Abstract
Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) with energies exceeding eV are believed to originate from extragalactic environments, potentially associated with relativistic jets in active galactic nuclei (AGN). Among AGNs, blazars, particularly those detected in very-high-energy (VHE) gamma rays, are promising candidates for UHECR acceleration and high-energy neutrino production. In this work, we investigate three blazar sources, AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+178, using multiwavelength spectral energy distribution (SED) modeling. These sources span a range of synchrotron peak classes and redshifts, providing a diverse context to explore the physical conditions in relativistic jets. We employ both leptonic and lepto-hadronic models to describe their broadband emission from radio to TeV energies, aiming to constrain key jet parameters such as magnetic field strength, emission region size, and particle energy distributions. Particular attention is given to evaluating their potential as sources of UHECRs and high-energy neutrinos. Our results shed light on the complex interplay between particle acceleration mechanisms, radiative processes, and multi-messenger signatures in extreme astrophysical environments.
1. Introduction
Cosmic rays (CRs) with energies above eV have Larmor radii that surpass the scale of the Milky Way, indicating that they likely originate from extragalactic sources. Data from the Pierre Auger Observatory suggest a possible correlation between the arrival directions of the highest-energy cosmic rays (UHECRs, eV) and nearby active galactic nuclei (AGN) [1]. However, this connection remains uncertain and requires further observational support to be confirmed. The foundational idea for particle acceleration in astrophysical environments was introduced by Enrico Fermi in 1949 [2], who proposed that charged particles could gain energy through stochastic interactions with magnetic fields. This mechanism is applicable to acceleration processes in shock fronts, such as those formed in the aftermath of gravitational collapses or around accreting black holes at the centers of galaxies [3], including those found in blazars [4].
Blazars have been extensively observed across multiple wavelengths, particularly in the radio, X-ray, and gamma-ray bands, and they are known for their variability in both flux and spectral features on timescales ranging from several years down to mere minutes [5,6,7]. These sources have also been proposed as potential emitters of high-energy astrophysical neutrinos [6,8,9]. With the accumulation of long-term observational data, especially from the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, statistical searches for neutrino counterparts have become increasingly viable [10].
Understanding the mechanisms responsible for the broadband emission observed in blazars is crucial for interpreting their multi-messenger signatures. Their electromagnetic radiation is predominantly non-thermal, and the spectral energy distributions (SEDs) typically exhibit two broad peaks (see Figure 1). The low-energy peak, spanning the infrared to X-ray range, is widely attributed to synchrotron radiation from relativistic electrons within the jet. Depending on the peak frequency of this synchrotron component, BL Lac objects are further classified as low-, intermediate-, or high-frequency peaked (LBL, IBL, and HBL, respectively). The high-energy peak, located in the gamma-ray band, remains the subject of ongoing investigation. Leptonic models attribute this emission to inverse Compton scattering, involving either synchrotron photons from the jet itself (in synchrotron self-Compton (SSC) models) or external photon fields such as those from the accretion disk, BLR, or dusty torus (in external Compton (EC) models). Hadronic scenarios, on the other hand, invoke processes such as synchrotron emission from ultra-relativistic protons and photohadronic interactions, which may also lead to the production of high-energy neutrinos [8,9] (see also [11] and the references therein).
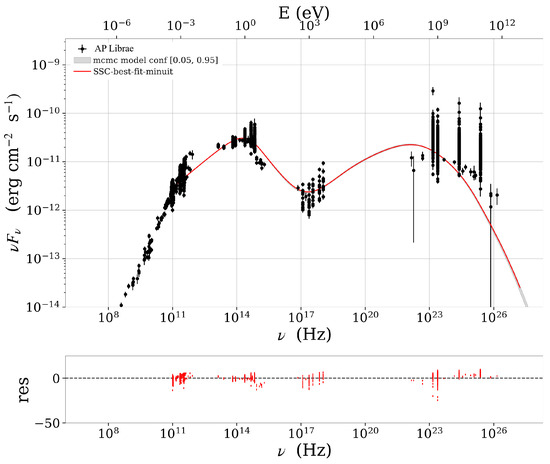
Figure 1.
Broadband SED of AP Librae fitted with a one-zone SSC model. The solid red curve indicates the best-fit spectrum, while the shaded gray band denotes the 1 confidence interval. Low-frequency radio measurements (< eV) are plotted for reference but were excluded from the fit, since synchrotron self-absorption in the compact emission zone prevents these data from constraining the model parameters.
In this study, we perform a detailed SED analysis of three blazar sources: AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+178. These sources are of particular interest due to their detection in the gamma-ray band and, in some cases, in very-high-energy (VHE) gamma rays, offering a valuable opportunity to probe the physical conditions within their relativistic jets. Through broadband multiwavelength modeling, we aim to constrain key jet parameters such as magnetic field strength, emission region size, particle energy distributions, and bulk motion. Additionally, we assess the relative contributions of leptonic and hadronic emission processes to the high-energy component of their SEDs. This approach enables us to investigate the potential role of these blazars as sources of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays and high-energy neutrinos, contributing to the broader understanding of particle acceleration and multi-messenger astrophysics in AGN jets.
The structure of this paper is as follows: in Section 2, we describe the selection of our blazar sample and summarize the key observational properties. Section 3 presents the modeling framework, the computational tools employed, and the methodology used for parameter estimation. This includes the physical assumptions adopted, the spectral fitting procedures, and the criteria for model selection. Section 4 presents the results of our modeling along with a discussion of the implications for blazar physics and multi-messenger astrophysics. We conclude our findings in Section 5. Throughout this work, we adopt a flat CDM cosmology with the Hubble constant , matter density parameter , radiation density , and dark energy density , consistent with [12].
While our work focuses on blazars as case studies for potential UHECR acceleration, we note that other radio-loud AGNs with jets oriented away from our line of sight could also contribute to the observed UHECR population, since cosmic rays are charged particles and can be deflected by extragalactic and galactic magnetic fields.
2. Blazar Sample Overview: AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+178
In this section, we present an overview of the three blazar sources selected for leptonic and lepto-hadronic modeling: AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+178. These sources were chosen based on their gamma-ray detection, multiwavelength coverage, and potential relevance as candidates for UHECR production.
2.1. AP Librae
AP Librae, one of the earliest identified BL Lac objects [13], has a reliably measured redshift of [14], consistent with the 6dF galaxy survey measurement [15]. The source was initially detected in the radio band as PKS 1514–24 during the Parkes survey [16] and was later associated with the optically variable counterpart AP Librae [17,18]. Its host galaxy contains a supermassive black hole with a mass of approximately based on stellar velocity dispersion measurements [19].
