Abstract
Being ionized nebulae where star formation events take place, H ii regions are not only natural laboratories for studying physical processes of star formation and photoionization but also signatures reflecting evolution of their internal stellar populations and hosting galaxies. In this paper, we present a comprehensive analysis of spectral emission-line data for H ii regions in the nearby spiral galaxy NGC 2403, aimed at gaining deep insight into underlying properties and evolution for the H ii regions and the galaxy. The spectroscopic data are obtained through observations with the 2.16 m telescope at National Astronomical Observatories of China and a collection of published data in the literature. Photoionization modeling is combined in the analysis for diagnosing the spectral features and interpreting the observational data with certain physical mechanisms. Results of this work not only involve estimates of a set of parameters such as metallicity, the ionization parameter, etc., and evolution stages for the H ii regions in NGC 2403 but also reveal distinct characteristics of different spectral features and their sensitivities to specific parameters, which provides an instructive implication for proper usages of emission-line diagnostics for H ii regions or galaxies nearby and far away.
1. Introduction
Being gaseous nebulae irradiated by recently formed massive stars, H ii regions are conspicuous sites where star formation activities accompanying photoionization processes occur, and young stellar populations surrounded by ionized interstellar medium reside. Spectra of H ii regions contain a great number of emission lines, which serve as a useful tool for probing not only astrophysical mechanisms/properties in H ii regions but also evolution history of host galaxies (Peimbert et al. [1], Maiolino and Mannucci [2], Kewley et al. [3]).
Metallicity is an important parameter derivable from emission-line features for H ii regions. It behaves like a signature of element enrichment with star formation, and hence its spatial distributions are an imprint of chemical evolution for galaxies. The most accurate method for deriving metallicity from spectral emission lines is based on estimates of electron temperature () and referred to as the or direct method (Peimbert et al. [1]). However, the method requires measurements of auroral lines such as [O iii, [N ii, or [S iii, which are intrinsically weak in spectra and even undetectable at high metallicity. In this case, strong collisionally excited emission lines such as [O ii, [O iii, [N ii, and [S ii are applied to estimating metallicity with empirical or theoretical calibrations, and they have provided more widely used diagnostics in studies of external galaxies (Alloin et al. [4], Pagel et al. [5], Pettini and Pagel [6], Pilyugin and Thuan [7], Bresolin [8]).
In addition to metallicity, the collisionally excited emission lines have been found to also relate with the ionization parameter and electron density at different levels of sensitivities. Some spectral indices combining certain emission lines have been adopted to probe the physical parameters for H ii regions or emission-line galaxies (e.g., [O iii or [S iii[S ii for probing the ionization parameter, Kewley and Dopita [9], Morisset et al. [10]; [O ii[O ii or [S ii[S ii for probing electron density, Wang et al. [11]).1
Since H ii regions are excited by young massive stars, aging of the ionizing sources is considered to have an effect on the excitation and the subsequent spectral features (Levesque et al. [12], Xiao et al. [13]). Variations of commonly adopted diagnostic indices with stellar population age can be non-negligible, as they may affect the inferred metallicity, ionization parameter, electron density, and other physical properties. Nevertheless, the impact of age on the emission lines of H iiregions has yet to be systematically addressed in observational studies of galaxies.
Kong et al. [14] conducted a spectroscopic survey of 20 nearby galaxies and obtained a substantial collection of H ii region spectra. These data provide critical information on metallicity, ionization parameters, and dust extinction, offering observational constraints for theoretical models of galaxy formation, chemical evolution, and photoionization. As one of the target galaxies in this project, NGC 2403 is a late-type spiral galaxy (classified into the SAB(s)cd morphological type) located in the M81 galaxy group at the distance ∼ Mpc from the Milky Way (Tully et al. [15]). Basic information on astrometry for this galaxy includes the celestial coordinates R.A. = 07:36:51.3, Dec. = +65:36:09.7 (Skrutskie et al. [16]), the apparent size ∼, the inclination ∼, and the position angle ∼ (de Vaucouleurs et al. [17]). There are a number of bright H ii regions widespread in NGC 2403, making it possible to conduct a spatially resolved spectroscopic analysis. Mao et al. [18] performed a spatially resolved study of 11 large, bright H ii regions in NGC 2403 using the Kong et al. [14] dataset. They examined the performance of various metallicity calibration indicators within individual H ii regions.
In the present work, we target H ii regions in the late-type spiral galaxy NGC 2403 and carry out an observational investigation in combination with modeling. Spectroscopy is taken for the sampled H ii regions and aimed at a comprehensive inspection of emission-line characteristics related to underlying physical properties. In particular, we attempt to derive the parameters from certain diagnostics on the one hand and scrutinize specific influences of certain parameters on different emission-line features on the other hand.
Subsequent content of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents observations, data reduction, measurements, and ancillary data from the literature. Section 3 introduces the photoionization model employed in this study. Results are described in Section 4, followed by a discussion about implications and suggestions in Section 5. Section 6 in the end summarizes conclusions drawn in this work.
2. Data
2.1. Observations
A total of 84 H ii regions in NGC 2403 were selected from the catalog of Sivan et al. [19] and observed with the 2.16 m telescope at the Xinglong Station of National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) as part of a spectroscopic survey of H ii regions in 20 nearby large galaxies (Kong et al. [14]). The 2.16 m telescope equips the Optomechanics Research Inc. (OMR) long-slit spectrograph with a TEKTRONIX TEK1024, AR-coated back-illuminated CCD. A 200 Å/mm dispersion grating, blazed at ∼5500 Å, was used in the spectrograph with a -length slit, providing a dispersion sampling of 4.8 Å per pixel and a spectral resolution of 500–550 in at 5000 Å with a wavelength coverage of 3500–8000 Å (Fan et al. [20]).
The long-slit spectroscopic observations were carried out over several nights from January 2007 to December 2008 (Kong et al. [14], Mao et al. [18]). During the observing runs, the slit width was set to to match the average local seeing disk. The position angle of the long slit was oriented to cross as many H ii regions as possible at one exposure frame. The exposure time for each slit position was 1800 s × 2 or 1200 s × 3 to achieve a suitable signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio. Instrument bias and dome flats were recorded at the beginning and the end of each night. A He-Ar lamp was observed immediately after observing each object at the same position for wavelength calibration. Spectrophotometric standard stars including Feige 34 and He 3 (Corbin and Warren [21]) were observed in each night for flux calibration. Table 1 lists statistics of the observations. The orientations of the spectrographic slit and the locations of the H ii regions are shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Observations.

Figure 1.
(Left panel): H narrow-band image for NGC 2403 taken with the 2.1 m telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory, with the coverages of the spectrographic slit (red solid lines) superimposed. The information of each of the slit coverages are listed in Table 1. (Right panel): The same image as the left panel but with H ii regions studied in this work marked by different symbols in different colors; the H ii regions observed with the 2.16 m telescope at NAOC are marked with red open circles; those collected from other studies are colored in green and symbolized as listed in the lower-right corner of the panel. The scale in the bottom right corner in the left panel indicates the 4 arcmin length which is the same in the right panel. In each of the panels, north is up, and east is to the left.
2.2. Data Reduction
Data reduction was conducted using PyRAF 2.2.0, a Python-based interface to IRAF V2.17,2 employing the CCDRED, TWODSPEC, and ONEDSPEC packages. The conventional routine including bias removal, flat-field correction, and cosmic-ray rejection was implemented in the two-dimensional (2D) data in the form of a space–dispersion plane. One-dimensional spectra were extracted using apertures, corresponding to the ∼154 pc local scale (by taking the distance ∼ Mpc addressed in Tully et al. [15] into account). These apertures were placed along the spatial axis in the spatial–dispersion plane of the 2D spectra to extract the H ii region profiles. When placing the apertures, we prioritized centering them on the peaks of the H emission, provided that adjacent apertures would not overlap. In cases where two nearby H peaks were closely spaced, we slightly shifted the aperture centers to avoid overlap, while still ensuring coverage of the emission peaks.
Spectral trajectories along the dispersion were traced by sampling and fitting continuum points with certain tracing function; the continuum points were obtained by summing enough dispersion lines; for some H ii regions with very weak continua, spectra for the standard stars were used as reference for tracing the dispersion trajectories. Background levels were estimated in blank areas along the spatial axis of the 2D data and subtracted from the spectra of the objects during the spectral extraction process.
