Abstract
We examine the use of a novel variant of Physics-Informed Neural Networks to predict cosmological parameters from recent supernovae and baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO) datasets. Our machine learning framework generates uncertainty estimates for target variables and the inferred unknown parameters of the underlying PDE descriptions. Built upon a hybrid of the principles of Evidential Deep Learning, Physics-Informed Neural Networks, Bayesian Neural Networks, and Gaussian Processes, our model enables learning the posterior distribution of the unknown PDE parameters through standard gradient-descent-based training. We apply our model to an up-to-date BAO dataset (Bousis et al. 2024) calibrated with the CMB-inferred sound horizon, and the Pantheon+ Sne Ia distances (Scolnic et al. 2018), examining the relative effectiveness and mutual consistency among the standard CDM, wCDM and CDM models. Unlike previous results arising from the standard approach of minimizing an appropriate function, the posterior distributions for parameters in various models trained purely on Pantheon+ data were found to be largely contained within the contours of their counterparts trained on BAO data. Our study illustrates how a data-driven machine learning approach can be suitably adapted for cosmological parameter inference.
1. Introduction
In this paper, we present a framework based on using a neural network to infer cosmological parameters from the Pantheon+ dataset of [1] and a recent collection of the BAO dataset presented in [2]. The neural network model we use is a surrogate model quantifying the luminosity distance L vs. redshift z relationship, and its weight parameters are obtained through maximizing the degree of adherence to the following one-dimensional ODE
where is the Hubble function parametrized by and c is the speed of light. Equation (1) follows from the defining relation
where L is in units of Mpc, and its form is more convenient for us to infer unknown parameters of which depend on the underlying cosmological model assumed. In this work, we will consider two classes of deviations from the standard CDM model described via the wCDM and CDM models. The former refers to the standard CDM model but with the equation of state parameter for dark energy w being not necessarily −1 (see ref. [3] for a recent study). In fitting it to the data, we take the free parameters of the wCDM model to be , where are the Hubble constant and total matter density, respectively. For the CDM model [4], here we take its free parameters to be , where is a transition redshift value from which the cosmological constant switches sign, representing a toy model of vacua transition from anti-de Sitter to de Sitter spacetime at some point in the early universe. These models are parametrically deformable to the standard CDM model in the limits of for the wCDM model and for the CDM model.
In standard regression techniques invoking the principle of maximum likelihood estimation, cosmological parameters are inferred through minimizing a likelihood of the form (see [5])
where C is the covariance matrix expressing uncertainties and is the parameter residuals, with being an observed value and being the corresponding theoretical estimate computed with Equation (2).
A fundamental difference between using (3) and a neural network-based approach is that the latter is structured around a surrogate model that represents the target variable as a function of the input variable, apart from an inference of the unknown parameters. Analogous to the pure numerical solution equipped with the best-fit parameters that minimizes (3), the final model is characterized by a set of network parameters that correspond to the minimum of a loss function that generalizes (3). For a multilayer-perceptron model trained using just a mean-squared error loss term, model training then translates to solving (3) through a gradient-descent-based approach with being the neural network. For more complicated frameworks such as that of Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) [6] where PDE constraints are simultaneously imposed, the loss function can be much more complex than (3). In this work, we examine the use of as an independent data-driven model to infer probability distributions for the parameters from data, in a manner consistent with Bayesian principles. To do so, we need a framework that ideally yields together with its predictive uncertainty. It should also yield the posterior distribution for each unknown parameter of the cosmological model upon completion of model training.
Recently in [7,8], Evidential Physics-Informed Neural Networks (or E-PINNs for short) was proposed as a framework for PDE-based scientific modeling that encapsulates uncertainty quantification robustly. It realizes a hybrid implementation of the algorithms of Evidential Deep Learning [9,10] and those of PINN. In [8], a principled approach was proposed for constructing priors for the unknown parameters and the learnable loss weight of the PDE residual term which is taken as the likelihood function for the unknown parameters. Gradient-descent-based training then translates to the maximum a posteriori learning of the distribution of the unknown parameters and weights of the surrogate model . In this paper, we will use E-PINN as the machine learning framework for learning cosmological parameters from the Pantheon+ and BAO datasets.
We examine the differences in the inferred cosmological parameters when E-PINN is trained on these datasets separately and examine how E-PINN differentiates among the alternative cosmological models with respect to each dataset and their synthesis. In the aspect of the model training algorithm, while still leveraging the basic framework of E-PINN as proposed in [8], we also incorporate Gaussian Process Regression [11] within the training algorithm in a few ways to refine the parameter inference process. Gaussian Process is used to guide the construction of the prior distributions for . The predictive variance values provided by Gaussian Process Regression are employed as proxy targets to supervise the learning of epistemic uncertainty in our model. Although our primary motivation for incorporating Gaussian Processes into the framework stems from the relatively small size of the BAO dataset [2], the methods we propose are readily transferable to other scientific modeling problems and extend the versatility of the E-PINN toolkit of [8].
Previous to our work, there have been studies [12,13,14,15,16,17,18] related to the use of neural network-based models for analyzing cosmological data and the inference of parameters. In [12], PINN was applied to the Union 2.1 dataset, and an uncertainty framework was proposed where the perceptron model’s outputs were taken to be the (mean) luminosity distance and its associated uncertainty, with the loss function being the log-likelihood of the Gaussian with the outputs as its moments. For us, following the framework of Evidential Deep Learning, we assert a prior distribution (normal-inverse-gamma) for the mean and variances, integrating them out to obtain a t-distribution as the marginal likelihood. Our model’s outputs then correspond to the learnable parameters of this higher-order distribution. In contrast to our work, in [12], there was no methodology proposed to infer unknown cosmological parameters from the data. In [13], the authors essentially used PINN (see Equation (33) of [13]) and were focused primarily on whether PINN can be used to reproduce numerical solutions of PDE (in the context of cosmological models). Ref. [13] performed parameter inference but it was performed using the standard regression method of minimizing the . In [14,19], no PINN-related formalism was invoked but a perceptron model trained on simulated data generated based on some chosen fiducial values of the cosmological parameters and synthetic noise added to the redshift. The statistical inference was performed using the standard method as in [13], rather than through a learned posterior distribution supported by a data-informed prior in our framework.
Our paper is organized as follows. We begin by presenting the theoretical formulation of the E-PINN model in Section 2, including how we invoked Gaussian Processes to enhance the original framework of [8]. This is followed by a discussion on methodology such as model training implementation details, metrics, etc., in Section 3. Our main results on the cosmological parameters are collected in Section 4. We end with a summary and some comments on the relevance of our work to the Hubble tension problem [20] in Section 5. Appendix A contains some technical details related to the loss function, including a detailed derivation for the hyperparameters of the prior for the PDE residual loss weight, while Appendix B gathers various corner plots for the posterior distributions predicted by our models. Our study illustrates how a data-driven machine learning approach can be suitably adapted for cosmological parameter inference.
2. Model Formulation
In this section, we introduce the main ideas and practical implementation of E-PINN, and explain how we extend the original algorithm of [8] by incorporating Gaussian Processes to construct the parameters’ prior and supervise learning of the epistemic uncertainty. We refer the reader to [8] for a more technical exposition of E-PINN.
2.1. Basic Structure of the Neural Network and the Loss Function
For our purpose (and for the general context of regression), we take the base neural network of E-PINN to be a multilayer perceptron , where z denotes its input, and its weight parameters. In our work here, z is the redshift value associated with the measured luminosity distance of some astrophysical object/phenomenon. Our model has four output neurons , with one of them () pertaining to the mean of the target (luminosity distance) and the other three related () to the predictive uncertainty as follows:
The uncertainty is the variance of a probability distribution that describes the statistical fluctuation of the observed target about its mean. This probability distribution is a t-distribution defined by the following density function:
where is the observed luminosity distance, and is the model prediction (to be interpreted as a mean value), with being its other parameters which set the scale for its variance (Equation (4)) and other moments. (In Appendix A, we provide more details on how this is related to Gaussian distributions.) In Equation (5), denotes the probability of observing the data given the model . Here, and henceforth, we suppress the input z for simplicity, and all variables on the RHS of Equation (5) are to be understood as functions of z which is the input variable of the model, with being the model’s outputs. For them to be interpreted as what we have described thus far, we need a suitable loss function that is derived based on these principles. Here, we take the negative log-likelihood of Equation (5) to be part of our complete loss function:
If we do not allude to any PDE constraints, i.e., asserting that Equation (1) describes the data, then would constitute our complete loss function, and model training typically means using a gradient-descent-based method to find weights such that they minimize . We call the set of points the training dataset, with model training translating to iterations in the gradient-descent-based algorithm.
Now, let us bring in the putative PDE description for the observed data. For this work, this would be Equation (1) with some ansatz for that is in turn derived from cosmological approximations in General Relativity, etc. With the parameters unknown, we add the following loss term:
where k is a subscript denoting each data point, is the number of observations, and suppressing the data point index, we define
which refers to the RHS of Equation (1), with representing the mean luminosity distance. The parameter is a learnable parameter that evolves during model training, and from Equation (7), we can see that it acts as a weighting factor quantifying the magnitude of this loss term relative to other loss terms in the complete loss function. Equation (7) guides the model towards adhering to the ODE (1) when added to the complete loss function to be minimized. We also used the symbol to denote the interpretation of this term as the likelihood of obtaining as a surrogate model assuming the parameters .
In standard PINN, is a free parameter and, to our knowledge, there is no principled approach towards determining its choice. For our E-PINN model, we lift to be a learnable parameter that evolves as the model shifts towards a minimum in the loss landscape. We regularize this procedure by introducing another loss term that represents the negative logarithm of the prior density function for as follows:
In Appendix A.3, we furnish more detailed explanations of how (8) is derived, in particular showing that one can set of (8) such that these values align consistently with other aspects of our framework.
Thus far, we have motivated the inclusion of three different loss terms , with each of them being interpretable as the negative logarithm of some density/likelihood function. If we follow the principles of Bayesian statistics, we can further consider incorporating a prior density function for the unknown parameters. In Appendix A.2, we show that such a prior can be derived from considering the family of numerical solutions to the ODE and the model that is trained purely on data based on . Corresponding to , we thus introduce another loss term . Taking into account all the loss terms considered so far, we have the loss function
with the product being the joint likelihood function for . Upon completion of model training, we can place confidence intervals on the model’s predictions using of Equation (4). Since we infer the posterior distribution of at the end of model training, our framework thus appears as a maximum a posteriori estimation of , or more precisely1 a MLE estimation that is regularized by a prior .
From Equation (5), we can see that while the empirical data correlates with the mean output (through the factor ), there is no other external information supervising the three other uncertainty-related outputs . In our context, the cosmological datasets are already equipped with uncertainty estimates which we can potentially use to refine model training. In the following Section 2.2, we discuss this issue in detail and introduce Gaussian Processes as a complementary tool to supervise the learning of the model’s uncertainty. For model training, this further introduces a couple more loss terms to be added to (9) for our complete loss function.
2.2. Using Gaussian Processes to Supervise Uncertainties
Although model training can proceed without additional information on data uncertainties, the datasets selected for our work here are already equipped with measurement uncertainties—for the BAO data, these were computed in [2] from raw uncertainties of each sample as collected in Table 1 of [2], whereas for the Pantheon data, we used the diagonal elements of the covariance matrix presented in [21]. They correspond to what is known in the machine learning terminology as ‘aleatoric uncertainties’ which generally refer to uncertainties that are measurement or observation-related such as noise, etc. We add a simple mean-squared-loss term in the form
where denotes the measurement’s statistical variance for each point, and denotes taking the average over all the training samples. In Appendix A, we explain more carefully why the factor of arises in (10).
