Photon–Photon Interactions and the Opacity of the Universe in Gamma Rays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Photon–Photon Interaction in the Astrophysical Context: Brief Historical Account
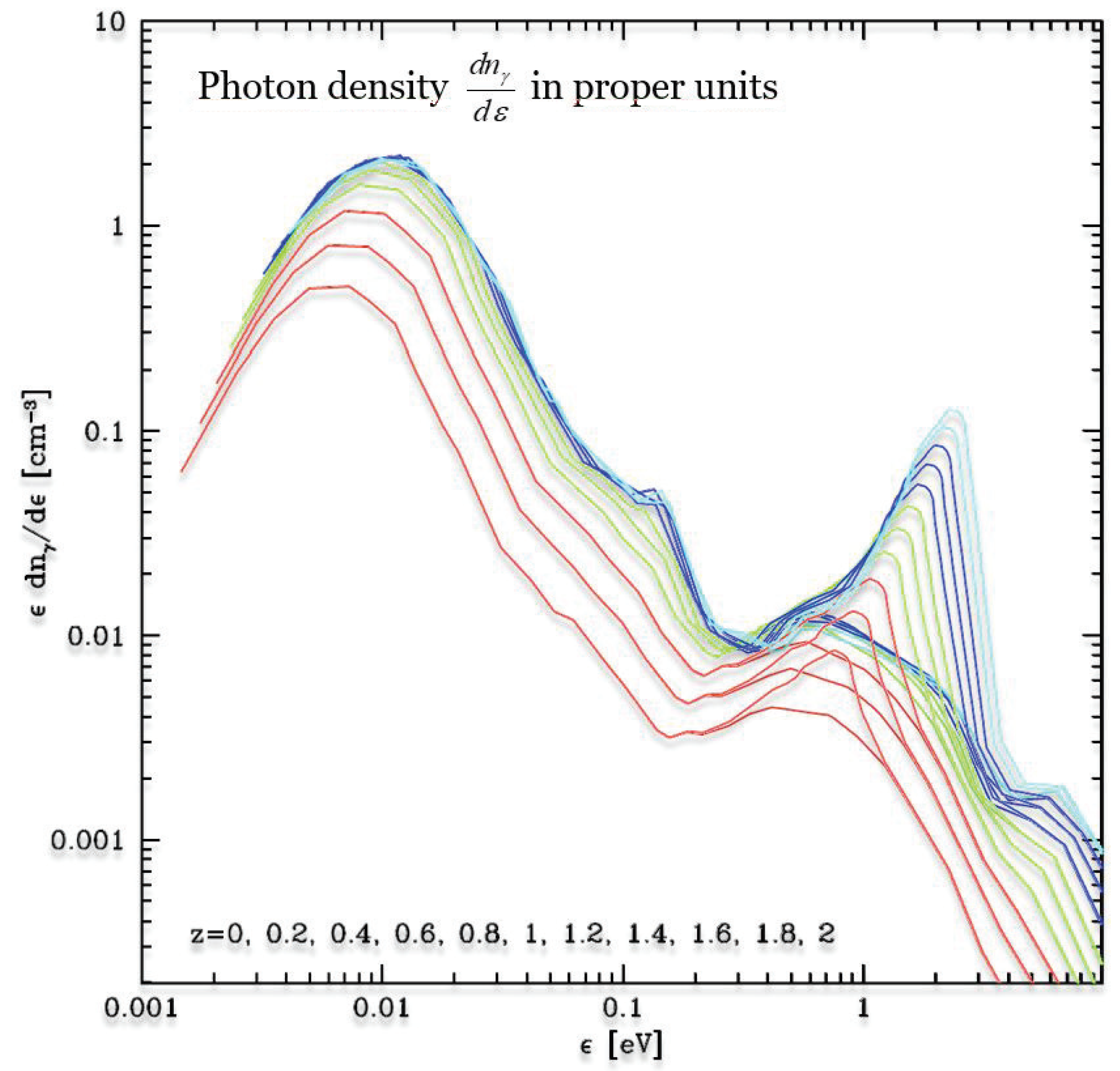
3. The Low-Energy Extragalactic Background Radiation (EBL)
3.1. Origin and Cosmological Significance of the EBL
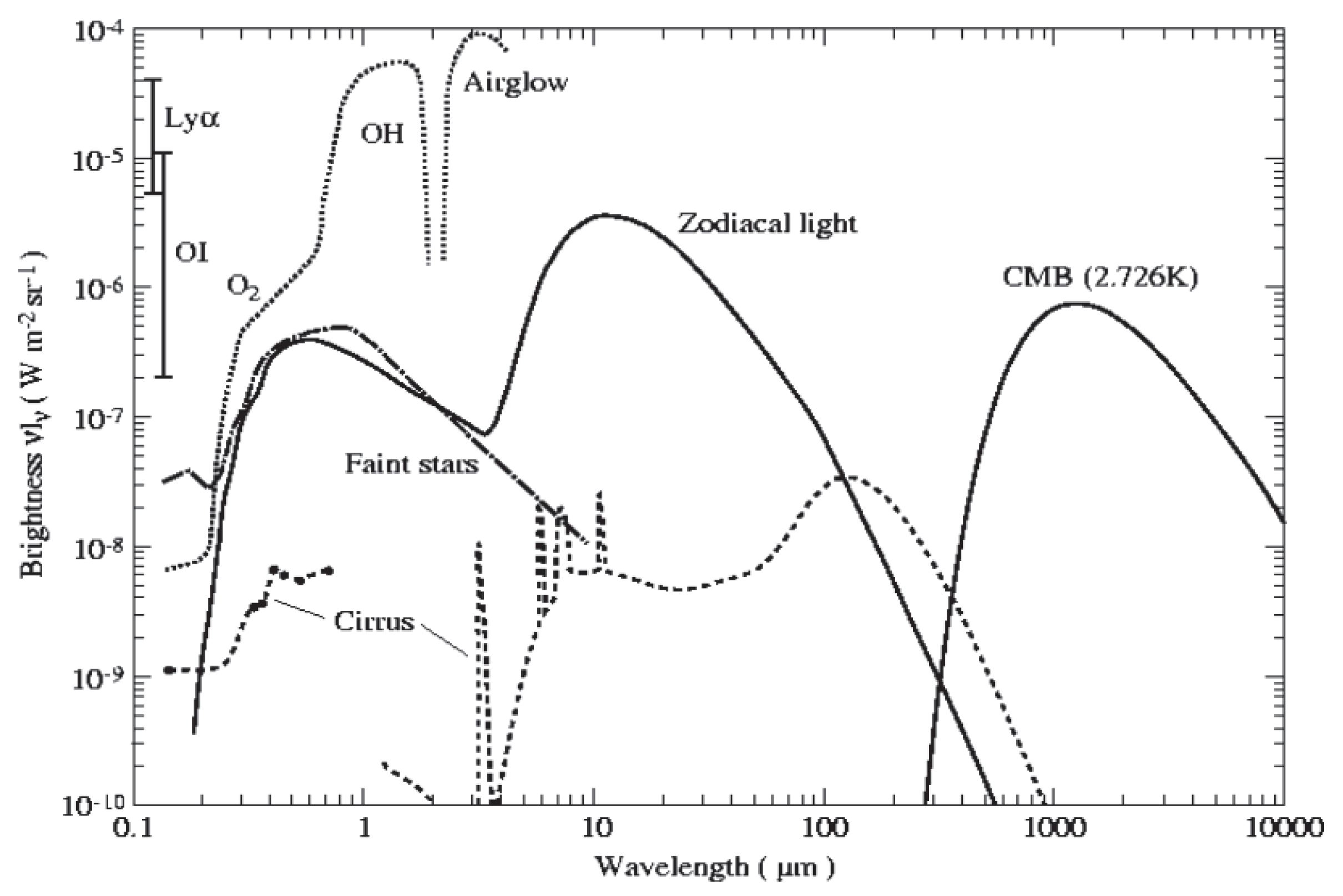
3.2. Observational Issues Related with the Background Radiations
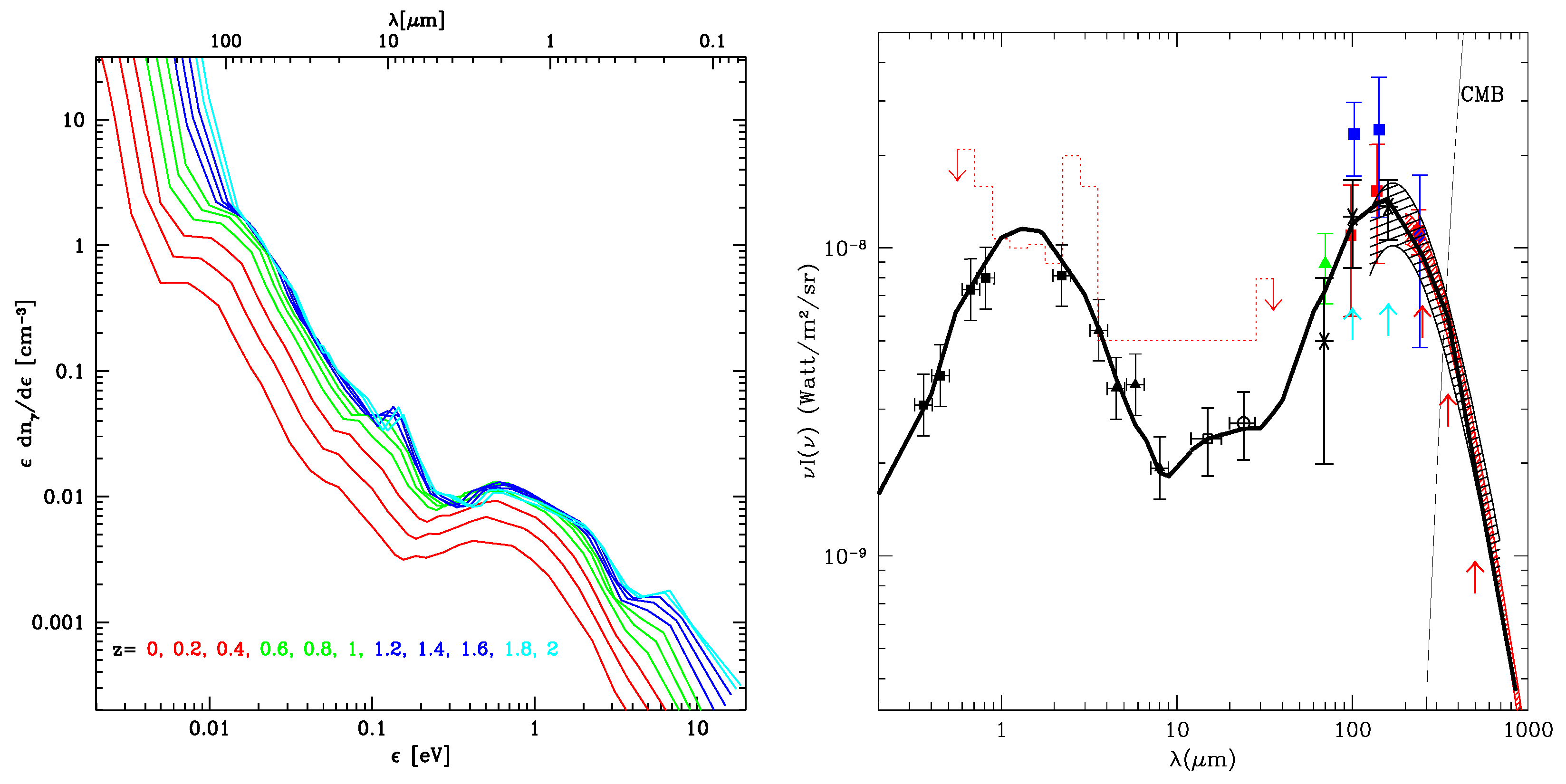
3.3. Modelling the Known-Source Contributions to the EBL
3.3.1. Empirical Models
3.3.2. Physical Models
3.3.3. Other Approaches
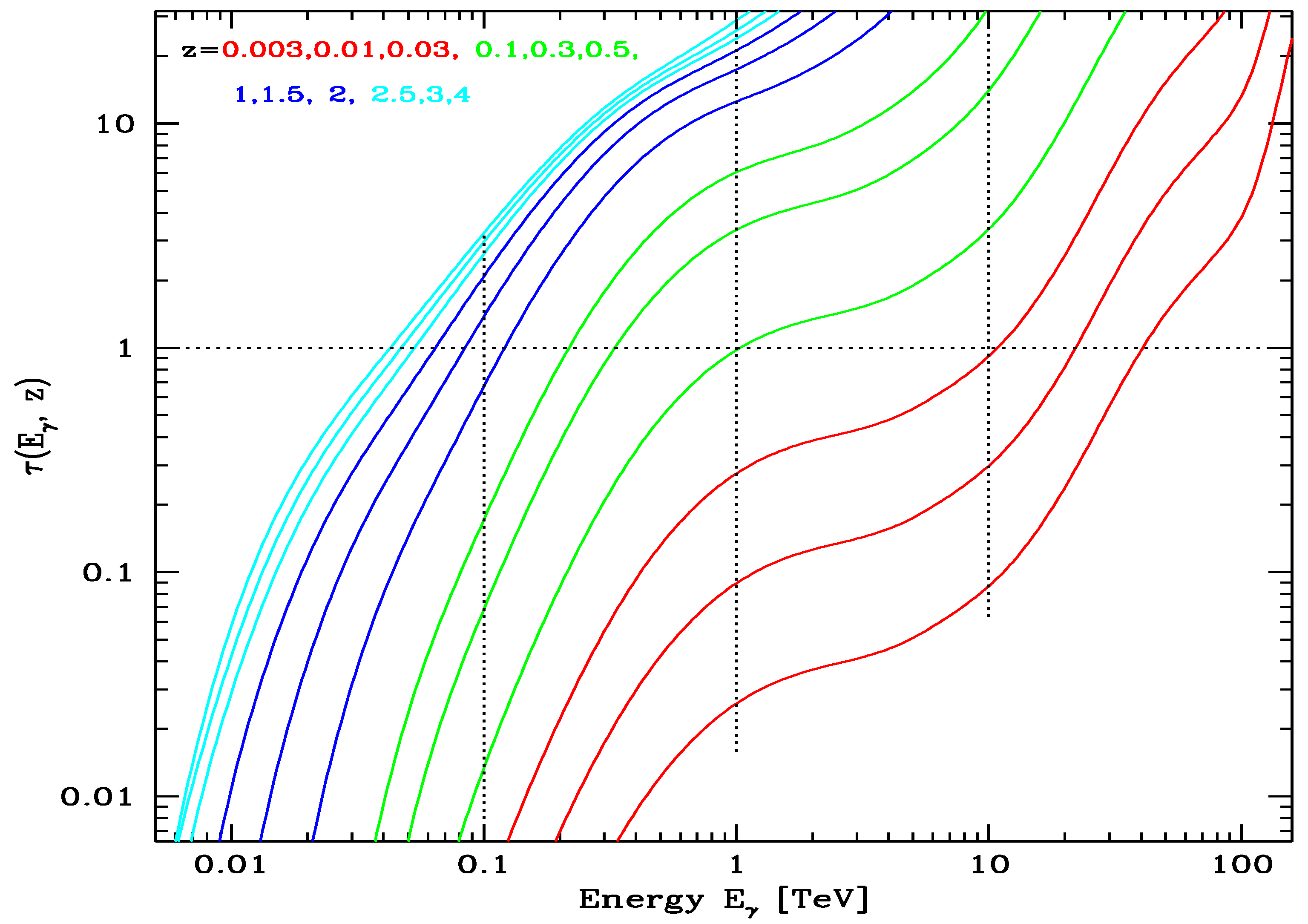
4. EBL and the Cosmological Photon–Photon Opacity
4.1. Cosmic Opacity due to Known Sources
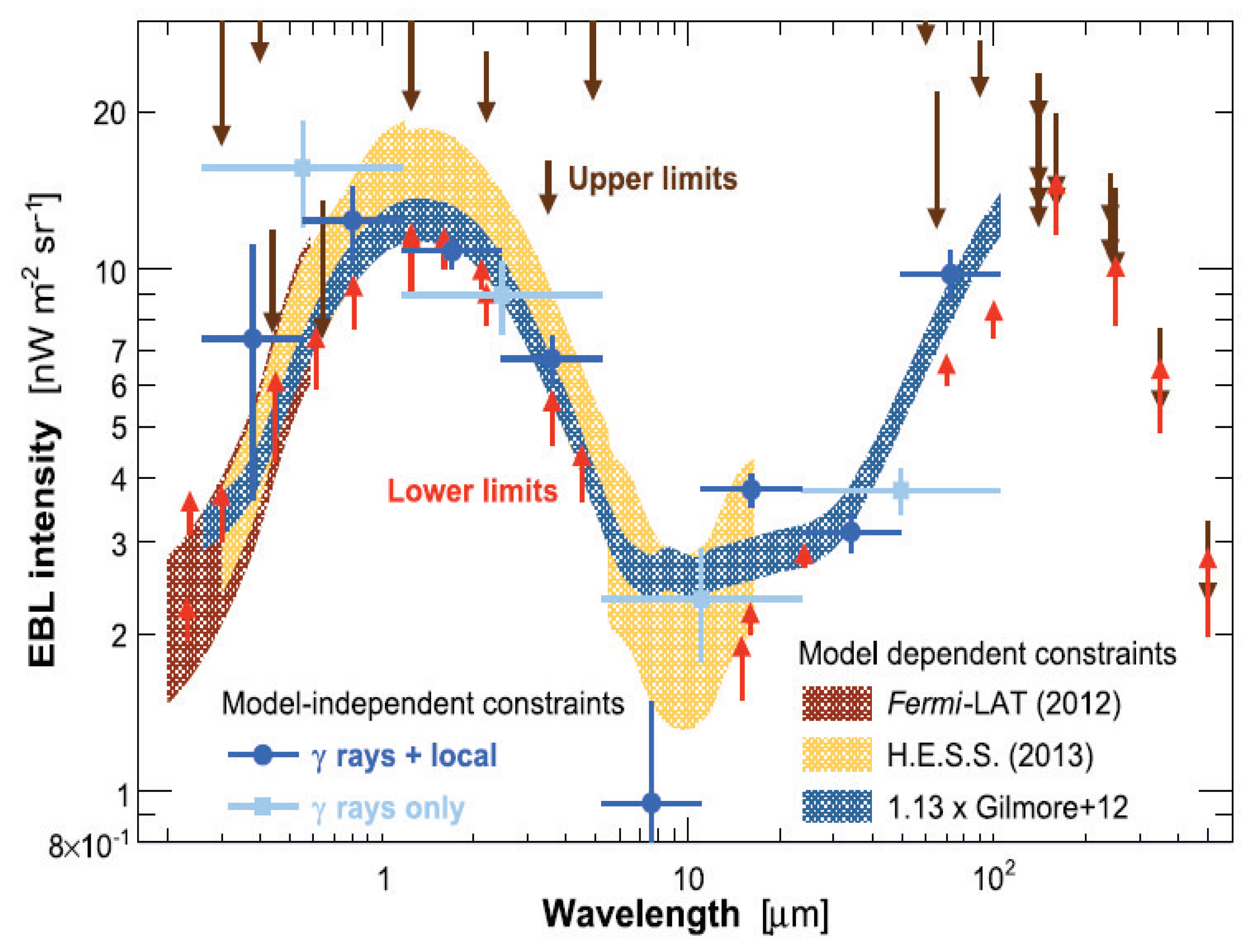
4.2. Constraining the Near-IR EBL (NIR-EBL)
4.3. Constraining the UV-Optical EBL (UV-EBL)
4.4. Constraining the Far-IR EBL (FIR-EBL)
5. Discussion
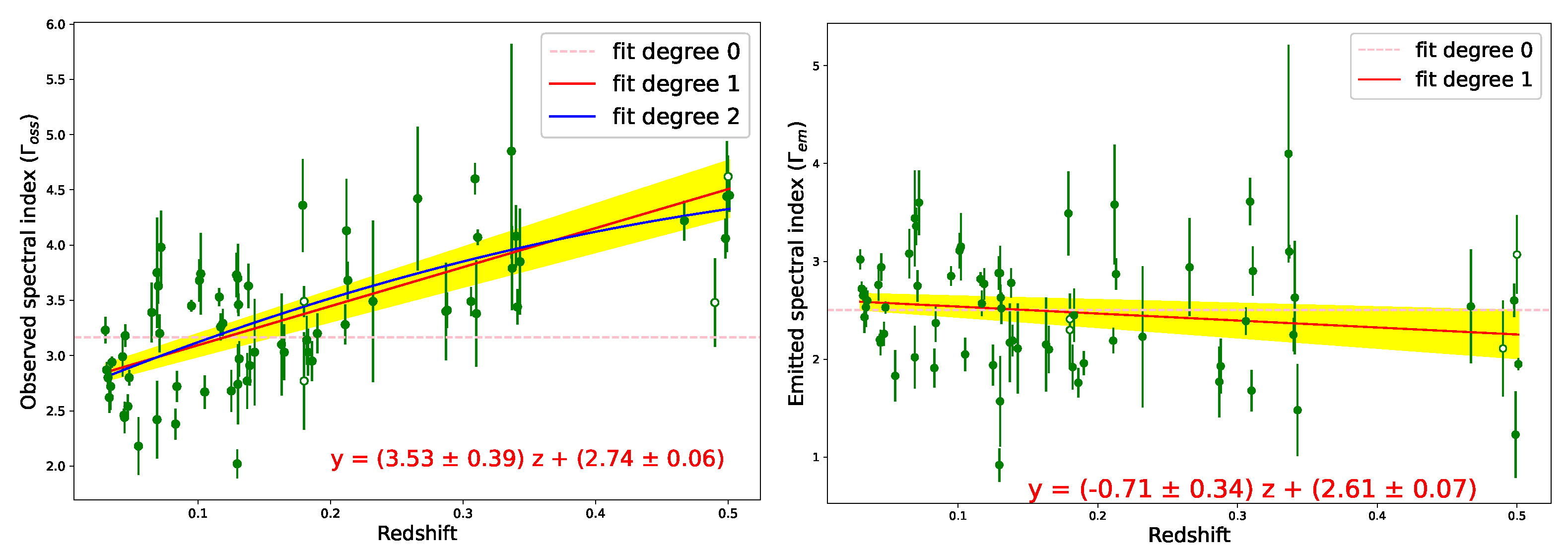
5.1. Some (Resolved?) Controversy
5.2. The Present Understanding: Constraints on Astrophysics and Cosmology
5.2.1. The History of Star-Formation
5.2.2. Potential Constraints on Primeval Re-Ionization Sources
5.3. Constraints on New Physics: Lorentz Invariance Violations and Photon to Axion-Like Particle Mixing
5.4. Other Open Questions and Prospects for Astrophysics and Cosmology
5.4.1. Jet Astrophysics
5.4.2. Cosmology
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stiavelli, M.S. From First Light to Reionization: The End of the Dark Ages; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nikishov, A.I. Absorption of High-Energy Photons in the Universe. JETP 1962, 14, 393. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, R.J.; Schréder, G. Opacity of the Universe to High-Energy Photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitler, W. The Quantum Theory of Radiation; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Coppi, P.S.; Voelk, H.J. Very High Energy Gamma Rays from Active Galactic Nuclei: Cascading on the Cosmic Background Radiation Fields and the Formation of Pair Halos. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1994, 423, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G.; Bonnoli, G.; Foschini, L. Extreme TeV blazars and the intergalactic magnetic field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 414, 3566–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biteau, J.; Williams, D.A. The extragalactic background light, the Hubble constant, and anomalies: Conclusions from 20 years of TeV gamma-ray observations. Astrophys. J. 2015, 812, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Wojtak, R.; Finke, J.; Ajello, M.; Helgason, K.; Prada, F.; Desai, A.; Paliya, V.; Marcotulli, L.; Hartmann, D.H. A New Measurement of the Hubble Constant and Matter Content of the Universe Using Extragalactic Background Light γ-Ray Attenuation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 885, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, O.C.; Stecker, F.W.; Salamon, M.H. Estimate of the intergalactic infrared radiation field from γ-ray observations of the galaxy Mrk421. Nature 1994, 369, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandini, E.; Bonnoli, G.; Maraschi, L.; Mariotti, M.; Tavecchio, F. Constraining blazar distances with combined Fermi and TeV data: An empirical approach. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.: Lett. 2010, 405, L76–L80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Buckley, J.; Kifune, T.; Sinnis, G. High energy astrophysics with ground-based gamma ray detectors. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2008, 71, 096901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.; Nanopoulos, D.V.; Sarkar, S. Tests of quantum gravity from observations of gamma ray bursts. Nature 1998, 1998 393, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M.; Harvey, J.A.; Kostelecký, V.A.; Lane, C.D.; Okamoto, T. Noncommutative Field Theory and Lorentz Violation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 141601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V.; Sakharov, A.S.; Sarkisyan, E.K.G. Robust limits on Lorentz violation from gamma-ray bursts. Astropart. Phys. 2006, 25, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, S. Tests of Lorentz invariance: A 2013 update. Class. Quantum Gravity 2013, 30, 133001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Piran, T. Planck-scale deformation of Lorentz symmetry as a solution to the ultrahigh energy cosmic ray and the TeV-photon paradoxes. