Why Are Some Radio Galaxies Detected by Fermi, but Others Not?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample
3. Parameters
3.1. Radio Loudness and Luminosity in Radio and Optical Bands
3.2. Doppler Factor
3.3. Core-Dominance Parameters and Black Hole Mass
4. Results
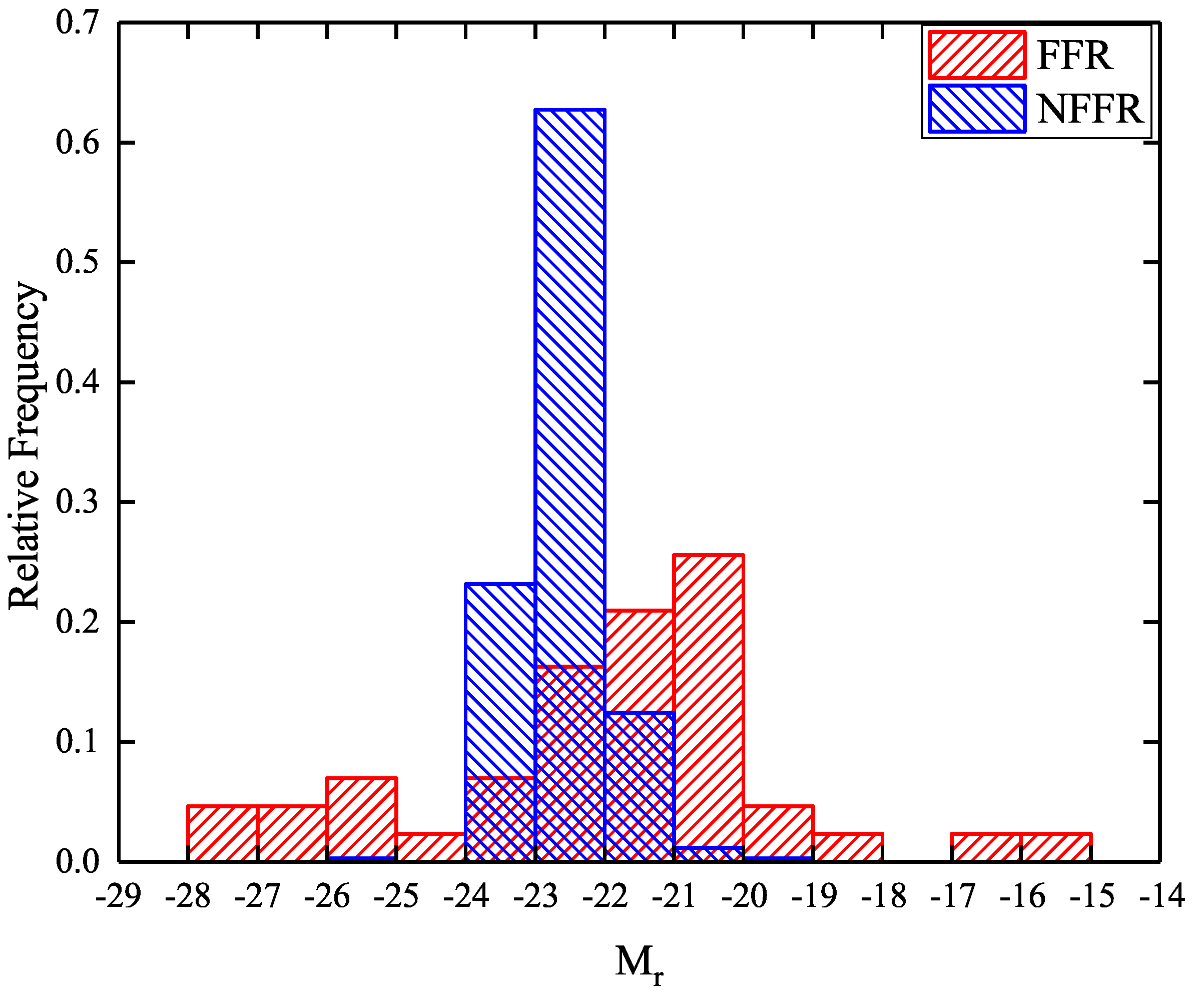
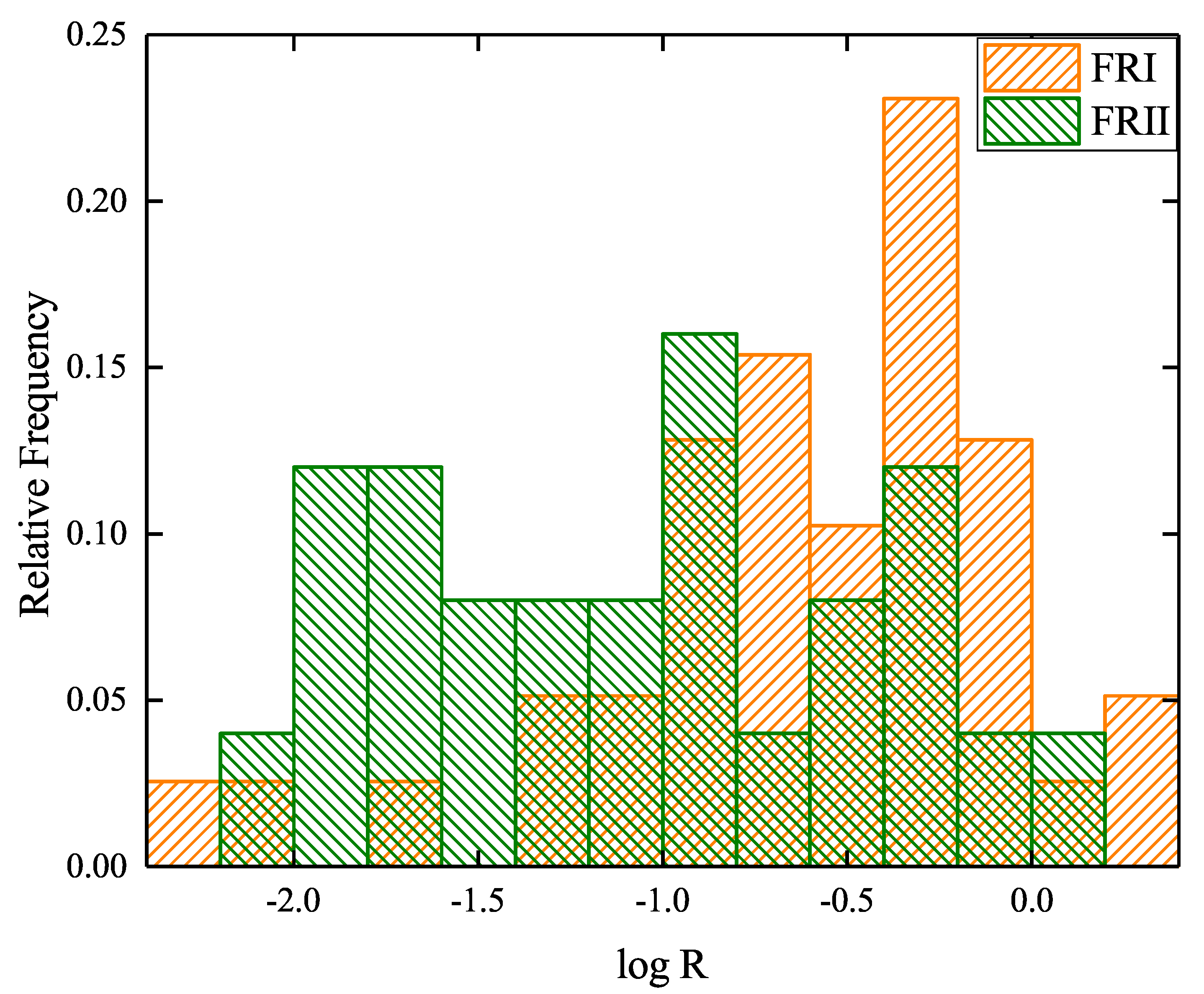
4.1. Distribution of Luminosity and Radio Loudness
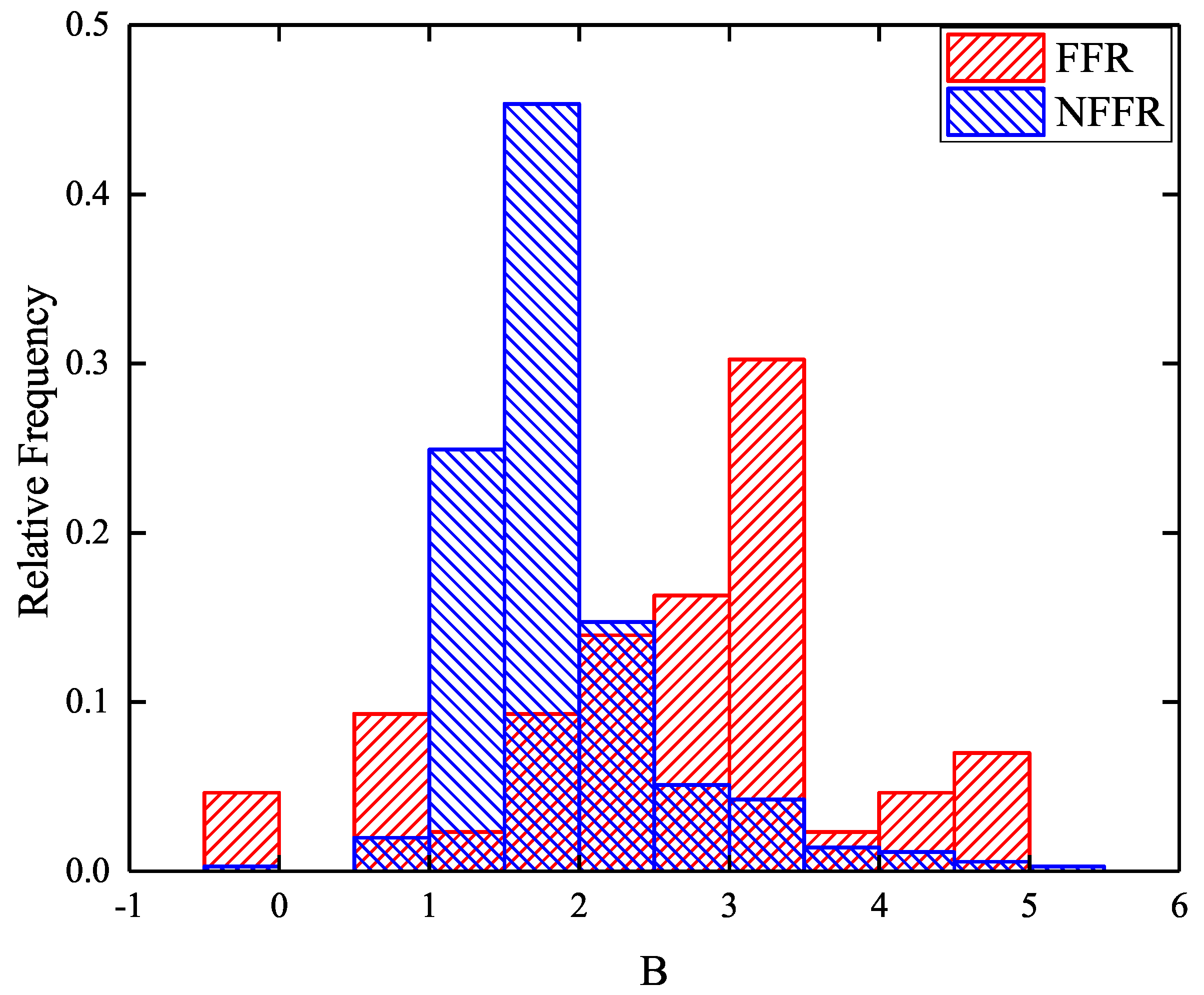