For each of the extracted spectra, the dispersion scale was calibrated to wavelength by referencing the emission-line spectra of the He-Ar lamp. Flux calibration was performed by adopting the spectra of the spectrophotometric standard stars and the atmospheric extinction curve at the XingLong station. During our observations, the air mass ranged from 1.105 to 1.159 (mean 1.120). A fixed slit width was adopted to match the average seeing of (Fan et al. [20]). The slit was not oriented at the parallactic angle in order to maximize target coverage. Following Filippenko [22], we estimated differential atmospheric refraction (DAR) offsets at to be at and at , relative to 5000 Å. At , the offsets were and , respectively. Because the slit width direction was not always perpendicular to the atmospheric dispersion direction, the actual centroid shifts were smaller than the full DAR. At 3721 Å, all DAR-induced shifts were substantially smaller than both the local seeing and the slit width. Consequently, no DAR or slit-loss corrections were applied in this work. All of the calibrated spectra were corrected for galactic foreground extinction, by utilizing the Cardelli et al. [23] (hereafter denoted as CCM) extinction curve and the total-to-selective extinction ratio . The color excess of the galactic extinction mag for NGC 2403 was obtained from the Schlegel et al. [24] galactic dust map and applied to the correction.
2.3. Emission-Line Measurements
The STARLIGHT software (Cid Fernandes et al. [25]) was employed to reproduce the underlying stellar continuum, for the purpose of subtraction the continuum from each of the calibrated spectra to obtain sole emission-line spectra. Before the continuum fits, all of the observed spectra were corrected for redshift (shifted to the rest frame) and resampled to 1 Å per pixel using the SpectRes code (Carnall [26]), suiting the requirement of STARLIGHT. The model was composed of simple stellar populations (SSPs) selected from the Bruzual and Charlot [27] spectral library of stellar population synthesis, encompassing 75 ages spanning from 1 Myr to 18 Gyr and 3 metallicities (Z = 0.008, 0.02, 0.05), on the basis of the Chabrier [28] initial mass function (IMF) and the Padova 1994 evolutionary tracks (Le Borgne et al. [29]). Dust attenuation was imposed on the model spectra with the CCM extinction law taken into account. The fits for the observed spectra were performed through a -minimization approach using the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm, and the best-fit model spectra were obtained.
Emission-line fluxes were measured in the continuum-subtracted spectra via Gaussian-profile fits. Each of the emission lines [O ii, H, and [O iii was fitted with a single Gaussian profile; the three blended lines [N ii + H as well as the two blended lines [S ii were deblended by fitting them with multiple Gaussian components. The flux ratio of [O iii to [O iii was fixed to 1:3, and so was [N ii to [N ii.
Uncertainties of the emission-line fluxes were estimated using the expression in Mao et al. [18], Gonzalez-Delgado et al. [30]:
where is the standard deviation of the continuum close to the emission line, is the number of pixels covering the measured emission line, is the equivalent width of the emission line, and is the dispersion in units of Å/pixel.
The measured emission-line fluxes were corrected for dust attenuation using the Balmer decrement, following the prescription in Calzetti [31]:
where is the observed -to- flux ratio, is the assumed intrinsic -to- flux ratio ratio in accordance with the Case B recombination at the electron temperature and the electron density (Osterbrock and Ferland [32]), and are quoted from the CCM extinction law.
The attenuation-corrected fluxes for the emission lines are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Attenuation-corrected emission-line fluxes.
2.4. Ancillary Data from the Literature
Complementary with the observed spectra, we additionally compiled a dataset of spectral emission lines for 104 H ii regions in NGC 2403 from the literature, all of which have been corrected for dust attenuation. Specifically, the supplementary sample contained 6 H ii regions collected from McCall et al. [33], 5 H ii regions collected from Fierro et al. [34], 12 H ii regions collected from Garnett et al. [35], 9 H ii regions collected from Bresolin et al. [36], 3 H ii regions collected from Garnett et al. [37], 17 H ii regions collected from van Zee et al. [38], 7 H ii regions collected from Berg et al. [39], 12 H ii regions collected from Mao et al. [18], and 33 H ii regions collected from Rogers et al. [40]. The spatial locations for these H ii regions along with the observed ones are all shown in Figure 1.
For the common H ii regions observed in this work and collected from other studies, we compared the emission-line fluxes, and the result is shown in Figure 2. Most of the data points were enveloped within the ( dex) demarcation, which verified the consistency of the data. Differences between the apertures in size and position for extracting the spectra for the same H ii regions in the different studies were considered to be a general source of the deviation. Specifically, a few of [O ii and [S ii lines deviated to a relatively large extent, which was ascribed to influences of different noise levels at the blue end of the spectra on [O ii and different deblending qualities for [S ii doublets, respectively.
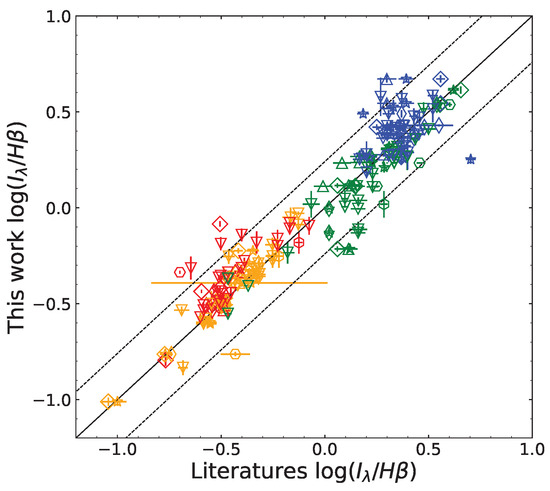
Figure 2.
Comparison between the emission-line fluxes for the same H ii regions measured in this work and those quoted from other studies, including McCall et al. [33], Fierro et al. [34], Garnett et al. [35], Bresolin et al. [36], Garnett et al. [37], Mao et al. [18], and Rogers et al. [40]. The emission lines include [O ii] 3727 (blue), [O iii] 4959,5007 (green), [N ii] 6584 (yellow), and [S ii] 6717,6731 (red), and they are normalized by H. The data points are marked using the same symbols as in Figure 1. The line of unity is represented as the black solid line. The ( dex, i.e., the standard deviation of the data) range are enveloped by the black dotted lines.
3. Photoionization Model
We adopted model grids developed by Levesque et al. [12], which combine the STARBURST99 stellar population synthesis model (Leitherer et al. [41], Vázquez and Leitherer [42]) with the MAPPINGS III photoionization model (Sutherland and Dopita [43], Allen et al. [44]). In this work, ionizing stellar populations were modeled by assuming star formation history of an instantaneous burst in the range 0–9.5 Myr with the step length 0.5 Myr in age, 5 metallicity values including Z = 0.001, 0.004, 0.008, 0.02, and 0.04 (corresponding to 0.05, 0.2, 0.4, 1, and 2 ), and the Geneva “High” mass-loss star evolutionary tracks (Schaller et al. [45], Schaerer et al. [46], Charbonnel et al. [47], Schaerer et al. [48]; recommended in Levesque et al. [12]).
Ionized gaseous nebulae were configured in a parallel-plane geometry. The ionization parameter q at the inner surface of the nebulae was set to spanning , , , , , , . The gas-phase metallicity matched with that of the model stellar populations. The electron density was chosen in accordance with the low-density limit for H ii regions in NGC 2403 (Garnett et al. [35], Berg et al. [39], Rogers et al. [40]).
4. Results
Strong emission lines in optical spectra for ionized gaseous nebulae encode a wealth of information and serve as effective diagnostics for a series of physical parameters. In this section, we present results of diagnoses from a series of strong-line indices for the H ii regions in NGC 2403 and in turn inspect influences of underlying parameters on the emission lines.
4.1. BPT Diagram
The diagnostic diagram of the indices [O iii versus (vs.) [N ii proposed by Baldwin, Phillips, and Terlevich (denoted as BPT, Baldwin et al. [49]) is a powerful tool for classifying emission-line objects into active galactic nuclei (AGNs), low-ionization-emission regions (LINERs), or star-forming regions (Kewley et al. [50], Kauffmann et al. [51]). Figure 3 is the BPT diagram for the H ii regions in NGC 2403, with the 0.0 Myr model grid as well as the Kewley et al. [50] and Kauffmann et al. [51] demarcation curves for the classification superimposed. Almost all of the points are consistent with the Kauffmann et al. [51] curve, and only one falls between the Kauffmann et al. [51] and Kewley et al. [50] curves, indicating that nearly all samples originate from star formation activity. By comparing the color-coded data points with the model grid, the data locus in the BPT diagram reflects a sequence of metallicity or/and the ionization parameter varying with the galactocentric distance and suggests a correlation of the two indices with both metallicity and the ionization parameter.

Figure 3.
as a function of (the BPT diagram) for the H ii regions in NGC 2403 with the Levesque et al. [12] model grid (the constant age 0 Myr, variations in the metallicity Z (in units of ), and the ionization parameter q) superimposed. The data points are marked using the same symbols as in Figure 1 and color-coded by the galactocentric distance (de-projected) in units of . The criteria for classifying ionizing sources (stars and AGNs) are quoted from Kewley et al. [50] (black dotted line) and Kauffmann et al. [51] (black solid line).
