Abstract
In our previous study, (Eur Phys J Plus 135:362, 2020 & Eur Phys J Plus 135:637, 2020), we have discussed the possible existence of the dark-matter-admixed pulsars, located in dwarf as well as in massive spiral galaxies (based on Singular Isothermal Sphere dark-matter density profile) and in the Milky Way galaxy (based on Universal Rotational Curve dark-matter density profile). In this article, we use the Navarro–Frenk–White (NFW) dark-matter density profile to get analogous results for the pulsars in the disk region of the Milky Way galaxy. These findings may be treated as valuable complements to the previous findings. We conclude from our findings that there is a unique possibility of the presence of dark-matter-admixed pulsars in all the regions of the galaxies.
1. Introduction
The unique properties of compact objects have been getting more attention for the last few decades. White dwarfs, strange stars, and neutron stars fall into the category of compact objects. These stars become stable as the outward degeneracy pressure from the Fermi gas balances the inward gravitational force. The Fermi gases in white dwarf and neutron stars mostly consist of electrons and neutrons, whereas the strange stars consist of strange quark matter. The gravitational force is the main cause for the neutron star to be bound. On the other hand, a strange star is more bound than a neutron star owing to the strong interaction and gravitational force. The source of enormous energy required for the formation of a strange star comes from the superluminous supernovae [1]. A strange star and a neutron star can be differentiated based on their vanishing surface energy density [2,3,4,5,6]. According to Lattimer and Prakash [7], the radius and mass of a neutron star having a particular Equation of State (EoS) depend on its central density. The solutions of Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff (TOV) equations can lead us to the theoretical estimation of the mass and radii of spherically symmetric compact stars. They can also be measured from pulsar timing, surface explosions, thermal emission from cooling stars, and gravity-wave emissions. Fixing the EoS is quite challenging due to the complex structure of the star [8,9,10,11,12,13]. The radius of the compact star is not completely known to us, whereas the mass can be estimated from its presence in binaries [14,15,16,17,18]. Due to some observational constraints, we need to theoretically study the stellar structure of the newly discovered stellar objects [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
In 1933, the concept of dark matter was introduced by Zwicky during the study of the dynamic properties of the Coma galaxy cluster [45,46]. Rubbin and Ford [47] have come to the same conclusion about dark matter through the optical studies of galaxies (e.g., M31). Some discussions on this topic are available in the literature [48,49]. Though the nature and origin of dark matter are not clear till now, some scientists have provided new concepts on dark matter that explain its properties [50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58]. Although normal matters have no such direct interaction with dark matter, stellar objects have some remarkable gravitational effect due to dark matter [59,60,61]. The gravitational effect of fermionic dark matter influences the physical properties of the strange stars [62,63,64,65,66]. Spergel and Steinhardt have also introduced the concept of self-interaction of dark matter [67].
