Horizon Areas and Logarithmic Correction to the Charged Accelerating Black Hole Entropy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Thermodynamic Properties of Charged Accelerating BH
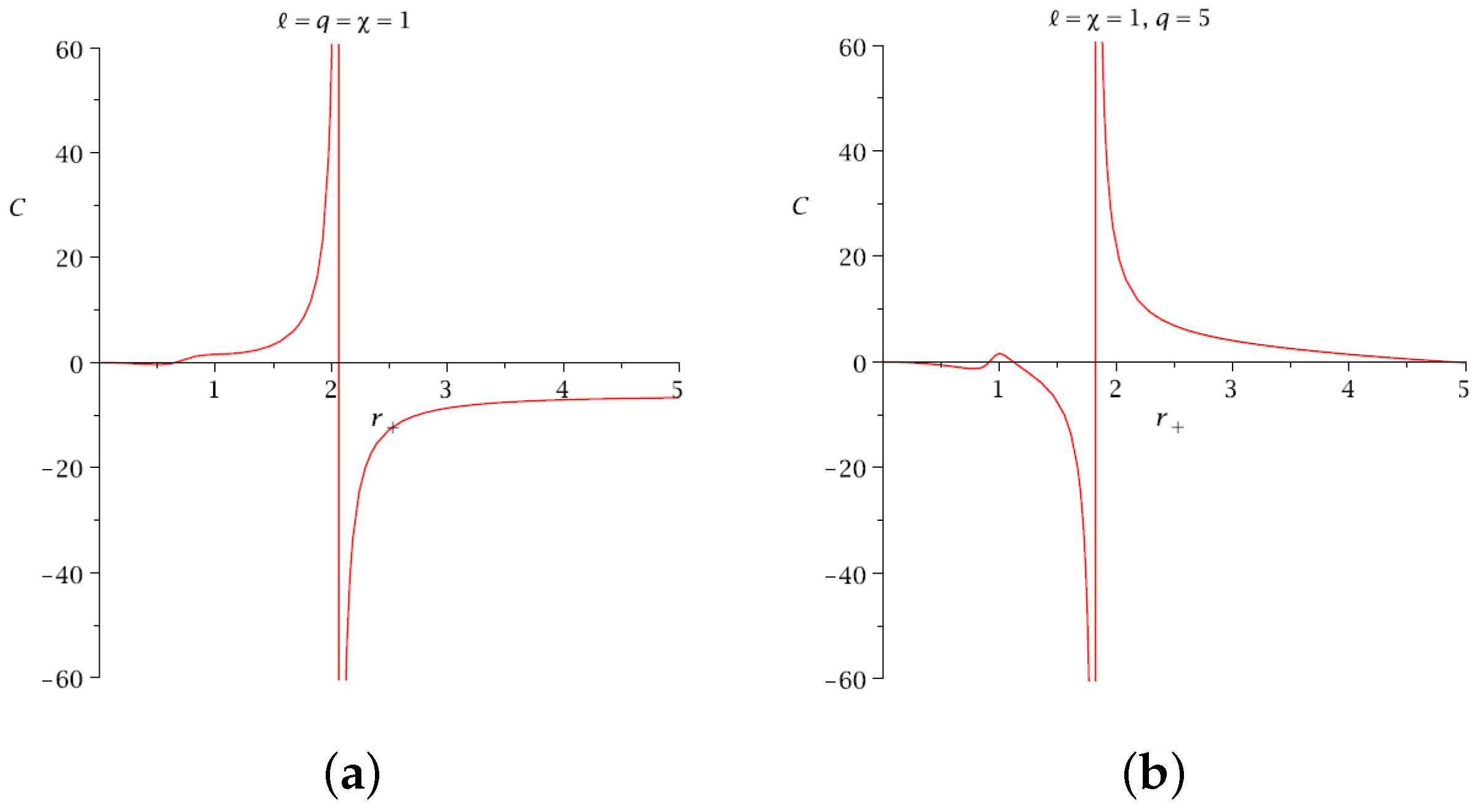
3. Logarithmic Corrections to Entropy for Charged Accelerating BH
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bekenstein, J.D. Black holes and entropy. Phys. Rev. D 1973, 7, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Carter, B.; Hawking, S.W. The Four laws of black hole mechanics. Commun. Math. Phys. 1973, 31, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorg, M.; Hennig, J. Inner Cauchy horizon of axisymmetric and stationary black holes with surrounding matter in Einstein-Maxwell theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 221102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvetič, M.; Gibbons, G.W.; Pope, C.N. Universal Area Product Formulae for Rotating and Charged Black Holes in Four and Higher Dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F. A String model of black hole microstates. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 56, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Rodriguez, M.J. Universal properties and the first law of black hole inner mechanics. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 024008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detournay, S. Inner Mechanics of 3d Black Holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 031101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V.; Moreno, A.F.Z. Are quantization rules for horizon areas universal? Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 044011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, S.X.; Zhang, J.J. Thermodynamics of black hole horizons and Kerr/CFT correspondence. J. High Energy Phys. 2012, 2012, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curir, A. Spin entropy of a rotating black hole. Nuovo Cimento 1979, 51B, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M. Area products for stationary black hole horizons. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 044014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, J. Geometric relations for rotating and charged AdS black holes. Class. Quant. Grav. 2014, 31, 135005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P. Area (or entropy) product formula for a regular black hole. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2016, 48, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P. Black Hole Interior Mass Formula. Eur. Phys. J. C 2014, 74, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P. Thermodynamic product formula for Horava–Lifshitz black hole. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 747, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P. Thermodynamic Products in Extended Phase Space. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2017, 26, 1750010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, M.; Gregory, R.; Kubizňák, D. Thermodynamics of Accelerating Black Holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 131303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astorino, M. CFT Duals for Accelerating Black Holes. Phys. Lett. B 2016, 760, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnersley, W.; Walker, M. Uniformly accelerating charged mass in general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 2, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plebanski, J.F.; Demianski, M. Rotating, charged, and uniformly accelerating mass in general relativity. Ann. Phys. D 1976, 98, 98–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, O.J.C.; Lemos, J.P.S. Pair of accelerated black holes in anti-de Sitter background: AdS C metric. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.B.; Podolsky, J. New look at the Plebanski-Demianski family of solutions. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 335–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Civita, T. ds2 einsteiniani in campi newtoniani. Rend. Acc. Lincei 1918, 27, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, E.T.; Tamburino, L.A. New Approach to Einstein’s Empty Space Field Equations. J. Math. Phys. 1961, 2, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, I.; Trautman, A. Some spherical gravitational waves in general relativity. Proc. Roy. Soc. (Lond.) 1962, A265, 463–473. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, J.; Kundt, W. Gravitation, An Introduction to Current Research; Witten, L., Ed.; Wiely: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky, J.; Ortaggio, M.; Krtouš, P. Radiation from accelerated black holes in an anti-de Sitter universe. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, J. Accelerating black holes in anti-de Sitter universe. Czech. J. Phys. 2002, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krtous, P. Accelerated black holes in an anti-de Sitter universe. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emparan, R.; Horowitz, G.T. Exact description of black holes on branes II: Comparison with BTZ black holes and black strings. J. High Energy Phys. 2000, 2000, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. Naked singularities. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1973, 224, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, H.L. The Penrose inequality. Not. AMS 2002, 49, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, H.L.; Chruściel, P.T. The Penrose Inequality. arXiv, 2004; arXiv:gr-qc/0312047. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, P.S.; Wald, R.M. Positive energy conjecture and the cosmic censor hypothesis. J. Math. Phys. 1977, 18, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geroch, R. Energy Extraction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1973, 224, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, G.W. Some comments on gravitational entropy and the inverse mean curvature flow. Class. Quant. Grav. 1999, 16, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, G.W.; Perry, M.J.; Pope, C.N. Bulk/boundary thermodynamic equivalence, and the Bekenstein and cosmic-censorship bounds for rotating charged AdS black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 084028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawking, S.; Page, D.N. Thermodynamics of Black Holes in anti-De Sitter Space. Commun. Math. Phys. 1983, 87, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubizňák, D.; Mann, R.B. P-V criticality of charged AdS black holes. J. High Energy Phys. 2012, 2012, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Majumdar, P.; Bhaduri, R.K. General logarithmic corrections to black hole entropy. Class. Quant. Grav. 2001, 19, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, G.W.; Hawking, S. Action Integrals and Partition Functions in Quantum Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1976, 15, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlip, S. Logarithmic corrections to black hole entropy from the Cardy formula. Class. Quant. Grav. 2000, 17, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P. CFT and Logarithmic Corrections to the Black Hole Entropy Product Formula. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:gr-qc/1607.01702. [Google Scholar]
- Suskind, L. The World as a hologram. J. Math. Phys. 1995, 36, 6377–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virbhadra, K.S. Naked Singularity and Seifert Conjecture. Phys. Rev. D 1999, 60, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
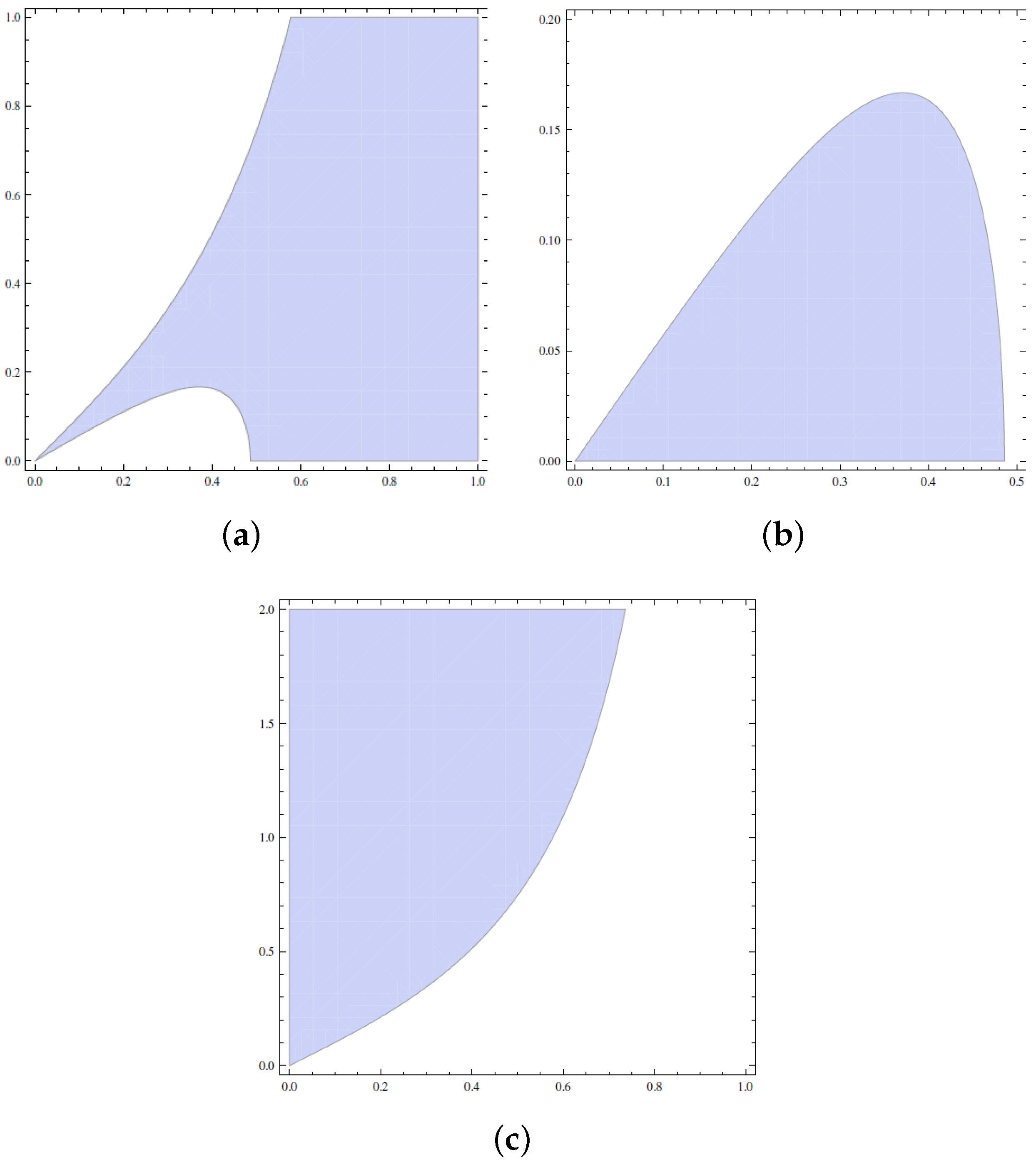
| 1 | The Penrose inequality is indeed violated for charged accelerating BH because in the right side of the Equation (14) the factor K depends on the mass parameter. |

© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pradhan, P. Horizon Areas and Logarithmic Correction to the Charged Accelerating Black Hole Entropy. Universe 2019, 5, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5020057
Pradhan P. Horizon Areas and Logarithmic Correction to the Charged Accelerating Black Hole Entropy. Universe. 2019; 5(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5020057
Chicago/Turabian StylePradhan, Parthapratim. 2019. "Horizon Areas and Logarithmic Correction to the Charged Accelerating Black Hole Entropy" Universe 5, no. 2: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5020057
APA StylePradhan, P. (2019). Horizon Areas and Logarithmic Correction to the Charged Accelerating Black Hole Entropy. Universe, 5(2), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5020057




