Ultra-High-Energy Astroparticles as Probes for Lorentz Invariance Violation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. LIV Framework
3. Testing LIV with UHE Photons
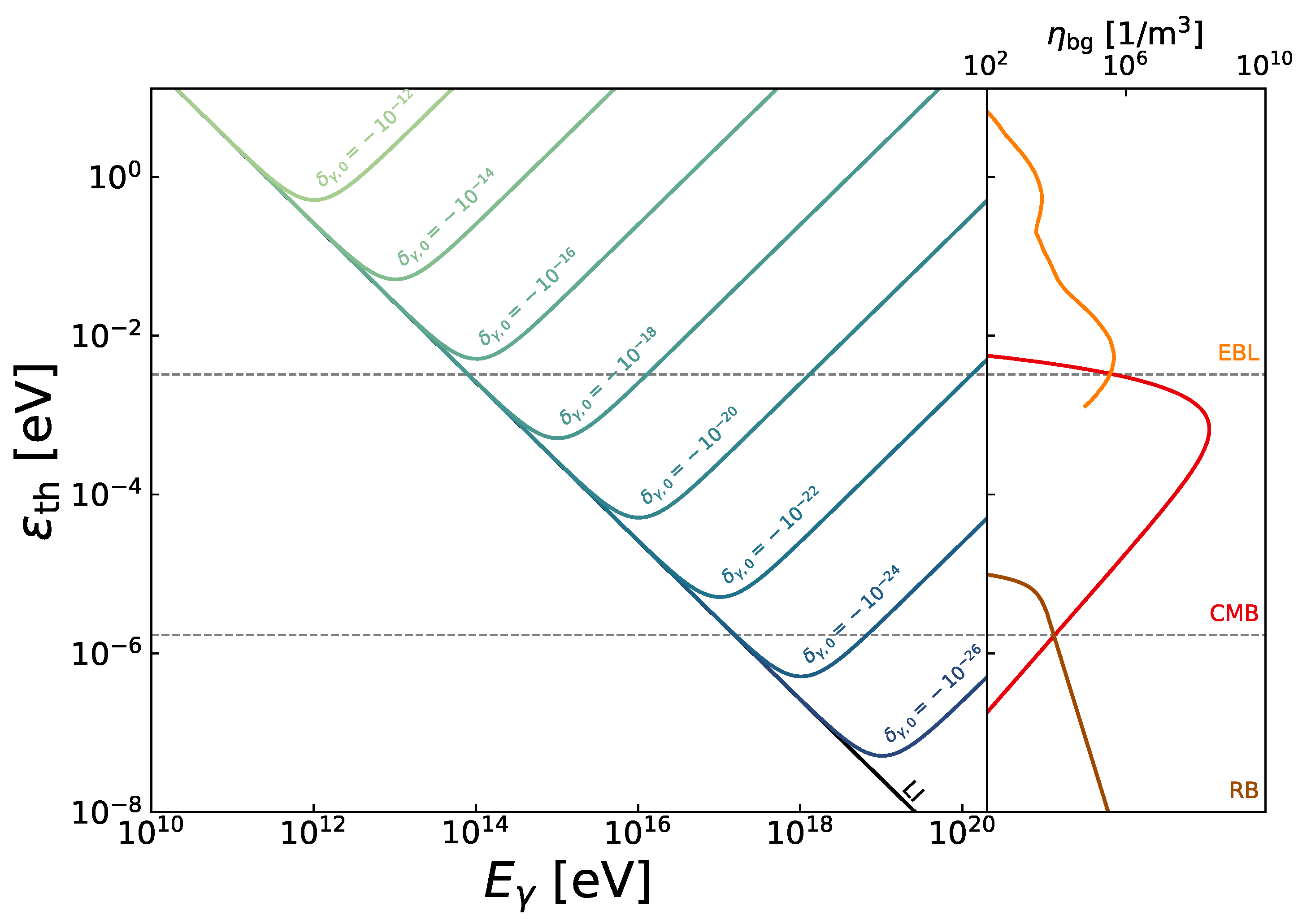
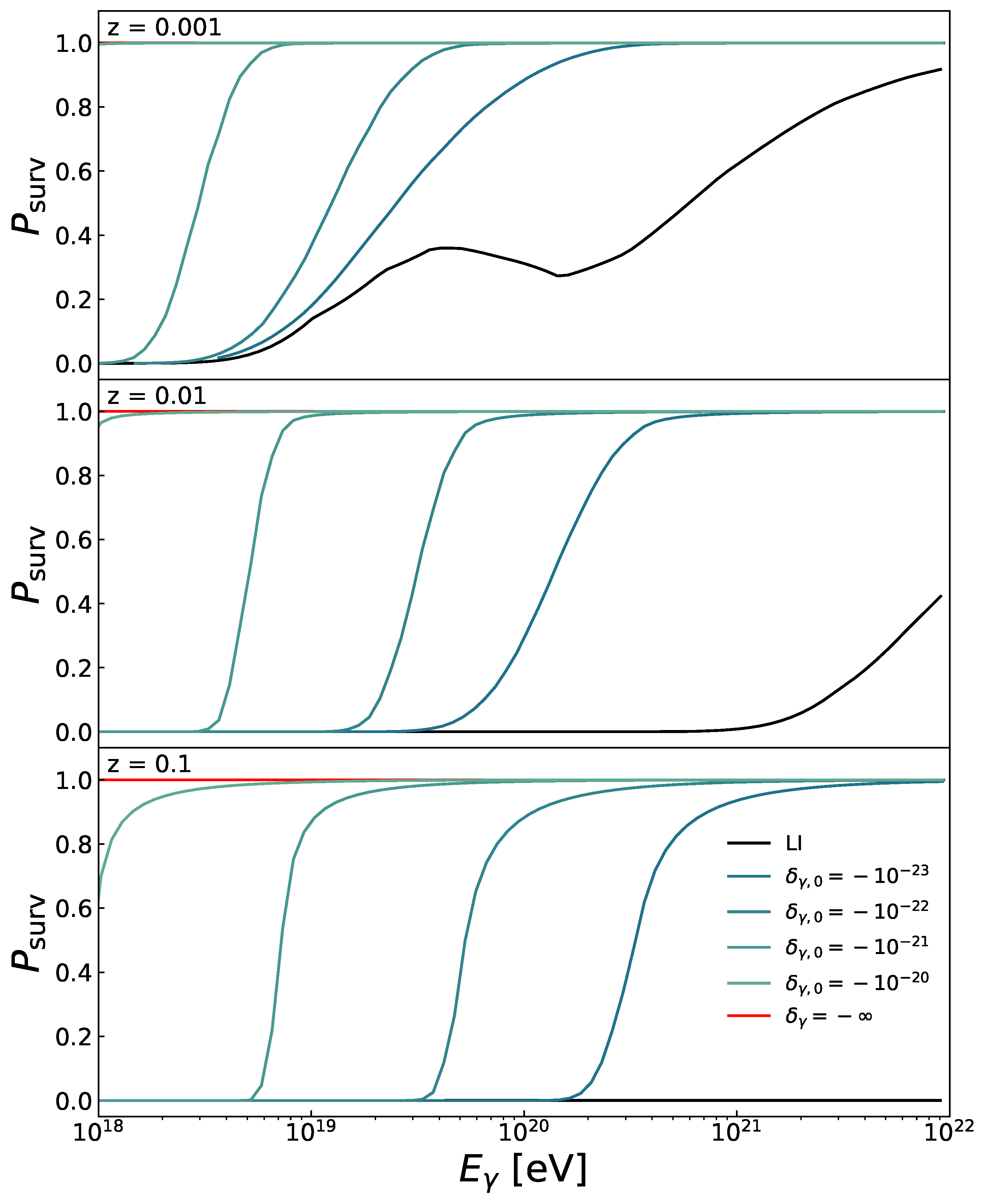
3.1. Propagation of UHE Photons Considering LIV
3.2. Searching for LIV in UHE Photon Data
LIV Limits from Different UHECR Astrophysical Models
4. Testing LIV with UHECR
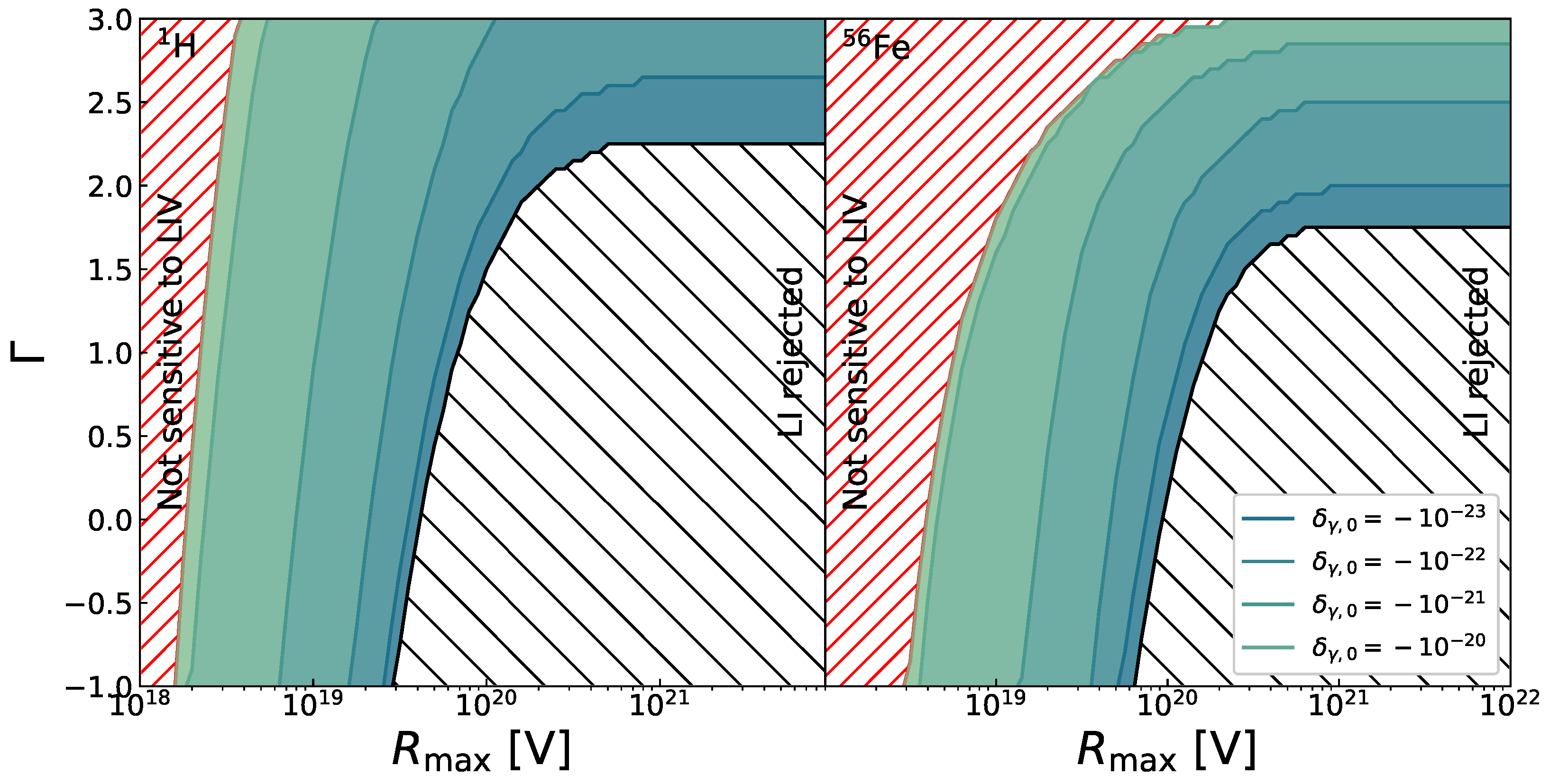
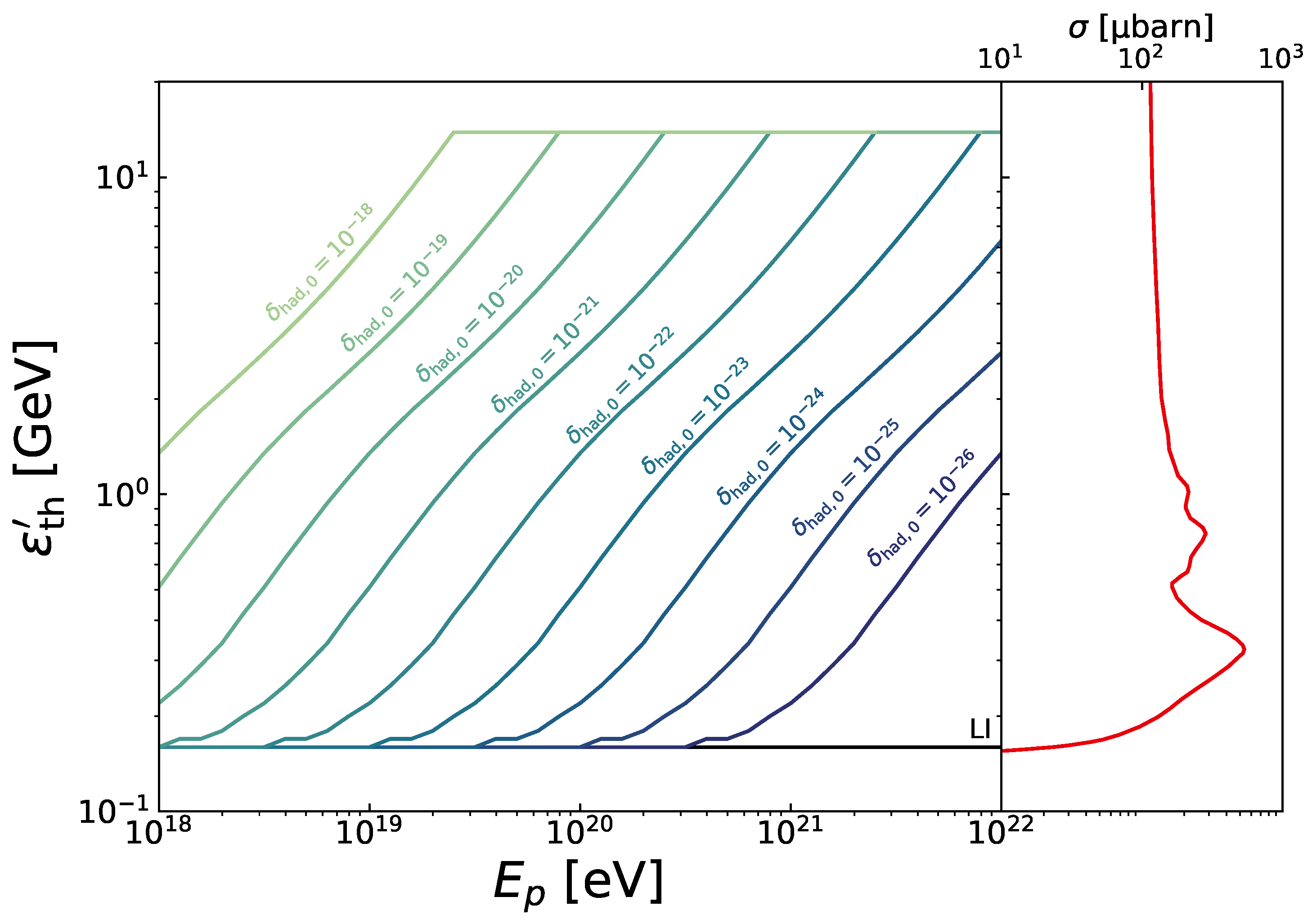
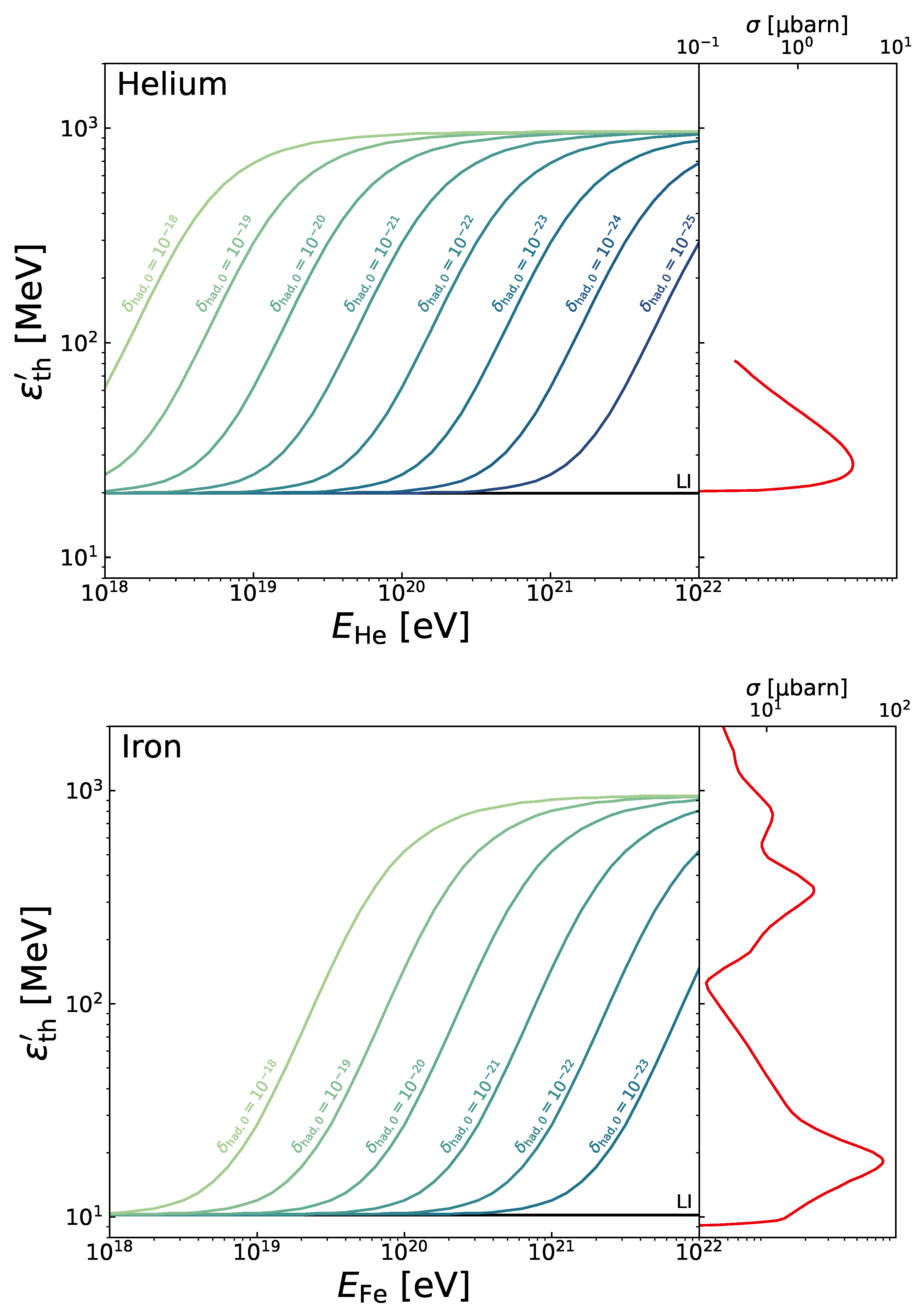
4.1. Kinematics of Interactions of UHECR with the Photon Background Considering LIV
4.2. Searching for LIV in UHECR Data
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGASA | Akeno Giant Air Shower Array |
| CMB | Cosmic microwave background |
| CR | Cosmic rays |
| EBL | Extragalactic background bight |
| HiRes | High Resolution Fly’s Eye Cosmic Ray Detector |
| LI | Lorentz invariant |
| LIV | Lorentz invariance violation |
| MDR | Modified dispersion relation |
| NRF | Nucleus reference frame |
| SM | Standard Model |
| UHE | Ultra-high energy |
| UHECR | Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays |
References
- Addazi, A.; Alvarez-Muniz, J.; Alves Batista, R.; Amelino-Camelia, G.; Antonelli, V.; Arzano, M.; Asorey, M.; Atteia, J.L.; Bahamonde, S.; Bajardi, F.; et al. Quantum gravity phenomenology at the dawn of the multi-messenger era—A review. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2022, 125, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, J. Quantum Gravity and Lorentz Invariance Violation in the Standard Model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 221302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. A phenomenological description of space-time noise in quantum gravity. Nature 2001, 410, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluhm, R. Observational Constraints on Local Lorentz Invariance. In Springer Handbook of Spacetime; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 485–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colladay, D.; Kostelecky, V.A. Lorentz violating extension of the standard model. Phys. Rev. 1998, D58, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V. A Microscopic Recoil Model for Light-Cone Fluctuations in Quantum Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 61, 027503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambini, R.; Pullin, J. Nonstandard optics from quantum spacetime. Phys. Rev. 1999, 59, 124021. [Google Scholar]