Now there is another notion of uncertainty known as the ‘epistemic uncertainty’, which pertains to the model itself instead of the data measurement process. In contrast to aleatoric uncertainty, this is a quantity that characterizes the degree of data sufficiency and model complexity. It can be supervised in model training if there is some independent knowledge of the model variance. Here, we use a Gaussian Process Regression model to furnish information on the epistemic uncertainty distribution. A Gaussian Process (GP) is essentially a distribution over functions. Ref. [11] Denoting the GP by , schematically
where is the mean function and is the covariance kernel function. Here we took , a RBF function with a characteristic length scale l that we determine by maximizing the log marginal likelihood using the implementation in scikit-learn [22]. This length scale can be understood as a factor that controls the rate at which the correlation (as modeled by the kernel) decays with increasing separation. A relatively larger choice of l implies a kernel that is smoother and more slowly varying. Conditioned on an observed set of data , the posterior distribution for f evaluated at some arbitrary redshift is a Gaussian distribution with moments
where is the aleatoric uncertainty, and is used to supervise the learning of the epistemic uncertainty. To see why this is a natural choice, we recall that our framework assumes an auxiliary Gaussian target (the luminosity distance in our context) with normal-inverse-gamma distribution being the prior for its mean and variance, and the epistemic uncertainty being the expectation value of the auxiliary Gaussian’s variance. Thus, the GP variance in (11) is a natural candidate for supervising the learning of the epistemic uncertainty. Like aleatoric uncertainty in (10), we introduce an additional mean-squared loss term of the form
where is the GP variance at each training datapoint, and we are averaging over the training dataset. In Appendix A, we explain more carefully how the factor of arises in (12). Adding both uncertainty-related losses to Equation (9), our complete loss function is thus
The addition of the loss terms (10) and (12) guides the learning of the uncertainty-related model outputs to complement how the observed data supervises the learning of the mean target variable . We weighted each loss term with tunable coefficients that can be adjusted as hyperparameters to yield a good error calibration at the end of model training.
2.3. A Summary List of Model Implementation
For clarity, in the following, we provide a brief overview of the model implementation process. Our framework is structured around a two-phase training algorithm where in the first phase, the neural network is trained purely on the empirical dataset without alluding to the ODE in Equation (1). Apart from being used to derive one of the loss term (), this initial model also furnishes the general initial conditions (e.g., initial values for some of the learnable parameters) for model training in the second phase which uses the full loss function of (13).
- (I)
- (II)
- Independently, a GP regression model is fitted to data so as to gain epistemic uncertainty information for supervising , and for constructing (see Appendix A.2 for full details)
- (III)
- Upon convergence of the purely data-fitted model, we can now determine the prior following the steps described in Appendix A.3. (This essentially involves solving for using (A14) and (A16).)
- (IV)
- We then proceed with the second phase of model training. This phase of training refines the purely data-fitted model such that it conforms to the presumed PDE description. Apart from the model’s weights, are also learnable parameters. In this final phase, the model is trained using the full loss functionwith each of the six individual loss terms defined in Equations (6)–(8), (10), (12) and (A9).
- (V)
- Upon completion of training, the model predictions are expressed by the target variable while confidence bands can be constructed from . We also infer the PDE parameters with its uncertainty as defined by the median and credible intervals of the posterior distribution.
In [8], this framework was validated and compared against two other more popularly known models (Bayesian Physics-Informed Neural Networks and Deep Ensemble) for its uncertainty quantification and accuracy in recovering unknown PDE parameters. The controlled case studies used in [8] were nonlinear second-order differential equation in 1D (Poisson equation with Gaussian source) and 2D (Fisher–KPP equation). As shown in [8], the most significant superiority of E-PINN over these two standard uncertainty quantification frameworks is that it yields uncertainty estimates that are calibrated much more consistently (i.e., the confidence intervals deduced are much more consistent with actual model errors). In our context of inferring cosmological parameters, E-PINN thus appears to be well-suited since having a robust uncertainty quantification framework that can generate reliable posterior distributions is particularly critical for our purpose.
3. Methodology
3.1. On the Datasets and Some Limitations
The BAO dataset collected in Table 1 of [2] consists of 32 measurements. It is a list of transverse BAO measurements of the comoving angular diameter distance , where is the sound horizon scale at the end of the baryonic drag epoch. These samples include recent data such as those made by DESI [23,24], the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] and the Dark Energy Survey (DES) [39,40]. As described in [2], the samples involved anisotropic BAO analyses which incorporate the full 3D galaxies’ distributions, often based on some fiducial cosmological model to convert observed angles and redshifts into physical distances. In [2], the sound horizon was taken to be 147.18 Mpc following Planck18 report [41], and here we adopted the same value for in when translating values of in Table 1 of [2] to . This is a limitation of our work which, in principle, can be overcome by deriving expressions for for each cosmological models (equipped with unknown, learnable parameters) and then replacing numerical luminosity distance targets with where is the numerical value in Table 1 of [2]. In practice, this would complicate the gradient-descent-based model training because can only be expressed through a numerical integral and not an explicit function of . An ideal approach would be to adopt a model-independent value for if possible. Interestingly, we note that lowering the sound horizon to 140 Mpc recently proposed by Liu et al. in [42]) to be a model-independent result would naively yield the BAO dataset to be visually compatible with that of Pantheon+ data on the plane. Another model-independent determination of was performed in [43], which employed another set of combined SNe Ia and BAO data to yield a value of in units of Mpc. Since we have chosen to use the collection of BAO data of [2] for definiteness to enable comparison of the posterior distributions and best-fit values to the standard analysis performed in [2], we used the same Planck18 Mpc value as was used in [2], leaving a more extensive investigation of dependence for future work.
Another caveat that we would like to emphasize is that the data points presented in Table 1 of [2] are however characterized by correlations2, since several entries are obtained from surveys that partially overlap in sky coverage and source populations (e.g., galaxies and quasars). For example, the pair of points labeled in [2] with values being (0.32, 8.54), (0.32, 8.76) both originated from SDSS-III data. A limitation of our model is that it does not enable any external knowledge of correlations among points to be used directly in the learning of weights. The fundamental reason is that the t-distribution (A1) underpinning the data loss term is derived from marginalizing over the means and variances of products of univariate Gaussian distributions (rather than multivariate ones). On the other hand, we note that there are also pairs of points in Table 1 of [2] sharing the same redshifts but originating from different surveys, e.g., , .
The Pantheon+ dataset [1] provides Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) luminosity distance and distance moduli measurements for redshifts in the range , calibrated by the second rung of the distance ladder using Cepheids with the absolute magnitude being . The samples consists of 1701 light curves of 1550 spectroscopically confirmed SNe Ia. The data together with the uncertainties can be found at their GitHub website: https://github.com/PantheonPlusSH0ES, accessed on 2 December 2025. A limitation of our usage of this dataset is that we only used the diagonal elements of the covariance matrix for supervising the aleatoric uncertainty. Similar to the case for the BAO dataset, any external knowledge of correlations among data points cannot be used in our formalism. There are no output variables of our neural network model that can interpreted as correlations (or their functions) between different data points. By construction, the four outputs of our model are related to the mean and uncertainty of the luminosity distance at each individual data point. Any generalization of our model to enable the full covariance matrix to be used would have to admit a much larger output layer with targets that are related to the correlations. Each cosmological model is associated with a different Hubble function. In our work here, we set the curvature density term to be zero for simplicity, leaving generalizations that treat it as a learnable parameter for future work. The wCDM and CDM models are defined as follows:
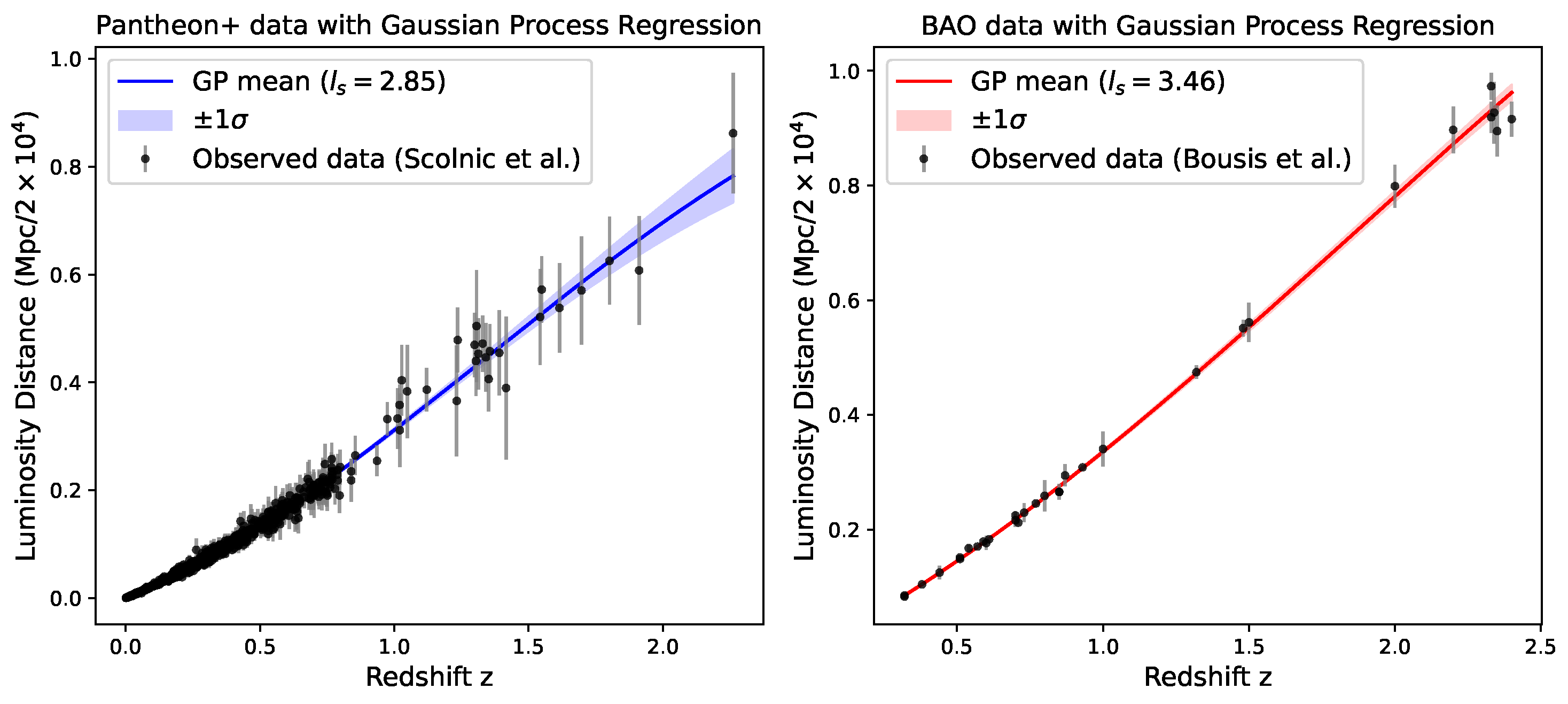
where we assume the Planck-measured radiation density parameter for simplicity. We take the free parameters of the wCDM model to be where w is the dark energy equation of state parameter. For CDM model, its free parameters are taken to be where is a transition redshift value from which the cosmological constant switches sign representing a toy model of vacua transition from anti-de Sitter to de Sitter spacetime at some point in the early universe. For computational convenience, here we use a hyperbolic tangent function as a smooth representation of the signum function. These models are parametrically deformable to the standard CDM model in the limits of for the wCDM model and for the CDM model. In Figure 1, we plot the Pantheon and BAO datasets equipped with Gaussian Process regression curves and uncertainty bands.
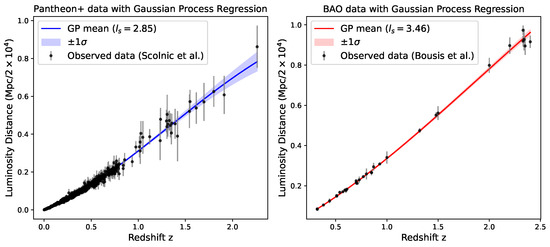
Figure 1.
Diagrams showing both the Pantheon+ [1] and BAO [2] datasets together with the fitted Gaussian Process Regression curves. The confidence bands were used to supervise epistemic uncertainty, whereas the empirical error bars were used to guide learning of aleatoric uncertainty in our model.
3.2. Model Training Setup and Implementation Details
In the following, we furnish some details of the model training, organizing them in terms of the dataset that was used. The base surrogate model was implemented as a fully connected perceptron with two hidden layers of 32 neurons each and an output layer of 4 neurons corresponding to the variables of (A1). For each training dataset, the same initial model was used for training the different cosmological model-based neural networks. The finite parameter domains were chosen to be . We implemented Gaussian Process (GP) regression with a radial-basis function kernel via the scikit-learn library [22], with the optimized kernel’s characteristic length-scales being 2.85 for the Pantheon+ data, 3.46 for the BAO data, and 2.89 for the combined dataset.