4.2. Metallicity Estimates
The oxygen abundance for the H ii regions in NGC 2403 was estimated for assessing the metallicity. There are a number of recipes for obtaining the oxygen abundance but considerable discrepancies among them, leaving an important challenge in metallicity studies (Maiolino and Mannucci [2], Kewley et al. [3], Mao et al. [18], Kewley and Ellison [52]). In this work, we adopted four widely used empirical diagnostics for estimating oxygen abundance. They are described as follows.
(Pettini and Pagel [6]):
where ;
(Pettini and Pagel [6]):
where ;
(Bresolin [8]):
where .
From the above diagnostics, we estimated the oxygen abundances for the H ii regions in NGC 2403, whose radial profiles are displayed in Figure 4, with the best-fit linear curves superimposed. The uncertainty of the slope was quantified as a standard deviation derived from bootstrapping the sample 3000 times, and the corresponding fit parameters are listed in Table 3. A negative gradient is obviously seen from each of the profiles, consistent with the inside-out scenario of galaxy evolution. However, differences in gradient slope and data dispersion between these radial profiles are evident and imply greater complexity for the emission-line indices, which inevitably affects and biases relevant studies based on metallicity gradients derived from these recipes.
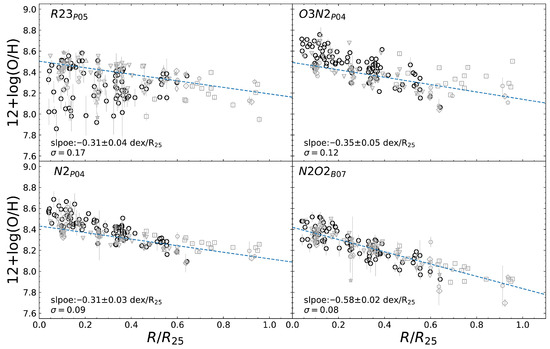
Figure 4.
Radial distributions of the oxygen abundance derived from the indices ((top-left panel), the calibration is addressed in Pilyugin and Thuan [7] and denoted as ), ((top-right panel), the calibration is addressed in Pettini and Pagel [6] and denoted as ), ((bottom-left panel), the calibration is addressed in Pettini and Pagel [6] and denoted as ), and ((bottom-right panel), the calibration is addressed in Bresolin [8] and denoted as ) for the H ii regions (represented by the same symbols as assigned in Figure 1) in NGC 2403 with the weighted linear best-fit curves (cyan dashed lines) superimposed. The fitting parameters are compiled in Table 3.

Table 3.
Fitting parameters of radial metallicity distribution.
4.3. Index–Index Diagrams
In order to inspect the emission-line indices in more depth, we carried out a series of diagnoses by diagramming relations of the indices for the data in combination with the model grids. These diagnoses result in a further understanding of not only underlying parameters in the observed features but also more properties for the H ii regions in NGC 2403. In this section, the emission-line indices inspected in the diagnoses included the metallicity indicators , , , and . As a widely used proxy of the ionization parameter, (≡ [O iii) was also employed in our work for specially tracing ionization states.4
4.3.1. Diagnosis at Fixed Age
Figure 5 shows the interrelations between , , , , and , with the model grid reflecting the initial situation (i.e., the 0 Myr age) superimposed in each of the panels. As illustrated in these diagrams, among the four metallicity indicators, the correlation with is strong for and (Pearson coefficients and , respectively), moderate for (), and weak for (). Different levels of degeneracy of metallicity and the ionization parameter in the different indices are disclosed by the model grids. Specifically, for constant values of metallicity, increases monotonically with the ionization parameter, whereas decreases at higher ionization states with a slight curvature; dependence of on the ionization parameter appears complicated, with two opposite trends to the low- and high-metallicity ends, similar to the so-called double-value effect of on its estimates of the oxygen abundance; by contrast, stays robust against variations in the ionization parameter, as manifested by the extensive model grid and the widespread data distribution in the - diagram in Figure 5. This result verifies the non-negligible sensitivities of and to the ionization parameter, as well as the reliability of for estimating metallicity, particularly at variable ionization states. The sensitivity of to the ionization parameter was inherently weaker than that of and ; furthermore, the correction for the ionization influence was taken into account in the calibration (Pilyugin and Thuan [7]).

Figure 5.
Interrelations between every two indices among , , , , for the H ii regions in NGC 2403, with the Levesque et al. [12] model grid (the constant age of 0 Myr, variations in metallicity Z (in units of ) and the ionization parameter q) superimposed. The data points are marked using the same symbols as in Figure 1 and color-coded the same as in Figure 3. The rate of the data covered by the model grid (defining the number ratio of the data points falling within the grid to the total of the data points, denoted as the coverage rate or “CR”) is presented in the lower-right corner in each of the panels. Histograms of the indices are also shown.
Nonetheless, the data points from the outer part of the galaxy () lie in the conjunction zone of the higher and lower branches of the calibration and thus appear with dispersion in the -based estimates of metallicity. For the H ii regions located in the inner area of the galaxy (), even larger dispersion emerges in the -based estimates of metallicity (see the top-left panel of Figure 4). This is likely due to an inherent problem in the Pilyugin and Thuan [7] calibration. We found these data points in possession of lower excitation levels (quantified by the excitation parameter P as defined in Equation (3)). As pointed out in Moustakas et al. [56], the R23 calibration lacks sufficient low-excitation () data, which prevents its good performance in such a regime and thereby induces the dispersion in estimates of metallicity.5
The metallicity diagnostic is based on the relation of – at high metallicity, where secondary nitrogen production leads to a correlation between and (Maiolino and Mannucci [2], Kewley and Dopita [9]). For NGC 2403, Berg et al. [39] found that within (our estimate), and exhibited a tight linear correlation, without the plateau characteristic of primary nitrogen production. Together with its insensitivity to the ionization parameter and immunity to the double-valued degeneracy, this supports the robustness of as a metallicity indicator.
As a consequence, among the four panels in Figure 4, the metallicity estimated from shows the most reliable radial metallicity gradient for NGC 2403, with a slope of dex , a dispersion of dex, and a coefficient of determination of .
Comparison of the data distribution with the model grid in each of the index–index diagrams in Figure 5 manifests different extents of coverage of the model to the data points. Specifically, there are approximately 93–94% of the data points covered by the model grid in each of the -, -, and - diagrams, about 84% in the – diagram, and around 60% or even less in the - and -relative diagrams. The model appears to characterize the data well in the -, -, -, and – diagrams but not in the others. In each of the - and -relative diagrams, the data locus fails to follow the bending regime of the model grid but keeps a more linear trend in the plane. As a result, some of the data points exceed the model coverage, and they are the H ii regions located in the outskirts of NGC 2403.
4.3.2. Diagnosis with Age Evolution
The model grids in Figure 3 and Figure 5 were established at the fixed age of 0 Myr (in an initial situation) for the purpose of eliminating effects of age but specially focusing on behaviors of metallicity and the ionization parameter. As a matter of fact, emission lines are supposed to tightly relate with the age of ionizing stellar populations, due to a decrease in the number of ionizing photons when stellar populations age. With the diagrammatic diagnosis independent of age worked out above, we conducted modeling of the spectral indices by varying the age (range of 0–9.5 Myr) in this section, to inspect the age evolution of the index–index relationships, whose results are shown in Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 and Appendix A. The coverage rates for all diagnostic diagrams are summarized in Table 4.
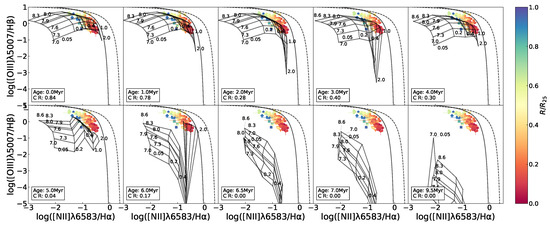
Figure 6.
BPT diagrams for the H ii regions in NGC 2403 with the Levesque et al. [12] model grids (constant age, variations in metallicity Z (in units of ) and the ionization parameter q in each of the panels) superimposed. The data points and the dotted and solid lines have the same meaning in all of the panels as in Figure 3). In the different panels, the model grids vary with the age ranging from 0 to 9.5 Myr (This only shows part of the age grid as a representative.) The age and the CR (the same definition as in Figure 5) are listed in the lower-right corner in each of panels. The data points are marked using the same symbols as in Figure 1 and color-coded the same as in Figure 3.
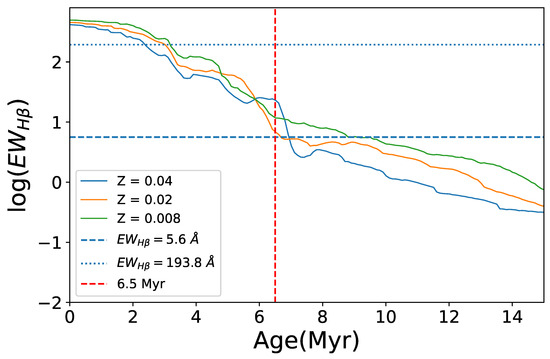
Figure 7.
