L.M. Inflation-produced, large-scale magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.T. Equivalence Principles and Electromagnetism. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1977, 38, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.T. Equivalence principles and precision experiments. In Precision Measurements and Fundamental Constants II; Taylor, B.N., Phillips, W.D., Eds.; U.S. National Bureau of Standards Publication 617; U.S. GPO: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Solanki, S.K.; Preuss, O.; Haugan, M.P.; Gandorfer, A.; Povel, H.P.; Steiner, P.; Stucki, K.; Bernasconi, P.N.; Soltau, D. Solar constraints on new couplings between electromagnetism and gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 062001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, O.; Haugan, M.P.; Solanki, S.K.; Jordan, S. An astronomical search for evidence of new physics: Limits on gravity-induced birefringence from the magnetic white dwarf RE J0317-853. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 067101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itin, Y.; Hehl, F.W. Maxwell’s field coupled nonminimally to quadratic torsion: Axion and birefringence. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 127701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, T.; Sert, O. Non-minimal ln(R)F2 couplings of electromagnetic fields to gravity: Static, spherically symmetric solutions. Eur. Phys. J. C 2011, 71, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakin, A.B.; Lemos, J.P.S. Non-minimal coupling for the gravitational and electromagnetic fields: A general system of equations. Class. Quantum Gravity 2005, 22, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakin, A.B.; Bochkarev, V.V.; Lemos, J.P.S. Nonminimal coupling for the gravitational and electromagnetic fields: Black hole solutions and solitons. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 084013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F.W.; Obukhov, Y.N. How does the electromagnetic field couple to gravity, in particular to metric, nonmetricity, torsion, and curvature? Lect. Notes Phys. 2001, 562, 479. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzitelli, F.D.; Spedalieri, F.M. Scalar electrodynamics and primordial magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 52, 6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambiase, G.; Prasanna, A.R. Gauge invariant wave equations in curved space-times and primordial magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 063502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raya, A.; Aguilar, J.E.M.; Bellini, M. Gravitoelectromagnetic inflation from a 5D vacuum state. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 638, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, L.; Cea, P.; Fogli, G.L.; Tedesco, L. Inflation-produced magnetic fields in RnF2 and IF2 models. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Odintsov, S.D. Inflation and late-time cosmic acceleration in non-minimal Maxwell-F(R) gravity and the generation of large-scale magnetic fields. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 0804, 024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Kronberg, P.P.; Dewdney, P.E.; Landecker, T.L. The Halo and Magnetic Field of the Coma Cluster of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1990, 355, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Tribble, P.C.; Kronberg, P.P. Detection of Excess Rotation Measure Due to Intracluster Magnetic Fields in Clusters of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1991, 379, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.E.; Kronberg, P.P.; Boehringer, H. A New Radio-X-Ray Probe of Galaxy Cluster Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 2001, 547, L111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, A.; Ward, J. Weyl corrections to holographic conductivity. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 066003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Cao, Y.; Kuang, X.M.; Li, W.J. The 3+1 holographic superconductor with Weyl corrections. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 697, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.Z.; Cao, Y.; Wu, J.P. The Stückelberg holographic superconductors with Weyl corrections. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 704, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, D.; Setare, M.R. A note on holographic superconductors with Weyl corrections. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 26, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, D.; Majd, N.; Myrzakulov, R. p-Wave holographic superconductors with Weyl corrections. Europhys. Lett. 2012, 97, 61001. [Google Scholar]