In X-rays, the source was first detected by the Einstein Observatory [20]. At high energies ( MeV), it was tentatively identified as 3EG J1517−2538 in the EGRET catalog, though its soft photon index () implied a low flux at very high energies (VHEs) [21]. Earlier VHE observations using the Mark 6 gamma-ray telescope yielded only upper limits [22,23].
AP Librae was later confirmed as a gamma-ray emitter by Fermi-LAT (0FGL J1517.9−2423) with a harder photon index () [24], increasing the likelihood of detection at VHEs. In 2010, H.E.S.S. announced the first VHE detection of the source [25]. Subsequent studies presented a broadband SED from radio to TeV [26], and Chandra observations revealed an extended X-ray jet [27], making AP Librae the only known TeV-detected BL Lac with a resolved X-ray jet.
The high-energy to very-high-energy (HE–VHE) emission of AP Librae has been modeled using a log-parabolic function, yielding a peak energy of approximately 450 MeV () [28]. This value lies near the lower bound of the Fermi-LAT sensitivity and may be interpreted as an upper limit. Such a low peak energy is uncommon among extragalactic VHE emitters, which typically exhibit peak emissions above hundreds of GeV. The broadband SED of AP Librae is similarly atypical, being dominated by inverse-Compton emission with an X-ray component that cannot be attributed to synchrotron processes. This suggests a common origin for the X-ray and gamma-ray emissions, with a high-energy component that may be shifted toward lower energies, potentially even below the Fermi-LAT range [26,29].
The VHE emission from AP Librae has been explored through a lepto-hadronic framework in which the extended kiloparsec-scale jet serves as the primary emission region [30]. In this model, synchrotron radiation from ultrarelativistic protons is proposed as the mechanism behind the observed TeV gamma rays. To match the VHE spectrum detected by H.E.S.S., the model requires extreme conditions, including proton energies exceeding eV and magnetic fields around 1 mG. Such parameters lead to a total jet power estimate of erg s−1, which significantly exceeds the Eddington luminosity for the source. Despite this, the model successfully reproduces the broadband SED when combined with standard synchrotron and SSC emission from electrons in the inner jet. However, the study concludes that while proton synchrotron emission is a viable explanation, the extreme energetics required impose strong constraints on the plausibility of this scenario [30].
2.2. 1H 1914–194
1H 1914–194, located at a redshift of [31], was first detected by NASA’s HEAO 1 (High-Energy Astronomy Observatory 1) during its mission from 1977 to 1979. The primary objective of HEAO 1 was to survey the sky for X-ray and gamma-ray point sources across the 150 eV to 10 MeV energy range, and it was notably the first mission to detect diffuse background radiation (see [32]). Among the sources in the current sample, 1H 1914–194 remains undetected in the TeV gamma-ray band and has the most limited multiwavelength coverage. Detailed radio observations of this X-ray-selected BL Lacertae object (XBL) were later provided by Kollgaard et al. (1996) [32], who described it as having a bright core and a jet-like feature extending northwest, ending in a localized brightening within a diffuse halo.
1H 1914–194 is listed in the Third Catalog of Hard Fermi-LAT Sources (3FHL), which compiles results from the first seven years of Fermi-LAT observations using the Pass 8 data analysis. Within the energy range of 10–1000 GeV, the source exhibits a photon flux of approximately 3.96 × 10−10 photons cm−2 s−1, with a statistical uncertainty of 3.70 × 10−11. Additionally, a power-law fit across the broader 10 MeV to 1000 GeV range yields an energy flux of 2.78 × 10−11 erg cm−2 s−1, accompanied by an uncertainty of 4.45 × 10−12 [33].
1H 1914–194 has garnered attention as a potential candidate in high-energy neutrino studies. The IceCube Neutrino Observatory detected a flux of diffuse cosmic neutrinos with energies in the PeV range during 2013 and 2014 [34], but the sources of these neutrinos remain unidentified. Among the proposed astrophysical counterparts are HBLs, which have been suggested as plausible neutrino emitters due to the potential for hadronic acceleration within their jets to energies exceeding eV, adequate for neutrino production through hadronic interactions [35,36]. Interestingly, while HBLs show some degree of spatial correlation with the IceCube neutrino arrival directions, other blazar subclasses, such as Flat-Spectrum Radio Quasars (FSRQs), despite their higher gamma-ray luminosity and richer external photon environments, appear not to be associated with these events [34,37]. This observation challenges some expectations and further highlights the importance of investigating individual BL Lac sources such as 1H 1914–194.
While Resconi et al. (2017) [38] report a statistical significance of 2.91 (p-value of 0.18%) for a possible association between blazar subclasses and high-energy neutrinos, the current angular resolution of IceCube events does not allow for a definitive identification of individual astrophysical sources. Despite this limitation, 1H 1914–194 has emerged as a promising candidate, with its flaring activity and gamma-ray emission aligning with the arrival directions of some detected neutrinos [35]. Based on this association, the expected contribution from this source to the IceCube signal is estimated at approximately 0.44 muon neutrinos per year [35]. Among the potential counterparts studied, Petropoulou et al. (2015) [34] identify 1H 1914–194 as having the strongest consistency between the modeled neutrino flux and IceCube observations.
2.3. PKS 0735+178
PKS0735+178, classified as an intermediate-synchrotron-peaked BL Lac (IHBL), is among the most luminous BL Lac objects across multiple wavelengths. In the NRAO VLA Sky Survey (NVSS), its radio flux density at 1.4 GHz reaches 2.3 Jy, ranking it as the fifth brightest BL Lac in the fifth edition of the Roma-BZCat catalog [39,40]. Historical radio observations from the early 1990s reported flux densities as high as ∼ 5 Jy at 4.8 and 8 GHz, placing the source among the most powerful blazars overall [41]. In the high-energy (HE; MeV) gamma-ray band, PKS0735+178 also stands out, being listed among the top 20 most luminous IHBLs in the Fermi 4LAC-DR2 catalog [42].
The optical spectrum of the source is notably featureless, complicating the determination of a precise redshift. A strong intervening absorption line has established a firm lower limit of [43,44,45], while the tentative detection of its host galaxy led to an estimated redshift of [46]. More recently, a redshift of has been proposed based on the hypothesis that the source is associated with a group of nearby faint galaxies [47]. Even adopting the conservative estimate of , the inferred radio and gamma-ray luminosities are exceptionally high for this class of objects, with WHz−1 and erg s−1.
Notably, during its intense flaring activity in December 2021, PKS 0735+178 was temporally and spatially correlated with high-energy neutrino detections reported by multiple observatories, including IceCube [48], Baikal-GVD [49], Baksan [50], and KM3NeT [51], highlighting its relevance in multi-messenger astrophysics.