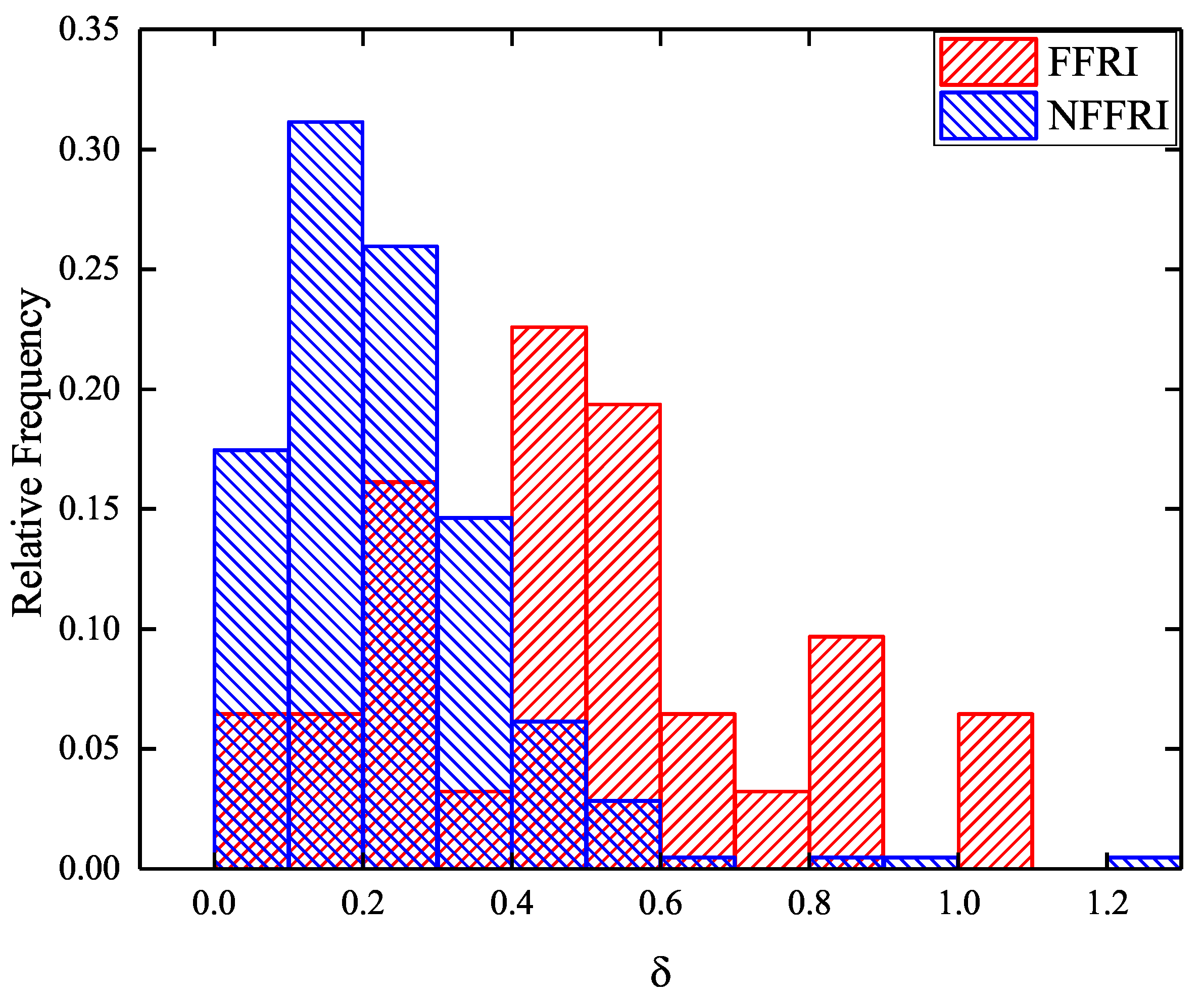
4.2. Distribution of Core Dominance Parameter and Doppler Factor
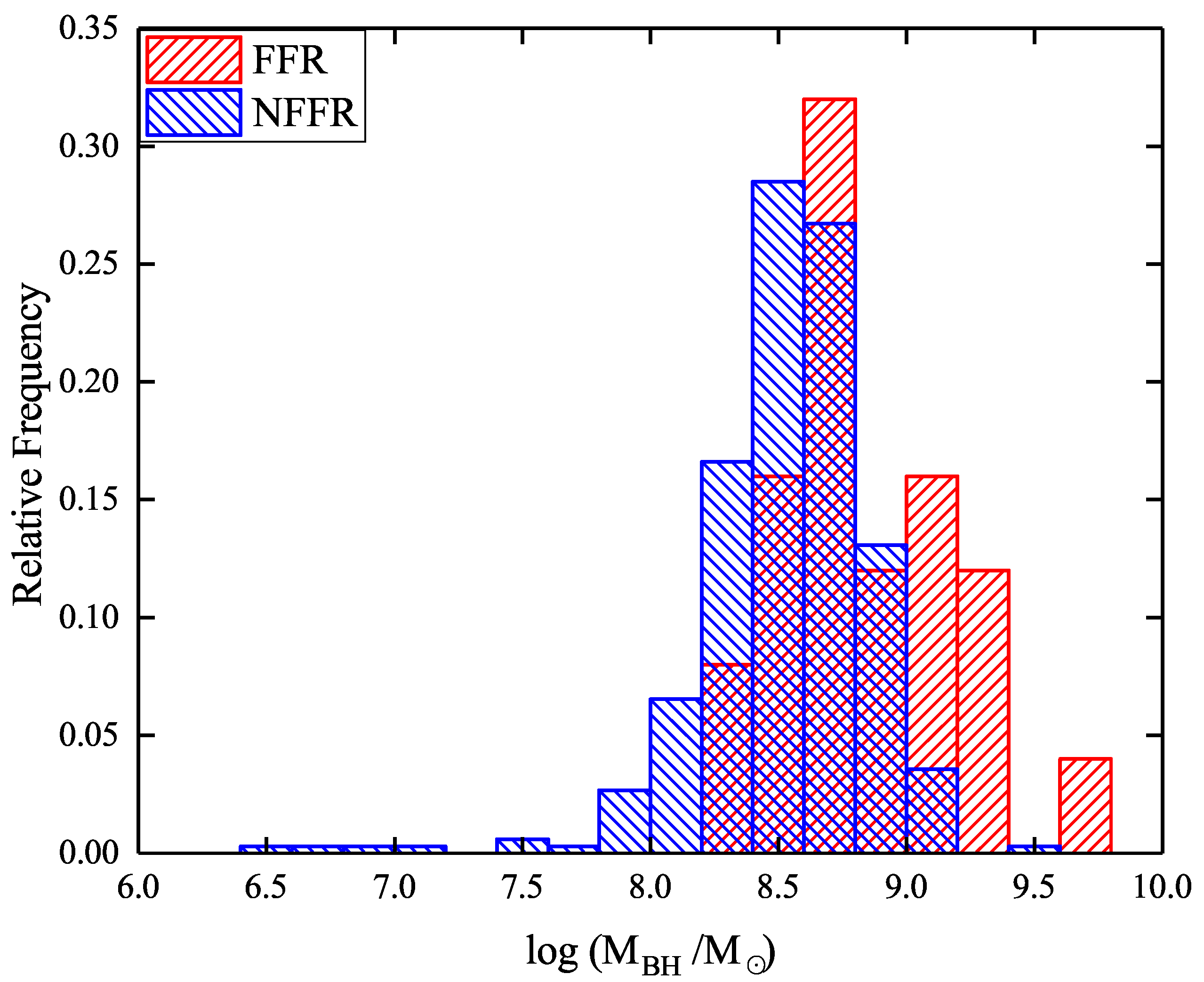
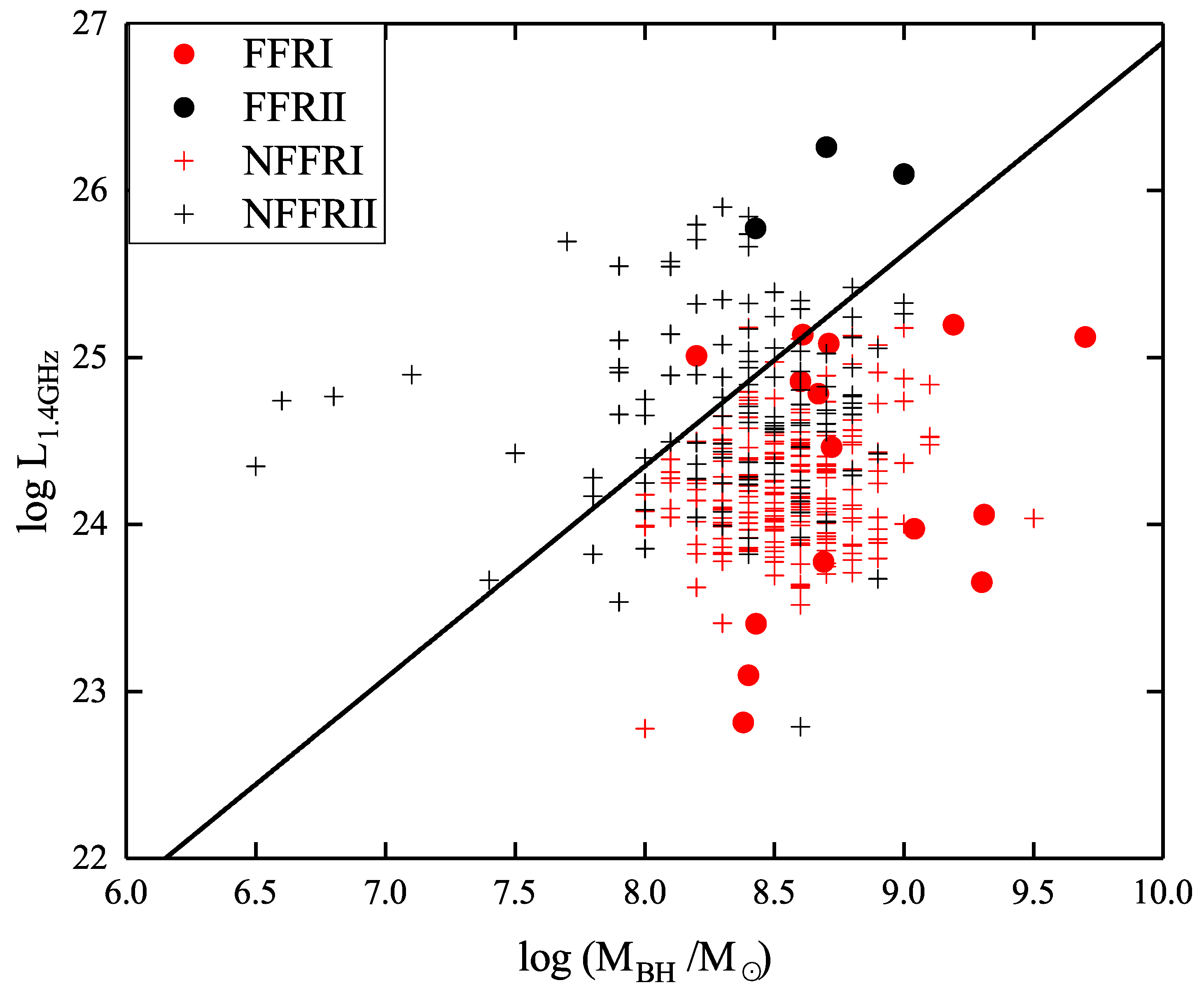
4.3. Distribution of Black Hole Mass
5. Discussion
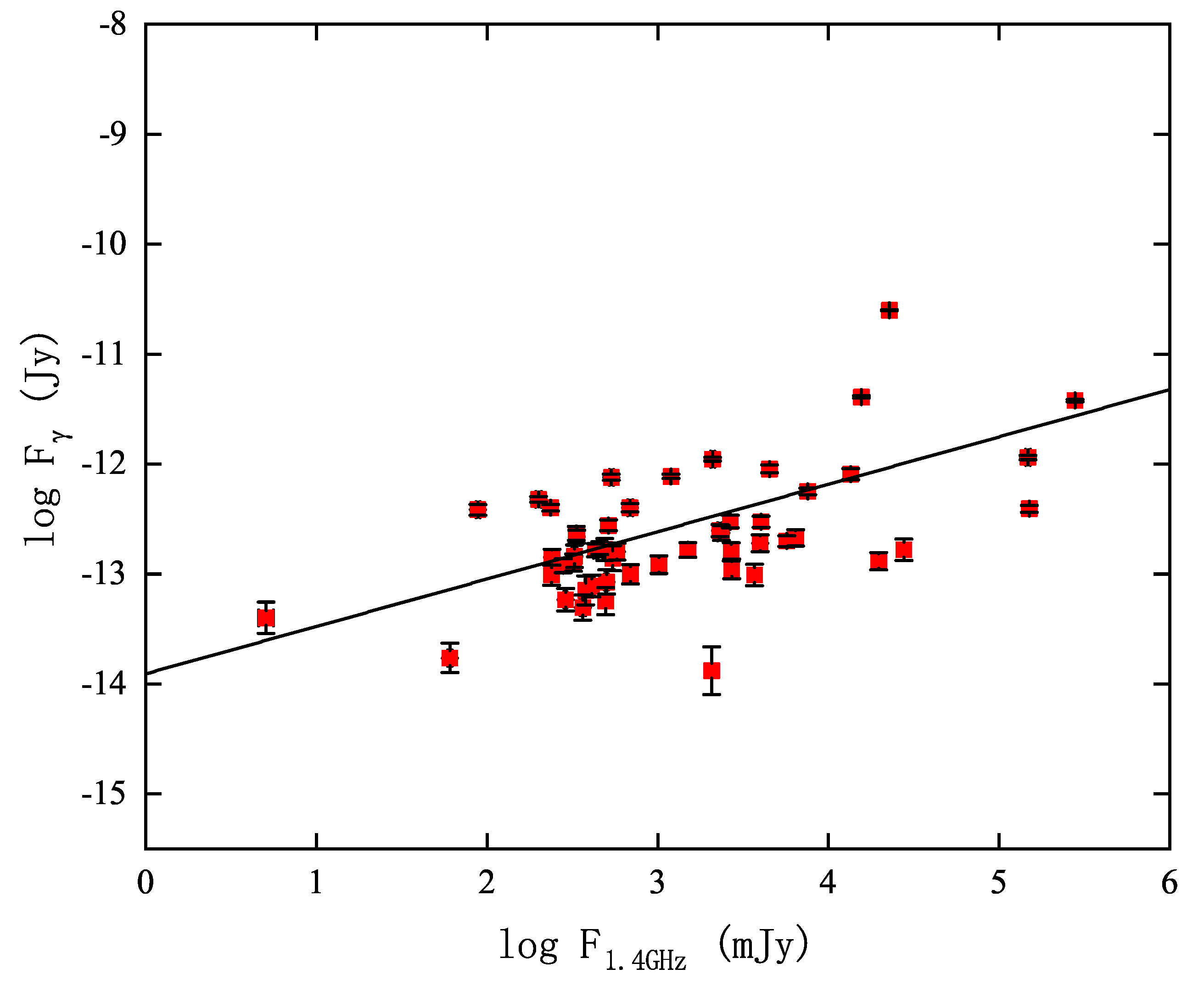
5.1. Predicting the -ray Flux of NFFRs
5.2. FR Is–FR IIs Dichotomy
5.3. Why Are FR IIs Fewer Than FR Is in the Fermi-LAT Source Catalog?
5.4. Can NFFRs Be Detected by CTA?
6. Conclusions
- From our results of the comparison on 1.4 GHz radio luminosities and radio loudness parameters, we ascertain that FFRs are jet-dominant while NFFRs are disk-dominant sources.
- Combining our discussion on the core dominance parameters and Doppler factors, we believe that the observed differences between FFRs and NFFRs are significantly related to the orientation of the jet with respect to the observer. We suggest that the NFFRs can be considered to have a weak jet beaming effect, and thus -ray emission is faint, making them difficult to be captured by Fermi-LAT.
- We estimated the GeV flux at 1 GeV for all NFFRs using the positive correlation observed between the 1 GeV flux and radio flux at 1.4 GHz for FFRs with a -ray counterpart. We find that a handful of NFFRs are above the Fermi-LAT sensitivity threshold.
- We also discuss an interesting issue about why FR II radio galaxies seem to be excluded in -ray emission. Since the Doppler boosting is stronger and the beaming cone will be narrower compared with synchrotron processes if the emission is due to External Compton (EC) scattering within jets, and if the high energy emission is dominated by the EC process in powerful radio sources and by Synchrotron Self-Compton (SSC) process in low-power radio galaxies, a beaming difference may account for the handful of FR IIs detected by Fermi-LAT compared with FR Is.
