The Gamma-ray Window to Intergalactic Magnetism
Abstract
:| Contents | ||
| 1 | Introduction ............................................................................................................................................... | 2 |
| 2 | Intergalactic Magnetic Fields .................................................................................................................. | 3 |
| 2.1 Statistical Observables .................................................................................................................... | 4 | |
| 2.2 Origin ................................................................................................................................................ | 5 | |
| 2.2.1 Cosmological Scenarios ................................................................................................... | 5 | |
| 2.2.2 Astrophysical Scenarios .................................................................................................. | 7 | |
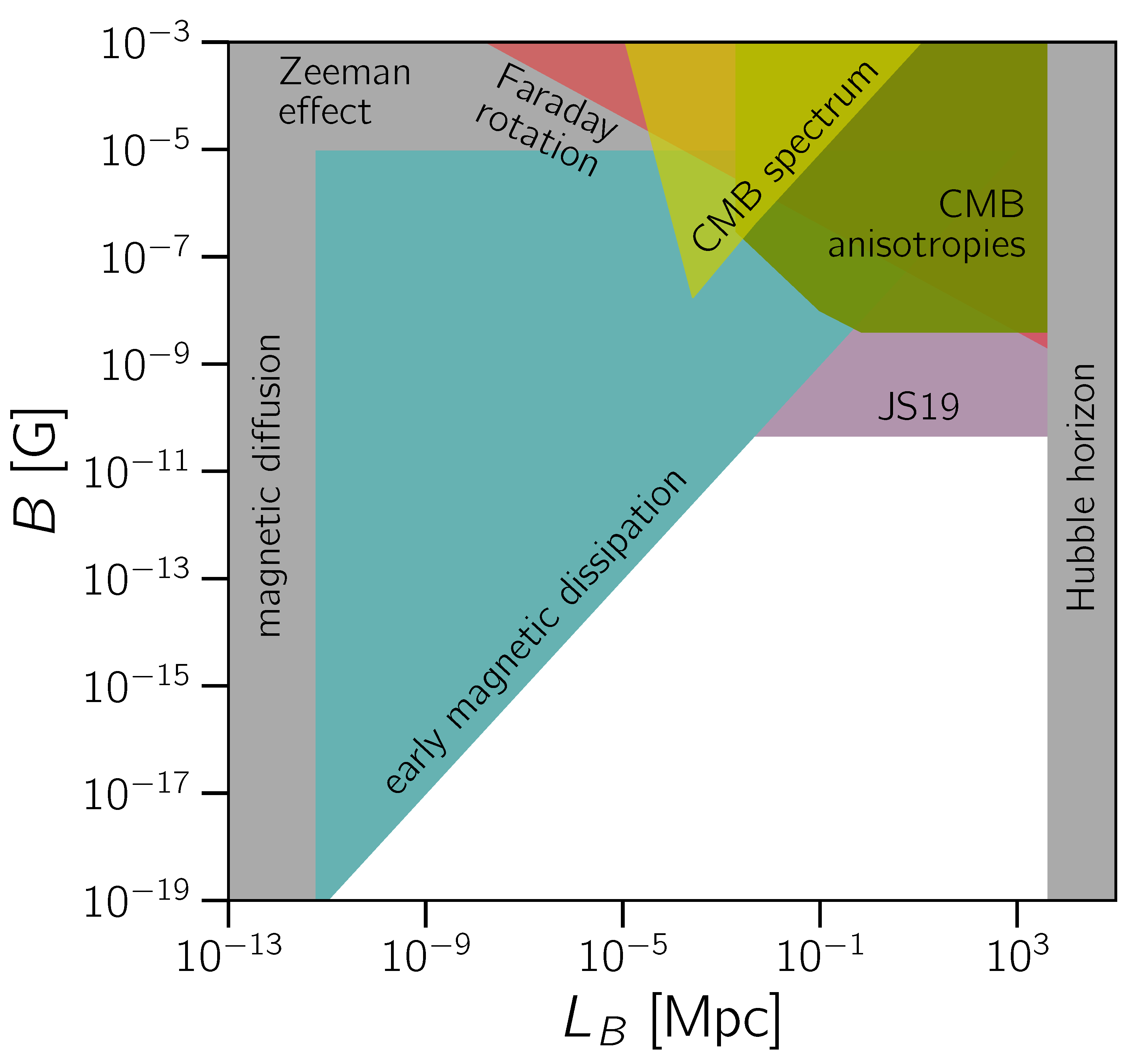
| 2.3 General Constraints ........................................................................................................................ | 8 | |
| 3 | Electromagnetic Cascades ........................................................................................................................ | 10 |
| 3.1 Origin ............................................................................................................................................... | 10 | |
| 3.2 Theory of Propagation ................................................................................................................... | 12 | |
| 3.3 Analytical Description of Propagation and Observables ........................................................... | 16 | |
| 3.4 Plasma Instabilities ......................................................................................................................... | 18 | |
| 3.5 Other Propagation Phenomena ..................................................................................................... | 19 | |
| 3.6 Propagation Codes .......................................................................................................................... | 21 | |
| 3.7 Examples .......................................................................................................................................... | 22 | |
| 4 | Results ........................................................................................................................................................ | 24 |
| 4.1 Analyses of Individual Sources ..................................................................................................... | 24 | |
| 4.2 Stacked and Diffuse Analyses ....................................................................................................... | 28 | |
| 4.3 Bounds on the Coherence Length ................................................................................................. | 29 | |
| 4.4 Constraints on the Magnetic Helicity ........................................................................................... | 29 | |
| 4.5 Constraints from UHECR-Produced Gamma Rays .................................................................... | 30 | |
| 4.6 Prospects for Measurements of IGMFs ........................................................................................ | 30 | |
| 5 | Outlook ...................................................................................................................................................... | 33 |
| References .......................................................................................................................................................... | 35 | |
1. Introduction
2. Intergalactic Magnetic Fields
2.1. Statistical Observables
2.2. Origin
2.2.1. Cosmological Scenarios
2.2.2. Astrophysical Scenarios
2.3. General Constraints
3. Electromagnetic Cascades
3.1. Origin
3.2. Theory of Propagation
- spectral effects;
- angular distribution;
- time delays.
3.3. Analytical Description of Propagation and Observables
3.4. Plasma Instabilities
3.5. Other Propagation Phenomena
3.6. Propagation Codes
3.7. Examples
4. Results
4.1. Analyses of Individual Sources
4.2. Stacked and Diffuse Analyses
4.3. Bounds on the Coherence Length
4.4. Constraints on the Magnetic Helicity
4.5. Constraints from UHECR-Produced Gamma Rays
4.6. Prospects for Measurements of IGMFs

5. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGN | active galactic nucleus |
| ALP | axion-like particle |
| AMEGO | All-sky Medium Energy Gamma-ray Observatory |
| AMON | Astrophysical Multimessenger Observatory Network |
| ARGO-YBJ | Astrophysical Radiation with Ground-based Observatory at YangBaJing |
| ASTRI | Astrofisica con Specchi a Tecnologia Replicante Italiana |
| BBN | Big Bang nucleosynthesis |
| BL Lac | BL Lacertae |
| BSM | beyoud the Standard Model |
| C.L. | confidence level |
| CMB | cosmic microwave background |
| CRB | cosmic radio background |
| CTA | Cherenkov Telescope Array |
| DGRB | diffuse gamma-ray background |
| DPP | double pair production |
| EBL | extragalactic background light |
| EGRET | Energetic Gamma-Ray Experiment Telescope |
| EWPT | electroweak phase transition |
| Fermi-LAT | Fermi Large Area Telescope |
| FoV | field of view |
| FRB | fast radio burst |
| FSRQ | flat-spectrum radio quasar |
| GRB | gamma-ray burst |
| HAWC | High Altitude Water Cherenkov Experiment |
| H.E.S.S. | High-Energy Stereoscopic System |
| IC | inverse Compton |
| IGM | intergalactic medium |
| IGMF | intergalactic magnetic field |
| ΛCDM | Lambda cold dark matter |
| LHAASO | Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory |
| LIV | Lorentz invariance violation |
| LOFAR | Low-Frequency Array |
| MAGIC | Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov |
| MHD | magnetohydrodynamics |
| PMF | primordial magnetic field |
| PP | pair production |
| PSF | point spread function |
| QCDPT | quantum chromodynamics phase transition |
| SED | spectral energy distribution |
| RM | rotation measure |
| SGSO | Southern Gamma-ray Survey Observatory |
| SKA | Square Kilometre Array |
| SM | Standard Model of particle physics |
| SWGO | Southern Wide-field Gamma-ray Observatory |
| TPP | triplet pair production |
| VERITAS | Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System |
| VHE | very-high-energy |
| UHECR | ultra-high-energy cosmic ray |
| 1 | In the following, unless noted otherwise, we refer to both electrons and positrons as “electrons”. |
| 2 | This mechanism can be viewed as cosmological, since it involves density perturbations. However, the necessary conditions for the vorticity generation involve protogalaxies, so we chose to classify it as an astrophysical magnetogenesis model. |
| 3 | There are other decay channels. For the purposes of this review, we present only the most relevant one. One example is the electronic mode () that occurs much more rarely (≲) than the main one. |
| 4 | The differential photon number density is defined in a way such that gives the local energy density of the photon field. |
References
- Hinton, J.A. The status of the HESS project. New Astron. Rev. 2004, 48, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MAGIC Collaboration. The major upgrade of the MAGIC telescopes, Part I: The hardware improvements and the commissioning of the system. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 72, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MAGIC Collaboration. The major upgrade of the MAGIC telescopes, Part II: A performance study using observations of the Crab Nebula. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 72, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weekes, T.C.; Badran, H.; Biller, S.D.; Bond, I.; Bradbury, S.; Buckley, J.; Carter-Lewis, D.; Catanese, M.; Criswell, S.; Cui, W.; et al. VERITAS: The Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System. Astropart. Phys. 2002, 17, 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VERITAS Collaboration. VERITAS: The Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System. New Astron. Rev. 2004, 48, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAWC Collaboration. Sensitivity of the High Altitude Water Cherenkov detector to sources of multi-TeV gamma rays. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 50–52, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Sciascio, G. Latest results from the ARGO-YBJ experiment. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 632, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LHAASO Collaboration. The Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) Science White Paper. arXiv 2019, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1905.02773. [Google Scholar]
- Tibet ASγ Collaboration. Underground water Cherenkov muon detector array with the Tibet air shower array for gamma-ray astronomy in the 100 TeV region. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2007, 309, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fermi-LAT Collaboration. The Large Area Telescope on the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 1071–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padovani, P.; Alexander, D.M.; Assef, R.J.; De Marco, B.; Giommi, P.; Hickox, R.C.; Richards, G.T.; Smolčić, V.; Hatziminaoglou, E.; Mainieri, V.; et al. Active galactic nuclei: What’s in a name? Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2017, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blandford, R.; Meier, D.; Readhead, A. Relativistic jets from active galactic nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 467–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Punch, M.; Akerlof, C.W.; Cawley, M.F.; Chantell, M.; Fegan, D.J.; Fennell, S.; Gaidos, J.A.; Hagan, J.; Hillas, A.M.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Detection of TeV photons from the active galaxy Markarian 421. Nature 1992, 358, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- E.S.S. Collaboration. A low level of extragalactic background light as revealed by γ-rays from blazars. Nature 2006, 440, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Very-High-Energy gamma rays from a distant quasar: How transparent is the Universe? Science 2008, 320, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. Measurement of the extragalactic background light imprint on the spectra of the brightest blazars observed with H.E.S.S. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 550, A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGIC Collaboration. MAGIC observations of the February 2014 flare of 1ES 1011+496 and ensuing constraint of the EBL density. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 590, A24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. Measurement of the EBL spectral energy distribution using the VHE γ-ray spectra of H.E.S.S. blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 606, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VERITAS Collaboration. Measurement of the extragalactic background light spectral energy distribution with VERITAS. Astrophys. J. 2019, 885, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Measurement of the extragalactic background light using MAGIC and Fermi-LAT gamma-ray observations of blazars up to z = 1. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 486, 4233–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Search for an extended VHE γ-ray emission from Mrk 421 and Mrk 501 with the MAGIC Telescope. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 524, A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. Search for extended γ-ray emission around AGN with H.E.S.S. and Fermi-LAT. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 562, A145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VERITAS Collaboration. Search for magnetically broadened cascade emission from blazars with VERITAS. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.; Nanopoulos, D.; Sakharov, A.; Sarkisyan, E. Probing Quantum Gravity using photons from a flare of the active galactic nucleus Markarian 501 Observed by the MAGIC telescope. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 668, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. Search for Lorentz Invariance breaking with a likelihood fit of the PKS 2155-304 flare data taken on MJD 53944. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 34, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. The 2014 TeV γ-ray flare of Mrk 501 seen with H.E.S.S.: Temporal and spectral constraints on Lorentz invariance violation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 870, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelley, J.V. High-energy γ-ray absorption in Space by a 3.5 °K microwave field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, R.J.; Schréder, G. Opacity of the Universe to high-energy photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillas, A.M. Cosmic rays in an evolving universe. Can. J. Phys. Suppl. 1968, 46, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.W.; Wdowczyk, J.; Wolfendale, A.W. The gamma-ray background: A consequence of metagalactic cosmic ray origin? J. Phys. A 1974, 7, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berezinsky, V.S.; Smirnov, A.Y. Cosmic neutrinos of ultra-high energies and detection possibility. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1975, 32, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonometto, S.A.; Lucchin, F. On the transparency of extragalactic space very-high-energy protons. Lett. Nuovo Cimento 1971, 2, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowczyk, J.; Tkaczyk, W.; Wolfendale, A.W. Primary cosmic γ-rays above 1012 eV. J. Phys. A 1972, 5, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protheroe, R.J. Effect of electron-photon cascading on the observed energy spectra of extragalactic sources of ultra-high-energy gamma-rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1986, 221, 769–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanenko, I.P.; Sizov, V.V. Generation of gamma-rays in electron-photon cascades-Part one-monoenergetic photon field. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1991, 182, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanenko, I.P.; Sizov, V.V. Generation of gamma-rays in electron-photon cascades-Part two-photon field of the power-law spectrum. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1991, 182, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Coppi, P.S.; Voelk, H.J. Very high energy gamma rays from active galactic nuclei: Cascading on the cosmic background radiation fields and the formation of pair halos. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1994, 423, L5–L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaga, R. Detecting intergalactic magnetic fields using time delays in pulses of gamma-rays. Nature 1995, 374, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M. A Study of the Intergalactic Magnetic Field using Extragalactic Ultra–High-Energy Gamma-Ray Sources. Astrophys. J. 1989, 339, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neronov, A.; Vovk, I. Evidence for strong extragalactic magnetic fields from Fermi observations of TeV blazars. Science 2010, 328, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G.; Foschini, L.; Bonnoli, G.; Ghirlanda, G.; Coppi, P. The intergalactic magnetic field constrained by Fermi/Large Area Telescope observations of the TeV blazar 1ES0229+200. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, L70–L74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G.; Bonnoli, G.; Foschini, L. Extreme TeV blazars and the intergalactic magnetic field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 3566–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huan, H.; Weisgarber, T.; Arlen, T.; Wakely, S.P. A new model for gamma-ray cascades in extragalactic magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 735, L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.M.; Vovk, I.; Neronov, A. Extragalactic magnetic fields constraints from simultaneous GeV-TeV observations of blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 529, A144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vovk, I.; Taylor, A.M.; Semikoz, D.; Neronov, A. Fermi/LAT observations of 1ES 0229+200: Implications for extragalactic magnetic fields and background light. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 747, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolag, K.; Kachelrieß, M.; Ostapchenko, S.; Tomas, R. Lower limit on the strength and filling factor of extragalactic magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 727, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fermi-LAT Collaboration. The Search for Spatial Extension in High-latitude Sources Detected by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 237, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finke, J.D.; Reyes, L.C.; Georganopoulos, M.; Reynolds, K.; Ajello, M.; Fegan, S.J.; McCann, K. Constraints on the intergalactic magnetic field with gamma-ray observations of blazars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 814, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiede, P.; Broderick, A.E.; Shalaby, M.; Pfrommer, C.; Puchwein, E.; Chang, P.; Lamberts, A. Constraints on the intergalactic magnetic field from bow ties in the gamma-ray sky. Astrophys. J. 2020, 892, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Saveliev, A. Multimessenger constraints on intergalactic magnetic fields from the flare of TXS 0506+056. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 902, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asseo, E.; Sol, H. Extragalactic magnetic fields. Phys. Rep. 1987, 148, 307–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, J.P. Magnetic fields in the galactic Universe, as observed in supershells, galaxies, intergalactic and cosmic realms. New Astron. Rev. 2011, 55, 91–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, F.; Orrù, E.; Bonafede, A.; Iacobelli, M.; Paladino, R.; Vazza, F.; Murgia, M.; Vacca, V.; Giovannini, G.; Feretti, L.; et al. A radio ridge connecting two galaxy clusters in a filament of the cosmic web. Science 2019, 364, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, S.P.; Brüggen, M.; Vazza, F.; Carretti, E.; Locatelli, N.T.; Stuardi, C.; Vacca, V.; Vernstrom, T.; Heald, G.; Horellou, C.; et al. New constraints on the magnetization of the cosmic web using LOFAR Faraday rotation observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, D.; Rubinstein, H.R. Magnetic fields in the early Universe. Phys. Rep. 2001, 348, 163–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widrow, L.M. Origin of galactic and extragalactic magnetic fields. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 775–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, D.; Schleicher, D.R.G.; Treumann, R.A.; Tsagas, C.G.; Widrow, L.M. Magnetic fields in the large-scale structure of the Universe. Space Sci. Rev. 2012, 166, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durrer, R.; Neronov, A. Cosmological magnetic fields: Their generation, evolution and observation. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2013, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vachaspati, T. Progress on cosmological magnetic fields. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 074901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedamzik, K.; Saveliev, A. Stringent limit on primordial magnetic fields from the cosmic microwave background radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 021301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jedamzik, K.; Pogosian, L. Relieving the Hubble tension with primordial magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 181302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, A.; Nardini, G.; Quiros, M.; Riotto, A. Magnetic fields at first order phase transition: A threat to electroweak baryogenesis. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Shankaranarayanan, S. Helical Magnetic Fields from Riemann Coupling Lead to Baryogenesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:hep-ph/2103.05339. [Google Scholar]
- Kulsrud, R.M.; Zweibel, E.G. On the origin of cosmic magnetic fields. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2008, 71, 046901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vazza, F.; Brunetti, G.; Brüggen, M.; Bonafede, A. Resolved magnetic dynamo action in the simulated intracluster medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 1672–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertone, S.; Vogt, C.; Ensslin, T. Magnetic field seeding by galactic winds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 370, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, Y.; Teyssier, R. On the onset of galactic winds in quiescent star forming galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 477, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furlanetto, S.R.; Loeb, A. Intergalactic magnetic fields from quasar outflows. Astrophys. J. 2001, 556, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.N. The generation of magnetic fields in astrophysical bodies. II. The galactic field. Astrophys. J. 1971, 163, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Ruzmaikin, A.A.; Sokoloff, D.D. Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics; The Fluid Mechanics of Astrophysics and Geophysics; Gordon and Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Dolag, K.; Bartelmann, M.; Lesch, H. Evolution and structure of magnetic fields in simulated galaxy clusters. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 387, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.A.; Field, G.B. The topological properties of magnetic helicity. J. Fluid Mech. 1984, 147, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandenburg, A.; Subramanian, K. Astrophysical magnetic fields and nonlinear dynamo theory. Phys. Rep. 2005, 417, 1–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolmogorov, A. Lokal’naya struktura turbulentnosti v neszhimayemoy vyazkoy zhidkosti pri ochen’ bol’shikh chislakh Reynol’dsa. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1941, 30, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. The local structure of turbulence in incompressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds numbers. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1968, 10, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroshnikov, P.S. Turbulence of a conducting fluid in a strong magnetic field. Sov. Astron. 1964, 7, 566. [Google Scholar]