- Kostelecky, V.A.; Samuel, S. Spontaneous Breaking of Lorentz Symmetry in String Theory. Phys. Rev. 1989, D39, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, Y. Quantum Electrodynamics in Nonlinear Gauge. Suppl. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1968, E68, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potting, R. Lorentz and CPT violation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 447, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huerta, H.; Lang, R.G.; de Souza, V. Lorentz Invariance Violation Tests in Astroparticle Physics. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biteau, J.; Williams, D.A. The extragalactic background light, the Hubble constant, and anomalies: Conclusions from 20 years of TeV gamma-ray observations. Astrophys. J. 2015, 812, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.G.; Martínez-Huerta, H.; de Souza, V. Improved limits on Lorentz invariance violation from astrophysical gamma-ray sources. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 043015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes Lang, R.; Martínez-Huerta, H.; de Souza, V. Limits on the Lorentz Invariance Violation from UHECR astrophysics. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, S.T.; Stecker, F.W. Lorentz Invariance Violation and the Observed Spectrum of Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 31, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; Scully, S.T. Searching for New Physics with Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 085003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaverni, M.; Sigl, G. Lorentz Violation in the Photon Sector and Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; Glashow, S.L. New tests of Lorentz invariance following from observations of the highest energy cosmic gamma-rays. Astropart. Phys. 2001, 16, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W. Constraints on Lorentz invariance violating quantum gravity and large extra dimensions models using high energy gamma-ray observations. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 20, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martínez-Huerta, H.; Pérez-Lorenzana, A. Restrictions from Lorentz invariance violation on cosmic ray propagation. Phys. Rev. 2017, D95, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astapov, K.; Kirpichnikov, D.; Satunin, P. Photon splitting constraint on Lorentz Invariance Violation from Crab Nebula spectrum. JCAP 2019, 1904, 054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, M. Vacuum Cherenkov radiation for Lorentz-violating fermions. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 095026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, M. (Gravitational) Vacuum Cherenkov Radiation. Symmetry 2018, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkhamer, F.R.; Schreck, M. New two-sided bound on the isotropic Lorentz-violating parameter of modified Maxwell theory. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 085026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Ellis, J.R.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V.; Sarkar, S. Tests of quantum gravity from observations of gamma-ray bursts. Nature 1998, 393, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.R.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V.; Sakharov, A.S. Quantum-gravity analysis of gamma-ray bursts using wavelets. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 402, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satunin, P. Two-sided constraints on Lorentz invariance violation from Tibet-ASγ and LHAASO very-high-energy photon observations. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; He, H. Strong constraints on Lorentz violation using new γ-ray observations around PeV. Chin. Phys. C 2021, 45, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelecky, V.A.; Russell, N. Data Tables for Lorentz and CPT Violation. arXiv 2008, arXiv:hep-ph/0801.0287. [Google Scholar]
- Aab, A. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Search for photons with energies above 1018 eV using the hybrid detector of the Pierre Auger Observatory. JCAP 2017, 04, 009, Erratum in JCAP 2020, 9, E02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenberg, J. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Limits on ultra-high energy photons with the Pierre Auger Observatory. PoS 2019, ICRC2019, 398. [Google Scholar]
- Savina, P. [Pierre Auger Collaboration]. A search for ultra-high-energy photons at the Pierre Auger Observatory exploiting air-shower Universality. PoS 2021, ICRC2021, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, D.; Sarkar, S.; Taylor, A.M. The intergalactic propagation of ultrahigh energy cosmic ray nuclei. Astropart. Phys. 2007, 27, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, D. Extragalactic propagation of ultrahigh energy cosmic-rays. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 39–40, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaverni, M.; Sigl, G. Lorentz Violation and Ultrahigh-Energy Photons. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Galanti, G.; Roncadelli, M. Transparency of the Universe to gamma rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breit, G.; Wheeler, J.A. Collision of Two Light Quanta. Phys. Rev. 1934, 46, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, R.; Somerville, R.; Primack, J.; Dominguez, A. Semi-analytic modeling of the EBL and consequences for extragalactic gamma-ray spectra. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasi, M.; Tartari, A.; Zannoni, M.; Boella, G.; Sironi, G. The Contribution of the Unresolved Extragalactic Radio Sources to the Brightness Temperature of the Sky. Astrophys. J. 2008, 682, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Albury, J.; Allekotte, I.; Cheminant, K.A.; Almela, A.; Alvarez-Muñiz, J.; Batista, R.A.; Anastasi, G.; Anchordoqui, L.; et al. Testing effects of Lorentz invariance violation in the propagation of astroparticles with the Pierre Auger Observatory. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 2022, 023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampert, K.H.; Sarkar, B. Ultra-High Energy Photon and Neutrino Fluxes in Realistic Astrophysical Scenarios. In Proceedings of the International Cosmic Ray Conference, Beijing, China, 11–18 August 2011; Volume 2, p. 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aab, A. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Combined fit of spectrum and composition data as measured by the Pierre Auger Observatory. JCAP 2017, 04, 038, Erratum in JCAP 2018, 03, E02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, R.; Dundovic, A.; Erdmann, M.; Kampert, K.H.; Kuempel, D.; Müller, G.; Sigl, G.; van Vliet, A.; Walz, D.; Winchen, T. CRPropa 3—A Public Astrophysical Simulation Framework for Propagating Extraterrestrial Ultra-High Energy Particles. JCAP 2016, 05, 038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settimo, M.; De Domenico, M.; Lyberis, H. EleCa: A Monte Carlo code for the propagation of extragalactic photons at ultra-high energy. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 2013, 239–240, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aab, A. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Measurement of the cosmic-ray energy spectrum above 2.5 × 1018 eV using the Pierre Auger Observatory. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 062005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aab, A. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Features of the Energy Spectrum of Cosmic Rays above 2.5 × 1018 eV using the Pierre Auger Observatory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aab, A. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Depth of maximum of air-shower profiles at the Pierre Auger Observatory. II. Composition implications. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 122006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aab, A. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Depth of Maximum of Air-Shower Profiles at the Pierre Auger Observatory: Measurements at Energies above 1017.8 eV. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 122005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Joint analysis of the energy spectrum of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays as measured at the Pierre Auger Observatory and the Telescope Array. PoS 2021, ICRC2021, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezinsky, V.; Gazizov, A.Z.; Grigorieva, S.I. On astrophysical solution to ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 043005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, D.; Busca, N.G.; Decerprit, G.; Olinto, A.V.; Parizot, E. Implications of the cosmic ray spectrum for the mass composition at the highest energies. JCAP 2008, 10, 033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisio, R.; Berezinsky, V.; Blasi, P. Ultra high energy cosmic rays: Implications of Auger data for source spectra and chemical composition. JCAP 2014, 10, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.M.; Ahlers, M.; Hooper, D. Indications of Negative Evolution for the Sources of the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 063011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.; Farrar, G.R.; Anchordoqui, L.A. Origin of the ankle in the ultrahigh energy cosmic ray spectrum, and of the extragalactic protons below it. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, M.S.; Unger, M.; Farrar, G.R. Progress towards characterizing ultrahigh energy cosmic ray sources. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luce, Q.; Marafico, S.; Biteau, J.; Condorelli, A.; Deligny, O. Observational constraints on cosmic-ray escape from UHE accelerators. arXiv 2022, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/2207.08092. [Google Scholar]
