The Effective Fluid Approach for Modified Gravity and Its Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Models
The Quasi-Static and Sub-Horizon Approximations
2.2. Horndeski Models
- f(R) theories: These are equivalent to a non-minimally coupled scalar field written as [101]where has units of mass and we have set .
- Brans–Dicke theories: These are the archetype of a scalar–tensor theory, withwhere is the potential and is the well-known Brans–Dicke parameter [102].
- Kinetic gravity braiding: These models contain a mixing of the scalar and tensor kinetic terms [103] and are given by
- In the case of inflation, the Higgs-like inflation model is given by and .
2.2.1. Background Expansion
2.2.2. Linear Perturbations
2.2.3. The Effective Fluid Approach for Horndeski Models
2.3. Scalar–Vector–Tensor Models
The Effective Fluid Approach for SVT Theories with Non-Vanishing Anisotropic Stress
3. The Effective Fluid Approach and the Boltzmann Codes
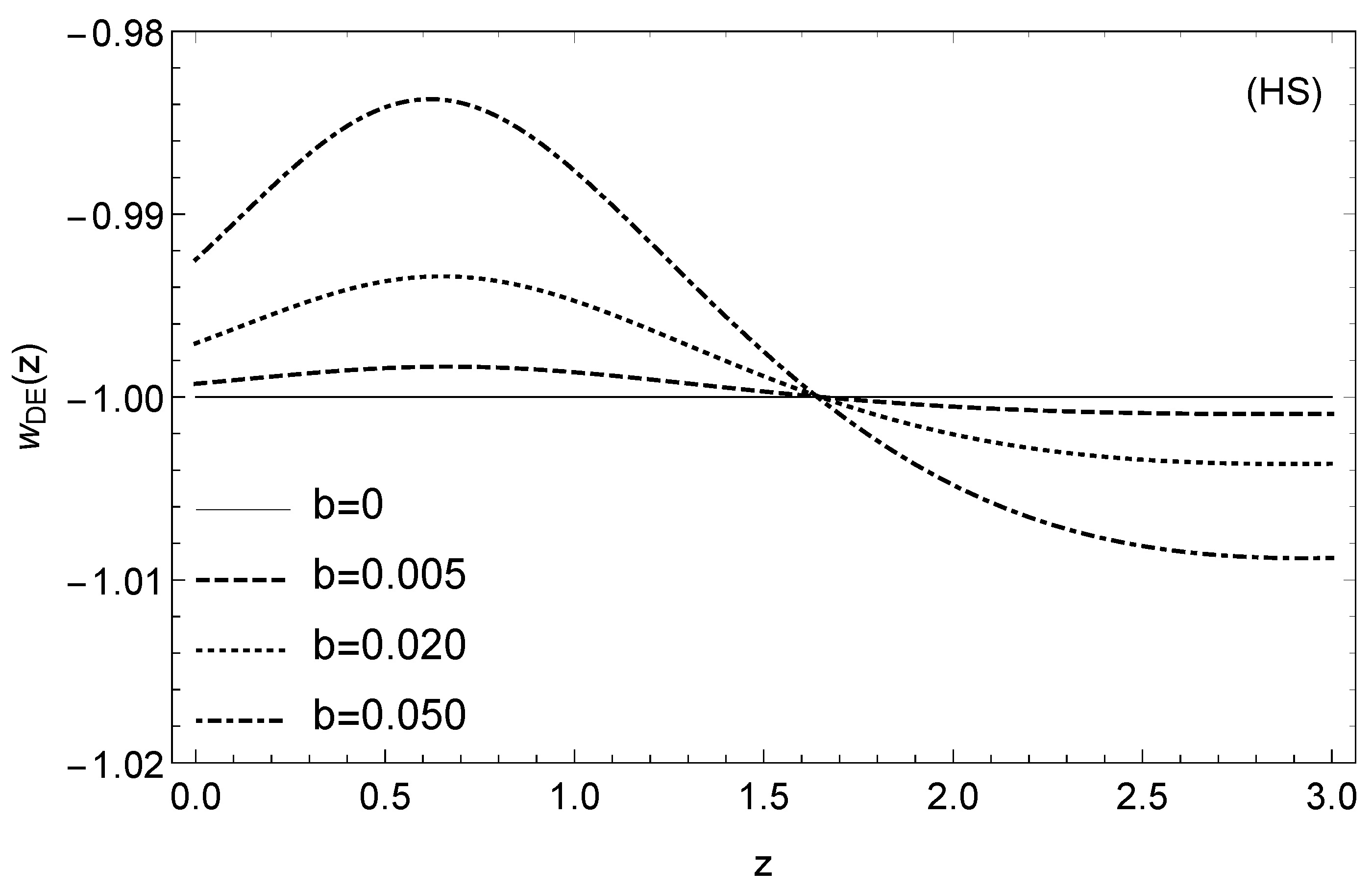
3.1. Designer Horndeski
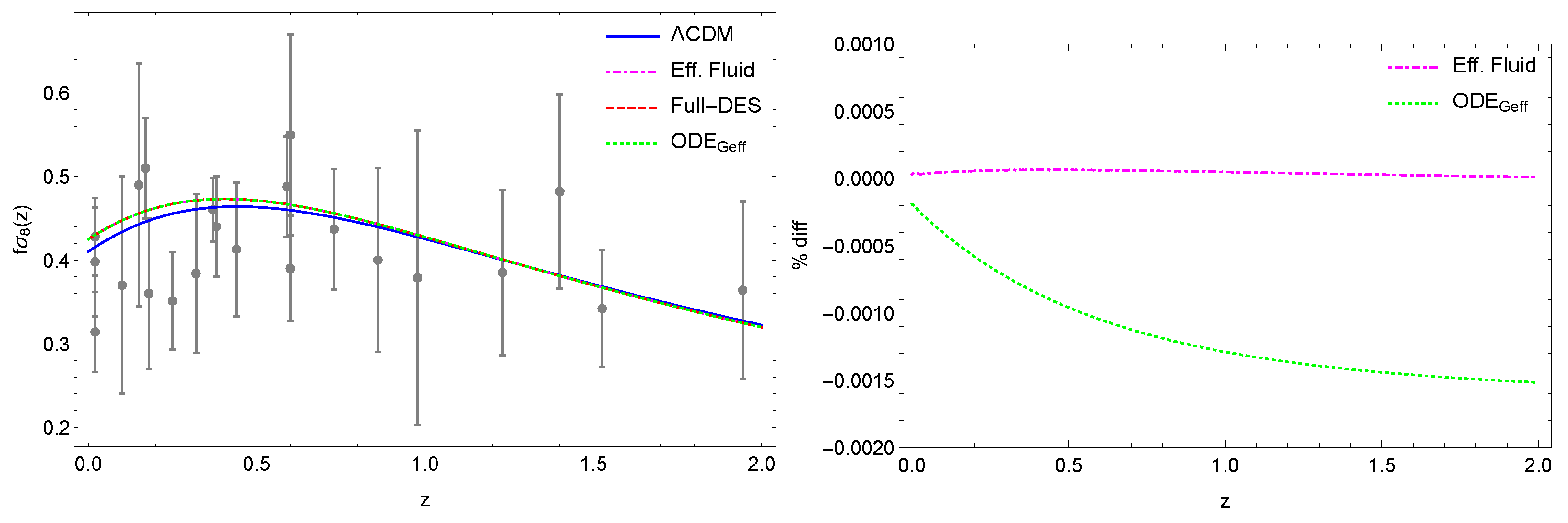
3.2. Numerical Solutions of the Perturbation Equations
- Third, we consider the numerical solution of the growth factor Equation (39) using the appropriate expression for , which we call “ODE-Geff”.
- Finally, we also consider the CDM model.
