Non-Singular “Gauss” Black Hole from Non-Locality
Abstract
1. Introduction
- They do not solve the vacuum Einstein equations exactly, but their Einstein tensor decreases polynomially with distance away from the center at . Alternatively, this can be viewed as the presence of an effective energy–momentum tensor, and the properties of this matter source can be analyzed with respect to energy conditions. In accordance with Penrose’s singularity theorem, an energy condition is violated if the inner black hole singularity is avoided.
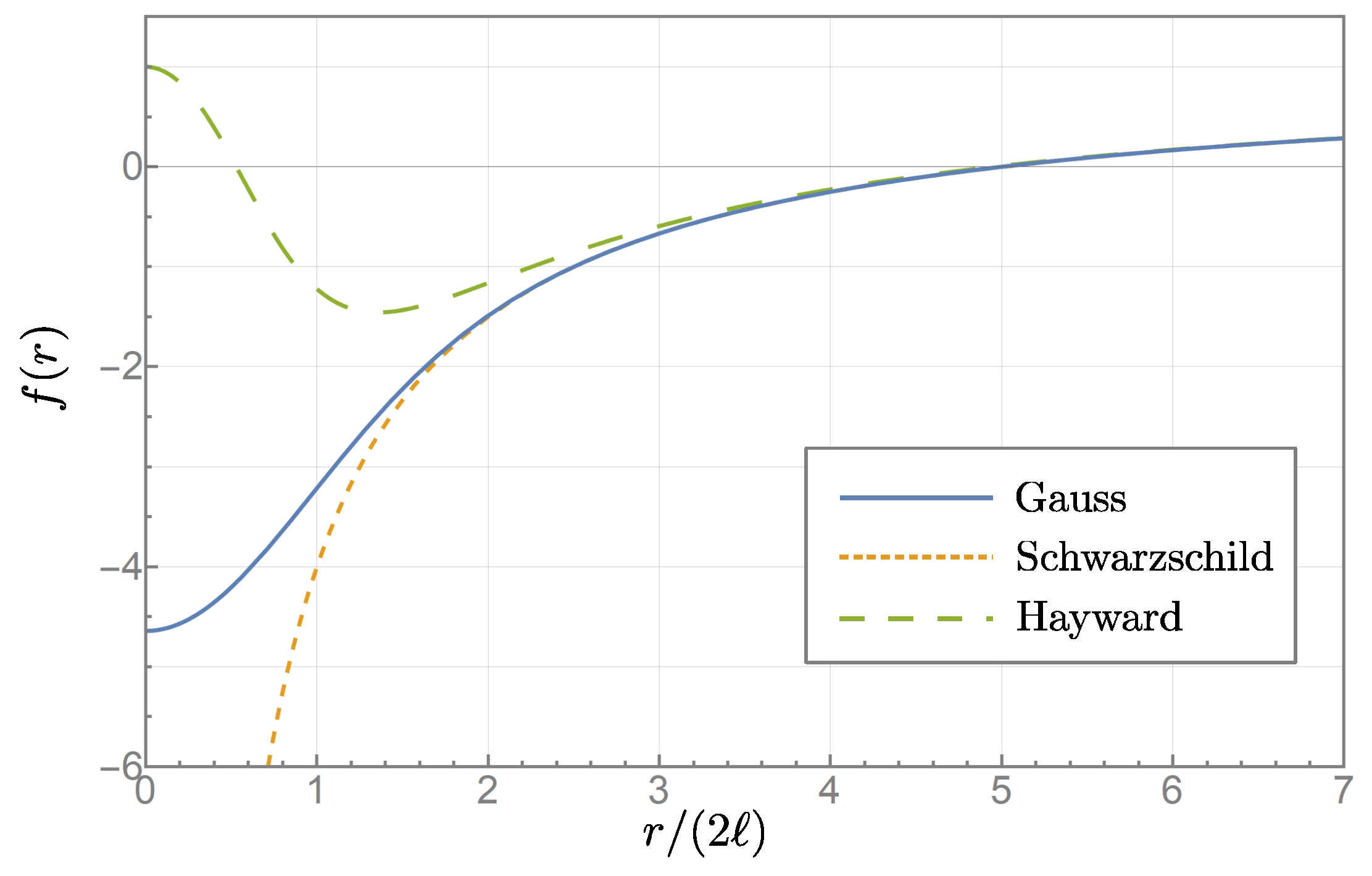
- In addition to the outer event horizon at , there exists an inner horizon at as well, where ℓ is the regularization scale.