Some astrophysicists [60,63,65,66,68,69,70,71,72] have worked on the dark matter neutron star. Inspired by their work, we have investigated [73] the existence of dark matter in pulsars by using the singular isothermal sphere (SIS) density profile. We have assumed the pulsars to be made of ordinary matter admixed with dark matter having a density distribution of
where K is the velocity dispersion. The dark matter contribution comes from the rotational curve fitting of the SPARC sample of galaxies [74]. We have shown the possibility of dark matter with ordinary matter in the pulsars, namely, PSR J1748-2021B in NGC 6440B, PSR J1911-5958A in NGC 6752, PSR B1802-07 in NGC 6539, and PSR J1750-37A in NGC 6441 galaxies.
We have also investigated the existence of dark-matter-admixed pulsars in the Milky Way galaxy by using the universal rotation curve (URC) dark-matter density profile [75]. We have used the URC dark-matter density profile as
where is the core radius and is the effective core density. For the Milky Way galaxy (in a particular case), and gm/c.c. [76,77]. The pulsars that we have studied in the Milky Way are PSR J0740+6620, PSR J1012+5307, PSR J0751+1807, and PSR J1614-2230.
In the present article, we have considered the Navarro–Frenk–White (NFW) density profile as it is a well accepted (dark matter) model, particularly in the disk regions of the galaxy. We have also studied the pulsars, namely, PSR J0045-7319 and PSR J0537-6910, which are located in the disk region of the Milky Way galaxy. In the NFW density profile, the dark matter density can be represented as [78]
where is the scale radius and is the effective density. Particularly for the Milky Way galaxy, kpc and GeV/c.c. [79]. This article aims to investigate the possible existence of dark-matter-admixed pulsars, namely, PSR J0045-7319, PSR J0537-6910, which are located in the disk region of the Milky Way galaxy.
2. Interior Spacetime
The interior spacetime of the spherically symmetric pulsar [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] has been described as,
According to the Heintzmann metric [93]
where A (dimensionless), C (dimensionless), and a () are constants.
For the interior of the isotropic pulsar, we consider the energy-momentum tensor as
where is the effective energy density and is the effective isotropic pressure.
Considering the pulsars are made of ordinary matter mixed with dark matter, the effective density and pressure can be expressed as,
The pressure appears due to dark matter as , where m is a constant [94].
3. Study of Physical Properties
3.1. Energy Density and Pressure
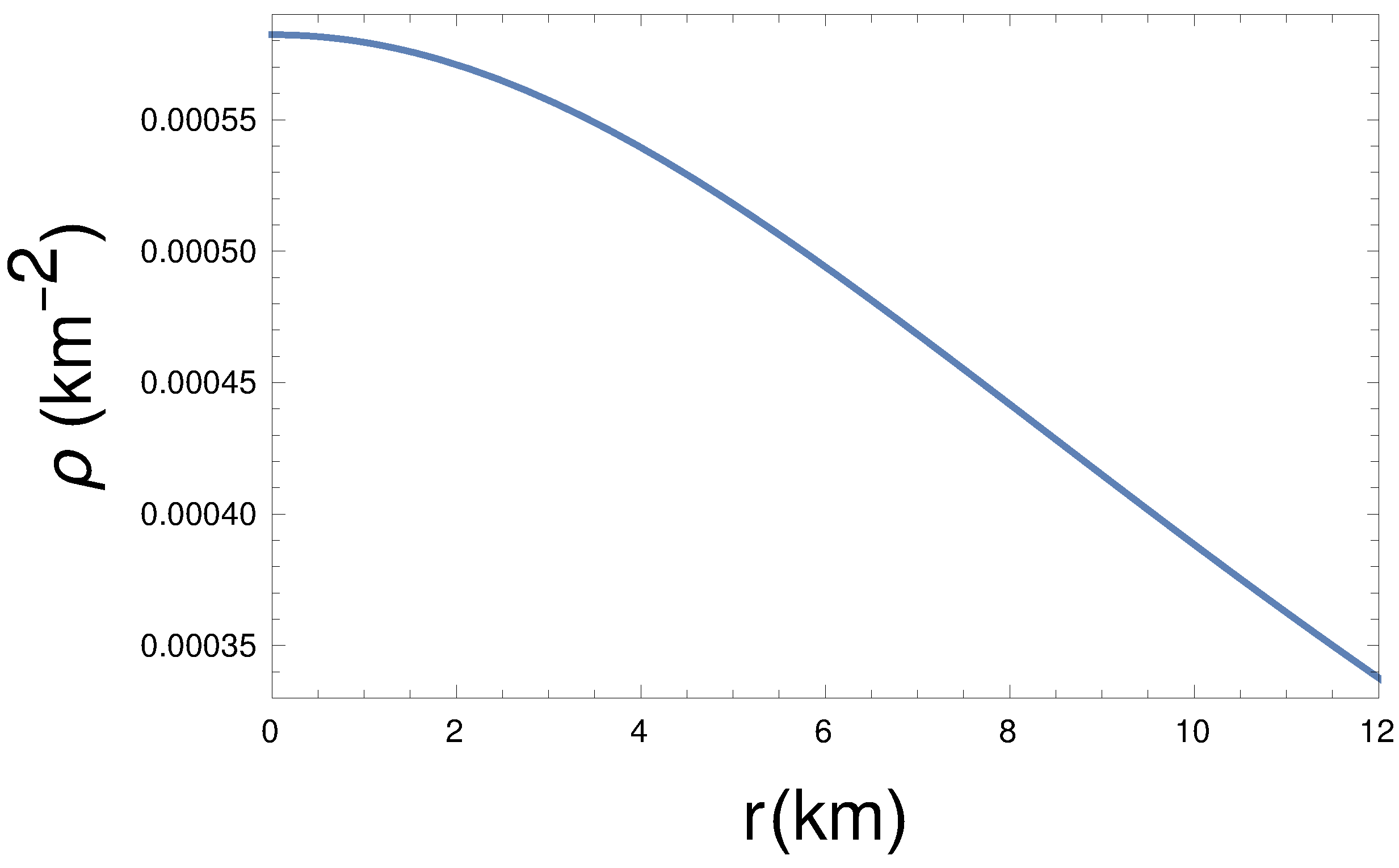
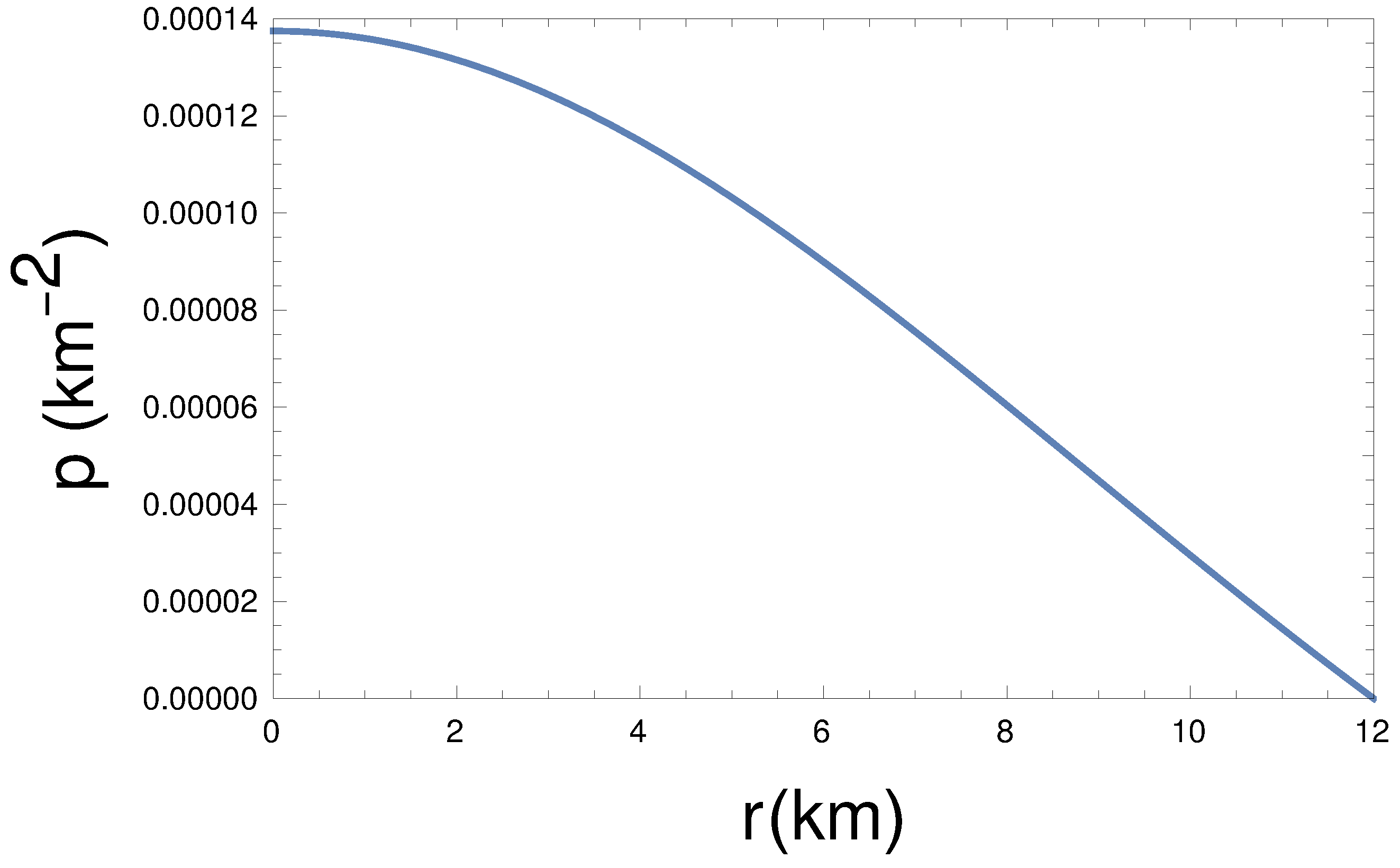
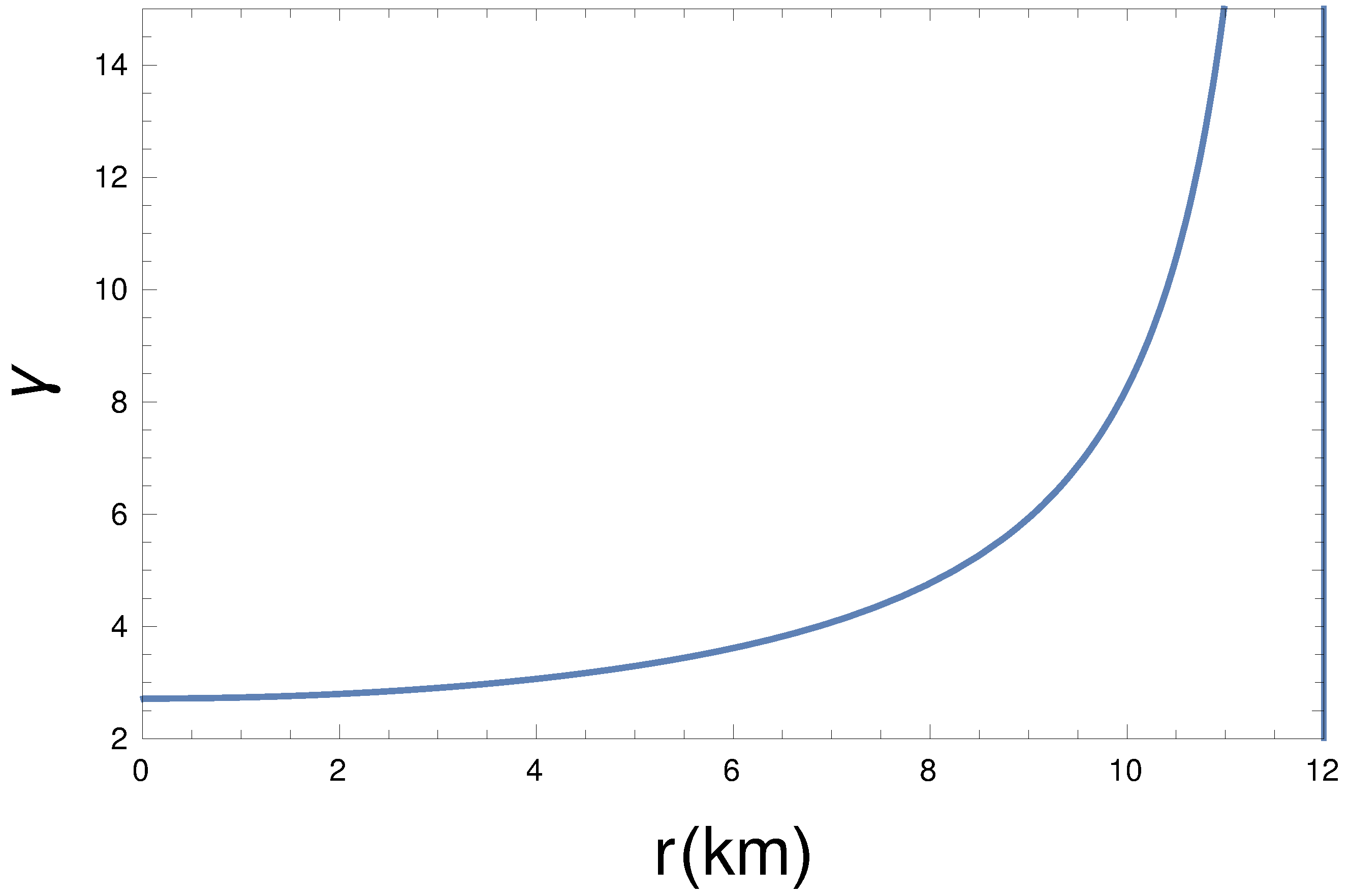
From the plot of energy density and pressure (see the Figure 1 and Figure 2), we see that at the center, energy density and pressure are maximum, and both decrease monotonically towards the boundary. Therefore, the energy density and pressure are well behaved in the interior of the stellar structure. Here, we have taken the constants km, , , , and GeV/c.c. in such a way that all other required conditions must be obeyed, including the pressure, which goes to zero at the boundary.