For models trained on the Pantheon+ and the combined Pantheon+BAO datasets, in the initial training phase, we used a learning rate of for the first epochs and for the subsequent ones with the total number of epochs being . The data uncertainty hyperparameters were taken to be . For the second phase, the learning rate was for the first epochs followed by for another epochs. On the other hand, for the smaller BAO dataset, convergence was attained for various cosmological models in epochs with a learning rate of for the first epochs and followed by for the remaining ones. The data uncertainty hyperparameters were taken to be . Final relative tolerance was of the order for Pantheon+ data-based models and higher at for BAO data-based ones.
Table 1 shows the parameters’ prior densities for each model. These parameters were determined from the empirical distribution that measures the likelihood of each parametrized family of numerical solutions of the PDE using its deviations from the corresponding purely data-fitted model.

Table 1.
Prior density function for each parameter was taken to be univariate Gaussians, of which the means and standard deviations are tabulated here for all three models trained on each dataset. The means and variances are the modes and variances of so that the Gaussian priors are representative of the highest density regions of .
3.3. On Empirical Coverage Probability and Log Model Evidence
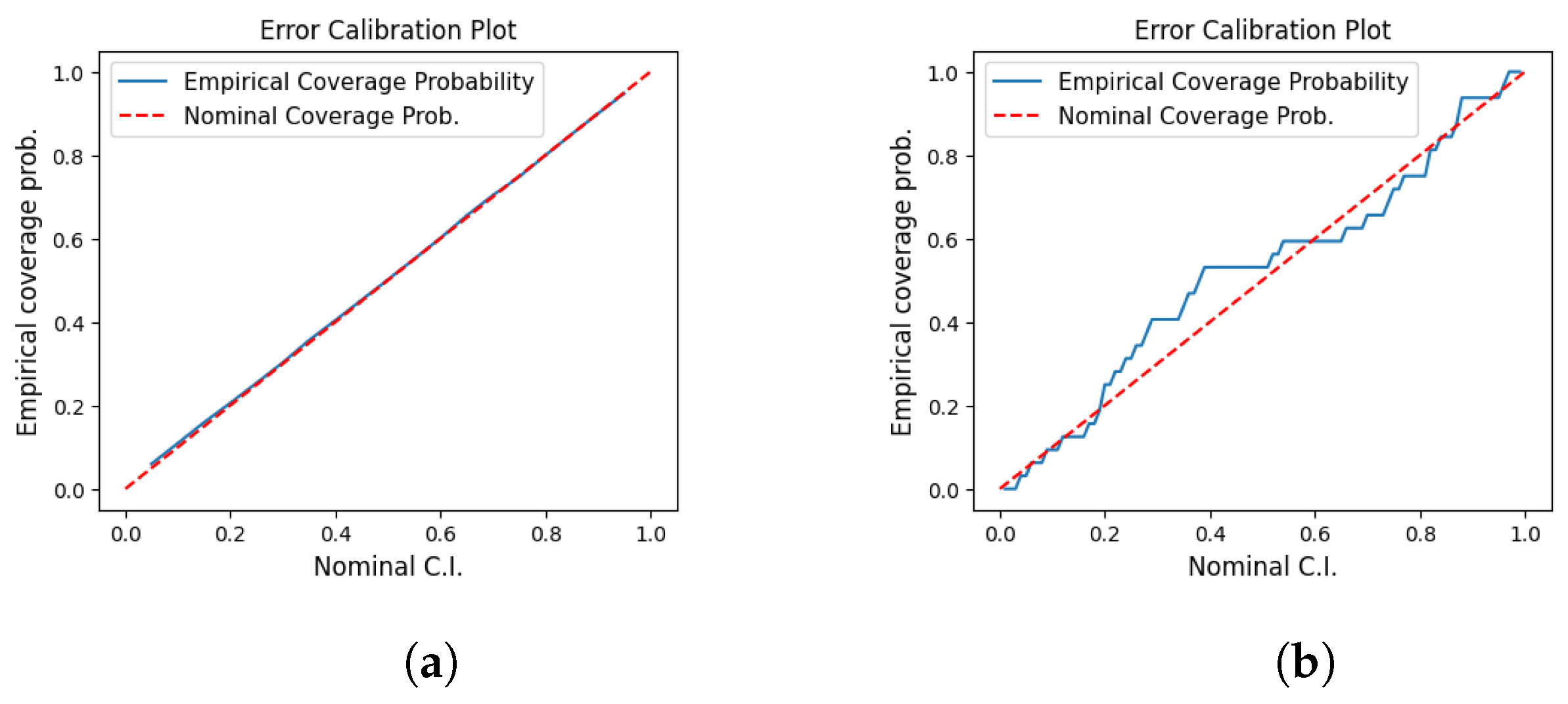
Upon completion of model training, we assess the uncertainty quantification through computing the empirical coverage probability (ECP). The ECP at level is the proportion of observed target values that fall within the corresponding t-distribution-based confidence band of (A1). To assess the degree of calibration, one can compare the ECP values to their nominal target level () (nominal coverage probabilities). On the ECP vs. NCP plane, a robust uncertainty quantification would yield a curve that is close to the straight line joining the origin to (1, 1). A representative index would be the mean of the absolute discrepancy between the ECP and NCP. For each model, we compute this mean calibration error (MCE) (see also [44]) and examined plots of ECP vs. NCP, finding that all MCE are very small ≲0.05, with models trained on Pantheon data being better calibrated with an MCE that is 0.1 smaller than those trained on BAO data. Most crucially, none of the 9 models had a ECP curve that is dominantly above or below the ideal line which would have indicated a systematic bias (see Figure 2 for a couple of illustrative ECP plots).
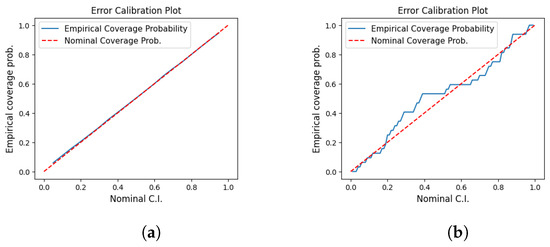
Figure 2.
Plots of empirical coverage probabilities vs. their nominal values for a couple of models. The perfectly calibrated uncertainty-aware model would exhibit a straight line joining the origin to . Models trained on BAO data exhibited less ideal ECP plots compared to those trained on Pantheon data, most likely attributable to the much smaller size of the dataset. (a) CDM model (Pantheon data). (b) wCDM model (BAO data).
The loss function of our model is, up to a normalization factor, the posterior distribution. The completion of model training yields quantities are directly related the log model evidence that can be further used to discriminate between models. Integrating out the parameters , the model likelihood M and its logarithm are
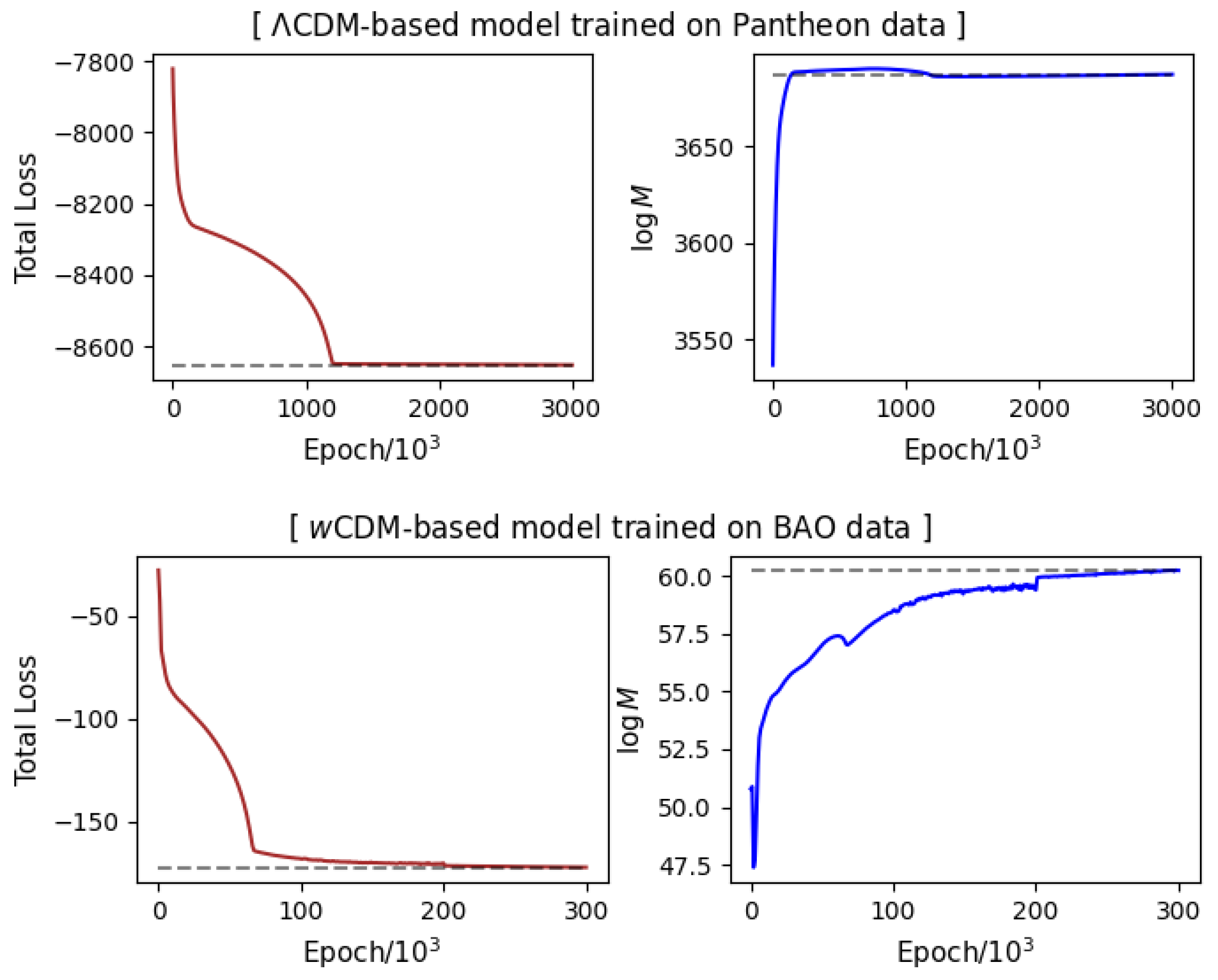
where are the final model weights and biases. The log model evidence (log M) is often used as a measure to quantify and compare support between competing statistical models from data [5,45]. In Table 2, we display the log model evidence for each model as a comparison index among models trained on the same dataset. In Figure 3, we show the evolution of log M for a couple of models together with the associated loss function. All models were checked to display convergence with a relative tolerance < in both the loss and log M term.

Table 2.
Table of inferred parameters (posterior medians with 0.68 C.I.) and logarithm of model evidence (log M). For each dataset (combined, Pantheon+, BAO), the cosmological model with the highest log M is shaded in gray.
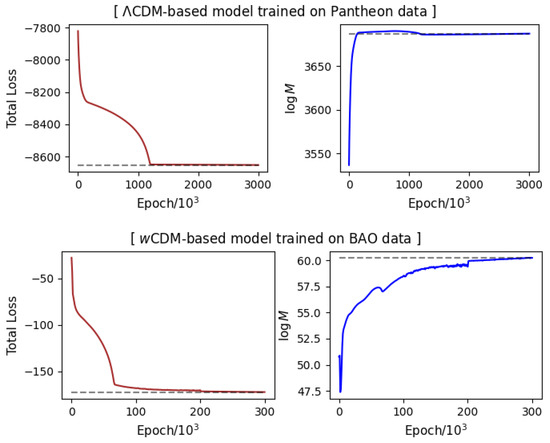
Figure 3.
Evolution of loss function and log M for a couple of models (Top: CDM trained on Pantheon data; Bottom: wCDM model trained on BAO data). All models have been checked to display convergence with a relative tolerance in both the loss and log M term.
