On the Nucleosynthetic Origin of Presolar Silicon Carbide X-Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Parametric Core-Collapse Supernova Neutrino-Driven Wind Model
3. Nuclear Data Input—A Unified Approach
4. Nucleosynthesis of Zr, Mo and Ru Isotopes in the Neutrino-Driven Wind
5. Observations from SiC-X Grains
5.1. Discovery and Classification of SiC-X Grains
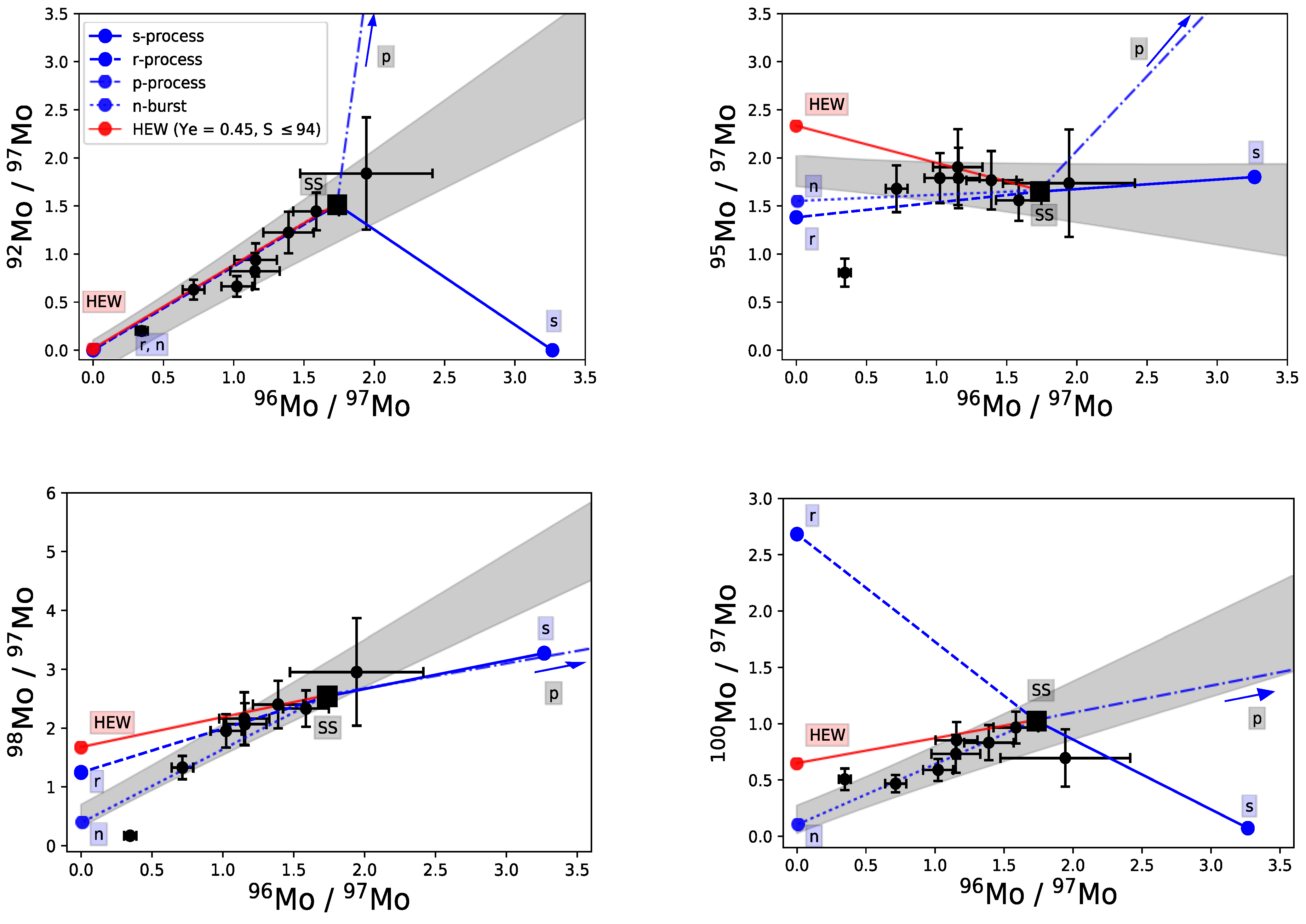
5.2. Anomalous Zr, Mo and Ru Isotope Compositions of SiC-X Grains
6. The Nucleosynthetic Source of SiC-X Grains
6.1. s-Process
| SiC-X End-Member Limit a | This Work b | n-Burst c | s-Process d | r-Process e | p-Process f | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iMo/kMo: | ||||||
| 92Mo/97Mo | ≤0.528 | 2.74 × 10−3 | 1.43 × 10−3 | 0 | 0 | ≈27 |
| 94Mo/97Mo | ≤0.238 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 3.28 × 10−3 | 0.013 | 0 | ≈18 |
| 95Mo/97Mo | ≈1.649 | 2.321 | 1.540 | 1.801 | 1.382 | ≈5 |
| 96Mo/97Mo | ≤0.638 | 6.69 × 10−5 | 0.010 | 3.27 | 0 | ≈4 |
| 98Mo/97Mo | ≤1.133 | 1.654 | 0.379 | 3.28 | 1.247 | ≈4 |
| 100Mo/97Mo | ≤0.390 | 0.637 | 0.095 | 0.072 | 2.683 | ≈2 |
| 92Mo/94Mo | ≥2.578 | 1.587 | 0.437 | 0 | 0 | 1.527 |
| iZr/90Zr: | ||||||
| 91Zr/90Zr | ≥0.255 | 0.085 (0.193) g | 0.459 | 0.272 | 0 | 0.013 |
| 92Zr/90Zr | ≥0.447 | 0.288 (0.700) g | 0.680 | 0.395 | 0 | 0.050 |
| 94Zr/90Zr | ≥0.518 | 0.338 (0.844) g | 0.537 | 0.500 | 0 | 0.043 |
| 96Zr/90Zr | ≥0.379 | 0.087 (0.298) g | 0.612 | 0.033 | 0.174 | 0.138 |
| iRu/101Ru: | ||||||
| 96Ru/101Ru | ≥0.935 | 3.86 × 10−5 | 3.70 × 10−9 | 0 | 0 | ≈135 |
| 98Ru/101Ru | ≥0.177 | 2.76 × 10−7 | 5.72 × 10−7 | 0 | 0 | ≈62 |
| 99Ru/101Ru | ≥1.141 | 0.184 | 0.473 | 1.398 | 0.607 | ≈13 |
| 100Ru/101Ru | ≤0.338 | 5.76 × 10−8 | 1.42 × 10−3 | 4.576 | 0 | ≈16 |
| 102Ru/101Ru | ≥2.755 | 4.489 | 10.20 | 5.223 | 1.123 | ≈1 |
| 104Ru/101Ru | ≥2.883 | 0.542 | 7.41 | 0.152 | 1.294 | ≈7 |
6.2. r-Process
6.3. p-Process
6.4. Neutron-Burst
6.5. Neutrino-Driven Wind Component
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merrill, P.W. Spectroscopic observations of stars of class. Astrophys. J. 1952, 116, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, V.M. Geochemische Verteilungsgesetze der Elemente; Skrifter Norske Videnskaps-Acd: Oslo, Norway, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Suess, H.E.; Urey, H.C. Abundances of the elements. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1956, 28, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbidge, E.M.; Burbidge, G.R.; Fowler, W.A.; Hoyle, F. Synthesis of the elements in stars. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1957, 29, 547–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.G.W. Stellar Evolution, Nuclear Astrophysics, and Nucleogenesis; Chalk River Report 1957, CRL-41; Atomic Energy of Canada Ltd.: Chalk River, ON, Canada, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Arnould, M. Possibility of synthesis of proton-rich nuclei in highly evolved stars II. Astron. Astrophys. 1976, 46, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Woosley, S.E.; Howard, W.M. The p-process in supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1978, 36, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.D. Principles of Stellar Evolution and Nucleosynthesis; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Käppeler, F.; Beer, H.; Wisshak, K. S-process nucleosynthesis-nuclear physics and the classical model. Rep. Prog. Physics. 