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 036005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G. Spacetime quantum solves three experimental paradoxes. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 528, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massó, E. Axions and Their Relatives. In Axions; Kuster, M., Raffelt, G., Beltrán, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germary, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Greisen, K. End to the Cosmic-Ray Spectrum? Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 16, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, G.T.; Kuz’min, V.A. Upper Limit of the Spectrum of Cosmic Rays. JETP Lett. 1996, 4, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, G.G. Gamma Ratiation from Celestial Objects. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1967, 5, 481–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W. The Cosmic Gamma-Ray Spectrum from Secondary-Particle Production in the Metagalaxy. Astrophys. J. 1969, 157, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rieke, G.H.; Lebofsky, M.J. Infrared Emission of Extragalactic Sources. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 17, 477–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puget, J.L.; Stecker, F.W.; Bredekamp, J.H. Photonuclear interactions of ultrahigh energy cosmic rays and their astrophysical consequences. Astrophys. J. 1976, 205, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; Puget, J.L.; Fazio, G.G. The cosmic far-infrared background at high galactic latitudes. Astrophys. J. 1977, 214, L51–L55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soifer, B.T.; Neugebauer, G.; Houck, J.R. The IRAS View of the Extragalactic Sky. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1987, 25, 187–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; de Jager, O.C.; Salamon, M.H. TeV Gamma Rays from 3C 279: A Possible Probe of Origin and Intergalactic Infrared Radiation Fields. Astrophys. J. 1992, 390, L49–L52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, G.; Akerlof, C.W.; Cawley, M.F.; Fegan, D.J.; Fennell, S.; Gaidos, J.A.; Hillas, A.M.; Kerrick, A.D.; Lamb, R.C.; Lewis, D.A.; et al. The Very High Energy Photon spectrum of Markarian 421. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Cosmic Ray Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 19–30 July 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Stecker, F.W.; de Jager, O.C. New Upper Limits on Intergalactic Infrared Radiation from High-Energy Astrophysics. Astrophys J. 1993, 415, L71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMinn, D.; Primack, J.R. Probing the era of galaxy formation via TeV gamma ray absorption by the near infrared extragalactic background. Space Sci. Rev. 1996, 75, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Mazzei, P.; de Zotti, G.; Danese, L. Luminosity Evolution and Dust Effects in Distant Galaxies: Implications for the Observability of the Early Evolutionary Phases. Astrophys. J. 1994, 427, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecker, F.W.; de Jager, O.C. On the Absorption of High-Energy Gamma-Rays by Intergalactic Infrared Radiation. Astrophys. J. 1997, 476, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Barrio, J.A.; Bernloehr, K.; Beteta, J.J.G.; Bradbury, S.M.; Contreras, J.L.; Cortina, J.; Daum, A.; Deckers, T.; et al. Measurement of the flux, spectrum, and variability of TeV γ-rays from MKN 501 during a state of high activity. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 327, L5. [Google Scholar]