4. Results
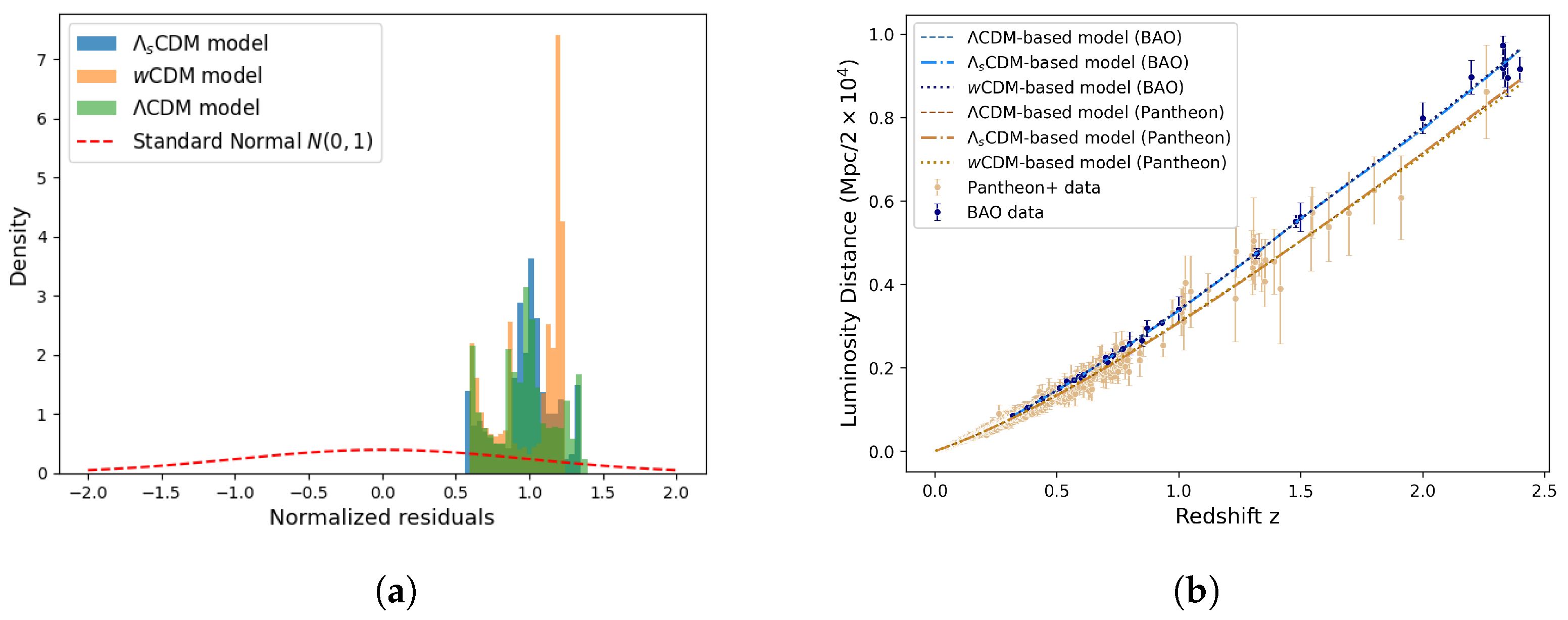
We collect the inferred parameters together with their uncertainties in Table 2 below. Generally, we found that for each class of cosmological models, the neural networks trained separately on Pantheon and BAO data exhibited a systematic difference evident in the residuals in their luminosity–redshift curves (see Figure 4) and the inferred posterior distributions of the parameters (see Figure 5). When trained on the combined dataset, all models yielded higher and lower compared to when being trained only on the Pantheon+ dataset, with CDM being associated with a clearly lower log model evidence compared to CDM and wCDM models.
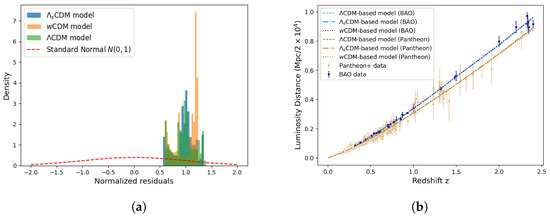
Figure 4.
Left diagram shows residuals between BAO data and Pantheon+ data-trained models, normalized by the combined model uncertainties, highlighting systematic differences induced by dataset choice. Right diagram collects all model predictions. (a) Normalized residuals. (b) Model prediction curves.
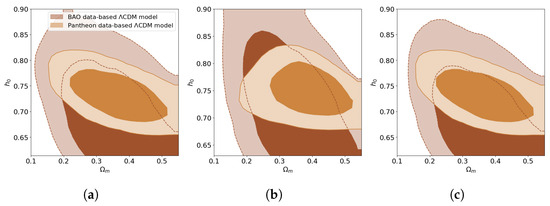
Figure 5.
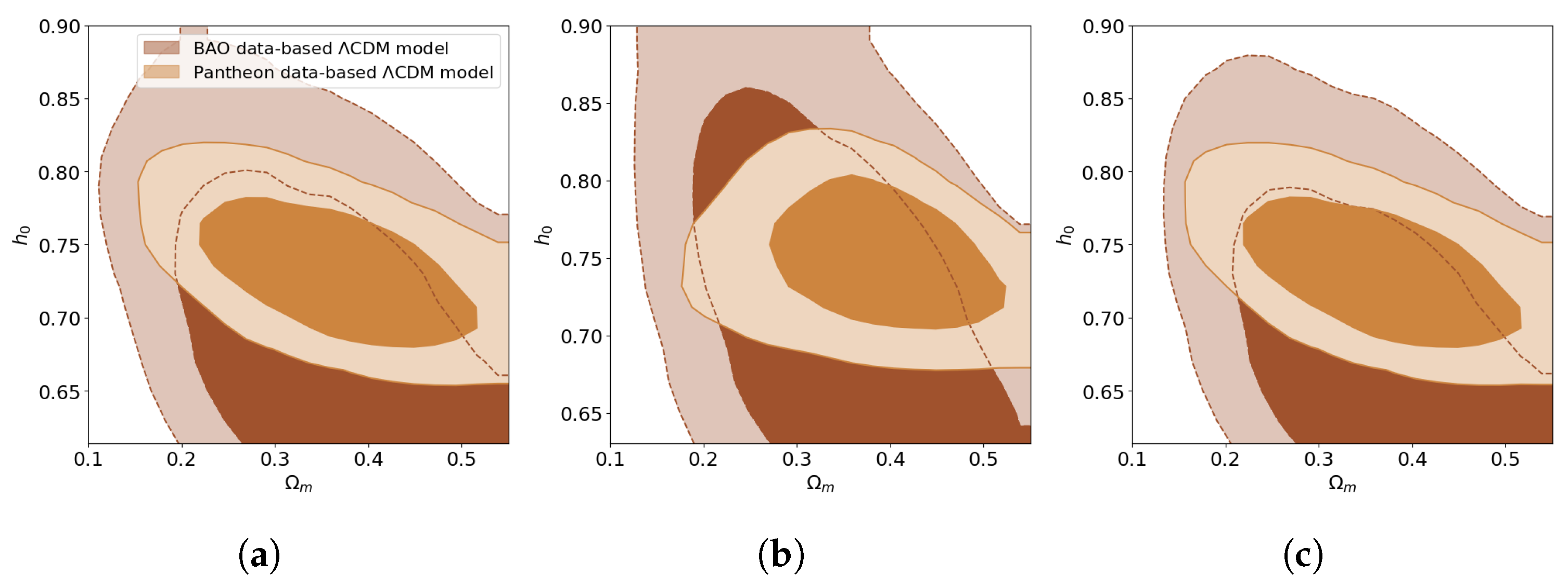
Joint marginal distributions of and for the three models, each trained separately on the Pantheon+ (light brown) and BAO data (dark brown). The 68% and 95% credible contours are shown for each panel. For the wCDM and CDM models, the distributions shown were obtained after marginalizing over w and parameters, respectively. (a) CDM model. (b) wCDM model. (c) CDM model.
4.1. On Tensions Between Models Trained Separately on Pantheon+ and BAO Data
We examined the difference in the joint marginal distributions of and for the three models, each trained separately on the Pantheon+ and BAO data. Figure 5 shows the 68% and 95% contours for each model. The CDM and CDM models yielded similar distributions with the Jensen–Shannon divergence [46] between the Pantheon and BAO data-based distributions being 2.495 and 2.592, respectively, while that of wCDM model was characterized by the lowest Jensen–Shannon divergence of 2.342. The posterior distributions for the cosmological parameters in various models trained purely on Pantheon+ data were found to be largely contained within the contours of their counterparts trained on BAO data (Figure 5). This is in stark contrast to Figure 4 of [2], where the posterior distributions did not overlap at .
For each cosmological model, we consider the differences in the predicted luminosity–distance curves resulting from the model being trained purely on either BAO or Pantheon+ datasets. The normalized residuals between the predictions of the BAO-trained and Pantheon-trained models are shown in Figure 4. We found that these residuals exhibited strong deviations from the distribution () associated with statistical noise. This indicates the presence of dataset-dependent systematic effects, whereby each dataset favors a different best-fit model.
