Matter Growth in Imperfect Fluid Cosmology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Energy-Momentum Tensors
3. General Conservation Equations
4. Perturbation Dynamics
4.1. Metric and Fluid Quantities
4.2. Modified Poisson Equation
4.3. Combination of Conservation and Raychaudhuri Equations
4.4. Relative Perturbations
4.5. Perturbations of (an-)Isotropic Pressures and Energy Flux
4.6. Coupled System of Equations for and
4.7. Anisotropic Pressure and Gravitational Potentials
4.8. Matter Perturbations
5. CDM Cosmology
5.1. Jordan–Brans–Dicke Theory
5.2. JBD Inspired Effective Background Model
5.2.1. General Einstein-Frame Dynamics
5.2.2. Interacting Fluid Approach in Einstein-Frame Dynamics
5.2.3. Effective Hubble Rate
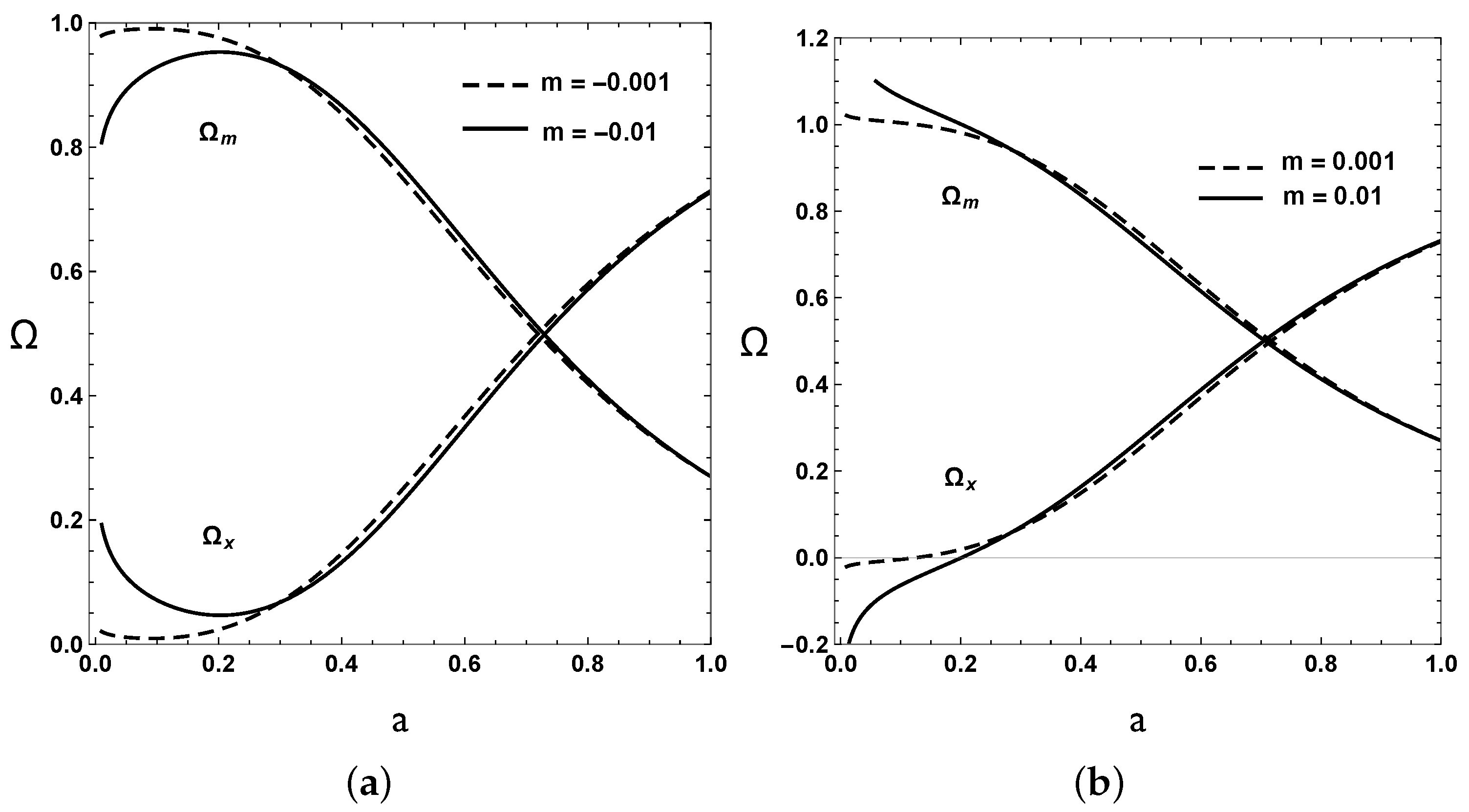
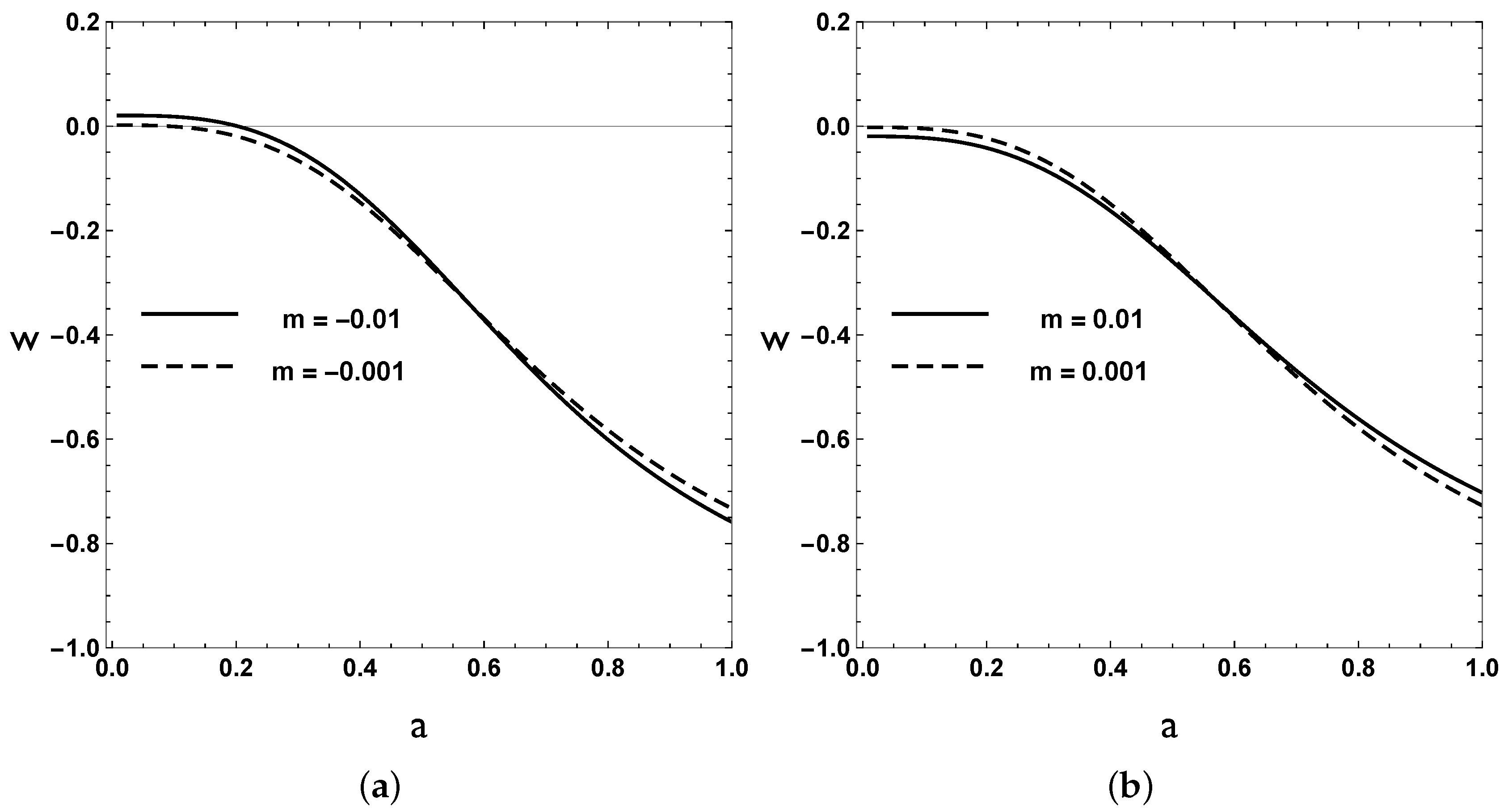
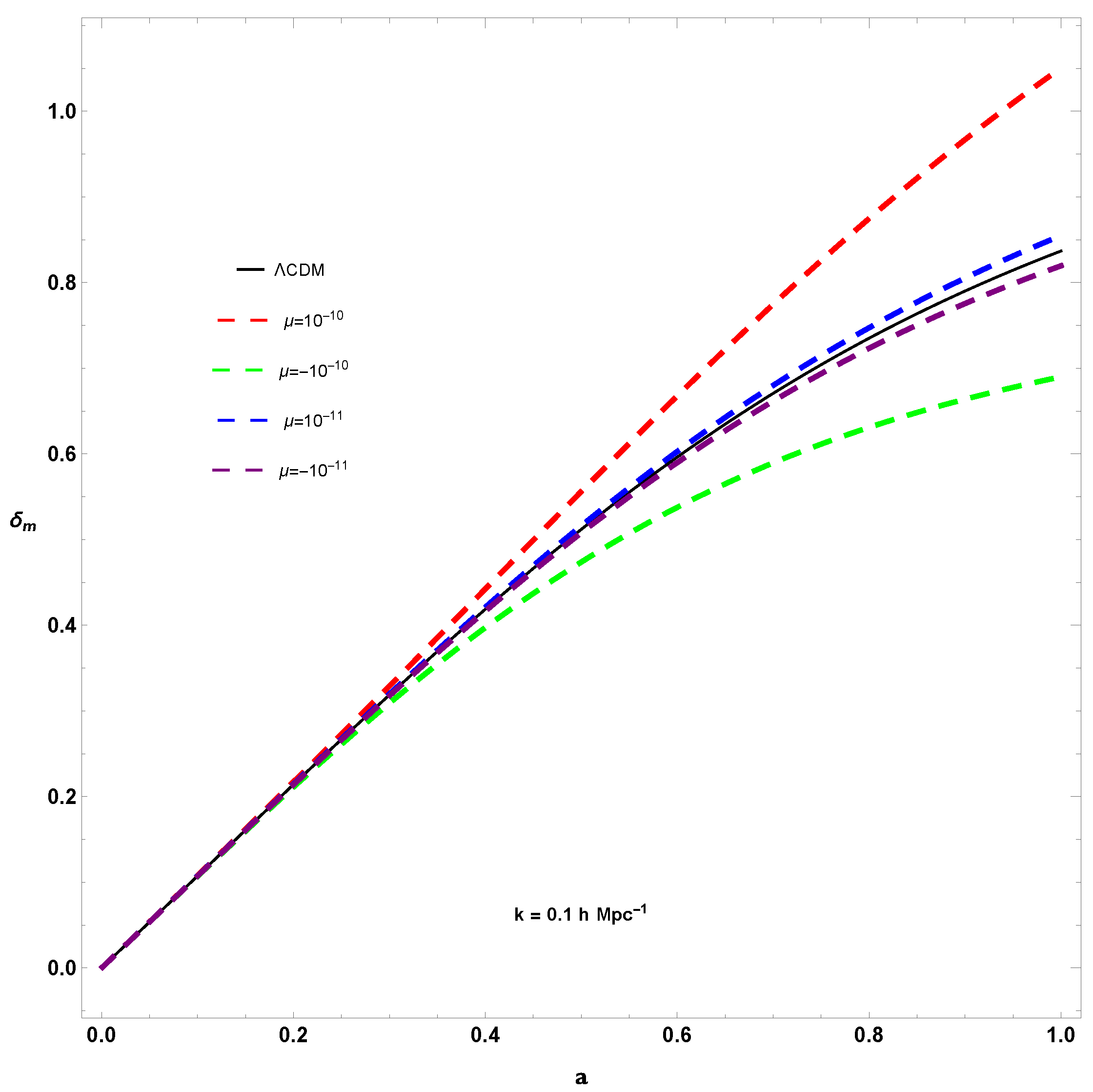
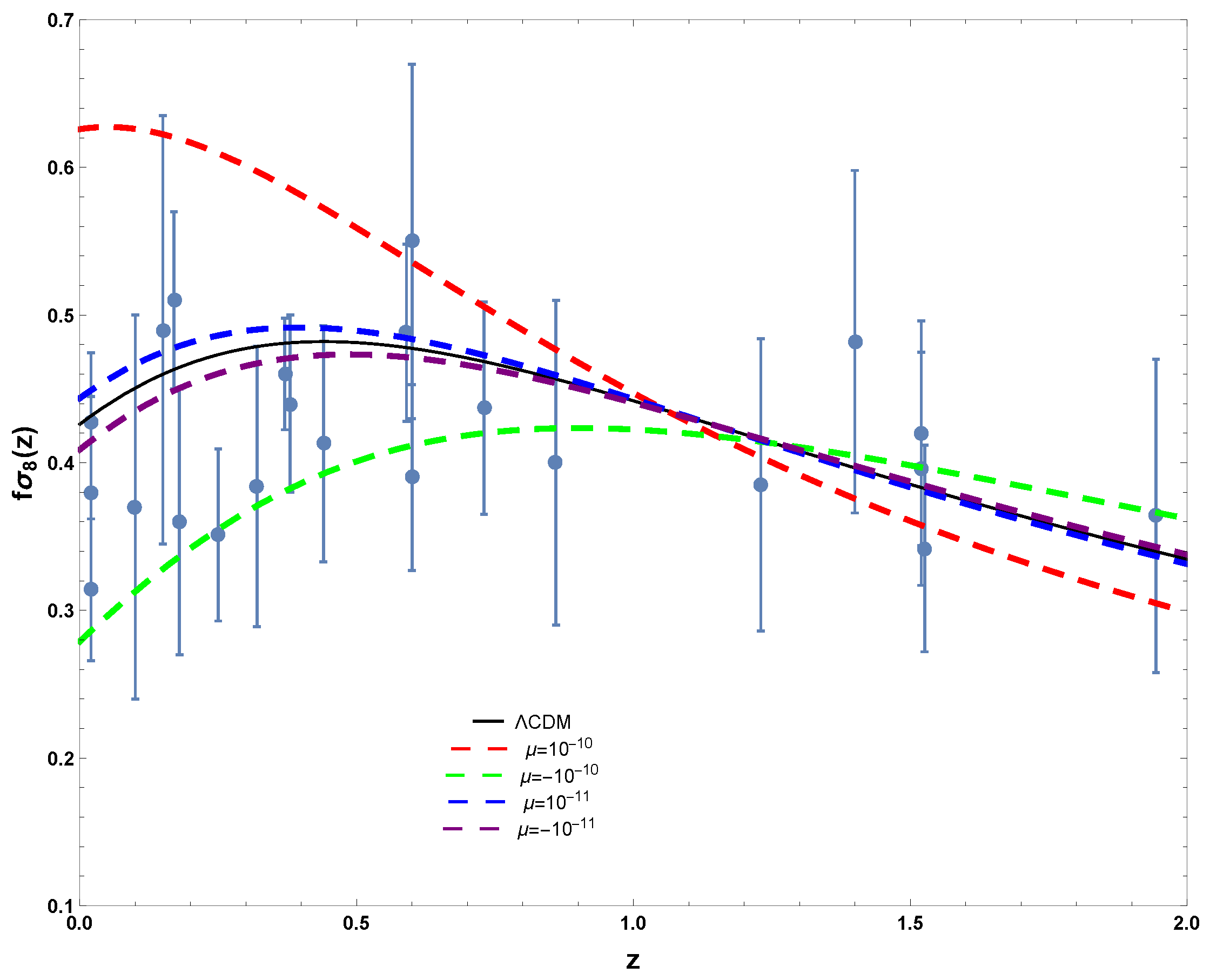
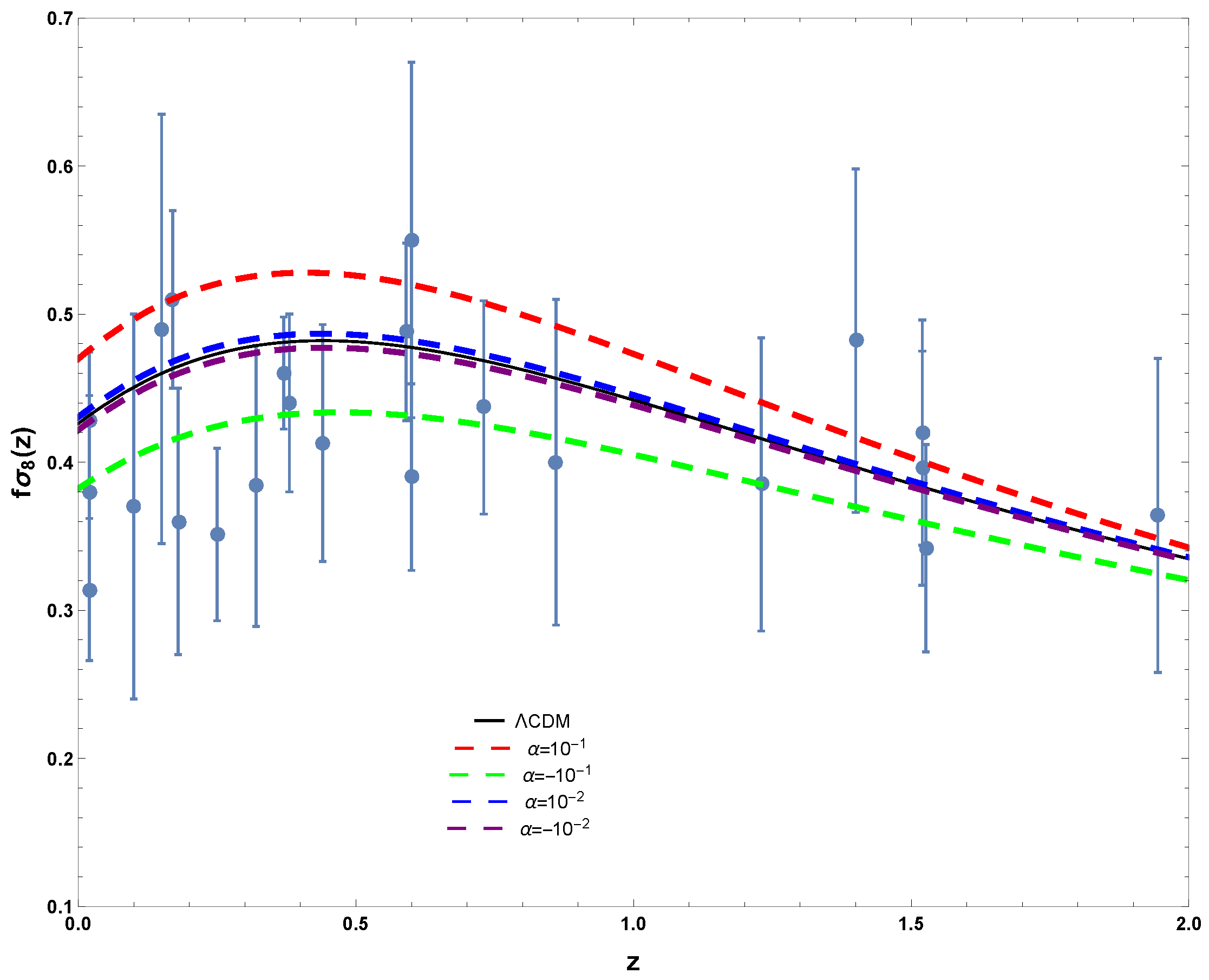
6. Growth of Matter Perturbations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahcall, N.A.; Ostriker, J.P.; Perlmutter, J.P.; Steinhardt, P.J. The cosmic triangle: Revealing the state of the universe. Science 1999, 284, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark Energy: Theory and Observations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, G.F.R.; Maartens, R.; Maccallum, M.A.H. Relativistic Cosmology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J. Everything you always wanted to know about the cosmological constant problem (but were afraid to ask). C. R. Phys. 2012, 13, 566–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatev, I.; Wang, L.M.; Steinhardt, P.J. Quintessence, cosmic coincidence, and the cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, P.J.; Wang, L.M.; Zlatev, I. Cosmological tracking solutions. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 59, 123504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malquarti, M.; Copeland, E.J.; Liddle, A.R. k-essence and the coincidence problem. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 023512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, A.; Avelino, P.P. Anthropic versus cosmological solutions to the coincidence problem. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, H.E.S.; vom Marttens, R.F.; Zimdahl, W. Aspects of the cosmological “coincidence problem”. Eur. Phys. J. C 2014, 74, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrami, Y.; et al. [Planck Collaboration] Planck 2018 results. I. Overview and the cosmological legacy of Planck. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1807.06205. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, T.M.C.; et al. [DES Collaboration] Dark Energy Survey Year 1 Results: Constraints on Extended Cosmological Models from Galaxy Clustering and Weak Lensing. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1810.02499. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, P.; Camera, S.; Kelley, K.; Padmanabhan, H.; Pritchard, J.; Raccanelli, A.; Riemer-Sørensen, S.; Shao, L.; Andrianomena, S.; Athanassoula, E.; et al. Fundamental Physics with the Square Kilometre Array. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1810.02680. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.P.; et al. [LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration] GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, M.S. Scalar fields in curved spacetimes. Class. Quantum Grav. 2017, 5, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, L.O. Energy-momentum tensor in the general scalar-tensor theory. Class. Quantum Grav. 1989, 6, L263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, R.A.; Pearson, J.A. Effective action approach to cosmological perturbations in dark energy and modified gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, R.A.; Pearson, J.A. Parametrizing dark sector perturbations via equations of state. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 061301(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battye, R.A.; Bolliet, B.; Pearson, J.A. f(R) gravity as a dark energy fluid. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 044026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V.; Coté, J. Imperfect fluid description of modified gravities. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 084019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, I.; Saltas, I.D.; Amendola, L.; Kunz, M. Consistent perturbations in an imperfect fluid. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 2013, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Perivolaropoulos, S. Testing LCDM with the Growth Function δ(a): Current Constraints. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 023504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilakos, S.; Pouri, A. The growth index of matter perturbations and modified gravity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 423, 3761–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huterer, D.; Kirkby, D.; Bean, R.; Connolly, A.; Dawson, K.; Dodelson, S.; Evrard, A.; Jain, B.; Jarvis, M.; Linder, E.; et al. Growth of Cosmic Structure: Probing Dark Energy Beyond Expansion. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 63, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Sapone, D. Accuracy of the growth index in the presence of dark energy perturbations. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 023013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Ata, M.; Bailey, S.; Beutler, F.; Bizyaev, D.; Blazek, J.A.; Bolton, A.S.; Brownstein, J.R.; Burden, A.; Chuang, C.-H.; et al. The clustering of galaxies in the completed SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Cosmological analysis of the DR12 galaxy sample. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 2617–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algoner, W.C.; Velten, H.E.S.; Zimdahl, W. Scalar-tensor extension of the ΛCDM model. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimdahl, W.; Velten, H.E.S.; Algoner, W.C. Matter growth in extended ΛCDM cosmology. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1706.06143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipólito-Ricaldi, W.S.; Velten, H.E.S.; Zimdahl, W. Non-adiabatic dark fluid cosmology. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 2009, 016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipólito-Ricaldi, W.S.; Velten, H.E.S.; Zimdahl, W. Viscous dark fluid universe. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 063507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Campo, S.; Fabris, J.C.; Herrera, J.C.; Zimdahl, W. Cosmology with Ricci dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Fuño, A.; Hipólito-Ricaldi, W.S.; Zimdahl, W. Matter perturbations in scaling cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 2958–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.; Sapone, M. Dark Energy versus Modified Gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, W.; Hollenstein, L.; Kunz, M. The traces of anisotropic dark energy in light of Planck. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2014, 032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas, D.; Floerchinger, S.; Garny, M.; Tetradis, N.; Wiedemann, U.A. Large scale structure from viscous dark matter. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, P. Zum gegenwärtigen Stand der Diracschen kosmologischen Hypothesen. Z. Physik 1959, 157, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, C.; Dicke, R.H. Mach’s principle and a relativistic theory of gravitation. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, R.H. Mach’s principle and invariance under transformation of units. Phys. Rev. 1962, 125, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Bean, R. The Dynamical viability of scalar-tensor gravity theories. Class. Quantum Grav. 2008, 25, 165001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, C.E.M.; Zimdahl, W. Power-law solutions and accelerated expansion in scalar-tensor theories. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 023527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.; Ferreira, P.; Padilla, A.; Skordis, C. Modified Gravity and Cosmology. Phys. Rep. 2012, 513, 1–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Yamaguchi, M. Conformal-Frame (In)dependence of Cosmological Observations in Scalar-Tensor Theory. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 2013, 040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-S.; Percival, W.J. Reconstructing the history of structure formation using redshift distortions. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 2009, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Pantazis, G.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Tension and constraints on modified gravity parametrizations of Geff(z) from growth rate and Planck data. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 023542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Marín, H.; Guy, J.; Zarrouk, P.; Burtin, E.; Chuang, C.-H.; Percival, W.J.; Ross, A.J.; Ruggeri, R.; Tojerio, R.; Zhao, G.-B.; et al. The clustering of the SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey DR14 quasar sample: Structure growth rate measurement from the anisotropic quasar power spectrum in the redshift range 0.8<z<2.2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 477, 1604–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Sánchez, A.G.; Scoccimarro, R.; Salazar-Albornoz, S.; Burtin, E.; Gil-Marín, H.; Percival, W.J.; Ruggeri, R.; Zarrouk, P.; Zhao, G.-B.; et al. The clustering of the SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey DR14 quasar sample: Anisotropic clustering analysis in configuration-space. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, arXiv:1801.02656480, 2521–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-B.; Wang, Y.; Saito, S.; Gil-Marín, H.; Percival, W.J.; Wang, D.; Chuang, C.-H.; Ruggeri, R.; Mueller, E.-M.; Zhu, F.; et al. The clustering of the SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey DR14 quasar sample: A tomographic measurement of cosmic structure growth and expansion rate based on optimal redshift weights. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 482, 3497–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
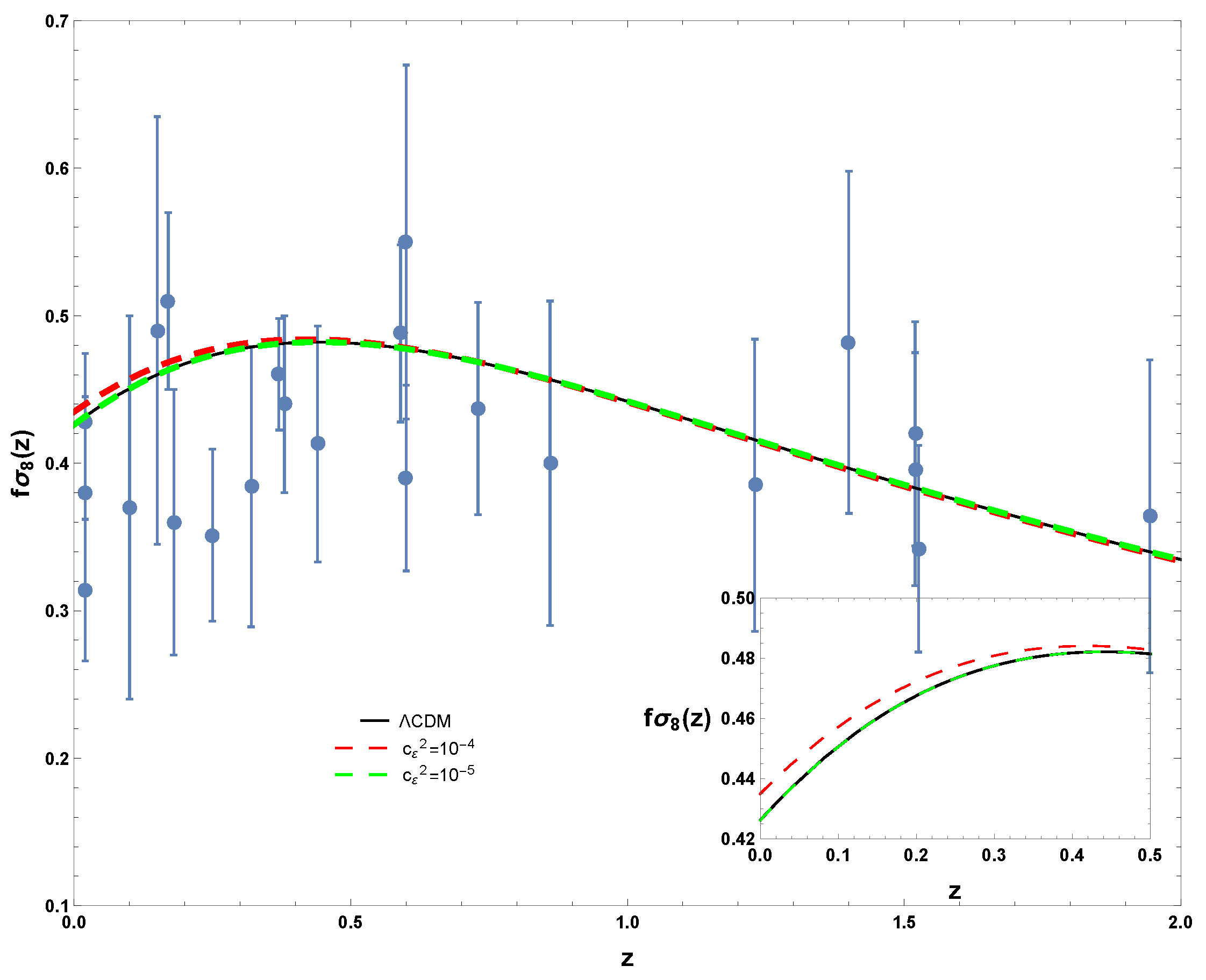

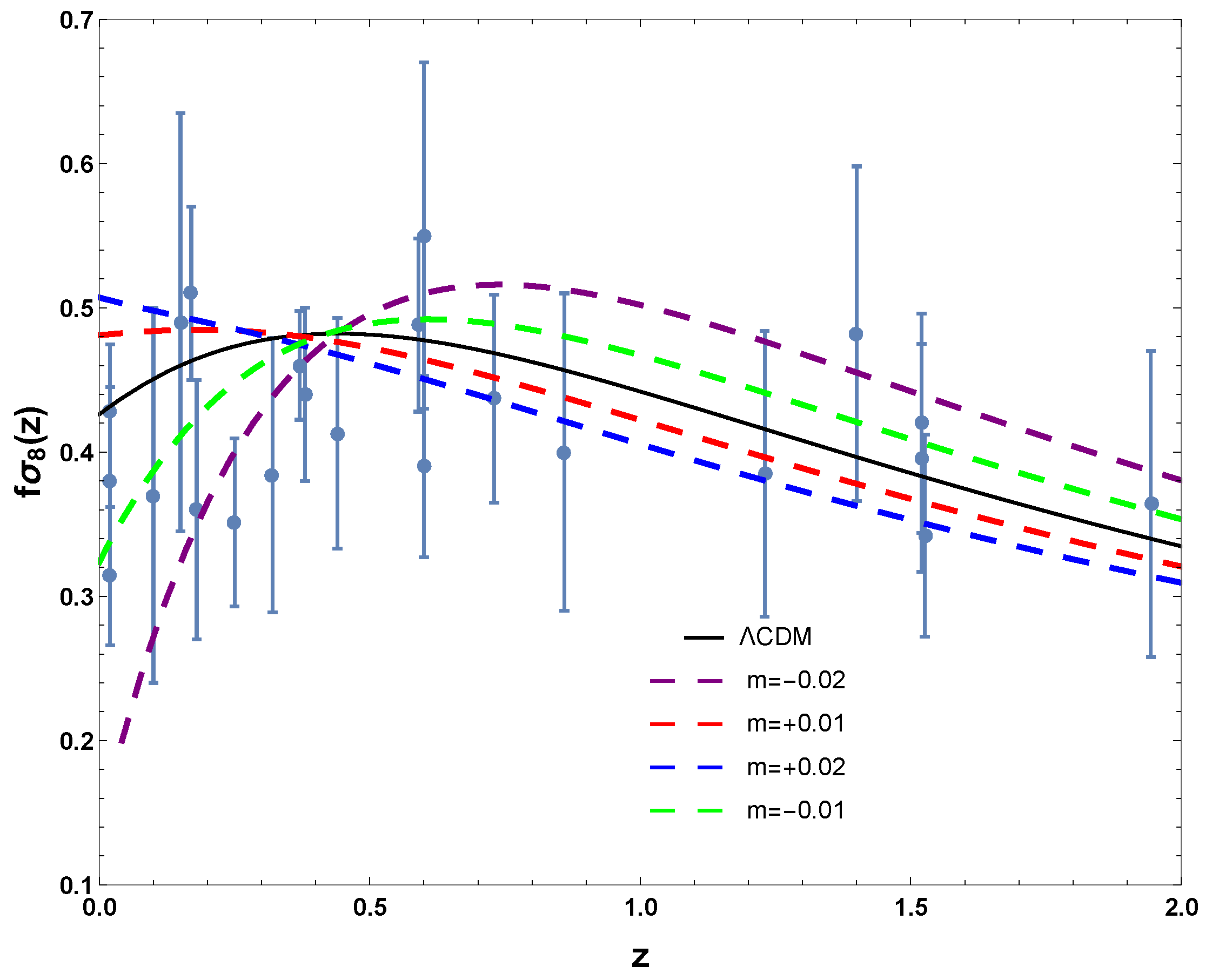
| Index | Data set | z | Year | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6dFGS + SnIa | 0.02 | 0.428 ± 0.0465 | 2016 | (, h, ) = (0.3, 0.683, 0.8) |
| 2 | SnIa + IRAS | 0.02 | 0.398 ± 0.065 | 2011 | (, ) = (0.3, 0) |
| 3 | 2MASS | 0.02 | 0.314 ± 0.048 | 2010 | (, ) = (0.266, 0) |
| 4 | SDSS-veloc | 0.10 | 0.370 ± 0.130 | 2015 | (, ) = (0.3, 0) |
| 5 | SDSS-MGS | 0.15 | 0.490 ± 0.145 | 2014 | (, h, ) = (0.31, 0.67, 0.83) |
| 6 | 2dFGRS | 0.17 | 0.510 ± 0.060 | 2009 | (, ) = (0.3, 0) |
| 7 | GAMA | 0.18 | 0.360 ± 0.090 | 2013 | (, ) = (0.27, 0) |
| 8 | GAMA | 0.38 | 0.440 ± 0.060 | 2013 | |
| 9 | SDSS-LRG-200 | 0.25 | 0.3512 ± 0.0583 | 2011 | (, ) = (0.25, 0) |
| 10 | SDSS-LRG-200 | 0.37 | 0.4602 ± 0.0378 | 2011 | |