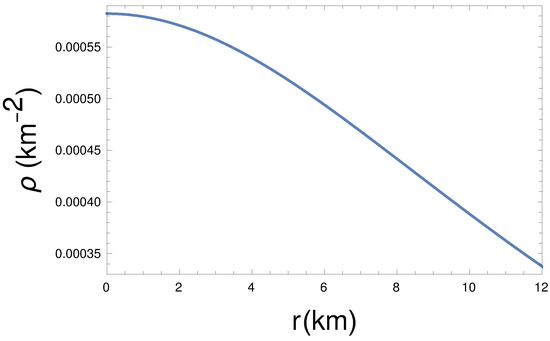
Figure 1.
Energy density () variation with radial distance (r) for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
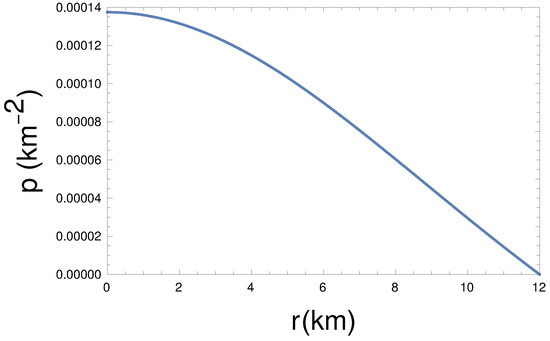
Figure 2.
Pressure (p) variation with radial distance (r) for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
3.2. Energy Conditions
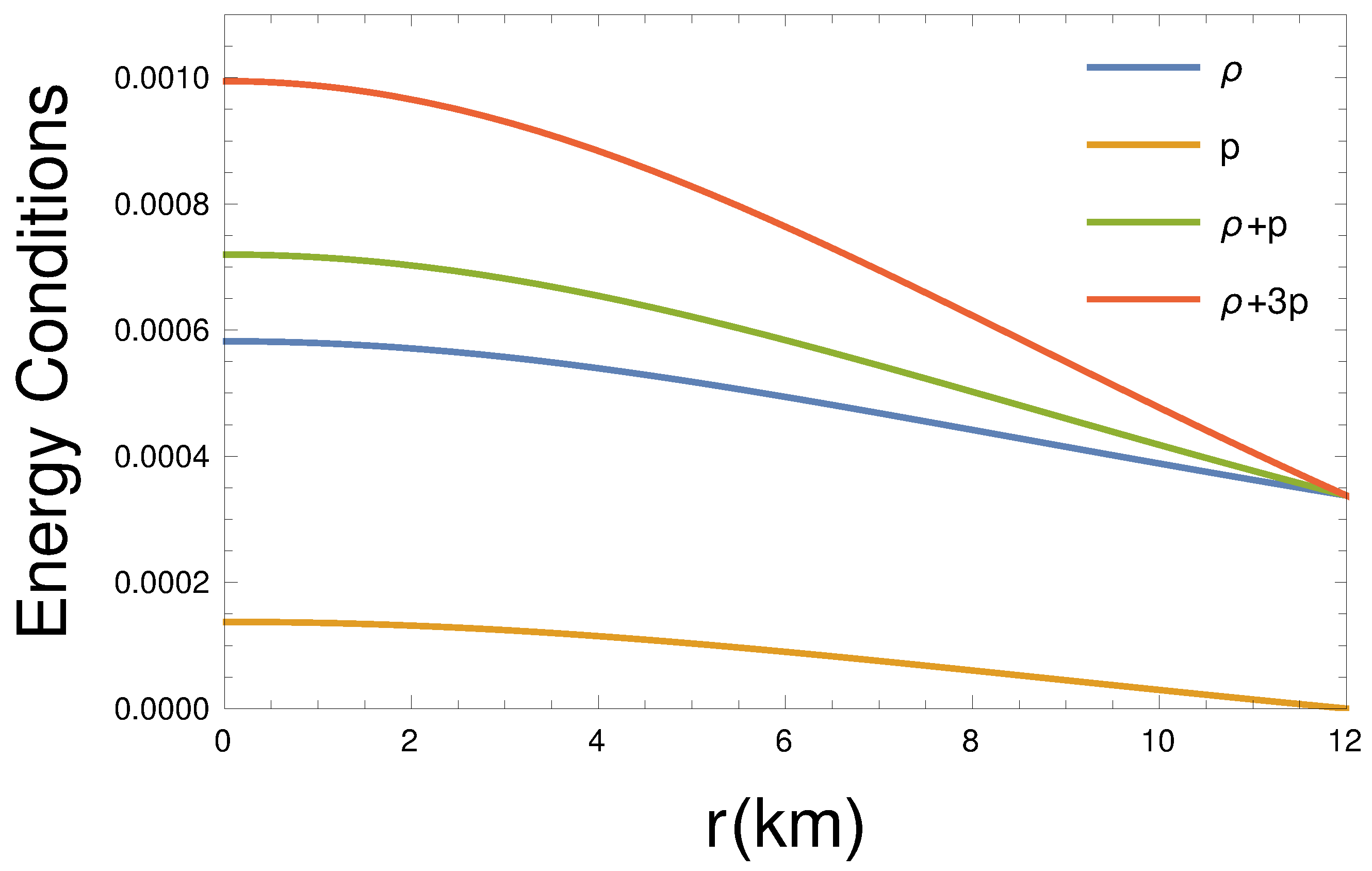
Figure 3 indicates that all the energy conditions, namely, the null energy condition (NEC), the weak energy condition (WEC), the strong energy condition (SEC), and the dominant energy condition (DEC), are satisfied at the interior of the pulsar.
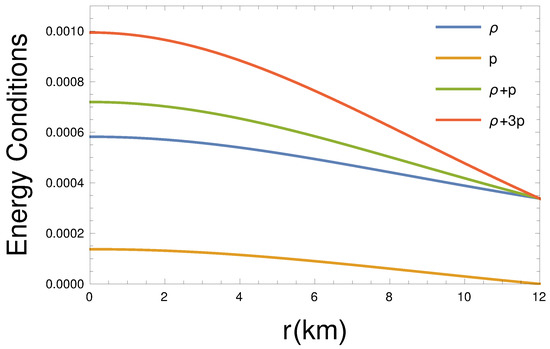
Figure 3.