- Protheroe, R.J.; Meyer, H. An infrared background-TeV gamma-ray crisis? Phys. Lett. B 2000, 493, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanev, T.; Franceschini, A. Constraints on the extragalactic infrared background from gamma-ray observations of MKN 501. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1998, 494, L159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cesarsky, C.J.; Abergel, A.; Agnese, P.; Altieri, B.; Augueres, J.L.; Aussel, H.; Biviano, A.; Blommaert, J.; Bonnal, J.F.; Bortoletto, F.; et al. ISOCAM in flight. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 315, L32. [Google Scholar]
- Stecker, F.W.; de Jager, O.C. Absorption of very high energy gamma-rays by intergalactic infared radiation: A new determination. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 334, L85. [Google Scholar]
- Renault, C.; Barrau, A.; Lagache, G.; Puget, J.L. New constraints on the cosmic mid-infrared background using TeV gamma-ray astronomy. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 371, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkan, M.A.; Stecker, F.W. An Empirically Based Calculation of the Extragalactic Infrared Background. Astrophys. J. 1998, 496, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopelko, A.K.; Kirk, J.G.; Stecker, F.W.; Mastichiadis, A. Evidence for Intergalactic Absorption in the TEV Gamma-Ray Spectrum of Markarian 501. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1999, 518, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, O.C.; Stecker, F.W. Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Absorption and the Intrinsic Spectrum of Markarian 501 during the 1997 Flare. Astrophys. J. 2002, 566, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazin, D.; Raue, M. New limits on the density of the extragalactic background light in the optical to the far infrared from the spectra of all known TeV blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 471, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneiske, T.M.; Mannheim, K.; Hartmann, D.H. Implications of cosmological gamma-ray absorption. I. Evolution of the metagalactic radiation field. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 386, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; Borrel, V.; et al. A low level of extragalactic background light as revealed by γ-rays from blazars. Nature 2006, 440, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Matsuura, S.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, M.; Freund, M.; Lim, M.; Cohen, M.; Kawada, M.; Noda, M. Infrared Telescope in Space Observations of the Near-Infrared Extragalactic Background Light. Astrophys. J. 2005, 626, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Abramowski, A.; Aharonian, F.; Benkhali, F.A.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Andersson, T.; Angüner, E.O.; Arakawa, M.; Arrieta, M.; Aubert, P.; et al. Measurement of the EBL spectral energy distribution using the VHE γ-ray spectra of HESS blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 606, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Allafort, A.; Schady, P.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Blandford, R.D.; et al. The Imprint of the Extragalactic Background Light in the Gamma-Ray Spectra of Blazars. Science 2012, 338, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longair, M.S. Galaxy Formation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Madau, P.; Dickinson, M. Cosmic Star-Formation History. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 415–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Aussel, H.; Cesarsky, C.J.; Elbaz, D.; Fadda, D. A long-wavelength view on galaxy evolution from deep surveys by the Infrared Space Observatory. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 378, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magorrian, J.; Tremaine, S.; Richstone, D.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Gebhardt, K.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; et al. The Demography of Massive Dark Objects in Galaxy Centers. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heger, A.; Woosley, S.E. The Nucleosynthetic Signature of Population III. Astrophys. J. 2002, 567, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaerer, D. On the properties of massive Population III stars and metal-free stellar populations. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 382, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.J.; Bond, J.R.; Arnett, W.D. Cosmological consequences of Population III stars. Astrophys. J. 1984, 277, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, M.G.; Dwek, E. The Cosmic Infrared Background: Measurements and Implications. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 39, 249–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, K.; Väisänen, P. Extragalactic background light: Inventory of light throughout the cosmic history. Contemp. Phys. 2019, 60, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinert, C.; Bowyer, S.; Haikala, L.K.; Hanner, M.S.; Hauser, M.G.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.-C.; Mann, I.; Mattila, K.; Reach, W.T.; Schlosser, W.; et al. The 1997 reference of diffuse night sky brightness. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1998, 127, 1–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puget, J.-L.; Abergel, A.; Bernard, J.-P.; Boulanger, F.; Burton, W.B.; Desert, F.-X.; Hartmann, D. Tentative detection of a cosmic far-infrared background with COBE. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 308, L5. [Google Scholar]
- Lagache, G.; Haffner, L.M.; Reynolds, R.J.; Tufte, S.L. Evidence for dust emission in the Warm Ionised Medium using WHAM data. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 354, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.L. DIRBE minus 2MASS: Confirming the Cosmic Infrared Background at 2.2 Microns. Astrophys. J. 2001, 553, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashlinsky, A.; Arendt, R.G.; Mather, J.; Moseley, S.H. New Measurements of Cosmic Infrared Background Fluctuations from Early Epochs. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2007, 654, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matsumoto, T.; Seo, H.J.; Jeong, W.-S.; Lee, H.M.; Matsuura, S.; Matsuhara, H.; Oyabu, S.; Pyo, J.; Wada, T. AKARI Observation of the Fluctuation of the Near-infrared Background. Astrophys. J. 2011, 742, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Kim, M.G.; Pyo, J.; Tsumura, K. Reanalysis of the Near-infrared Extragalactic Background Light Based on the IRTS Observations. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemcov, M.; Smidt, J.; Arai, T.; Bock, J.; Cooray, A.; Gong, Y.; Kim, M.G.; Korngut, P.; Lam, A.; Lee, D.H.; et al. On the origin of near-infrared extragalactic background light anisotropy. Science 2014, 346, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwek, E.; Arendt, R.G. A Tentative Detection of the Cosmic Infrared Background at 3.5 μm from COBE/DIRBE Observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1998, 508, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambrésy, L.; Reach, W.T.; Beichman, C.A.; Jarrett, T.H. The Cosmic Infrared Background at 1.25 and 2.2 Microns Using DIRBE and 2MASS: A Contribution Not Due to Galaxies? Astrophys. J. 2001, 555, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashlinsky, A.; Arendt, R.; Gardner, J.P.; Mather, J.C.; Moseley, S.H. Detecting Population III Stars through Observations of Near-Infrared Cosmic Infrared Background Anisotropies. Astrophys. J. 2004, 608, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T. On the origin of the optical and near-infrared extragalactic background light. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2020, 96, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashlinsky, A.; Arendt, R.G.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Cappelluti, N.; Ferrara, A.; Hasinger, G. Looking at cosmic near-infrared background radiation anisotropies. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2018, 90, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashlinsky, A.; Arendt, R.G.; Mather, J.; Moseley, S.H. Tracing the first stars with fluctuations of the cosmic infrared background. Nature 2005, 438, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashlinsky, A.; Arendt, R.G.; Ashby, M.L.N.; Fazio, G.G.; Mather, J.; Moseley, S.H. New Measurements of the Cosmic Infrared Background Fluctuations in Deep Spitzer/IRAC Survey Data and Their Cosmological Implications. Astrophys. J. 2012, 753, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell-Wynne, K.; Cooray, A.; Gong, Y.; Ashby, M.; Dolch, T.; Ferguson, H.; Finkelstein, S.; Grogin, N.; Kocevski, D.; Koekemoer, A.; et al. Ultraviolet luminosity density of the universe during the epoch of reionization. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgason, K.; Komatsu, E. AKARI near-infrared background fluctuations arise from normal galaxy populations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.: Lett. 2017, 467, L36–L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, T.R.; Postman, M.; Weaver, H.A.; Spencer, J.R.; Stern, S.A.; Buie, M.W.; Durda, D.D.; Lisse, C.M.; Poppe, A.R.; Binzel, R.P.; et al. New Horizons Observations of the Cosmic Optical Background. Astrophys. J. 2021, 906, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemcov, M.; Immel, P.; Nguyen, C.; Cooray, A.; Lisse, C.M.; Poppe, A.R. Measurement of the cosmic optical background using the long range reconnaissance imager on New Horizons. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madau, P.; Pozzetti, L. Deep galaxy counts, extragalactic background light and the stellar baryon budget. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 312, L9–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Rodighiero, G.; Vaccari, M. Extragalactic optical-infrared background radiation, its time evolution and the cosmic photon-photon opacity. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 487, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.D.; Razzaque, S.; Dermer, C.D. Modeling the Extragalactic Background Light from Stars and Dust. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Primack, J.R.; Rosario, D.J.; Prada, F.; Gilmore, R.C.; Faber, S.M.; Koo, D.C.; Somerville, R.S.; Pérez-Torres, M.A.; Pérez-González, P.; et al. Extragalactic background light inferred from AEGIS galaxy-SED-type fractions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 2556–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwek, E.; Krennrich, F. The extragalactic background light and the gamma-ray opacity of the universe. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 43, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Inoue, S.; Kobayashi, M.A.R.; Makiya, R.; Niino, Y.; Totani, T. Extragalactic Background Light from Hierarchical Galaxy Formation: Gamma-Ray Attenuation up to the Epoch of Cosmic Reionization and the First Stars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Rodighiero, G. The extragalactic background light revisited and the cosmic photon-photon opacity. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 603, A34, Erratum in 2018, 614, C1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.K.; Driver, S.P.; Davies, L.J.M.; Lagos, C.D.P.; Robotham, A.S.G. Modelling the cosmic spectral energy distribution and extragalactic background light over all time. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primack, J.R.; Bullock, J.S.; Somerville, R.S.; MacMinn, D. Probing galaxy formation with TeV gamma ray absorption. Astropart. Phys. 1999, 11, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gilmore, R.C.; Somerville, R.S.; Primack, J.R.; Domínguez, A. Semi-analytic modelling of the extragalactic background light and consequences for extragalactic gamma-ray spectra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 3189–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, R.S.; Gilmore, R.C.; Primack, J.R.; Domínguez, A. Galaxy properties from the ultraviolet to the far-infrared: A cold dark matter models confront observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 1992–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, J.C.; Cheng, E.S.; Cottingham, D.A.; Eplee, R.E., Jr.; Fixsen, D.J.; Hewagama, T.; Isaacman, R.B.; Jensen, K.A.; Meyer, S.S.; Noerdlinger, P.D.; et al. Measurement of the Cosmic Microwave Background Spectrum by the COBE FIRAS Instrument. Astrophys. J. 1994, 420, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Galanti, G.; Roncadelli, M. Transparency of the Universe to gamma-rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 3245–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneiske, T.M.; Dole, H. A lower-limit flux for the extragalactic background light. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 515, A19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi-LAT Collaboration. A gamma-ray determination of the Universe’s star formation history. Science 2018, 362, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, A.W.; Smail, I.; Ivison, R.J.; Kneib, J.-P.; Frayer, D.T. Submillimeter galaxies. Phys. Rep. 2002, 369, 111–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Foffano, L.; Prandini, E.; Tavecchio, F. Very high-energy constraints on the infrared extragalactic background light. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 629, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Andronache, M.; Barrio, J.A.; Bernlöhr, K.; Bojahr, H.; Calle, I.; Contreras, J.L.; Cortina, J.; Daum, A.; et al. Observations of MKN 421 during 1997 and 1998 in the energy range above 500 GeV with the HEGRA stereoscopic Cherenkov telescope system. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 350, 757. [Google Scholar]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Barrio, J.A.; Bernlöhr, K.; Bolz, O.; Börst, H.; Bojahr, H.; Contreras, J.L.; Cortina, J.; Denninghoff, S.; et al. Reanalysis of the high energy cutoff of the 1997 Mkn 501 TeV energy spectrum. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 366, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.; Beilicke, M.; Bernlöhr, K.; Börst, H.; Bojahr, H.; Bolz, O.; Coarasa, T.; Contreras, J.; Cortina, J.; et al. Variations of the TeV energy spectrum at different flux levels of Mkn 421 observed with the HEGRA system of Cherenkov telescopes. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 393, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Angelis, A.; Mansutti, O.; Persic, M.; Roncadelli, M. Photon propagation and the very high energy γ-ray spectra of blazars: How transparent is the Universe? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.: Lett. 2009, 394, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horns, D.; Meyer, M. Indications for a pair-production anomaly from the propagation of VHE gamma-rays. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meyer, M.; Horns, D.; Raue, M. First lower limits on the photon-axion-like particle coupling from very high energy gamma-ray observations. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 035027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamante, L. Gamma-Rays from Blazars and the Extragalactic Background Light. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2013, 22, 1330025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horns, D.; Jacholkowska, A. Gamma rays as probes of the Universe. C. R. Phys. 2016, 17, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horns, D. The transparency of the universe for very high energy gamma-rays. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth Marcel Grossmann Meeting On Recent Developments in Theoretical and Experimental General Relativity, Astrophysics, and Relativistic Field Theories, Rome, Italy, 12–18 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, D.A.; Fegan, S.; Giebels, B. Evidence for a cosmological effect in γ-ray spectra of BL Lacertae. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 554, A75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddington, A.S. On a formula for correcting statistics for the effects of a known error of observation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1913, 73, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, D.W.; Turner, E.L. A Maximum Likelihood Method to Improve Faint-Source Flux and Color Estimates. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1998, 110, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M. Indirect Axion and Axionlike Particle Searches at Gamma-Ray Energies. In Proceedings of the 7th International Fermi Symposium, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, 15–20 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Madau, P.; Rees, M.J. Massive Black Holes as Population III Remnants. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2001, 551, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madau, P.; Silk, J. Population III and the near-infrared background excess. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc.: Lett. 2005, 359, L37–L41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabrier, G. Galactic Stellar and Substellar Initial Mass Function. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driver, S.P.; Andrews, S.K.; da Cunha, E.; Davies, L.J.; Lagos, C.; Robotham, A.S.G.; Vinsen, K.; Wright, A.H.; Alpaslan, M.; Bland-Hawthorn, J.; et al. GAMA/G10-COSMOS/3D-HST: The 0 < z < 5 cosmic star formation history, stellar-mass, and dust-mass densities. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 2891–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eales, S.; Smith, D.; Bourne, N.; Loveday, J.; Rowlands, K.; van der Werf, P.; Driver, S.; Dunne, L.; Dye, S.; Furlanetto, C.; et al. The new galaxy evolution paradigm revealed by the Herschel surveys. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 3507–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Rodighiero, G.; Vaccari, M.; Berta, S.; Marchetti, L.; Mainetti, G. Galaxy evolution from deep multi-wavelength infrared surveys: A prelude to Herschel. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 517, A74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruppioni, C.; Pozzi, F.; Rodighiero, G.; Delvecchio, I.; Berta, S.; Pozzetti, L.; Zamorani, G.; Andreani, P.; Cimatti, A.; Ilbert, O.; et al. The Herschel PEP/HerMES luminosity function—I. Probing the evolution of PACS selected Galaxies to z ≃ 4. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 23–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherenkov Telescope Array Consortium. Science with the Cherenkov Telescope Array; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, M.; Kneiske, T.; Mazin, D. First stars and the extragalactic background light: How recent γ-ray observations constrain the early universe. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 498, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V. Distance Measurement and Wave Dispersion in a Liouville-String Approach to Quantum Gravity. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 1997, 12, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V.; Sarkar, S. Tests of quantum gravity from observations of γ-ray bursts. Nature 1998, 395, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifune, T. Invariance Violation Extends the Cosmic-Ray Horizon? Astrophys. J. Lett. 1999, 518, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Aharonian, F.; Benkhali, F.A.; Angüner, E.O.; Arakawa, M.; Arcaro, C.; Armand, C.; Arrieta, M.; Backes, M.; Barnard, M.; et al. The 2014 TeV -ray flare of Mrk 501 seen with HESS: Temporal and spectral constraints on Lorentz invariance violation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 870, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi LAT Collaboration. Testing Einstein’s special relativity with Fermi’s short hard -ray burst GRB090510. Nature 2009, 462, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [MAGIC Collaboration]; Ahnen M., L.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Arcaro, C.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Bangale, P.; De Almeida, U.B.; Barrio, J.A.; et al. Constraining Lorentz Invariance Violation Using the Crab Pulsar Emission Observed up to TeV Energies by MAGIC. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2017, 232, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.G.; Martínez-Huerta, H.; de Souza, V. Improved limits on Lorentz invariance violation from astrophysical gamma-ray sources. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 043015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The CTA Consortium. Design Concepts for the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Exp. Astron. 