Estimating Galactic Structure Using Galactic Binaries Resolved by Space-Based Gravitational Wave Observatories
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Resolving Galactic Binaries
2.1. Overview of GBSIEVER Algorithm
2.1.1. Parameter Estimation with -Statistic
2.1.2. Frequency Binning and Undersampling
2.1.3. Cross-Validation Procedure
2.2. GBSIEVER Terminology
- True sources—those present in the original LDC simulated source catalog;
- Identified sources—the initial, comprehensive collection of candidate sources generated during the single-source search phases (primary or secondary) of GBSIEVER, before applying any selection criteria;
- Reported sources—the final subset of primary search identified sources returned by GBSIEVER which exceed the thresholds;
- Confirmed sources—those reported sources that correspond to true sources and the correlation between reported and true sources calculated from Equation (3) exceeds a predefined threshold.
2.3. Detection Results
3. Galactic Structure Estimation
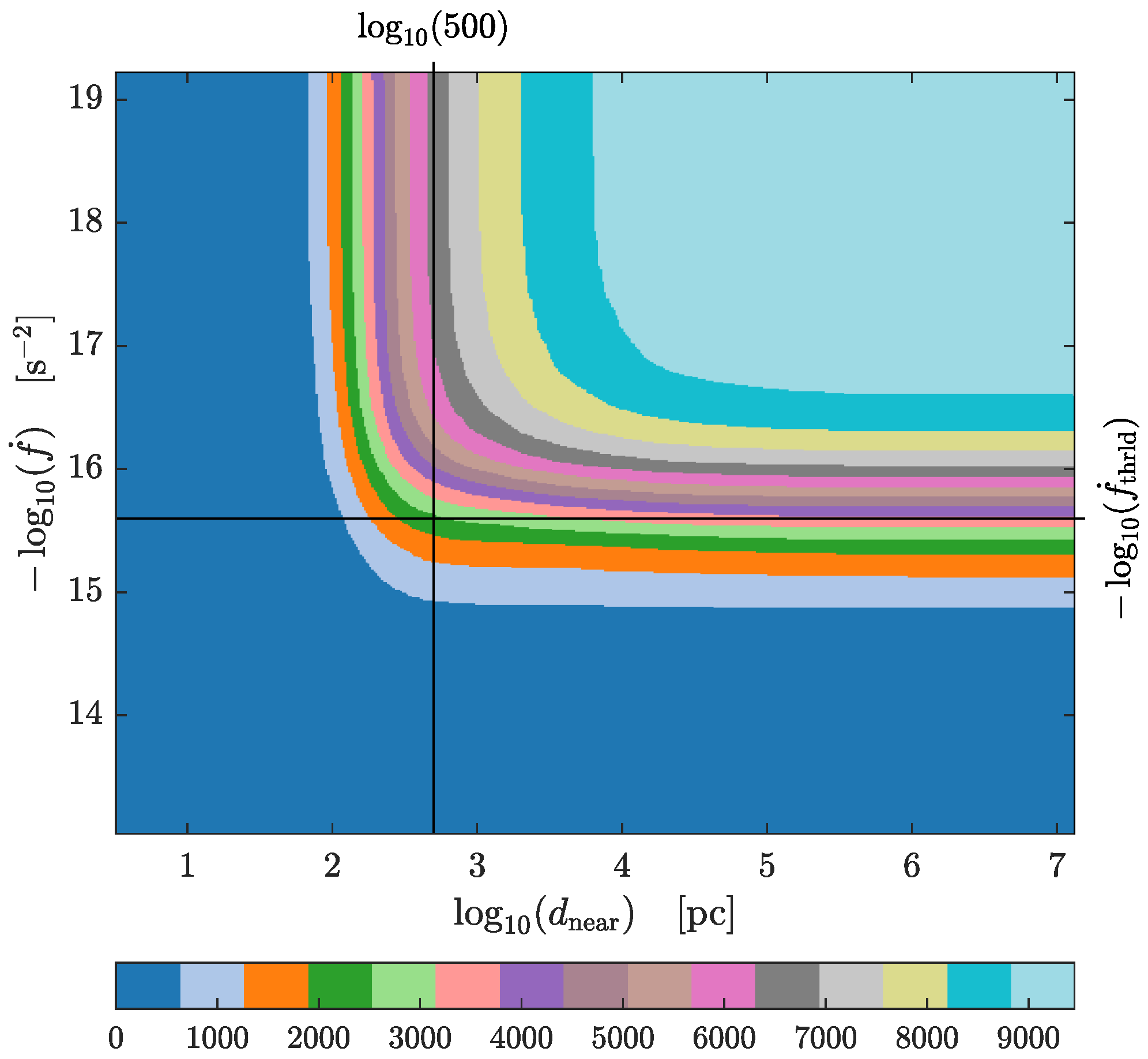
3.1. Distance Determination and Source Selection Methodology
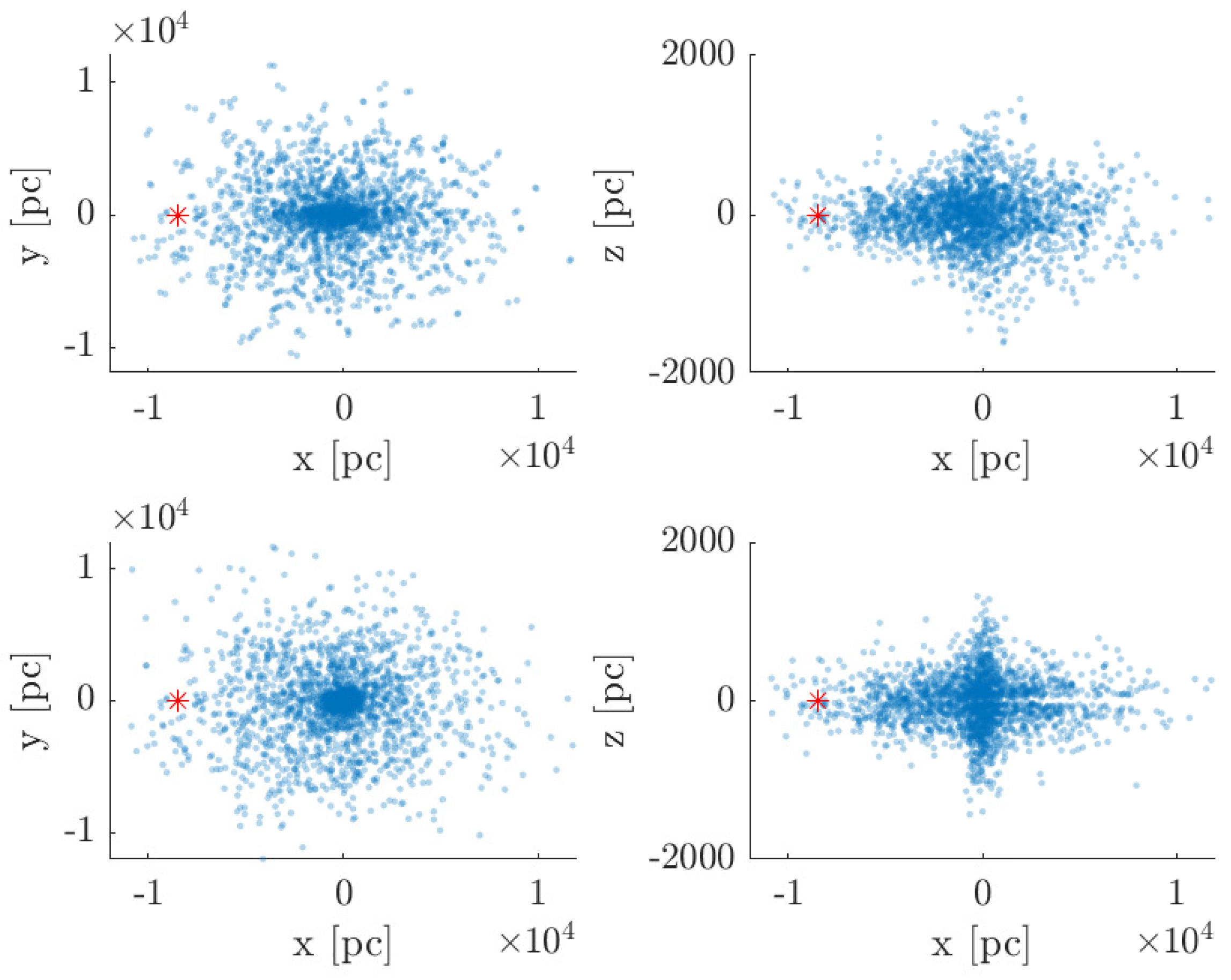
3.2. Galactic Spatial Distribution Model
3.3. Maximum Likelihood Estimation
4. Results
4.1. Galactic Structure Parameter Estimation
4.2. Effect of Measurement Errors
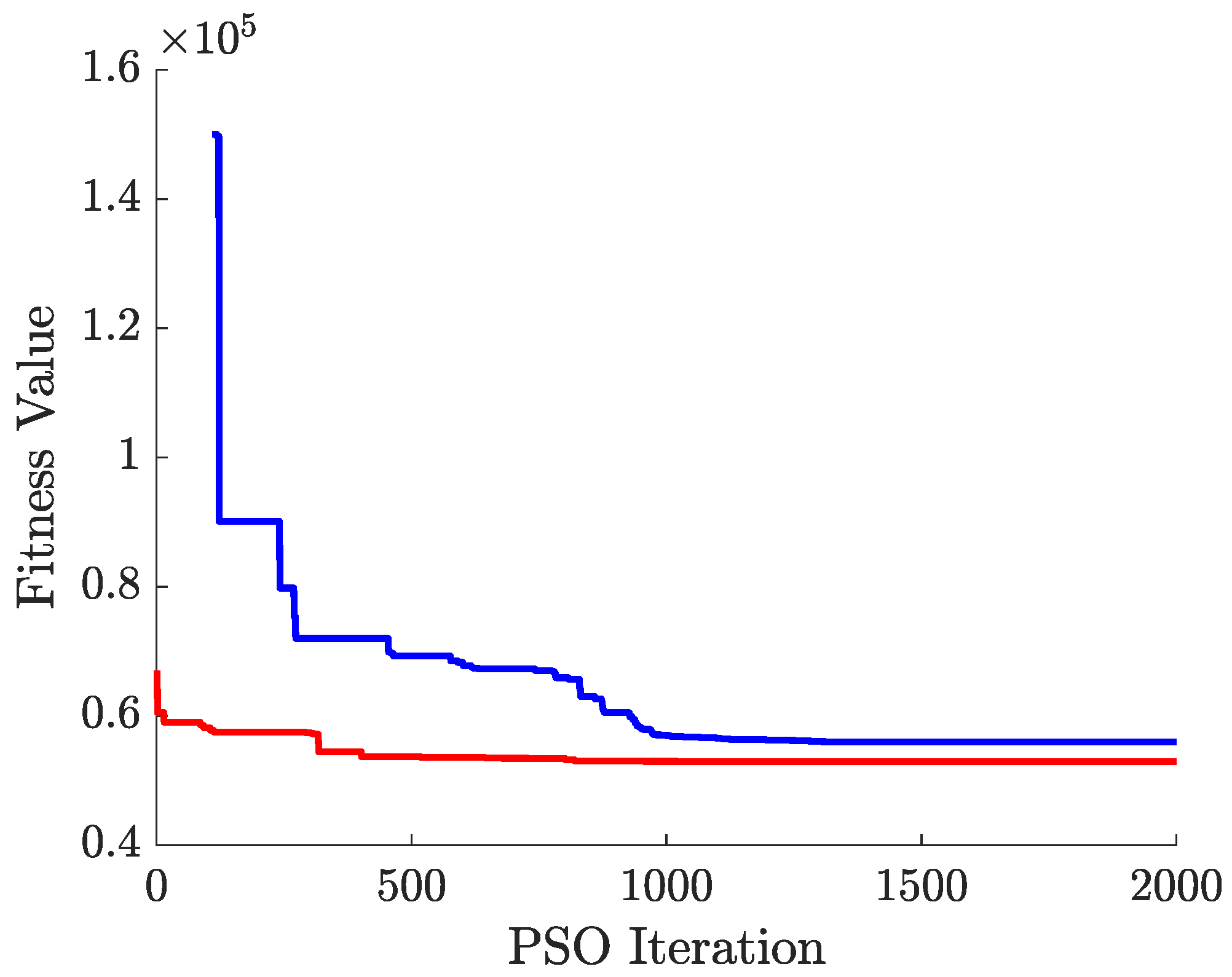
4.3. PSO Algorithm Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amaro-Seoane, P.; Audley, H.; Babak, S.; Baker, J.; Barausse, E.; Bender, P.; Berti, E.; Binetruy, P.; Born, M.; Bortoluzzi, D.; et al. Laser Interferometer Space Antenna. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.00786. [Google Scholar]