Energy condition variation with radial distance at the pulsar interior for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
- (i)
- NEC:
- (ii)
- WEC: ,
- (iii)
- SEC: ,
- (iv)
- DEC:
3.3. Matching Conditions
For a stellar body, at the boundary (), the interior metric must be matched with the exterior Schwarzschild metric,
Assuming the continuity of metric functions , , and at the boundary , we obtain
This yields the gravitational mass of the pulsar as,
Solving Equations (9)–(11) and considering , we obtain
3.4. Mass-Radius Relation and Surface Red-Shift
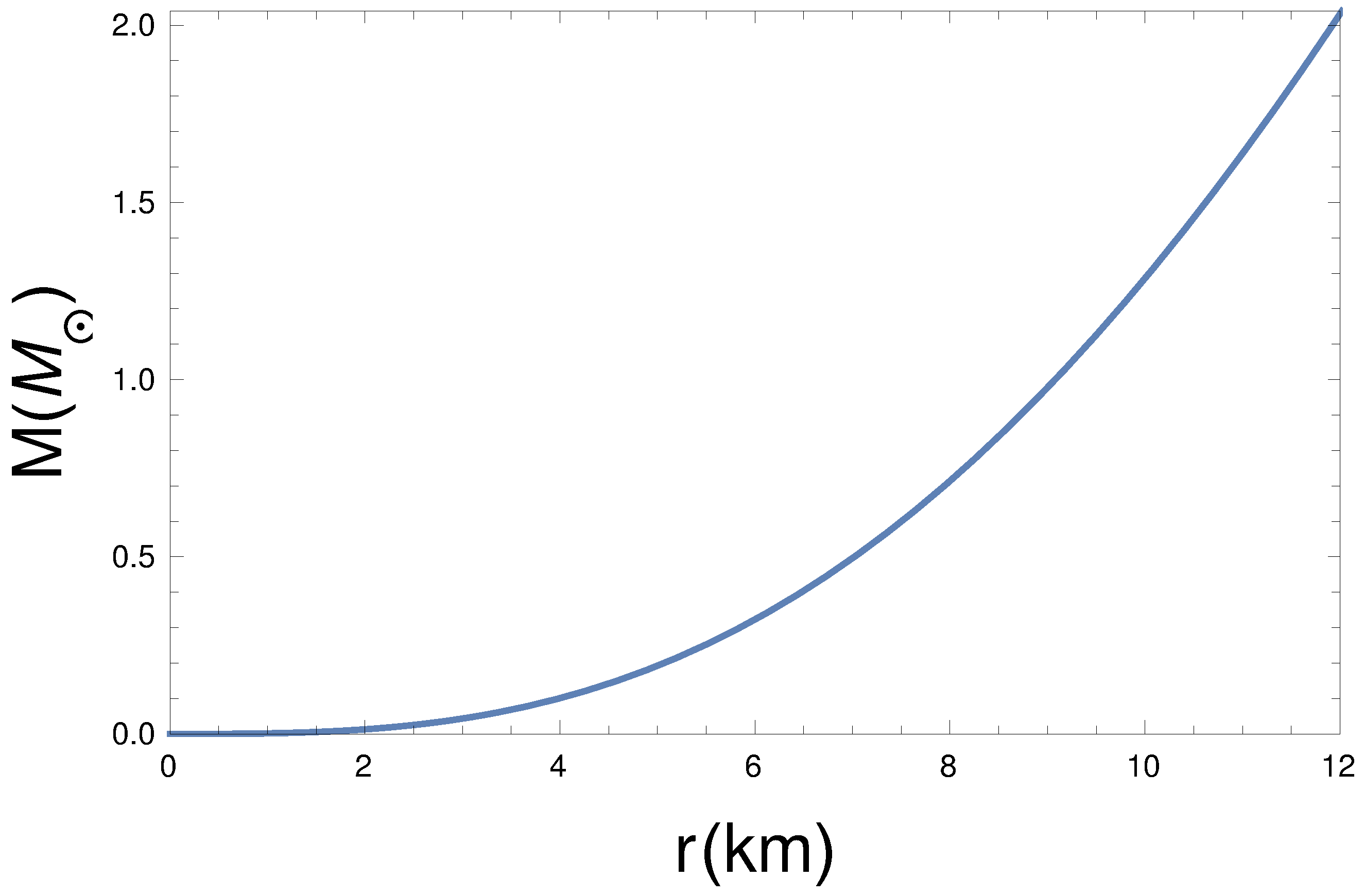
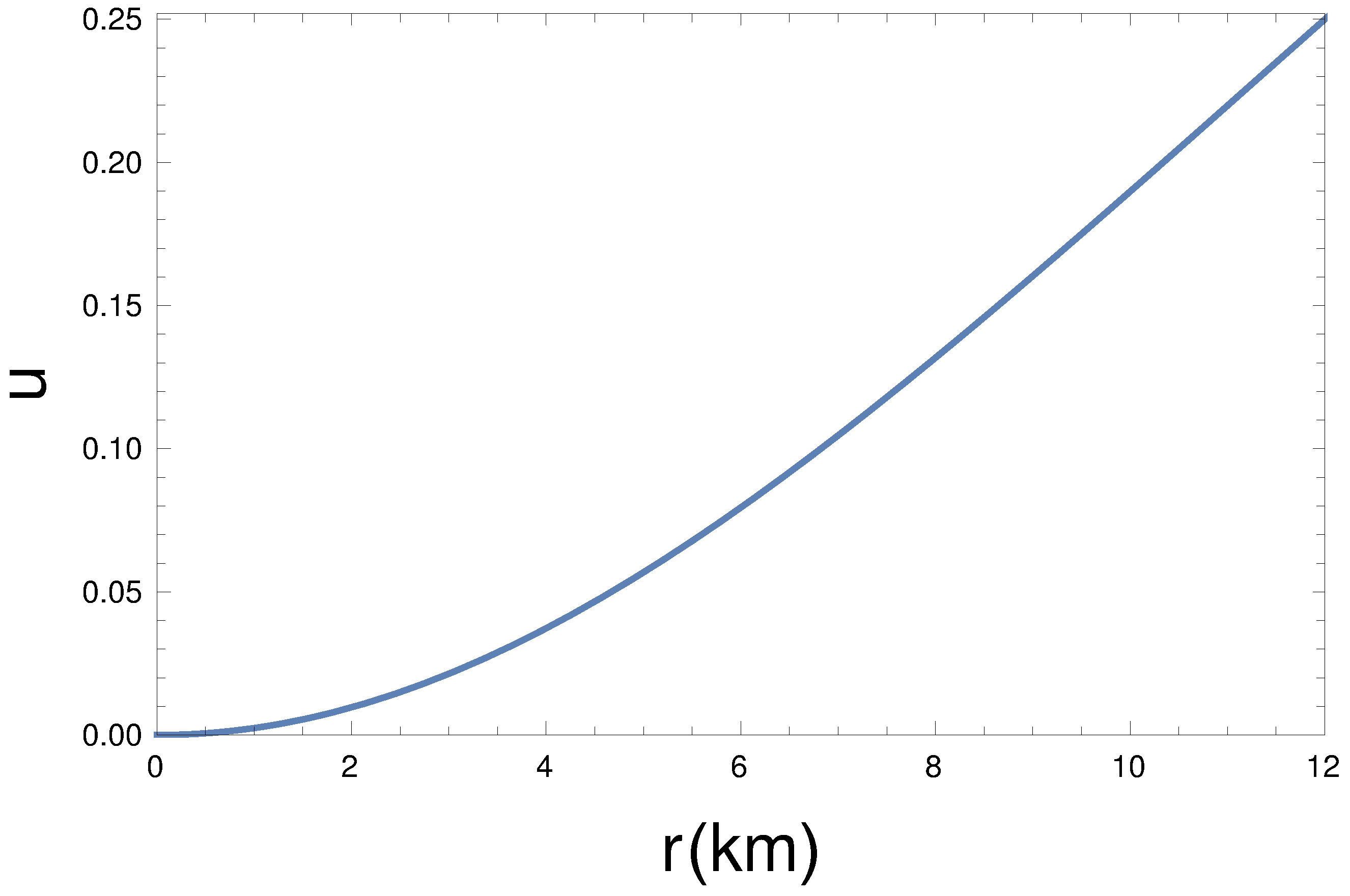
Here, we have calculated the radial dependence gravitational mass function M(r) as,
The mass function has been plotted in Figure 4. Therefore, the compactness of the pulsar can be written as,

Figure 4.