- Kraichnan, R.H. Inertial-Range Spectrum of Hydromagnetic Turbulence. Phys. Fluids 1965, 8, 1385–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, C.S.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Munsi, D.; Isenberg, P.A.; Smith, C.W. Kolmogorov versus Iroshnikov-Kraichnan spectra: Consequences for ion heating in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. (Space Sci.) 2010, 115, A02101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treumann, R.; Baumjohann, W.; Narita, Y. Ideal MHD turbulence: The inertial range spectrum with collisionless dissipation. Front. Phys. 2015, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durrer, R.; Caprini, C. Primordial magnetic fields and causality. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saveliev, A.; Jedamzik, K.; Sigl, G. Time evolution of the large-scale tail of non-helical primordial magnetic fields with back-reaction of the turbulent medium. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 103010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahniashvili, T.; Brandenburg, A.; Tevzadze, A.G.; Ratra, B. Numerical simulations of the decay of primordial magnetic turbulence. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jedamzik, K.; Sigl, G. The evolution of the large-scale tail of primordial magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, T.; Durrer, R. Scale-invariant helical magnetic fields from Inflation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 09, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harari, D.; Mollerach, S.; Roulet, E.; Sanchez, F. Lensing of ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays in turbulent magnetic fields. J. High Energy Phys. 2002, 03, 045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandus, A.; Kunze, K.E.; Tsagas, C.G. Primordial magnetogenesis. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, J. Cosmic Inflation: Trick or treat. In Fine-Tuning in the Physical Universe; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 111–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.S.; Widrow, L.M. Inflation produced, large scale magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmjeet, K.; Pahwa, I.; Seshadri, T.R.; Subramanian, K. Cosmological magnetogenesis from extra-dimensional Gauss Bonnet gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratra, B. Cosmological ‘seed’ magnetic field from Inflation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 391, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, J.; Yokoyama, J. Generation of large-scale magnetic fields in single-field Inflation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 01, 025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, K. Magnetic fields in the early universe. Astron. Nachrichten 2010, 331, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunze, K.E. Large scale magnetic fields from gravitationally coupled electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 043526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motta, L.; Caldwell, R.R. Non-Gaussian features of primordial magnetic fields in power-law Inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 103532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.K.; Sloth, M.S. Consistency relation for cosmic magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domènech, G.; Lin, C.; Sasaki, M. Inflationary magnetogenesis with on-shell local U(1) symmetry. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 883, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Markkanen, T.; Nurmi, S.; Rasanen, S.; Vennin, V. Narrowing the window of Inflationary magnetogenesis. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 06, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, S.; Pal, S.; SenGupta, S. Inflationary Magnetogenesis and Anomaly Cancellation in Electrodynamics. arXiv 2018, arXiv:gr-qc/1810.03478. [Google Scholar]
- Bamba, K.; Elizalde, E.; Odintsov, S.D.; Paul, T. Inflationary magnetogenesis with reheating phase from higher curvature coupling. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T. Primordial magnetic fields from the post-inflationary universe. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, A.J.; Sabancilar, E.; Vachaspati, T. Leptogenesis and primordial magnetic fields. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirón-Granese, N.; Calzetta, E.; Kandus, A. Primordial Weibel Instability. arXiv 2021, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/2101.03644. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, Y. Four-dimensional simulation of the hot electroweak phase transition with the SU(2) gauge Higgs model. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 56, 3860–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, J.R.; Konstandin, T.; Riva, F. Strong electroweak phase transitions in the Standard Model with a singlet. Nucl. Phys. B 2012, 854, 592–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachaspati, T. Magnetic fields from cosmological phase transitions. Phys. Lett. B 1991, 265, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Fairbairn, M.; Lewicki, M.; Vaskonen, V.; Wickens, A. Intergalactic magnetic fields from first-order phase transitions. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fodor, Z.; Katz, S.D. Critical point of QCD at finite T and mu, lattice results for physical quark masses. J. High Energy Phys. 2004, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, Y.; Endrodi, G.; Fodor, Z.; Katz, S.D.; Szabo, K.K. The order of the quantum chromodynamics transition predicted by the Standard Model of particle physics. Nature 2006, 443, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bali, G.S.; Bruckmann, F.; Endrodi, G.; Fodor, Z.; Katz, S.D.; Krieg, S.; Schafer, A.; Szabo, K.K. The QCD phase diagram for external magnetic fields. J. High Energy Phys. 2012, 2, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, T. QCD phase transition with chiral quarks and physical quark masses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 82001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.J.; Stuke, M. Lepton asymmetry and the cosmic QCD transition. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quashnock, J.M.; Loeb, A.; Spergel, D.N. Magnetic field generation during the cosmological QCD phase transition. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1989, 344, L49–L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.l.; Olinto, A.V. Primordial magnetic fields generated in the quark—Hadron transition. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 50, 2421–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigl, G.; Olinto, A.V.; Jedamzik, K. Primordial magnetic fields from cosmological first order phase transitions. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 55, 4582–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, R.; Jedamzik, K. Evolution of cosmic magnetic fields: From the very early Universe, to Recombination, to the present. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahniashvili, T.; Brandenburg, A.; Campanelli, L.; Ratra, B.; Tevzadze, A.G. Evolution of Inflation-generated magnetic field through phase transitions. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tevzadze, A.G.; Kisslinger, L.; Brandenburg, A.; Kahniashvili, T. Magnetic fields from QCD phase transitions. Astrophys. J. 2012, 759, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahniashvili, T.; Tevzadze, A.G.; Brandenburg, A.; Neronov, A. Evolution of primordial magnetic fields from phase transitions. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 083007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, K. The origin, evolution and signatures of primordial magnetic fields. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 76901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandenburg, A.; Kahniashvili, T.; Mandal, S.; Roper Pol, A.; Tevzadze, A.G.; Vachaspati, T. Evolution of hydromagnetic turbulence from the electroweak phase transition. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saveliev, A.; Jedamzik, K.; Sigl, G. Evolution of helical cosmic magnetic fields as predicted by magnetohydrodynamic closure theory. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandenburg, A.; Durrer, R.; Kahniashvili, T.; Mandal, S.; Yin, W.W. Statistical properties of scale-invariant helical magnetic fields and applications to cosmology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandenburg, A.; Durrer, R.; Huang, Y.; Kahniashvili, T.; Mandal, S.; Mukohyama, S. Primordial magnetic helicity evolution with a homogeneous magnetic field from Inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 23536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, A.; Kahniashvili, T.; Tevzadze, A.G. Nonhelical inverse transfer of a decaying turbulent magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 75001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vachaspati, T. Estimate of the primordial magnetic field helicity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 251302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atmjeet, K.; Seshadri, T.R.; Subramanian, K. Helical cosmological magnetic fields from extra-dimensions. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campanelli, L.; Giannotti, M. Magnetic helicity generation from the cosmic axion field. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprini, C.; Sorbo, L. Adding helicity to inflationary magnetogenesis. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kushwaha, A.; Shankaranarayanan, S. Helical magnetic fields from Riemann coupling. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtanov, Y. Viable inflationary magnetogenesis with helical coupling. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vachaspati, T.; Vilenkin, A. Cosmological chirality and magnetic fields from parity violating particle decays. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, L. Über den Ursprung der Magnetfelder auf Sternen und im interstellaren Raum (mit einem Anhang von A. Schlüter). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A 1950, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, L.; Schlüter, A. Cosmic radiation and cosmic magnetic fields. II. Origin of cosmic magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. 1951, 82, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoz, S.; Narayan, R. Generation of primordial magnetic fields on linear over-density scales. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 51303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulsrud, R.M.; Cen, R.; Ostriker, J.P.; Ryu, D. The protogalactic origin for cosmic magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 1997, 480, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, G.; Widrow, L.M. A possible mechanism for generating galactic magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 2000, 540, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graziani, C.; Tzeferacos, P.; Lee, D.; Lamb, D.Q.; Weide, K.; Fatenejad, M.; Miller, J. The Biermann catastrophe in numerical magnetohydrodynamics. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnedin, N.Y.; Ferrara, A.; Zweibel, E.G. Generation of the primordial magnetic fields during cosmological Reionization. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widrow, L.M.; Ryu, D.; Schleicher, D.R.G.; Subramanian, K.; Tsagas, C.G.; Treumann, R.A. The first magnetic fields. Space Sci. Rev. 2012, 166, 37–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attia, O.; Teyssier, R.; Katz, H.; Kimm, T.; Martin-Alvarez, S.; Ocvirk, P.; Rosdahl, J. Cosmological magnetogenesis: The Biermann battery during the epoch of Reionization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 504, 2346–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arieli, Y.; Rephaeli, Y.; Norman, M.L. Dispersal of galactic magnetic fields into intracluster space. Astrophys. J. 2011, 738, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.M.; Hanasz, M.; Lesch, H.; Remus, R.S.; Stasyszyn, F.A. On the magnetic fields in voids. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, L60–L64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samui, S.; Subramanian, K.; Srianand, R. Efficient cold outflows driven by cosmic rays in high redshift galaxies and their global effects on the IGM. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 1680–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arámburo García, A.; Bondarenko, K.; Boyarsky, A.; Nelson, D.; Pillepich, A.; Sokolenko, A. Magnetization of the intergalactic medium in the IllustrisTNG simulations: The importance of extended, outflow-driven bubbles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 505, 5038–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronberg, P.P.; Dufton, Q.W.; Li, H.; Colgate, S.A. Magnetic energy of the intergalactic medium from galactic black holes. Astrophys. J. 2001, 560, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barai, P. Large-scale impact of the cosmological population of expanding radio galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 682, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barai, P.; Martel, H.; Germain, J. Anisotropic active galactic nucleus outflows and enrichment of the intergalactic medium. II. Metallicity. Astrophys. J. 2011, 727, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miniati, F.; Bell, A.R. Resistive magnetic field generation at cosmic dawn. Astrophys. J. 2011, 729, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohira, Y. Magnetic field generation by an inhomogeneous return current. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 896, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrive, J.B.; Langer, M. Intergalactic magnetogenesis at cosmic dawn by photoionization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durrive, J.B.; Tashiro, H.; Langer, M.; Sugiyama, N. Mean energy density of photogenerated magnetic fields throughout the Epoch of Reionization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langer, M.; Durrive, J.B. Magnetizing the cosmic web during Reionization. Galaxies 2018, 6, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garaldi, E.; Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Magnetogenesis around the first galaxies: The impact of different field seeding processes on galaxy formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, 5726–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, E.R. Origin of magnetic fields in the early Universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1973, 30, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishustin, I.N.; Ruzmaǐkin, A.A. Occurrence of “priming” magnetic fields during the formation of protogalaxies. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1972, 34, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Matarrese, S.; Mollerach, S.; Notari, A.; Riotto, A. Large-scale magnetic fields from density perturbations. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 043502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Ichiki, K.; Ohno, H.; Hanayama, H. Magnetic field generation from cosmological perturbations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banik, N.; Christopherson, A.J. Recombination era magnetic fields from axion dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 043003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnert, J.; Vazza, F.; Brüggen, M.; ZuHone, J. Magnetic field amplification in galaxy clusters and its simulation. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domínguez-Fernández, P.; Vazza, F.; Brüggen, M.; Brunetti, G. Dynamical evolution of magnetic fields in the intracluster medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 486, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D.V. Sensitivity of γ-ray telescopes for detection of magnetic fields in the intergalactic medium. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 123012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiles, C.; Troland, T.H. The Millennium Arecibo 21 Centimeter Absorption-Line Survey. III. Techniques for spectral polarization and results for Stokes V. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2004, 151, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfe, A.M.; Jorgenson, R.A.; Robishaw, T.; Heiles, C.; Prochaska, J.X. An 84 microGauss magnetic field in a galaxy at redshift z=0.692. Nature 2008, 455, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfe, A.M.; Jorgenson, R.A.; Robishaw, T.; Heiles, C.; Prochaska, J.X. Spectral polarization of the redshifted 21 cm absorption line toward 3C 286. Astrophys. J. 2011, 733, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kronberg, P.P.; Bernet, M.L.; Miniati, F.; Lilly, S.J.; Short, M.B.; Higdon, D.M. A global probe of cosmic magnetic fields to high redshifts. Astrophys. J. 2008, 676, 7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafede, A.; Feretti, L.; Murgia, M.; Govoni, F.; Giovannini, G.; Dallacasa, D.; Dolag, K.; Taylor, G.B. The Coma cluster magnetic field from Faraday rotation measures. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 513, A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D.; Banafsheh, M. Magnetic Fields in the Large Scale Structure from Faraday Rotation Measurements. arXiv 2013, arXiv:astro-ph.CO/1305.1450. [Google Scholar]
- Akahori, T.; Kumazaki, K.; Takahashi, K.; Ryu, D. Exploring the intergalactic magnetic field by means of Faraday tomography. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jap. 2014, 66, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Han, J.L. Redshift evolution of extragalactic rotation measures. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 3329–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pshirkov, M.S.; Tinyakov, P.G.; Urban, F.R. New limits on extragalactic magnetic fields from rotation measures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 191302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaral, A.D.; Vernstrom, T.; Gaensler, B.M. Constraints on large-scale magnetic fields in the intergalactic medium using cross-correlation methods. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 503, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, J.; Ensslin, T.A.; Miniati, F.; Stalin, C.S.; Singh, M.; Raychaudhury, S.; Humeshkar, N.B. Evidence for shock acceleration and intergalactic magnetic fields in a large scale filament of galaxies ZwC1 2341.1+0000. New Astron. 2002, 7, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gennaro, G. Fast magnetic field amplification in distant galaxy clusters. Nature Astron. 2021, 5, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackstein, S.; Brüggen, M.; Vazza, F.; Gaensler, B.M.; Heesen, V. Fast radio burst dispersion measures and rotation measures and the origin of intergalactic magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 4220–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akahori, T.; Ryu, D.; Gaensler, B.M. Fast Radio Bursts as Probes of Magnetic Fields in the Intergalactic Medium. Astrophys. J. 2016, 824, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazza, F.; Brüggen, M.; Hinz, P.M.; Wittor, D.; Locatelli, N.; Gheller, C. Probing the origin of extragalactic magnetic fields with Fast Radio Bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 3907–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Novikov, I.D. Relativistic Astrophysics, Vol. 2: The Structure and Evolution of the Universe; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, J.D.; Ferreira, P.G.; Silk, J. Constraints on a primordial magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 3610–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planck Collaboration. Planck 2013 results. XVI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 571, A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jedamzik, K.; Katalinic, V.; Olinto, A.V. A limit on primordial small scale magnetic fields from CMB distortions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprini, C.; Durrer, R.; Kahniashvili, T. The cosmic microwave background and helical magnetic fields: The tensor mode. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 63006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahniashvili, T.; Ratra, B. Effects of cosmological magnetic helicity on the cosmic microwave background. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hortúa, H.J.; Castañeda, L. Reduced bispectrum seeded by helical primordial magnetic fields. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachen, J.; Biermann, P.L. Ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays from Fanaroff Riley class II radio galaxies. AIP Conf. Proc. 1992, 264, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachen, J.P.; Biermann, P.L. Extragalactic ultra-high energy cosmic rays. I. Contribution from hot spots in FR-II radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 272, 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kronberg, P.P. Extragalactic magnetic fields. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1994, 57, 325–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Olinto, A.V.; Sigl, G. Extragalactic Magnetic Field and the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1995, 455, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M.; Sigl, G.; Olinto, A.V.; Schramm, D.N. Ultra–high-Energy Cosmic-Ray Sources and Large-Scale Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1997, 486, L115–L118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yüksel, H.; Stanev, T.; Kistler, M.D.; Kronberg, P.P. The Centaurus A Ultrahigh-energy Cosmic-Ray Excess and the Local Extragalactic Magnetic Field. Astrophys. J. 2012, 758, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bray, J.D.; Scaife, A.M.M. An upper limit on the strength of the extragalactic magnetic field from ultra-high-energy cosmic-ray anisotropy. Astrophys. J. 2018, 861, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Vliet, A.; Palladino, A.; Taylor, A.; Winter, W. Extragalactic Magnetic Field Constraints from Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays from Local Galaxies. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.05732. [Google Scholar]
- Kahniashvili, T.; Vachaspati, T. On the detection of magnetic helicity. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 63507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Saveliev, A. On the measurement of the helicity of intergalactic magnetic fields using ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Biteau, J.; Bustamante, M.; Dolag, K.; Engel, R.; Fang, K.; Kampert, K.H.; Kostunin, D.; Mostafa, M.; Murase, K.; et al. Open questions in cosmic-ray research at ultrahigh energies. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2019, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolag, K.; Grasso, D.; Springel, V.; Tkachev, I. Constrained simulations of the magnetic field in the local Universe and the propagation of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2005, 2005, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Shin, M.S.; Devriendt, J.; Semikoz, D.; Sigl, G. Implications of strong intergalactic magnetic fields for ultrahigh-energy cosmic-ray astronomy. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 023010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hackstein, S.; Vazza, F.; Brüggen, M.; Sorce, J.G.; Gottlöber, S. Simulations of ultra-high energy cosmic rays in the local Universe and the origin of cosmic magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 2519–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aramburo Garcia, A.; Bondarenko, K.; Boyarsky, A.; Nelson, D.; Pillepich, A.; Sokolenko, A. Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays Deflection by the Intergalactic Magnetic Field. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.07207. [Google Scholar]
