Probing the Propeller Regime with Symbiotic X-ray Binaries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. Stellar Wind
2.2. Spin Evolution of NSs
3. Propeller Stage
4. Results
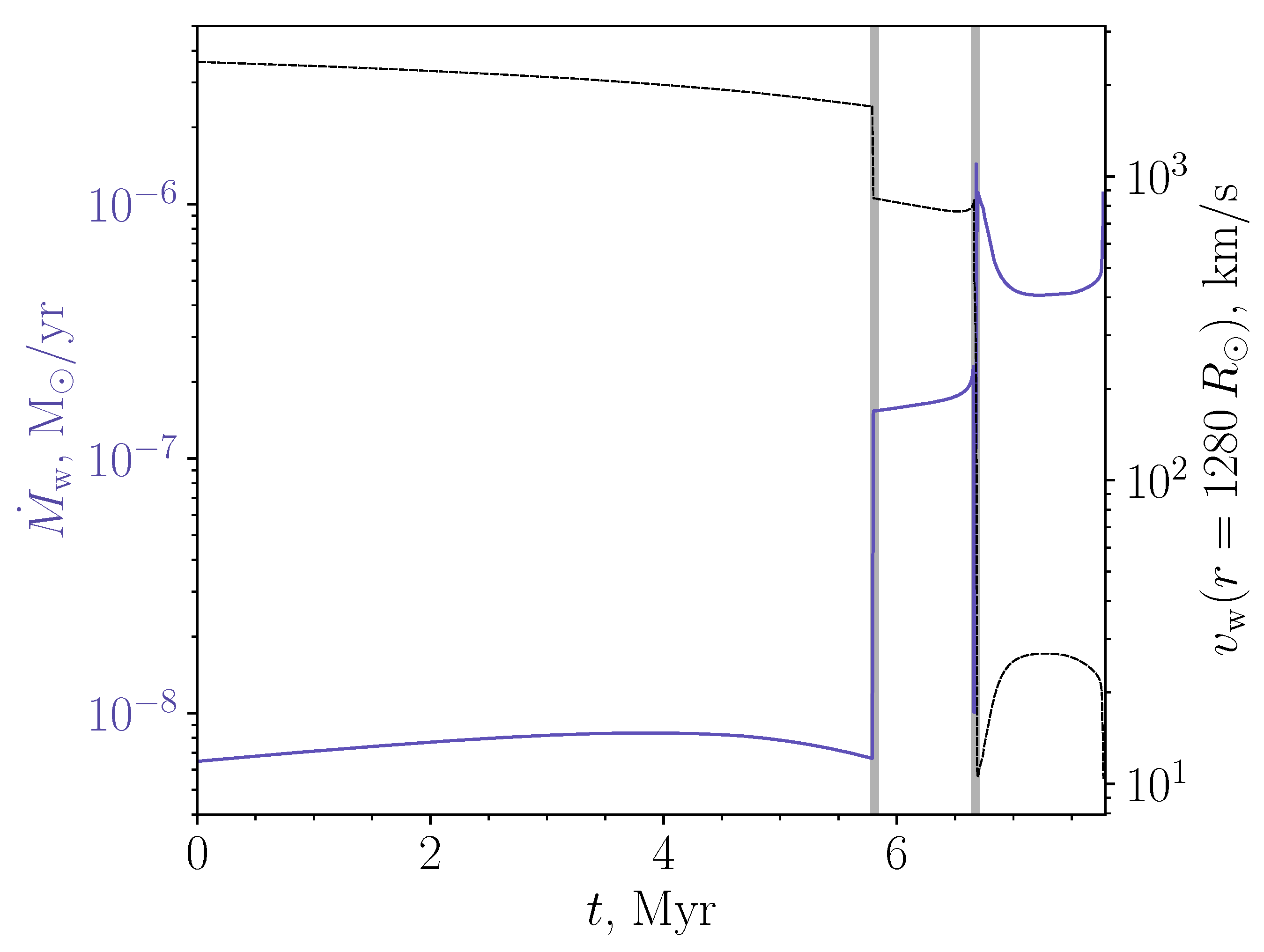
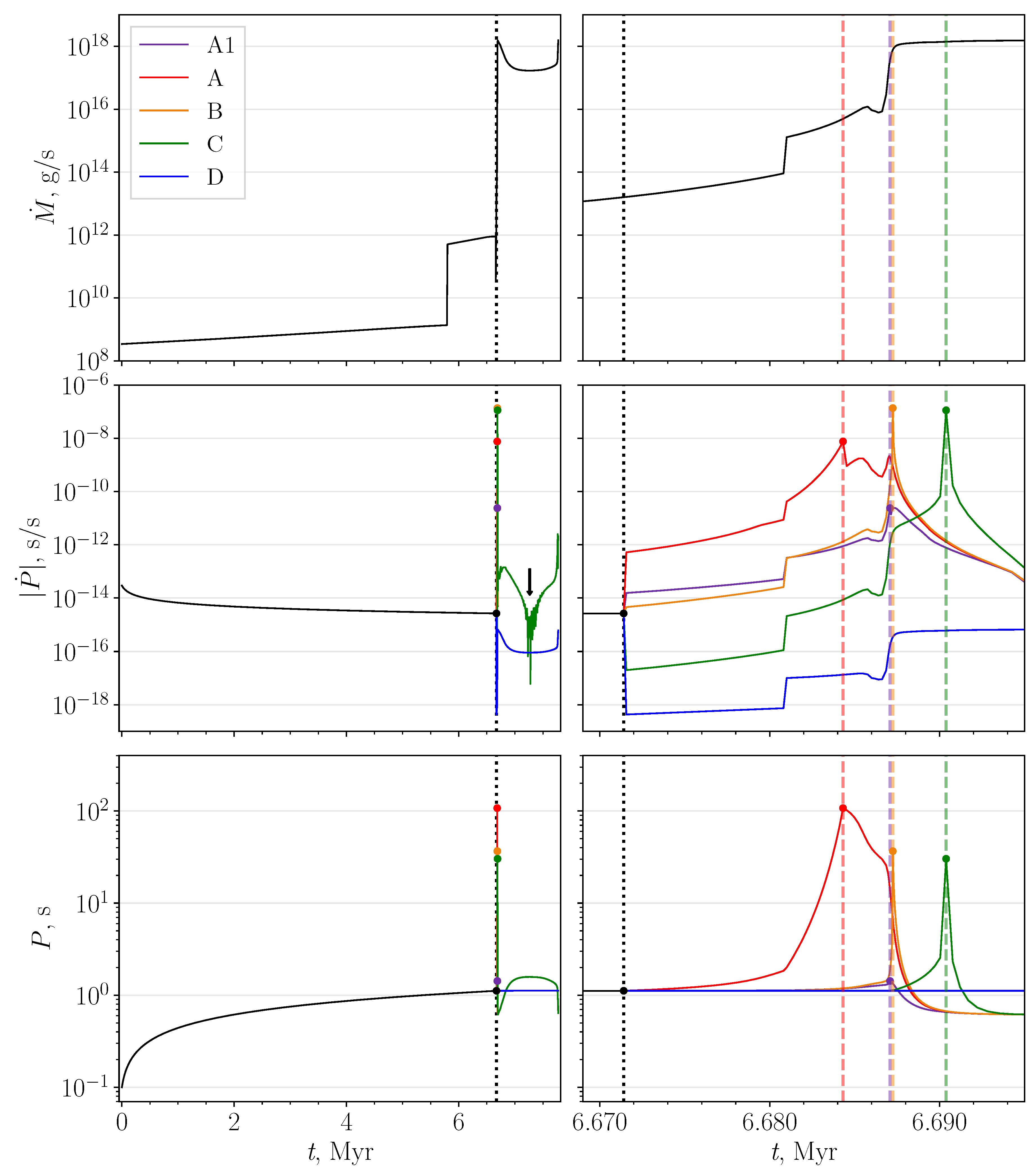
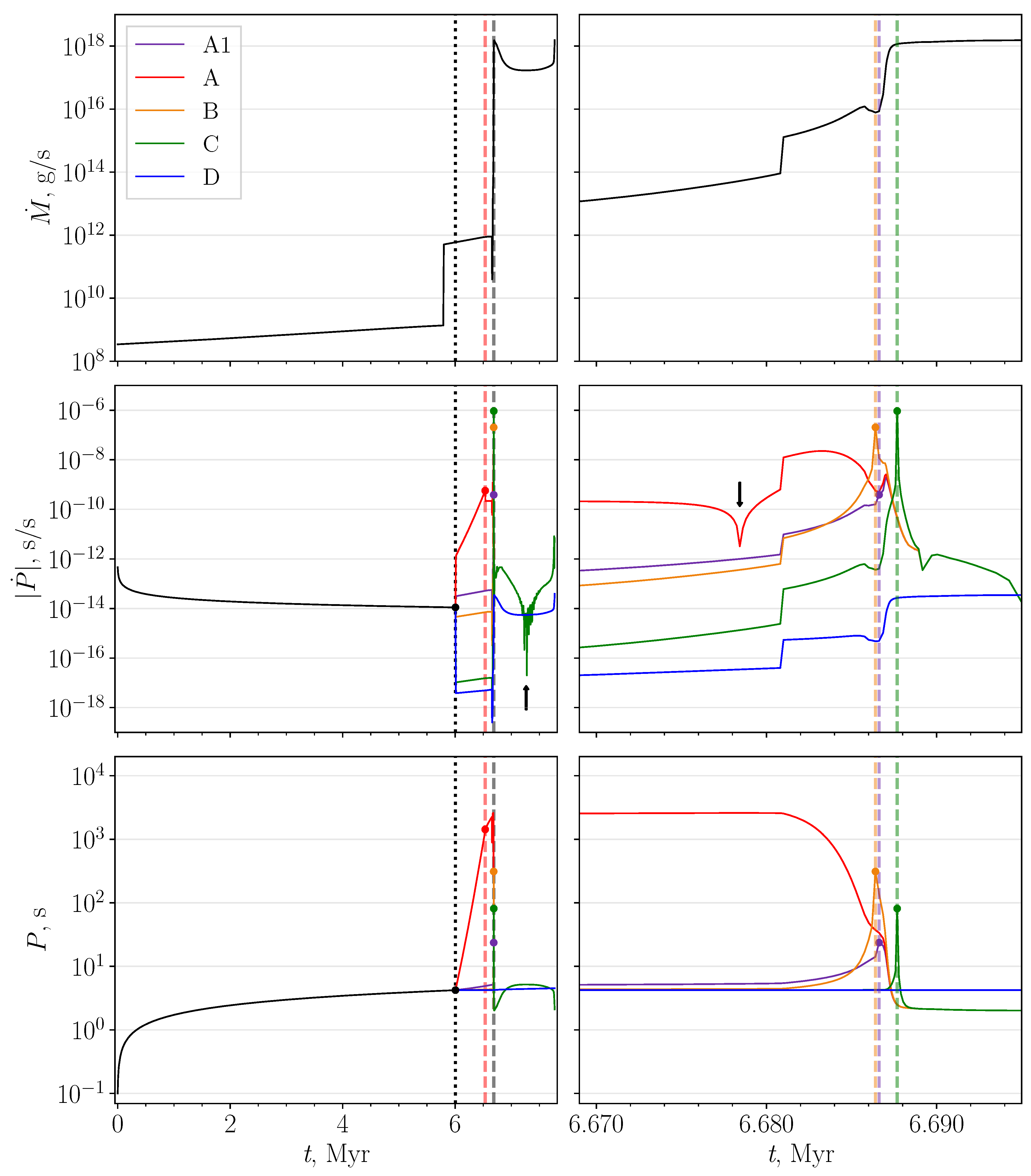
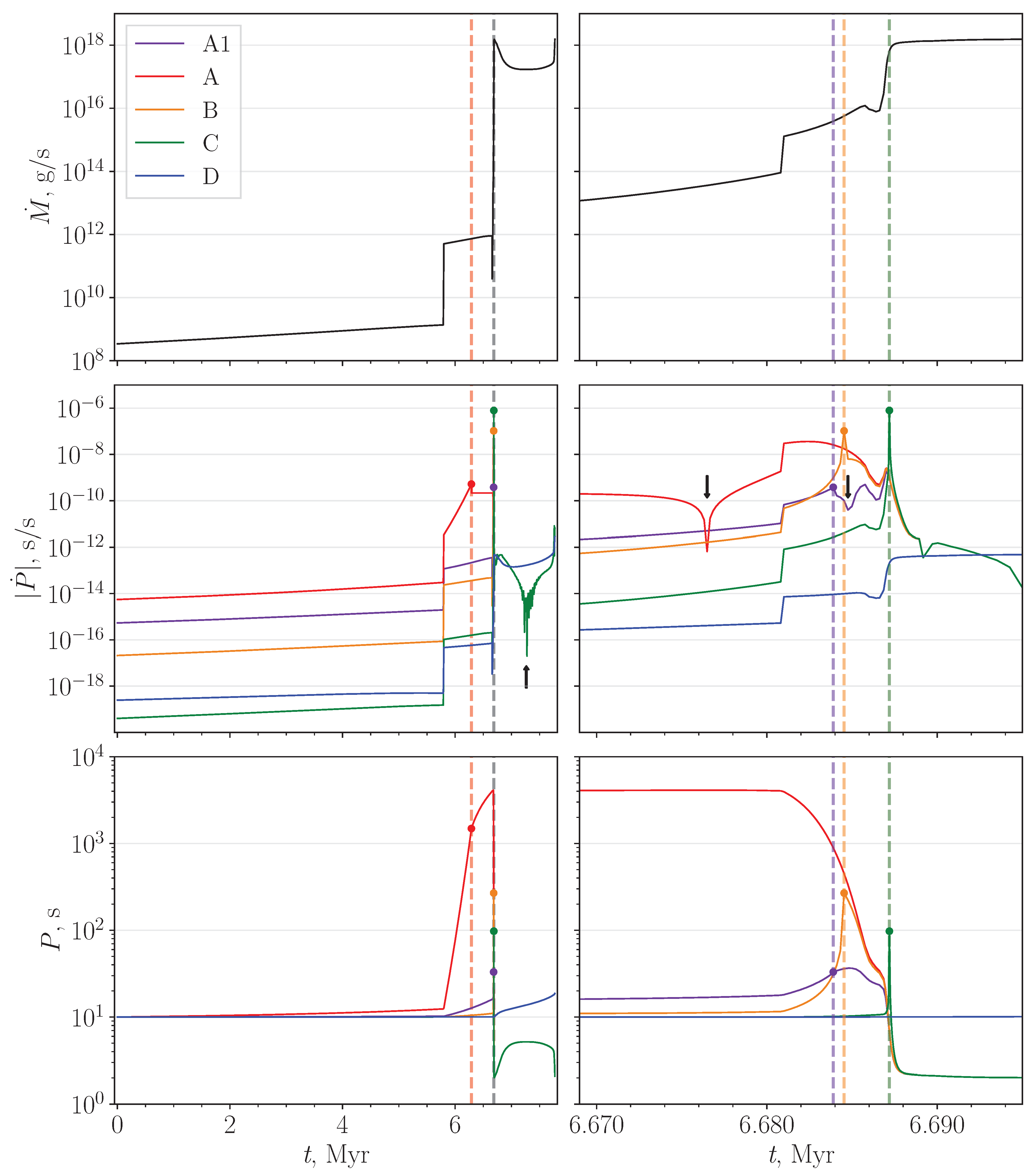
4.1. Detailed Spin Evolution of a Typical Neutron Star in a Binary
4.2. Evolutionary Stages of NSs in a Wide Range of the Magnetic Field
5. Discussion
5.1. Magnetar Evolution
5.2. Relative Spin-Down Rates for Ejectors and Different Propeller Regimes
5.3. Disc Formation at the Propeller Stage
5.4. Wind Accretion Flow in a Red Supergiant Binary
5.5. The Corotation Radius Value and Magnetic Inclination
5.6. Luminosity at the Propeller Stage
5.7. The Possibility of Settling Accretion in SWIFT J0850.8-4219
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMXB | High-mass X-ray binary |
| NS | Neutron star |
| RGB | Red giant branch |
| RSG | Red supergiant |
| SyXB | Symbiotic X-ray binary |
References
- Nättilä, J.; Kajava, J.J.E. Fundamental Physics with Neutron Stars. In Handbook of X-ray and Gamma-ray Astrophysics; Springer: Singapore, 2022; p. 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B. The Zoo of Isolated Neutron Stars. Universe 2023, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, S.; Graber, V.; Rea, N. Neutron-star Measurements in the Multi-messenger Era. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.14930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvartsman, V.F. Two generations of pulsars. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 1970, 13, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, J.E.; Rees, M.J. Accretion Disc Models for Compact X-ray Sources. Astron. Astrophys. 1972, 21, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, K.; Ostriker, J.P. Neutron-Star Accretion in a Stellar Wind: Model for a Pulsed X-ray Source. Astrophys. J. 1973, 179, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.I. The long-period X-ray pulsar 3U 0900-40 as a neutron star with an abnormally strong magnetic field. Sov. Astron. Lett. 1975, 1, 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Illarionov, A.F.; Sunyaev, R.A. Why the Number of Galactic X-ray Stars Is so Small? Astron. Astrophys. 