Further support for this potential association was provided by Prince et al. [52], who conducted a detailed lepto-hadronic modeling of the blazar’s broadband emission to explore its role as a neutrino source. They focused on the ∼172 TeV IceCube track-like event, in addition to the Baikal and KM3NeT detections, and they tested scenarios with and without external blackbody photon fields as targets for photohadronic interactions. Although the predicted neutrino fluxes fall below IceCube’s current sensitivity, the analysis revealed a strong connection between the X-ray emission and possible neutrino production. Their findings indicate that PKS 0735+178 may contribute non-negligibly to the diffuse astrophysical neutrino background. As emphasized in their study, future neutrino detectors with enhanced angular resolution and sensitivity will be crucial to identifying such sources and refining theoretical flux predictions.
3. Multi-Wavelength SED Modeling of BL Lacs
3.1. Leptonic SED Fitting
For the leptonic modeling of the SEDs, we used version 1.3.0 of the JetSeT codebase [53,54,55], an open-source platform implemented in C and Python. JetSeT is designed to simulate both the radiation and particle dynamics in relativistic jets, and it is applicable to a wide range of astrophysical objects. It enables detailed modeling of several leptonic emission processes, including synchrotron, synchrotron self-Compton (SSC), and inverse Compton scattering of external photon fields originating from structures such as the accretion disk, broad-line region (BLR), dusty torus (DT), and the cosmic microwave background (CMB). In addition, it accounts for attenuation due to pair production with EBL photons, using widely accepted models [56,57,58].
Our modeling adopts a one-zone leptonic scenario where the emission region is approximated as a homogeneous sphere. The size of this region is linked to the observed variability timescale through the relation
with [59,60], and z is the source redshift. The emitting blob travels with a bulk Lorentz factor and is viewed at an angle , resulting in the following Doppler factor [61]:
The electron population within the jet is assumed to follow a broken power-law distribution [62,63,64]:
where and are the electron spectral indices below and above the break Lorentz factor, , respectively; , , and represent the minimum, break, and maximum electron Lorentz factors, and is the normalization constant.
JetSeT’s modeling strategy involves an initial exploratory phase followed by a detailed physical fit. The first step leverages the SEDShape module, which performs empirical fits using power-law and log-parabolic functions across the observed SED. These empirical profiles help to approximate the synchrotron and SSC components, thereby informing the parameter ranges used in the subsequent modeling. Physical modeling is then initialized via the ObsConstrain module, using the broken power-law form in Equation (3).
The parameter space is explored using a Bayesian framework, where prior distributions are imposed to constrain the models to physically meaningful values. JetSeT expresses all parameters using Astropy units, ensuring interoperability with other Python-based libraries. The fitting routines support both frequentist and Bayesian methodologies. For deterministic optimization, JetSeT integrates with iminuit [65] and SciPy’s bounded least-squares solver [66].
For probabilistic inference, we employed the MCMC engine provided by emcee [67], which implements an affine-invariant ensemble sampler. This algorithm evolves an ensemble of independent chains (“walkers”) that adapt their proposal steps to the geometry of the target posterior distribution, making it efficient and robust for problems with correlated parameters and broad parameter ranges, as often encountered in blazar SED modeling. Convergence was assessed through the integrated autocorrelation time of the chains and visual inspection of the trace plots. The resulting posterior distributions were used to derive parameter uncertainties and correlations, which were then propagated into the model spectra. Throughout the modeling, the redshift is fixed, and we assume a cold proton content corresponding to 10% of the relativistic electron energy density, consistent with [68].
The code then calculates the kinetic power carried by relativistic electrons in the AGN frame as
where R is the radius of the emitting region in the AGN frame, and is the bulk velocity in units of the speed of light.
The magnetic power (Poynting flux) is given by
where B is the magnetic field in the emission region.
In addition, the code computes the kinetic luminosity of cold protons, under the assumption of charge neutrality provided by one cold proton per electron (i.e., neglecting electron–positron pairs):
If electron–positron pairs are also present in the jet, they would reduce the total kinetic luminosity, which is defined as .
3.2. Lepto-Hadronic SED Modeling
We investigated hadronic scenarios using the open-source AM3 (Astrophysical Multi-Messenger Modeling) framework [69], which self-consistently evolves coupled populations of photons, electrons, positrons, protons, neutrons, and neutrinos (plus intermediate products) in an isotropic magnetic field. AM3 solves the time-dependent kinetic equations governing nonlinear processes, such as electromagnetic cascades and secondary-particle feedback, thereby capturing the full lepto-hadronic interplay within astrophysical sources.
Our emission zone is represented by a spherical “blob” of comoving radius R, propagating with bulk Lorentz factor along the jet. Primary electrons and protons are injected isotropically; electrons follow a broken power-law energy spectrum, while protons obey a single power law up to a maximum Lorentz factor . High-energy protons interact with the ambient photon bath according to the prescriptions of Hümmer et al. [70], yielding charged and neutral pions. Subsequent pion decays produce secondary gamma rays, neutrinos, electrons, and positrons, which seed further electromagnetic cascades.
AM3 includes all relevant radiative and particle-interaction processes, synchrotron emission (with self-absorption), inverse-Compton scattering by both electrons and protons, Bethe–Heitler pair production
photon–photon pair production and annihilation, and the dynamical evolution of the resulting secondaries. The magnetic field B is treated as turbulent and randomly oriented within the blob, significantly influencing the resulting SED and multi-messenger signatures.
By incorporating the extragalactic background light (EBL) attenuation model from Domínguez et al. (2011) [56] into our lepto-hadronic framework, we accurately account for photon absorption along the line of sight to Earth. This allows us to quantify the hadronic component of the blazar’s SED while simultaneously modeling both neutrino and gamma-ray emission from a single compact region. The resulting combined fit offers crucial constraints on the temporal and spectral correlations between high-energy neutrino events and gamma-ray flare episodes in blazars.
4. Results and Discussion
Utilizing the approaches described in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2, we carried out a time-dependent, non-thermal spectral modeling of the blazars AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+178 across multiple wavebands. To this end, we compiled archival measurements, spanning from radio frequencies through very-high-energy gamma rays, sourced from the Firmamento database 1. We note that the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS 2) is a valuable archival resource for future optical variability studies, offering deep photometry and excellent cadence. ATLAS data could complement datasets such as GAIA and SDSS in future analyses, particularly for investigating high- and low-flux states. Initially, the broadband spectral points were fitted via a Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm implemented in JetSeT, and the resulting posterior parameter distributions were then adopted as inputs for the subsequent lepto-hadronic simulations using the AM3 framework.
