Slow Neutron-Capture Process: Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars and Presolar Silicon Carbide Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Presolar Grains and In Situ Isotope Analyses
2.1. Presolar SiC Grains from Low-Mass C-Rich AGB Stars
2.2. In Situ Isotope Analysis of Presolar SiC Grains
2.2.1. NanoSIMS and Isotope Analyses of Light Elements
2.2.2. RIMS and Isotope Analyses of Heavy Elements
3. Isotope versus Element Abundances
4. Constraints on AGB Stellar Models from Presolar Grain Data
4.1. Minor Neutron Source 22Ne and Branch Points
4.2. Formation of Major Neutron Source 13C
- (1)
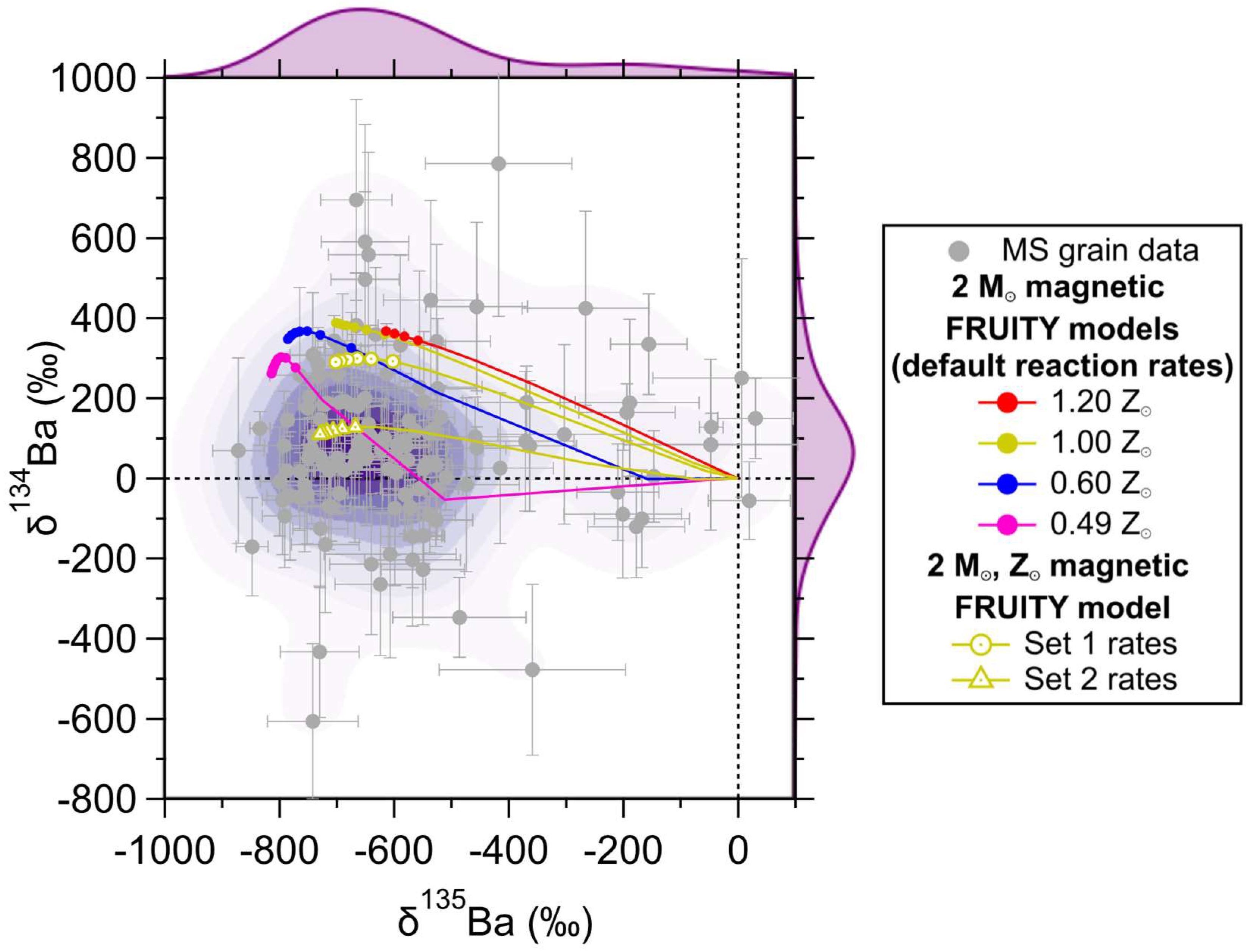
- Presolar Grains: Correlated Sr and Ba isotope analyses of more MS grains using the new generation of RIMS instruments [60,69] are needed to better quantify the MS grain distribution. The study of [42] showed that compared to the exponential distribution by overshooting, the deeper, more flattened 13C distribution resulting from magnetic buoyancy reduces the sensitives of δ88Sr and δ138Ba to the H mixing depth. Thus, we need more MS grain data for δ88Sr and δ138Ba to determine the data variability, which will help to assess the primary mechanism responsible for the 13C formation. A better understanding of the MS grain data distribution will also allow for a quantitative assessment of the quality of data-model comparisons, which, so far, have been conducted mainly in a qualitative way.