4.2. On Models Trained on the Combined Pantheon+ and BAO Data
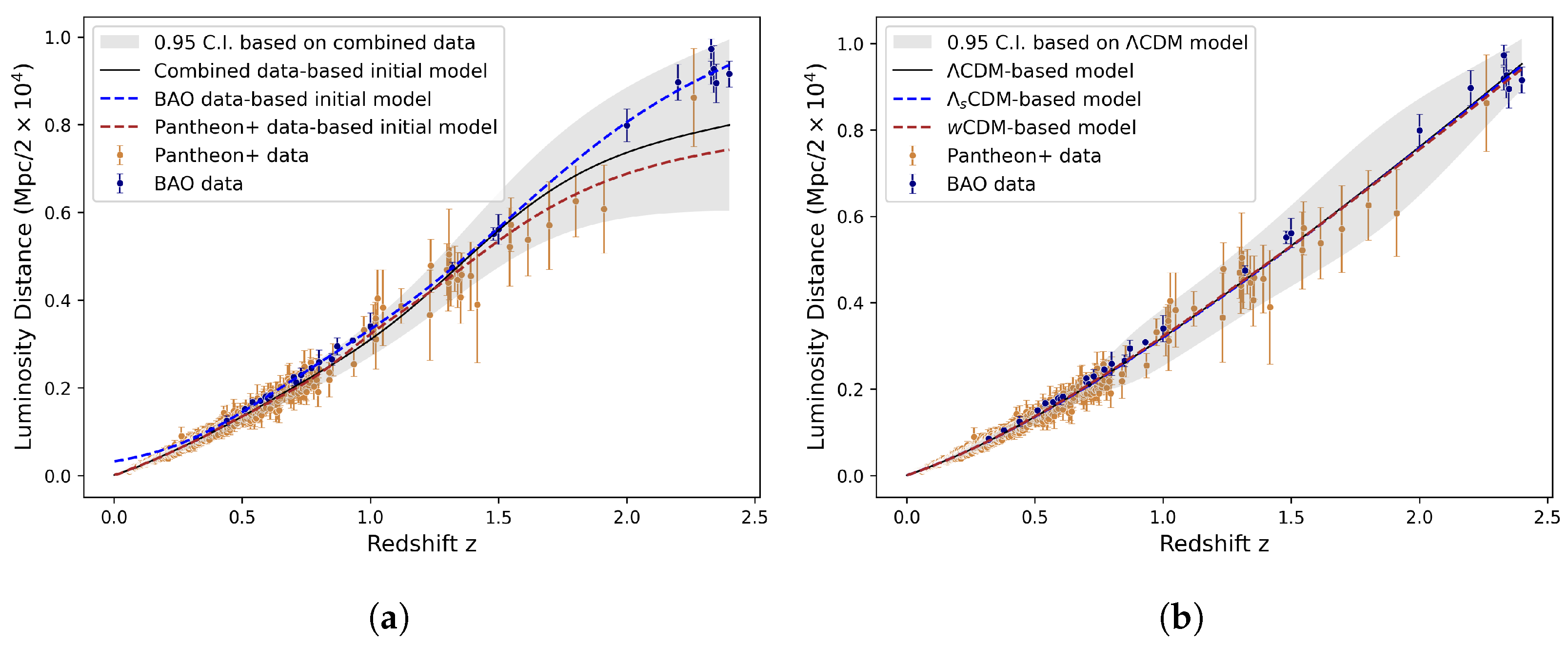
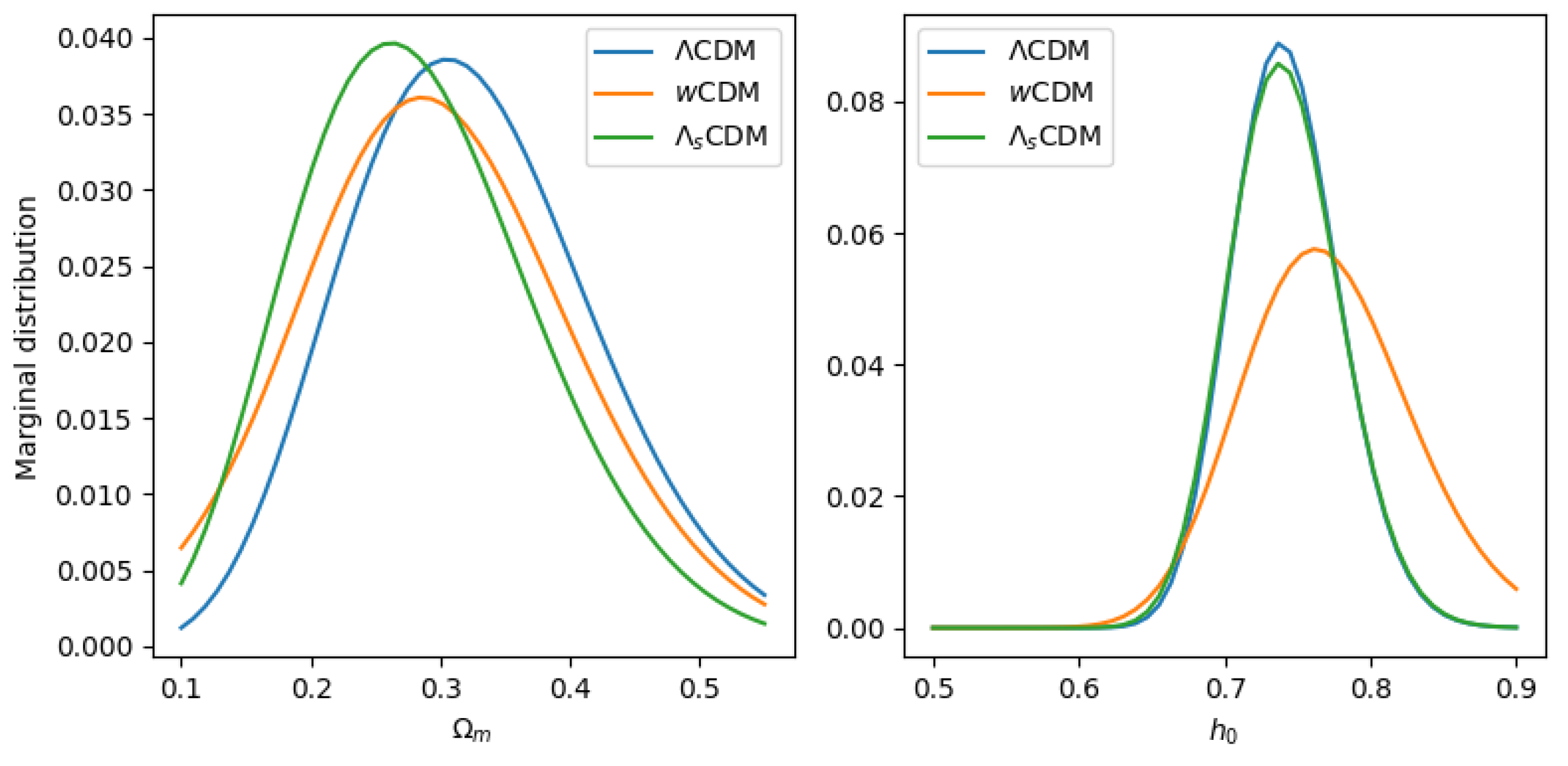
When trained on the combined dataset, all three models yielded similar prediction curves as depicted in Figure 6 below. Figure 7 shows the marginal posteriors for . The CDM and wCDM models showed the highest log Bayes factor, and all three models yielded posterior medians of that agree within one standard deviation. The posterior medians for for all models were all larger than , with a standard deviation falling within . Each model yielded lower values of and higher values of than when trained on the individual datasets separately.
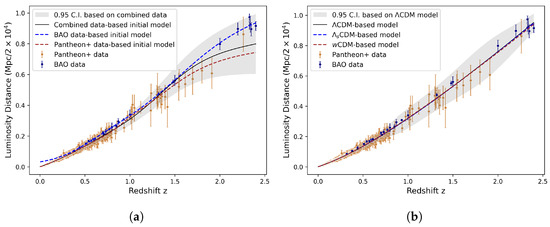
Figure 6.
Left diagram shows initial models fitted on only Pantheon+, BAO datasets and their combination. Right diagram shows the final models fitted on the combined Pantheon+ and BAO data. Numerical solutions equipped with the posterior medians (omitted) are all very close to their respective neural network predictions. The purely data-fitted models without PDE constraints suggest that the empirical data trends alone would yield luminosity vs. redshift curves of decreasing slope at higher redshift values , in contrast to the numerical solutions governed by Friedmann equations. (a) Initial models. (b) Final models.
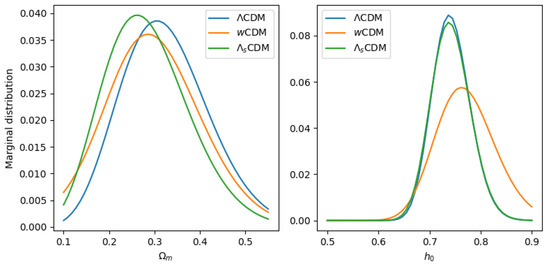
Figure 7.
Marginalized posterior distributions for h0, Ωm for all models trained on the combined dataset. Each model yielded lower values of and higher values of than when trained on the individual datasets separately. All three models yielded posterior medians of h0, Ωm that agree within one standard deviation.
5. Discussion
In this work, we have applied E-PINN—a novel variant of Physics-Informed Neural Networks—to predict cosmological parameters from recent supernovae [21] and baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO) datasets [2]. Built upon a hybrid of the principles of Evidential Deep Learning, Physics-Informed Neural Networks, and Bayesian Neural Networks, our model enables learning the posterior distribution of the unknown PDE parameters through standard gradient-descent-based training. We also introduced a novel refinement of the original E-PINN framework [7,8] that integrates Gaussian Processes into its algorithm, enabling supervised learning of epistemic uncertainty and the construction of prior functions for the model parameters.
Our neural network-based approach introduces a higher degree of model independence relative to standard regression-based statistical analysis since the perceptron model does not descend from any solutions of some presumed cosmological model while being a fundamental part of the learnable likelihood function. Our approach fundamentally differs from the usual statistical analysis in a few ways: (i) instead of some uniform prior, we use a data-informed prior, constructed to represent an empirical distribution derived from the deviations between the observed data trend and the numerical solution of the presumed PDE; (ii) the loss function that is minimized is generalized from the negative log-likelihood of a Gaussian to a combination of terms (Equation (15)) that incorporates both PDE constraints and data loss terms; (iii) Gaussian Process Regression is invoked to supervise learning of epistemic uncertainty; (iv) the surrogate perceptron model extends the standard approach of only using families of PDE solutions for best-fit estimation, enabling the identification of regions where data trends deviate from the presumed PDE descriptions.
With regards to the Hubble tension problem [20], the essential finding of our work is that the posterior distributions for cosmological parameters in various models trained purely on Pantheon+ data were found to be largely contained within the contours of their counterparts trained on BAO data (Figure 5). As tabulated in Table 2, the values were within about of one another as defined through the marginal distributions in , in contrast to those in [2] exhibiting more than tension as inferred from the standard approach of minimizing an appropriate function. The normalized residuals (Figure 4) indicated the presence of dataset-dependent systematic effects, where each dataset favors a different set of cosmological parameters—a trend supportive of some degree of Hubble tension that is consistent with [2]. In [2], the best-fit values for the CDM model associated with the BAO dataset were , while the Pantheon dataset yielded . Their posterior distributions showed large deviations as depicted in Figure 4 of [2] where one can see that their probability contours at 3 do not even overlap. While our framework yielded parameter estimates similar to theirs— based on BAO data and based on Pantheon data—these posterior medians were inferred with larger uncertainties, with posterior distributions that showed a much larger degree of overlap in Figure 5, compared to Figure 4 of [2]. One contributing factor can be traced to the nature of the prior density functions that we derived for the parameters (see Table 1). Their uncertainties were slightly larger yet similar in order of magnitude to those characterizing the joint marginal distributions in Figure 5. In contrast, typically flat priors are used in the standard analysis, with the eventual parameter uncertainties only dependent on the minimization of the likelihood function in Equation (3). Apart from the prior, our framework also assumes a different likelihood function. Instead of Equation (3) which is expressed in terms of the solutions to the Friedmann equations, we have Equation (7). These differences led to our joint marginals as shown in Figure 5 to deviate from those in the standard analysis of [2]. Notably, our models’ inferences of were equipped with much larger uncertainties (at least twice for and thrice for ) compared to those arising from the standard analysis in [2].
Overall, our simulation results showed that a more data-informed approach can seemingly reduce statistical tensions between models trained separately on Pantheon and BAO data. This is fundamentally due to different sets of assumptions underlying the statistics of model parameters, most crucially the choice of prior and form of the likelihood functions, and how they relate to cosmological ones. A caveat is that the sound horizon was taken to be fixed at 147.18 Mpc following the Planck18 results [41] when translating in the BAO dataset of [2] to luminosity distances. While this enables us to compare our results fairly with those of [2], it should also be interpreted as a limitation since the tension is sensitive to .
All initial models in the absence of PDE constraints arising from the presumed cosmological models appeared to suggest that the luminosity–redshift curve should flatten out towards higher redshift gradually, in contrast to the numerical solutions for all three cosmological models considered here. It would be interesting to observe if future empirical data from supernovae light curves at high redshift support this trend. With regards to model selection, we note that the log model evidence appeared to disfavor CDM when the combined Pantheon and BAO data were taken into account but otherwise showed no other notable model preferences. The wCDM model yielded the highest values relative to the two other models irrespective of the dataset used.
An immediate future direction worth pursuing as a follow-up to our work here would be to use a model-independent sound horizon for training models on BAO data, or to lift it to be a learnable parameter. A recent analysis [42] inferred a value for Mpc by leveraging time-delay measurements of gravitationally lensed quasars from H0LiCOW collaboration [47] in a model-independent approach. Such a value would naively reduce deviations between the models trained separately on Pantheon and BAO datasets as shown in Figure 4. An earlier model-independent analysis in [43] estimated Mpc, taking into account a combined SNe Ia+BAO dataset. If we used our inferred value based on the model trained on the combined Pantheon+BAO data, this translates to Mpc, which is notably close to the value determined in [42]. The degree of sensitivity to suggests that any future analysis should ideally treat and other cosmological parameters to be simultaneously learnable ones right from the outset, although this would increase computational cost and complexity. As noted in [42], future cosmological probes may bring in greater diversity of data sources, such as gravitational wave standard sirens [48], with which we can infer the sound horizon and other cosmological parameters. Our data-driven neural network methodology is poised to leverage such increasingly diverse observations to infer parameters with robust data-informed priors. More generally, in the aspect of machine learning techniques, we expect our proposed method of synergizing Gaussian Processes with E-PINN to be transferable to other scientific modeling problems, and to be particularly useful for contexts where data is relatively scarce and the learning of epistemic uncertainty then becomes crucial to the model training process.