4.1. Synchrotron Self-Compton (SSC) Modeling
Each free parameter in our fitting procedure is constrained by physically motivated limits. We fix the source redshift, set the emission-region distance from the central black hole to (the JetSeT default), and prescribe allowed intervals for the remaining quantities to accelerate convergence and avoid unphysical solutions. In particular, we bound the emission-region radius R, the magnetic field strength B, the minimum, break, and maximum Lorentz factors , , and , and the particle spectral indices and . These ranges are chosen to conform with values reported in the literature [71,72]. The resulting best-fit parameter values are listed in Table 1. The calculated energy densities and luminosities for the three sources are presented in Table 2. The total radiative output is given by
where and represent the powers emitted via synchrotron and synchrotron self-Compton processes, respectively [73]. Here, refers only to the leptonic contribution from the SSC model. Hadronic contributions, such as the proton synchrotron, Bethe–Heitler cascades, and pion decay channels, are modeled separately in the AM3 framework.

Table 1.
Best-fit parameters for the leptonic emission models of AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+17.

Table 2.
Derived physical quantities for AP Librae, 1H 1914-194, and PKS 0735+17.
The SEDs presented here are constructed from archival, non-simultaneous multiwavelength data. Variability, therefore, plays a significant role in the observed scatter, especially in the optical and X-ray bands, where multiple flux states are evident. For the sources in our sample, the available data do not allow us to isolate strictly contemporaneous high- and low-state SEDs. Nonetheless, it is well known that variability in blazars can cause shifts in the synchrotron and inverse-Compton peaks, as well as changes in spectral slopes. Exploring whether such peak shifts occur in these sources will require future time-resolved, multiwavelength campaigns, which could provide valuable constraints on particle acceleration and energy dissipation processes in relativistic jets.
Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 present the one-zone SSC fits to the SEDs of AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+17, respectively. In AP Librae (Figure 1), the synchrotron peak occurs at ∼ Hz, which is characteristic of an intermediate-synchrotron-peaked (ISP) BL Lac, while the inverse-Compton peak appears at ∼ Hz, extending into the very-high-energy gamma-ray band. In contrast, both 1H 1914–194 (Figure 2) and PKS 0735+178 (Figure 3) exhibit high-synchrotron-peaked (HSP) BL Lac behavior, with synchrotron peaks at ∼ Hz and ∼ Hz, as well as inverse-Compton peaks at ∼ Hz and ∼ Hz, respectively. In all three cases, the residuals plotted in the lower panels cluster tightly around zero, indicating that the SSC model provides a robust fit to the multiwavelength observations.
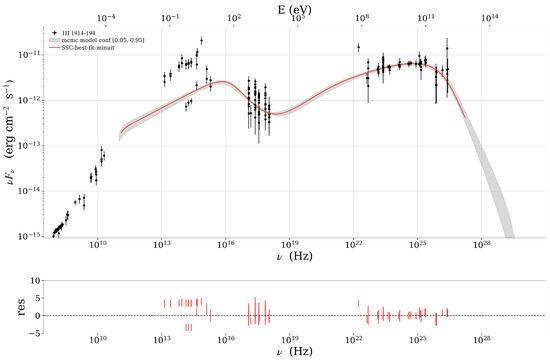
Figure 2.
Broadband SED of 1H 1914–194 fitted with a one-zone SSC model. The solid red curve indicates the best-fit spectrum, while the shaded gray band denotes the 1 confidence interval. Low-frequency radio measurements (< eV) are plotted for reference but were excluded from the fit, since synchrotron self-absorption in the compact emission zone prevents these data from constraining the model parameters. The large spread of points in the optical and X-ray bands is primarily due to intrinsic variability, with data collected at different epochs and likely representing both high- and low-flux states.
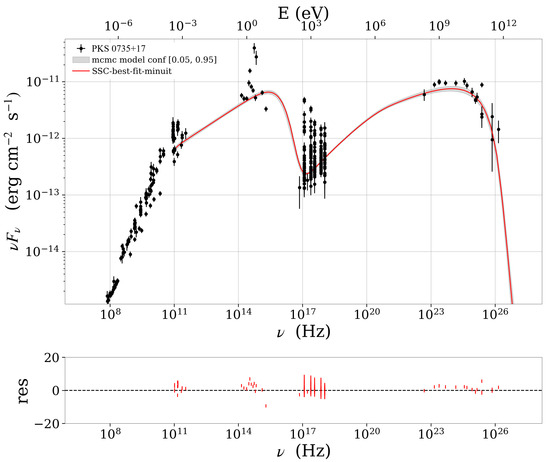
Figure 3.
Broadband SED of PKS 0735+178 fitted with a one-zone SSC model. The solid red curve indicates the best-fit spectrum, while the shaded gray band denotes the 1 confidence interval. Low-frequency radio measurements (< eV) are plotted for reference but were excluded from the fit, since synchrotron self-absorption in the compact emission zone prevents these data from constraining the model parameters. The large spread of points in the optical and X-ray bands is primarily due to intrinsic variability, with data collected at different epochs and likely representing both high- and low-flux states.
4.2. Lepto-Hadronic Spectral Energy Distribution Modeling
The lepto–hadronic SED modeling was performed using the publicly available AM3 code. The nonthermal electron population was adopted from our JetSeT fits (see Section 4.1), yielding jet electron luminosities of
for AP Librae,
for 1H 1914–194, and
for PKS 0735+17. For the hadronic component, the proton luminosity was constrained to the Eddington limit,
where
Adopting black hole masses of for AP Librae [74], for 1H 1914–194 [75], and for PKS 0735+178 [76] yields Eddington luminosities of
respectively. While transient super-Eddington jet loading may occur during flares, sustained quiescent emission at such rates is unlikely [77]. Informed by a suite of relativistic shock acceleration simulations, which employ both Monte Carlo methods and particle-in-cell techniques to model proton energization at collisionless shocks, spectral indices in the range of are routinely recovered for strong, ultrarelativistic shocks with magnetic obliquities up to (e.g., [78,79]). These studies demonstrate that the combination of rapid first-order Fermi acceleration and efficient particle scattering off self-generated turbulence leads to unusually hard power-law tails compared to the canonical result for nonrelativistic shocks. Motivated by these findings, we adopt a single power-law injection spectrum for the jet protons of the form
with
The choice =1.5 provides a realistic representation of efficient acceleration in strong shocks. Moderate variations in (1.2–1.8) affect the balance between proton synchrotron emission and predicted neutrino fluxes but do not qualitatively change our conclusions regarding the potential of these blazars as UHECR sources; represents the approximate threshold above which protons begin to participate in the diffusive acceleration cycle, while is set by balancing the acceleration timescale against both radiative losses and particle escape in the jet environment.