1989, 52, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, P.A.; Fowler, W.A.; Clayton, D.D. Nucleosynthesis of heavy elements by neutron capture. Astrophys. J. 1965, 11, 121–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrandt, W. The rapid neutron-capture process and the synthesis of heavy and neutron-rich elements. Space Sci. Rev. 1978, 21, 639–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, J.J.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Truran, J.W. The r-process and nucleochronology. Phys. Rep. 1991, 208, 267–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roederer, I.U.; Cowan, J.J.; Karakas, A.I.; Kratz, K.-L.; Lugaro, M.; Simmerer, J.; Farouqi, K.; Sneden, C. The ubiquity of the rapid neutron-capture process. Astrophys. J. 2010, 724, 975–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, V.; Christlieb, N.; Beers, T.C.; Barklem, P.S.; Kratz, K.-L.; Nordström, B.; Pfeiffer, B.; Farouqi, K. The Hamburg/ESO r-process enhanced star survey (HERES). Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 607, A91. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, T.T.; Holmbeck, E.M.; Beers, T.C.; Placco, V.M.; Roederer, I.U.; Frebel, A.; Sakari, C.M.; Simon, J.D.; Thompson, I.B. The r-process alliance: First release from the southern search for r-process-enriched stars in the galactic halo. Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frebel, A.; Beers, T.C. The formation of the heaviest elements. Phys. Today 2018, 71, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Bitouzet, J.-P.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Möller, P.; Pfeiffer, B. Isotopic r-process abundances and nuclear structure far from stability: Implications for the r-process mechanism. Astrophys. J. 1993, 403, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Farouqi, K.; Pfeiffer, B.; Truran, J.W.; Sneded, C.; Cowan, J.J. Explorations of the r-process: Comparisons between calculations and observations of low-metallicity stars. Astrophys. J. 2007, 662, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Farouqi, K.; Möller, P. A high-entropy-wind r-process study based on nuclear-structure quantities from the new finite-range droplet model FRDM(2012). Astrophys. J. 2014, 792, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.D.; Woosley, S.E.; Fuller, G.M.; Meyer, B.S. Production of the light p-process nuclei in neutrino-driven winds. Astrophys. J. 1996, 460, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.D.; Woosley, S.E.; Qian, Y.-Z. Nucleosynthesis in neutrino-driven winds II-implications for heavy element synthesis. Astrophys. J. 1997, 482, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.D.; Müller, B.; Janka, H.-T. Nucleosynthesis in O-Ne-Mg supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2008, 676, L127–L130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, T.; Heger, A.; Hoffman, R.D.; Woosley, S.E. Nucleosynthesis in massive stars with improved nuclear and stellar physics. Astrophys. J. 2002, 576, 323–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatari, M.; Gallino, R.; Meynet, G.; Hirschi, R.; Herwig, F.; Wiescher, M. The s-process in massive stars at low metallicity: The effect of primary 14N from fast rotating stars. Astrophys. J. 2008, 687, L95–L98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanajo, S.; Nomoto, K.; Janka, H.