Constraints on the stellar population age derived from the equivalent width of the emission line (). The model curves show –age relations for instantaneous bursts at different metallicities from the STARBURST99 model (Leitherer et al. [41]) using the publicly available 1999 dataset downloaded from the official website. Horizontal dotted and dashed lines mark the observed maximum and minimum values of the emission lines across the galaxy. The red vertical line indicates the 6.5 Myr upper-age limit inferred from the BPT diagram coverage. The minimum value is found in the central, higher-metallicity region, consistent with an age of ∼7 Myr (Z = 0.02).
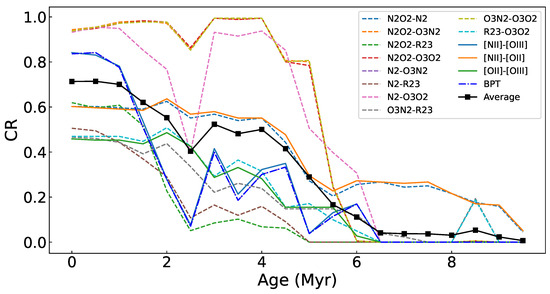
Figure 8.
The CR (the same definition as in Figure 5) of the model grid as a function of the age ranging from 0 to 9.5 Myr, for the diagrams in Figure 3, Figure 5 and Figure 10. The dashed lines are color-coded by specific index–index relations with the legend displayed in the top-right corner. The black filled boxes connected by the black solid line represent the average evolution of the CR among all of the diagrams.
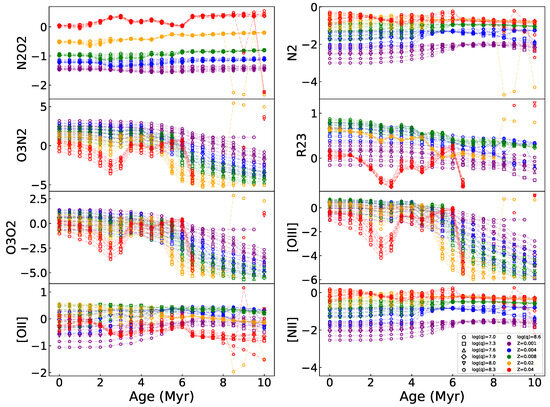
Figure 9.
Spectral index or H-normalized emission lines of [O iii], [N ii], and [O ii] (hereafter referred to as [O iii], [N ii], and [O ii], respectively) as a function of age reproduced by the Levesque et al. [12] model. In each of the panels, the model products are color-coded by metallicity and symbol-coded by the ionization parameter, with the legend listed in the lower-left corner in the bottom-right panel.

Table 4.
Coverage rates of diagnostic diagram.
Figure 6 shows a modeled evolution of the BPT relationship superimposed on the observed data. The most apparent behavior of the model grid is a progressive downward shift with aging, i.e., an intensive decline in [O iii relative to a weak change in [H ii. It is because the [O iii] emission lines are more preferentially excited at a higher degree of ionization, in contrast to the emission lines associated with low-ionization environments (Kewley et al. [3], Osterbrock and Ferland [32]); with the aging of stellar populations and resultant softening of stellar radiations, H ii regions have lower ionization states and more delicate [O iii] excitation. A direct aftermath of the change in the spectral features is a decrease in the coverage rate of the model to the data in the diagram. The model grids with 0–1 Myr cover ∼80% of the data points, but the coverage rate rapidly reduces to <30% at ≥2 Myr and 0% (no coverage) at ≥ Myr. The total separation of the model grid from the observed data suggests the upper age limit ∼ Myr for the H ii regions in NGC 2403 under this framework. We further cross-checked the age constraint using the equivalent width of () as predicted by the Starburst99 models for instantaneous bursts (Leitherer et al. [41]), based on the 1999 dataset from the official website6. For each metallicity, we compared the model –age relations with the observed maximum and minimum values in Figure 7. The smallest was found in the central high-metallicity regions, corresponding to an age of ∼7 Myr (for ) in the models. Given that the observed continuum contains contributions from the underlying stellar populations of the galactic disk in addition to the H iiregions, the measured is likely underestimated, thus biasing the age estimate toward older values. Taking this effect into account, the upper limit of ∼ Myr inferred from the BPT coverage remains a reasonable estimate.
Combining Figure 3, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3, Figure A4, Figure A5, Figure A6, Figure A7, Figure A8 and Figure A9, we find that a few of the data points from the central area of the galaxy are missed by the 0 Myr model but covered by the 2–6 Myr grids, which indicates an older stage for these H ii regions than others in the sample. It is interesting that at the 3–6 Myr evolution phase, the model grids emerge with peculiar fluctuation at the high-metallicity part, which is ascribed to an influence of Wolf–Rayet (W-R) stars on the [O iii] emission lines (Levesque et al. [12]).
Variations in the model coverage to the observed data in the index–index diagrams with age are shown in Figure 8, with an evolutionary trend of the average coverage among all of the diagrams superimposed. We can see that in general, for almost all of the diagrams, the model coverage stands at the highest levels at 0–1 Myr but drops sharply at 2–6 Myr and is lowest after 6 Myr. The highest coverage rates differ between the various diagrams by ∼50% at most. All of the -relative diagrams possess the coverage rate ≤. It is suspected that the model grids are likely to have some problem in reproducing the [O ii emission line or/and sampling the parameter spaces, which is discussed in Section 5.2. By contrast, the - and - curves maintain high coverage rates for a long period (≥4 Myr timescale), because the ionization parameter and metallicity are more effectively decoupled in the two diagrams, leading to larger areas of the model grids with higher possibilities for covering the data points. After 6 Myr, the coverage rate for most of the diagrams decreases to <10%, except for - and [N ii]-[O ii], which are able to keep ∼ coverage rate after 6 Myr. This is because the [O ii] and [N ii] emission lines are low-ionization emission lines not as sensitive to age as others, which is depicted in Figure 97.
By modeling , , , , , [O ii], [O iii], and [N ii] at a variety of values for metallicity, the ionization parameter, and stellar population age addressed in Levesque et al. [12], Figure 9 reproduces the age evolution of the spectral indices and the emission line ratios, at each constant metallicity and ionization parameter, respectively, as an underlying factor interpreting the above features in the diagrams (Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 10, Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3, Figure A4, Figure A5, Figure A6, Figure A7, Figure A8, Figure A9, Figure A10, Figure A11, Figure A12, Figure A13, Figure A14, Figure A15, Figure A16, Figure A17 and Figure A18). We can see from the evolutionary tracks that the indices and are the least sensitive to age; even appears invariant with respect to the ionization parameter in the whole age range of 0–10 Myr, suggesting negligible degeneracy (if any) of metallicity, ionization parameter, and stellar population age in these indices, but jointly depends on both metallicity and ionization parameter for H ii regions during the first 6 Myr.
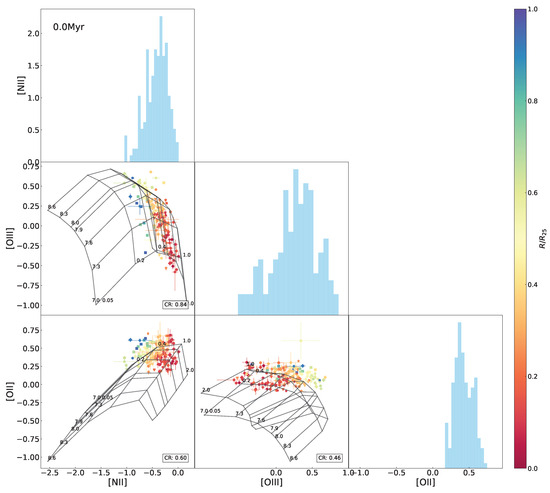
Figure 10.
Interrelations between every two emission-line ratio (normalized by H) among [O ii], [N ii], and [O iii] for the H ii regions in NGC 2403, with the Levesque et al. [12] model grid (constant age of 0 Myr, variations in metallicity Z (in units of ) and the ionization parameter q) superimposed. The data points are marked using the same symbols as in Figure 1 and color-coded the same as in Figure 3. The CR (same definition as in Figure 5) is presented in the lower-right corner in each of the panels. Histograms of the indices are also shown.