- Siebenmorgen, R.; Voshchinnikov, N.; Bagnulo, S. Dust in the diffuse interstellar medium-Extinction, emission, linear and circular polarisation. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 561, A82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontcharov, G. Interstellar extinction. Astrophysics 2016, 59, 548–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littenberg, T.B. Detection pipeline for Galactic binaries in LISA data. Phys. Rev. D—Part Fields, Gravit. Cosmol. 2011, 84, 063009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, S.; Baker, J.G.; Benacquista, M.J.; Cornish, N.J.; Larson, S.L.; Mandel, I.; McWilliams, S.T.; Petiteau, A.; Porter, E.K.; Robinson, E.L.; et al. The mock LISA data challenges: From challenge 3 to challenge 4. Class. Quantum Gravity 2010, 27, 084009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korol, V.; Rossi, E.M.; Barausse, E. A multimessenger study of the Milky Way’s stellar disc and bulge with LISA, Gaia, and LSST. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 483, 5518–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korol, V.; Toonen, S.; Klein, A.; Belokurov, V.; Vincenzo, F.; Buscicchio, R.; Gerosa, D.; Moore, C.; Roebber, E.; Rossi, E.; et al. Populations of double white dwarfs in Milky Way satellites and their detectability with LISA. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 638, A153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, M.J.; Korol, V.; Rossi, E.M.; D’Onghia, E. The Milky Way’s bar structural properties from gravitational waves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 500, 4958–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.M. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Sathyaprakash, B.S.; Dhurandhar, S. Gravitational waves from coalescing binaries: Detection strategies and Monte Carlo estimation of parameters. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 53, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, S.; Petiteau, A. LISA Data Challenge Manual; Technical Report LISA-LCST-SGS-MAN-002; APC: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: https://sbgvm-151-90.in2p3.fr/static/data/pdf/LDC-manual-002.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Breivik, K.; Mingarelli, C.M.; Larson, S.L. Constraining galactic structure with the LISA white dwarf foreground. Astrophys. J. 2020, 901, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgousi, M.; Karnesis, N.; Korol, V.; Pieroni, M.; Stergioulas, N. Gravitational waves from double white dwarfs as probes of the milky way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 519, 2552–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Deng, F.; Lu, Y.; Yu, S. Constraining the Galactic Structure Using Time Domain Gravitational Wave Signal from Double White Dwarfs Detected by Space Gravitational Wave Detectors. Astrophys. J. 2024, 978, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.H.; Guo, Z.K.; Cai, R.G.; Zhang, Y.Z. Taiji program: Gravitational-wave sources. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2020, 35, 2050075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnesis, N.; Babak, S.; Pieroni, M.; Cornish, N.; Littenberg, T. Characterization of the stochastic signal originating from compact binary populations as measured by LISA. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 043019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Mohanty, S.D.; Zou, X.B.; Liu, Y.X. Resolving Galactic binaries in LISA data using particle swarm optimization and cross-validation. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 024023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zhao, S.D.; Mohanty, S.D.; Liu, Y.X. Resolving Galactic binaries using a network of space-borne gravitational wave detectors. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghi, Q. The LISA Data Challenges. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.12142. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhart, R.; Kennedy, J. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Jaranowski, P.; Krolak, A.; Schutz, B.F. Data analysis of gravitational—Wave signals from spinning neutron stars. 1. The Signal and its detection. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinto, M.; Dhurandhar, S.V. Time-delay interferometry. Living Rev. Relativ. 2014, 17, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Tanner, J. Precise undersampling theorems. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.R.; Cornish, N.J.; Littenberg, T.B. Astrophysical model selection in gravitational wave astronomy. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 124032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.J.; Brunthaler, A. The proper motion of Sagittarius A*. II. The mass of Sagittarius A. Astrophys. J. 2004, 616, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.; Menten, K.; Brunthaler, A.; Zheng, X.; Dame, T.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Sanna, A.; Sato, M.; et al. Trigonometric parallaxes of high mass star forming regions: The structure and kinematics of the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. 2014, 783, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Bovy, J. Vertical waves in the solar neighbourhood in Gaia DR2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, R.; Vieira, K.; Lutsenko, A.; Korchagin, V.; Carraro, G. Determining the Scale Length and Height of the Milky Way’s Thick Disc Using RR Lyrae. Universe 2025, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| mHz | mHz | mHz | Overall | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | SNR | SNR | SNR | SNR | - | |