-T.; Kitaura, F.S.; Müller, B. Nucleosynthesis in electron capture supernovae of asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2009, 695, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglio, C.; Gallino, R.; Arnone, E.; Cowan, J.; Jordan, F.; Sneden, C. Galactic evolution of Sr, Y, and Zr: A multiplicity of nucleosynthetic processes. Astrophys. J. 2004, 601, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglio, C.; Röpke, F.K.; Gallino, R.; Hillebrandt, W. Type Ia supernovae as sites of the p-process: Two-dimensional models coupled to nucleosynthesis. Astrophys. J. 2011, 793, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglio, C.; Gallino, R.; Rauscher, T.; Röpke, F.K.; Hillebrandt, W. Testing the role of SNe Ia for galactic chemical evolution of p-nuclei with two-dimensional models and with s-process seeds at different metallicities. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouqi, K.; Kratz, K.-L.; Cowan, J.J.; Mashonkina, L.I.; Pfeiffer, B.; Sneden, C.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Truran, J.W. Nucleosynthesis modes in the high-entropy-wind scenario of type II supernovae. In AIP Conference Proceedings; O’Shea, B.W., Heger, A., Abel, T., Eds.; First Stars III; AIP Publishing: Long Island, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 990, pp. 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Farouqi, K.; Kratz, K.-L.; Mashonkina, L.I.; Pfeiffer, B.; Cowan, J.J.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Truran, J.W. Nucleosynthesis modes in the high-entropy wind of type II supernovae: Comparison of calculations with halo-star observations. Astrophys. J. 2009, 694, L49–L53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouqi, K.; Kratz, K.-L.; Pfeiffer, B. Co-production of light p-, s- and r-process isotopes in the high-entropy wind of type II supernovae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2009, 26, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouqi, K.; Kratz, K.-L.; Pfeiffer, B.; Rauscher, T.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Truran, J.W. Charged-particle and neutron-capture processes in the high-entropy wind of core-collapse supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 1359–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellin, M.J.; Davis, A.M.; Calaway, W.F.; Lewis, R.S.; Clayton, R.N. Zr and Mo isotopic constraints on the origins of unusual types of presolar SiC grains. In Proceedings of the 31st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2000; Available online: https://www.lpi.usra.edu/lpi/meteorites/lpsc31abs.html (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Pellin, M.J.; Savina, M.R.; Calaway, W.F.; Tripa, C.E.; Barzyk, J.G.; Davis, A.M.; Gyngard, F.; Amari, S.; Zinner, E.; Lewis, R.S.; et al. Heavy metal isotopic anomalies in supernovae presolar grains. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference Proceedings, XXXVII 2006, #2041, League City, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Birck, J.-L. An overview of isotopic anomalies in extraterrestrial materials and their nucleosynthetic heritage. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2004, 55, 25–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, W.; Schönbächler, M.; Sprung, P.; Vogel, N. Zirconium-hafnium isotope evidence from meteorites for the decoupled synthesis of light and heavy neutron-rich nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2013, 777, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, U. Isotope variations in the solar system: Supernova fingerprints. In Handbook of Supernovae; Alsabi, A.W., Murdin, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zinner, E. Presolar Grains. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, D.D. Handbook of Isotopes in the Cosmos; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Marhas, K.K.; Hoppe, P.; Ott, U. NanoSIMS studies of Ba isotopic compositions in single presolar silicon carbon grains from AGB stars and supernovae. MAPS 2007, 42, 1077–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, W.M.; Meyer, B.S.; Clayton, D.D. Heavy-element abundances from a neutron burst that produces Xe-H. Meteoritics 1992, 27, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.S.; Clayton, D.D.; The, L.S. Molybdenum and zirconium isotopes from a supernova neutron burst. Astrophys. J. 2000, 540, L49–L52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, O.; Farouqi, K.; Kratz, K.-L.; Ott, U. Origin of Anomalous Zr, Mo and Ru Abundances in SiC X-grains: Indications of a Primary Charged-Particle Process. 76th Annual Meteoritical Society Meeting 2013, #5082. Available online: https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/metsoc2013/pdf/5082.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Kratz, K.L.; Akram, W.; Farouqi, K.; Hallmann, O. Production of light trans-Fe elements in core collapse supernovae: Implications from presolar SiC-X grains. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2076, 030002. [Google Scholar]
- Thielemann, F.-K.; Ken’Ichi, N.; Masa-Aki, H. Core-collapse supernova and their ejecta. Astrophys. J. 1996, 460, 408–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, C.; Martínez-Pinedo, G.; Liebendörfer, M.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Bravo, E.; Hix, W.R.; Langanke, K.; Zinner, N.T. Neutrino-induced nucleosynthesis of A > 64 nuclei: The nu-p process. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 145502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiburghaus, C.; Rembges, J.-F.; Rauscher, T.; Kolbe, E.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Kratz, K.-L.; Pfeiffer, B.; Cowan, J.J. The astrophysical r-process: A comparison of calculations following adiabatic expansion with classical calculations based on neutron densities and temperatures. Astrophys. J. 1999, 516, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.S.; Matthews, G.J.; Howard, W.M.; Woosley, S.E.; Hoffman, R.D. R-process nucleosynthesis in the high-entropy supernova bubble. Astrophys. J. 1992, 399, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Willebrandt, W.; Möller, P.; Harms, V.; Wohr, A.; Truran, J.W. Constraints on r-process conditions from beta-decay properties far off stability and r-abundances. J. Phys. G 1988, 14, S331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Nix, J.R. Calculation of fission barriers with the droplet model and folded Yukawa single-particle model. Nucl. Phys. A 1974, 229, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Nix, J.R. Atomic masses and nuclear ground-state deformations calculated with a new macroscopic-microscopic model. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1981, 26, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumlinde, J.; Möller, P. Calculation of Gamow-Teller beta-strength functions in the rubidium region in the RPA approximation with Nilsson-model wave functions. Nucl. Phys. A 1984, 417, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Randrup, J. New developments in the calculation of beta-strength functions. Nucl. Phys. A 1990, 514, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Nix, J.R.; Myers, W.D.; Swiatecki, W.J. Nuclear ground-state masses and deformations. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1995, 59, 185–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Nix, J.R.; Kratz, K.-L. Nuclear properties for astrophysical and radioactive ion-beam applications. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1997, 66, 131–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Pfeiffer, B.; Kratz, K.