- Momeni, D.; Setare, M.R.; Myrzakulov, R. Condensation of the scalar field with Stuckelberg and Weyl corrections in the background of a planar AdS-Schwarzschild black hole. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2012, 27, 1250128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, D. Effect of external magnetic field on holographic superconductors in presence of nonlinear corrections. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.X.; Pan, Q.Y.; Jing, J.L. Holographic insulator/superconductor phase transition with Weyl corrections. Phys. Lett. B 2013, 719, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, Q.Y.; Jing, J.L. Holographic p-wave superconductor models with Weyl corrections. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 743, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Dynamical evolution of the electromagnetic perturbation with Weyl corrections. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 064058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Dynamical evolution of a vector field perturbation coupled to the Einstein tensor. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 124059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Absorption cross section and Hawking radiation of the electromagnetic field with Weyl corrections. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 728, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.L.; Chen, S.B.; Pan, Q.Y. Geometric optics for a coupling model of electromagnetic and gravitational fields. Ann. Phys. 2016, 367, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.L.; Chen, S.B.; Pan, Q.Y.; Wang, M.J. Detect black holes using photons for coupling model of electromagnetic and gravitational fields. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.08794. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.B.; Jing, J.L. Strong gravitational lensing for the photons coupled to Weyl tensor in a Schwarzschild black hole spacetime. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 10, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.G.; Xie, Y. Weak deflection gravitational lensing for photons coupled to Weyl tensor in a Schwarzschild black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, F.W.; Xie, Y. Strong gravitational field time delay for photons coupled to Weyl tensor in a Schwarzschild black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xie, Y. Time delay of photons coupled to Weyl tensor in a regular phantom black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, Z.; Gergely, L.A.; Keresztes, Z.; Harko, T.; Lobo, F.S.N. Constraining Hořava-Lifshitz gravity by weak and strong gravitational lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 083006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiroa, E.F.; Sendra, C.M. Gravitational lensing by massless braneworld black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 083009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izmailov, R.N.; Karimov, R.K.; Zhdanov, E.R.; Nandi, K.K. Modified gravity black hole lensing observables in weak and strong field of gravity. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 3754–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Xie, Y. Gravitational lensing by hairy black holes in Einstein-scalar-Gauss-Bonnet theories. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 043008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.T.; Xie, Y. Probing a black-bounce, traversable wormhole with weak deflection gravitational lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 064040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y. Gravitational lensing by a black-bounce-Reissner–Nordström spacetime. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.M.; Övgün, A. Strong gravitational lensing and shadow constraint from M87* of slowly rotating Kerr-like black hole. Ann. Phys. 2022, 447, 169147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, W.; Atique, M.; Pantig, R.C.; Övgün, A. Weak Deflection Angle, Hawking Radiation and Greybody Bound of Reissner-Nordström Black Hole Corrected by Bounce Parameter. Symmetry 2023, 15, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, W.; Riaz, S.; Pantig, R.C.; Övgün, A. Weak gravitational lensing in dark matter and plasma mediums for wormhole-like static aether solution. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, W.; Irshad, H.; Pantig, R.C.; Övgün, A. Weak Deflection Angle by Kalb–Ramond Traversable Wormhole in Plasma and Dark Matter Mediums. Universe 2022, 8, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantig, R.C.; Mastrototaro, L.; Lambiase, G.; Övgün, A. Shadow, lensing, quasinormal modes, greybody bounds and neutrino propagation by dyonic ModMax black holes. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantig, R.C.; Övgün, A. Testing dynamical torsion effects on the charged black hole’s shadow, deflection angle and greybody with M87* and Sgr. A* from EHT. Ann. Phys. 2023, 448, 169197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, A.; Pantig, R.C.; Övgün, A. Probing a non-linear electrodynamics black hole with thin accretion disk, shadow, and deflection angle with M87* and Sgr A* from EHT. Phys. Dark Univ. 2023, 40, 101178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusufi, K.; Övgün, A. Gravitational Lensing by Rotating Wormholes. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 024042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Övgün, A. Light deflection by Damour-Solodukhin wormholes and Gauss-Bonnet theorem. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 044033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantig, R.C.; Övgün, A. Dark matter effect on the weak deflection angle by black holes at the center of Milky Way and M87 galaxies. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Deng, X.M. Classical tests of photons coupled to Weyl tensor in the Solar System. Ann. Phys. 2017, 382, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Deng, X.M. Testing Photons Coupled to Weyl Tensor with Gravitational Time Advancement. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2018, 70, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Jia, J. Gravitational lensing of massive particles in Reissner–Nordström black hole spacetime. Class. Quantum Gravity 2019, 36, 065012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, N. Deflection angle in the strong deflection limit in a general asymptotically flat, static, spherically symmetric spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 064035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.F.; de Paolis, F.; Ingrosso, G.; Nucita, A.A. Direct measurements of black hole charge with future astrometrical missions. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 442, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Shen, Y.F.; Xie, Y. Weak and strong deflection gravitational lensings by a charged Horndeski black hole. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 04, 022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xie, Y. Weak and strong deflection gravitational lensing by a renormalization group improved Schwarzschild black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whisker, R. Strong gravitational lensing by braneworld black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 064004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Xie, Y. Strong field gravitational lensing by a charged Galileon black hole. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 07, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Xie, Y. Strong deflection gravitational lensing by a modified Hayward black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Jing, J.; Wang, S. Strong gravitational lensing for the photons coupled to a Weyl tensor in a Kerr black hole spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 104017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J. Strong gravitational lensing for photons coupled to Weyl tensor in a regular phantom black hole. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Mahmood, A.; Zubair, M. Strong gravitational lensing for photon coupled to Weyl tensor in Kiselev black hole. Chin. Phys. C 2020, 44, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Mahmood, A.; Zubair, M. Strong deflection gravitational lensing for photon coupled to Weyl tensor in a charged Kiselev black hole. Phys. Dark Universe 2021, 31, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, P.D.; Kazanas, D. Current status of conformal Weyl gravity. AIP Conf. Proc. 1991, 222, 541. [Google Scholar]
- Riegert, R.J. Birkhoff’s Theorem in Conformal Gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D. Topological black holes in Weyl conformal gravity. Class. Quant. Grav. 1998, 15, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Yung, M.-H. Black hole evaporation in conformal (Weyl) gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 793, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, R.D.; Shore, G.M. “Faster than light” photons and charged black holes. Nucl. Phys. B 1994, 425, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R.D.; Shore, G.M. “Faster than light” photons and rotating black holes. Phys. Lett. B 1996, 367, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, G.M. Faster than light photons in gravitational fields II.: Dispersion and vacuum polarisation. Nucl.Phys. B 2002, 633, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.G. Propagation of vacuum polarized photons in topological black hole spacetimes. Nucl. Phys. B 1998, 524, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.T. “Faster than light” photons in dilaton black hole spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 56, 6416–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenci, V.A.D.; Klippert, R.; Novello, M.; Salim, J.M. Light propagation in non-linear electrodynamics. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 482, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, N. Geodesic structure of the Born–Infeld black hole. Class. Quantum Grav. 2002, 19, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virbhadra, K.S.; Ellis, G.F.R. Gravitational lensing by naked singularities. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 103004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudel, C.M.; Virbhadra, K.S.; Ellis, G.F.R. The geometry of photon surfaces. J. Math. Phys. 2001, 42, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, S.; Plewa, P.M.; Eisenhauer, F.; Sari, R.; Waisberg, I.; Habibi, M.; Pfuhl, O.; George, E.; Dexter, J.; von Fellenberg, S.; et al. An Update on Monitoring Stellar Orbits in the Galactic Center. Astrophys. J. 2017, 837, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration; Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.-K.; Ball, D.; Baloković, M.; Barrett, J.; et al. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. VI. The Shadow and Mass of the Central Black Hole. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 875, L6. [Google Scholar]
- Virbhadra, K.S.; Narasimha, D.; Chitre, S.M. Role of the scalar field in gravitational lensing. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 337, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bozza, V.; Luca, F.D.; Scarpetta, G.; Sereno, M. Analytic Kerr black hole lensing for equatorial observers in the strong deflection limit. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 083003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozza, V.; Luca, F.D.; Scarpetta, G. Kerr black hole lensing for generic observers in the strong deflection limit. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration; Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.-K.; Ball, D.; Baloković, M.; Barrett, J.; et al. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 875, L1. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).