The tracks gradually decline with age at lower metallicity than the solar value () but fluctuate conspicuously in the 3–6 Myr range at higher metallicities (); is also sensitive to both metallicity and ionization parameter, similar to but spanning the whole 0–10 Myr range. is similar to in terms of age tracks but more dependent on the ionization parameter than metallicity, and this is the reason for this index being commonly adopted as an ionization proxy. The index exhibits a weak declining trend with age and a decreasing sensitivity to the ionization parameter as metallicity increases. The fluctuation in the 3–6 Myr range is a noticeable feature in all of the tracks for , , and at the metallicity , coincident with the [O iii] tracks at the same age and metallicity. As explained above, this feature is caused by the influence of W-R stars on the [O iii] emission line, which results in the peculiar behaviors of the 3–6 Myr model grids in all of the [O iii] relative diagrams and has potential impact on observed data loci in this special age interval. The relation with age is strong for [O iii] but weak for [O ii] and [N ii] emission lines, which suggests strong age dependence of and but insensitivity to and .
5. Discussion
5.1. Effects of Apertures
Differences in position and size of apertures for spectral extraction have much potential to introduce extra uncertainties in the measurements. The specific effects of apertures on different emission lines and different spectral indices are suspected to be different. For instance, higher-ionization emission lines such as [O iii] tend to be more compact and concentrated in central parts of H ii regions, whereas lower-ionization emission lines such as [O ii] and [N ii] often extend over a wider scale (Kewley et al. [3]); for the behaviors of spectral indices, spatially resolved observations of large H ii regions have revealed that peaks around the nebular centers, while is relatively invariable across different locations within the H ii regions (Mao et al. [18]).
As a consequence, if apertures are more centrally placed, they are more likely to capture stronger [O iii] emission lines, leading to higher values for . By contrast, larger apertures enclosing more outer areas of H ii regions are more likely to extract stronger [O ii] and [N ii] emission lines and hence obtain a decrease in or .
5.2. Potential Limitation in the Model on the [O ii] Emission Line
In the above results, the model fails to adequately fit the observed data in the - diagram as well as -relative diagrams, particularly for the H ii regions located in outskirts of the galaxy with relatively low metallicities. In order to find an interpretation, we further inspected line–line diagrams, as shown in Figure 10. We can see that the model grid covers almost all of the data points in the [O iii-[N ii diagram but only one half in the [N ii–[O ii and [O iii–[O ii diagrams. Variations in age are sufficient to account for the low coverage in the [N ii–[O ii and [O iii–[O ii diagrams (see Figure 8).
The parameter space of metallicity and the ionization parameter in the model, in principle, is supposed to cover the observed data. It is unclear whether the failure of the coverage in the [O iii–[O ii diagram is caused by inadequate sampling resolution or other inherent limitations in the model. From the [N ii–[O ii diagram, we can affirm that the Levesque et al. [12] model grids are unable to reproduce the observed lines at low metallicity end typically in the galactic outskirts. Specifically, for a given [N ii, the model fails to reproduce a sufficient range of [O ii intensities to match the observed data. This limitation also provides an interpretation of the lack of model coverage in the – diagrams as presented above. Indeed, generation of certain emission lines in photoionization modeling is an intrinsically complicated mechanism. In addition to metallicity, the ionization parameter, and gas density, many other parameters, such as the shape and the intensity of ionizing radiation field, as well as the gas geometry and physics, play critical roles in predicting emission lines.
5.3. Impact of Rotation of Stars or Binary Populations
Spectral types of ionizing sources are a dominant factor for determining emission lines in photoionization processes and dependent on several assumptions in stellar population synthesis such as initial mass function, star formation history, stellar evolutionary tracks, stellar rotation, binary-population interactions, etc. It is mentioned in Levesque et al. [12] that the model is likely to require harder spectra to create sufficient ionizing fields and yield enough [S ii] to successfully reproduce observed data. In this case, rotation of stars is suggested to achieve this. The stellar rotation is expected to create harder ultraviolet spectra for a longer period of time (Levesque et al. [57], Dorn-Wallenstein and Levesque [58]). Alternatively, binary stars are another possible requisite for maintaining hardness of ultraviolet radiation despite aging stellar populations (Stanway et al. [59]). Binary stellar population models make it possible to continuously reproduce observed data after 10 Myr in the BPT diagram and those at low metallicity or high redshifts in the [O iii]-[S ii] diagram (Xiao et al. [13], Zhang et al. [60]).
6. Summary
In this paper, we presented an investigation of spectral emission-line characteristics of H ii regions in the nearby spiral galaxy NGC 2403. Spectroscopic observations were taken with the 2.16 m telescope at the National Astronomical Observatories of China, with supplementary data collected from the literature. As a consequence, a total of 188 H ii regions in NGC 2403 were compiled in the final sample. A combined model of photoionization and stellar population synthesis was employed for comparing and interpreting the observed data.
Through the BPT diagnosis, nearly all of the samples were confirmed to originate from stellar irradiation and hence classified as star-forming regions. Radial profiles of metallicity for NGC 2403 were obtained by applying the four widely used strong-line diagnostics, , , , and , respectively, and all of them exhibited negative gradients, reflecting an inside-out evolution process for this galaxy, but the slopes and the dispersions of the gradients were different. resulted in the gradient with the steepest slope and the least dispersion, while the and indicators yielded the flattest gradients, and exhibited the largest dispersion.
Via a series of diagrammatic inspections on the four spectral indices , , , and , as well as individual emission lines within them, we demonstrated strong sensitivities of and to the ionization parameter; was comparatively less sensitive to the ionization parameter but had a double-value effect which was especially influential for the H ii regions in NGC 2403; appeared to be the most robust diagnostic, in monotonic correlation with metallicity and with negligible sensitivity to the ionization parameter. By inspecting the individual emission lines, we disclosed that the [O iii] emission line was strongly related with the age of ionizing stellar populations, in contrast to the [O ii] or [N ii] emission line in relatively weak relation with stellar population age. As a consequence, the indices and involving the [O iii] emission line were dependent on stellar population age, while and were less affected by stellar population age, but the influence of the ionization parameter on became more serious for young stellar populations (≲6 Myr). Thus, is suggested to more reliably indicate metallicity than the other three diagnostics. Furthermore, within the adopted photoionization model framework, the grid corresponding to an age of 0–1 Myr provided the best overall match to the observational data, whereas models older than 6.5 Myr showed poor agreement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.-M.W. and Y.-W.M.; Methodology, Q.-M.W. and Y.-W.M.; Software, Q.-M.W.; Validation, Q.-M.W. and Y.-W.M.; Formal analysis, Q.-M.W.; Investigation, Q.-M.W. and Y.-W.M.; Resources, Y.-W.M. and L.L.; Data curation, Q.-M.W., Y.-W.M. and S.-T.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.-M.W. and Y.-W.M.; writing—review and editing, Q.-M.W., Y.-W.M., L.L., H.Z. and S.-T.W.; Visualization, Q.-M.W.; Supervision, Y.-W.M.; Project administration, Y.-W.M.; Funding acquisition, Y.-W.M., L.L. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFA1602902), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Nos. U2031106, U2031201, 12120101003, and 12373010), China Manned Space Project (Nos. CMS-CSST-2025-A06 and CMS-CSST-2021-B04), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (id. 2022260).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support of the staff of the Xinglong 2.16 m telescope. This work was partially supported by the Open Project Program of the Key Laboratory of Optical Astronomy, National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences. This research has made use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED) which is funded by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and operated by the California Institute of Technology; this research has also made use of the SAO/NASA’s Astrophysics Data System Bibliographic Services.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
Appendix A. Index–Index Diagrams with Age Evolution
In this appendix, we present the index–index diagrams and the line–line diagrams, with the model grids at different ages superimposed, corresponding to the analysis in Section 4.3.2. The index–index diagrams are shown in Figure A1, Figure A2, Figure A3, Figure A4, Figure A5, Figure A6, Figure A7, Figure A8 and Figure A9, and the line–line diagrams are shown in Figure A10, Figure A11, Figure A12, Figure A13, Figure A14, Figure A15, Figure A16, Figure A17 and Figure A18.
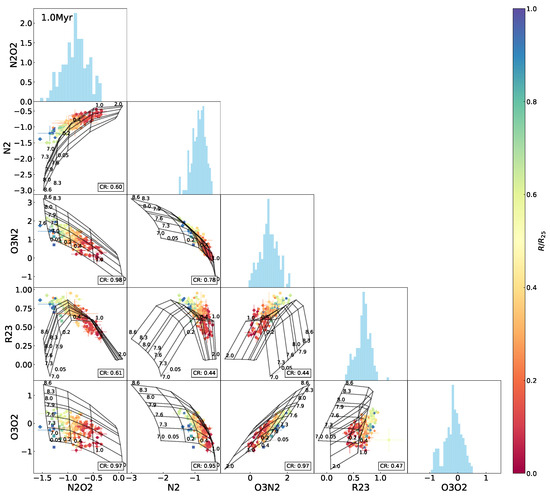
Figure A1.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 1.0 Myr model grids.