-L. New calculations of gross beta-decay properties for astrophysical applications: Speeding up the classical r process. Phys. Rev. C 2003, 67, 055802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K. Application of the Gross theory of beta-decay to delayed neutron emissions. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1972, 47, 1500–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kratz, K.L.; Ohm, H.; Schröder, A.; Gabelmann, H.; Ziegert, W.; Pfeiffer, B.; Jung, G.; Monnand, E.; Pinston, J.A.; Schussler, F.; et al. The beta-decay of 95Rb and 97Rb. Z. Phys. 1983, 312, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.; Fogelberg, B.; Harvey, J.A.; Macklin, R.L.; Stelson, P.H.; Schröder, A.; Kratz, K.-L. Overlapping beta decay and resonance neutron spectroscopy of levels in 87Kr. Phys. Rev. C 1983, 28, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberth, J.; Meyer, R.A.; Sistemich, K. Int. Workshop in Nuclear Structure in the Zirconium Region; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Lhersonneau, G.; Pfeiffer, B.; Kratz, K.-L.; Enqvist, T.; Jauho, P.P.; Jokinen, A.; Kantele, J.; Leino, M.; Parmonen, J.M.; Penttilä, H.; et al. Evolution of deformation in the neutron-rich Zr region from excited intruder state to the ground state. Phys. Rev. C 1994, 49, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Gabelmann, H.; Pfeiffer, B.; Möller, P. Onset of deformation in neutron-rich krypton isotopes. Z. Phys. 1988, 330, 229–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lhersonneau, G.; Wöhr, A.; Pfeiffer, B.; Kratz, K.-L.; the ISOLDE Collaboration. First decay study of the very neutron-rich isotope 93Br. Phys. Rev. C 2001, 63, 034316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, B.; Kratz, K.-L.; Möller, P. Status of delayed-neutron precursor data: Half-lives and neutron emission probabilities. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2002, 41, 39–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergemann, U.C.; Diget, C.A.; Riisager, K.; Weissman, L.; Auböck, G.; Cederkäll, J.; Fraile, L.M.; Fynbo, H.O.U.; Gausemel, H.; Jeppensen, H.; et al. Beta-decay properties of the neutron-rich 94-99Kr and 142-147Xe isotopes. Nucl. Phys. A 2003, 714, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Ziegert, W.; Hillebrandt, W.; Thielemann, F.-K. Determination of stellar neutron-capture rates for radioactive nuclei with the aid of beta-delayed neutron emission. Astron. Astrophys. 1983, 125, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Kratz, K.-L. Relevance of beta-delayed neutron data for reactor, nuclear physics and astrophysics applications. In Exotic Nuclei and Nuclear/Particle Astrophysics V: From Nuclei to Stars. AIP Conf. Proc. 2014, 1645, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Thielemann, F.-K.; Arnould, M.; Truran, J.W. Advances in Nuclear Physics: Proceedings of the Second IAP Workshop, Paris, France; Vangioni-Flam, E., Audouze, J., Casse, M., Chieze, J.-P., Tran Thanh Van, J., Eds.; Gif-sur-Yvette, France: Editions Frontières; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 1986; p. 525. [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher, T.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Kratz, K.-L. The nuclear level density and the determination of thermonuclear rates for astrophysics. Mem. Soc. Astron. Ital. 1996, 67, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, T.; Thielemann, F.-K.; Kratz, K.-L. Applicability of the Hauser-Feshbach approach for the determination of astrophysical reaction rates. Nucl. Phys. A 1997, 621, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, T.; Thielemann, F.