1975, 39, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Campana, S.; Stella, L.; Mereghetti, S.; de Martino, D. A universal relation for the propeller mechanisms in magnetic rotating stars at different scales. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 610, A46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papitto, A.; Torres, D.F. A Propeller Model for the Sub-luminous State of the Transitional Millisecond Pulsar PSR J1023+0038. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsygankov, S.S.; Lutovinov, A.A.; Doroshenko, V.; Mushtukov, A.A.; Suleimanov, V.; Poutanen, J. Propeller effect in two brightest transient X-ray pulsars: 4U 0115+63 and V 0332+53. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 593, A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.N.; Yu, W.; Zhang, W. Spectral State Transitions in Aquila X-1: Evidence for “Propeller” Effects. Astrophys. J. 1998, 494, L71–L74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, S.N.; Ding, G.Q. Propeller-driven Spectral State Transition in the Low-Mass X-ray Binary 4U 1608-52. Astrophys. J. 2006, 650, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutovinov, A.A.; Tsygankov, S.S.; Krivonos, R.A.; Molkov, S.V.; Poutanen, J. Propeller Effect in the Transient X-ray Pulsar SMC X-2. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilopoulos, G.; Koliopanos, F.; Haberl, F.; Treiber, H.; Brightman, M.; Earnshaw, H.P.; Gúrpide, A. Chandra Probes the X-ray Variability of M51 ULX-7: Evidence of Propeller Transition and X-ray Dips on Orbital Periods. Astrophys. J. 2021, 909, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnov, K.A.; Yungelson, L.R. The Evolution of Compact Binary Star Systems. Living Rev. Relativ. 2014, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, F.; García, F.; Simaz Bunzel, A.; Chaty, S. A catalogue of high-mass X-ray binaries in the Galaxy: From the INTEGRAL to the Gaia era. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 671, A149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Avakyan, A.; Doroshenko, V.; Santangelo, A. XRBcats: Galactic High Mass X-ray Binary Catalogue★. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 677, A134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yungelson, L.R.; Kuranov, A.G.; Postnov, K.A. Wind-accreting symbiotic X-ray binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 485, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, K.H.; Lebzelter, T.; Fekel, F.C.; Straniero, O.; Joyce, R.R.; Prato, L.; Karnath, N.; Habel, N. The M Supergiant High-mass X-ray Binary 4U 1954+31. Astrophys. J. 2020, 904, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzo, E.; Ferrigno, C.; Oskinova, L.; Ducci, L. Accretion of a clumped wind from a red supergiant donor on to a magnetar is suggested by the analysis of the XMM-Newton and NuSTAR observations of the X-ray binary 3A 1954+319. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 510, 4645–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, K.; Daly, F.A.; Soria, R. Infrared spectroscopy of SWIFT J0850.8-4219: Identification of the second red supergiant X-ray binary in the Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 528, L38–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, J.; Vink, J.S.; Najarro, F. Mass loss from hot massive stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 16, 209–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bressan, A.; Girardi, L.; Marigo, P.; Kong, X.; Lanza, A. PARSEC evolutionary tracks of massive stars up to 350 M⊙ at metallicities 0.0001 ≤ Z ≤ 0.04. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, P.P. Aproximations to the radii of Roche lobes. Astrophys. J. 1983, 268, 368–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. New theoretical mass-loss rates of O and B stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 362, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. On the nature of the bi-stability jump in the winds of early-type supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 350, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.D. Chromospheres and Winds of Red Supergiants: An Empirical Look at Outer Atmospheric Structure. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1004.1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, H. On spherically symmetrical accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1952, 112, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglizzo, T.; Ruffert, M. An analytic study of Bondi-Hoyle-Lyttleton accretion. I. Stationary flows. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 320, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prust, L.J.; Glanz, H.; Bildsten, L.; Perets, H.B.; Roepke, F.K. Morphology and Mach Number Dependence of Subsonic Bondi-Hoyle Accretion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipunov, V.M. Astrophysics of Neutron Stars; Astronomy and Astrophysics Library: Toronto, ON, Canada; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Abolmasov, P.; Biryukov, A.; Popov, S.B. Spin Evolution of Neutron Stars. Galaxies 2024, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Turolla, R. Initial spin periods of neutron stars in supernova remnants. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2012, 341, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Frantsuzova, A.; Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Tsichli, S.; Konstantinou, L.; Popov, S.B. Initial periods and magnetic fields of neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 514, 4606–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Popov, S.B.; Hollerbach, R. Evolution of Neutron Star Magnetic Fields. Universe 2021, 7, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Popov, S.B. Modified pulsar current analysis: Probing magnetic field evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gourgouliatos, K.N.; Cumming, A. Hall Attractor in Axially Symmetric Magnetic Fields in Neutron Star Crusts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, S.; Bhattacharya, D. Magnetic field evolution of accreting neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 284, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyutikov, M. Centrifugal barriers in magnetospheric accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 520, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chashkina, A.; Abolmasov, P.; Poutanen, J. Super-Eddington accretion on to a magnetized neutron star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 2799–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M. On the Torque Exerted by a Magnetically Threaded Accretion Disk. Astrophys. J. 1995, 449, L153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.E.; Pringle, J.E. Spindown of neutron stars in close binary systems—II. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 196, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.; Postnov, K.; Kochetkova, A.; Hjalmarsdotter, L. Theory of quasi-spherical accretion in X-ray pulsars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 216–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francischelli, G.J.; Wijers, R.A.M.J. On Fossil Disk Models of Anomalous X-ray Pulsars. arXiv 2002, arXiv:astro-ph/0205212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipunov, V.M.; Popov, S.B. Spin evolution of isolated neutron stars—Spindown theorem. Astron. Zhurnal 1995, 72, 711. [Google Scholar]
- Alpar, M.A. On Young Neutron Stars as Propellers and Accretors with Conventional Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 2001, 554, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R. A review of Bondi-Hoyle-Lyttleton accretion. New Astron. Rev. 2004, 48, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mellah, I.; Bolte, J.; Decin, L.; Homan, W.; Keppens, R. Wind morphology around cool evolved stars in binaries. The case of slowly accelerating oxygen-rich outflows. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 637, A91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Podsiadlowski, P. Wind Roche-Lobe Overflow: A New Mass-Transfer Mode for Wide Binaries. In Proceedings of the 15th European Workshop on White Dwarfs, Leicester, UK, 7–11 August 2006; Napiwotzki, R., Burleigh, M.R., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series. Volume 372, p. 397. [Google Scholar]