- Urry, C.M.; Padovani, P. Unified schemes for radio-loud active galactic nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1995, 107, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnoli, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G.; Sbarrato, T. An emerging population of BL Lacs with extreme properties: Towards a class of EBL and cosmic magnetic field probes? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 451, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; De Almeida, U.B.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Behera, B.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; et al. New constraints on the mid-IR EBL from the HESS discovery of VHE γ-rays from 1ES 0229+200. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 475, L9–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; De Almeida, U.B.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Behera, B.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; et al. Discovery of VHE γ-rays from the distant BL Lacertae 1ES 0347-121. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 473, L25–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramowski, A.; Acero, F.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Anton, G.; Balzer, A.; Barnacka, A.; de Almeida, U.B.; Becherini, Y.; Becker, J.; et al. Discovery of hard-spectrum γ-ray emission from the BL Lacertae object 1ES 0414+009. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; Borrel, V.; et al. Detection of VHE gamma-ray emission from the distant blazar 1ES 1101-232 with HESS and broadband characterisation. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 470, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VERITAS Collaboration. VERITAS Observations of the BL Lac Object 1ES 1218+304. Astrophys. J. 2009, 695, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. E.S.S. Collaboration. HESS and Fermi-LAT discovery of γ-rays from the blazar 1ES 1312-423. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 434, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. Discovery of VHE γ-ray emission and multi-wavelength observations of the BL Lacertae object 1RXS J101015.9-311909. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 542, A94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VERITAS Collaboration. Detection of the BL Lacertae object H1426+428 at TeV gamma-ray energies. Astrophys. J. 2002, 571, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; Borrel, V.; et al. Discovery of very high energy γ-ray emission from the BL Lacertae object H 2356-309 with the HESS Cherenkov telescopes. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 455, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, J.; Akerlof, C.W.; Biller, S.; Buckley, J.; Carter-Lewis, D.A.; Cawley, M.F.; Catanese, M.; Connaughton, V.; Fegan, D.J.; Finley, J.P.; et al. Detection of gamma rays with E > 300 GeV from Markarian 501. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 456, L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Detection of very high energy radiation from the BL Lacertae object PG 1553+113 with the MAGIC telescope. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2007, 654, L119–L122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. Discovery of VHE γ-rays from the BL Lacertae object PKS 0548-322. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 521, A69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Lyons, K.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Osborne, J.L.; Rayner, S.M.; Shaw, S.E.; Turver, K.E.; Wieczorek, G.J. PKS 2155-304 - a source of VHE γ-rays. Astropart. Phys. 1999, 11, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; De Almeida, U.B.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Behera, B.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Borrel, V.; et al. Discovery of VHE γ-rays from the high-frequency-peaked BL Lacertae object RGB J0152+017. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 481, L103–L107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VERITAS Collaboration. The Discovery of γ-Ray Emission from the Blazar RGB J0710+591. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 715, L49–L55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VERITAS Collaboration. Discovery of a new TeV gamma-ray source: VER J0521+211. Astrophys. J. 2013, 776, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parma, P.; Murgia, M.; de Ruiter, H.R.; Fanti, R. The lives of FR I radio galaxies. New Astron. Rev. 2002, 46, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Unraveling the complex behavior of Mrk 421 with simultaneous X-ray and VHE observations during an extreme flaring activity in 2013 April. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2020, 248, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HEGRA Collaboration. Measurement of the flux, spectrum, and variability of TeV γ-rays from Mkn 501 during a state of high activity. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 327, L5–L8. [Google Scholar]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Variable VHE gamma-ray emission from Markarian 501. Astrophys. J. 2007, 669, 862–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- HAWC Collaboration. Daily monitoring of TeV gamma-ray emission from Mrk 421, Mrk 501, and the Crab Nebula with HAWC. Astrophys. J. 2017, 841, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D.; Kachelrieß, M.; Ostapchenko, S.; Elyiv, A. Degree-scale GeV “jets” from active and dead TeV blazars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 719, L130–L133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehrels, N.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Fox, D.B. Gamma-ray bursts in the Swift era. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 567–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piron, F. Gamma-ray bursts at high and very high energies. C. R. Phys. 2016, 17, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schady, P. Gamma-ray bursts and their use as cosmic probes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Teraelectronvolt emission from the γ-ray burst GRB 190114C. Nature 2019, 575, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzhatdoev, T.A.; Podlesnyi, E.I.; Vaiman, I.A. Can we constrain the extragalactic magnetic field from very high energy observations of GRB 190114C? Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 123017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.R.; Xi, S.Q.; Liu, R.Y.; Xue, R.; Wang, X.Y. Constraints on the intergalactic magnetic field from γ-ray observations of GRB 190114C. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 083004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guetta, D.; Granot, J. High energy emission from the prompt gamma-ray burst. Astrophys. J. 2003, 585, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, K.S.; Dai, Z.G.; Lu, T. Constraining the origin of TeV photons from gamma-ray bursts with delayed MeV-GeV emission formed by interaction with cosmic infrared/microwave background photons. Astrophys. J. 2004, 604, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veres, P.; Mészáros, P. Prospects for GeV-TeV detection of short gamma-ray bursts with extended emission. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichiki, K.; Inoue, S.; Takahashi, K. Probing the nature of the weakest intergalactic magnetic fields with the high energy emission of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 2008, 682, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Murase, K.; Ichiki, K.; Inoue, S.; Nagataki, S. Detectability of pair echoes from gamma-ray bursts and intergalactic magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 2008, 687, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Inoue, S.; Ichiki, K.; Nakamura, T. Probing early cosmic magnetic fields through pair echoes from high-redshift GRBs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kardashev, N.S. Nonstationarity of spectra of young sources of nonthermal radio emission. Sov. Astron. 1962, 6, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Katarzyński, K.; Ghisellini, G.; Mastichiadis, A.; Tavecchio, F.; Maraschi, L. Stochastic particle acceleration and synchrotron self-Compton radiation in TeV blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 453, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giebels, B.; Dubus, G.; Khélifi, B. Unveiling the X-ray/TeV engine in Mkn 421. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 462, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawarz, L.; Petrosian, V. On the momentum diffusion of radiating ultrarelativistic electrons in a turbulent magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 2008, 681, 1725–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, J.H.; Bell, A.R.; Blundell, K.M. Particle acceleration in astrophysical jets. New Astron. Rev. 2020, 89, 101543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveliev, A.; Alves Batista, R. The intrinsic gamma-ray spectrum of TXS 0506+056: Intergalactic propagation effects. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 500, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uryson, A.V. Identification of sources of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays. Astron. Rep. 2001, 45, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, C.; Blasi, P.; De Marco, D. High energy gamma ray counterparts of astrophysical sources of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays. Astropart. Phys. 2005, 23, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabici, S.; Aharonian, F.A. Gamma ray signatures of ultrahigh energy cosmic ray accelerators: Electromagnetic cascade versus synchrotron radiation of secondary electrons. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2007, 309, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotera, K.; Allard, D.; Lemoine, M. Detectability of ultrahigh energy cosmic ray signatures in gamma rays. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 527, A54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlers, M.; Anchordoqui, L.A.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.C.; Halzen, F.; Sarkar, S. GZK Neutrinos after the Fermi-LAT Diffuse Photon Flux Measurement. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 34, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Kelner, S.R.; Prosekin, A.Y. Angular, spectral, and time distributions of highest energy protons and associated secondary gamma-rays and neutrinos propagating through extragalactic magnetic and radiation fields. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waxman, E.; Coppi, P. Delayed Gev-TeV photons from gamma-ray bursts producing high-energy cosmic rays. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1996, 464, L75–L78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essey, W.; Kalashev, O.E.; Kusenko, A.; Beacom, J.F. Secondary photons and neutrinos from cosmic rays produced by distant blazars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 141102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essey, W.; Kalashev, O.; Kusenko, A.; Beacom, J.F. Role of Line-of-sight Cosmic-ray Interactions in Forming the Spectra of Distant Blazars in TeV Gamma Rays and High-energy Neutrinos. Astrophys. J. 2011, 731, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takami, H.; Murase, K.; Dermer, C.D. Disentangling Hadronic and Leptonic Cascade Scenarios from the Very-high-energy Gamma-Ray Emission of Distant Hard-spectrum Blazars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 771, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essey, W.; Kusenko, A. A new interpretation of the gamma-ray observations of distant active galactic nuclei. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 33, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essey, W.; Ando, S.; Kusenko, A. Determination of intergalactic magnetic fields from gamma ray data. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 35, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlers, M.; Salvado, J. Cosmogenic gamma-rays and the composition of cosmic rays. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 085019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzhatdoev, T.A.; Khalikov, E.V.; Kircheva, A.P.; Lyukshin, A.A. Electromagnetic cascade masquerade: A way to mimic γ-axion-like particle mixing effects in blazar spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalikov, E.V.; Dzhatdoev, T.A. Observable Spectral and Angular Distributions of γ-rays from Extragalactic Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Ray Accelerators: The Case of Extreme TeV blazars. arXiv 2019, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1912.10570. [Google Scholar]