Another follow-up work would be to explore generalizations of evidential deep learning that can facilitate the learning of known correlations among data points. Naively, one can consider the multivariate t-distribution obtained by marginalizing out means and covariances of a multivariate Gaussian with the Normal-Inverse-Wishart prior, but this would imply that the input’s dimensionality is fixed to the specific value of the training dataset size, and the number of target variables would be increased by over an order of . Another line of approach would be to consider adjusting the relative weightage of data points that are correlated, for example taking some form of weighted mean of a pair of correlated points instead of treating them as separate entities within the sum over all training points. One would need to examine how to take such a weighted mean that is robustly consistent with the off-diagonal elements of the covariance matrix. In the absence of a framework that enables external knowledge of correlation to be used in the supervised learning, a cleaner approach would be to simply use datasets that are not characterized by significant correlations.3 For example, in the context of our work, it would thus be interesting to see how our various results change when we use BAO data that is sourced from SDSS [49], DESI [50], etc., separately instead of Table 1 of [2].
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Rafe McBeth for many discussions on related topics, including our recent collaborations in [7,8], and to Phuntsok Tseten for his moral support. I dedicate this work to the loving memory of my aunt, Tan Siew Huan, and my uncle, Tan Hang Song.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Some Technical Aspects of the Loss Function
In this appendix, we present more detailed explanations for certain specific aspects of the loss function.
Appendix A.1. On the t-Distribution in EDL
Our framework (E-PINN) generates uncertainty estimates for its output by leveraging the principle of Evidential Deep Learning (EDL) [9,10]. The framework of EDL in the context of regression can be summarized as follows. One first considers a probabilistic model where each output neuron is accompanied by another one representing its uncertainty. This pair of neurons can be interpreted as the Gaussian mean and variance for the probabilistic target. We can further assume prior distributions for the mean and variance and integrate out to obtain a marginal distribution that depends on the observed data and the parameters of the prior distribution. Specifically taking the prior to be a normal-inverse-gamma distribution (NIG) with , , we obtain the marginal distribution to be a t-distribution as follows:
where denotes the auxiliary Gaussian distribution, the NIG prior, and the observed data. Instead of just a single output neuron or a pair representing (), our model has four output neurons (), where represents the mean and are related to the predictive variance as follows:
where denote the ‘aleatoric’ and ‘epistemic’ uncertainties, respectively, with the expectation and variance operators defined with respect to . We note that the aleatoric uncertainty is typically interpreted as the uncertainty related to measurement noise while represents the uncertainty due to data insufficiency and the underlying model’s capacity to represent the observed knowledge (see [51] for a nice discussion). Both types of uncertainties sum up to yield the variance of the t-distribution of (5) (reproduced below for reading convenience):
Its negative logarithm is the data loss term discussed in Section 2.
Appendix A.2. On Uncertainty of and Its Prior Distribution
In the Bayesian approach, one should consider specifying a prior density function for . For example, a reasonable choice would be one that is derived from other empirical measurements and the inference of . Taking into account , the loss function then reads
in a form interpretable as the negative logarithm of a posterior distribution for . The model’s weights are latent variables, with model training that is based on minimizing equivalent to a maximum a posteriori estimation. We can compute the uncertainty of as being defined with respect to the posterior density function
where we discarded -independent terms. Restoring the input indices, we note that since the data loss term and PDE residual term are products of i.i.d. individual observations, the likelihood function can be expressed as
In the following, we will derive a form for the prior that can be used generally. Let denote the finite, discretized domain for the unknown parameters . At each point of , we can evaluate the mean squared deviation between the solution to the PDE characterized by and the Gaussian Process mean in Equation (11):
where denotes a numerical solution to the differential equation with parameters , and GP regression model evaluated on . We assert a Gaussian likelihood based on the mean squared deviation in (A7) for , with the variance parameter being the mean averaged over the domain . This defines a density function f at each point of the form
where N is the normalization constant, and all integrals are implemented as numerical Riemann over the discretized domain . We would like the prior distribution of to be characterized by the same mode and dispersion scales as the highest density region [52] of f. At some confidence level, say 68%, this region is generally a complex subset of the domain . Since our choice of prior distribution affects model training dynamics in the second phase, we adopt a simple Gaussian surrogate distribution for this region, with the means being the modes and the standard deviations being those of each marginal distribution:
where is a diagonal covariance matrix, of which the elements are the variances of the marginal distribution for each component of , while the mean vector are the modes of
This choice of the prior distribution yields a simple approximation of the highest density region of (Equation (A8)), which is in turn based on the mean squared deviation between the data-fitted model’s curve and the numerical solution equipped with , with the dispersion scale in each parameter component set by the variance of its marginal distribution.
Appendix A.3. Determination of
In this appendix, we present a detailed discussion of a method that can be used to set the prior density for —the dynamical, learnable weight for the PDE residual loss term. Its prior density is intended to guide and regularize the evolution of during the gradient-descent-based training as the model adapts to both data and PDE constraint. Assuming an inverse-gamma distribution for its form,
We pick its hyperparameters such that it is consistent with other aspects of our formalism. These parameters are known as the shape and scale factors, respectively, in particular leading to the mode and mean values being and , respectively. Here we restrict ourselves to the case where so that the mean is well-defined. We pick the initial value of () to be the mean. As decreases during model training, it approaches the mode of at which the derivative with respect to vanishes:
where denotes the initial value, and denotes an asymptotic lower bound at the completion of model training. Since the distribution of is defined through Equation (A5), preceding model training, we would like the initial likelihood function to be close to the prior distribution for . This motivates setting such that the initial induced statistics of is similar to .
To proceed, we first obtain the initial data-fitted model by training the model using only the EDL loss function augmented with the aleatoric and epistemic loss terms in the first training phase:
where is defined in Equation (A1), is defined in Equation (10), and is defined in Equation (12). Thus, this first phase of model training is performed without alluding to any PDE description. Upon convergence, we then obtain —a purely data-fitted model.
We would like the initial induced statistics of in the likelihood function | to be similar to since the latter represents the prior. Using the Kullback–Leibler divergence as a measure of similarity, we set
where
More intuitively, the parameter controls the overall scale of the dispersion of each component of . The constraint (A14) sets the initial such that the likelihood function is initially close (in the sense of KL measure) to the prior function for .
As the model adapts to the PDE residual condition, decreases and moves from the mean towards the mode, where the derivative with respect to vanishes. We would like the minimum uncertainties at this point to be consistent with our model implementation, in particular, the discrete nature of the domains for the parameters . These domains are necessarily characterized by finite resolutions. Consider a diagonal multivariate Gaussian distribution , where each standard deviation of is set as the minimal spacing in each parameter’s domain. This then yields a natural choice for the mode of :
Appendix B. Some Plots of Posterior Distributions
Here, we collect the corner plots for various models trained separately on the BAO (Figure A1 and Figure A2) and Pantheon (Figure A3 and Figure A4) datasets.
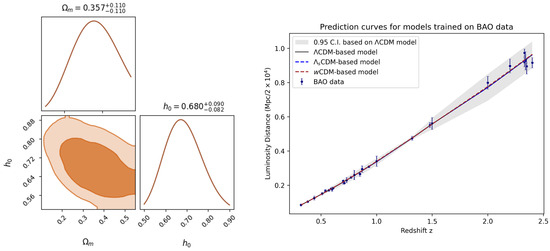
Figure A1.
(left) Inferred posterior distribution for CDM-based model trained purely on BAO data; (right) Prediction curves for all models trained purely on BAO data.
Figure A1.
(left) Inferred posterior distribution for CDM-based model trained purely on BAO data; (right) Prediction curves for all models trained purely on BAO data.
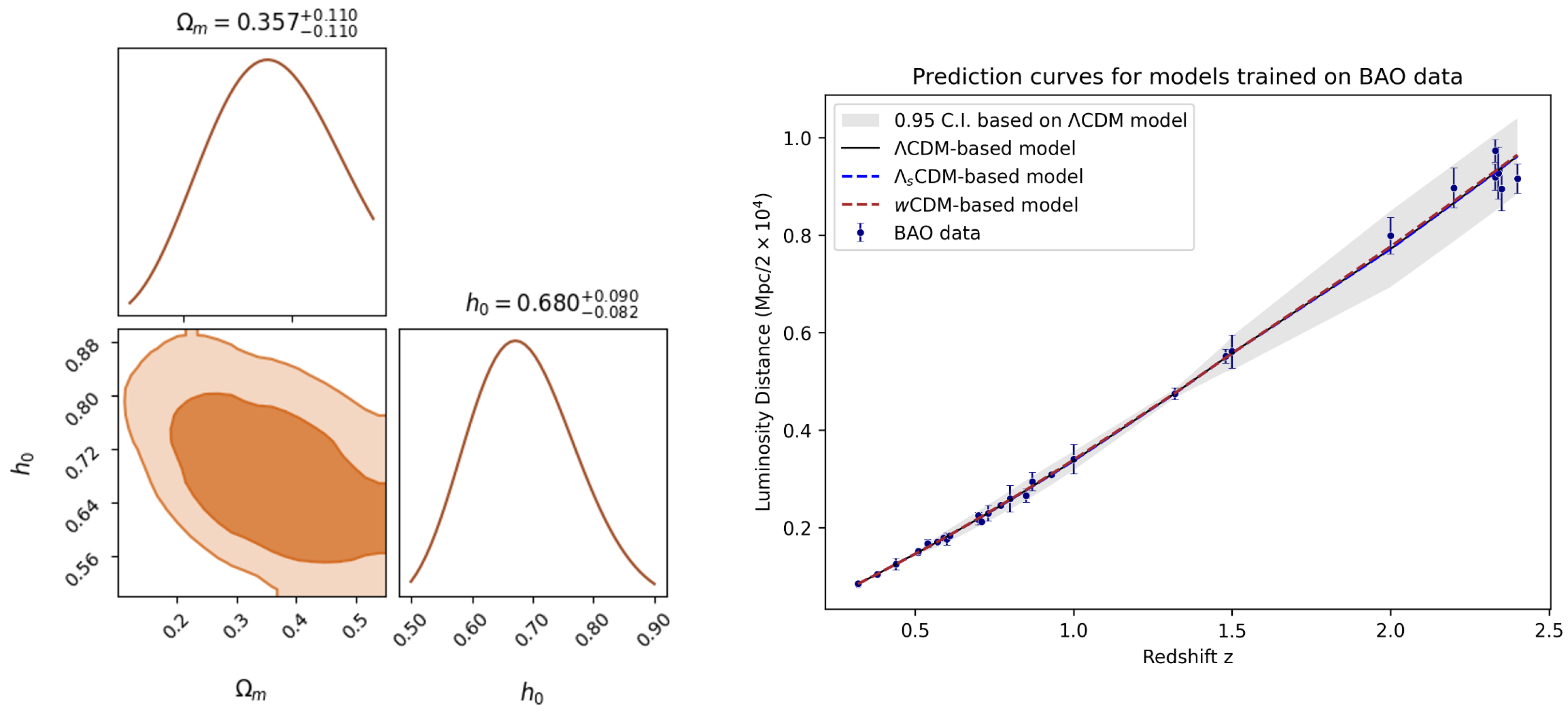
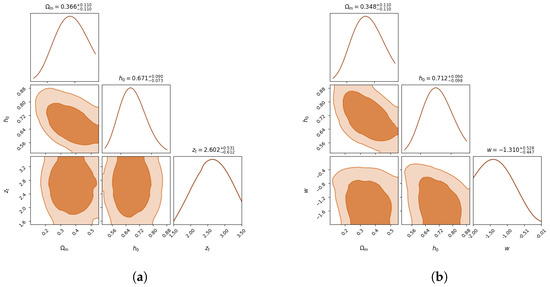
Figure A2.
Corner plots for the posterior distributions inferred from the CDM-based and wCDM-based models trained purely on BAO data. (a) CDM-based model (BAO). (b) wCDM-based model (BAO).
Figure A2.
Corner plots for the posterior distributions inferred from the CDM-based and wCDM-based models trained purely on BAO data. (a) CDM-based model (BAO). (b) wCDM-based model (BAO).