- Close to , the geometry approaches a de Sitter form.
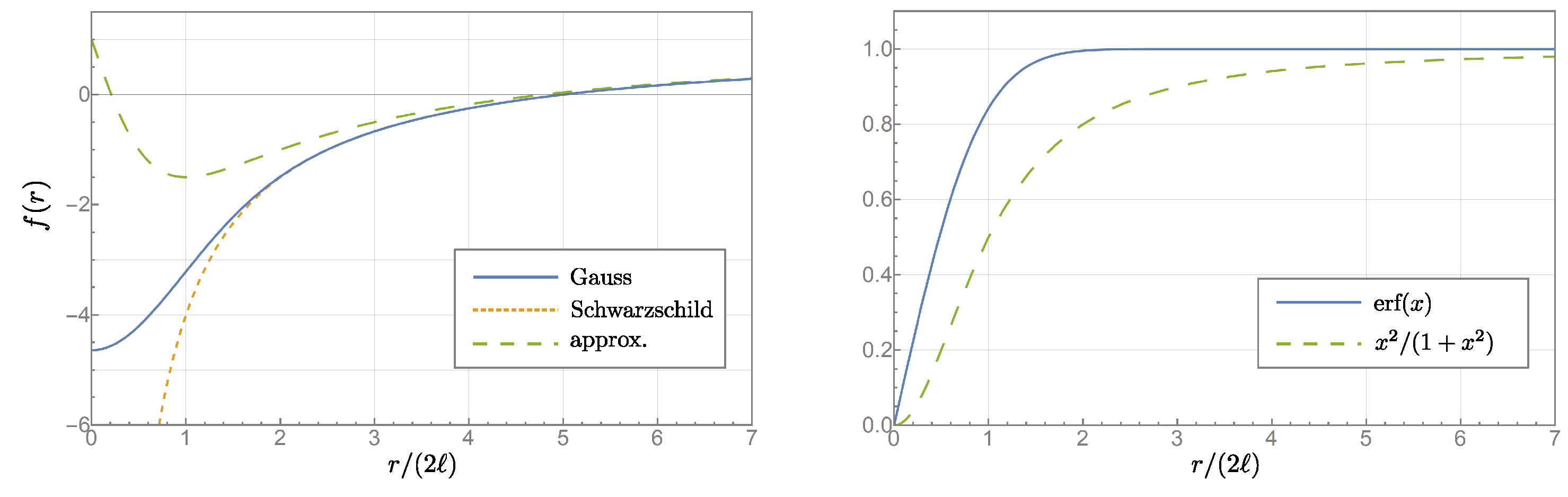
- At large distances , the regulator terms decrease rapidly and the metric increasingly approximates the Schwarzschild metric of general relativity.
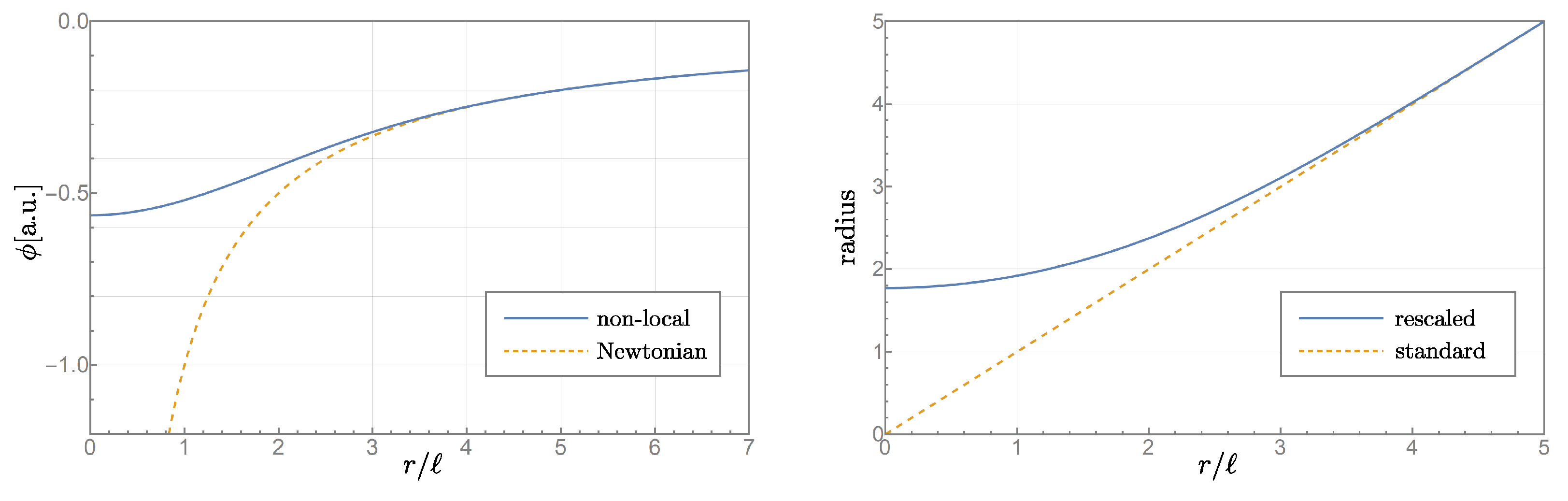
2. Modified Radius Variable
3. Non-Singular “Gauss” Black Hole Model
3.1. Horizons
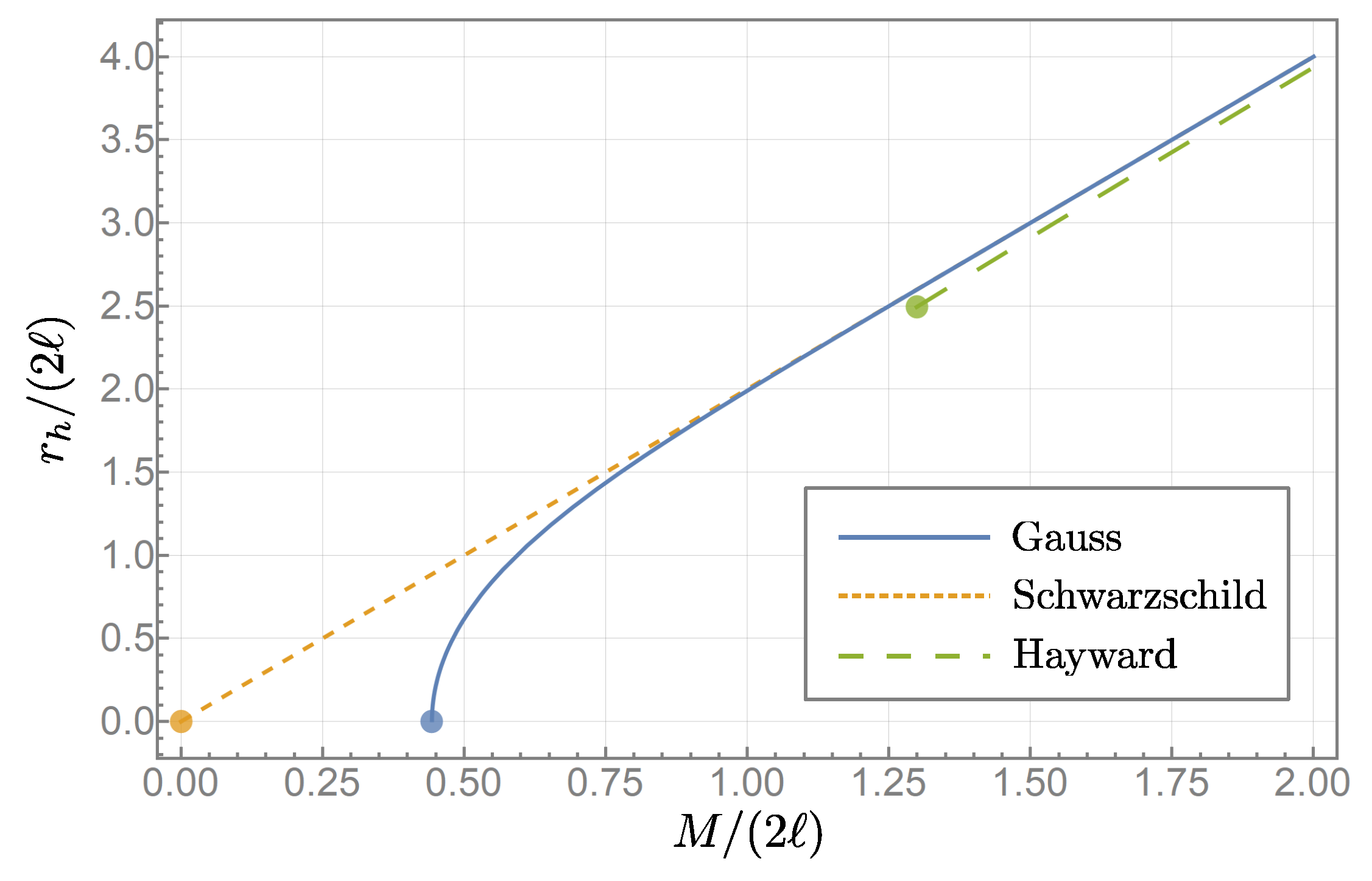
3.2. Mass Gap
3.3. Regularity and Curvature Invariants
3.4. Limiting Curvature Condition
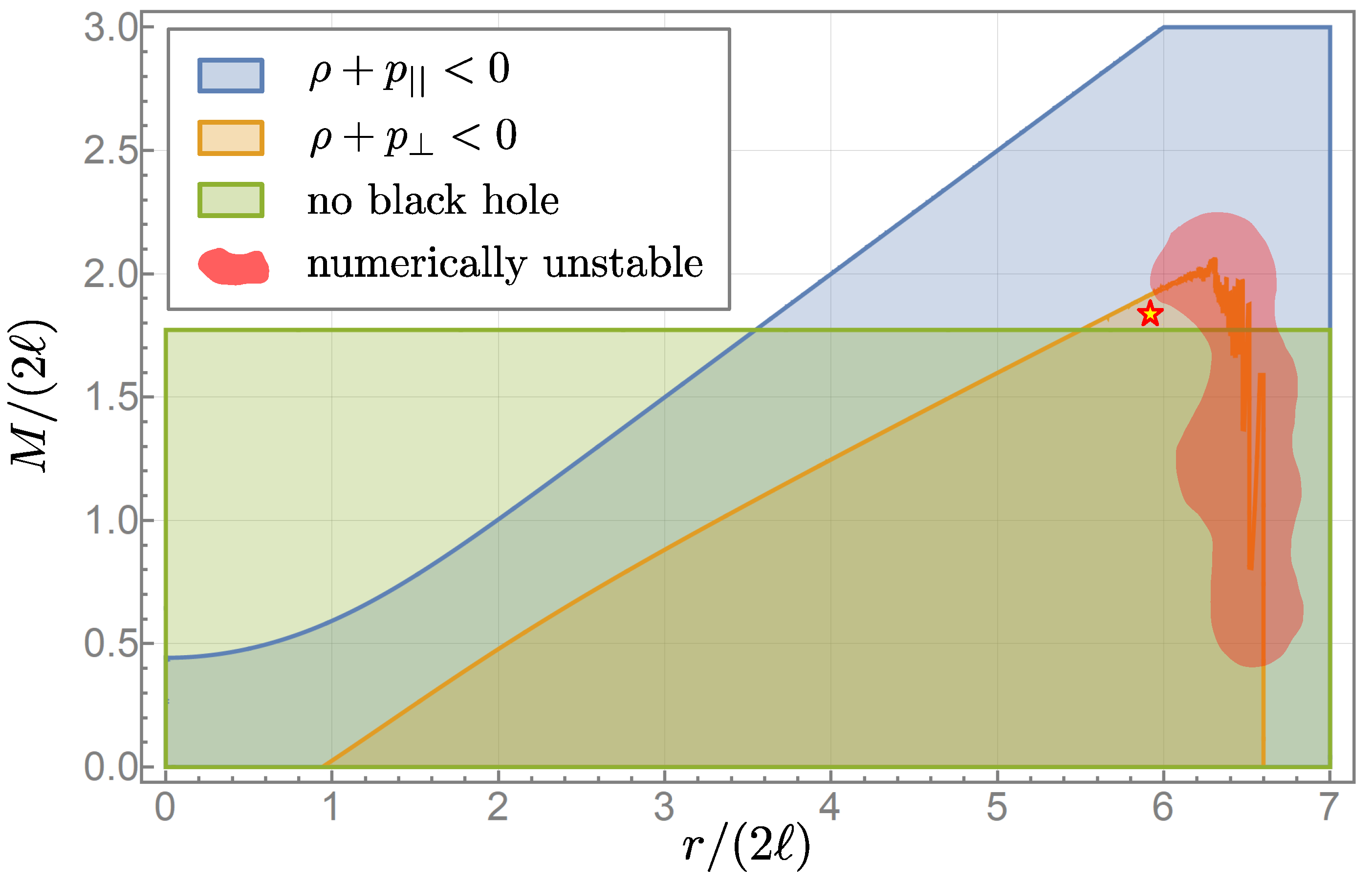
3.5. Effective Energy–Momentum Tensor and Energy Conditions
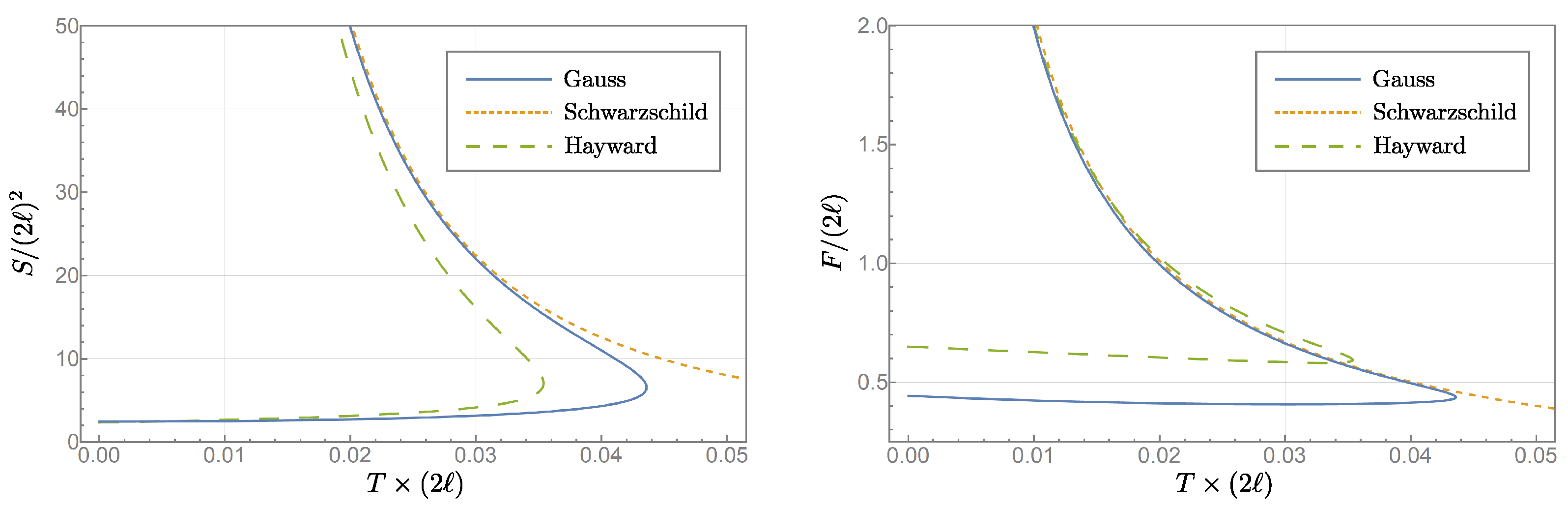
3.6. Black Hole Thermodynamics
3.7. Properties of , Wormholes, and Geodesic (In)Completeness
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bardeen, J.M. Non-singular general relativistic gravitational collapse. In Proceedings of the International Conference GR5; U.S.S.R.: Tbilisi, Georgia, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Dymnikova, I. Vacuum nonsingular black hole. Gen. Rel. Grav. 1992, 24, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, A.; Reuter, M. Renormalization group improved black hole spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 043008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.A. Formation and evaporation of regular black holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 31103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P. Information loss problem and a `black hole’ model with a closed apparent horizon. J. High Energy Phys. 2014, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P. Notes on non-singular models of black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P.; Zelnikov, A. Quantum radiation from an evaporating non-singular black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 124028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, P.A.; Chimento, S.; Ortín, T.; Ruipérez, A. Regular stringy black holes? Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 46014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Black-bounce to traversable wormhole. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, P.; Spallucci, E.; Wondrak, M.F. Quantum corrected black holes from string T-duality. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 797, 134888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Visser, M. Regular black holes with asymptotically Minkowski cores. Universe 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, A.; Khosravi, A.P.; Saueressig, F. Regular black holes have stable cores. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 124027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, M.A. Limiting density of matter as a universal law of nature. JETP Lett. 1982, 36, 266. [Google Scholar]
- Markov, M.A. Problems of a perpetually oscillating universe. Ann. Phys. 1984, 155, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polchinski, J. Decoupling versus excluded volume or return of the giant wormholes. Nucl. Phys. B 1989, 325, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomboulis, E.T. Superrenormalizable gauge and gravitational theories. arXiv 1997, arXiv:hep-th/9702146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Mazumdar, A.; Siegel, W. Bouncing universes in string-inspired gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2006, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto, L. Super-renormalizable quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 44005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Gerwick, E.; Koivisto, T.; Mazumdar, A. Towards singularity and ghost-free theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 31101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edholm, J.; Koshelev, A.S.; Mazumdar, A. Behavior of the Newtonian potential for ghost-free gravity and singularity-free gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacchini, B.L.; Netto, T.d. Effective delta sources and regularity in higher-derivative and ghost-free gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, J.; Frolov, V.P.; Zelnikov, A. Gravitational field of static p-branes in linearized ghost-free gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 84021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, J. Effects of Non-Locality in Gravity and Quantum Theory; Springer Theses; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, P. A model of radiating black hole in non-commutative geometry. J. Phys. A 2005, 38, L631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, P.; Smailagic, A.; Spallucci, E. Noncommutative geometry inspired Schwarzschild black hole. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 632, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallucci, E.; Smailagic, A.; Nicolini, P. Trace anomaly in quantum spacetime manifold. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 84004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto, L.; Moffat, J.W.; Nicolini, P. Black holes in an ultraviolet complete quantum gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 695, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, E.; Stojkovic, D. Quantum gravitational collapse: Non-singularity and non-locality. J. High Energy Phys. 2008, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, A.; Stojkovic, D. Non-local (but also non-singular) physics at the last stages of gravitational collapse. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 44003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olver, F.W.; Lozier, D.W.; Boisvert, R.F.; Clark, C.W. NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Poisson, E.; Israel, W. Inner-horizon instability and mass inflation in black holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 63, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, E.; Israel, W. Internal structure of black holes. Phys. Rev. D 1990, 41, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Koivisto, T.; Mazumdar, A. Non-local theories of gravity: The flat space propagator. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1302.0532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buoninfante, L.; Lambiase, G.; Mazumdar, A. Ghost-free infinite derivative quantum field theory. Nucl. Phys. B 2019, 944, 114646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P.; Zelnikov, A.; Netto, T.d. Spherical collapse of small masses in the ghost-free gravity. J. High Energy Phys. 2015, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P. Mass gap for black hole formation in higher derivative and ghost-free gravity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 51102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayon-Beato, E.; Garcia, A. Regular black hole in general relativity coupled to nonlinear electrodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartle, J.B.; Hawking, S.W. Path integral derivation of black hole radiance. Phys. Rev. D 1976, 13, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, G.W.; Hawking, S.W. Action integrals and partition functions in quantum gravity. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 15, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, G.W.; Perry, M.J. Black holes and thermal Green’s functions. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 1978, 358, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, V.P.; Zelnikov, A. Introduction to Black Hole Physics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bambi, C.; Modesto, L.; Rachwał, L. Spacetime completeness of non-singular black holes in conformal gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo-Rubio, R.; Filippo, F.D.; Liberati, S.; Visser, M. Geodesically complete black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 84047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkhamer, F.R. Black hole solution without curvature singularity. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 28, 1350136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boos, J. Non-Singular “Gauss” Black Hole from Non-Locality. Universe 2025, 11, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040112
Boos J. Non-Singular “Gauss” Black Hole from Non-Locality. Universe. 2025; 11(4):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040112
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoos, Jens. 2025. "Non-Singular “Gauss” Black Hole from Non-Locality" Universe 11, no. 4: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040112
APA StyleBoos, J. (2025). Non-Singular “Gauss” Black Hole from Non-Locality. Universe, 11(4), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040112