- Morejon, L.; Fedynitch, A.; Boncioli, D.; Biehl, D.; Winter, W. Improved photomeson model for interactions of cosmic ray nuclei. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anchordoqui, L.A. Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. Phys. Rep. 2019, 801, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franceschini, A.; Rodighiero, G.; Vaccari, M. Extragalactic optical-infrared background radiation, its time evolution and the cosmic photon-photon opacity. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 487, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finke, J.D.; Razzaque, S.; Dermer, C.D. Modeling the extragalactic background light from stars and dust. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Primack, J.R.; Rosario, D.J.; Prada, F.; Gilmore, R.C.; Faber, S.M.; Koo, D.C.; Somerville, R.S.; Pérez-Torres, M.A.; Pérez-González, P.; et al. Extragalactic background light inferred from AEGIS galaxy-SED-type fractions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 2556–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilmore, R.C.; Somerville, R.S.; Primack, J.R.; Domínguez, A. Semi-analytic modelling of the extragalactic background light and consequences for extragalactic gamma-ray spectra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 3189–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stecker, F.W.; Scully, S.T.; Malkan, M.A. An empirical determination of the intergalactic background light from UV to FIR wavelengths using FIR deep galaxy surveys and the gamma-ray opacity of the Universe. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Protheroe, R.J.; Biermann, P.L. A new estimate of the extragalactic radio background and implications for ultra-high-energy γ-ray propagation. Astropart. Phys. 1996, 6, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niţu, I.C.; Bevins, H.T.J.; Bray, J.D.; Scaife, A.M.M. An updated estimate of the cosmic radio background and implications for ultra-high-energy photon propagation. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 126, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fixsen, D.J.; Kogut, A.; Levin, S.; Limon, M.; Lubin, P.; Mirel, P.; Seiffert, M.; Singal, J.; Wollack, E.; Villela, T.; et al. ARCADE 2 Measurement of the Absolute Sky Brightness at 3–90 GHz. Astrophys. J. 2011, 734, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Wu, T.T. Cross Sections for Two-Pair Production at Infinite Energy. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 2, 2103–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.W.; Hunt, W.F.; Mikaelian, K.O.; Muzinich, I.J. Role of γ + γ → e+ + e− + e+ + e− in Photoproduction, Colliding Beams, and Cosmic Photon Absorption. Phys. Rev. D 1973, 8, 3083–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidov, S.V.; Kalashev, O.E. Double pair production by ultra-high-energy cosmic ray photons. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2009, 108, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruffini, R.; Vereshchagin, G.V.; Xue, S.S. Cosmic absorption of ultra high energy particles. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2016, 361, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonometto, S.A.; Marcolungo, P. Metagalactic opacity to photons of energy larger than 1017 eV. Lett. Nuovo Cimento 1972, 5, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonometto, S.A.; Lucchin, F.; Marcolungo, P. Induced Pair Production and Opacity Due to Black-body Radiation. Astron. Astrophys. 1974, 31, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Dermer, C.D.; Schlickeiser, R. Effects of triplet pair production on ultrarelativistic electrons in a soft photon field. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 252, 414. [Google Scholar]
- Mastichiadis, A.; Protheroe, R.J.; Szabo, A.P. The Effect of Triplet Production on Pair/Compton Cascades in Thermal Radiation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 266, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planck Collaboration. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caprini, C.; Gabici, S. Gamma-ray observations of blazars and the intergalactic magnetic field spectrum. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 123514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlers, M. Gamma-ray halos as a measure of intergalactic magnetic fields: A classical moment problem. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 063006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tashiro, H.; Vachaspati, T. Cosmological magnetic field correlators from blazar induced cascade. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tashiro, H.; Chen, W.; Ferrer, F.; Vachaspati, T. Search for CP violating signature of intergalactic magnetic helicity in the gamma-ray sky. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, L41–L45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, H.; Vachaspati, T. Parity-odd correlators of diffuse gamma-rays and intergalactic magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Chowdhury, B.D.; Ferrer, F.; Tashiro, H.; Vachaspati, T. Intergalactic magnetic field spectra from diffuse gamma-rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 3371–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, A.J.; Vachaspati, T. Morphology of blazar-induced gamma ray halos due to a helical intergalactic magnetic field. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vachaspati, T. Fundamental implications of intergalactic magnetic field observations. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 63505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Saveliev, A.; Sigl, G.; Vachaspati, T. Probing intergalactic magnetic fields with simulations of electromagnetic cascades. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 83005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duplessis, F.; Vachaspati, T. Probing stochastic inter-galactic magnetic fields using blazar-induced gamma ray halo morphology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Saveliev, A. Morphological properties of blazar-induced gamma-ray haloes. Proc. Sci. 2017, ICRC2017, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplund, J.; Jóhannesson, G.; Brandenburg, A. On the measurement of handedness in Fermi Large Area Telescope data. Astrophys. J. 2020, 898, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachelrieß, M.; Martinez, B.C. Searching for primordial helical magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, A.E.; Chang, P.; Pfrommer, C. The cosmological impact of luminous TeV blazars. I. Implications of plasma instabilities for the intergalactic magnetic field and extragalactic gamma-ray background. Astrophys. J. 2012, 752, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Ibscher, D.; Supsar, M. Plasma effects on fast pair beams in cosmic voids. Astrophys. J. 2012, 758, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, L.; Gnedin, N.Y. Equation of state of the photoionized intergalactic medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 292, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Krakau, S.; Supsar, M. Plasma effects on fast pair beams. II. Reactive versus kinetic instability of parallel electrostatic waves. Astrophys. J. 2013, 777, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempf, A.; Kilian, P.; Spanier, F. Energy loss in intergalactic pair beams: Particle-in-cell simulation. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 585, A132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vafin, S.; Rafighi, I.; Pohl, M.; Niemiec, J. The electrostatic instability for realistic pair distributions in blazar/EBL cascades. Astrophys. J. 2018, 857, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sironi, L.; Giannios, D. Relativistic pair beams from TeV blazars: A source of reprocessed GeV emission rather than intergalactic heating. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, P.; Broderick, A.E.; Pfrommer, C.; Puchwein, E.; Lamberts, A.; Shalaby, M. The effect of nonlinear Landau damping on ultrarelativistic beam plasma instabilities. Astrophys. J. 2014, 797, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, R.; Lyubarsky, Y. The role of resonant plasma instabilities in the evolution of blazar induced pair beams. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 503, 2215–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.; Broderick, A.E.; Chang, P.; Pfrommer, C.; Puchwein, E.; Lamberts, A. The growth of the longitudinal beam-plasma instability in the presence of an inhomogeneous background. J. Plasma Phys. 2020, 86, 535860201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miniati, F.; Elyiv, A. Relaxation of blazar induced pair beams in cosmic voids: Measurement of magnetic field in voids and thermal history of the IGM. Astrophys. J. 2013, 770, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafighi, I.; Vafin, S.; Pohl, M.; Niemiec, J. Plasma effects on relativistic pair beams from TeV blazars: PIC simulations and analytical predictions. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 607, A112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saveliev, A.; Evoli, C.; Sigl, G. The Role of Plasma Instabilities in the Propagation of Gamma-rays from Distant Blazars. arXiv 2013, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1311.6752. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, J. Impact of plasma instability on constraint of the intergalactic magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 2019, 870, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Batista, R.; Saveliev, A.; de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M. The impact of plasma instabilities on the spectra of TeV blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnacka, A.; Glicenstein, J.F.; Moudden, Y. First evidence of a gravitational lensing-induced echo in gamma rays with Fermi LAT. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 528, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, C.C.; Larsson, S.; Scargle, J.D.; Amin, M.A.; Blandford, R.D.; Bulmash, D.; Chiang, J.; Ciprini, S.; Corbet, R.H.D.; Falco, E.E.; et al. Fermi Large Area Telescope Detection of Gravitational Lens Delayed γ-Ray Flares from Blazar B0218+357. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 782, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnacka, A.; Geller, M.J.; Dell’Antonio, I.P.; Benbow, W. Resolving the High-energy Universe with Strong Gravitational Lensing: The Case of PKS 1830-211. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fermi-LAT Collaboration. Gamma-Ray Flaring Activity from the Gravitationally Lensed Blazar PKS 1830-211 Observed by Fermi LAT. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. H.E.S.S. observations of the flaring gravitationally lensed galaxy PKS 1830-211. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 486, 3886–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnacka, A.; Böttcher, M.; Sushch, I. How Gravitational Lensing Helps γ-Ray Photons Avoid γ–γ Absorption. Astrophys. J. 2014, 790, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Böttcher, M.; Thiersen, H. Gravitational light-bending prevents γγ absorption in gravitational lenses. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colladay, D.; Kostelecky, V.A. Lorentz violating extension of the standard model. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 116002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattingly, D. Modern tests of Lorentz invariance. Living Rev. Rel. 2005, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galaverni, M.; Sigl, G. Lorentz violation and ultrahigh-energy photons. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 63003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Huerta, H.; Lang, R.G.; de Souza, V. Lorentz invariance violation tests in astroparticle physics. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bietenholz, W. Cosmic rays and the search for a Lorentz invariance violation. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 145–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saveliev, A.; Maccione, L.; Sigl, G. Lorentz invariance violation and chemical composition of ultra high energy cosmic rays. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vankov, H.; Stanev, T. Lorentz invariance violation and the QED formation length. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 538, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peccei, R.D.; Quinn, H.R. CP conservation in the presence of pseudoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1977, 38, 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peccei, R.D.; Quinn, H.R. Constraints imposed by CP conservation in the presence of pseudoparticles. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 16, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffelt, G.; Stodolsky, L. Mixing of the photon with low-mass particles. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Angelis, A.; Mansutti, O.; Roncadelli, M. Axion-like particles, cosmic magnetic fields and gamma-ray astrophysics. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 659, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochmuth, K.A.; Sigl, G. Effects of axion-photon mixing on gamma-ray spectra from magnetized astrophysical sources. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Conde, M.A.; Paneque, D.; Bloom, E.; Prada, F.; Domínguez, A. Hints of the existence of axionlike particles from the gamma-ray spectra of cosmological sources. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 123511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Galanti, G.; Roncadelli, M. Transparency of the Universe to gamma-rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 3245–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrynina, A.; Kartavtsev, A.; Raffelt, G. Photon-photon dispersion of TeV gamma rays and its role for photon-ALP conversion. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 83003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Angelis, A.; Mansutti, O.; Persic, M.; Roncadelli, M. Photon propagation and the very high energy γ-ray spectra of blazars: How transparent is the Universe? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 394, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horns, D.; Meyer, M. Indications for a pair-production anomaly from the propagation of VHE gamma-rays. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, M.; Horns, D.; Raue, M. First lower limits on the photon-axion-like particle coupling from very high energy gamma-ray observations. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 035027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubtsov, G.I.; Troitsky, S.V. Breaks in gamma-ray spectra of distant blazars and transparency of the Universe. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2014, 100, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirizzi, A.; Montanino, D. Stochastic conversions of TeV photons into axion-like particles in extragalactic magnetic fields. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, M.; Montanino, D.; Conrad, J. On detecting oscillations of gamma rays into axion-like particles in turbulent and coherent magnetic fields. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montanino, D.; Vazza, F.; Mirizzi, A.; Viel, M. Enhancing the spectral hardening of cosmic TeV photons by mixing with axionlike particles in the magnetized cosmic web. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramowski, A.; Acero, F.; Aharonian, F.; Benkhali, F.A.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Angüner, E.; Anton, G.; Balenderan, S.; Balzer, A.; Barnacka, A.; et al. Constraints on axionlike particles with H.E.S.S. from the irregularity of the PKS 2155-304 energy spectrum. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fermi-LAT Collaboration. Search for Spectral Irregularities due to Photon-Axionlike-Particle Oscillations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buehler, R.; Gallardo, G.; Maier, G.; Domínguez, A.; López, M.; Meyer, M. Search for the imprint of axion-like particles in the highest-energy photons of hard γ-ray blazars. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, E.; Aoki, A.; Soda, J. Photon-axion conversion, magnetic field configuration, and polarization of photons. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 43519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redondo, J.; Ringwald, A. Light shining through walls. Contemp. Phys. 2011, 52, 211–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horns, D.; Jacholkowska, A. Gamma rays as probes of the Universe. C. R. Phys. 2016, 17, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M. Searches for Axionlike Particles Using γ–Ray Observations. In Proceedings of the 12th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs and WISPs, AXION-WIMP 2016, Jeju Island, Korea, 20–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Propagation of extragalactic high energy cosmic and γ rays. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 43004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dermer, C.D.; Cavadini, M.; Razzaque, S.; Finke, J.D.; Chiang, J.; Lott, B. Time delay of cascade radiation for TeV blazars and the measurement of the intergalactic magnetic field. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 733, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kachelrieß, M.; Ostapchenko, S.; Tomàs, R. ELMAG: A Monte Carlo simulation of electromagnetic cascades on the extragalactic background light and in magnetic fields. Comp. Phys. Commun. 2012, 183, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Dundovic, A.; Erdmann, M.; Kampert, K.H.; Kuempel, D.; Müller, G.; Sigl, G.; van Vliet, A.; Walz, D.; Winchen, T. CRPropa 3 - a public astrophysical simulation framework for propagating extraterrestrial ultra-high energy particles. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 5, 038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitoussi, T.; Belmont, R.; Malzac, J.; Marcowith, A.; Cohen-Tanugi, J.; Jean, P. Physics of cosmological cascades and observable properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 466, 3472–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blytt, M.; Kachelrieß, M.; Ostapchenko, S. ELMAG 3.01: A three-dimensional Monte Carlo simulation of electromagnetic cascades on the extragalactic background light and in magnetic fields. Comp. Phys. Commun. 2020, 252, 107163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, J.; Jokipii, J.R. Charged-particle motion in multidimensional magnetic field turbulence. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1994, 430, L137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, J.; Jokipii, J.R. The transport of cosmic rays across a turbulent magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 1999, 520, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengaud, E.; Sigl, G.; Beau, T.; Miniati, F. CRPropa: A numerical tool for the propagation of UHE cosmic rays, γ-rays and neutrinos. Astropart. Phys. 2007, 28, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kampert, K.H.; Kulbartz, J.; Maccione, L.; Nierstenhoefer, N.; Schiffer, P.; Sigl, G.; van Vliet, A.R. CRPropa 2.0-A public framework for propagating high energy nuclei, secondary gamma rays and neutrinos. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 42, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiter, C.; Kuempel, D.; Walz, D.; Erdmann, M. Production and propagation of ultra-high energy photons using CRPropa 3. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 102, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tautz, R.C.; Dosch, A. On numerical turbulence generation for test-particle simulations. Phys. Plasmas 2013, 20, 22302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlegel, L.; Frie, A.; Eichmann, B.; Reichherzer, P.; Becker Tjus, J. Interpolation of turbulent magnetic fields and its consequences on cosmic ray propagation. Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Settimo, M.; De Domenico, M. Propagation of extragalactic photons at ultra-high energy with the EleCa code. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 62, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, C. γ-cascade: A simple program to compute cosmological gamma-ray propagation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Avezac, P.; Dubus, G.; Giebels, B. Cascading on extragalactic background light. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 469, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Z.; Dai, Z.G.; Wei, D.M. Strong GeV emission accompanying TeV blazar H1426+428. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 415, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kneiske, T.M.; Dole, H. A lower-limit flux for the extragalactic background light. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 515, A19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- H.E.S.S. Collaboration. VHE γ-ray emission of PKS 2155-304: Spectral and temporal variability. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 520, A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VERITAS Collaboration. Discovery of Variability in the Very High Energy γ-Ray Emission of 1ES 1218+304 with VERITAS. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 709, L163–L167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H.E.S.S. and Fermi-LAT Collaborations. Gamma-ray blazar spectra with H.E.S.S. II mono analysis: The case of PKS 2155-304 and PG 1553+113. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 600, A89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VERITAS Collaboration. A Three-year Multi-wavelength Study of the Very-high-energy γ-Ray Blazar 1ES 0229+200. Astrophys. J. 2014, 782, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.P.; Dai, Z.G. Time delay and extended halo for constraints on the intergalactic magnetic field. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 15, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanev, T.; Franceschini, A. Constraints on the extragalactic infrared background from gamma-ray observations of MKN 501. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1998, 494, L159–L162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.G.; Zhang, B.; Gou, L.J.; Meszaros, P.; Waxman, E. GeV emission from TeV blazars and intergalactic magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 580, L7–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Fang, J.; Lin, G.F.; Zhang, L. Possible GeV Emission from TeV Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2008, 682, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D.; Taylor, A.M. Very hard gamma-ray emission from a flare of Mrk 501. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 541, A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Mori, M.; Ichiki, K.; Inoue, S. Lower bounds on intergalactic magnetic fields from simultaneously observed GeV-TeV light curves of the blazar Mrk 501. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 744, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korochkin, A.; Kalashev, O.; Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D. Sensitivity reach of gamma-ray measurements for strong cosmological magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 2021, 906, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Takahashi, K.; Inoue, S.; Ichiki, K.; Nagataki, S. Probing intergalactic magnetic fields in the GLAST era through pair echo emission from TeV blazars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 686, L67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Mori, M.; Ichiki, K.; Inoue, S.; Takami, H. Lower bounds on magnetic fields in intergalactic voids from long-term GeV-TeV light curves of the blazar Mrk 421. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 771, L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arlen, T.C.; Vassilev, V.V.; Weisgarber, T.; Wakely, S.P.; Yusef Shafi, S. Intergalactic magnetic fields and gamma-ray observations of extreme TeV blazars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 796, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veres, P.; Dermer, C.D.; Dhuga, K.S. Properties of the intergalactic magnetic field constrained by gamma-ray observations of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 2017, 847, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MAGIC Collaboration. Observation of inverse Compton emission from a long γ-ray burst. Nature 2019, 575, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyiv, A.; Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D.V. Gamma-ray induced cascades and magnetic fields in the intergalactic medium. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 023010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broderick, A.E.; Tiede, P.; Shalaby, M.; Pfrommer, C.; Puchwein, E.; Chang, P.; Lamberts, A. Bow ties in the sky I: The angular structure of inverse compton gamma-ray halos in the Fermi sky. Astrophys. J. 2016, 832, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broderick, A.E.; Tiede, P.; Chang, P.; Lamberts, A.; Pfrommer, C.; Puchwein, E.; Shalaby, M.; Werhahn, M. Missing gamma-ray halos and the need for new physics in the gamma-ray sky. Astrophys. J. 2018, 868, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ando, S.; Kusenko, A. Evidence for gamma-ray halos around active galactic nuclei and the first measurement of intergalactic magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2010, 722, L39–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neronov, A.; Semikoz, D.V.; Tinyakov, P.G.; Tkachev, I.I. No evidence for gamma-ray halos around active galactic nuclei resulting from intergalactic magnetic fields. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 526, A90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fermi-LAT Collaboration. Determination of the point-spread function for the Fermi Large Area Telescope from on-orbit data and limits on pair halos of active galactic nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2013, 765, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Buckley, J.H.; Ferrer, F. Search for GeV γ-ray pair halos around low redshift blazars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 211103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Errando, M.; Buckley, J.H.; Ferrer, F. Novel search for TeV-initiated pair cascades in the intergalactic medium. arXiv 2018, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1811.05774]. [Google Scholar]
- Prokhorov, D.A.; Moraghan, A. A search for pair haloes around active galactic nuclei through a temporal analysis of Fermi-Large Area Telescope data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiede, P.; Broderick, A.E.; Shalaby, M.; Pfrommer, C.; Puchwein, E.; Chang, P.; Lamberts, A. Bow ties in the sky. II. Searching for gamma-ray halos in the Fermi sky using anisotropy. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venters, T.M.; Pavlidou, V. Probing the intergalactic magnetic field with the anisotropy of the extragalactic gamma-ray background. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, D.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, L. Contribution from blazar cascade emission to the extragalactic gamma-ray background: What role does the extragalactic magnetic field play? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdalla, H.; Böttcher, M. EBL Inhomogeneity and Hard-Spectrum Gamma-Ray Sources. Astrophys. J. 2017, 835, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neronov, A.; Taylor, A.M.; Tchernin, C.; Vovk, I. Measuring the correlation length of intergalactic magnetic fields from observations of gamma-ray induced cascades. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 554, A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IceCube Collaboration. Neutrino emission from the direction of the blazar TXS 0506+056 prior to the IceCube-170922A alert. Science 2018, 361, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aartsen, M.G.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J. Multimessenger observations of a flaring blazar coincident with high-energy neutrino IceCube-170922A. Science 2018, 361, eaat1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prosekin, A.; Essey, W.; Kusenko, A.; Aharonian, F. Time structure of gamma-ray signals generated in line-of-sight interactions of cosmic rays from distant blazars. Astrophys. J. 2012, 757, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murase, K.; Dermer, C.D.; Takami, H.; Migliori, G. Blazars as Ultra-high-energy Cosmic-ray Sources: Implications for TeV Gamma-Ray Observations. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, F.; Murase, K.; Kotera, K. Synchrotron pair halo and echo emission from blazars in the cosmic web: Application to extreme TeV blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 568, A110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Q.; Zheng, Y.G.; Yang, C.Y. Two components model for TeV gamma-ray emission from extreme high-energy BL Lac objects. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2021, 366, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Batista, R.; Boncioli, D.; di Matteo, A.; van Vliet, A.; Walz, D. Effects of uncertainties in simulations of extragalactic UHECR propagation, using CRPropa and SimProp. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 10, 063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves Batista, R.; Boncioli, D.; di Matteo, A.; van Vliet, A. Secondary neutrino and gamma-ray fluxes from SimProp and CRPropa. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 5, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CTA Consortium. Science with the Cherenkov Telescope Array; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sol, H.; Zech, A.; Boisson, C.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Biteau, J.; Contreras, J.L.; Giebels, B.; Hassan, T.; Inoue, Y.; Katarzyński, K.; et al. Active Galactic Nuclei under the scrutiny of CTA. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 43, 215–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, M.; Conrad, J.; Dickinson, H. Sensitivity of the Cherenkov Telescope Array to the Detection of Intergalactic Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaté, F.; Alves Batista, R.; Biteau, J.; Lefaucheur, J.; Mangano, S.; Meyer, M.; Piel, Q.; Pita, S.; Sanchez, D.; Vovk, I. Studying cosmological γ-ray propagation with the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Proc. Sci. 2016, ICRC2017, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández Alonso, M.; Supanitsky, A.D.; Rovero, A.C. Probing the IGMF with the next generation of Cherenkov telescopes. Astrophys. J. 2018, 869, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherenkov Telescope Array Consortium. Sensitivity of the Cherenkov Telescope Array for probing cosmology and fundamental physics with gamma-ray propagation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SWGO Collaboration. Science case for a wide field-of-view very-high-energy gamma-ray observatory in the southern hemisphere. arXiv 2019, arXiv:astro-ph.HE/1902.08429. [Google Scholar]
- e-ASTROGAM Collaboration. Science with e-ASTROGAM. A space mission for MeV-GeV gamma-ray astrophysics. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2018, 19, 1–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMEGO Collaboration. All-sky medium energy gamma-ray observatory: Exploring the extreme multimessenger Universe. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2019, 51, 245. [Google Scholar]
- Bruel, P.; Burnett, T.H.; Digel, S.W.; Johannesson, G.; Omodei, N.; Wood, M. Fermi-Lat Improv. Pass8 Event Sel. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N. Performance of the VERITAS experiment. Proc. Sci. 2016, ICRC2015, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holler, M.; Berge, D.; van Eldik, C.; Lenain, J.P.; Marandon, V.; Murach, T.; de Naurois, M.; Parsons, R.D.; Prokoph, H.; Zaborov, D. Observations of the Crab Nebula with H.E.S.S. Phase II. Proc. Sci. 2016, ICRC2015, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAWC Collaboration. Observation of the Crab Nebula with the HAWC Gamma-Ray Observatory. Astrophys. J. 2017, 843, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasche, J.; Wandelt, B.D. Bayesian physical reconstruction of initial conditions from large-scale structure surveys. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 894–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala Solares, H.A.; Coutu, S.; Cowen, D.F.; DeLaunay, J.J.; Fox, D.B.; Keivani, A.; Mostafá, M.; Murase, K.; Oikonomou, F.; Seglar-Arroyo, M.; et al. The Astrophysical Multimessenger Observatory Network (AMON): Performance and science program. Astropart. Phys. 2020, 114, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaensler, B.M.; Beck, R.; Feretti, L. The origin and evolution of cosmic magnetism. New Astron. Rev. 2004, 48, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SKA Magnetism Science Working Group. Magnetism science with the Square Kilometre Array. Galaxies 2020, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, V.; Oppermann, N.; Ensslin, T.A.; Selig, M.; Junklewitz, H.; Greiner, M.; Jasche, J.; Hales, C.A.; Reneicke, M.; Carretti, E.; et al. Statistical methods for the analysis of rotation measure grids in large scale structures in the SKA era. Proc. Sci. 2015, AASKA14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
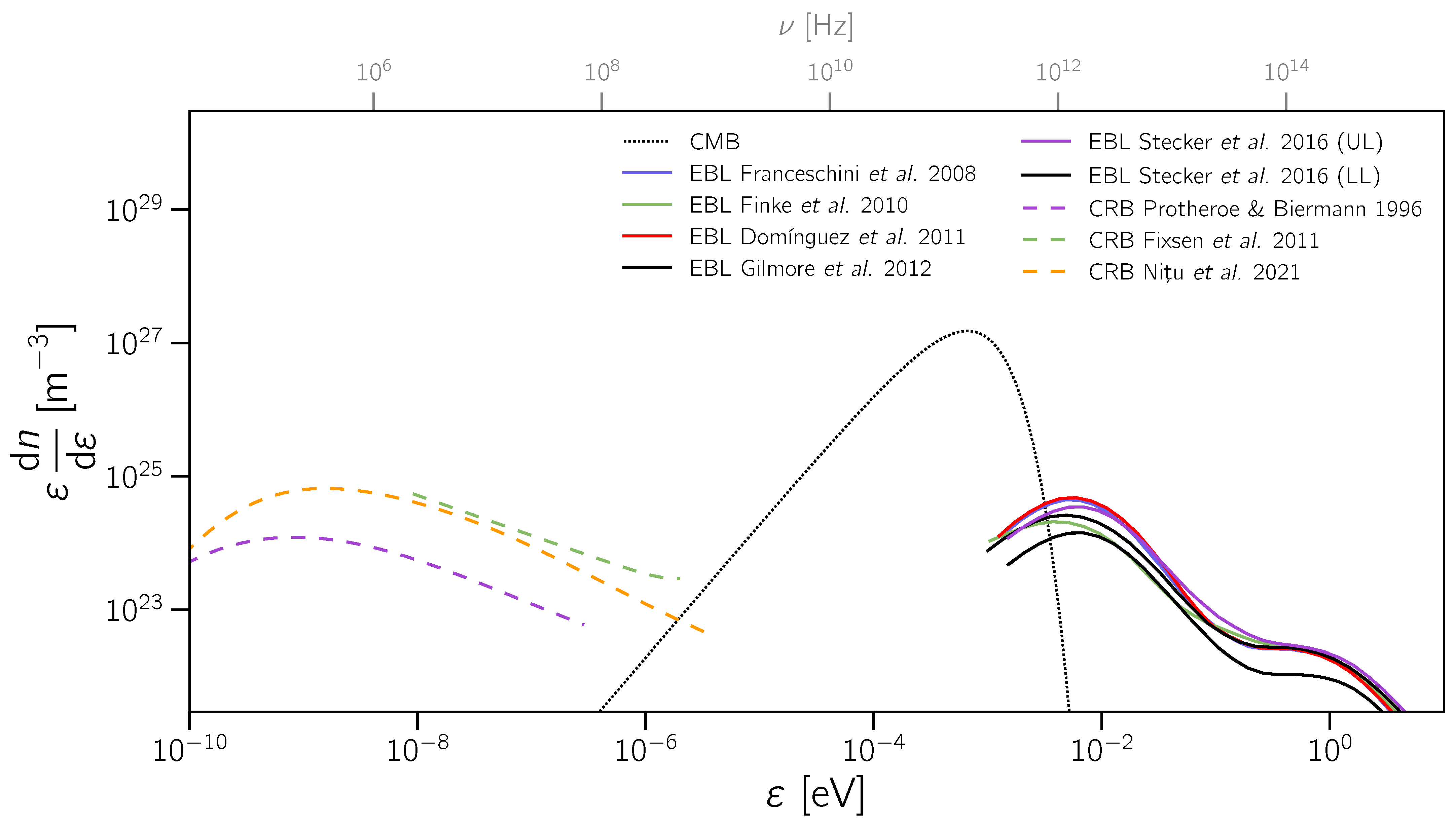



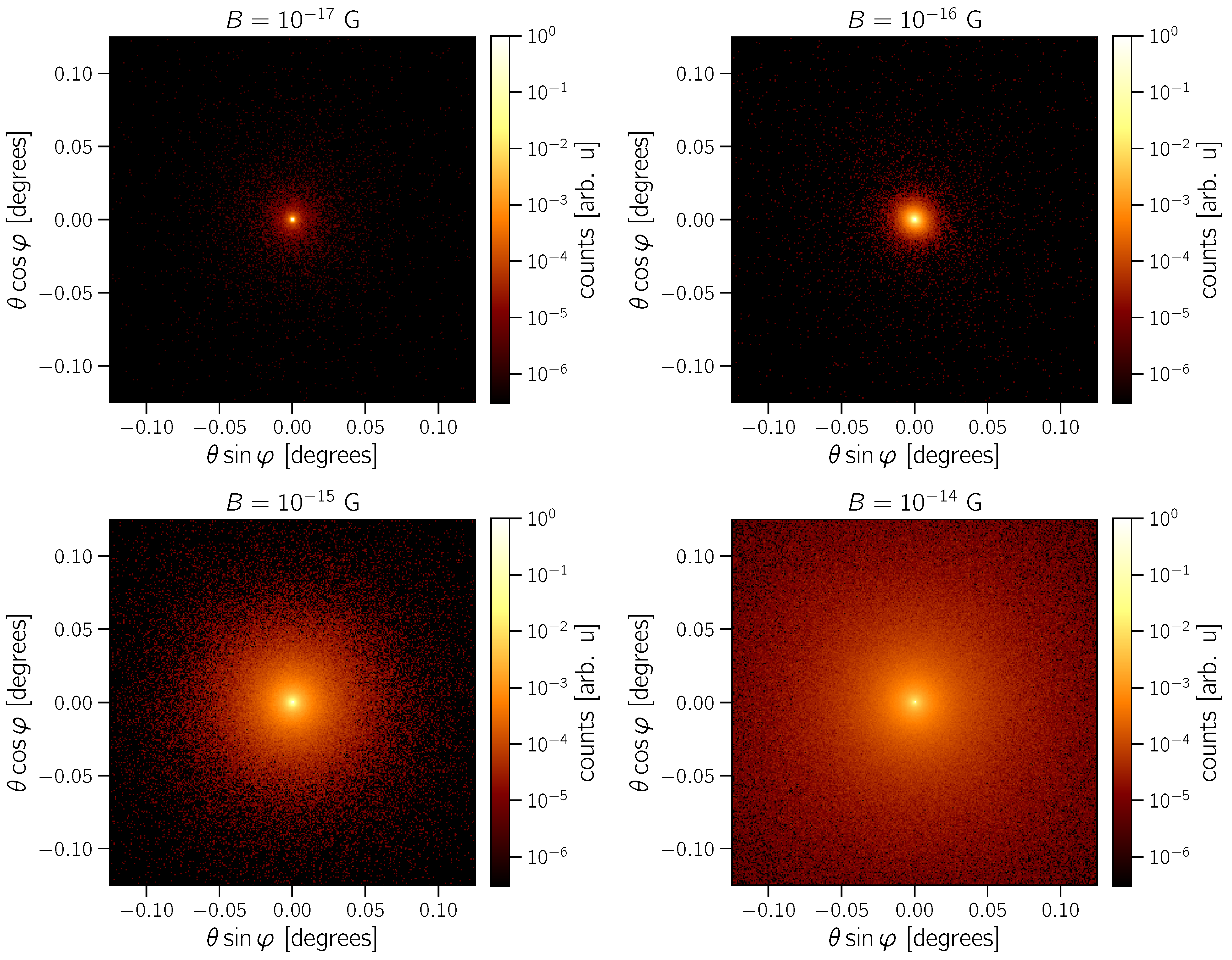



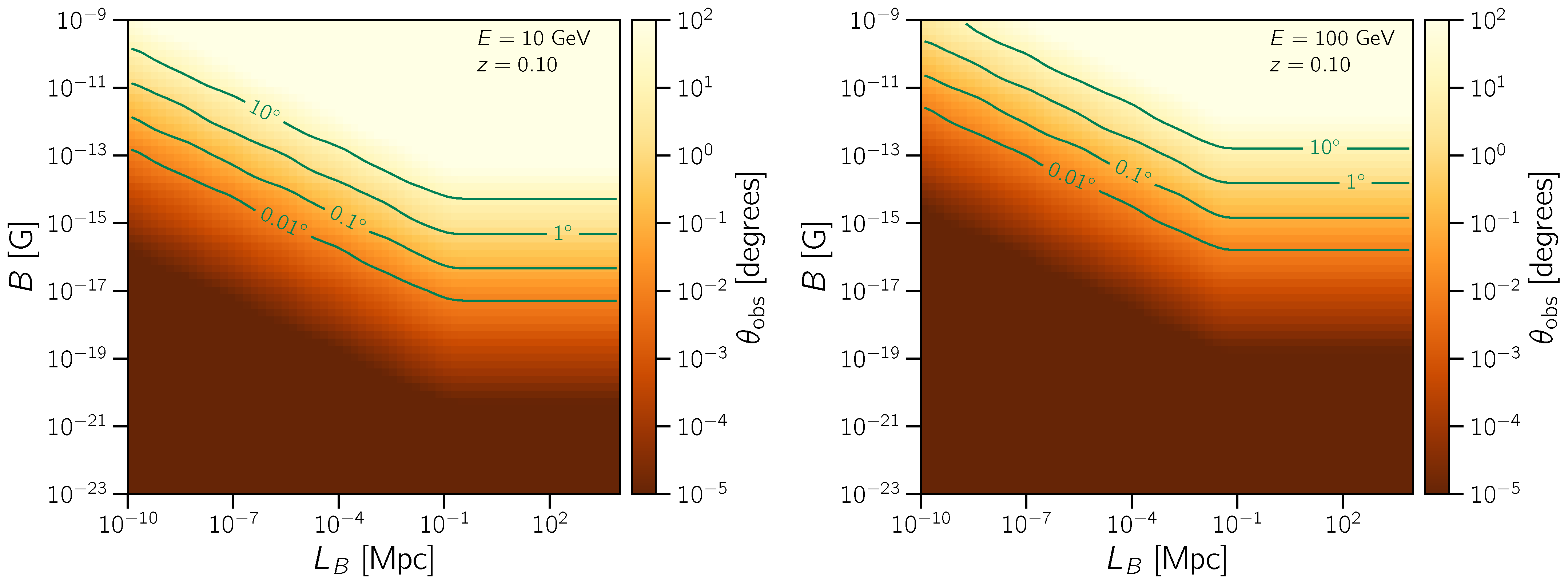
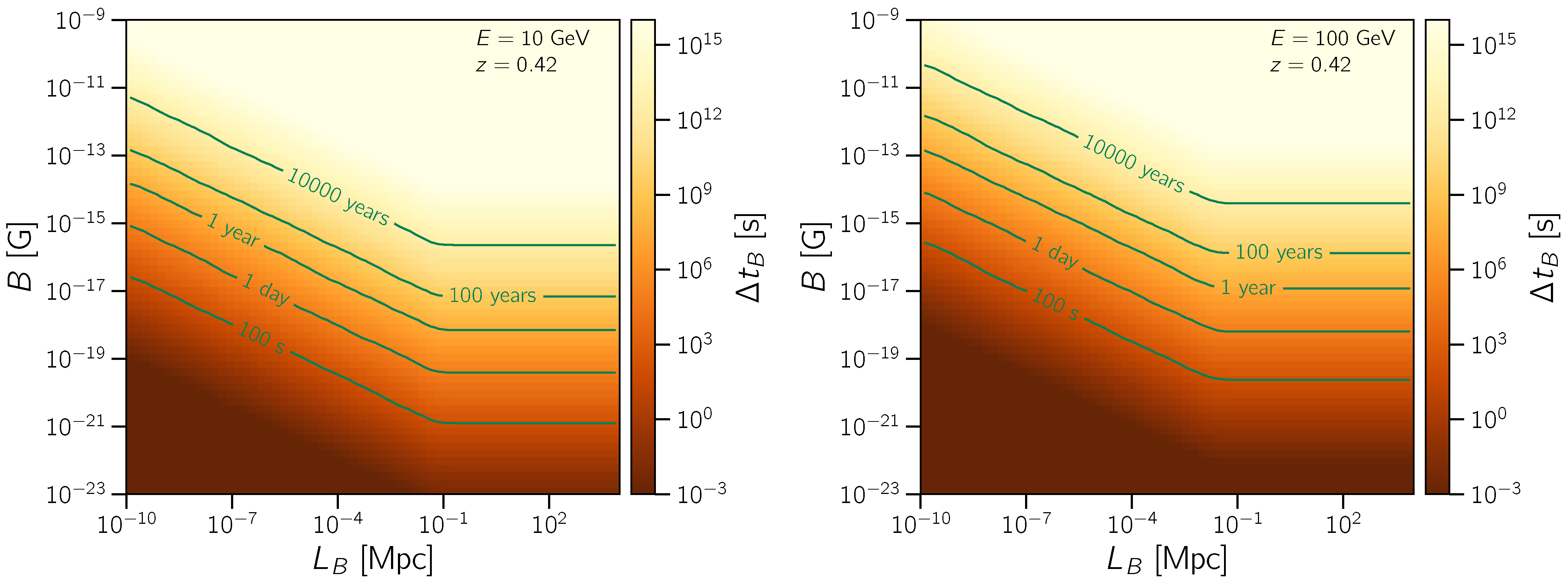
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves Batista, R.; Saveliev, A. The Gamma-ray Window to Intergalactic Magnetism. Universe 2021, 7, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7070223
Alves Batista R, Saveliev A. The Gamma-ray Window to Intergalactic Magnetism. Universe. 2021; 7(7):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7070223
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves Batista, Rafael, and Andrey Saveliev. 2021. "The Gamma-ray Window to Intergalactic Magnetism" Universe 7, no. 7: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7070223
APA StyleAlves Batista, R., & Saveliev, A. (2021). The Gamma-ray Window to Intergalactic Magnetism. Universe, 7(7), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7070223