Radial dependence mass function, for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
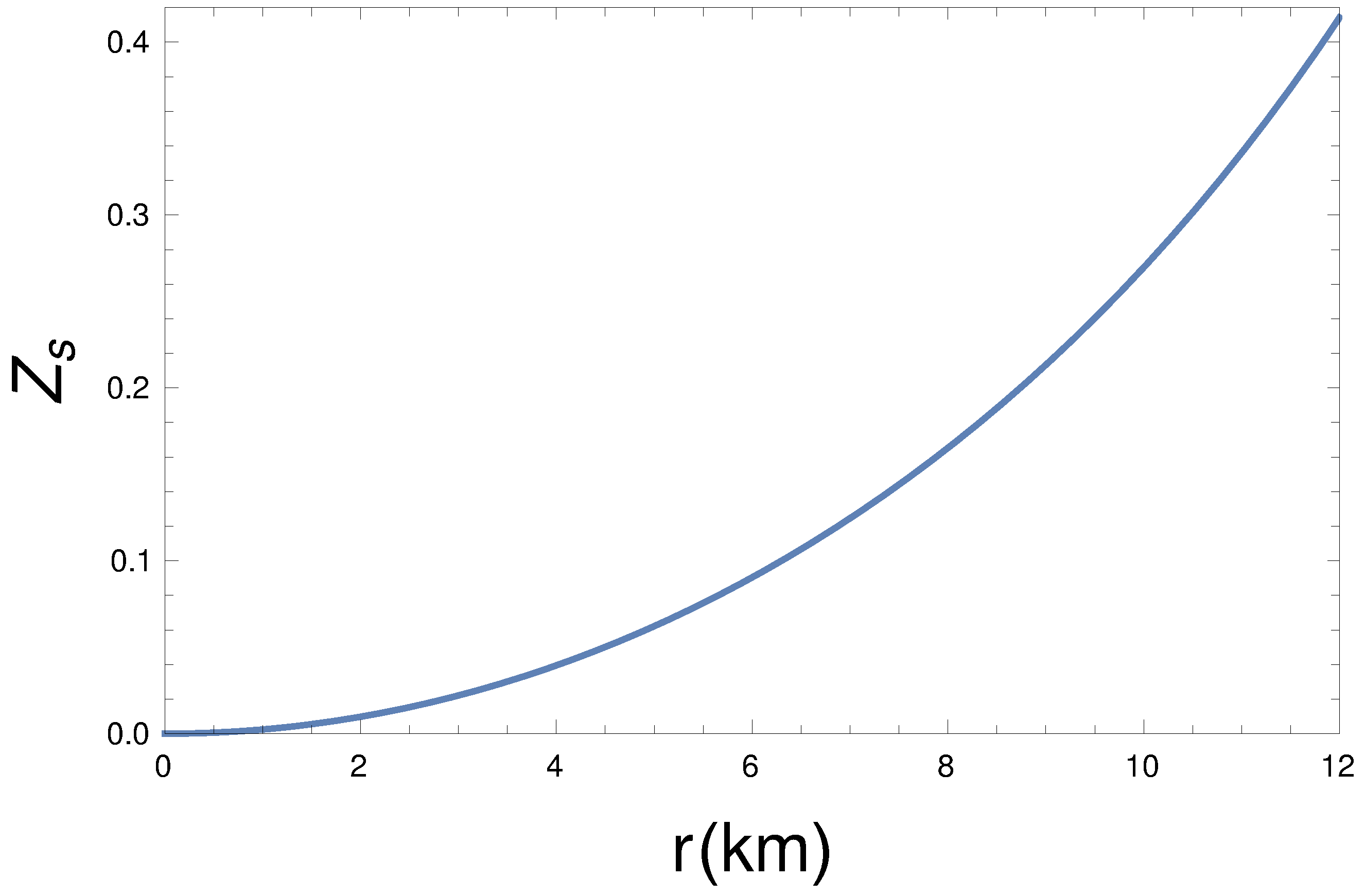
The surface red-shift corresponding to the compactness can be written as,
From Figure 5, we see that the compactness is an increasing function. In our model, the maximum value of is , which satisfies the Buchdahl limit [] [95]. The gravitational red-shift at the surface comes out as , as shown in Figure 6, which is lower than the allowed maximum limit () [96].
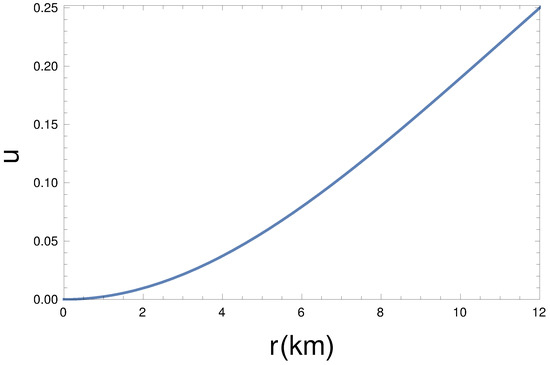
Figure 5.
Radial dependence compactness () for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.

Figure 6.
Radial dependence red-shift () for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
3.5. TOV Equation
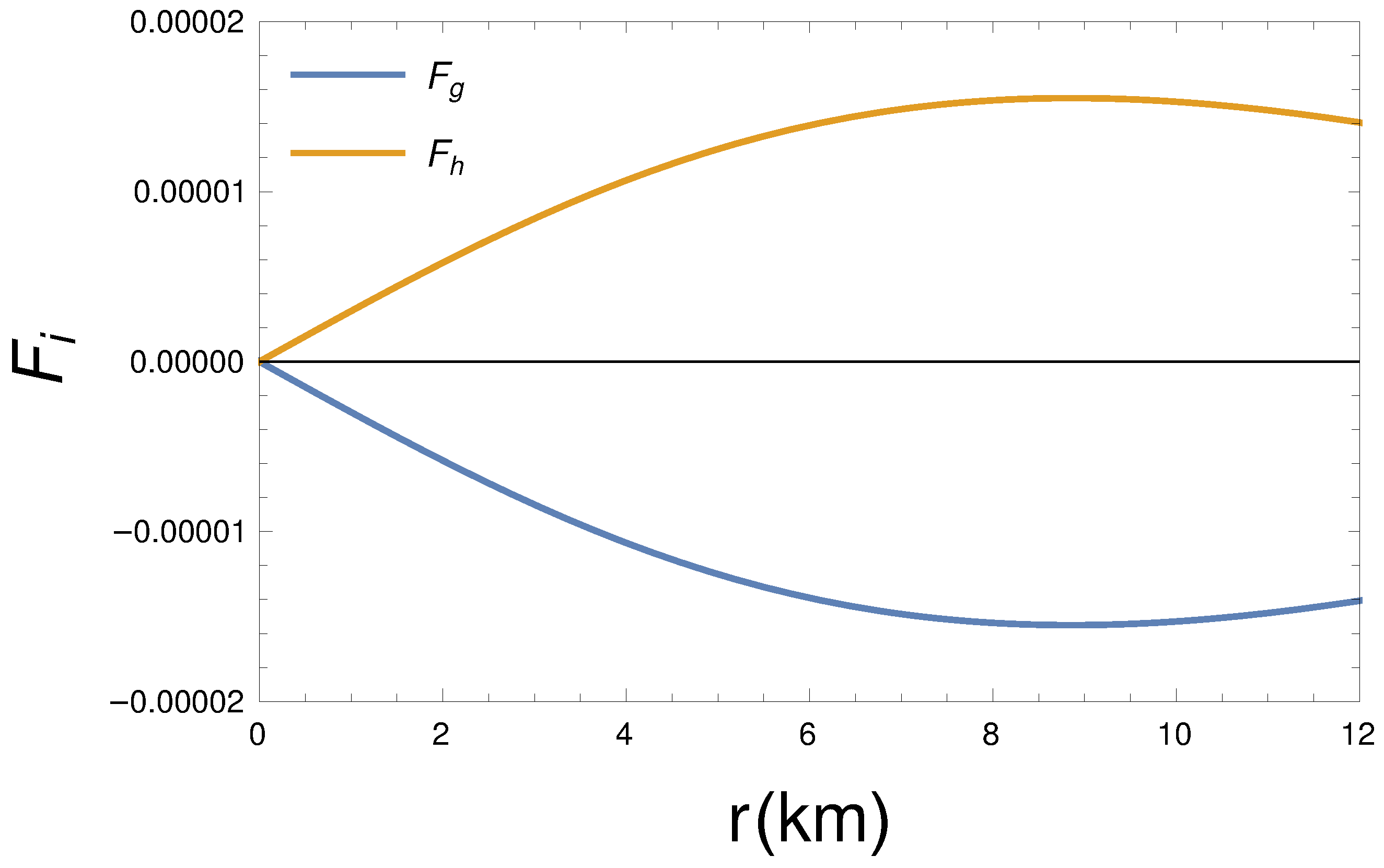
For the isotropic stellar body, the generalized TOV equation is written as,
The stable equilibrium condition has been found (see Figure 7) under gravitational force, , and hydrostatic force, , of the stellar body by the following equation:
where

Figure 7.