- We set up a dividing line in the plane of radio flux versus black hole mass to effectively distinguish FR I and FR II sources. Thus, we first propose a “changing-look” phenomenon in radio galaxies, namely that some FR Is are masquerading as FR II galaxies due to the beaming effect, and vice versa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | http://ned.ipac.caltech.edu/forms/byname.html (accessed on 24 April 2023). |
| 2 | Astrogeo VLBI FITS image database maintained by Leonid Petrov: http://astrogeo.org/ (accessed on 24 April 2023). |
References
- Samudre, A.; George, L.T.; Bansal, M.; Wadadekar, Y. Data-efficient classification of radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 509, 2269–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, P.; Frank, P.; Haim, P.; Knollmüller, J.; Leike, R.; Reinecke, M.; Enßlin, T. Variable structures in M87* from space, time and frequency resolved interferometry. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration; Akiyama, K.; Algaba, J.C.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Anantua, R.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.K.; Ball, D.; et al. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. VII. Polarization of the Ring. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 910, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijbring, D.; de Bruyn, A.G. Multifrequency radio continuum observations of head-tail galaxies in the Perseus cluster. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 331, 901–915. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, F.N.; Rudnick, L. Radio sources with wide-angle tails in Abell clusters of galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1976, 205, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, L.; Owen, F.N. Interferometer observations of radio sources in clusters of galaxies. IV. Astron. J. 1977, 82, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaglia, S.; Bodo, G.; Rossi, P.; Capetti, A.; Mignone, A. Making Fanaroff-Riley I radio sources. III. The effects of the magnetic field on relativistic jets’ propagation and source morphologies. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 659, A139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaroff, B.L.; Riley, J.M. The morphology of extragalactic radio sources of high and low luminosity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1974, 167, 31P–36P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Rees, M.J. Extended and compact extragalactic radio sources: Interpretation and theory. Phys. Scr. 1978, 17, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, G.E.; Cellone, S.A.; Combi, J.A.; Andruchow, I. Optical microvariability of EGRET blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 390, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H.; Romero, G.E.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, J.S. Separation of Different Contributions to the Total X-ray Luminosity in Gamma-ray Loud Blazars. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 5, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirlanda, G.; Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Foschini, L. Correlation of Fermi Large Area Telescope sources with the 20-GHz Australia Telescope Compact Array radio survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 407, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marscher, A.; Jorstad, S.G.; Larionov, V.M.; Aller, M.F.; Lähteenmäki, A. Multi-Waveband Emission Maps of Blazars. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2011, 32, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.W.; Browne, I.W.A.; Perley, R.A. VLA obseravtions of a complete sample of core-dominated radio source. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1993, 264, 298–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, R. Unified models for active galactic nuclei and quasars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 31, 473–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, C.M.; Padovani, P. Unified Schemes for Radio-Loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1995, 107, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, H. Revisiting the Unified Model of Active Galactic Nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 53, 365–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, W.B.; Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Althouse, W.; Anderson, B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Band, D.L.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. The Large Area Telescope on the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 1071–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.; Acero, F.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope Fourth Source Catalog. Astrophys. J. 2020, 247, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piner, B.G.; Pushkarev, A.B.; Kovalev, Y.Y.; Marvin, C.J.; Arenson, J.G.; Charlot, P.; Fey, A.L.; Collioud, A.; Voitsik, P.A. Relativistic Jets in the Radio Reference Frame Image Database. II. Blazar Jet Accelerations from the First 10 Years of Data (1994–2003). Astrophys. J. 2012, 758, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkarev, A.B.; Kovalev, Y.Y. Single-epoch VLBI imaging study of bright active galactic nuclei at 2 GHz and 8 GHz. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 544, A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, P.; Torresi, E. Exploring the FRI/FRII radio dichotomy with the Fermi satellite. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1205.1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.Y.; Fan, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.H.; Cai, W.; Xiao, H.B.; Lin, C.; Yang, J.H. Radio core dominance of Fermi blazars. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Fan, J.; Bastieri, D.; Yang, J.; Xiao, H. Radio core dominance of Fermi/LAT-detected AGNs. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2020, 63, 259511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.H.; Zeng, X.T.; Huang, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Pei, Z.Y.; Fan, J.H. The Beaming Effect for Fermi-LAT-detected FR-I Radio Galaxies. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2023, 135, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, R.; Ros, E.; Kadler, M.; Ojha, R.; Müller, C.; Edwards, P.G.; Burd, P.R.; Carpenter, B.; Dutka, M.S.; Gulyaev, S.; et al. Gamma-ray emission in radio galaxies under the VLBI scope. I. Parsec-scale jet kinematics and high-energy properties of γ-ray-detected TANAMI radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 627, A148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capetti, A.; Massaro, F.; Baldi, R.D. FRICAT: A FIRST catalog of FR I radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 598, A49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capetti, A.; Massaro, F.; Baldi, R.D. FRIICAT: A FIRST catalog of FR II radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 601, A81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliocchetti, M.; Maddox, S.J.; Jackson, C.A.; Bland-Hawthorn, J.; Bridges, T.; Cannon, R.; Cole, S.; Colless, M.; Collins, C.; Couch, W.; et al. The 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey: The population of nearby radio galaxies at the 1-mJy level. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 333, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, C.M.; Chapman, S.C.; Muxlow, T.W.B.; Beswick, R.J.; Alexander, D.M.; Conselice, C.J. Constraining star formation and AGN in z ~2 massive galaxies using high-resolution MERLIN radio observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 395, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.C. Difmap: An Interactive Program for Synthesis Imaging. In Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Hunt, G., Payne, H., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1997; Volume 125, p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter, P.A.; Hill, P.; Pauliny-Toth, I.I.K.; Steppe, H.; Witzel, A. Radio observations of optically selected quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 1980, 88, L12–L15. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Zhu, J.; Fu, L.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J. The radio dichotomy of active galactic nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2022, 74, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Padovani, P.; Celotti, A.; Maraschi, L. Relativistic Bulk Motion in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 1993, 407, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H. Relation between BL Lacertae Objects and Flat-Spectrum Radio Quasars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2003, 585, L23–L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.Y.; Fan, J.H.; Bastieri, D.; Sawangwit, U.; Yang, J.H. The relationship between the radio core-dominance parameter and spectral index in different classes of extragalactic radio sources (II). Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 19, 070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.Y.; Fan, J.H.; Bastieri, D.; Yang, J.H.; Xiao, H.B.; Yang, W.X. The relationship between the radio core-dominance parameter and spectral index in different classes of extragalactic radio sources (III). Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 20, 025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, G.; Feretti, L.; Venturi, T.; Lara, L.; Marcaide, J.; Rioja, M.; Spangler, S.R.; Wehrle, A.E. VLBI Observations of a Complete Sample of Radio Galaxies. IV. The Radio Galaxies NGC 2484, 3C 109, and 3C 382. Astrophys. J. 1994, 435, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, J.R.; Bertsch, D.L.; Chiang, J.; Dingus, B.L.; Fichtel, C.E.; Hartman, R.C.; Hunter, S.D.; Kanbach, G.; Kniffen, D.A.; Kwok, P.W.; et al. The EGRET Detection of Quasar 1633+382. Astrophys. J. 1993, 410, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenmäki, A.; Valtaoja, E. Total Flux Density Variations in Extragalactic Radio Sources. III. Doppler Boosting Factors, Lorentz Factors, and Viewing Angles for Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 1999, 521, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liodakis, I.; Hovatta, T.; Huppenkothen, D.; Kiehlmann, S.; Max-Moerbeck, W.; Readhead, A.C.S. Constraining the Limiting Brightness Temperature and Doppler Factors for the Largest Sample of Radio-bright Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2018, 866, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. On the Jet Properties of γ-Ray-loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2018, 235, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Fan, J.; Yang, J.; Bastieri, D. The estimation of γ-ray Doppler factor for Fermi/LAT-detected blazars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2020, 37, e043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Xiao, H.; Cai, J.; Fan, J. Doppler Factor Estimation for Fermi Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2020, 897, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähteenmäki, A.; Valtaoja, E. Testing of Inverse Compton Models for Active Galactic Nuclei with Gamma-Ray and Radio Observations. Astrophys. J. 2003, 590, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, Y.Y.; Aller, H.D.; Aller, M.F.; Homan, D.C.; Kadler, M.; Kellermann, K.I.; Kovalev, Y.A.; Lister, M.L.; McCormick, M.J.; Pushkarev, A.B.; et al. The Relation Between AGN Gamma-Ray Emission and Parsec-Scale Radio Jets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 696, L17–L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayanoki, T.; Fukazawa, Y. Relationship between gamma-ray loudness and X-ray spectra of radio galaxies. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2022, 74, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulten, C.B.; Brown, A.M.; Chadwick, P.M. A search for Centaurus A-like features in the spectra of Fermi-LAT detected radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 4666–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ho, L.C.; Zhuang, M.Y. An Elusive Population of Massive Disk Galaxies Hosting Double-lobed Radio-loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2022, 941, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadhunter, C. Radio AGN in the local universe: Unification, triggering and evolution. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, F.N.; Ledlow, M.J. The FRI/Il Break and the Bivariate Luminosity Function in Abell Clusters of Galaxies. In Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Bicknell, G.V., Dopita, M.A., Quinn, P.J., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1994; Volume 54, p. 319. [Google Scholar]
- Kormendy, J.; Ho, L.C. Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Host Galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 51, 511–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. The dividing line between FR I and FR II radio-galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 379, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearst, M.; Dumais, S.; Osuna, E.; Platt, J.; Scholkopf, B. Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Their Appl. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, G.; Guainazzi, M.; Maiolino, R. Changing look: From Compton-thick to Compton-thin, or the rebirth of fossil active galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 342, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, S.; Guainazzi, M.; Matt, G.; Chiaberge, M.; Iwasawa, K.; Fiore, F.; Maiolino, R. A search for changing-look AGN in the Grossan catalog. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 442, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, H.D.; Dai, X.; Chen, P.; Cheng, J.; Jayasinghe, T.; Tucker, M.A.; Vallely, P.J.; Bersier, D.; Bose, S.; Do, A.; et al. The Changing Look Blazar B2 1420+32. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.08707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Herazo, H.A.; Massaro, F.; Gu, M.; Paggi, A.; Landoni, M.; D’Abrusco, R.; Ricci, F.; Masetti, N.; Chavushyan, V. An Optical Overview of Blazars with LAMOST. I. Hunting Changing-look Blazars and New Redshift Estimates. Astron. J. 2021, 161, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.M.; Ferrarese, L.; Gilbert, K.M.; Kaspi, S.; Malkan, M.A.; Maoz, D.; Merritt, D.; Netzer, H.; Onken, C.A.; Pogge, R.W.; et al. Central Masses and Broad-Line Region Sizes of Active Galactic Nuclei. II. A Homogeneous Analysis of a Large Reverberation-Mapping Database. Astrophys. J. 2004, 613, 682–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sniegowska, M.; Czerny, B.; Bon, E.; Bon, N. Possible mechanism for multiple changing-look phenomena in active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.G.; Carswell, R.F.; Whelan, J.A.J.; Wilkes, B.J.; Boksenberg, A.; Clowes, R.G.; Savage, A.; Cannon, R.D.; Wall, J.V. Observations of the Lyman limit in 19 QSOs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 195, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, G.; Ghisellini, G.; Colpi, M.; Dotti, M. Black hole mass estimate for a sample of radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 210–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, Q. The black hole mass, jet power and accretion in blazars and flat-spectrum radio-loud narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F. Rapid variability in TeV blazars: The case of PKS2155-304. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 386, L28–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Foschini, L.; Ghirlanda, G. The transition between BL Lac objects and flat spectrum radio quasars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 2674–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Fan, J.; Yang, J.; Huang, D.; Li, Z. The Estimation of Fundamental Physics Parameters for Fermi-LAT Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2022, 925, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, L.E.H.; Shabala, S.S. AGN Jet Kinetic Power and the Energy Budget of Radio Galaxy Lobes. Astrophys. J. 2013, 767, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; Berenji, B.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope Observations of Misaligned Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2010, 720, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Alexander, P.; Pooley, G.G.; Riley, J.M. FR II radio galaxies with z<0.3 - II. Beaming and unification. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 304, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arshakian, T.G.; Longair, M.S. On the jet speeds of classical double radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 351, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanas, D.; Georganopoulos, M. Decelerating Flows in TeV Blazars: A Resolution to the BL Lacertae-FR I Unification Problem. Astrophys. J. 2003, 594, L27–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliani, Z.; Keppens, R. Decelerating Relativistic Two-Component Jets. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioni, R.; Grandi, P.; Torresi, E.; Vignali, C.; Knödlseder, J. Radio galaxies from Fermi to the CTA. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1792, 050006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherenkov Telescope Array Consortium; Acharya, B.S.; Agudo, I.; Al Samarai, I.; Alfaro, R.; Alfaro, J.; Alispach, C.; Alves Batista, R.; Amans, J.P.; Amato, E.; et al. Science with the Cherenkov Telescope Array; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.A.; Rani, B.; Oh, J.; Marscher, A.; Jorstad, S.; Mizuno, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, S.S.; Trippe, S.; Mertens, F. A Detailed Kinematic Study of 3C 84 and Its Connection to γ-Rays. Astrophys. J. 2021, 914, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Fan, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Tao, J.; Costantin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Comparison between Fermi-detected and non-Fermi-detected superluminal sources. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2019, 62, 129811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F. Fermi/LAT broad emission line blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 1060–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbarrato, T.; Ghisellini, G.; Maraschi, L.; Colpi, M. The relation between broad lines and γ-ray luminosities in Fermi blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 421, 1764–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 4FGL | Associated | Class | z | m | B | R | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Name | (mJy) | (W Hz) | (mag) | (mJy) | ( ) | (Jy) | |||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | (15) |
| J0009.7−3217 | IC 1531 | FRI | 0.025641 | 642 | 23.98 | 12.05 | 46.57 | 1.14 | 1.50 | 9.04 | 0.17 | |||
| J0014.2+0854 | TXS 0011+086 | FRI | 0.1632 | 325.6 | 25.40 | 17.19 | 13.69 | 1.38 | 1.13 | 0.53 | ||||
| J0028.8−0112 | PKS 0026−014 | FRI | 0.083 | 378 | 24.82 | 16.46 | 0.80 | 2.67 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 0.29 | |||
| ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ |
| Associated Name | Class | z | m | B | R | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mJy) | (W Hz) | (mag) | (mJy) | ( ) | (Jy) | ||||||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) |
| SDSS J001247.57+004715.8 | FRII | 0.148 | 62.7 | 24.59 | 16.35 | 0.89 | 1.85 | 0.34 | 8.6 | 0.68 | |||
| SDSS J002107.62−005531.4 | FRII | 0.108 | 112.9 | 24.55 | 15.35 | 2.23 | 1.70 | 0.35 | 8.5 | 0.48 | |||
| 0034−014B | FRII | 0.0736 | 4400 | 25.72 | 15.18 | 2.60 | 3.23 | 0.72 | 0.81 | ||||
| ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ | ⋯ |
| Parameter | KS Statistic | Probability | NFFRs | FFRs | Average (NFFRs) | Average (FFRs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.48 | 2.18 × 10−8 | 354 | 43 | |||
| 0.33 | 5.68 × 10−5 | 364 | 53 | 24.38 | 24.86 | |
| B | 0.52 | 1.71 × 10−9 | 353 | 43 | 1.74 | 2.89 |
| (for FR Is) | 0.58 | 3.59 × 10−9 | 212 | 31 | 0.21 | 0.49 |
| R | 0.50 | 7.30 × 10−5 | 32 | 47 | ||
| 0.44 | 1.07 × 10−4 | 337 | 25 | 8.49 | 8.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, D.; Ye, X.; Ye, X.; Huang, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Liao, J.; Zhang, H.; Pei, Z.; et al. Why Are Some Radio Galaxies Detected by Fermi, but Others Not? Universe 2023, 9, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110479
Huang D, Ye X, Ye X, Huang X, Qian Y, Li Z, Li C, Liao J, Zhang H, Pei Z, et al. Why Are Some Radio Galaxies Detected by Fermi, but Others Not? Universe. 2023; 9(11):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110479
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Danyi, Xuhong Ye, Xiao Ye, Xiulin Huang, Yanjun Qian, Ziyan Li, Chengfeng Li, Jiru Liao, Hengji Zhang, Zhiyuan Pei, and et al. 2023. "Why Are Some Radio Galaxies Detected by Fermi, but Others Not?" Universe 9, no. 11: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110479
APA StyleHuang, D., Ye, X., Ye, X., Huang, X., Qian, Y., Li, Z., Li, C., Liao, J., Zhang, H., Pei, Z., Yang, J., & Fan, J. (2023). Why Are Some Radio Galaxies Detected by Fermi, but Others Not? Universe, 9(11), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110479