- Huarte-Espinosa, M.; Carroll-Nellenback, J.; Nordhaus, J.; Frank, A.; Blackman, E.G. The formation and evolution of wind-capture discs in binary systems. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 433, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.I.; Postnov, K.A.; Kochetkova, A.Y.; Hjalmarsdotter, L. Quasispherical subsonic accretion in X-ray pulsars. Phys. Uspekhi 2013, 56, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.I.; Postnov, K.A.; Kochetkova, A.Y.; Hjalmarsdotter, L. Theory of wind accretion. In Proceedings of the European Physical Journal Web of Conferences, Geneva, Switzerland, 25–28 June 2013; Volume 64, p. 02001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, S.B.; Postnov, K.A.; Shakura, N.I. Settling accretion on to isolated neutron stars from interstellar medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 2817–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igoshev, A.P.; Chruslinska, M.; Dorozsmai, A.; Toonen, S. Combined analysis of neutron star natal kicks using proper motions and parallax measurements for radio pulsars and Be X-ray binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 508, 3345–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afonina, M.D.; Popov, S.B. Probing the Propeller Regime with Symbiotic X-ray Binaries. Universe 2024, 10, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050205
Afonina MD, Popov SB. Probing the Propeller Regime with Symbiotic X-ray Binaries. Universe. 2024; 10(5):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050205
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfonina, Marina D., and Sergei B. Popov. 2024. "Probing the Propeller Regime with Symbiotic X-ray Binaries" Universe 10, no. 5: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050205
APA StyleAfonina, M. D., & Popov, S. B. (2024). Probing the Propeller Regime with Symbiotic X-ray Binaries. Universe, 10(5), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe10050205