- Martello, D. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] The Pierre Auger Observatory Upgrade. PoS 2017, ICRC2017, 383. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldi, G. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] The upgrade of the Pierre Auger Observatory with the Scintillator Surface Detector. PoS 2021, ICRC2021, 251. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, R.U. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Surface detectors of the TAx4 experiment. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2021, 1019, 165726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olinto, A.V. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] The POEMMA (Probe of Extreme Multi-Messenger Astrophysics) observatory. JCAP 2021, 06, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörandel, J.R. GCOS-The Global Cosmic Ray Observatory. PoS 2021, ICRC2021, 027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greisen, K. End to the cosmic ray spectrum? Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, G.; Kuzmin, V. Upper limit of the spectrum of cosmic rays. JETP Lett. 1966, 4, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, A.M.; Ahlers, M.; Aharonian, F.A. The need for a local source of UHE CR nuclei. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.G.; Taylor, A.M.; Ahlers, M.; de Souza, V. Revisiting the distance to the nearest ultrahigh energy cosmic ray source: Effects of extragalactic magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 063012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.G. Effects of Lorentz Invariance Violation on the Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays Spectrum. Master’s Thesis, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisio, R.; Boncioli, D.; Di Matteo, A.; Grillo, A.F.; Petrera, S.; Salamida, F. SimProp v2r4: Monte Carlo simulation code for UHECR propagation. JCAP 2017, 11, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucke, A.; Engel, R.; Rachen, J.P.; Protheroe, R.J.; Stanev, T. SOPHIA: Monte Carlo simulations of photohadronic processes in astrophysics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2000, 124, 290–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachen, J.P. Interaction Processes and Statistical Properties of the Propagation of Cosmic Rays in Photon Backgrounds. Ph.D. Thesis, Max-Planck-Institute for Radioastronomy, Bonn, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Stecker, F.W.; Scully, S.T. Lorentz