We note that “double Compton scattering”, the inverse Compton upscattering of already upscattered (e.g., TeV) photons by relativistic electrons, is not included as a separate component in our modeling. In a compact one-zone emission region, the Klein–Nishina regime strongly suppresses the scattering cross-section for such high-energy photons, rendering this process negligible compared to the primary SSC, external Compton, and hadronic channels considered here.
Rodrigues et al. (2024) [77] adopt a conservative strategy in which the X-ray and radio measurements serve only as upper bounds on the leptonic contribution. However, for some objects, a standard electron synchrotron model can, in fact, account for the observed flux in these bands. This choice stems from the compactness of the high-energy emission zone, which produces both gamma rays and neutrinos, as well as its concomitant synchrotron self-absorption at radio frequencies, rendering it optically thick below GHz wavelengths [77]. Extending this hadronic picture, we incorporate proton–proton () collisions alongside the originally considered photohadronic () interactions. In reactions, a relativistic proton impacts a thermal proton, producing both neutral and charged pions that subsequently decay via
thus providing additional channels for very-high-energy gamma ray and neutrino generation. By unifying and processes, including all relevant flavor and charge channels, our model offers a more complete depiction of hadronic interactions and their role in shaping the multiwavelength and neutrino outputs of blazar jets.
Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 display the multiwavelength SEDs of AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+17, respectively, together with archival data from radio through gamma rays. The red curve corresponds to the synchrotron and inverse-Compton emission of primary electrons (JetSeT best-fit); the black curve shows proton synchrotron and proton-induced inverse-Compton emission. The light blue curve denotes Bethe–Heitler pair production (), while the green curve marks the emission from secondary pairs produced via photon–photon interactions (). The yellow curve represents the cascade from charged-pion decay (), and the purple dotted line illustrates gamma rays from neutral-pion decay in photopion processes (). The dark blue dashed curve shows the gamma-ray output from neutral-pion decay in proton–proton collisions (). Finally, the pink curve represents the all-flavor neutrino fluxes from interactions, while the brown curve represents those from interactions.
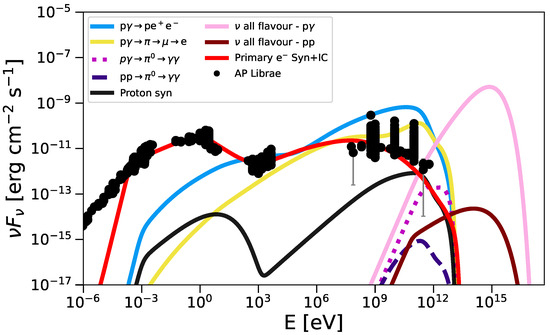
Figure 4.
Lepto-hadronic SED model for AP Librae, overlaid with archival multiwavelength data. The solid red curve shows primary electron synchrotron emission (∼– eV) and primary inverse-Compton scattering (∼– eV). Hadronic contributions include Bethe–Heitler pair production (, light blue; ∼– eV), photopion cascades from charged pions (, yellow; ∼– eV), and gamma rays from neutral-pion decay (, pink dotted; ∼– eV). Proton–proton interactions are shown by the purple dashed curve (∼– eV), and proton synchrotron and inverse-Compton emissions are shown by the solid black curve (∼– eV). The all-flavor neutrino fluxes from photohadronic (, pink) and proton–proton (, brown) channels dominate above – eV and – eV, respectively.
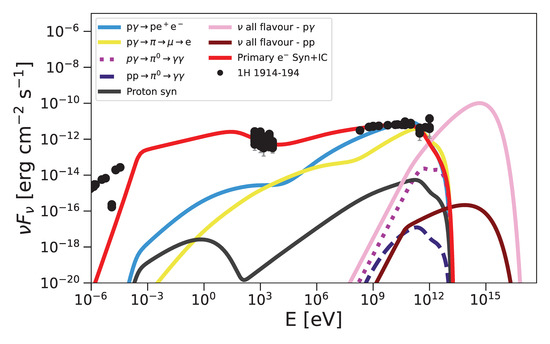
Figure 5.
Lepto-hadronic SED model for 1H 1914–194, overlaid with archival multiwavelength data. The solid blue curve shows primary electron synchrotron emission (∼– eV), and the solid red curve shows primary inverse-Compton scattering (∼– eV). Hadronic contributions include Bethe–Heitler pair production (, light blue; ∼– eV), photopion cascades from charged pions (, yellow; ∼– eV), and gamma rays from neutral-pion decay (, pink dotted; ∼– eV). Proton–proton interactions are shown by the purple dashed curve (∼– eV), and proton synchrotron and inverse-Compton emissions are shown by the solid black curve (∼– eV). The all-flavor neutrino fluxes from photohadronic (, pink) and proton–proton (, brown) channels dominate above – eV and – eV, respectively.
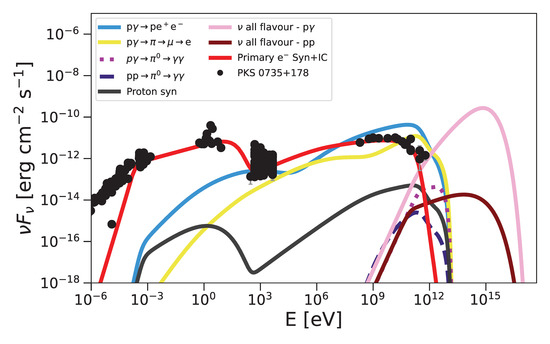
Figure 6.
Lepto-hadronic SED model for PKS 0735+17, overlaid with archival multiwavelength data. The solid red curve shows primary electron synchrotron emission (∼– eV) and primary inverse-Compton scattering (∼– eV). Hadronic contributions include Bethe–Heitler pair production (, light blue; ∼– eV), photopion cascades from charged pions (, yellow; ∼– eV), and gamma rays from neutral-pion decay (, pink dotted; ∼– eV). Proton–proton interactions are shown by the purple dashed curve (∼– eV), and proton synchrotron and inverse-Compton emissions are shown by the solid black curve (∼– eV). The all-flavor neutrino fluxes from photohadronic (, pink) and proton–proton (, brown) channels dominate above – eV and – eV, respectively.