-K. Astrophysical reaction rates from statistical model calculations. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2000, 75, 1–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, T.; Thielemann, F.-K. Tables of nuclear cross sections and reaction rates. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2001, 79, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhummer, H.; Staudt, G. Nuclei in the Cosmos; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Kraussmann, E.; Balogh, W.; Oberhummer, H.; Rauscher, T.; Kratz, K.-L.; Ziegert, W. Direct neutron capture for magic-shell nuclei. Phys. Rev. C 1996, 53, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauscher, T.; Bieber, R.; Oberhummer, H.; Kratz, K.-L.; Dobaczewski, J.; Möller, P.; Sharma, M.M. Dependence of direct neutron capture on nuclear-structure models. Phys. Rev. C 1998, 57, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Böhmer, W.; Freiburghaus, C.; Möller, P.; Pfeiffer, B.; Rauscher, T.; Thielemann, F.-K. On the origin of the Ca-Ti-Cr isotopic anomalies in the inclusion EK-1-4-1 of the Allende-meteorite. Mem. Della Soc. Astron. Ital. 2001, 72, 453–466. [Google Scholar]
- Nuh, F.M.; Slaughter, D.R.; Prussin, S.G.; Ohm, H.; Rudolph, W.; Kratz, K.-L. Delayed neutrons and high-energy gamma rays from decay of 87Br. Nucl. Phys. A 1977, 293, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, K.-L.; Rudolph, W.; Ohm, H.; Franz, H.; Zendel, M.; Herrmann, G.; Prussin, S.G.; Nuh, F.M.; Shihab-Elbin, A.A.; Slaughter, D.R.; et al. Investigation of beta strength functions by neutron and gamma-ray spectroscopy. Nucl. Phys. A 1979, 317, 335–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leist, B.; Ziegert, W.; Wiescher, M.; Kratz, K.-L.; Thielemann, F.-K. Neutron capture cross sections for neutron-rich isotopes. Z. Phys. 1985, 322, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewan, G.T.; Hoff, P.; Jonson, B.; Kratz, K.-L.; Larsson, P.O.; Nyman, G.; Ravn, H.L.; Ziegert, W. Intense mass-separated beams of halogens and beta-delayed neutron emission from heavy bromine isotopes. Z. Phys. 1984, 318, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Kratz, K.L. Proc. Consultants’ Meeting on Delayed Neutron Properties. Vienna, 1979. International Nuclear Data Committee, International Atomic Energy Agency (NDS)-107, 103. Available online: https://www-nds.iaea.org/publications/indc/indc-nds-0107/ (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Schröder, A.; Ohm, H.; Rudolph, W.; Sümmerer, K.; Kratz, K.-L.; Wünsch, K.D.; Jung, G.; Crançon, J.; Ristori, C. Spectroscopy of beta-delayed neutrons in coincidence with gamma-rays depopulating excited states in 93Sr. Phys. Lett. B 1980, 90, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.A.; Woosley, S.E.; William, A.; Fowler, B.A.; Zimmerman, B.A. Tables of thermonuclear-reaction-rate data for neutron-induced reactions on heavy nuclei. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1976, 18, 305–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.E.; Thomas, R.G. Fluctuations of nuclei reaction widths. Phys. Rev. 1956, 104, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohm, H.; Zendel, M.; Prussin, S.G.; Rudolph, W.; Schröder, A.; Kratz, K.-L.; Ristori, C.; Pinston, J.A.; Monnand, E.; Schussler, F.; et al. Beta-delayed neutrons and high-energy gamma-rays from decay of 137I. Z. Phys. 1980, 296, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.H.; Turner, G. Rare gases in the chondrite Renazzo. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 3263–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.S.; Anders, E.; Draine, B.T. Properties, detectability and origin of interstellar diamonds in meteorites. Nature 1987, 339, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatowicz, T.; Fraundorf, G.; Ming, T.; Anders, E.; Wopenka, B.; Zinner, E.; Fraundorf, P. Evidence for interstellar SiC in the Murray carbonaceous chondrite. Nature 1987, 330, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Anders, E. Isotopic anomalies of Ne, Xe, and C in meteorites. II. Interstellar diamond and SiC: Carriers of exotic noble gases. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Amari, S.; Anders, E.; Virag, A.; Zinner, E. Interstellar graphite in meteorites. Nature 1990, 345, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSween, H.Y., Jr.; Huss, G.R. Cosmochemistry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Amari, S.; Hoppe, P.; Zinner, E.; Lewis, R.S. Interstellar SiC with unusual isotopic compositions: Grains from a supernova? Astrophys. J. 1992, 394, L43–L46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, S.; Lewis, R.S.; Anders, W. Interstellar grains in meteorites: I. isolation of SiC, graphite, and diamond; size distributions of SiC and graphite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.M.; Pellin, M.; Lewis, R.; Amari, S.; Clayton, R. Molybdenum and Zirconium Isotopic Compositions of Supernova Grains. 62nd Annual Meteoritical Society Meeting 1999, #5202. Available online: https://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/metsoc99/pdf/5202.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Savina, M.R.; Pellin, M.J.; Tripa, C.E.; Veryovkin, I.V.; Calaway, W.F.; Davis, A.M. Analyzing individual presolar grains with CHARISMA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 3215–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allègre, C.J. Isotope Geology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lugaro, M.; Davis, A.M.; Gallino, R.; Pellin, M.J.; Straniero, O.; Käppeler, F. Isotopic compositions of strontium, zirconium, molybdenum, and barium in single presolar SiC grains and asymptotic giant branch stars. Astrophys. J. 2003, 593, 486–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisterzo, S.; Gallino, R.; Straniero, O.; Cristallo, S.; Käppeler, F. The s-process in low metallicity stars-II. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 418, 284–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlandini, C.; Käppeler, F.; Wisshak, K.; Gallino, R.; Lugaro, M.; Busso, M.; Straniero, O. Neutron capture in low-mass asymptotic giant branch stars: Cross sections and abundance signatures. Astrophys. J. 1999, 525, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, W.; Schönbächler, M.; Bisterzo, S.; Gallino, R. Zirconium isotope evidence for the heterogeneous distribution of s-process materials in the solar system. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 165, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; Piersanti, L.; Straniero, O.; Gallino, R.; Domínguez, I.; Abia, C.; Rico, G.D.; Quintini, M.; Bisterzo, S. Evolution, nucleosynthesis, and yields of low-mass asymptotic giant branch stars at different metallicities II-the fruity database. Astrophys. J. 2011, 197, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; Piersanti, L.; Straniero, O. The FRUITY database on AGB stars: Past, present and future. J. Phys. Config. Ser. 2016, 665, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatari, M.; Herwig, F.; Hirschi, R.; Bennett, M.; Rockefeller, G.; Fryer, C.; Timmes, F.X.; Ritter, C.; Heger, A.; Jones, S.; et al. Nugrid stellar data set I. stellar yields from H to Bi for stars with metallicities Z = 0.02 and Z 0.01. Astrophys. J. 2016, 225, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battino, U.; Tattersall, A.; Lederer-Woods, C.; Herwig, F.; Denissenkov, P.; Hirschi, R.; Trappitsch, R.; den Hartogh, J.W.; Pignatari, M. Nugrid stellar data set III. updated low-mass AGB models and s-process nucleosynthesis with metallicities Z = 0.01, Z = 0.02, and Z = 0.03. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisterzo, S.; Travaglio, C.; Gallino, R.; Wiescher, M.; Käppeler, F. Galactic chemical evolution and solar s-process abundances: Dependence on the 13C-pocket structure. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battino, U.; Pignatari, M.; Travaglio, C.; Lederer-Woods, C.; Denissenkov, P.; Herwig, F.; Thielemann, F.; Rauscher, T. Heavy elements nucleosynthesis on accreting white dwarfs: Building seeds for the p-process. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 497, 4981–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, T.; Dauphas, N.; Dillmann, I.; Fröhlich, C.; Fülöp, Z.; Gyürky, G. Constraining the astrophysical origin of the p-nuclei through nuclear physics and meteoritic data. Rep. Prog. Physics. 2013, 76, 066201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travaglio, C.; Rauscher, T.; Heger, A.; Pignatari, M.; West, C. Role of core-collapse supernovae in explaining solar system abundances of p nuclides. Astrophys. J. 2018, 854, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, D.; Dziczkaniec, M. Xenon from intermediate zones of supernovae. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference Proceedings, X 1979, #1943, Houston, TX, USA, 19–23 March 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, W.M.; Arnett, W.D.; Clayton, D.D.; Woosley, S.E. Nucleosynthesis of rare nuclei from seed nuclei in explosive carbon burning. Astrophys. J. 1972, 175, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.D. Origin of heavy xenon in meteoritic diamonds. Astrophys. J. 1989, 340, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.; Adams, D.C. Neutron burst production of 60Fe necessarily implies production of 182Hf. In Proceedings of the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference Proceedings, XXXVII 2006, #1403, League City, TX, USA, 13–17 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Quitté, G.; Halliday, A.N.; Meyer, B.S.; Markowski, A.; Latkoczy, C.; Günther, D. Correlated iron 60, nickel 62, and zirconium 96 in refractory inclusions and the origin of the solar system. Astrophys. J. 2007, 655, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akram, W.; Hallmann, O.; Pfeiffer, B.; Kratz, K.-L. On the Nucleosynthetic Origin of Presolar Silicon Carbide X-Grains. Universe 2022, 8, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120629
Akram W, Hallmann O, Pfeiffer B, Kratz K-L. On the Nucleosynthetic Origin of Presolar Silicon Carbide X-Grains. Universe. 2022; 8(12):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120629
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkram, Waheed, Oliver Hallmann, Bernd Pfeiffer, and Karl-Ludwig Kratz. 2022. "On the Nucleosynthetic Origin of Presolar Silicon Carbide X-Grains" Universe 8, no. 12: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120629
APA StyleAkram, W., Hallmann, O., Pfeiffer, B., & Kratz, K.-L. (2022). On the Nucleosynthetic Origin of Presolar Silicon Carbide X-Grains. Universe, 8(12), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8120629