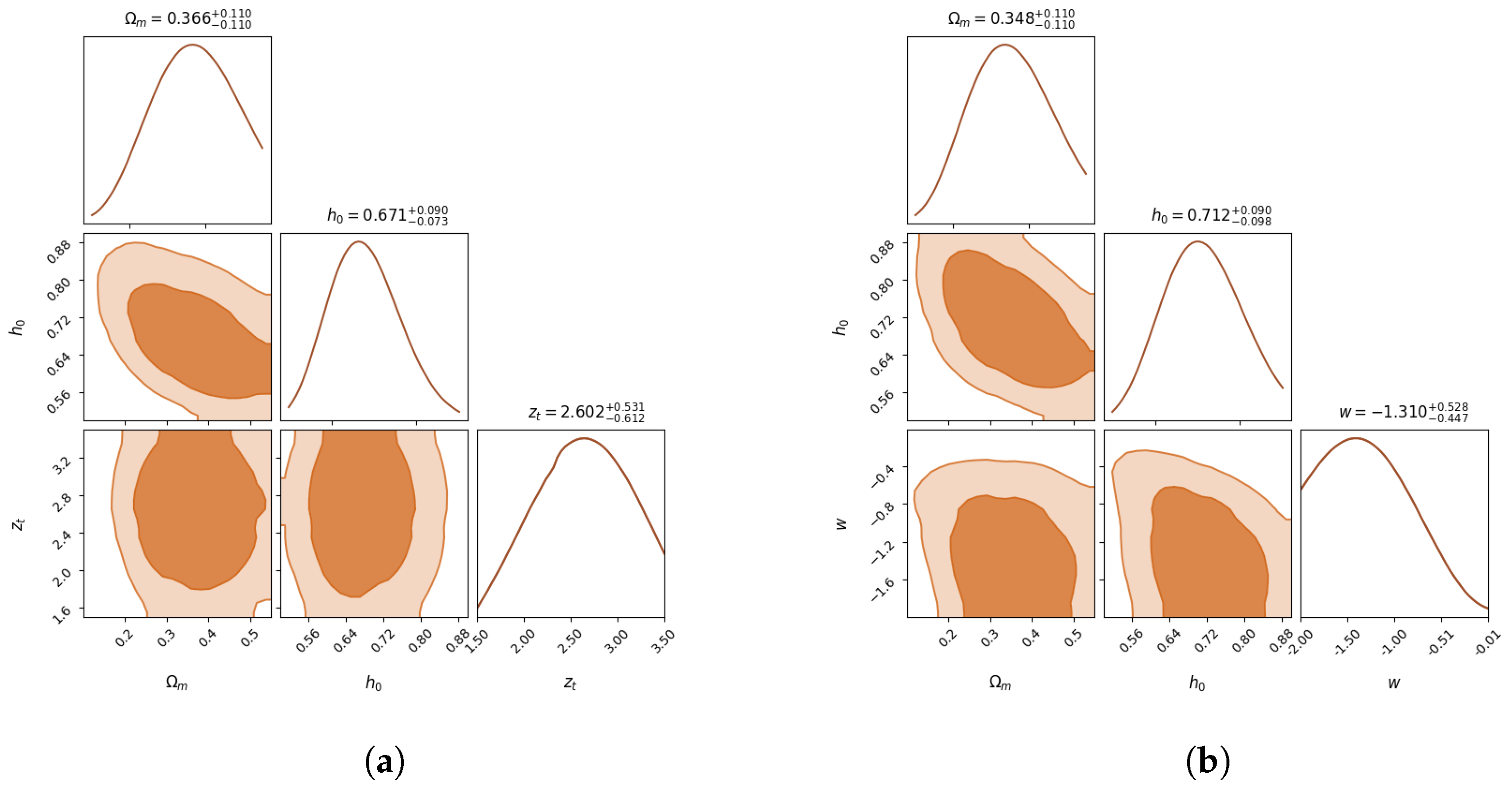
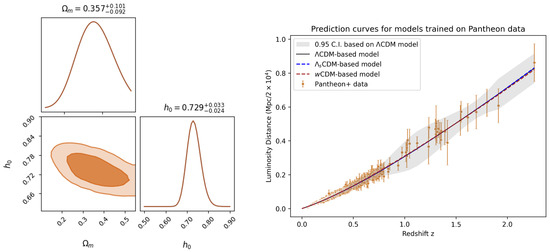
Figure A3.
(left) Inferred posterior distribution for CDM-based model trained purely on Pantheon+ data; (right) prediction curves for all models trained purely on Pantheon+ data.
Figure A3.
(left) Inferred posterior distribution for CDM-based model trained purely on Pantheon+ data; (right) prediction curves for all models trained purely on Pantheon+ data.
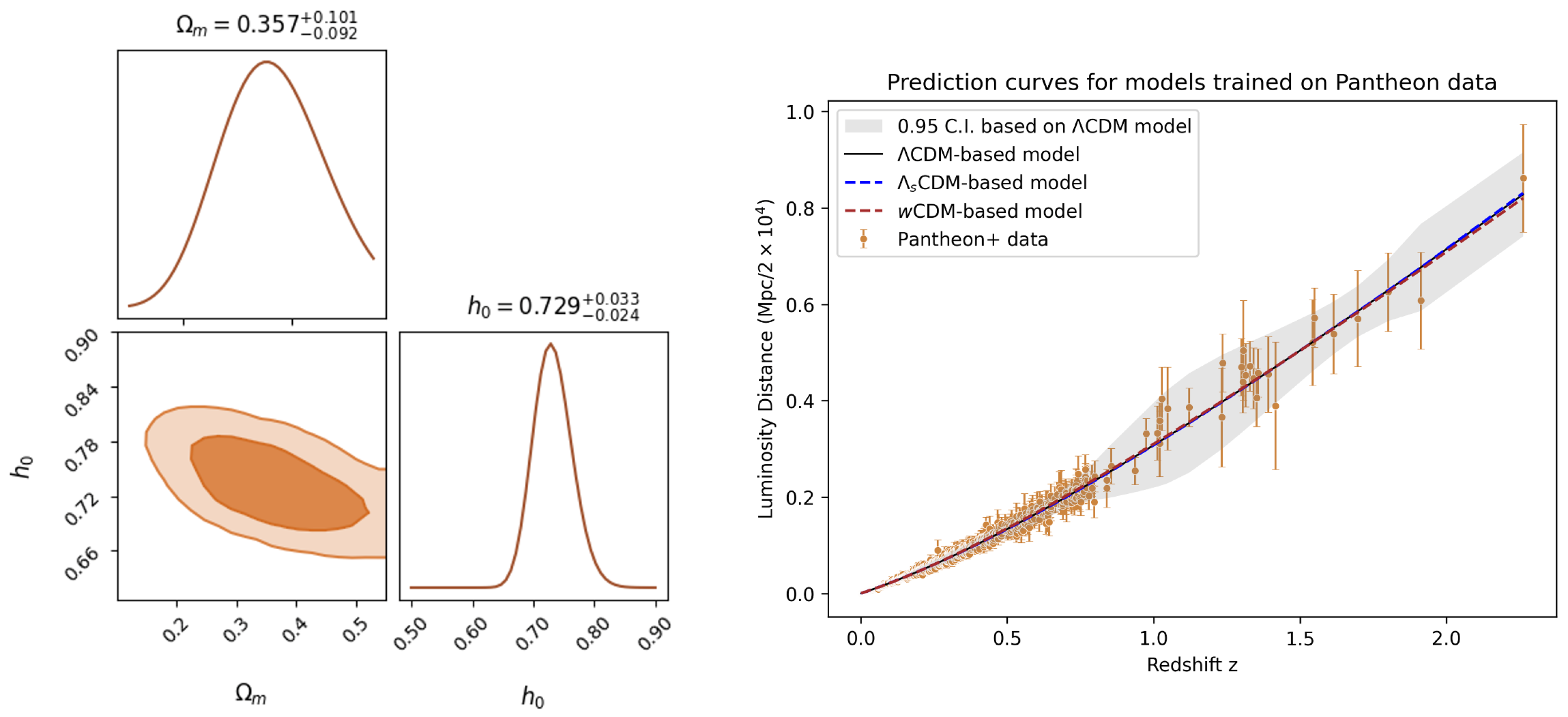
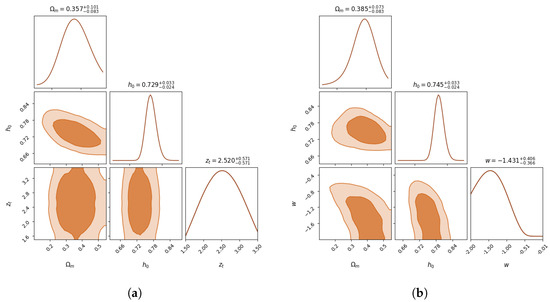
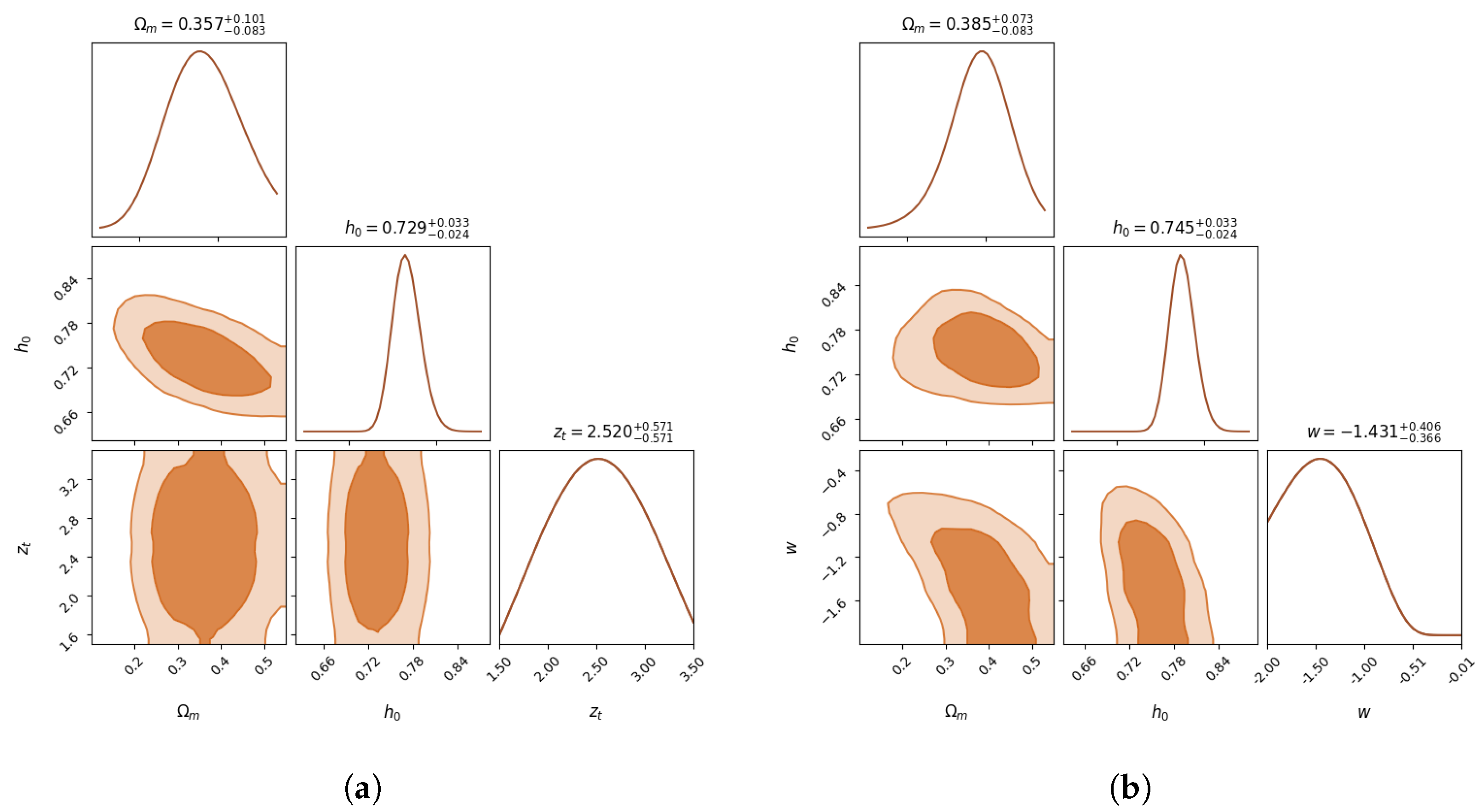
Figure A4.