| 11 | BOSS-LOWZ | 0.32 | 0.384 ± 0.095 | 2013 | (, ) = (0.274, 0) |
| 12 | SDSS-CMASS | 0.59 | 0.488 ± 0.060 | 2013 | (, h, ) = (0.307115, 0.6777, 0.8288) |
| 13 | WiggleZ | 0.44 | 0.413 ± 0.080 | 2012 | (, h) = (0.27, 0.71) |
| 14 | WiggleZ | 0.60 | 0.390 ± 0.063 | 2012 | |
| 15 | WiggleZ | 0.73 | 0.437 ± 0.072 | 2012 | |
| 16 | Vipers PDR-2 | 0.60 | 0.550 ± 0.120 | 2016 | (, ) = (0.3, 0.045) |
| 17 | Vipers PDR-2 | 0.86 | 0.400 ± 0.110 | 2016 | |
| 18 | FastSound | 1.40 | 0.482 ± 0.116 | 2015 | (, ) = (0.270, 0) |
| 19 | SDSS-IV | 1.52 | 0.420 ± 0.076 | 2018 | (, , ) = (0.26479, 0.02258, 0.8) |
| 20 | SDSS-IV | 1.52 | 0.396 ± 0.079 | 2018 | (,, ) = (0.31, 0.022, 0.8225) |
| 21 | SDSS-IV | 1.23 | 0.385 ± 0.099 | 2018 | (, ) = (0.31, 0.8) |
| 22 | SDSS-IV | 1.526 | 0.342 ± 0.070 | 2018 | |
| 23 | SDSS-IV | 1.944 | 0.364 ± 0.106 | 2018 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zimdahl, W.; Velten, H.E.S.; Algoner, W.C. Matter Growth in Imperfect Fluid Cosmology. Universe 2019, 5, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5030068
Zimdahl W, Velten HES, Algoner WC. Matter Growth in Imperfect Fluid Cosmology. Universe. 2019; 5(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleZimdahl, Winfried, Hermano E.S. Velten, and William C. Algoner. 2019. "Matter Growth in Imperfect Fluid Cosmology" Universe 5, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5030068
APA StyleZimdahl, W., Velten, H. E. S., & Algoner, W. C. (2019). Matter Growth in Imperfect Fluid Cosmology. Universe, 5(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5030068