invariance violation and the spectrum and source power of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays. Astropart. Phys. 2005, 23, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Sakaki, N.; Honda, K.; Chikawa, M.; Fukushima, M.; Hayashida, N.; Inoue, N.; Kadota, K.; Kakimoto, F.; Kamata, K.; et al. Energy determination in the Akeno Giant Air Shower Array experiment. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 19, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.U.; Abu-Zayyad, T.; Allen, M.; Amman, J.F.; Archbold, G.; Belov, K.; Belz, J.W.; Zvi, S.B.; Bergman, D.R.; Blake, S.A.; et al. First observation of the Greisen-Zatsepin-Kuzmin suppression. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, J.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Aguirre, C.; Allard, D.; Allekotte, I.; Allen, J.; Allison, P.; Alvarez-Muniz, J.; Ambrosio, M.; et al. Observation of the suppression of the flux of cosmic rays above 4 × 1019eV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 061101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.J.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Q. Testing Lorentz Invariance with Ultra High Energy Cosmic Ray Spectrum. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 083015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccione, L.; Taylor, A.M.; Mattingly, D.M.; Liberati, S. Planck-scale Lorentz violation constrained by Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays. JCAP 2009, 04, 022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, V. Testing the agreement between the Xmax distributions measured by the Pierre Auger and Telescope Array Observatories. PoS 2018, ICRC2017, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncioli, D. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Probing Lorentz symmetry with the Pierre Auger Observatory. PoS 2018, ICRC2017, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.G. et al. [Pierre Auger Collaboration] Testing Lorentz Invariance Violation at the Pierre Auger Observatory. PoS 2019, ICRC2019, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi, E. On the origin of the Cosmic Radiation. Phys. Rev. 1949, 75, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axford, W. Acceleration of Cosmic Rays by Shock Waves. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 375, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krymskii, G.F. A regular mechanism for the acceleration of charged particles on the front of a shock wave. Akad. Nauk SSSR Dokl. 1977, 234, 1306–1308. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1977DoSSR.234.1306K (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Bell, A.R. The acceleration of cosmic rays in shock fronts. I. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1978, 182, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.; Ostriker, J. Particle Acceleration by Astrophysical Shocks. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1978, 221, L29–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
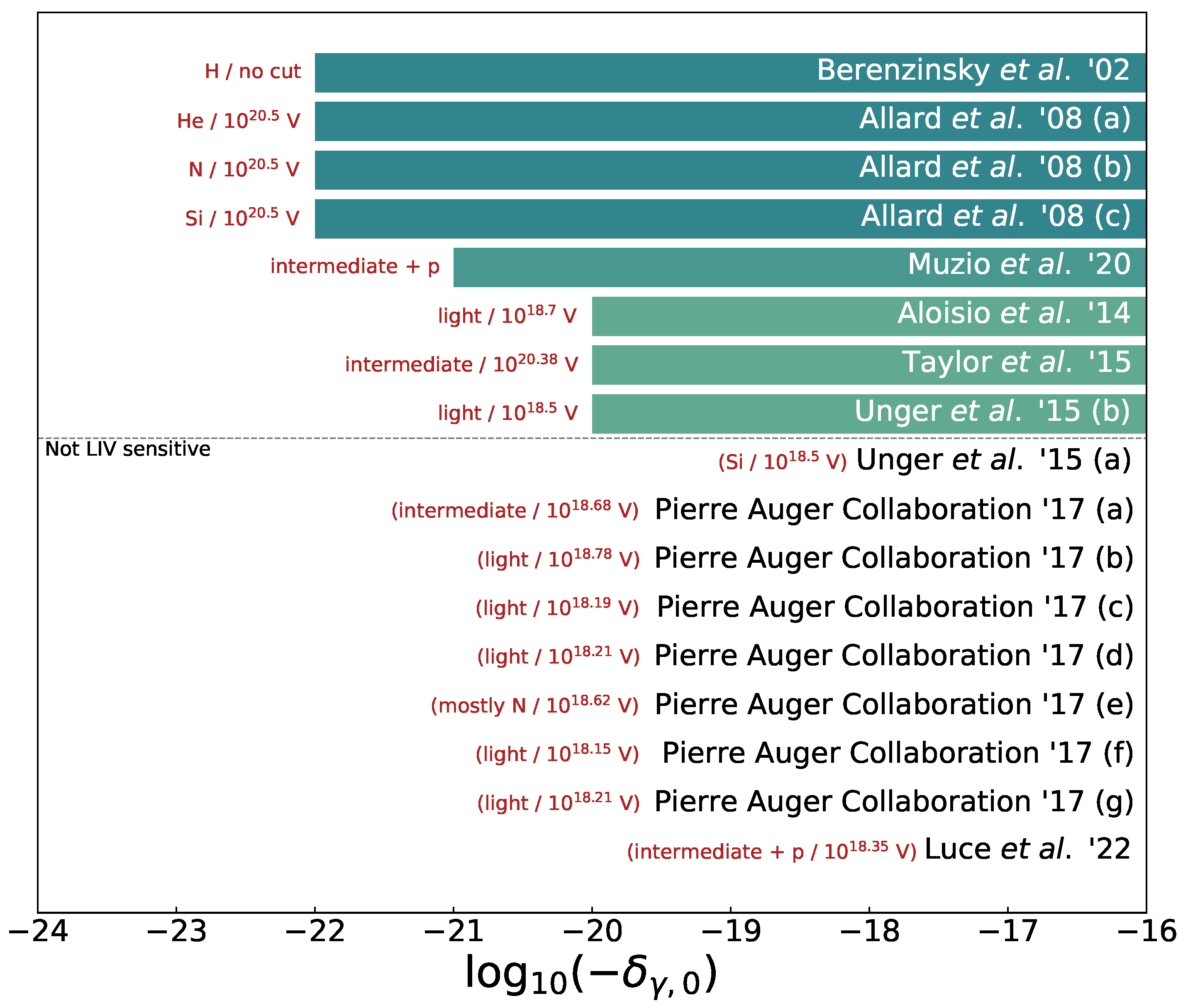
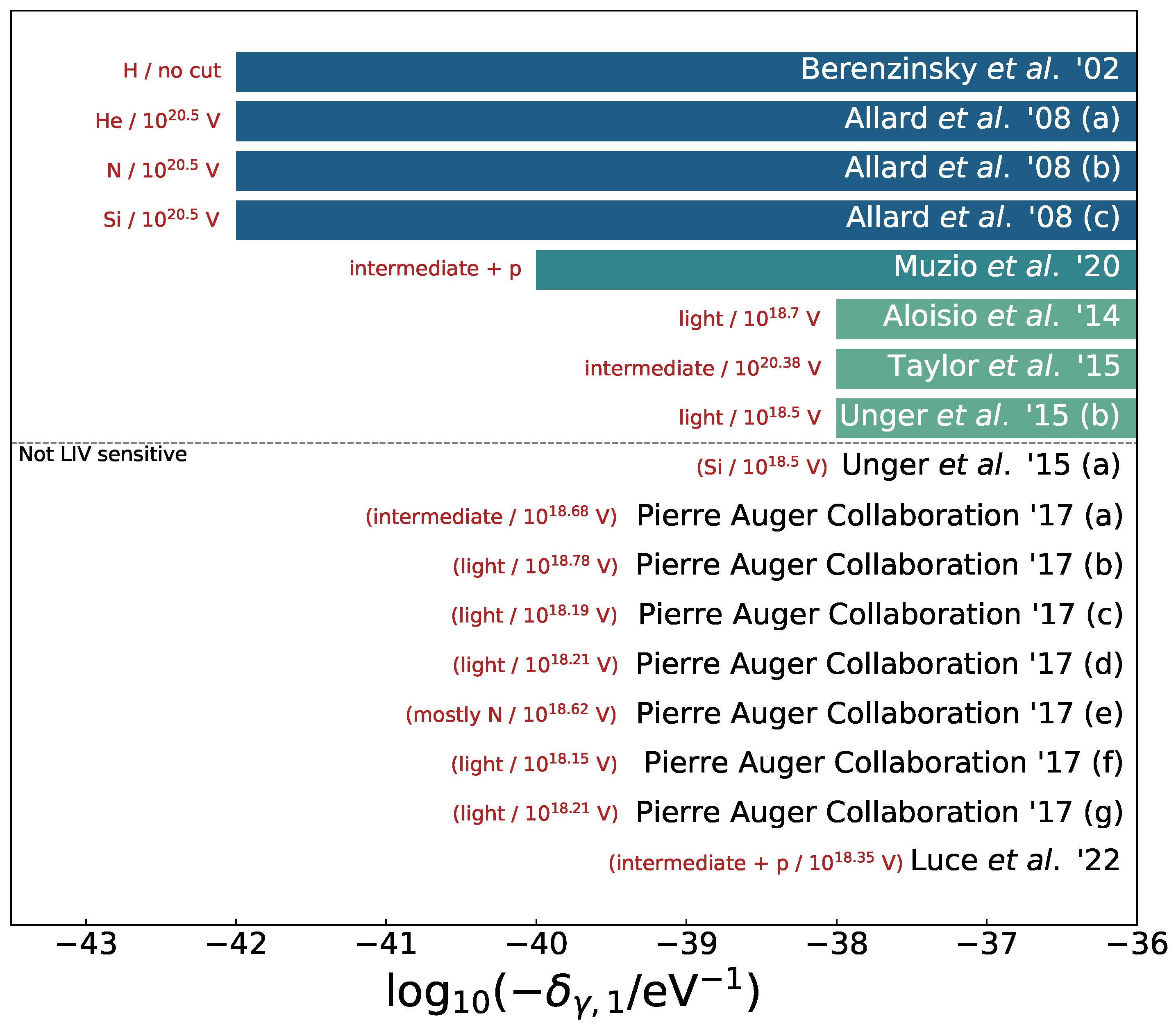
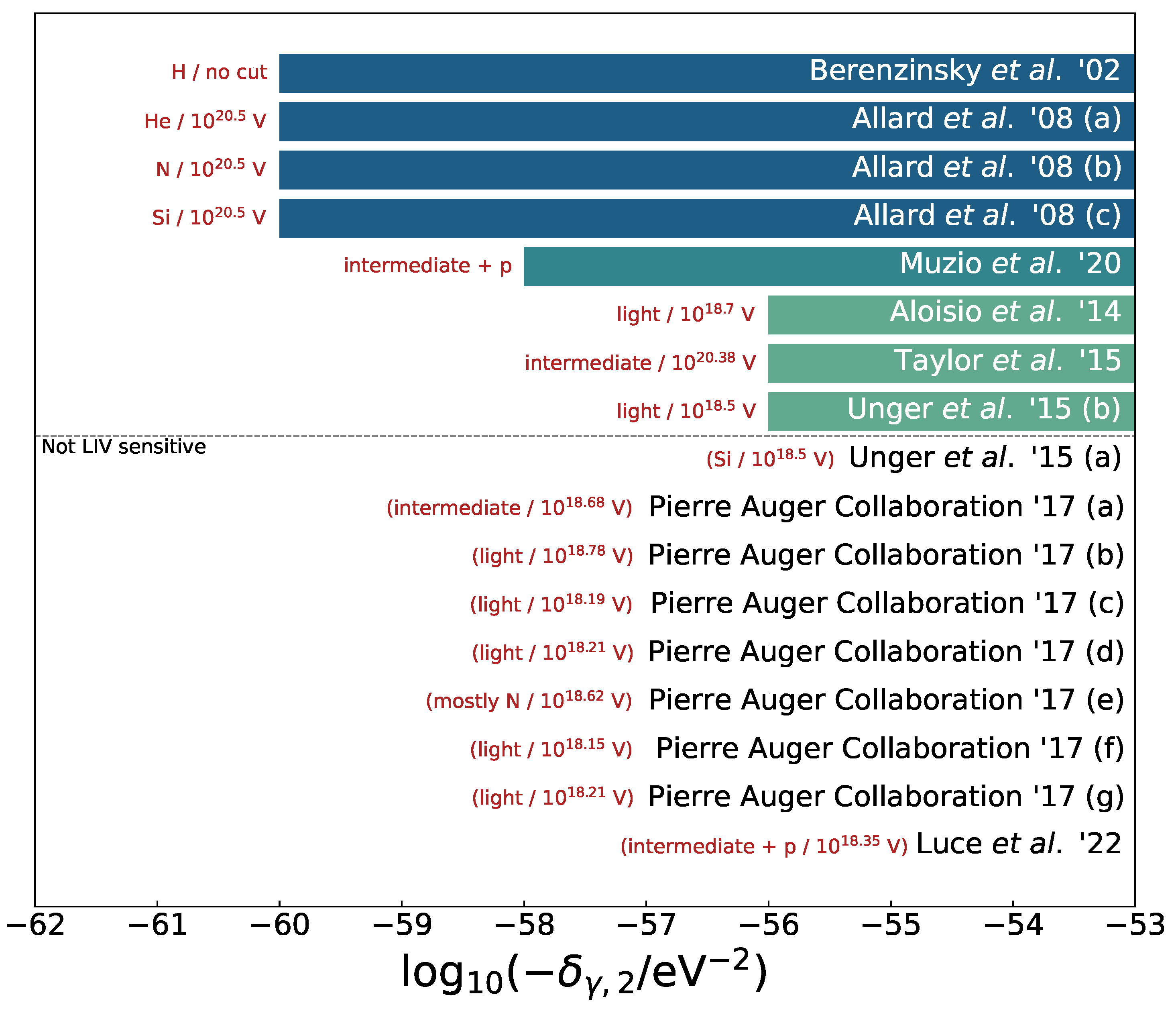
| Model | Details | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Berezinsky et al. ’02 | — | [50] |
| Allard et al. ’08 (a) | pure He | [51] |
| Allard et al. ’08 (b) | pure CNO | [51] |
| Allard et al. ’08 (c) | pure Si | [51] |
| Aloisio et al. ’15 | — | [52] |
| Taylor et al. ’15 (a) | [53] | |
| Unger et al. ’15 (a) | fiducial model | [54] |
| Unger et al. ’15 (a) | galactic abundance | [54] |
| Pierre Auger Collaboration ’17 (a) | SPG | [42] |
| Pierre Auger Collaboration ’17 (a) | STG | [42] |
| Pierre Auger Collaboration ’17 (a) | SPD | [42] |
| Pierre Auger Collaboration ’17 (a) | CTG () | [42] |
| Pierre Auger Collaboration ’17 (a) | CTG () | [42] |
| Pierre Auger Collaboration ’17 (a) | CTD | [42] |
| Pierre Auger Collaboration ’17 (a) | CGD | [42] |
| Muzio et al. ’20 | — | [55] |
| Luce et al. ’22 | — | [56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lang, R.G.; Martínez-Huerta, H.; de Souza, V. Ultra-High-Energy Astroparticles as Probes for Lorentz Invariance Violation. Universe 2022, 8, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8080435
Lang RG, Martínez-Huerta H, de Souza V. Ultra-High-Energy Astroparticles as Probes for Lorentz Invariance Violation. Universe. 2022; 8(8):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8080435
Chicago/Turabian StyleLang, Rodrigo Guedes, Humberto Martínez-Huerta, and Vitor de Souza. 2022. "Ultra-High-Energy Astroparticles as Probes for Lorentz Invariance Violation" Universe 8, no. 8: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8080435
APA StyleLang, R. G., Martínez-Huerta, H., & de Souza, V. (2022). Ultra-High-Energy Astroparticles as Probes for Lorentz Invariance Violation. Universe, 8(8), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8080435