- (2)
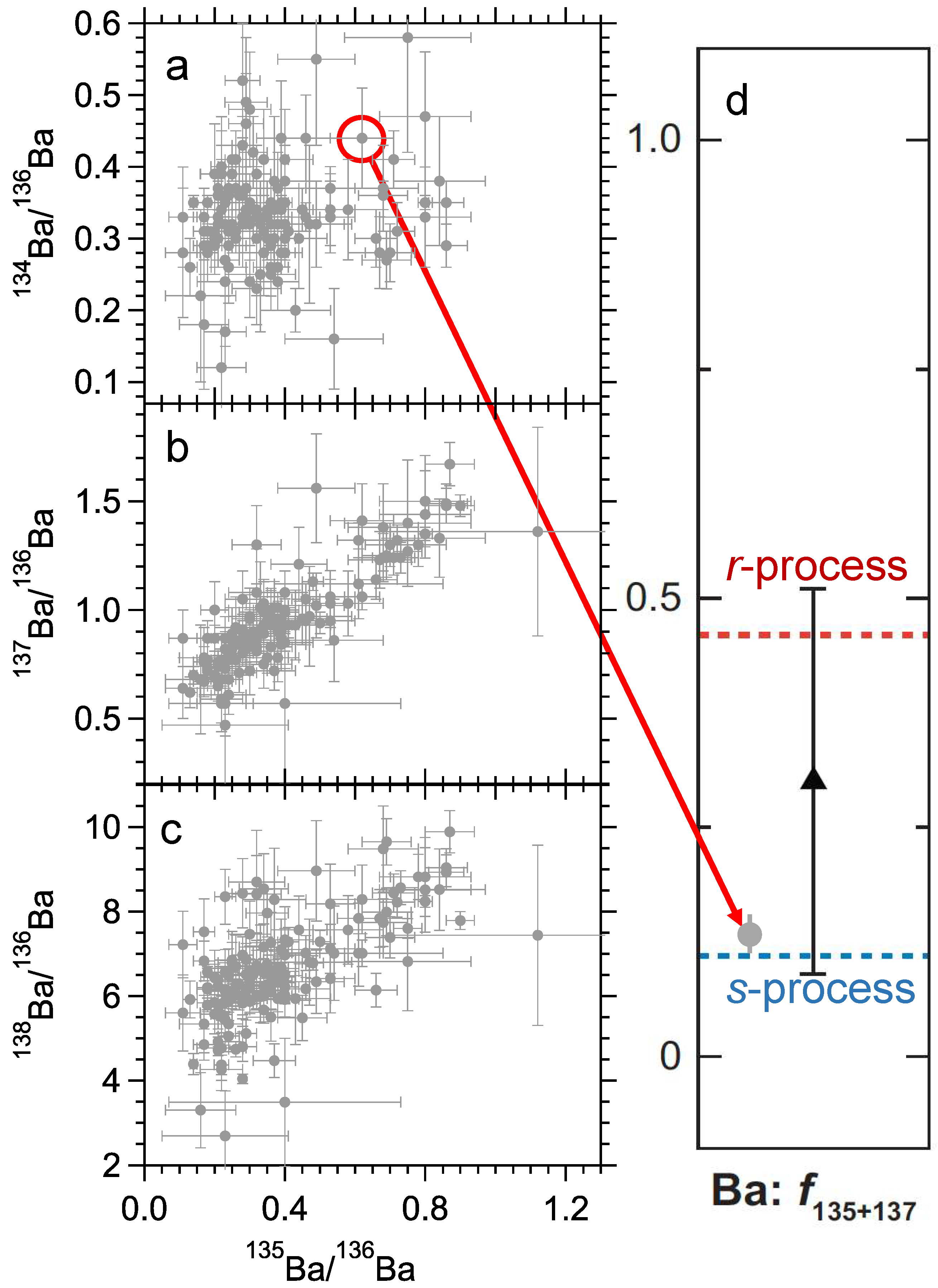
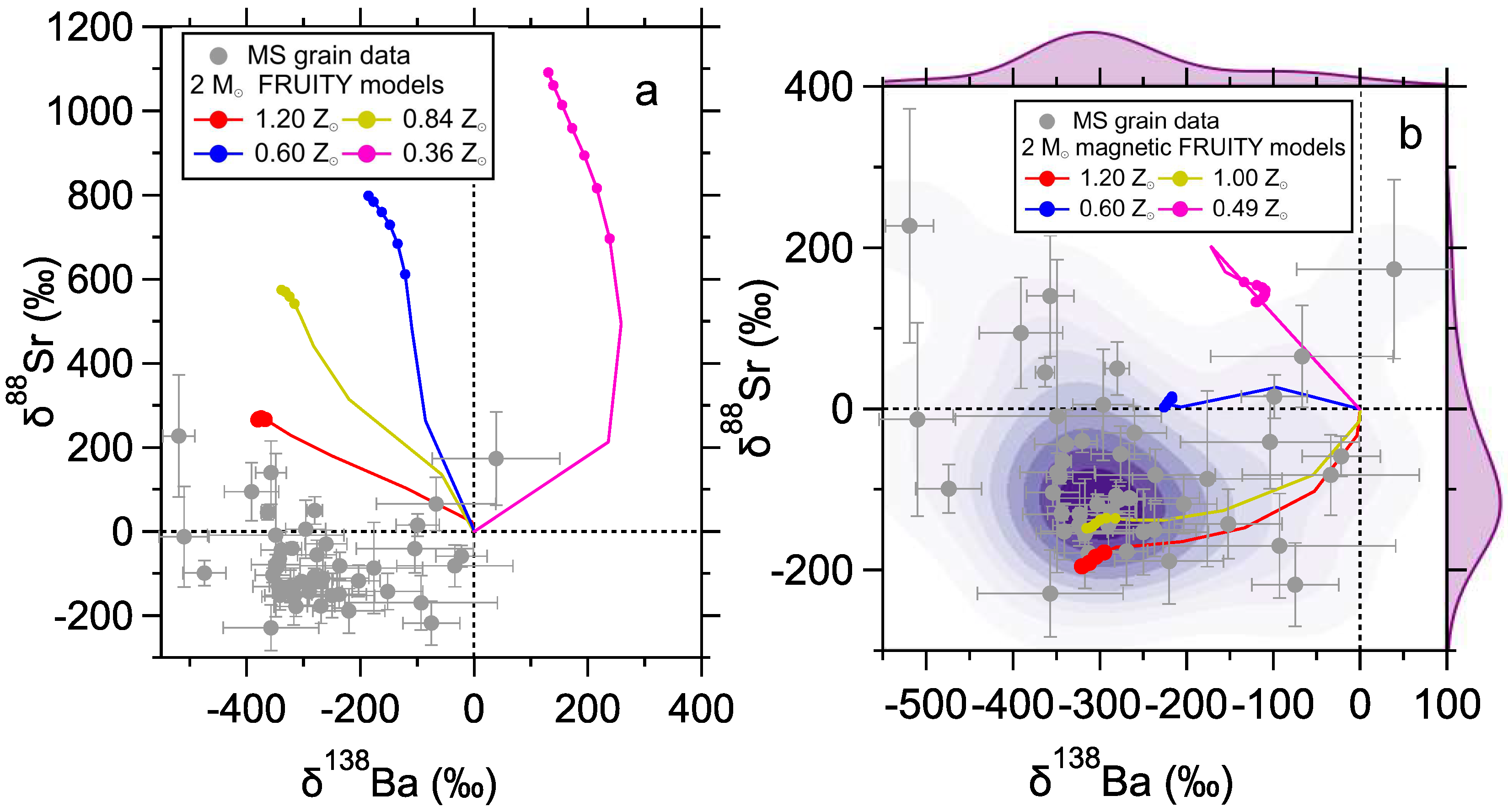
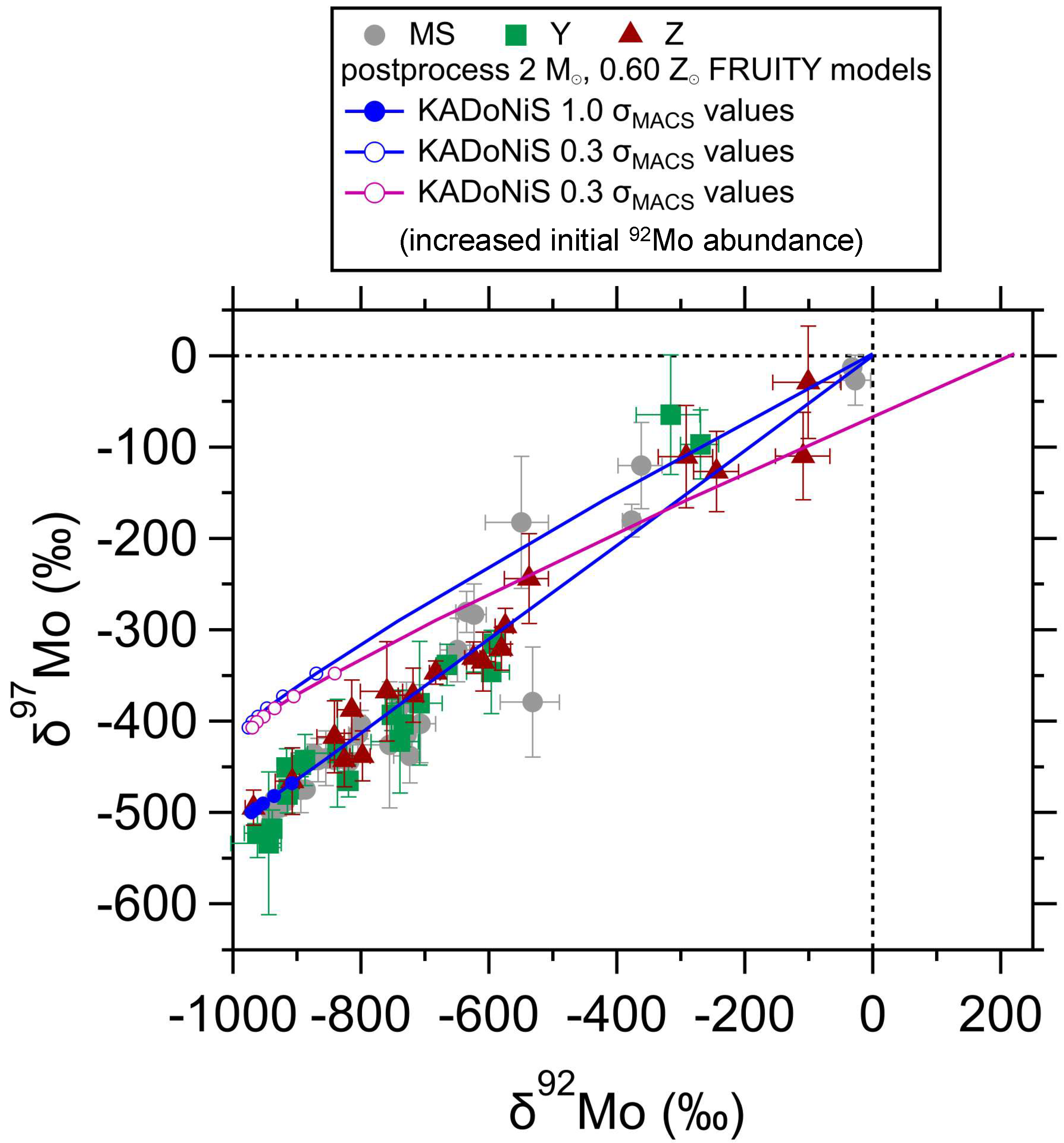
- Nuclear Experiments: AGB model predictions for δ88Sr and δ138Ba rely directly on the σMACS values of 86Sr, 88Sr, 136Ba, and 138Ba. Given the small 88Sr and 138Ba σMACS values, current AGB model uncertainties in δ88Sr and δ138Ba are controlled by uncertainties in the 86Sr (±10%) and 136Ba (±3%) σMACS values [96], respectively, which correspond to ~200‰ and ~50‰ uncertainties in low-mass AGB model predictions for δ88Sr and δ138Ba, respectively [34,62]. As the full range of δ88Sr values observed among MS grains is only ~400‰ (Figure 5), new measurements of 86Sr σMACS values are urgently needed to reduce the model uncertainty for δ88Sr.