Radial dependence of gravitational force and hydrostatic force for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
3.6. Speed of Sound and Adiabatic Index
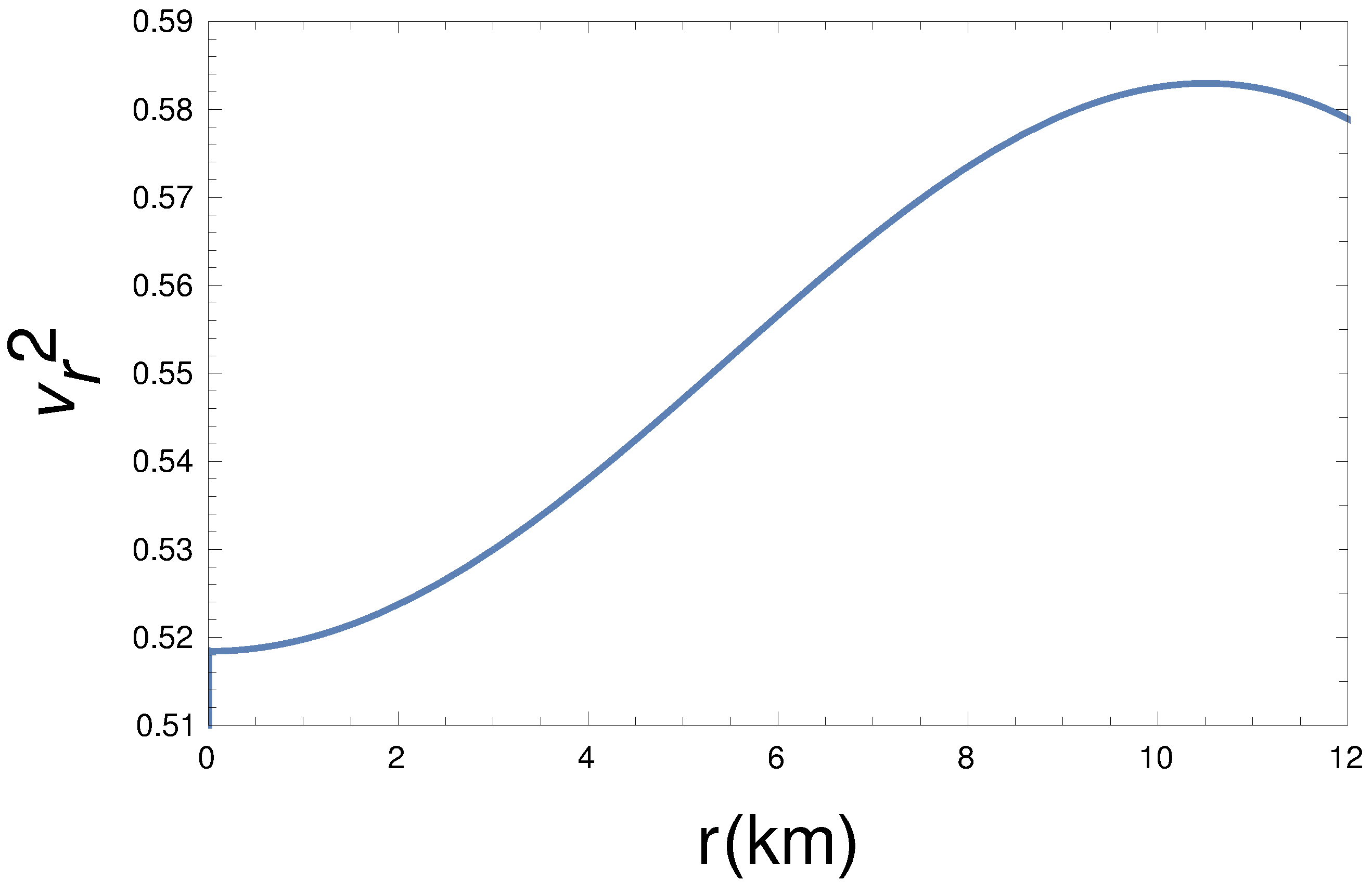
Here, we have seen that our dark-matter-admixed pulsar model has satisfied (see the Figure 8) the speed of sound, condition [97,98].
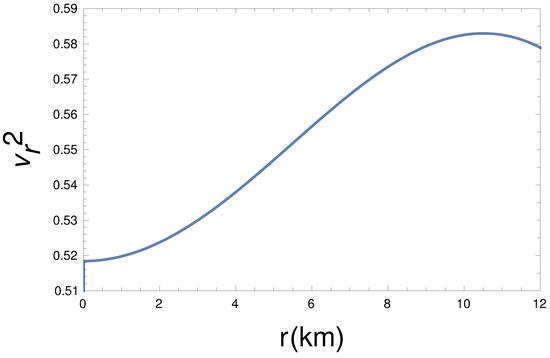
Figure 8.
Radial dependence of sound velocity () for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
The infinitesimal radial adiabatic perturbation must be checked if one needs to tune the model further. This concept was introduced by Chandrasekhar [99]. Later, Bardeen et al., Knusten, Harko, and Mak [100,101,102] used this stability condition for several astrophysical cases. For the radial stability, the adiabatic index for stellar body should be . We see from Figure 9 that throughout the stellar interior. Therefore, we can say that our dark-matter-admixed pulsar model is also stable under radial perturbation.

Figure 9.
Radial dependence of Adiabatic Index () for km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.
4. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Few astrophysicists [60,63,65,66,68,69,70,71,72] have worked on dark-matter-admixed pulsars. We have investigated the existence of dark-matter-admixed pulsar in the galactic halo region of the galaxy. In the present article, we are investigating its existence in the disk region of the Milky Way galaxy.
Previously [73,75], we have considered a two-fluid pulsar model, assuming it to be made of ordinary matter admixed with dark matter. We have investigated it based on
- (i)
- the singular isothermal sphere (SIS) profile for pulsars in the galactic halo region of different galaxies [73].
- (ii)
- the universal rotational curve (URC) profile for pulsars in the galactic halo region of Milky Way galaxy [75].
Here, we have considered the dark matter based on the Navarro–Frenk–White (NFW) [78] density profile (the acceptable dark matter profile in the disk region of the galaxy) for pulsars in the disk region of the Milky Way galaxy.
In this article, as earlier, we have considered the two-fluid dark-matter-admixed pulsar model, and the interior spacetime is described by the Heintzmann metric. Density and pressure at the interior of the pulsar are well behaved (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Here, we assume the value of the constants ( km, , , kpc, and GeV/c.c.) in such a way that all of the physical required conditions must satisfy. We also note that the value of and taken here are applicable for the Milky Way galaxy, and we have checked our model with the pulsars, namely, PSR J0045-7319 and PSR J0537-6910, located in the disk region of Milky Way galaxy.
Additionally, our pulsar model obeys all of the energy conditions and the generalized TOV equation. From the mass function (Equation (16)), all of the desired interior features of a pulsar can be evaluated, which satisfies the Buchdahl mass-radius relation () (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Figure 6 shows that the value of surface gravitational red-shift , which is much less than the maximum allowed value () [96]. From our mass function graphs Figure 4 and Figure 5, as well as Equations (19–21) and Figure 6, we have obtained the radii, compactness, and surface red-shift of the pulsars, namely, PSR J0045-7319 and PSR J0537-6910. The detailed evaluated chart is shown in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
Evaluated parameters for pulsar PSR J 0045-7319.

Table 2.
Evaluated parameters for pulsar PSR J 0537-6910.
Now, in comparison, if we use the URC dark-matter density profile () (by taking metric constants km, , ; core radius kpc; and effective core density, gm/c.c. [75] ) or the SIS dark-matter density profile () (by taking velocity dispersion, (as for spiral galaxies [73]) and metric constants km, , and ) instead of the NFW density profile and applied it to the same pulsars, located in Milky Way galaxy, we can obtain the comparison chart shown in Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 3.