In Figure 4 and Figure 6, our lepto-hadronic model naturally produces an emission component that bridges the gap between the low-energy synchrotron peak and the high-energy inverse-Compton peak; ultra-high-energy protons interact with ambient photons via the Bethe–Heitler process (), injecting secondary electrons and positrons whose synchrotron radiation reproduces the observed X-ray flux in the intermediate band (∼– eV). Simultaneously, charged pions from photopion interactions () decay through , and these decay electrons upscatter target photons via inverse-Compton to form the pronounced “yellow” hump in the – eV range, thereby filling the SED valley and achieving excellent agreement with the multiwavelength data. Furthermore, as shown in Figure 5, the same population of electrons, both those injected by Bethe–Heitler pair production and those originating from muon decay, can inverse-Compton scatter soft photons up to very high energies (– eV and beyond), accounting for the observed VHE gamma-ray tail in that source.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we have carried out a comprehensive multiwavelength study of three blazar sources, AP Librae, 1H 1914–194, and PKS 0735+178, using both leptonic (one-zone SSC) and time-dependent lepto-hadronic (AM3) models. Our SSC fits reproduce the low- and high-energy peaks of the SEDs with characteristic synchrotron and inverse-Compton components, confirming AP Librae as an ISP BL Lac and 1H 1914–194 and PKS 0735+178 as HSP BL Lacs. By coupling these results with lepto-hadronic simulations, we demonstrate that secondary processes, Bethe–Heitler pair cascades, and photopion interactions naturally fill the SED “valley,” accounting for the observed X-ray emission, and extend the gamma-ray spectrum into the VHE band.
We find that proton injection with , , and remains energetically viable under while providing adequate neutrino fluxes in both and channels. Notably, 1H 1914–194 exhibits an inverse-Compton tail from secondary electrons that can account for photons up to eV. Our modeling yields total jet kinetic powers of ∼– erg s−1 and electron-to-proton energy ratios consistent with other blazar studies.
These findings support the scenario in which HSP BL Lacs serve as promising UHECR accelerators and neutrino emitters. Future observations with next-generation Cherenkov telescopes and high-resolution neutrino detectors will be critical for testing the hadronic signatures predicted here.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A.S.P.; methodology, L.A.S.P. and S.V.B.d.S.; software, S.V.B.d.S.; validation, L.A.S.P. and S.V.B.d.S.; formal analysis, S.V.B.d.S.; investigation, L.A.S.P. and S.V.B.d.S.; resources, L.A.S.P.; data curation, L.A.S.P. and S.V.B.d.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A.S.P. and S.V.B.d.S.; writing—review and editing, L.A.S.P. and S.V.B.d.S.; visualization, L.A.S.P. and S.V.B.d.S.; supervision, L.A.S.P.; project administration, L.A.S.P.; funding acquisition, L.A.S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Stuani Pereira, L.A. gratefully acknowledges the financial support from FAPESP under grant numbers 2021/01089-1, 2024/02267-9, and 2024/14769-9 and from CNPq under grant numbers 403337/2024-0, 153839/2024-4, and 200164/2025-2.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AGN | Active Galactic Nucleus |
| BL Lac | BL Lacertae object |
| BLR | Broad-Line Region |
| CMB | Cosmic Microwave Background |
| DT | Dusty Torus |
| EBL | Extragalactic Background Light |
| EC | External Compton |
| HBL | High-Synchrotron-Peaked BL Lac |
| HE | High Energy |
| HSP | High-Synchrotron-Peaked BL Lac (synonym of HBL) |
| IBL | Intermediate-Synchrotron-Peaked BL Lac |
| ISP | Intermediate-Synchrotron-Peaked BL Lac |
| LEdd | Eddington Luminosity |
| LBL | Low-Synchrotron-Peaked BL Lac |
| MCMC | Markov Chain Monte Carlo |
| SSC | Synchrotron Self-Compton |
| SED | Spectral Energy Distribution |
| UHECR | Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Ray |
| VHE | Very High Energy |
| CDM | Lambda Cold Dark Matter cosmological model |
Notes
| 1 | https://firmamento.hosting.nyu.edu/home, accessed on 1 April 2025 |
| 2 | https://fallingstar-data.com/forcedphot/, accessed on 10 July 2025. |
References
- Aab, A.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Albuquerque, I.F.M.; Allekotte, I.; Almela, A.; Castillo, J.A.; Alvarez-Muñiz, J.; Anastasi, G.A.; Anchordoqui, L.; et al. An Indication of Anisotropy in Arrival Directions of Ultra-high-energy Cosmic Rays through Comparison to the Flux Pattern of Extragalactic Gamma-Ray Sources*. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 853, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermi, E. On the Origin of the Cosmic Radiation. Phys. Rev. 1949, 75, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.P.; Coimbra-Araújo, C.H.; dos Anjos, R.C.; Coelho, J.G. Binary Coalescences as Sources of Ultrahigh-Energy Cosmic Rays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 132, 091401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Dermer, C.D.; Takami, H.; Migliori, G. Blazars as Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic-Ray Sources: Implications for TeV Gamma-Ray Observations. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.; Cao, Z. TeV Blazars as the Sources of Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays. Int. J. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 4, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, P.; Padovani, P. Astrophysical Neutrinos and Blazars. Universe 2021, 7, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGIC Collaboration; MWL Collaborators. The variability patterns of the TeV blazar PG 1553 + 113 from a decade of MAGIC and multiband observations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 529, 3894–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Stecker, F.W. High-Energy Neutrinos from Active Galactic Nuclei. In The Encyclopedia of Cosmology. Set 2: Frontiers in Cosmology. Volume 2: Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics; Stecker, F.W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 483–540. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim, K.; Stanev, T.; Biermann, P.L. Neutrinos from flat-spectrum radio quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 260, L1–L3. [Google Scholar]
- Aartsen, M.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; Ansseau, I.; et al. The IceCube Neutrino Observatory: Instrumentation and online systems. J. Instrum. 2017, 12, P03012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahayanathan, S.; Godambe, S. Modelling the very high energy flare of 3C 279 using one-zone leptonic model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 419, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planck Collaboration; Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; et al. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strittmatter, P.A.; Serkowski, K.; Carswell, R.; Stein, W.A.; Merrill, K.M.; Burbidge, E.M. Compact extragalactic nonthermal sources. Astrophys. J. 1972, 175, L7–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.J.; Peterson, B.A.; Rodgers, A.W. The Redshift and Composite Nature of AP Librae (pks 1514-24). Astrophys. J. Lett. 1974, 194, L79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.H.; Read, M.A.; Saunders, W.; Colless, M.; Jarrett, T.; Parker, Q.A.; Fairall, A.P.; Mauch, T.; Sadler, E.M.; Watson, F.G.; et al. The 6dF Galaxy Survey: Final redshift release (DR3) and southern large-scale structures. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 399, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.G.; Gardner, F.F.; Mackey, M.B. The Parkes catalogue of radio sources, declination zone −20° to −60°. Aust. J. Phys. 1964, 17, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, H.E. The Optically Variable Radio Source PKS 1514-24 = AP Librae. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1971, 167, L79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biraud, F. Rapid Optical Variability of the Source PKS 1514-24. Nature 1971, 232, 178–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Urry, C.M.; van der Marel, R.P.; Lira, P.; Maza, J. Black Hole Masses and Host Galaxy Evolution of Radio-Loud Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2005, 631, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Ku, W.H.M. Studies of BL Lac objects with the Einstein X-ray Observatory: The absolute volume density. Astrophys. J. 1983, 266, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, R.C.; Bertsch, D.L.; Bloom, S.D.; Chen, A.W.; Deines-Jones, P.; Esposito, J.A.; Fichtel, C.E.; Friedlander, D.P.; Hunter, S.D.; McDonald, L.M.; et al. The Third EGRET Catalog of High-Energy Gamma-Ray Sources. Astrophys. J. 1999, 123, 79–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.; Chadwick, P.M.; Cottle, P.J.; Dickinson, J.E.; Dickinson, M.R.; Dipper, N.A.; Hilton, S.E.; Hogg, W.; Holder, J.; Kendall, T.R.; et al. The University of Durham Mark 6 Gamma Ray Telescope. Exp. Astron. 1999, 9, 51–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Lyons, K.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Osborne, J.L.; Rayner, S.M.; Shaw, S.E.; Turver, K.E. A Search for Very High Energy Gamma Rays from Active Galactic Nuclei Visible from the Southern Hemisphere. Astrophys. J. 1999, 521, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Axelsson, M.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Baughman, B.M.; et al. Bright Active Galactic Nuclei Source List from the First Three Months of the Fermi Large Area Telescope All-Sky Survey. Astrophys. J. 2009, 700, 597–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W. Very High Energy gamma-ray emission from AP Lib detected by H.E.S.S. Astron. Telegr. 2010, 2743, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, P.; Fegan, S.; Horan, D.; Sanchez, D.; Fermi LAT Collaboration; Gielbels, B.; Becherini, Y.; Dubus, G.; de Naurois, M.; Punch, M.; et al. Gamma-ray emission from AP Librae (PKS1514-241). In Proceedings of the 25th Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics, Heidelberg, Germany, 6–10 December 2010; p. 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, S. Extended X-ray jet and TeV emission in a low frequency peaked BL Lac object Extra-galactic sources II (Gamma-ray bursts). In Proceedings of the International Cosmic Ray Conference, Beijing, China, 11–18 August 2011; Volume 8, p. 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. E. S. S. Collaboration; Abramowski, A.; Aharonian, F.; Ait Benkhali, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Angüner, E.; Anton, G.; Backes, M.; Balenderan, S.; Balzer, A.; et al. The high-energy γ-ray emission of AP Librae. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 573, A31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, S.; Wagner, S.J.; Tibolla, O. Discovery of an Extended X-Ray Jet in AP Librae. Astrophys. J. 2013, 776, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basumallick, P.P.; Gupta, N. Constraints on Proton Synchrotron Origin of Very High Energy Gamma Rays from the Extended Jet of AP Librae. Astrophys. J. 2017, 844, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carangelo, N.; Falomo, R.; Kotilainen, J.; Treves, A.; Ulrich, M.H. Optical spectroscopy of BL Lac objects: New redshifts and mis-identified sources. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 412, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kollgaard, R.I.; Palma, C.; Laurent-Muehleisen, S.A.; Feigelson, E.D. Radio Constraints on Relativistic Beaming Models of BL Lacertae Objects. Astrophys. J. 1996, 465, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; Blandford, R.D.; Bloom, E.D.; et al. 3FHL: The Third Catalog of Hard Fermi-LAT Sources. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2017, 232, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Padovani, P.; Mastichiadis, A.; Resconi, E. Photohadronic origin of γ-ray BL Lac emission: Implications for IceCube neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 2412–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, C.; Tavecchio, F.; Guetta, D. High-energy emitting BL Lacs and high-energy neutrinos. Prospects for the direct association with IceCube and KM3NeT. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 598, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Resconi, E.; Giommi, P.; Arsioli, B.; Chang, Y.L. Extreme blazars as counterparts of IceCube astrophysical neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah Ramazani, V.; Lindfors, E.; Nilsson, K. Empirical multi-wavelength prediction method for very high energy gamma-ray emitting BL Lacertae objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 608, A68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resconi, E.; Coenders, S.; Padovani, P.; Giommi, P.; Caccianiga, L. Connecting blazars with ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays and astrophysical neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, J.J.; Cotton, W.D.; Greisen, E.W.; Yin, Q.F.; Perley, R.A.; Taylor, G.B.; Broderick, J.J. The NRAO VLA Sky Survey. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, E.; Maselli, A.; Leto, C.; Perri, M.; Giommi, P.; Piranomonte, S. The 5th edition of the Roma-BZCAT. A short presentation. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2015, 357, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britzen, S.; Witzel, A.; Gong, B.P.; Zhang, J.W.; Gopal-Krishna; Goyal, A.; Aller, M.F.; Aller, H.D.; Zensus, J.A. Understanding BL Lacertae objects. Structural and kinematic mode changes in the BL Lac object PKS 0735+178. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 515, A105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, B.; Gasparrini, D.; Ciprini, S. The Fourth Catalog of Active Galactic Nuclei Detected by the Fermi Large Area Telescope—Data Release 2. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.08406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carswell, R.F.; Strittmatter, P.A.; Williams, R.E.; Kinman, T.D.; Serkowski, K. Optical Observations of the Radio Source 0735+178. Astrophys. J. Letters 1974, 190, L101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falomo, R.; Ulrich, M.H. Optical imaging and spectroscopy of BL Lac objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 357, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, T.A.; Stocke, J.T. The Properties of the Radio-Selected 1 Jy Sample of BL Lacertae Objects*. Astron. J. 2001, 122, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, K.; Pursimo, T.; Villforth, C.; Lindfors, E.; Takalo, L.O.; Sillanpää, A. Redshift constraints for RGB 0136+391 and PKS 0735+178 from deep optical imaging. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 547, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falomo, R.; Treves, A.; Paiano, S. Optical view of neutrino emitter candidate PKS 0735 +178. Astron. Telegr. 2021, 15132. [Google Scholar]