- (3)
- Stellar Modeling: Implementation of magnetic buoyancy effects in other stellar codes such as NuGrid [10] is needed to test whether the effect of magnetic buoyancy on the s-process production is stellar code dependent. It was shown in [43,44] that 2 Z⊙ Monash models that adopt an exponentially decayed mixing profile also provide a good match to the heavy element isotope data of MS grains. It remains to see whether adoption of the formula for magnetic buoyancy can further improve the data-model agreements for 2 Z⊙ and other lower-metallicity Monash models, given uncertainties in the initial metallicities of the grains’ parent stars. Finally, we note that the good grain-model agreement in Figure 5b mainly points out that the MS grain data are in favor of a deep, flattened 13C distribution in the He-intershell. More modeling efforts are needed to investigate whether magnetic buoyancy is the sole mechanism that could lead to such a distribution.
4.3. Constraints on Neutron-Capture Cross Sections
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The s-process nucleosynthesis throughout the manuscript refers to the main s-process specifically. We remind the reader that there is also the weak s-process operating in massive stars, which can efficiently produce heavy elements before the first s-process peak at Sr (see [7] for details). |
| 2 | |
| 3 | Nonmagnetic FRUITY model calculations are available at http://fruity.oa-teramo.inaf.it/ (accessed on 1 March 2022), and magnetic FRUITY model calculations are not yet available online. |
| 4 | KADoNiS stands for Karlsruhe Astrophysical database of Nucleosynthesis in Stars. The KADoNiS v0.3 and v1.0 databases are available at https://www.kadonis.org/ and https://exp-astro.de/kadonis1.0/, respectively (accessed on 1 March 2022). |
References
- Burbidge, E.M.; Burbidge, G.R.; Fowler, W.A.; Hoyle, F. Synthesis of the elements in stars. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1957, 29, 547–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.G.W. Nuclear reactions in stars and nucleogenesis. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1957, 69, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, N.R.; Levan, A.J.; González-Fernández, C.; Korobkin, O.; Mandel, I.; Rosswog, S.; Hjorth, J.; D’avanzo, P.; Fruchter, A.S.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. The emergence of a lanthanide-rich kilonova following the merger of two neutron stars. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajino, T.; Aoki, W.; Balantekin, A.B.; Diehl, R.; Famiano, M.A.; Mathews, G.J. Current status of r-process nucleosynthesis. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2019, 107, 109–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnould, M.; Goriely, S. The p-process of stellar nucleosynthesis: Astrophysics and nuclear physics status. Phys. Rep. 2003, 384, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, P.W. Emission lines in the spectra of long-period variable stars. J. R. Astron. Soc. Can. 1952, 46, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Pignatari, M.; Gallino, R.; Heil, M.; Wiescher, M.; Käppeler, F.; Herwig, F.; Bisterzo, S. The weak s-process in massive stars and its dependence on the neutron capture cross sections. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 1557–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakas, A.I.; Lugaro, M. Stellar yields from metal-rich asymptotic giant branch models. Astrophys. J. 2016, 825, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; Straniero, O.; Gallino, R.; Piersanti, L.; Domínguez, I.; Lederer, M.T. Evolution, nucleosynthesis, and yields of low-mass asymptotic giant branch stars at different metallicities. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 797–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battino, U.; Tattersall, A.; Lederer-Woods, C.; Herwig, F.; Denissenkov, P.; Hirschi, R.; Trappitsch, R.; Den Hartogh, J.W.; Pignatari, M.; Collaboration, N. NuGrid stellar data set—III. updated low-mass AGB models and s-process nucleosynthesis with metallicities Z = 0.01, Z = 0.02, and Z = 0.03. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallino, R.; Busso, M.; Picchio, G.; Raiteri, C.M.; Renzini, A. On the role of low-Mass asymptotic giant branch stars in producing a solar system distribution of s-process isotopes. Astrophys. J. 1988, 334, L45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisterzo, S.; Gallino, R.; Käppeler, F.; Wiescher, M.; Imbriani, G.; Straniero, O.; Cristallo, S.; Görres, J.; Deboer, R.J. The branchings of the main s-process: Their sensitivity to α-induced reactions on 13C and 22Ne and to the uncertainties of the nuclear network. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 506–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppeler, F.; Gallino, R.; Bisterzo, S.; Aoki, W. The s process: Nuclear physics, stellar models, and observations. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 157–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; La Cognata, M.; Massimi, C.; Best, A.; Palmerini, S.; Straniero, O.; Trippella, O.; Busso, M.; Ciani, G.F.; Mingrone, F.; et al. The importance of the 13C(α,n)16O reaction in asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwig, F. Evolution of asymptotic giant branch stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 43, 435–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freytag, B.; Ludwig, H.-G.; Steffen, M. Hydrodynamical models of stellar convection. The role of overshoot in DA white dwarfs, A-type stars, and the Sun. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 313, 497–516. [Google Scholar]