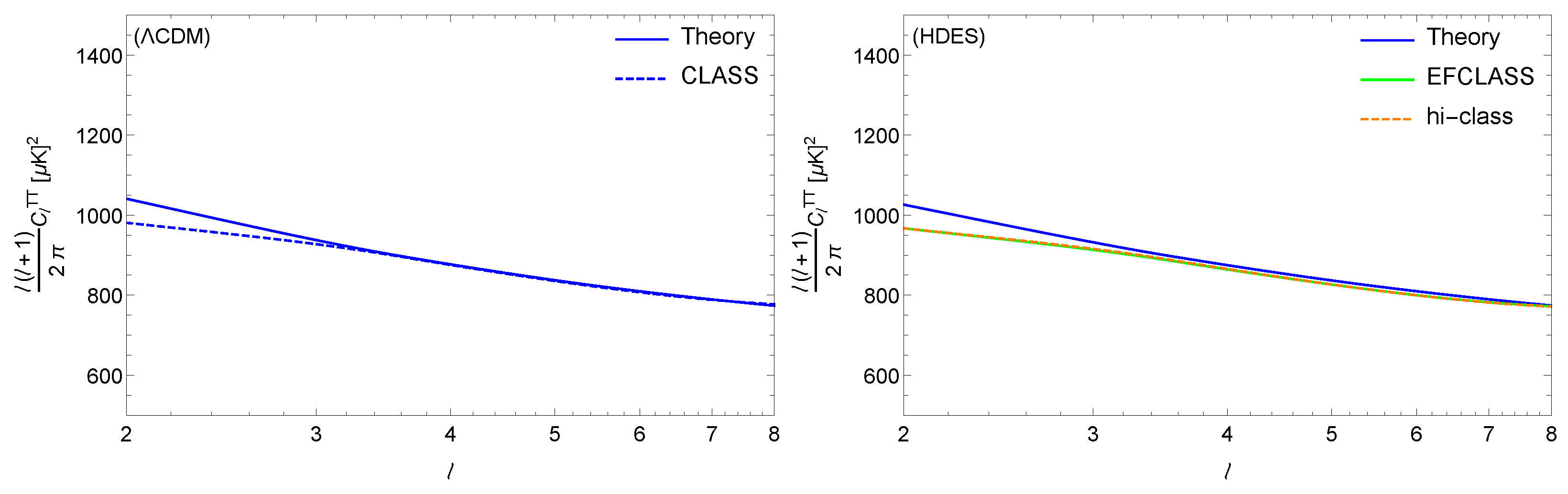
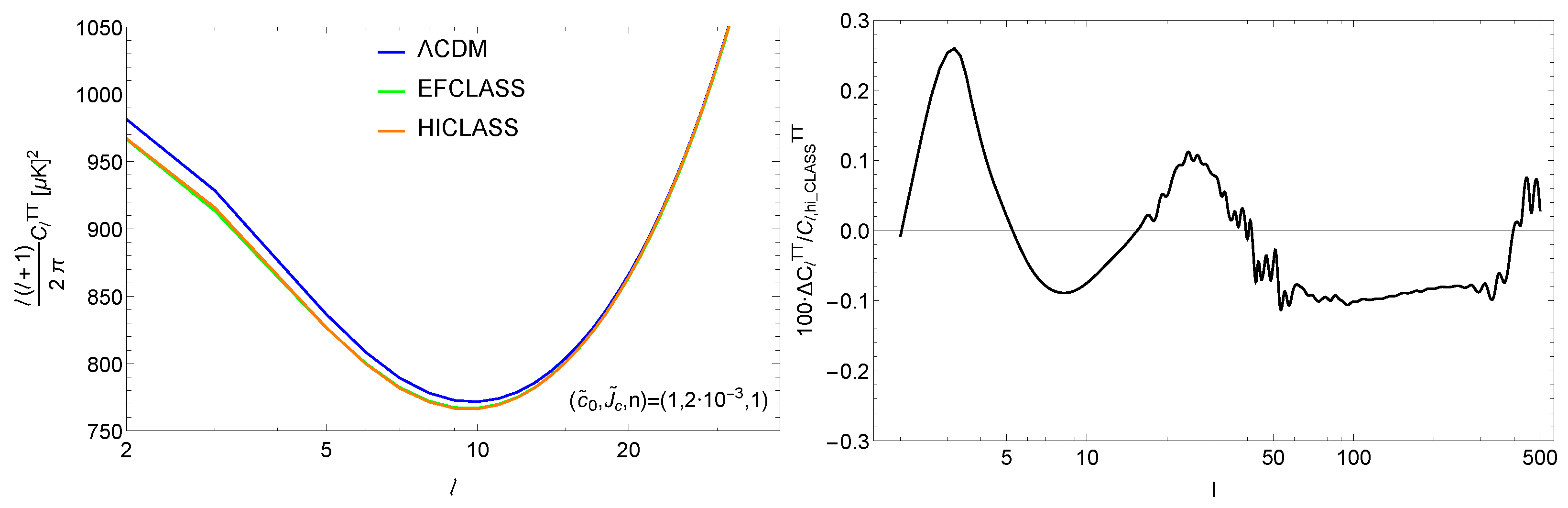
3.3. Modifications to CLASS and the ISW Effect
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBKS | Bardeen, Bond, Kaiser and Szalay (transfer function) |
| CAMB | Code for Anisotropies in the Microwave Background |
| CDM | Cold Dark Matter |
| CLASS | Cosmic Linear Anisotropy Solving System |
| CMB | Cosmic Microwave Background |
| DE | Dark Energy |
| DM | Dark Matter |
| EFCLASS | Effective Fluid CLASS |
| EOS | Equation of State |
| FLRW | Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker metric |
| GC | Galaxy Counts |
| GR | General Relativity |
| GW | Gravitational Wave |
| ISW | Integrated Sachs-Wolfe effect |
| HDES | Horndeski Designer model |
| HS | Hu–Sawicki model |
| KGB | Kinetic Gravity Braiding model |
| CDM | The cosmological constant () and cold dark matter (CDM) model |
| LSS | Large-Scale Structure |
| MG | Modified Gravity |
| SVT | Scalar–Vector–Tensor |
| 1 | In this review, our conventions are: (-+++) for the metric signature, the Riemann and Ricci tensors are given by and . The Einstein equations are for and is the bare Newton’s constant, while in what follows, we set the speed of light . |
| 2 | For the sake of brevity, we now set in what follows , and where . |
References
- Riess, A.G. et al. [The American Astronomical Society] Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S. et al. [The American Astronomical Society] Measurements of Omega and Lambda from 42 high redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofman, L.; Starobinsky, A.A. Effect of the cosmological constant on large scale anisotropies in the microwave backbround. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1985, 11, 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- Aghanim, N. et al. [Planck Collaboration] Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, T.M.C. et al. [Dark Energy Survey Collaboration] Dark Energy Survey year 1 results: Cosmological constraints from galaxy clustering and weak lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2018, D98, 043526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. The Cosmological Constant Problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M. The Cosmological constant. Living Rev. Rel. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, G. et al. [The American Astronomical Society] Nine-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Cosmological Parameter Results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2013, 208, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, E.J.; Sami, M.; Tsujikawa, S. Dynamics of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 1753–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratra, B.; Peebles, P.J.E. Cosmological Consequences of a Rolling Homogeneous Scalar Field. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendariz-Picon, C.; Mukhanov, V.F.; Steinhardt, P.J. A Dynamical solution to the problem of a small cosmological constant and late time cosmic acceleration. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 4438–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; Padilla, A.; Skordis, C. Modified Gravity and Cosmology. Phys. Rep. 2012, 513, 1–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collett, T.E.; Oldham, L.J.; Smith, R.J.; Auger, M.W.; Westfall, K.B.; Bacon, D.; Nichol, R.C.; Masters, K.L.; Koyama, K.; van den Bosch, R. A precise extragalactic test of General Relativity. Science 2018, 360, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific and Virgo Collaborations] Tests of general relativity with GW150914. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 221101, Erratum in Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 129902.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesseris, S.; Shafieloo, A. A model independent null test on the cosmological constant. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2010, 408, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Garcia-Bellido, J. A new perspective on Dark Energy modeling via Genetic Algorithms. JCAP 2012, 1211, 033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GW170814: A Three-Detector Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 141101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creminelli, P.; Vernizzi, F. Dark Energy after GW170817 and GRB170817A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 251302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakstein, J.; Jain, B. Implications of the Neutron Star Merger GW170817 for Cosmological Scalar-Tensor Theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 251303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquiaga, J.M.; Zumalacarregui, M. Dark Energy After GW170817: Dead Ends and the Road Ahead. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 251304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.; Bellini, E.; Ferreira, P.G.; Lagos, M.; Noller, J.; Sawicki, I. Strong constraints on cosmological gravity from GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 251301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, L.; Kunz, M.; Saltas, I.D.; Sawicki, I. Fate of Large-Scale Structure in Modified Gravity After GW170817 and GRB170817A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 131101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisostomi, M.; Koyama, K. Self-accelerating universe in scalar-tensor theories after GW170817. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 084004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusciante, N.; Peirone, S.; Casas, S.; Lima, N.A. Cosmology of surviving Horndeski theory: The road ahead. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 063538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kase, R.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark energy in Horndeski theories after GW170817: A review. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1942005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, R.; Lombriser, L.; Peñarrubia, J. Finding Horndeski theories with Einstein gravity limits. JCAP 2016, 1611, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombriser, L.; Taylor, A. Breaking a Dark Degeneracy with Gravitational Waves. JCAP 2016, 1603, 031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, T.P.; Faraoni, V. f(R) Theories Of Gravity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 451–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, A.; Tsujikawa, S. f(R) theories. Living Rev. Rel. 2010, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Modified Gravity Theories on a Nutshell: Inflation, Bounce and Late-time Evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified cosmic history in modified gravity: From F(R) theory to Lorentz non-invariant models. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 59–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multamaki, T.; Vilja, I. Cosmological expansion and the uniqueness of gravitational action. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 024018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz-Dombriz, A.; Dobado, A. A f(R) gravity without cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 087501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogosian, L.; Silvestri, A. The pattern of growth in viable f(R) cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 023503, Erratum in Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 049901.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S. Can the degeneracies in the gravity sector be broken? Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, S. Matter density perturbations and effective gravitational constant in modified gravity models of dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 023514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Sapone, D. Accuracy of the growth index in the presence of dark energy perturbations. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 023013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, C.A.; Basilakos, S.; Nesseris, S. Cosmological constraints on γ-gravity models. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 023516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Romero, J.; Nesseris, S. Cosmological constraints and comparison of viable f(R) models. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 023525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Sawicki, I. Models of f(R) Cosmic Acceleration that Evade Solar-System Tests. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 064004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Sawicki, I. A Parameterized Post-Friedmann Framework for Modified Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.; Sapone, D. Dark Energy versus Modified Gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivisto, T.; Mota, D.F. Cosmology and Astrophysical Constraints of Gauss-Bonnet Dark Energy. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 644, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, T.; Mota, D.F. Gauss-Bonnet Quintessence: Background Evolution, Large Scale Structure and Cosmological Constraints. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 023518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz-Dombriz, A.; Dobado, A.; Maroto, A.L. On the evolution of density perturbations in f(R) theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 123515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starobinsky, A.A. Disappearing cosmological constant in f(R) gravity. JETP Lett. 2007, 86, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, R.; Bernat, D.; Pogosian, L.; Silvestri, A.; Trodden, M. Dynamics of Linear Perturbations in f(R) Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 064020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Hollenstein, L.; Caldera-Cabral, G.; Koyama, K. Theoretical Priors On Modified Growth Parametrisations. JCAP 2010, 1004, 018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pogosian, L.; Silvestri, A.; Koyama, K.; Zhao, G.B. How to optimally parametrize deviations from General Relativity in the evolution of cosmological perturbations? Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 104023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, R.; Tangmatitham, M. Current constraints on the cosmic growth history. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 083534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.; Cooray, A.; Melchiorri, A. Constraints on a New Post-General Relativity Cosmological Parameter. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 023507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertschinger, E.; Zukin, P. Distinguishing Modified Gravity from Dark Energy. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 024015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; Skordis, C.; Zuntz, J. Towards a fully consistent parameterization of modified gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 124018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, A.; Pogosian, L.; Buniy, R.V. Practical approach to cosmological perturbations in modified gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 104015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.; Sanghai, V.A.A. Parameterizing theories of gravity on large and small scales in cosmology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, M. Testing General Relativity in Cosmology. Living Rev. Relativ. 2019, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.B.; Pogosian, L.; Silvestri, A.; Zylberberg, J. Searching for modified growth patterns with tomographic surveys. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 083513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Challinor, A.; Lasenby, A. Efficient computation of CMB anisotropies in closed FRW models. Astrophys. J 2000, 538, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjati, A.; Pogosian, L.; Zhao, G.B. Testing gravity with CAMB and CosmoMC. JCAP 2011, 1108, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.h. Testing f(R) dark energy model with the large scale structure. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. FRCAMB: An f(R) Code for Anisotropies in the Microwave Background. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.03232. [Google Scholar]
- Gubitosi, G.; Piazza, F.; Vernizzi, F. The Effective Field Theory of Dark Energy. JCAP 2013, 1302, 032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Raveri, M.; Frusciante, N.; Silvestri, A. Effective Field Theory of Cosmic Acceleration: An implementation in CAMB. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 103530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ade, P.A.R. et al. [Planck Collaboration] Planck 2015 results. XIV. Dark energy and modified gravity. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, R.A.; Bolliet, B.; Pearson, J.A. f(R) gravity as a dark energy fluid. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 044026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Dark energy: The Equation of state description versus scalar-tensor or modified gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 634, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Troisi, A. Cosmological viability of f(R)-gravity as an ideal fluid and its compatibility with a matter dominated phase. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 639, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Mantica, C.A.; Molinari, L.G. Cosmological perfect-fluids in f(R) gravity. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2019, 16, 1950008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas, D.; Lesgourgues, J.; Tram, T. The Cosmic Linear Anisotropy Solving System (CLASS) II: Approximation schemes. JCAP 2011, 1107, 034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, R.A.; Bolliet, B.; Pace, F. Do cosmological data rule out f(R) with w≠-1? Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 104070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M. The phenomenological approach to modeling the dark energy. C. R. Phys. 2012, 13, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltas, I.D.; Kunz, M. Anisotropic stress and stability in modified gravity models. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 064042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, I.; Bellini, E. Limits of quasistatic approximation in modified-gravity cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 084061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, W.; Hollenstein, L.; Kunz, M. The traces of anisotropic dark energy in light of Planck. JCAP 2014, 1407, 032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivisto, T.; Mota, D.F. Dark energy anisotropic stress and large scale structure formation. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 083502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, D.F.; Kristiansen, J.R.; Koivisto, T.; Groeneboom, N.E. Constraining Dark Energy Anisotropic Stress. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 382, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W. Structure formation with generalized dark matter. Astrophys. J. 1998, 506, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Putter, R.; Huterer, D.; Linder, E.V. Measuring the Speed of Dark: Detecting Dark Energy Perturbations. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 103513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, R.C.; Marra, V. Clustering dark energy and halo abundances. JCAP 2017, 1711, 048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Bridle, S. Cosmological parameters from CMB and other data: A Monte Carlo approach. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 103511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegmark, M. et al. [the SDSS collaboration] Cosmological parameters from SDSS and WMAP. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ade, P.A.R. et al. [Planck Collaboration] Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.B.; Raveri, M.; Pogosian, P.; Wang, Y.; Crittenden, R.G.; Handley, W.J.; Percival, W.J.; Beutler, F.; Brinkmann, J.; Chuang, C.; et al. Dynamical dark energy in light of the latest observations. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heavens, A.; Fantaye, Y.; Sellentin, E.; Eggers, H.; Hosenie, Z.; Kroon, S.; Mootoovaloo, A. No evidence for extensions to the standard cosmological model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, W.L. Cosmology at a Crossroads. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 0121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renk, J.; Zumalacarregui, M.; Montanari, F.; Barreira, A. Galileon gravity in light of ISW, CMB, BAO and H0 data. JCAP 2017, 1710, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.C. Structure formation in f(T) gravity and a solution for H0 tension. JCAP 2018, 1805, 052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.X.; Raveri, M.; Hu, W. Phenomenology of Modified Gravity at Recombination. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 043514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, M.; Santos da Costa, S.; Capozziello, S.; Alcaniz, J.S.; De Laurentis, M. Observational constraints on Gauss? Bonnet cosmology. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2018, 27, 1850084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, Z.; Ilic, S.; Blanchard, A. Cluster counts: Calibration issue or new physics? Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 620, A78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.P.; Bertschinger, E. Cosmological perturbation theory in the synchronous and conformal Newtonian gauges. Astrophys. J. 1995, 455, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark Energy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhanov, V.F.; Feldman, H.A.; Brandenberger, R.H. Theory of cosmological perturbations. Part 1. Classical perturbations. Part 2. Quantum theory of perturbations. Part 3. Extensions. Phys. Rept. 1992, 215, 203–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapone, D.; Kunz, M. Fingerprinting Dark Energy. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 083519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Crossing the Phantom Divide: Theoretical Implications and Observational Status. JCAP 2007, 0701, 018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, R.M. General Relativity; Chicago Univ. Pr.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjona, R.; Cardona, W.; Nesseris, S. Unraveling the effective fluid approach for f(R) models in the subhorizon approximation. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 043516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horndeski, G.W. Second-order scalar-tensor field equations in a four-dimensional space. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1974, 10, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P. et al. [The American Astronomical Society] Gravitational Waves and Gamma-rays from a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yokoyama, J. Generalized G-inflation: Inflation with the most general second-order field equations. Prog. Theor. Phys. 2011, 126, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T. 1/R gravity and scalar-tensor gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2003, 575, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, C.; Dicke, R.H. Mach’s principle and a relativistic theory of gravitation. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffayet, C.; Pujolas, O.; Sawicki, I.; Vikman, A. Imperfect Dark Energy from Kinetic Gravity Braiding. JCAP 2010, 10, 026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, I. Selected topics in scalar–tensor theories and beyond. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1930012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, R.; Yamamoto, K. Large Scale Structures in Kinetic Gravity Braiding Model That Can Be Unbraided. JCAP 2011, 1104, 025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsujikawa, S. Effective gravitational couplings for cosmological perturbations in the most general scalar-tensor theories with second-order field equations. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 706, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, J. Oscillating solutions of the matter density contrast in Horndeski’s theory. JCAP 2019, 1901, 054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjona, R.; Cardona, W.; Nesseris, S. Designing Horndeski and the effective fluid approach. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 063526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisenberg, L.; Kase, R.; Tsujikawa, S. Cosmology in scalar-vector-tensor theories. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 024038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, W.; Orjuela-Quintana, J.B.; Valenzuela-Toledo, C.A. An effective fluid description of scalar-vector-tensor theories under the sub-horizon and quasi-static approximations. JCAP 2022, 08, 059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. Horndessence: ΛCDM Cosmology from Modified Gravity. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.14560. [Google Scholar]
- Sagredo, B.; Nesseris, S.; Sapone, D. Internal Robustness of Growth Rate data. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 083543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumalacarregui, M.; Bellini, E.; Sawicki, I.; Lesgourgues, J.; Ferreira, P.G. hi_class: Horndeski in the Cosmic Linear Anisotropy Solving System. JCAP 2017, 1708, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Hu, W.; Sawicki, I. The Large Scale Structure of f(R) Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 044004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodelson, S. Modern Cosmology; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, F.; Battye, R.; Bellini, E.; Lombriser, L.; Vernizzi, F.; Bolliet, B. Comparison of different approaches to the quasi-static approximation in Horndeski models. JCAP 2021, 6, 017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nesseris, S. The Effective Fluid Approach for Modified Gravity and Its Applications. Universe 2023, 9, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9010013
Nesseris S. The Effective Fluid Approach for Modified Gravity and Its Applications. Universe. 2023; 9(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleNesseris, Savvas. 2023. "The Effective Fluid Approach for Modified Gravity and Its Applications" Universe 9, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9010013
APA StyleNesseris, S. (2023). The Effective Fluid Approach for Modified Gravity and Its Applications. Universe, 9(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9010013