2011, 32, 193–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareschi, G. The ASTRI SST-2M prototype and mini-array for the Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA). In Proceedings of the Ground-based and Airborne Telescopes VI, Edinburgh, UK, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sciascio, G.; Lhaaso Collaboration. The LHAASO experiment: From Gamma-Ray Astronomy to Cosmic Rays. In Proceedings of the CRIS 2015 Conference, Gallipoli, Italy, 14–16 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeYoung, T.; HAWC Collaboration. The HAWC observatory. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2012, 692, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Galanti, G.; Roncadelli, M. Relevance of axionlike particles for very-high-energy astrophysics. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 105030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanti, G.; Roncadelli, M.; De Angelis, A.; Bignami, G.F. Hint at an axion-like particle from the redshift dependence of blazar spectra. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenedese, F.; Franceschini, A.; University of Padova, Padova, Italy. Unpublished work. 2003.
- Wakely, S.P.; Horan, D. TeVCat: An online catalog for Very High Energy Gamma-Ray Astronomy. In Proceedings of the 30th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Mérida, Mexico, 3–11 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, H.; Abe, H.; Acero, F.; Acharyya, A.; Adam, R.; Agudo, I.; Aguirre-Santaella, A.; Alfaro, R.; Alfaro, J.; Alispach, C.; et al. Sensitivity of the Cherenkov Telescope Array for probing cosmology and fundamental physics with gamma-ray propagation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telescope, L.; Aartsen, M.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; et al. Multimessenger observations of a flaring blazar coincident with high-energy neutrino IceCube-170922A. Science 2018, 361, eaat1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, P.L. Powerful radio galaxies as sources of the highest energy cosmic rays. In Proceedings of the Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Ray Workshop on Observing Giant Cosmic Ray Air Showers for > 10**20 eV Particles from Space, College Park, MD, USA, 13–15 November 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Romano, P.; Landoni, M.; Vercellone, S. Putting the hadron beam scenario for extreme blazars to the test with the Cherenkov Telescope Array. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraschi, L.; Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. A Jet Model for the Gamma-Ray–emitting Blazar 3C 279. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 397, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Treu, T.; Riess, A.G. Tensions between the early and late Universe. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essey, W.; Kalashev, O.E.; Kusenko, A.; Beacom, J.F. Secondary Photons and Neutrinos from Cosmic Rays Produced by Distant Blazars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 141102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1. | Blazars are Active Galactic Nuclei hosting nuclear jets of plasma in directions close to the observer’s line-of-sight. They make, together with flat-spectrum radio sources, the most numerous population of extragalactic sources at HE and VHE energies. |


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franceschini, A. Photon–Photon Interactions and the Opacity of the Universe in Gamma Rays. Universe 2021, 7, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7050146
Franceschini A. Photon–Photon Interactions and the Opacity of the Universe in Gamma Rays. Universe. 2021; 7(5):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7050146
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranceschini, Alberto. 2021. "Photon–Photon Interactions and the Opacity of the Universe in Gamma Rays" Universe 7, no. 5: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7050146
APA StyleFranceschini, A. (2021). Photon–Photon Interactions and the Opacity of the Universe in Gamma Rays. Universe, 7(5), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7050146