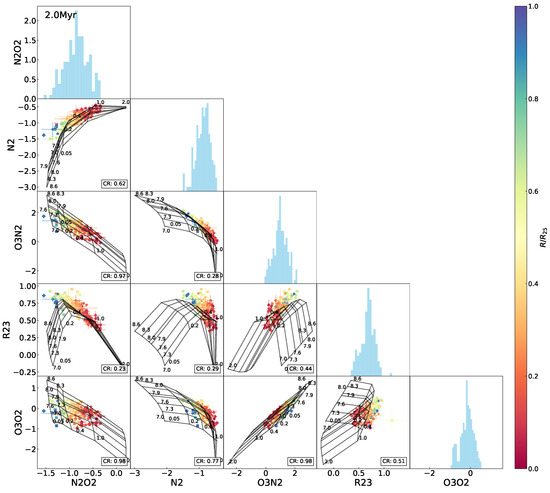
Figure A2.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 2.0 Myr model grids.

Figure A3.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 3.0 Myr model grids.
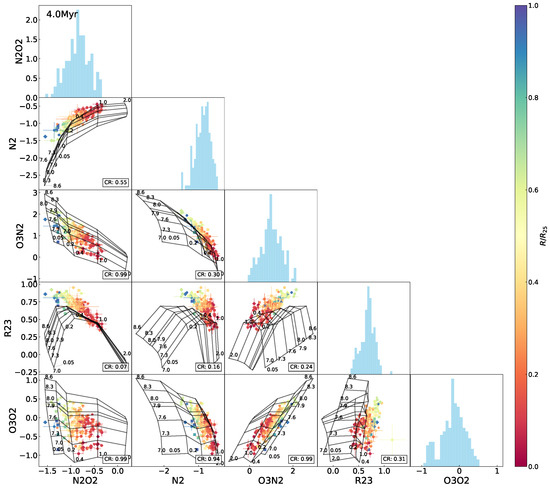
Figure A4.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 4.0 Myr model grids.

Figure A5.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 5.0 Myr model grids.
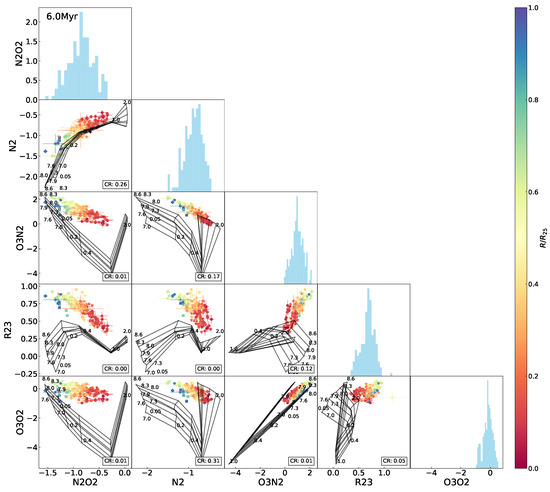
Figure A6.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 6.0 Myr model grids.
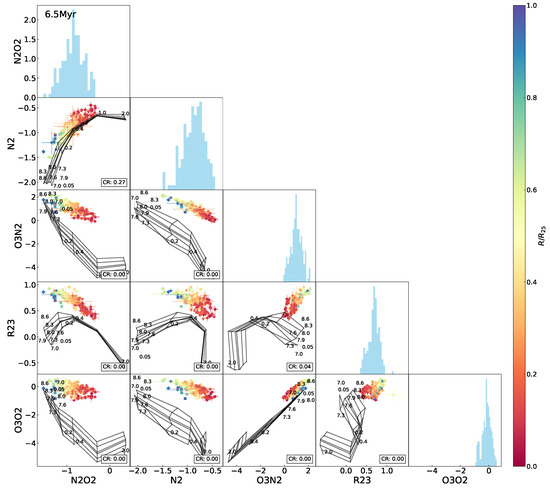
Figure A7.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 6.5 Myr model grids.
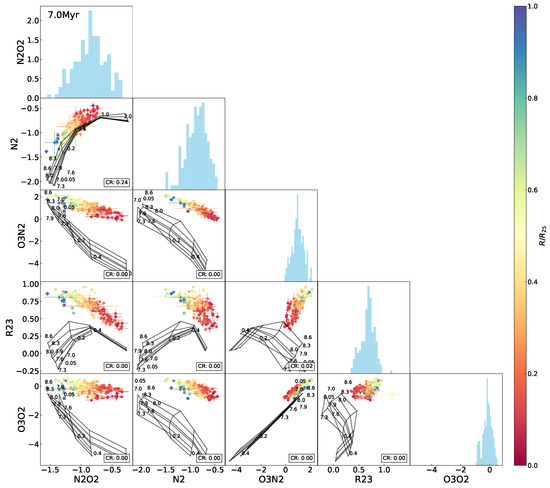
Figure A8.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 7.0 Myr model grids.

Figure A9.
The same as Figure 5 but superimposing the 9.5 Myr model grids.
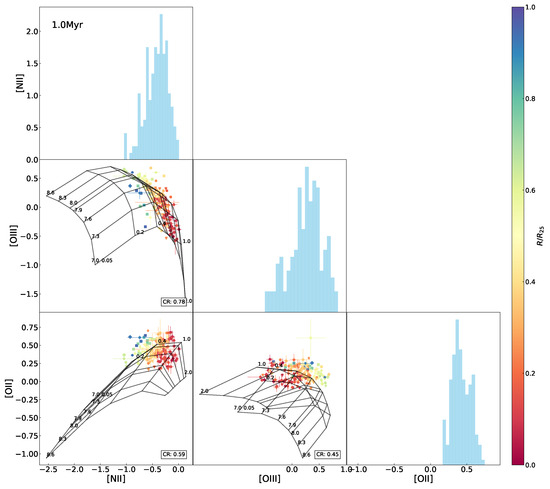
Figure A10.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 1.0 Myr model grids.
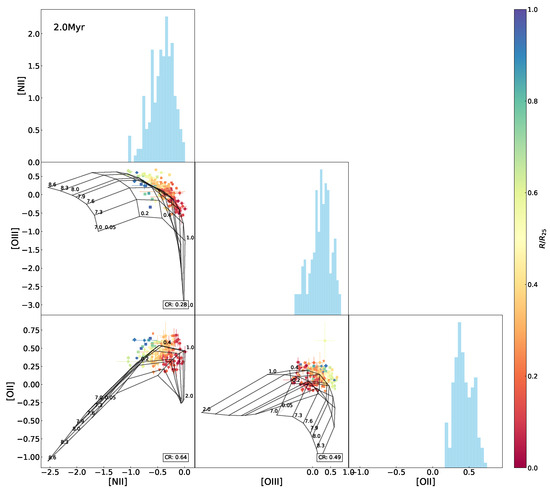
Figure A11.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 2.0 Myr model grids.
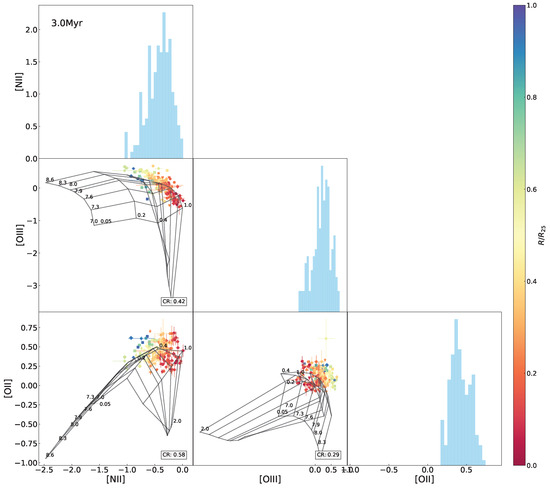
Figure A12.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 3.0 Myr model grids.
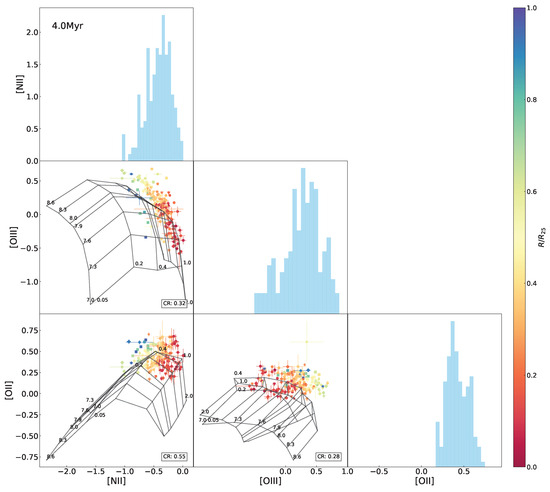
Figure A13.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 4.0 Myr model grids.