- IceCube Collaboration. IceCube-211208A—IceCube observation of a high-energy neutrino candidate track-like event. GRB Coord. Netw. 2021, 31191, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dzhilkibaev, Z.A.; Suvorova, O.; Baikal-GVD Collaboration. Baikal-GVD observation of a high-energy neutrino candidate event from the blazar PKS 0735+17 at the day of the IceCube-211208A neutrino alert from the same direction. Astron. Telegr. 2021, 15112, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Petkov, V.B.; Novoseltsev, Y.F.; Novoseltseva, R.V.; Baksan Underground Scintillation Telescope Group. Baksan Underground Scintillation Telescope observation of a GeV neutrino candidate event at the time of a gamma-ray flare of the blazar PKS 0735+17, a possible source of coinciding IceCube and Baikal high-energy neutrinos. Astron. Telegr. 2021, 15143, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Filippini, F.; Illuminati, G.; Heijboer, A.; Gatius, C.; Muller, R.; Dornic, D.; Huang, F.; Le Stum, S.; Palacios González, J.; Celli, S.; et al. Search for neutrino counterpart to the blazar PKS0735+178 potentially associated with IceCube-211208A and Baikal-GVD-211208A with the KM3NeT neutrino detectors. Astron. Telegr. 2022, 15290, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, R.; Das, S.; Gupta, N.; Majumdar, P.; Czerny, B. Dissecting the broad-band emission from γ-ray blazar PKS 0735+178 in search of neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 527, 8746–8754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramacere, A.; Giommi, P.; Perri, M.; Verrecchia, F.; Tosti, G. Swift observations of the very intense flaring activity of Mrk 421 during 2006. I. Phenomenological picture of electron acceleration and predictions for MeV/GeV emission. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 501, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramacere, A.; Massaro, E.; Taylor, A.M. Stochastic Acceleration and the Evolution of Spectral Distributions in Synchro-Self-Compton Sources: A Self-consistent Modeling of Blazars’ Flares. Astrophys. J. 2011, 739, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramacere, A. JetSeT: Numerical modeling and SED fitting tool for relativistic jets. Astrophysics Source Code Library, record ascl:2009.001, 2020. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020ascl.soft09001T/abstract (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Dominguez, A.; Primack, J.R.; Rosario, D.J.; Prada, F.; Gilmore, R.C.; Faber, S.M.; Koo, D.C.; Somerville, R.S.; Pérez-Torres, M.A.; Pérez-González, P.; et al. Extragalactic Background Light Inferred from AEGIS Galaxy SED-type Fractions. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2011, 410, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Rodighiero, G.; Vaccari, M. The extragalactic optical-infrared background radiations, their time evolution and the cosmic photon-photon opacity. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 487, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.D.; Razzaque, S.; Dermer, C.D. Modeling the Extragalactic Background Light from Stars and Dust. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H.; Yang, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.Y. The gamma-ray Doppler factor determinations for a Fermi blazar sample. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalewajko, K. The brightest gamma-ray flares of blazars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 430, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Maraschi, L.; Celotti, A.; Sbarrato, T. The power of relativistic jets is larger than the luminosity of their accretion disks. Nature 2014, 515, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchio, F.; Ghisellini, G.; Ghirlanda, G.; Foschini, L.; Maraschi, L. TeV BL Lac objects at the dawn of the Fermi era. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 401, 1570–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, E.W.; Zhang, S.N.; Bai, J.M. Radiation Mechanisms and Physical Properties of GeV–TeV BL Lac Objects. Astrophys. J. 2012, 752, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Yang, H.Y.; Zheng, Y.G.; Kang, S.J. The Energy Budget in the Jet of High-frequency Peaked BL Lacertae Objects. Astrophys. J. 2024, 967, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembinski, H.; Ongmongkolkul, P.; Deil, C.; Schreiner, H.; Feickert, M.; Burr, C.; Watson, J.; Rost, F.; Pearce, A.; Geiger, L.; et al. Scikit-Hep/Iminuit. 2024. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/13923658 (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman-Mackey, D.; Hogg, D.W.; Lang, D.; Goodman, J. emcee: The MCMC Hammer. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2013, 125, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisellini, G. Electron–positron pairs in blazar jets and γ-ray loud radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2012, 424, L26–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, M.; Rudolph, A.; Rodrigues, X.; Yuan, C.; de Clairfontaine, G.F.; Fedynitch, A.; Winter, W.; Pohl, M.; Gao, S. AM3: An Open-source Tool for Time-dependent Lepto-hadronic Modeling of Astrophysical Sources. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2024, 275, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hümmer, S.; Rüger, M.; Spanier, F.; Winter, W. Simplified Models for Photohadronic Interactions in Cosmic Accelerators. Astrophys. J. 2010, 721, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliu, E.; Archambault, S.; Arlen, T.; Aune, T.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Boettcher, M.; Bouvier, A.; Bugaev, V.; Cannon, A.; et al. Multiwavelength observations of the AGN 1ES 0414+ 009 with VERITAS, Fermi-LAT, Swift-XRT, and MDM. Astrophys. J. 2012, 755, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciari, M.C.V.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.; Arbet Engels, A.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Barres de Almeida, U.; Barrio, J.; Becerra González, J.; Bednarek, W.; et al. An intermittent extreme BL Lac: MWL study of 1ES 2344+ 514 in an enhanced state. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 3912–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.G.; Long, G.B.; Yang, C.Y.; Bai, J.M. Verification of the diffusive shock acceleration in Mrk 501. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 3855–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, M.; Wagner, S.J. The extended jet of AP Librae: Origin of the very high-energy γ-ray emission? Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 588, A110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, R.M.; Markoff, S.; Trager, S.C.; Anderson, S.F. Dynamical black hole masses of BL Lac objects from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 413, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Acharyya, A.; Adams, C.B.; Archer, A.; Bangale, P.; Bartkoske, J.T.; Batista, P.; Benbow, W.; Brill, A.; Buckley, J.H.; Christiansen, J.L.; et al. Multiwavelength Observations of the Blazar PKS 0735+178 in Spatial and Temporal Coincidence with an Astrophysical Neutrino Candidate IceCube-211208A. Astrophys. J. 2023, 954, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, X.; Paliya, V.S.; Garrappa, S.; Omeliukh, A.; Franckowiak, A.; Winter, W. Leptohadronic multi-messenger modeling of 324 gamma-ray blazars. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 681, A119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achterberg, A.; Gallant, Y.A.; Kirk, J.G.; Guthmann, A.W. Particle acceleration by ultrarelativistic shocks: Theory and simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 328, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.C.; Double, G.P. Diffusive shock acceleration in unmodified relativistic, oblique shocks. Astropart. Phys. 2004, 22, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).