About Jordan and Einstein Frames: A Study in Inflationary Magnetogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conformal Transformations between Jordan and Einstein Frames
3. U(1) Gauge Field Coupled with Scalar-Tensor Theories
3.1. Magnetogenesis in Jordan Frame
3.2. Magnetogenesis in Einstein Frame
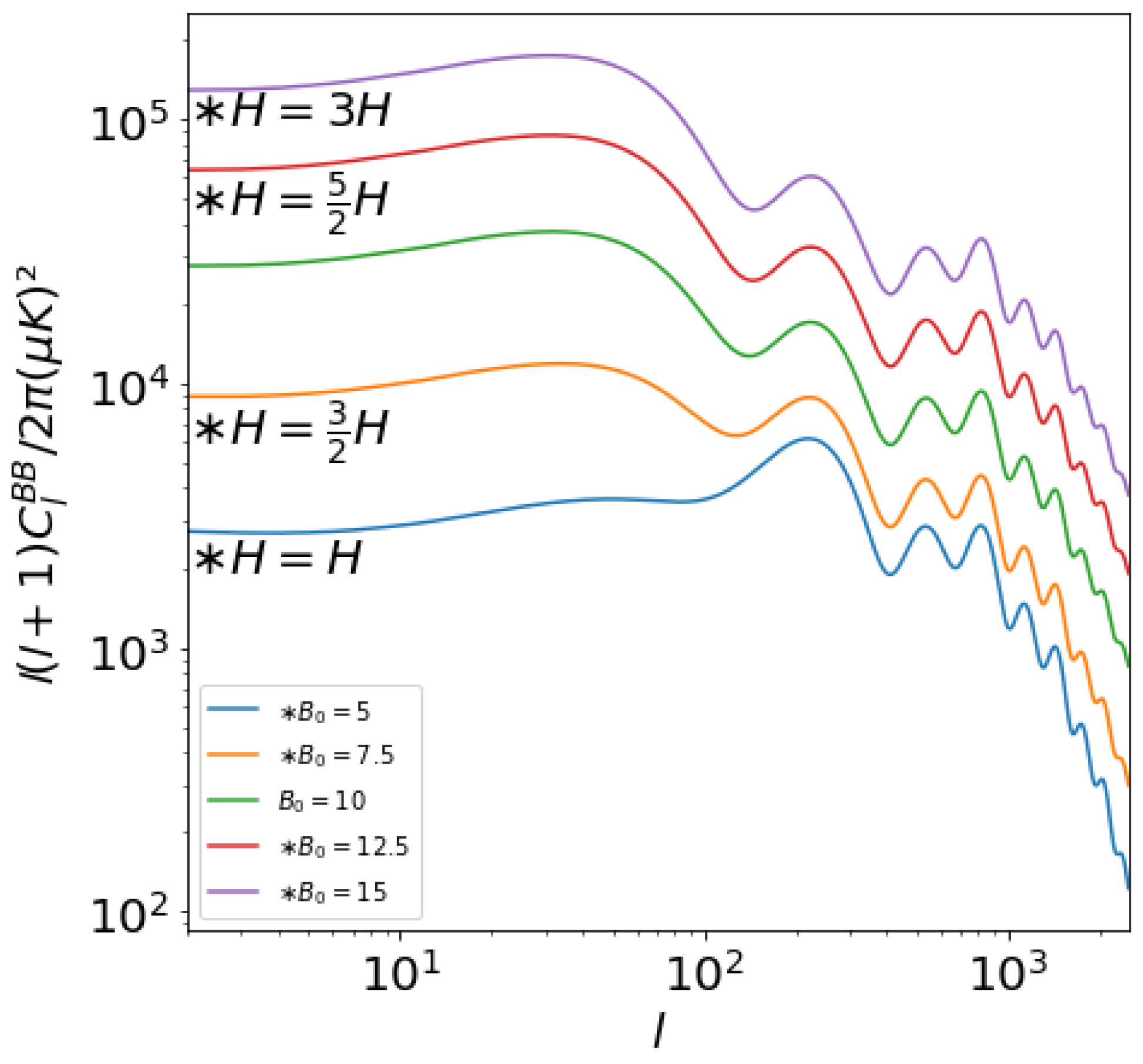
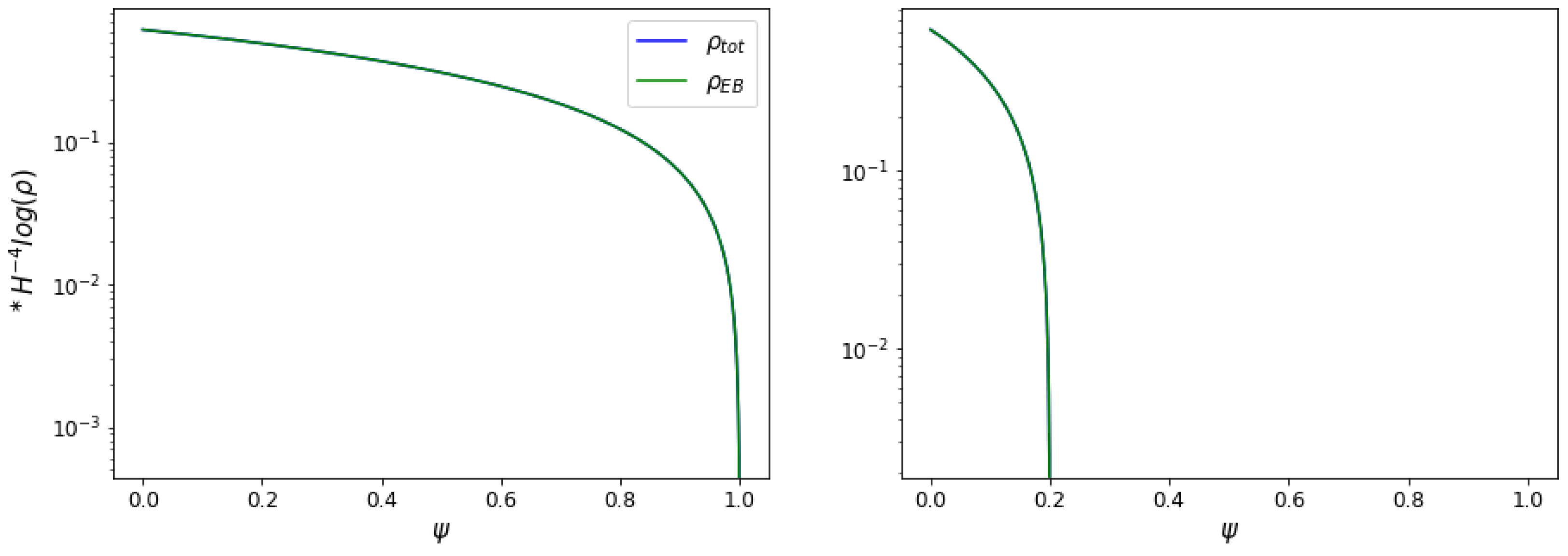
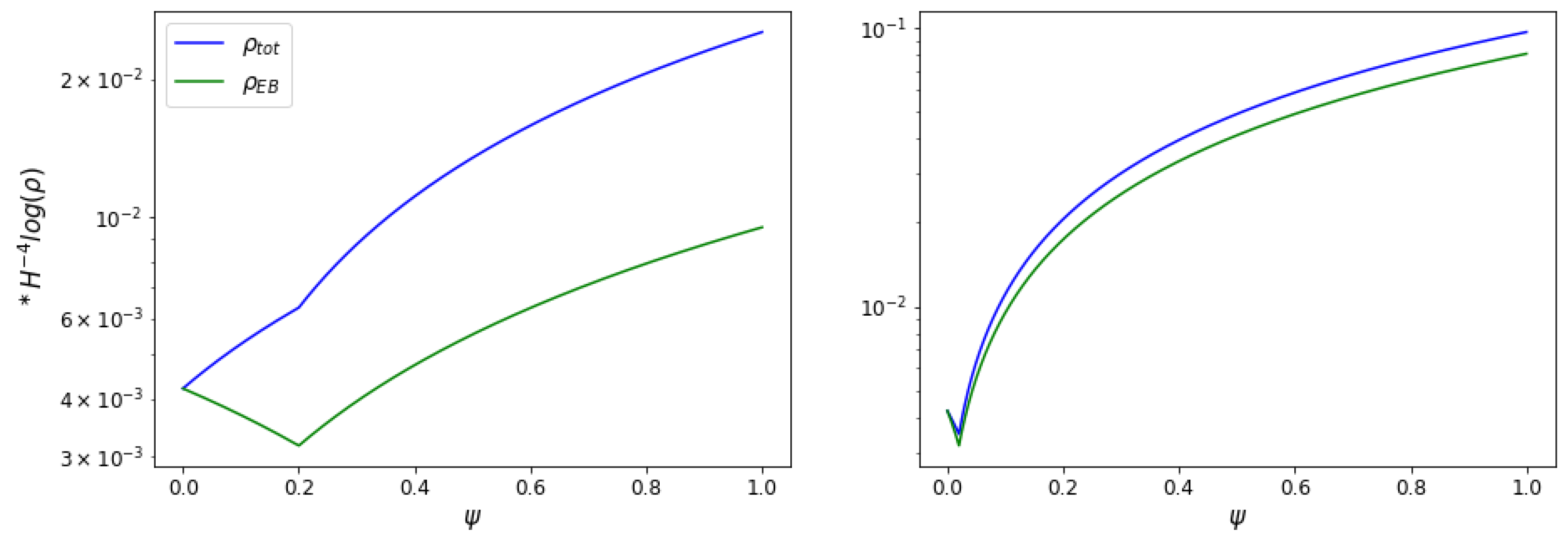
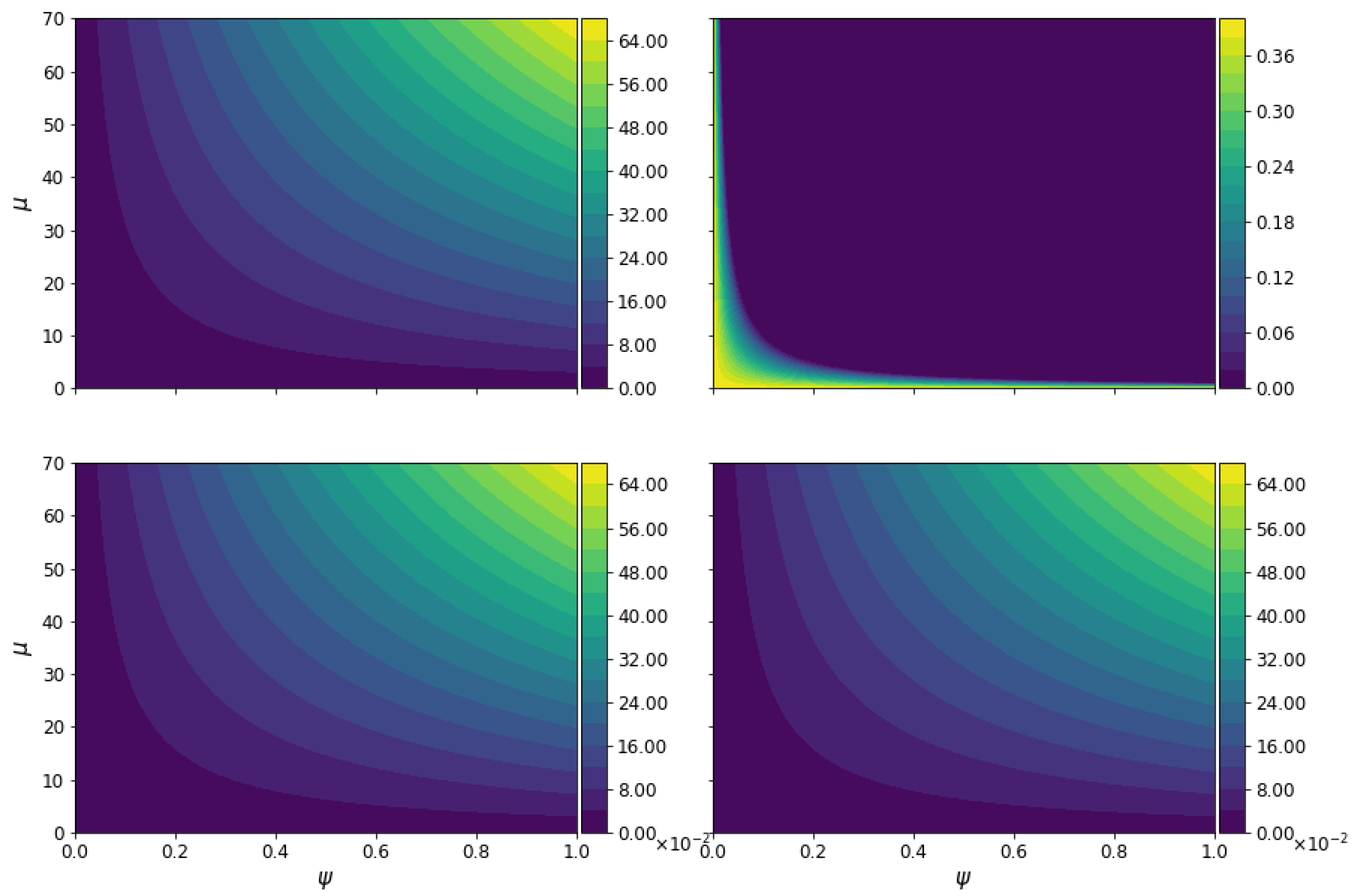
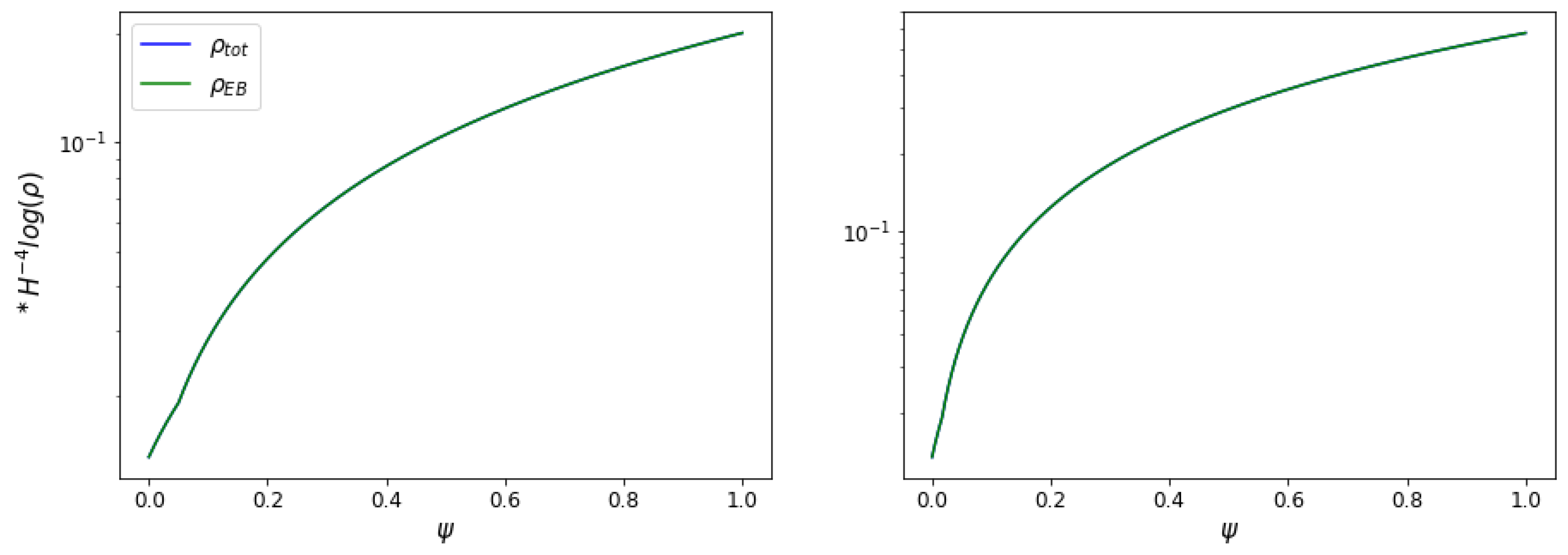
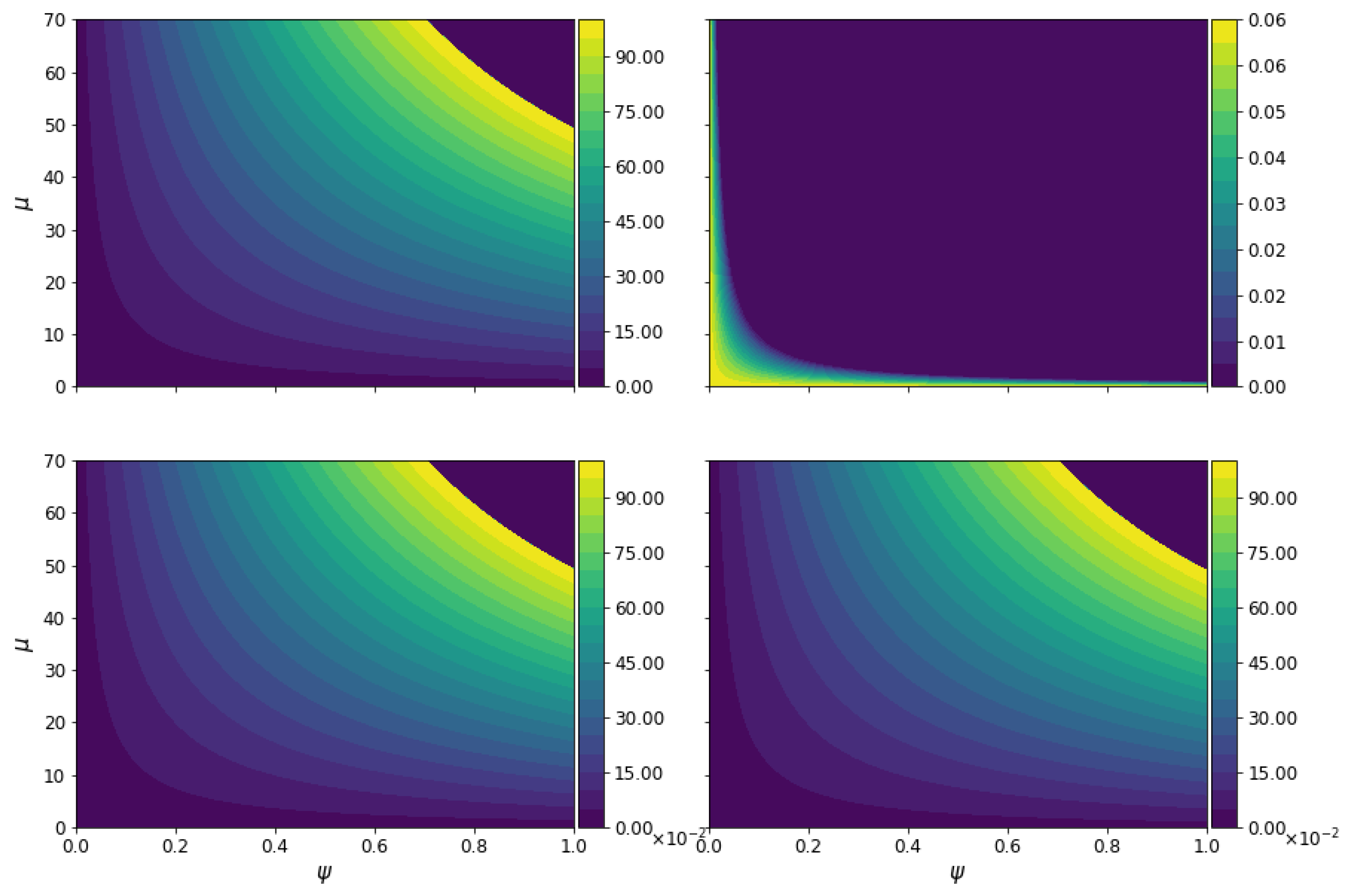
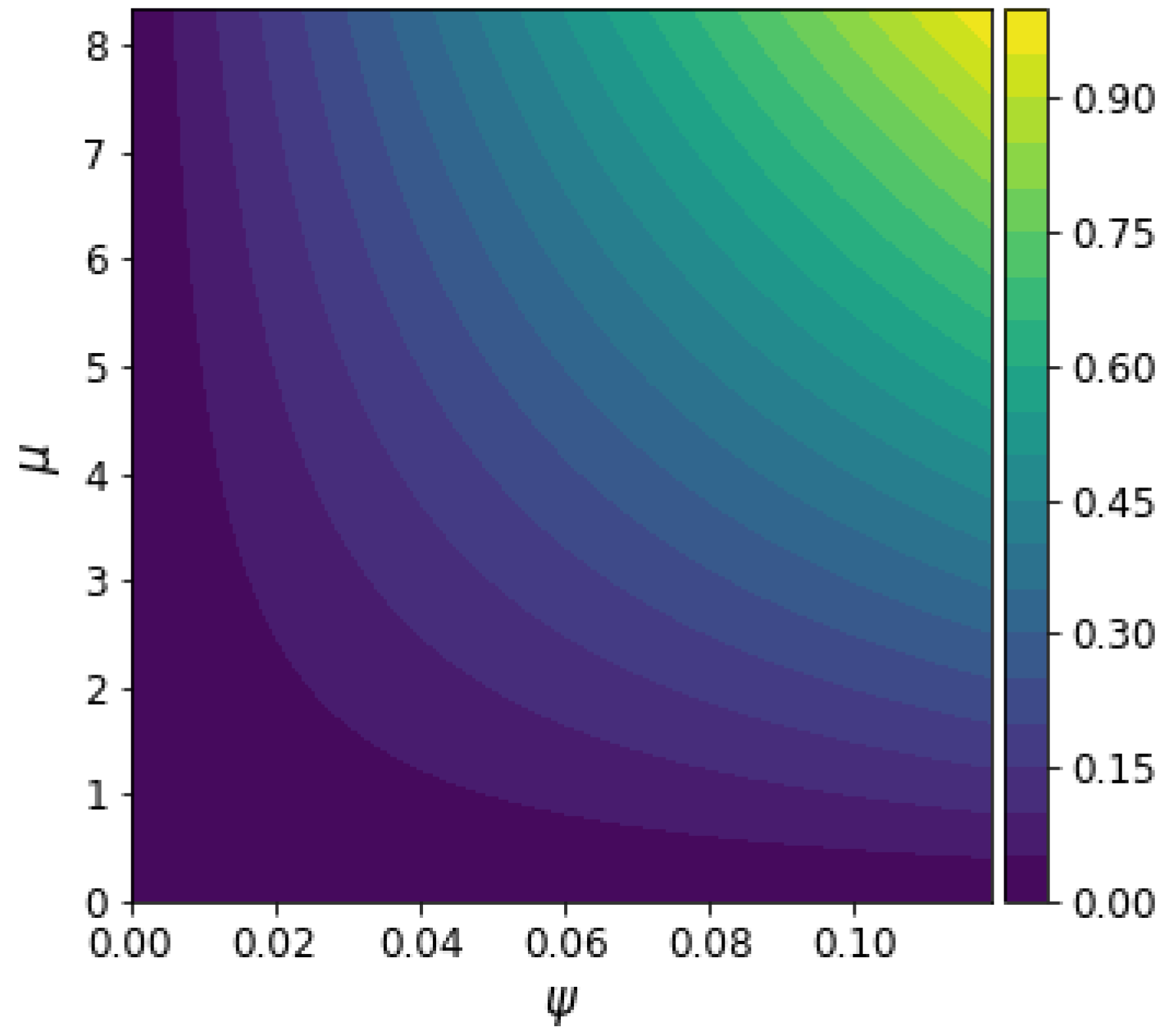
4. Magnetogenesis on Power–Law Inflation
4.1. Model in Jordan Frame
4.2. Magnetogenesis View from the Einstein Frame
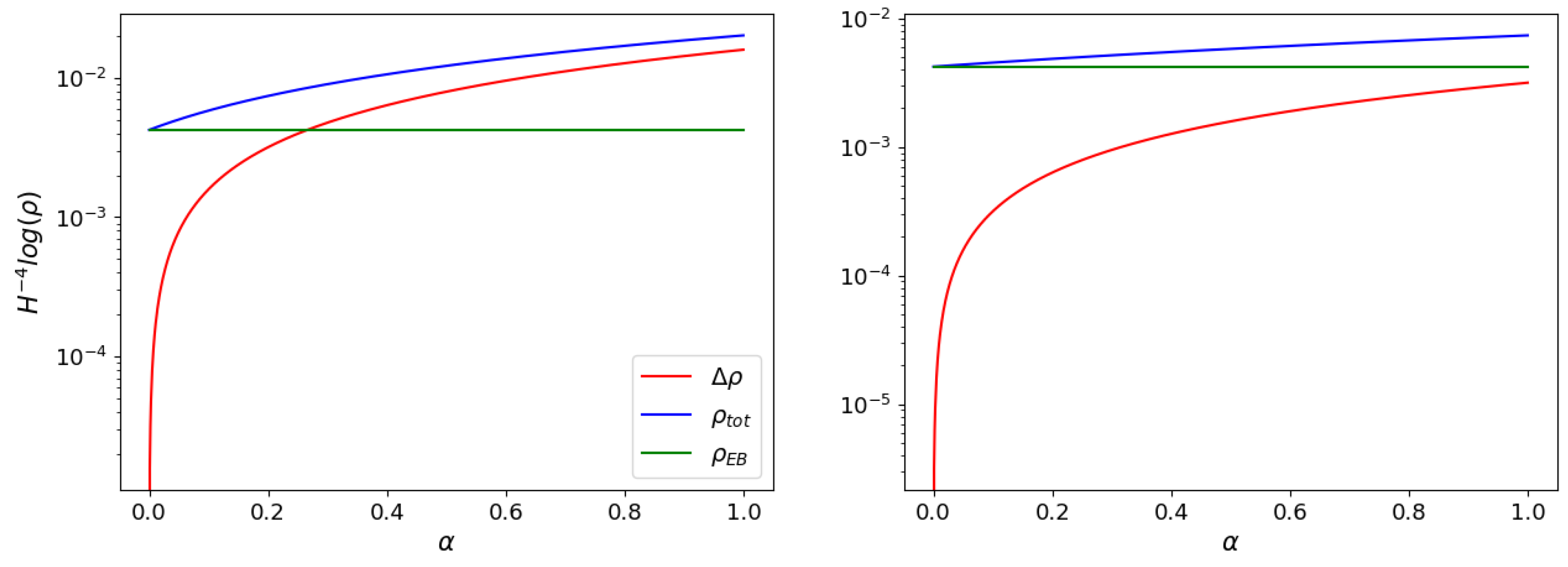
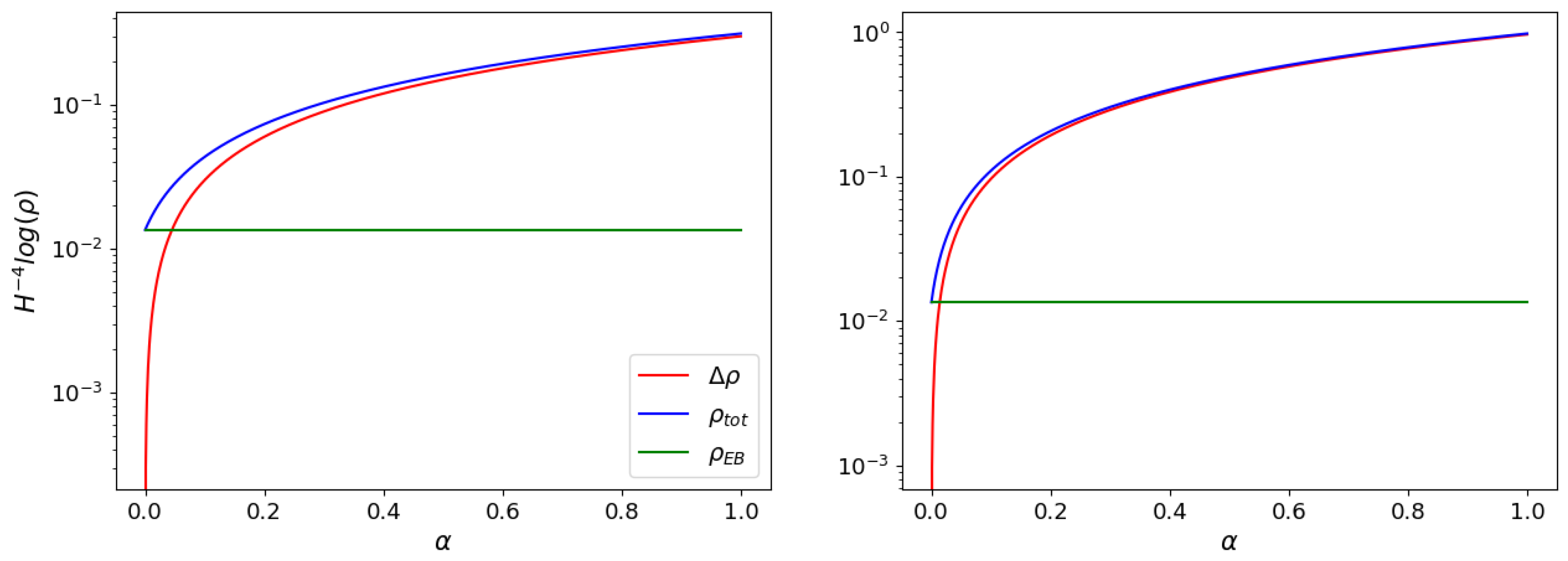
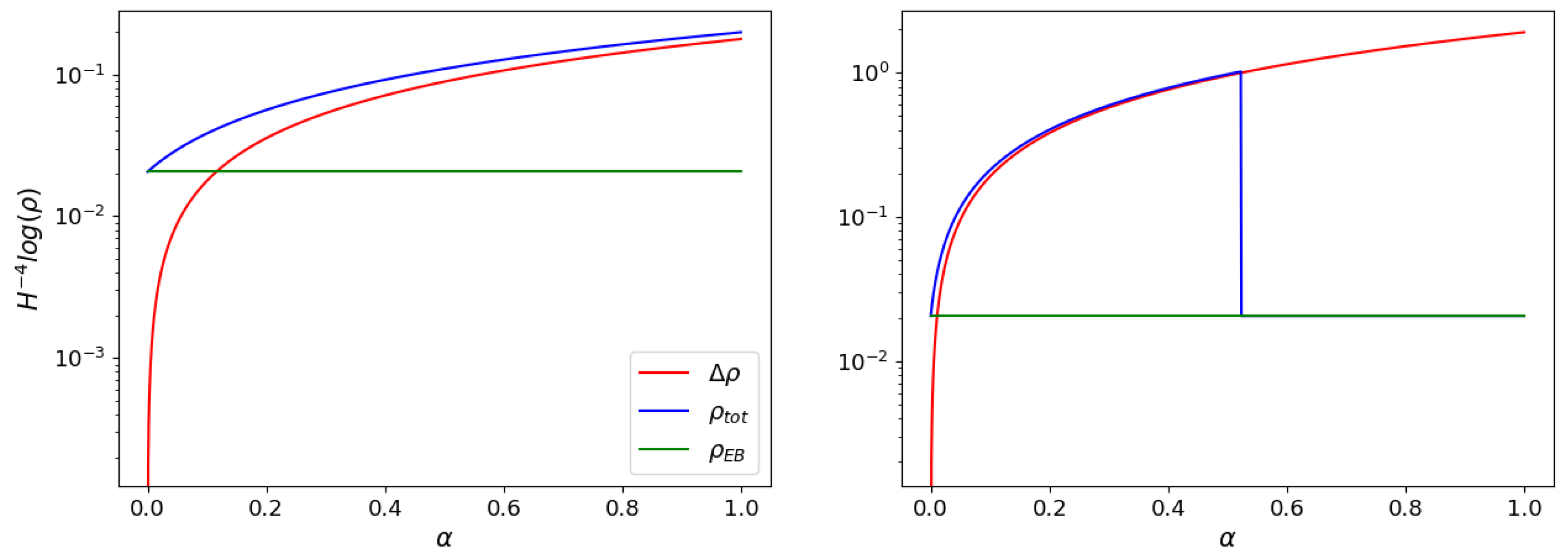
5. Discussion about Jordan and Einstein Frames
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Omega and Lambda from 42 high redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, T. Cosmological constant—the weight of the vacuum. Phys. Rep. 2003, 380, 235–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M. The Cosmological Constant. Living Rev. Relativ. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, C.; Dicke, R.H. Mach’s Principle and a Relativistic Theory of Gravitation. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Maeda, K. The Scalar-Tensor Theory of Gravitation; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V. Cosmology in Scalar Tensor Gravity; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, I. Selected topics in scalar–tensor theories and beyond. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1930012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M.; Duvvuri, V.; Trodden, M.; Turner, M.S. Is cosmic speed-up due to new gravitational physics? Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 043528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T. 1/R gravity and scalar-tensor gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2003, 575, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Where new gravitational physics comes from: M-theory? Phys. Lett. B 2003, 576, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Moniz, P.V. Gravity-driven acceleration and kinetic inflation in noncommutative brans-dicke setting. Odessa Astron. Publ. 2016, 29, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, R.G.; German, G. A comparison between the Jordan and Einstein Frames in Brans-Dicke theories with torsion. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2206.14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carloni, S.; Dunsby, P.K.S.; Capozziello, S.; Troisi, A. Cosmological dynamics of Rn gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2005, 22, 4839–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, A.D.; Tsujikawa, S. f(R) Theories. Living Rev. Relativ. 2010, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, L.; Polarski, D.; Tsujikawa, S. Are f(R) Dark Energy Models Cosmologically Viable? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 131302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Gorbunova, O.G. Dark energy problem: From phantom theory to modified Gauss–Bonnet gravity. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2006, 39, 6627–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Charmousis, C.; Davis, S.C. Constraints on Gauss–Bonnet gravity in dark energy cosmologies. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2006, 2006, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.G.S.; Carrilho, P.; Clifton, T.; Mulryne, D.J. The 4D Einstein–Gauss–Bonnet theory of gravity: A review. Class. Quantum Gravity 2022, 39, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvali, G.; Gabadadze, G.; Porrati, M. 4D gravity on a brane in 5D Minkowski space. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 485, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maartens, R.; Koyama, K. Brane-World Gravity. Living Rev. Relativ. 2010, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.M.M.; Bahrehbakhsh, A.F.; Jalalzadeh, S.; Farhoudi, M. Quantum mechanics and geodesic deviation in the brane world. Europhys. Lett. 2009, 87, 40006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.M.M.; Cheraghchi, S.; Moniz, P. Fractional Scalar Field Cosmology. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V.; Gunzig, E. Einstein frame or Jordan frame? arXiv 1999, arXiv:astro-ph/9910176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; de Ritis, R.; Marino, A.A. Some aspects of the cosmological conformal equivalence between the ‘Jordan frame’ and the ‘Einstein frame’. Class. Quantum Gravity 1997, 14, 3243–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, É.É. The conformal frame freedom in theories of gravitation. Class. Quantum Gravity 2004, 21, 3817–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros, I.; García-Salcedo, R.; Madriz-Aguilar, J.E.; Matos, T. The conformal transformation’s controversy: What are we missing? Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2012, 45, 489–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, R. Hubble diagrams in the Jordan and Einstein frames. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2018, 51, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, F.; Li, B. Equivalence of cosmological observables in conformally related scalar tensor theories. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 124009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicke, R.H. Mach’s Principle and Invariance under Transformation of Units. Phys. Rev. 1962, 125, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V.; Nadeau, S. (Pseudo)issue of the conformal frame revisited. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 023501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, M.; Volponi, M. Equivalence of the Einstein and Jordan frames. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.; Tretyakov, P.V. Deceleration versus acceleration universe in different frames of F(R) gravity. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 766, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M. On the equivalence of Jordan and Einstein frames in scale-invariant gravity. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francfort, J.; Ghosh, B.; Durrer, R. Cosmological number counts in Einstein and Jordan frames. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, K. The origin, evolution and signatures of primordial magnetic fields. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 076901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortúa, H.J.; Castañeda, L. Reduced bispectrum seeded by helical primordial magnetic fields. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 2017, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprini, C.; Sorbo, L. Adding helicity to inflationary magnetogenesis. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2014, 056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Elizalde, E.; Odintsov, S.; Paul, T. Inflationary magnetogenesis with reheating phase from higher curvature coupling. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 2021, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Odintsov, S.D.; Paul, T.; Maity, D. Helical magnetogenesis with reheating phase from higher curvature coupling and baryogenesis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2107.11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, K.; Uchida, F.; Fujita, T.; Tsujikawa, S. Low-Scale Inflationary Magnetogenesis without Baryon Isocurvature Problem. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.07938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adshead, P.; Giblin, J.T.; Scully, T.R.; Sfakianakis, E.I. Magnetogenesis from axion inflation. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.; Oikonomou, V. Modified gravity theories on a nutshell: Inflation, bounce and late-time evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, J.; Castañeda, L. Equivalence between Scalar-Tensor theories and f(R)-gravity: From the action to cosmological perturbations. J. Phys. Commun. 2020, 4, 055007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified cosmic history in modified gravity: From f(R) theory to Lorentz non-invariant models. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 59–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaie, A.H.; Atazadeh, K.; Rasouli, S.M.M. Naked singularity formation in f(R) gravity. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2011, 43, 2943–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahamonde, S.; Odintsov, S.; Oikonomou, V.; Wright, M. Correspondence of F(R) Gravity Singularities in Jordan and Einstein Frames. Ann. Phys. 2016, 373, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, K. Magnetic fields in the early Universe. Astron. Nachrichten 2010, 331, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markkanen, T.; Nurmi, S.; Räsänen, S.; Vennin, V. Narrowing the window of inflationary magnetogenesis. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 2017, 035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Subramanian, K.; Seshadri, T. Generation of helical magnetic field in a viable scenario of inflationary magnetogenesis. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 083503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrer, R.; Sobol, O.; Vilchinskii, S. Magnetogenesis in Higgs-Starobinsky inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 123520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Odintsov, S.D. Inflation and late-time cosmic acceleration in non-minimal Maxwell-F(R) gravity and the generation of large-scale magnetic fields. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 2008, 024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olver, F.W.J.; Lozier, D.W.; Boisvert, R.F.; Clark, C.W. The NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Savchenko, O.; Shtanov, Y. Magnetogenesis by non-minimal coupling to gravity in the Starobinsky inflationary model. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 2018, 040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, A.; Li, Y.; Pogosian, L. Constraints on primordial magnetic fields from Planck data combined with the South Pole Telescope CMB B-mode polarization measurements. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 063506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Challinor, A.; Lasenby, A. Efficient Computation of Cosmic Microwave Background Anisotropies in Closed Friedmann-Robertson-Walker Models. Astrophys. J. 2000, 538, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velásquez, J.; Hortua, H.J.; Castañeda, L. About Jordan and Einstein Frames: A Study in Inflationary Magnetogenesis. Universe 2024, 10, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090350
Velásquez J, Hortua HJ, Castañeda L. About Jordan and Einstein Frames: A Study in Inflationary Magnetogenesis. Universe. 2024; 10(9):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090350
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelásquez, Joel, Héctor J. Hortua, and Leonardo Castañeda. 2024. "About Jordan and Einstein Frames: A Study in Inflationary Magnetogenesis" Universe 10, no. 9: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090350
APA StyleVelásquez, J., Hortua, H. J., & Castañeda, L. (2024). About Jordan and Einstein Frames: A Study in Inflationary Magnetogenesis. Universe, 10(9), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10090350