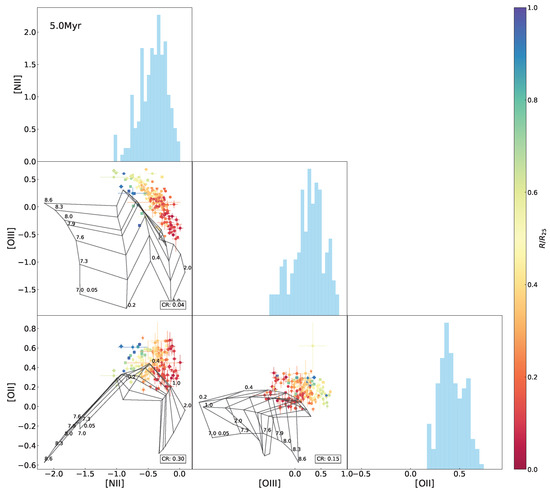
Figure A14.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 5.0 Myr model grids.
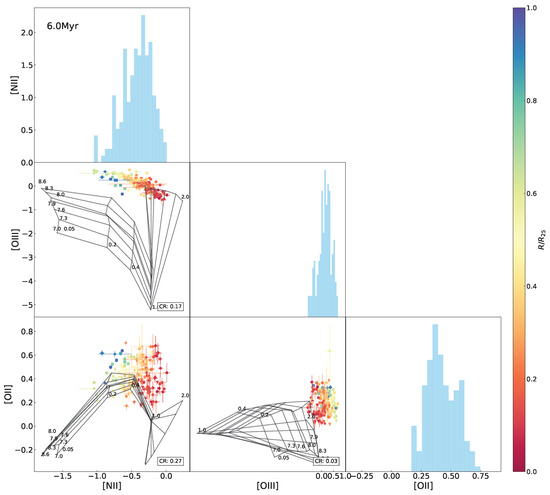
Figure A15.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 6.0 Myr model grids.
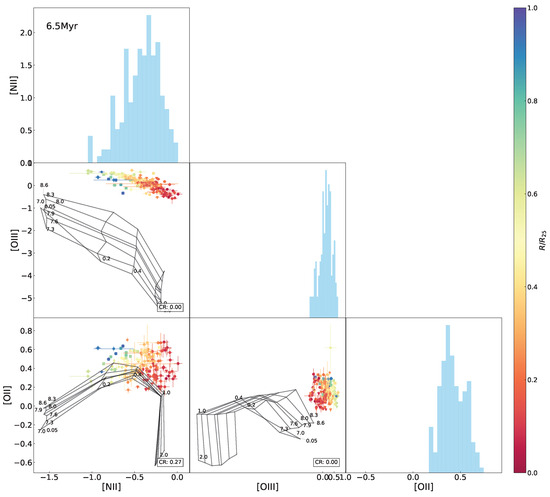
Figure A16.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 6.5 Myr model grids.
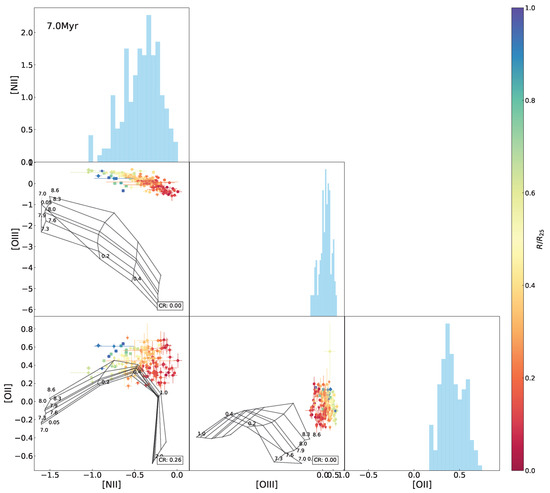
Figure A17.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 7.0 Myr model grids.
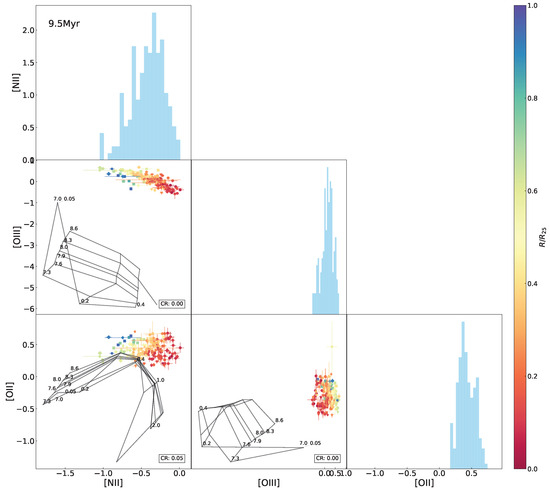
Figure A18.
The same as Figure 10 but superimposing the 9.5 Myr model grids.
Notes
| 1 | [O ii is a sum of the double lines [O ii[O ii, which are hardly resolvable for low-resolution spectroscopy and thus taken as one single line [O ii. |
| 2 | IRAF is distributed by the National Optical Astronomy Observatory, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under a cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation. |
| 3 | The method has a double-value effect. We choose the higher branch in this work, because the H ii regions in NGC 2403 are generally metal-rich according to our initial assessment. |
| 4 | In observational studies, a ratio between two emission lines for a certain ion at different ionization states is usually taken as a proxy of the ionization parameter (e.g., Kewley et al. [3], Mao et al. [18], Relano et al. [53]). The emission-line indices [O iii[O ii (denoted as ) and [S iii[S ii (denoted as Kewley et al. [3], Kewley and Dopita [9], Morisset et al. [10], Dopita et al. [54], Garner et al. [55]) are the most widely used ionization tracers. Owing to the wavelength coverage in our observations, we employed in the diagnoses. |
| 5 | Although the ionization parameter was taken into account, the sensitivity of the Pilyugin and Thuan [7] calibration to the ionization parameter was still found in our further analysis (Li et al., in preparation), which points to the complexity of the index as a reliable or questionable estimator of metallicity. |
| 6 | https://massivestars.stsci.edu/starburst99, accessed on 8 August 2025. |
| 7 | In Figure 9, we note that some of the high-metallicity model points (in red and yellow) exhibit abrupt jumps at older ages. We suspect that these anomalies are artifacts arising from the model calculations. However, since this cannot be confirmed and they do not significantly impact our analysis, we chose to retain them. |
References
- Peimbert, M.; Peimbert, A.; Delgado-Inglada, G. Nebular Spectroscopy: A Guide on H ii Regions and Planetary Nebulae. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2017, 129, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolino, R.; Mannucci, F. De re metallica: The cosmic chemical evolution of galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2019, 27, 1–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewley, L.J.; Nicholls, D.C.; Sutherland, R.S. Understanding Galaxy Evolution Through Emission Lines. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 511–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloin, D.; Collin-Souffrin, S.; Joly, M.; Vigroux, L. Nitrogen and oxygen abundances in galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 78, 200–216. [Google Scholar]
- Pagel, B.E.J.; Edmunds, M.G.; Blackwell, D.E.; Chun, M.S.; Smith, G. On the composition of H II regions in southern galaxies–I. NGC 300 and 1365. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1979, 189, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettini, M.; Pagel, B.E.J. [OIII]/[NII] as an abundance indicator at high redshift. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 348, L59–L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilyugin, L.S.; Thuan, T.X. Oxygen Abundance Determination in H II Regions: The Strong Line Intensities-Abundance Calibration Revisited. Astrophys. J. 2005, 631, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresolin, F. The Oxygen Abundance in the Inner H II Regions of M101: Implications for the Calibration of Strong-Line Metallicity Indicators. Astrophys. J. 2007, 656, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewley, L.J.; Dopita, M.A. Using Strong Lines to Estimate Abundances in Extragalactic H II Regions and Starburst Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2002, 142, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisset, C.; Delgado-Inglada, G.; Sánchez, S.F.; Galbany, L.; García-Benito, R.; Husemann, B.; Marino, R.A.; Mast, D.; Roth, M.M. Photoionization models of the CALIFA H II regions. I. Hybrid models. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.W.; Zhang, Y.; Barlow, M.J. A reexamination of electron density diagnostics for ionized gaseous nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 427, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, E.M.; Kewley, L.J.; Larson, K.L. Theoretical Modeling of Star-Forming Galaxies. I. Emission-Line Diagnostic Grids for Local and Low-Metallicity Galaxies. Astron. J. 2010, 139, 712–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Stanway, E.R.; Eldridge, J.J. Emission-line diagnostics of nearby H II regions including interacting binary populations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 477, 904–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Lin, L.; Li, J.r.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.y.; Chen, F.z.; Du, W.; Fan, Z.; Mao, Y.w.; et al. Spectroscopic Observations of the Star Formation Regions in Nearby Galaxies. Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 38, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, R.B.; Courtois, H.M.; Dolphin, A.E.; Fisher, J.R.; Héraudeau, P.; Jacobs, B.A.; Karachentsev, I.D.; Makarov, D.; Makarova, L.; Mitronova, S.; et al. Cosmicflows-2: The Data. Astron. J. 2013, 146, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrutskie, M.F.; Cutri, R.M.; Stiening, R.; Weinberg, M.D.; Schneider, S.; Carpenter, J.M.; Beichman, C.; Capps, R.; Chester, T.; Elias, J.; et al. The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS). Astron. J. 2006, 131, 1163–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vaucouleurs, G.; de Vaucouleurs, A.; Herold, G.C., Jr.; Buta, R.J.; Paturel, G.; Fouque, P. Third Reference Catalogue of Bright Galaxies; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.W.; Lin, L.; Kong, X. Internal Variations in Empirical Oxygen Abundances for Giant H II Regions in the Galaxy NGC 2403. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, J.P.; Petit, H.; Comte, G.; Maucherat, A.J. Optical HII regions in NGC 2403. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 237, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Xu, D.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. The Xinglong 2.16-m Telescope: Current Instruments and Scientific Projects. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2016, 128, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, T.E.; Warren, W.H., Jr. International Reference Stars Catalog (Corbin 1991). Documentation for the Machine-Readable Version; National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1991.