Corner plots for the posterior distributions inferred from the CDM-based and wCDM-based models trained purely on Pantheon+ data. (a) CDM-based model (Pantheon+). (b) wCDM-based model (Pantheon+).
Figure A4.
Corner plots for the posterior distributions inferred from the CDM-based and wCDM-based models trained purely on Pantheon+ data. (a) CDM-based model (Pantheon+). (b) wCDM-based model (Pantheon+).
Notes
| 1 | The posterior density implied by our loss function is not normalized, yet the normalization factor would involve which is not taken into account during model training. For this reason, we consider our inference procedure a maximum likelihood estimation regularized by a prior density. |
| 2 | We are grateful to an anonymous referee for advising us to emphasize this caveat. |
| 3 | We are grateful to an anonymous referee for raising this point. |
References
- Brout, D.; Scolnic, D.; Popovic, B.; Riess, A.G.; Carr, A.; Zuntz, J.; Kessler, R.; Davis, T.M.; Hinton, S.; Jones, D.; et al. The Pantheon+ Analysis: Cosmological Constraints. Astrophys. J. 2022, 938, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousis, D.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Hubble tension tomography: BAO vs SnIa distance tension. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.07039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alestas, G.; Kazantzidis, L.; Perivolaropoulos, L. H0 tension, phantom dark energy, and cosmological parameter degeneracies. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 123516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, O.; Valentino, E.D.; Kumar, S.; Nunes, R.C.; Vazquez, J.A.; Yadav, A. ΛsCDM model: A promising scenario for alleviation of cosmological tensions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.10899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, R. Bayes in the sky: Bayesian inference and model selection in cosmology. Contemp. Phys. 2008, 49, 71–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.S.; Wang, K.; McBeth, R. Evidential Physics-Informed Neural Networks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.15908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.S.; Wang, K.; McBeth, R. Evidential Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Scientific Discovery. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2509.14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Schwarting, W.; Soleimany, A.; Rus, D. Deep evidential regression. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–12 December 2020. NIPS ’20. [Google Scholar]
- Sensoy, M.; Kaplan, L.; Kandemir, M. Evidential Deep Learning to Quantify Classification Uncertainty. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.01768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röver, L.; Schäfer, B.M.; Plehn, T. PINNferring the Hubble Function with Uncertainties. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantada, A.T.; Landau, S.J.; Protopapas, P.; Scóccola, C.G.; Garraffo, C. Cosmology-informed neural networks to solve the background dynamics of the Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 063523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.Z.; Meng, P.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, X. Model-independent measurement of cosmic curvature with the latest H(z) and SNe Ia data: A comprehensive investigation. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 108, 063522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Rudin, C.; Shaposhnik, Y. Understanding How Dimension Reduction Tools Work: An Empirical Approach to Deciphering t-SNE, UMAP, TriMAP, and PaCMAP for Data Visualization. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2012.04456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, T.J. Model Comparison of Dark Energy models Using Deep Network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.00568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Said, J.L.; Mifsud, J. Neural network reconstruction of H’(z) and its application in teleparallel gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 2022, 029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.; Wang, G.J.; Ma, Y.Z.; Pan, S. In search of an interaction in the dark sector through Gaussian Process and ANN approaches. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2025, 540, 2253–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.J.; Ma, X.J.; Li, S.Y.; Xia, J.Q. Reconstructing Functions and Estimating Parameters with Artificial Neural Networks: A Test with a Hubble Parameter and SNe Ia. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2020, 246, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E.; Mena, O.; Pan, S.; Visinelli, L.; Yang, W.; Melchiorri, A.; Mota, D.F.; Riess, A.G.; Silk, J. In the realm of the Hubble tension—A review of solutions. Class. Quantum Gravity 2021, 38, 153001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scolnic, D.; Brout, D.; Carr, A.; Riess, A.G.; Davis, T.M.; Dwomoh, A.; Jones, D.O.; Ali, N.; Charvu, P.; Chen, R.; et al. The Pantheon+ Analysis: The Full Data Set and Light-curve Release. Astrophys. J. 2022, 938, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Adame, A.G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Alexander, D.M.; Alvarez, M.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, É.; et al. DESI 2024 VI: Cosmological constraints from the measurements of baryon acoustic oscillations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 2025, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Song, Y.S.; Ross, A.J.; Zhou, R.; Newman, J.A.; Chuang, C.H.; Blum, R.; Gaztañaga, E.; Landriau, M.; Prada, F. Clustering of LRGs in the DECaLS DR8 Footprint: Distance Constraints from Baryon Acoustic Oscillations Using Photometric Redshifts. Astrophys. J. 2020, 904, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, B.A.; Samushia, L.; White, M.; Percival, W.J.; Manera, M.; Padmanabhan, N.; Ross, A.J.; Sánchez, A.G.; Bailey, S.; Bizyaev, D.; et al. The clustering of galaxies in the SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Measurements of the growth of structure and expansion rate at z = 0.57 from anisotropic clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 426, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Ata, M.; Bailey, S.; Beutler, F.; Bizyaev, D.; Blazek, J.A.; Bolton, A.S.; Brownstein, J.R.; Burden, A.; Chuang, C.H.; et al. The clustering of galaxies in the completed SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Cosmological analysis of the DR12 galaxy sample. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 2617–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.J.; Ho, S.; White, M.; Cuesta, A.J.; Ross, A.J.; Saito, S.; Reid, B.; Padmanabhan, N.; Percival, W.J.; de Putter, R.; et al. Acoustic scale from the angular power spectra of SDSS-III DR8 photometric luminous galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2012, 761, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Aubert, M.; Avila, S.; Balland, C.; Bautista, J.E.; Bershady, M.A.; Bizyaev, D.; Blanton, M.R.; Bolton, A.S.; Bovy, J.; et al. Completed SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Cosmological implications from two decades of spectroscopic surveys at the Apache Point Observatory. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 083533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.B.; Zhao, C.; Philcox, O.H.E.; Alam, S.; Tamone, A.; de Mattia, A.; Ross, A.J.; Raichoor, A.; Burtin, E.; et al. The clustering of the SDSS-IV extended baryon oscillation spectroscopic survey DR16 luminous red galaxy and emission-line galaxy samples: Cosmic distance and structure growth measurements using multiple tracers in configuration space. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 3470–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Padmanabhan, N.; Ross, A.J.; White, M.; Percival, W.J.; Ruggeri, R.; Zhao, G.b.; Wang, D.; Mueller, E.M.; Burtin, E.; et al. The clustering of theSDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey DR14 quasar sample: Measuring the anisotropic baryon acoustic oscillations with redshift weights. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamone, A.; Raichoor, A.; Zhao, C.; de Mattia, A.; Gorgoni, C.; Burtin, E.; Ruhlmann-Kleider, V.; Ross, A.J.; Alam, S.; Percival, W.J.; et al. The completed SDSS-IV extended baryon oscillation spectroscopic survey: Growth rate of structure measurement from anisotropic clustering analysis in configuration space between redshift 0.6 and 1.1 for the emission-line galaxy sample. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 5527–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mattia, A.; Ruhlmann-Kleider, V.; Raichoor, A.; Ross, A.J.; Tamone, A.; Zhao, C.; Alam, S.; Avila, S.; Burtin, E.; Bautista, J.; et al. The Completed SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Measurement of the BAO and growth rate of structure of the emission line galaxy sample from the anisotropic power spectrum between redshift 0.6 and 1.1. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 501, 5616–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Sánchez, A.G.; Ross, A.J.; Smith, A.; Neveux, R.; Bautista, J.; Burtin, E.; Zhao, C.; Scoccimarro, R.; Dawson, K.S.; et al. The completed SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: BAO and RSD measurements from anisotropic clustering analysis of the quasar sample in configuration space between redshift 0.8 and 2.2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 500, 1201–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neveux, R.; Burtin, E.; de Mattia, A.; Smith, A.; Ross, A.J.; Hou, J.; Bautista, J.; Brinkmann, J.; Chuang, C.-H.; Dawson, K.S.; et al. The completed SDSS-IV extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: BAO and RSD measurements from the anisotropic power spectrum of the quasar sample between redshift 0.8 and 2.2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Mas des Bourboux, H.; Rich, J.; Font-Ribera, A.; Agathe, V.d.S.; Farr, J.; Etourneau, T.; Le Goff, J.-M.; Cuceu, A.; Balland, C.; Bautista, J.E.; et al. The Completed SDSS-IV Extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: Baryon Acoustic Oscillations with Lyα Forests. Astrophys. J. 2020, 901, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delubac, T.; Bautista, J.E.; Busca, N.G.; Rich, J.; Kirkby, D.; Bailey, S.; Font-Ribera, A.; Slosar, A.; Lee, K.-G.; Pieri, M.M.; et al. Baryon acoustic oscillations in the Lyα forest of BOSS DR11 quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 574, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, M.; Bourboux, H.d.M.D.; Busca, N.G.; Agathe, V.d.S.; Rich, J.; Balland, C.; Bautista, J.E.; Dawson, K.; Font-Ribera, A.; Guy, J.; et al. Baryon acoustic oscillations from the cross-correlation of Lyα absorption and quasars in eBOSS DR14. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 629, A86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Mas des Bourboux, H.; Le Goff, J.-M.; Blomqvist, M.; Busca, N.G.; Guy, J.; Rich, J.; Yèche, C.; Bautista, J.E.; Burtin, É.; Dawson, K.S.; et al. Baryon acoustic oscillations from the complete SDSS-III Lyα-quasar cross-correlation function at z = 2.4. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 608, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Davis, T.; Poole, G.B.; Parkinson, D.; Brough, S.; Colless, M.; Contreras, C.; Couch, W.; Croom, S.; Drinkwater, M.J.; et al. The WiggleZ Dark Energy Survey: Testing the cosmological model with baryon acoustic oscillations at z = 0.6: WiggleZ survey: BAOs at z = 0.6. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, 2892–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, D.; Abbott, T.M.C.; Adamow, M.; Aguena, M.; Allam, S.; Alves, O.; Amon, A.; Andrade-Oliveira, F.; Asorey, J.; Avila, S.; et al. Dark Energy Survey: A 2.1% measurement of the angular Baryonic Acoustic Oscillation scale at redshift zeff = 0.85 from the final dataset. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. Planck2018 results: VI. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cao, S.; Wang, J. A model-independent determination of the sound horizon using recent BAO measurements and strong lensing systems. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.18298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, L.; Bernal, J.L.; Heavens, A.F.; Jimenez, R. The length of the low-redshift standard ruler. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungo, A.; Reyes, M. Assessing Reliability and Challenges of Uncertainty Estimations for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.03338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, R.D.; Romeijn, J.W.; Rouder, J.N. The philosophy of Bayes factors and the quantification of statistical evidence. J. Math. Psychol. 2016, 72, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F. On the Jensen–Shannon Symmetrization of Distances Relying on Abstract Means. Entropy 2019, 21, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.C.; Suyu, S.H.; Chen, G.C.F.; Rusu, C.E.; Millon, M.; Sluse, D.; Bonvin, V.; Fassnacht, C.D.; Taubenberger, S.; Auger, M.W.; et al. H0LiCOW–XIII. A 2.4 per cent measurement of H0 from lensed quasars: 5.3σ tension between early- and late-Universe probes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 498, 1420–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giare, W.; Betts, J.; van de Bruck, C.; Di Valentino, E. Model-Independent Test of Prerecombination New Physics: Measuring the Sound Horizon with Gravitational Wave Standard Sirens and the Baryon Acoustic Oscillation Angular Scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2025, 135, 071003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanton, M.R.; Bershady, M.A.; Abolfathi, B.; Albareti, F.D.; Allende Prieto, C.; Almeida, A.; Alonso-García, J.; Anders, F.; Anderson, S.F.; Andrews, B.; et al. Sloan Digital Sky Survey IV: Mapping the Milky Way, Nearby Galaxies, and the Distant Universe. Astron. J. 2017, 154, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Karim, M.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Allen, L.; Prieto, C.A.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI DR2 results. II. Measurements of baryon acoustic oscillations and cosmological constraints. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 112, 083515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What uncertainties do we need in Bayesian deep learning for computer vision? In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; NIPS’17. pp. 5580–5590. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.J. Computing and Graphing Highest Density Regions. Am. Stat. 1996, 50, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).