- Herwig, F.; Bloecker, T.; Schoenberner, D.; El Eid, M. Stellar evolution of low and intermediate-mass stars. IV. Hydrodynamically-based overshoot and nucleosynthesis in AGB stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 324, L81–L84. [Google Scholar]
- Straniero, O.; Gallino, R.; Cristallo, S. s process in low-mass asymptotic giant branch stars. Nucl. Phys. A 2006, 777, 311–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battino, U.; Pignatari, M.; Ritter, C.; Herwig, F.; Denisenkov, P.; Den Hartogh, J.W.; Trappitsch, R.; Hirschi, R.; Freytag, B.; Thielemann, F.; et al. Application of a theory and simulation-based convective boundary mixing model for AGB star evolution and nucleosynthesis. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denissenkov, P.A.; Tout, C.A. Partial mixing and formation of the 13C pocket by internal gravity waves in asymptotic giant branch stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 340, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herwig, F.; Langer, N.; Lugaro, M. The s-process in rotating asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2003, 593, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersanti, L.; Cristallo, S.; Straniero, O. The effects of rotation on s-process nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 774, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucci, M.C.; Busso, M. Magnetohydrodynamics and deep mixing in evolved stars. I. two- and three-dimensional analytical models for the asymptotic giant branch. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trippella, O.; Busso, M.; Palmerini, S.; Maiorca, E.; Nucci, M.C. s-processing in AGB stars revisited. II. Enhanced 13C production through MHD-induced mixing. Astrophys. J. 2016, 818, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfner, S.; Olofsson, H. Mass loss of stars on the asymptotic giant branch. Mechanisms, models and measurements. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodders, K.; Fegley, B., Jr. The origin of circumstellar silicon carbide grains found in meteorites. Meteoritics 1995, 30, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, A.K.; Corman, A.B.; Wakeman, K.; Wheeler, C.H.; Thompson, G. Silicon carbide absorption features: Dust formation in the outflows of extreme carbon stars. Astrophys. J. 2009, 691, 1202–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, A.K.; Thompson, G.D.; Hofmeister, A.M. The effect of stellar evolution on SiC dust grain sizes. Astrophys. J. 2005, 634, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinner, E. Presolar grains. In Meteorites and Cosmochemical Processes; Davis, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- Nittler, L.R.; Ciesla, F. Astrophysics with extraterrestrial materials. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 54, 53–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittler, L.R.; Amari, S.; Zinner, E.; Woosley, S.E.; Lewis, R.S. Extinct 44Ti in presolar graphite and SiC: Proof of a supernova origin. Astrophys. J. 1996, 462, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D.; Wang, J. Late formation of silicon carbide in type II supernovae. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Stephan, T.; Boehnke, P.; Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D.; Wang, J.; Davis, A.M.; Trappitsch, R.; Pellin, M.J. J-type carbon stars: A dominant source of 14N-rich presolar SiC grains of type AB. Astrophys. J. 2017, 844, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Savina, M.R.; Davis, A.M.; Gallino, R.; Straniero, O.; Gyngard, F.; Pellin, M.J.; Willingham, D.G.; Dauphas, N.; Pignatari, M.; et al. Barium isotopic composition of mainstream silicon carbides from Murchison: Constraints for s-process nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.; Gao, X.; Nittler, L.R.; Zinner, E.; José, J.; Hernanz, M.; Lewis, R.S. Presolar grains from novae. Astrophys. J. 2001, 551, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittler, L.R.; Hoppe, P. Are presolar silicon carbide grains from novae actually from supernovae? Astrophys. J. 2005, 631, L89–L92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D.; Wang, J.; Pignatari, M.; José, J.; Nguyen, A. Stellar origins of extremely 13C- and 15N-enriched presolar SiC grains: Novae or supernovae? Astrophys. J. 2016, 820, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D. Automated isotopic measurements of micron-sized dust: Application to meteoritic presolar silicon carbide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4961–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmes, F.X.; Clayton, D.D. Galactic evolution of silicon isotopes: Application to presolar SiC grains from meteorites. Astrophys. J. 1996, 472, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.M.; Lugaro, M.; Gibson, B.K.; Pilkington, K. Decoding the message from meteoritic stardust silicon carbide grains. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; Nanni, A.; Cescutti, G.; Minchev, I.; Liu, N.; Vescovi, D.; Gobrecht, D.; Piersanti, L. Mass and metallicity distribution of parent AGB stars of presolar SiC. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 644, A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Gallino, R.; Cristallo, S.; Bisterzo, S.; Davis, A.M.; Trappitsch, R.; Nittler, L.R. New constraints on the major neutron source in low-mass AGB stars. Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugaro, M.; Karakas, A.I.; Pető, M.; Plachy, E. Do meteoritic silicon carbide grains originate from asymptotic giant branch stars of super-solar metallicity? Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 221, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugaro, M.; Cseh, B.; Világos, B.; Karakas, A.I.; Ventura, P.; Dell’agli, F.; Trappitsch, R.; Hampel, M.; D’orazi, V.; Pereira, C.B.; et al. Origin of large meteoritic SiC stardust grains in metal-rich AGB stars. Astrophys. J. 2020, 898, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.; Nittler, L.R.; Zinner, E.; Gallino, R.; Lugaro, M.; Lewis, R.S. Presolar SiC grains of type Y: Origin from low-metallicity asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2001, 546, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinner, E.; Nittler, L.R.; Gallino, R.; Karakas, A.I.; Lugaro, M.; Straniero, O.; Lattanzio, J.C. Silicon and carbon isotopic ratios in AGB stars: SiC grain data, models, and the Galactic evolution of the Si isotopes. Astrophys. J. 2006, 650, 350–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Stephan, T.; Cristallo, S.; Gallino, R.; Boehnke, P.; Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D.; Davis, A.M.; Trappitsch, R.; Pellin, M.J. Presolar silicon carbide grains of groups Y and Z: Their strontium and barium isotopic compositions and stellar origins. In Proceedings of the 50th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 18–22 March 2019. #1349 (abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Stephan, T.; Cristallo, S.; Gallino, R.; Boehnke, P.; Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D.; Davis, A.M.; Trappitsch, R.; Pellin, M.J.; et al. Presolar silicon carbide grains of types Y and Z: Their molybdenum isotopic compositions and stellar origins. Astrophys. J. 2019, 881, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boujibar, A.; Howell, S.; Zhang, S.; Hystad, G.; Prabhu, A.; Liu, N.; Stephan, T.; Narkar, S.; Eleish, A.; Morrison, S.M.; et al. Cluster analysis of presolar silicon carbide grains: Evaluation of their classification and astrophysical implications. Astrophys. J. 2021, 907, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hystad, G.; Boujibar, A.; Liu, N.; Nittler, L.R.; Hazen, R.M. Evaluation of the classification of pre-solar silicon carbide grains using consensus clustering with resampling methods: An assessment of the confidence of grain assignments. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 510, 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Barosch, J.; Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D.; Wang, J.; Cristallo, S.; Busso, M.; Palmerini, S. New multielement isotopic compositions of presolar SiC grains: Implications for their stellar origins. Astrophys. J. 2021, 920, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Alexander., C.M.O.D.; Nittler, L.R. Intrinsic nitrogen isotope ratios of presolar silicon carbide grains. In Proceedings of the 85th Annual Meeting of The Meteoritical Society, Glascow, UK, 14–19 August 2022. #6384 (abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, T.; Bose, M.; Boujibar, A.; Davis, A.M.; Gyngard, F.; Hoppe, P.; Hynes, K.M.; Liu, N.; Nittler, L.R.; Ogliore, R.C.; et al. The Presolar Grain Database for silicon carbide—Grain type assignments. In Proceedings of the 52nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 15–19 March 2021. #2358 (abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe, P.; Leitner, J.; Gröner, E.; Marhas, K.K.; Meyer, B.S.; Amari, S. NanoSIMS studies of small presolar SiC grains: New insights into supernova nucleosynthesis, chemistry, and dust formation. Astrophys. J. 2010, 719, 1370–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, J.; Hoppe, P. A new population of dust from stellar explosions among meteoritic stardust. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittler, L.R.; Alexander, C.M.O.’D.; Liu, N.; Wang, J. Extremely 54Cr- and 50Ti-rich presolar oxide grains in a primitive meteorite: Formation in rare types of supernovae and implications for the astrophysical context of solar system birth. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Dauphas, N.; Cristallo, S.; Palmerini, S.; Busso, M. Oxygen and aluminum-magnesium isotopic systematics of presolar nanospinel grains from CI chondrite Orgueil. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 319, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodders, K. Relative atomic solar system abundances, mass fractions, and atomic masses of the elements and their isotopes, composition of the solar photosphere, and compositions of the major chondritic meteorite groups. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.; Hoppe, P.; Zinner, E.; Lewis, R.S. Trace-element concentrations in single circumstellar silicon carbide grains from the Murchison meteorite. Meteoritics 1995, 30, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappitsch, R.; Ong, W.-J.; Dory, C.J.; Shulaker, D.Z.; Lugaro, M.; Savina, M.R.; Weber, P.K.; Isselhardt, B.H.; Amari, S. Simultaneous analyses of titanium and molybdenum isotopic compositions in presolar SiC grains. In Proceedings of the 84th Annual Meeting of the Meteoritical Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 15–21 August 2021. #6239 (abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Trappitsch, R.; Stephan, T.; Savina, M.R.; Davis, A.M.; Pellin, M.J.; Rost, D.; Gyngard, F.; Gallino, R.; Bisterzo, S.; Cristallo, S.; et al. Simultaneous iron and nickel isotopic analyses of presolar silicon carbide grains. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 221, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Savina, M.R.; Gallino, R.; Davis, A.M.; Bisterzo, S.; Gyngard, F.; Käppeler, F.; Cristallo, S.; Dauphas, N.; Pellin, M.J.; et al. Correlated strontium and barium isotopic compositions of acid-cleaned single mainstream silicon carbides from Murchison. Astrophys. J. 2015, 803, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Savina, R.M.; Davis, A.M.; Willingham, D.G.; Pellin, M.; Dauphas, N. Barium and neodymium isotopic composition of presolar SiC grains. In Proceedings of the 75th Annual Meeting of the Meteoritical Society, Cairns, Australia, 12–17 August 2012. #5249 (abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Barzyk, J.G.; Savina, M.R.; Davis, A.M.; Gallino, R.; Gyngard, F.; Amari, S.; Zinner, E.; Pellin, M.J.; Lewis, R.S.; Clayton, R.N. Constraining the 13C neutron source in AGB stars through isotopic analysis of trace elements in presolar SiC. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2007, 42, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolussi, G.K.; Pellin, M.J.; Lewis, R.S.; Davis, A.M.; Clayton, R.N.; Amari, S. Strontium isotopic composition in individual circumstellar silicon carbide grains: A record of s-process nucleosynthesis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 3583–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolussi, G.K.; Pellin, M.J.; Lewis, R.S.; Davis, A.M.; Amari, S.; Clayton, R.N. Molybdenum isotopic composition of individual presolar silicon carbide grains from the Murchison meteorite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, T.; Trappitsch, R.; Hoppe, P.; Davis, A.M.; Pellin, M.J.; Pardo, O.S. Molybdenum isotopes in presolar silicon carbide grains: Details of s-process nucleosynthesis in parent stars and implications for r- and p-processes. Astrophys. J. 2019, 877, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savina, M.R.; Davis, A.M.; Tripa, C.E.; Pellin, M.J.; Gallino, R.; Lewis, R.S.; Amari, S. Extinct technetium in silicon carbide stardust grains: Implications for stellar nucleosynthesis. Science 2004, 303, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, T.; Trappitsch, R.; Davis, A.M.; Pellin, M.J.; Rost, D.; Savina, M.R.; Yokochi, R.; Liu, N. CHILI—The Chicago Instrument for Laser Ionization—A new tool for isotope measurements in cosmochemistry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 407, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savina, M.R.; Pellin, M.J.; Tripa, C.E.; Veryovkin, I.V.; Calaway, W.F.; Davis, A.M. Analyzing individual presolar grains with CHARISMA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 3215–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.D.; Fowler, W.A.; Hull, T.E.; Zimmerman, B.A. Neutron capture chains in heavy element synthesis. Ann. Phys. 1961, 12, 331–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlandini, C.; Käppeler, F.; Wisshak, K.; Gallino, R.; Lugaro, M.; Busso, M.; Straniero, O. Neutron capture in low-mass asymptotic giant branch stars: Cross sections and abundance signatures. Astrophys. J. 1999, 525, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.D.; Ward, R.A. S-process studies: Exact evaluation of an exponential distribution of exposures. Astrophys. J. 1974, 193, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, M.; Gallino, R.; Lambert, D.L.; Travaglio, C.; Smith, V.V. Nucleosynthesis and mixing on the asymptotic giant branch. III. predicted and observed s-process abundances. Astrophys. J. 2001, 557, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; Piersanti, L.; Straniero, O.; Gallino, R.; Domínguez, I.; Abia, C.; Di Rico, G.; Quintini, M.; Bisterzo, S. Evolution, nucleosynthesis, and yields of low-mass asymptotic giant branch stars at different metallicities. II. The FRUITY database. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 197, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, D.; Cristallo, S.; Busso, M.; Liu, N. Magnetic-buoyancy-induced mixing in AGB stars: Presolar SiC grains. Astrophys. J. 2020, 897, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Gallino, R. Neutron-capture elements in the early Galaxy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 241–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.L.; Allende Prieto, C. The isotopic mixture of barium in the metal-poor subgiant HD 140283. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 335, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stephan, T.; Trappitsch, R.; Davis, A.M.; Pellin, M.J.; Rost, D.; Savina, M.R.; Jadhav, M.; Kelly, C.H.; Gyngard, F.; Hoppe, P.; et al. Strontium and barium isotopes in presolar silicon carbide grains measured with CHILI-two types of X grains. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 221, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savina, M.R.; Davis, A.M.; Tripa, C.E.; Pellin, M.J.; Clayton, R.N.; Lewis, R.S.; Amari, S.; Gallino, R.; Lugaro, M. Barium isotopes in individual presolar silicon carbide grains from the Murchison meteorite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 3201–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yokoi, K. Beta-decay rates of highly ionized heavy atoms in stellar interiors. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1987, 36, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longland, R.; Iliadis, C.; Karakas, A.I. Reaction rates for the s-process neutron source 22Ne + α. Phys. Rev. C 2012, 85, 065809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, M.; Gallino, R.; Wasserburg, G.J. Nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars: Relevance for Galactic enrichment and solar system formation. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 37, 239–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, D.; Cristallo, S.; Palmerini, S.; Abia, C.; Busso, M. Magnetic-buoyancy-induced mixing in AGB stars: Fluorine nucleosynthesis at different metallicities. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 652, A100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, D.; Piersanti, L.; Cristallo, S.; Busso, M.; Vissani, F.; Palmerini, S.; Simonucci, S.; Taioli, S. Effects of a revised 7Be e- capture rate on solar neutrino fluxes. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 623, A126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, D.; Mascaretti, C.; Vissani, F.; Piersanti, L.; Straniero, O. The luminosity constraint in the era of precision solar physics. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 2021, 48, 015201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsley, P.; Battino, U.; Best, A.; Caciolli, A.; Guglielmetti, A.; Imbriani, G.; Jayatissa, H.; La Cognata, M.; Lamia, L.; Masha, E.; et al. Reevaluation of the 22Ne(α,γ)26Mg and 22Ne(α,n)25Mg reaction rates. Phys. Rev. C 2021, 103, 015805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.Y.; Beer, H.; Käppeler, F.; Voss, F.; Wisshak, K.; Rauscher, T. Neutron cross sections for nucleosynthesis studies. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2000, 76, 70–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taioli, S.; Vescovi, D.; Busso, M.; Palmerini, S.; Cristallo, S.; Mengoni, A.; Simonucci, S. Theoretical estimate of the half-life for the radioactive 134Cs and 135Cs in astrophysical scenarios. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.14230. [Google Scholar]
- Patronis, N.; Dababneh, S.; Assimakopoulos, P.A.; Gallino, R.; Heil, M.; Käppeler, F.; Karamanis, D.; Koehler, P.E.; Mengoni, A.; Plag, R. Neutron capture studies on unsTable 135Cs for nucleosynthesis and transmutation. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 69, 025803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifarth, R.; Erbacher, P.; Fiebiger, S.; Göbel, K.; Heftrich, T.; Heil, M.; Käppeler, F.; Klapper, N.; Kurtulgil, D.; Langer, C.; et al. Neutron-induced cross sections. From raw data to astrophysical rates. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatissa, H.; Rogachev, G.V.; Goldberg, V.Z.; Koshchiy, E.; Christian, G.; Hooker, J.; Ota, S.; Roeder, B.T.; Saastamoinen, A.; Trippella, O.; et al. Constraining the 22Ne(α,γ)26Mg and 22Ne(α,n)25Mg reaction rates using sub-Coulomb α-transfer reactions. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 802, 135267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-A.; Qi, C.; Lugaro, M.; Yagüe López, A.; Karakas, A.I.; Den Hartogh, J.; Gao, B.-S.; Tang, X.-D. The stellar β-decay rate of 134Cs and its impact on the barium nucleosynthesis in the s-process. Astrophys. J. 2021, 919, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmerini, S.; Busso, M.; Vescovi, D.; Naselli, E.; Pidatella, A.; Mucciola, R.; Cristallo, S.; Mascali, D.; Mengoni, A.; Simonucci, S.; et al. Presolar grain isotopic ratios as constraints to nuclear and stellar parameters of asymptotic giant branch star nucleosynthesis. Astrophys. J. 2021, 921, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, M.; Vescovi, D.; Palmerini, S.; Cristallo, S.; Antonuccio-Delogu, V. s-processing in AGB stars revisited. III. Neutron captures from MHD mixing at different metallicities and observational constraints. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillmann, I. The new KADoNiS v1.0 and its influence on the s-process. Proc. Sci. 2014, 204, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kajino, T.; Kusakabe, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Cheoun, M.-K.; Ko, H.; Mathews, G.J. Impact of hypernova νp-process nucleosynthesis on the Galactic chemical evolution of Mo and Ru. Astrophys. J. 2022, 924, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugaro, M.; Davis, A.M.; Gallino, R.; Pellin, M.J.; Straniero, O.; Käppeler, F. Isotopic compositions of strontium, zirconium, molybdenum, and barium in single presolar SiC grains and asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2003, 593, 486–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
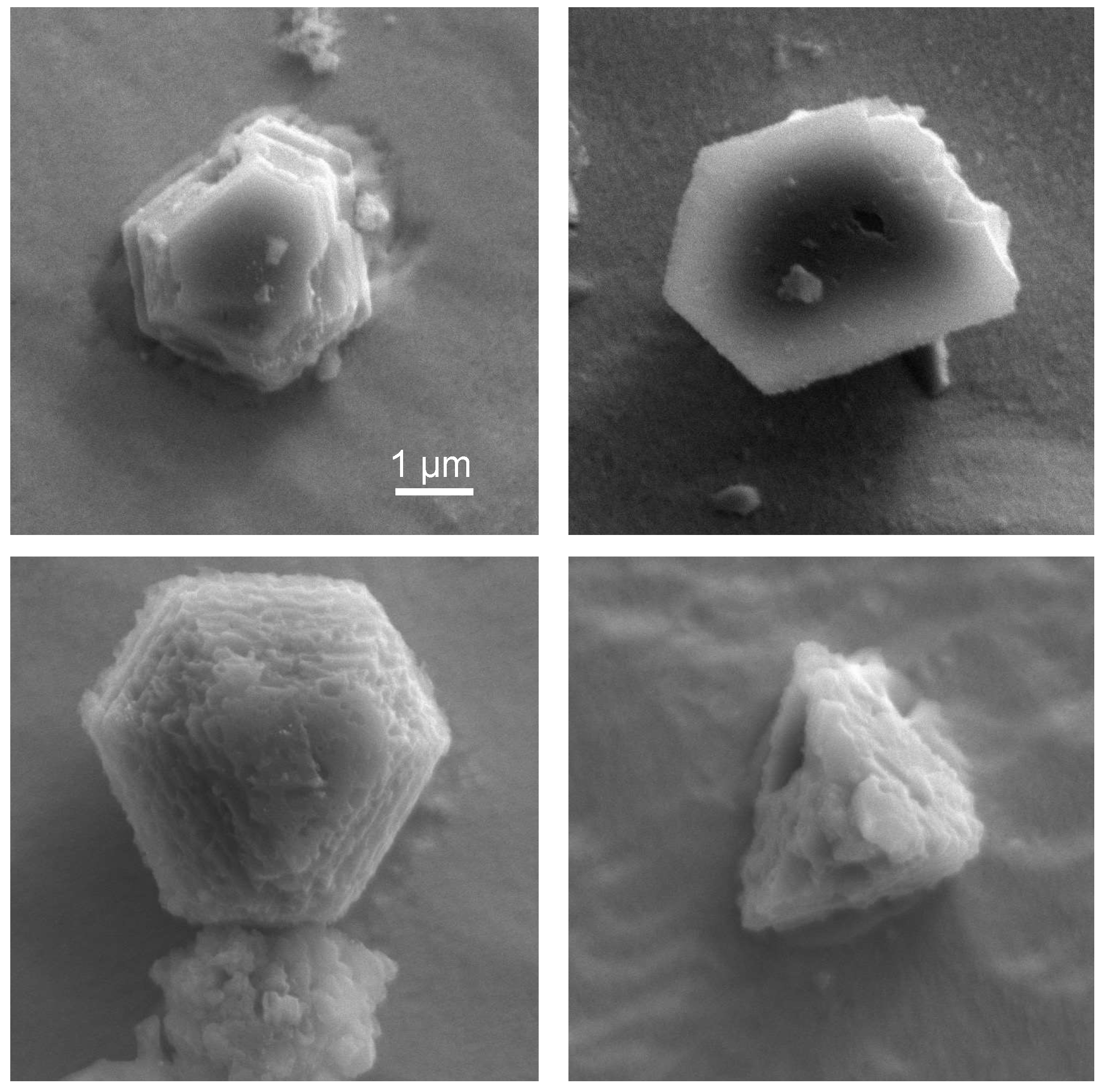

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Cristallo, S.; Vescovi, D. Slow Neutron-Capture Process: Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars and Presolar Silicon Carbide Grains. Universe 2022, 8, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070362
Liu N, Cristallo S, Vescovi D. Slow Neutron-Capture Process: Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars and Presolar Silicon Carbide Grains. Universe. 2022; 8(7):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070362
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Nan, Sergio Cristallo, and Diego Vescovi. 2022. "Slow Neutron-Capture Process: Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars and Presolar Silicon Carbide Grains" Universe 8, no. 7: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070362
APA StyleLiu, N., Cristallo, S., & Vescovi, D. (2022). Slow Neutron-Capture Process: Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars and Presolar Silicon Carbide Grains. Universe, 8(7), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070362