Comparison between the parameters evaluated for different dark matter profiles (pulsar PSR J 0045-7319).

Table 4.
Comparison between the parameters evaluated for different dark matter profiles (pulsar PSR J 0537-6910).

Table 5.
The values of the metric parameters and dark matter parameters used in different star modellings.
If we compare Table 3 and Table 4, we see that pulsars radii are at a minimum in URC profile, whereas they are at a maximum in NFW profile (due to change in mass function graph). As a result of that compactness, surface red-shift is highest in the URC profile and lowest in the NFW profile (since compactness and red-shift are directly dependent on the radius of the star). Moreover, it is to be mentioned that for using the URC profile or the NFW profile, the core radius/scale radius and the effective core density/effective density of Milky Way galaxy are known to us. However, for other galaxies, these essential parameters are not known. Therefore, we cannot investigate the pulsars located in other galaxies by using the URC/NFW profile. However, in the SIS model, we will be able to study the pulsars located in different galaxies since the K (velocity dispersion) value of dwarf galaxies, and the spiral galaxies, are available to us (they can be calculated from the fitting of the rotation curves of the SPARC sample of galaxies [74]). However, the Navarro–Frenk–White(NFW) density profile is a well-accepted dark matter model, particularly for the disk regions of the galaxy [78].
Therefore, our results confirm the possible existence of dark-matter-admixed pulsars (by using the NFW density profile) located in the disk region of the Milky Way galaxy. Earlier, we obtained similar results for the pulsars based on the URC (universal rotation curve) density profile, located in the Milky Way galaxy [75], and the SIS (singular isothermal sphere) density profile, located in the dwarf and massive spiral galaxies [73]. Hence, we hope that dark-matter-admixed pulsars are present in all the regions of the galaxies.
Author Contributions
N.R.: Software, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft. M.M.: Methodology, Software, Formal analysis. S.M.: Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation. M.K.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—review, editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
NR:UGC MANF (MANF-2018-19-WES-96213); MM:CSIR (Grand No.-09/1157(0007)/2019-EMR-I); MK and SM: IUCAA, Pune, India.
Informed Consent Statement
All authors are agreed to publish the article in universe.
Acknowledgments
N.R. is thankful to UGC MANF (MANF-2018-19-WES-96213) for providing financial support. M.M. is thankful to CSIR (Grand No.-09/1157(0007)/ 2019-EMR-I) for providing financial support. M.K. and S.M. are grateful to the Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), Pune, India for providing the associateship programme under which a part of this work was carried out.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors has no conflict of Interest.
References
- Leahy, D.; Ouyed, R. Supernova SN2006gy as a first ever Quark Nova? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 387, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haensel, P.; Zdunik, Z.L.; Schaeffer, R. On Bianchi Type III String Cloud Universe Containing Strange Quark Matter. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 160, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Alcock, C.; Farhi, E.; Olinto, A. On Bianchi Type III String Cloud Universe Containing Strange Quark Matter. Astrophys. J. 1986, 310, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhi, E.; Jaffe, R.L. Strange matter. Phys. Rev. D 1984, 30, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikov, S.; Prakash, M.; Lattimer, J.M. Tidal Love numbers of neutron and self-bound quark stars. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 024016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Bombaci, I.; Dey, J.; Ray, S.; Samanta, B.C. Strange stars with realistic quark vector interaction and phenomenological density-dependent scalar potential. Phys. Lett. B 1998, 438, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Prakash, M. The Effective Chiral Model of Quantum Hadrodynamics Applied to Nuclear Matter and Neutron Stars. Phys. Rep. 2007, 442, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, F. The Effective Chiral Model of Quantum Hadrodynamics Applied to Nuclear Matter and Neutron Stars. Nature 2006, 441, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, F.; Göver, T.; Psaitis, D. The black hole mass distribution in the galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2009, 693, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, F.; Psaitis, D. Reconstructing the neutron-star equation of state from astrophysical measurements. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, F.; Baym, G.; Göver, T. Astrophysical measurement of the equation of state of neutron star matter. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göver, T.; Özel, F.; Cabrera-Lavers, A. The Distance, Mass, and Radius of the Neutron Star in 4U 1608-52. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göver, T.; Wroblewski, P.; Camarota, L.; Özel, F. Measuring the basic parameters of neutron stars using model atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 2010, 719, 1807. [Google Scholar]
- Heap, S.R.; Corcoran, M.F. Properties of the massive X-ray binary 4U 1700-37 = HD 153919. Astrophys. J. 1992, 387, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Prakash, M. Ultimate Energy Density of Observable Cold Baryonic Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickland, D.; Lloyd, C.; Radzuin-Woodham, A. The orbit of the supergiant component of VELA X-1 derived from IUE radial velocities. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 286, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, J.A.; Kuulkers, E. The optical light curves of Cygnus X-2 (V1341 Cyg) and the mass of its neutron star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 305, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkwijk, J.H.V.; van Paradijis, J.; Zuiderwijk, E.J. On the masses of neutron stars. Astrophysics 1995, 303, 497. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, F.; Maulik, R.; Yadav, A.K.; Ray, S.; Sharma, R. Singularity-free dark energy star. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2012, 44, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, F.; Sharma, S.; Ray, S.; Maulick, R.; Karar, I. Strange stars in Krori-Barua space-time. Eur. Phys. J. C 2012, 72, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Rahaman, F.; Ray, S.; Hossein, S.; Karar, I.; Naskar, J. Anisotropic strange star with de Sitter spacetime. Eur. Phys. J. C 2012, 72, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Usmani, A.A.; Rahaman, F.; Hossein, S.M. A Relativistic Model for Strange Quark Star. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Rahaman, F.; Hossein, M.; Ray, S. Central density dependent anisotropic compact stars. Eur. Phys. J. C 2013, 73, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Rahaman, F.; Molla, S.; Jafry, M.; Kayum, A.; Hossein, S. Analytical model of strange star in the low-mass X-ray binary 4U 1820-30. Eur. Phys. J. C 2014, 74, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Rahaman, F.; Molla, S.; Hossein, S.M. Anisotropic quintessence stars. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 349, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Hossein, S.M.; Molla, S. Possible radii of compact stars: A relativistic approach. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2016, 31, 1650219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Hossein, S.M.; Islam, R.; Molla, S. Relativistic model of neutron stars in X-ray binary. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 32, 1750012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafry, M.A.K.; Molla, S.; Islam, R.; Kalam, M. Analytical model of massive Pulsar J0348+0432. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2017, 362, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, S.; Rahaman, F.; Naskar, J.; Kalam, M.; Ray, S. Anisotropic Compact stars with variable cosmological constant. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2012, 21, 1250088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F. Gravitation, Dark Matter and Dark Energy: The Real Universe. Class. Quantum Grav. 2006, 23, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnikov, K.; Fabris, J.C. Regular Phantom Black Holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 251101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, S.K.; Gupta, Y.K.; Ray, S.; Deb, D. Generalised model for anisotropic compact stars. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayanandan, B.; Maurya, S.K.; Gupta, Y.K.; Smitha, T.T. Anisotropic generalization of Matese & Whitman solution for compact star models in general relativity. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Maharaja, S.D.; Sunzub, J.M.; Ray, S. Some simple models for quark stars. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2014, 129, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngubelanga, S.; Maharaj, S.D.; Ray, S. Compact stars with quadratic equation of state. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 357, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.C.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Karmakar, S. Relativistic Anisotropic Star and its Maximum Mass in Higher Dimensions. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 356, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, N.; Pradhan, N.; Murad, M.H. A class of super dense stars models using charged analogues of Hajj-Boutros type relativistic fluid solutions. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2014, 53, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhar, P.; Singh, K.N.; Sarkar, N.; Rahaman, F. A comparative study on generalized model of anisotropic compact star satisfying the Karmarkar condition. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.; Hossein, S.M.; Molla, S. Neutron stars: A relativistic study. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 18, 025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.; Islam, R.; Jafry, M.A.K.; Kalam, M. Analytical model of compact star in low-mass X-ray binary with de Sitter spacetime. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 19, 026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Molla, S.; Kalam, M. Analytical model of strange star in Durgapal spacetime. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2019, 364, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendi, S.H.; Bordbar, G.H.; Eslam Panha, B.; Panahiyan, S. Modified TOV in gravity’s rainbow: Properties of neutron stars and dynamical stability conditions. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 9, 013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendi, S.H.; Bordbar, G.H.; Eslam Panha, B.; Panahiyan, S. Neutron stars structure in the context of massive gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 7, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panah, B.E.; Bordbar, G.H.; Hendi, S.H.; Ruffini, R.; Rezaei, Z.; Moradi, R. Expansion of Magnetic Neutron Stars in an Energy (in)Dependent Spacetime. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicky, F. Comparative Analysis of Existing and Alternative Version of the Special Theory of Relativity. Helv. Phys. Acta 1933, 6, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicky, F. Republication of: The Redshift of Extragalactic Nebulae. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2009, 41, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, V.C.; Ford, W.K., Jr. Rotation of the Andromeda Nebula from a Spectroscopic Survey of Emission Regions. Astrophys. J. 1970, 159, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, K.A. TASI Lectures on Dark Matter. arXiv 2003, arXiv:astro-ph/0301505. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz, C. Dark Matter Detection in the Light of Recent Experimental Results. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2004, 19, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoso, M.; Bertone, G.; Masiero, A. Dark matter candidates: A ten-point test. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 3, 022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.; Silk, J. Probing the existence of a dark matter isothermal core using gravity modes. Astrophys. J. 2010, 722, L95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaris, C.; Tinyakov, P. Can neutron stars constrain dark matter? Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 063531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck-Chièze, S.; Lopes, I. Solar-stellar astrophysics and dark matter. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.; Silk, J. A particle dark matter footprint on the first generation of stars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, I.; Kadota, K.; Silk, J. Constraint on light dipole dark matter from helioseismology. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 780, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.; Cardoso, V.; Okawa, H. Accretion of Dark Matter by Stars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 111301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.; Cardoso, V.; Macedo, C.F.B.; Okawa, H.; Palenzuela, C. Interaction between bosonic dark matter and stars. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 044045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Lopes, I.; Casanellas, J.; Martins, A.; Lopes, I.; Casanellas, J. Asteroseismic constraints on asymmetric dark matter: Light particles with an effective spin-dependent coupling. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 023507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Huang, F.; Xu, R.X. Too massive neutron stars: The role of dark matter? Astropart. Phys. 2012, 37, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, F.; Cheng, K.S. Gravitational effects of condensate dark matter on compact stellar objects. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 10, 031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panotopoulos, G.; Lopes, I. Gravitational effects of condensed dark matter on strange stars. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narain, G.; Schaffner-Bielich, J.; Mishustin, I.N. Compact stars made of fermionic dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.C.; Chu, M.C.; Lin, L.M. Equilibrium structure and radial oscillations of dark matter admixed neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Schaffner-Bielich, J. Quark stars admixed with dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 083009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panotopoulos, G.; Lopes, I. Radial oscillations of strange quark stars admixed with condensed dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 083004–083013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.C.; Chu, M.C.; Lin, L.M. Dark light, dark matter, and the misalignment mechanism. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 107301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.N.; Steinhardt, P.J. Observational evidence for self-interacting cold dark matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandin, F.; Ciarcelluti, P. Effects of mirror dark matter on neutron stars. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 32, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Atta, D.; Imam, K.; Basu, D.N.; Samanta, C. Compact bifluid hybrid stars: Hadronic matter mixed with self-interacting fermionic asymmetric dark matter. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, Z. Study of Dark-Matter Admixed Neutron Stars using the Equation of State from the Rotational Curves of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, Z. Double dark-matter admixed neutron star. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2018, 27, 1950002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takisa, P.M.; Leeuw, L.L.; Maharaj, S.D. Model of compact star with ordinary and dark matter. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2020, 365, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.; Ghosh, B.; Kalam, M. Does dark matter admixed pulsar exists? Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, F.; McGaugh, S.S.; Schombert, J.M. SPARC: Mass models for 175 disk galaxies with Spitzer photometry and accurate rotation curves. Astrophys. J. 2016, 152, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Molla, S.; Kalam, M. Possible existence of dark matter admixed pulsar. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccio, A.V.; Stinson, G.; Brook, C.B.; Wadsley, J.; Couchman, H.M.P.; Shen, S.; Gibson, B.K.; Quinn, T. Halo expansion in cosmological hydro simulations: Toward a baryonic solution of the cusp/core problem in massive spirals. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 744, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castignani, G.; Frusciante, N.; Vernieri, D.; Salucci, P. The density profiles of dark matter halos in spiral galaxies. Nat. Sci. 2012, 4, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. The Structure of Cold Dark Matter Halos. Astrophys. J. 1996, 462, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeira, M.; Mesquita, A. Accretion of dark matter in neutron stars. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 2011, 20, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takisa, P.M.; Maharaj, S.D.; Leeuw, L.L. Effect of electric charge on conformal compacts stars. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matondo, D.K.; Maharaj, S.D.; Ray, S. Relativistic stars with conformal symmetry. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 78, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.K.; Gupta, Y.K.; Ray, S.; Chowdhury, S.R. Spherically symmetric charged compact stars. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.K.; Banerjee, A.; Jasim, M.K.; Kumar, J.; Prasad, A.K.; Pradhan, A. Anisotropic compact stars in the Buchdahl model: A comprehensive study. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 044029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayanandana, B.; Maurya, S.K.; Smitha, T.T. Modeling of charged anisotropic compact stars in general relativity. Eur. Phys. J. A 2017, 53, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.K. Relativistic modeling of compact stars for anisotropic matter distribution. Eur. Phys. J. A 2017, 53, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedela, S.; Bisht, R.K.; Pant, N. Stellar modeling of PSR J1614-2230 using the Karmakar condition. Eur. Phys. J. A 2018, 54, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.N.; Pant, N.; Govender, M. Anisotropic compact stars in Karmarkar spacetime. Chin. Phys. C 2017, 41, 015103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, F.; Maharaj, S.D.; Sardar, I.H.; Chakraborty, K. Conformally symmetric relativistic star. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 32, 1750053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, M.K.; Maurya, S.K.; Gupta, Y.K.; Dayanandan, B. Well behaved anisotropic compact star models in general relativity. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takisa, P.M.; Maharaj, S.D. Anisotropic charged core envelope star. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, S.K.; Jasim, M.K.; Gupta, Y.K.; Smitha, T.T. Relativistic Polytropic Models for Neutral Stars with Vanishing Pressure Anisotropy. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.N.; Pradhan, N.; Pant, N. New interior solution describing relativistic fluid sphere. Pramana J. Phys. 2017, 89, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzmann, H. Newtonian Time in General Relativity. Z. Phys. 1969, 228, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco, J.; Bernal, A.; Nunez, D. Dark matter equation of state from rotational curves of galaxies. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1301.6785V1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchdahl, H.A. General Relativistic Fluid Spheres. Phys. Rev. 1959, 116, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haensel, P.; Lasopa, J.P.; Zdunik, J.L. Maximum redshift and minimum rotation period of neutron stars. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 2000, 80, 1110. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, L. Cracking of self-gravitating compact objects. Phys. Lett. A 1992, 165, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, H.; Hernandez, H.; Nunez, L.A. Sound Speeds, Cracking and Stability of Self-Gravitating Anisotropic Compact Objects. Class. Quantum Gravit. 2007, 24, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. The Dynamical Instability of Gaseous Masses Approaching the Schwarzschild Limit in General Relativity. Astrophys. J. 1964, 140, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Thorne, K.S.; Meltzer, D.W. Catalog of methods for studying the normal modes of radial pulsation of general relativistic stellar models. Astrophys. J. 1966, 145, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, H. On the stability and physical properties of an exact relativistic model for a superdense star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1988, 232, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, M.K.; Harko, T. Isotropic stars in general relativity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2013, 73, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.C.G.; Espinoza, C.M.; Antonopoulou, D.; Andersson, N. Pinning down the superfluid and measuring masses using pulsar glitches. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).