- Filippenko, A.V. The importance of atmospheric differential refraction in spectrophotometry. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1982, 94, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardelli, J.A.; Clayton, G.C.; Mathis, J.S. The Relationship between Infrared, Optical, and Ultraviolet Extinction. Astrophys. J. 1989, 345, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, D.J.; Finkbeiner, D.P.; Davis, M. Maps of Dust Infrared Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Foregrounds. Astrophys. J. 1998, 500, 525–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid Fernandes, R.; Mateus, A.; Sodré, L.; Stasińska, G.; Gomes, J.M. Semi-empirical analysis of Sloan Digital Sky Survey galaxies—I. Spectral synthesis method. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 358, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnall, A.C. SpectRes: A Fast Spectral Resampling Tool in Python. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.05165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzual, G.; Charlot, S. Stellar population synthesis at the resolution of 2003. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 344, 1000–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabrier, G. Galactic Stellar and Substellar Initial Mass Function. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2003, 115, 763–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Borgne, J.F.; Bruzual, G.; Pelló, R.; Lançon, A.; Rocca-Volmerange, B.; Sanahuja, B.; Schaerer, D.; Soubiran, C.; Vílchez-Gómez, R. STELIB: A library of stellar spectra at R ~ 2000. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 402, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Delgado, R.M.; Perez, E.; Tenorio-Tagle, G.; Vilchez, J.M.; Terlevich, E.; Terlevich, R.; Telles, E.; Rodriguez-Espinosa, J.M.; Mas-Hesse, M.; Garcia-Vargas, M.L.; et al. Violent Star Formation in NGC 2363. Astrophys. J. 1994, 437, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzetti, D. The Dust Opacity of Star-forming Galaxies. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2001, 113, 1449–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterbrock, D.E.; Ferland, G.J. Astrophysics of Gaseous Nebulae and Active Galactic Nuclei, 2nd ed.; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, M.L.; Rybski, P.M.; Shields, G.A. The chemistry of galaxies. I. The nature of giant extragalactic H II regions. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1985, 57, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, J.; Torres-Peimbert, S.; Peimbert, M. Chemical composition gradient in NGC 2403 and the stellar mass limit. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1986, 98, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, D.R.; Shields, G.A.; Skillman, E.D.; Sagan, S.P.; Dufour, R.J. Interstellar Abundance Gradients in NGC 2403: Comparison to M33. Astrophys. J. 1997, 489, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresolin, F.; Kennicutt, R.C., Jr.; Garnett, D.R. The Ionizing Stars of Extragalactic H II Regions. Astrophys. J. 1999, 510, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, D.R.; Shields, G.A.; Peimbert, M.; Torres-Peimbert, S.; Skillman, E.D.; Dufour, R.J.; Terlevich, E.; Terlevich, R.J. Carbon in Spiral Galaxies from Hubble Space Telescope Spectroscopy. Astrophys. J. 1999, 513, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zee, L.; Salzer, J.J.; Haynes, M.P.; O’Donoghue, A.A.; Balonek, T.J. Spectroscopy of Outlying H II Regions in Spiral Galaxies: Abundances and Radial Gradients. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 2805–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.A.; Skillman, E.D.; Garnett, D.R.; Croxall, K.V.; Marble, A.R.; Smith, J.D.; Gordon, K.; Kennicutt, R.C., Jr. New Radial Abundance Gradients for NGC 628 and NGC 2403. Astrophys. J. 2013, 775, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, N.S.J.; Skillman, E.D.; Pogge, R.W.; Berg, D.A.; Moustakas, J.; Croxall, K.V.; Sun, J. CHAOS. VI. Direct Abundances in NGC 2403. Astrophys. J. 2021, 915, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitherer, C.; Schaerer, D.; Goldader, J.D.; Delgado, R.M.G.; Robert, C.; Kune, D.F.; de Mello, D.F.; Devost, D.; Heckman, T.M. Starburst99: Synthesis Models for Galaxies with Active Star Formation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1999, 123, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, G.A.; Leitherer, C. Optimization of Starburst99 for Intermediate-Age and Old Stellar Populations. Astrophys. J. 2005, 621, 695–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.S.; Dopita, M.A. Cooling Functions for Low-Density Astrophysical Plasmas. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1993, 88, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.G.; Groves, B.A.; Dopita, M.A.; Sutherland, R.S.; Kewley, L.J. The MAPPINGS III Library of Fast Radiative Shock Models. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2008, 178, 20–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, G.; Schaerer, D.; Meynet, G.; Maeder, A. New Grids of Stellar Models from 0.8-SOLAR-MASS to 120-SOLAR-MASSES at Z=0.020 and Z=0.001. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1992, 96, 269. [Google Scholar]
- Schaerer, D.; Meynet, G.; Maeder, A.; Schaller, G. Grids of stellar models. II. From 0.8 to 120 M_solar at Z=0.008. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1993, 98, 523. [Google Scholar]
- Charbonnel, C.; Meynet, G.; Maeder, A.; Schaller, G.; Schaerer, D. Grids of stellar models. III. From 0.8 to 120 Msolar at Z = 0.004. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1993, 101, 415. [Google Scholar]
- Schaerer, D.; Charbonnel, C.; Meynet, G.; Maeder, A.; Schaller, G. Grids of stellar models. IV. From 0.8 to 120 M_solar at Z = 0.040. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1993, 102, 339. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, J.A.; Phillips, M.M.; Terlevich, R. Classification parameters for the emission-line spectra of extragalactic objects. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1981, 93, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewley, L.J.; Dopita, M.A.; Sutherland, R.S.; Heisler, C.A.; Trevena, J. Theoretical Modeling of Starburst Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2001, 556, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, G.; Heckman, T.M.; Tremonti, C.; Brinchmann, J.; Charlot, S.; White, S.D.M.; Ridgway, S.E.; Brinkmann, J.; Fukugita, M.; Hall, P.B.; et al. The host galaxies of active galactic nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 346, 1055–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewley, L.J.; Ellison, S.L. Metallicity Calibrations and the Mass-Metallicity Relation for Star-forming Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2008, 681, 1183–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relaño, M.; Monreal-Ibero, A.; Vílchez, J.M.; Kennicutt, R.C. Spatially resolved study of the physical properties of the ionized gas in NGC 595. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 402, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopita, M.A.; Kewley, L.J.; Heisler, C.A.; Sutherland, R.S. A Theoretical Recalibration of the Extragalactic H II Region Sequence. Astrophys. J. 2000, 542, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, R.; Kennicutt, R.; Rousseau-Nepton, L.; Olivier, G.M.; Fernández-Arenas, D.; Robert, C.; Martin, R.P.; Amram, P. NGC 628 in SIGNALS: Explaining the Abundance-ionization Correlation in H II Regions. Astrophys. J. 2025, 978, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, J.; Kennicutt, R.C., Jr.; Tremonti, C.A.; Dale, D.A.; Smith, J.D.T.; Calzetti, D. Optical Spectroscopy and Nebular Oxygen Abundances of the Spitzer/SINGS Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2010, 190, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, E.M.; Leitherer, C.; Ekstrom, S.; Meynet, G.; Schaerer, D. The Effects of Stellar Rotation. I. Impact on the Ionizing Spectra and Integrated Properties of Stellar Populations. Astrophys. J. 2012, 751, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn-Wallenstein, T.Z.; Levesque, E.M. A Comparison of Rotating and Binary Stellar Evolution Models: Effects on Massive Star Populations. Astrophys. J. 2020, 896, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanway, E.R.; Eldridge, J.J.; Becker, G.D. Stellar population effects on the inferred photon density at reionization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, L.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Kang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Han, Z. Radiation fields of intermediate-age stellar populations with binaries as ionizing sources of H II regions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).