| - | ||||||
| Identified | 23,231 | 2106 | 3696 | 1526 | 4279 | 34,838 |
| Reported | 2767 | 2073 | 1622 | 1510 | 4279 | 12,251 |
| Confirmed | 1760 | 1892 | 1303 | 1394 | 4039 | 10,388 |
| Parameter | Description | Recovered Value |
|---|---|---|
| Bulge scale radius | ||
| Disk scale length | ||
| Disk scale height | ||
| A | Bulge fraction | |
| Solar distance from Galactic Center | ||
| Solar height above galactic plane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.-D.; Zhang, X.-H.; Mohanty, S.D.; Fullana i Alfonso, M.J.; Liu, Y.-X.; Xie, Q.-Y. Estimating Galactic Structure Using Galactic Binaries Resolved by Space-Based Gravitational Wave Observatories. Universe 2025, 11, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11080248
Zhao S-D, Zhang X-H, Mohanty SD, Fullana i Alfonso MJ, Liu Y-X, Xie Q-Y. Estimating Galactic Structure Using Galactic Binaries Resolved by Space-Based Gravitational Wave Observatories. Universe. 2025; 11(8):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11080248
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shao-Dong, Xue-Hao Zhang, Soumya D. Mohanty, Màrius Josep Fullana i Alfonso, Yu-Xiao Liu, and Qun-Ying Xie. 2025. "Estimating Galactic Structure Using Galactic Binaries Resolved by Space-Based Gravitational Wave Observatories" Universe 11, no. 8: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11080248
APA StyleZhao, S.-D., Zhang, X.-H., Mohanty, S. D., Fullana i Alfonso, M. J., Liu, Y.-X., & Xie, Q.-Y. (2025). Estimating Galactic Structure Using Galactic Binaries Resolved by Space-Based Gravitational Wave Observatories. Universe, 11(8), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11080248







