A Comprehensive Plasma Metabolomics Dataset for a Cohort of Mouse Knockouts within the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium
Abstract
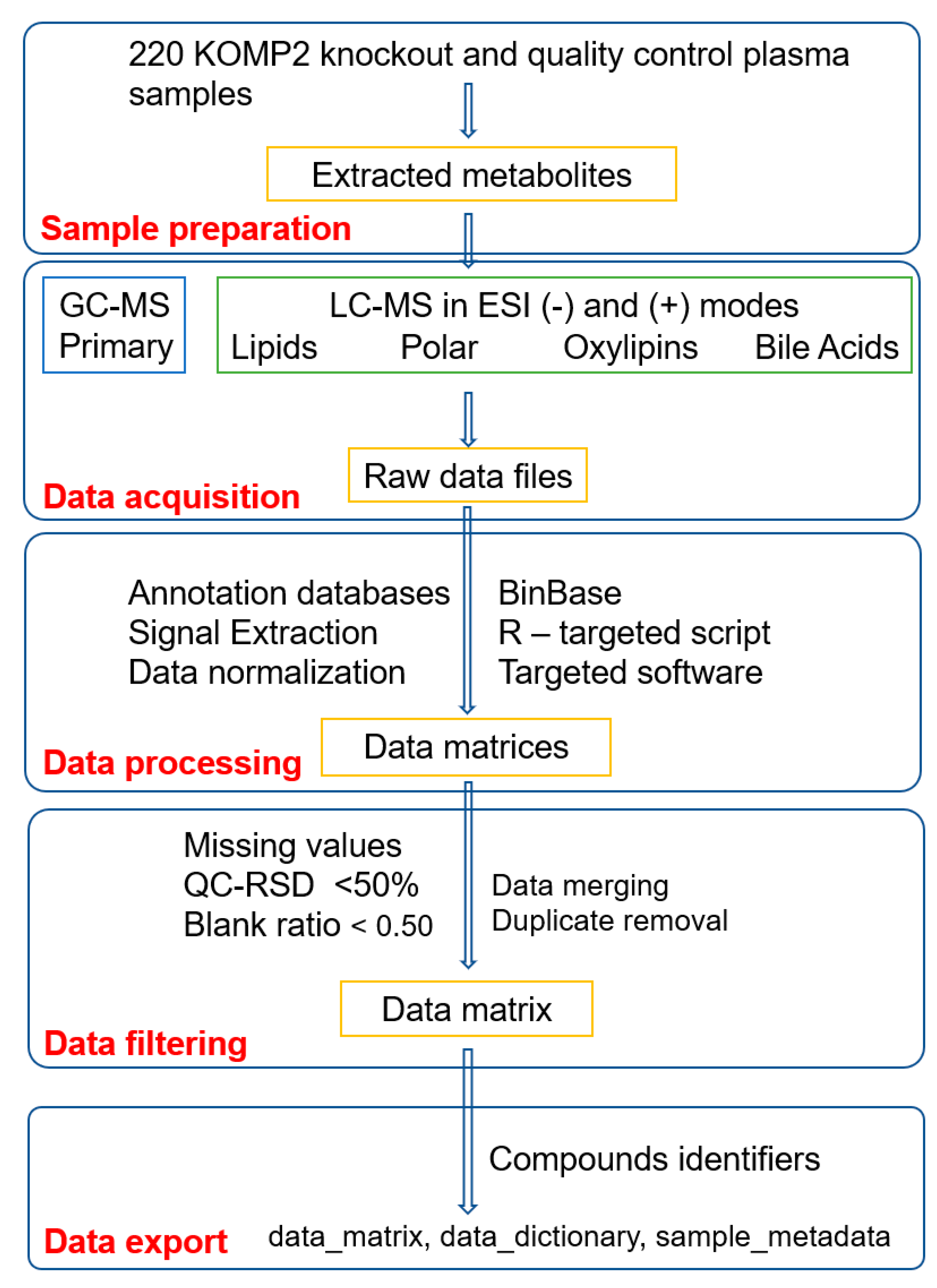
1. Summary
2. Data Description
3. Methods
3.1. IMPC Consortium, Mouse Knockout Selection and Plasma Samples
3.2. Metabolomics Facility
3.3. Annotation Databases for Untargeted Metabolomics
3.3.1. Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
3.3.2. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC) Mass Spectrometry
3.3.3. Charged Surface Hybrid Liquid Chromatography (CSH) and Mass Spectrometry
3.4. Assay 1. Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
3.4.1. Sample Preparation
3.4.2. Data Acquisition
3.4.3. Data Processing
3.5. Assay 2 and 3. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC) Q-Exactive HF Mass Spectrometry for Polar Metabolites
3.5.1. Sample Preparation
3.5.2. Data Acquisition
3.5.3. Data Processing
3.6. Assay 4 and 5. CSH-C18 Q-Exactive HF Mass Spectrometry for Lipidomics
3.6.1. Sample Preparation
3.6.2. Data Acquisition
3.6.3. Data Processing
3.7. Assay 6 and 7. Bile Acids-Steroids, and Oxylipin Targeted Analysis
3.7.1. Sample Preparation
3.7.2. Data Acquisition
3.7.3. Data Processing
3.8. Data Merging and Filtering
3.9. Phenotype Dataset
4. User Notes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Set
Data Set License
References
- Gallagher, M.D.; Chen-Plotkin, A.S. The Post-GWAS Era: From Association to Function. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barupal, D.K.; Lee, S.J.; Karoly, E.D.; Adhya, S. Inactivation of metabolic genes causes short- and long-range dys-regulation in Escherichia coli metabolic network. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Milburn, M.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Lonergan, S.C.; Mitchell, M.W.; Wulff, J.E.; Alexander, D.C.; Evans, A.M.; Bridgewater, B.; Miller, L.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiles enhance precision medicine for volunteers of normal health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4901–E4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Hicks, M.; Yu, H.C.; Biggs, W.H.; Kirkness, E.F.; Menni, C.; Zierer, J.; Small, K.S.; Mangino, M.; Messier, H.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies common-to-rare variants associated with human blood metabolites. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.Y.; Fauman, E.B.; Petersen, A.K.; Krumsiek, J.; Santos, R.; Huang, J.; Arnold, M.; Erte, I.; Forgetta, V.; Yang, T.P.; et al. An atlas of genetic influences on human blood metabolites. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.M.; Hoffman, D.; Junkins, H.A.; Maglott, D.; Phan, L.; Sherry, S.T.; Feolo, M.; Hindorff, L.A. Phenotype-Genotype Integrator (PheGenI): Synthesizing genome-wide association study (GWAS) data with existing genomic resources. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulland, T.K.; Song, W.M.; Huang, S.C.; Ulrich, J.D.; Sergushichev, A.; Beatty, W.L.; Loboda, A.A.; Zhou, Y.; Cairns, N.J.; Kambal, A.; et al. TREM2 Maintains Microglial Metabolic Fitness in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 649–663.e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarnes, W.C.; Rosen, B.; West, A.P.; Koutsourakis, M.; Bushell, W.; Iyer, V.; Mujica, A.O.; Thomas, M.; Harrow, J.; Cox, T.; et al. A conditional knockout resource for the genome-wide study of mouse gene function. Nature 2011, 474, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.D.; Moore, M.W. Towards an encyclopaedia of mammalian gene function: The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, T.F.; Conte, N.; West, D.B.; Jacobsen, J.O.; Mason, J.; Warren, J.; Chen, C.K.; Tudose, I.; Relac, M.; Matthews, P.; et al. Disease model discovery from 3,328 gene knockouts by The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, J.; Rathkolb, B.; Oestereicher, M.A.; Schutt, C.; Ravindranath, A.C.; Leuchtenberger, S.; Sharma, S.; Kistler, M.; Willershauser, M.; Brommage, R.; et al. Identification of genetic elements in metabolism by high-throughput mouse phenotyping. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunk, E.; Sahoo, S.; Zielinski, D.C.; Altunkaya, A.; Drager, A.; Mih, N.; Gatto, F.; Nilsson, A.; Preciat Gonzalez, G.A.; Aurich, M.K.; et al. Recon3D enables a three-dimensional view of gene variation in human metabolism. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showalter, M.R.; Nonnecke, E.B.; Linderholm, A.L.; Cajka, T.; Sa, M.R.; Lonnerdal, B.; Kenyon, N.J.; Fiehn, O. Obesogenic diets alter metabolism in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, A.; Ruppert, D.; Levine, S.M.; Hanson, M.R. Prospective Biomarkers from Plasma Metabolomics of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Implicate Redox Imbalance in Disease Symptomatology. Metabolites 2018, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy-Szakal, D.; Barupal, D.K.; Lee, B.; Che, X.; Williams, B.L.; Kahn, E.J.R.; Ukaigwe, J.E.; Bateman, L.; Klimas, N.G.; Komaroff, A.L.; et al. Insights into myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome phenotypes through comprehensive metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.R.; Grams, M.E.; Coresh, J.; Hwang, S.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Guallar, E.; Rhee, E.P.; Shafi, T. Serum Metabolites and Cardiac Death in Patients on Hemodialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fan, S.; Wancewicz, B.; Cajka, T.; Sa, M.; Showalter, M.R.; Baillie, R.; Tenenbaum, J.D.; Louie, G.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; et al. Generation and quality control of lipidomics data for the alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative cohort. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrmann, J.F.; Grapov, D.D.; Wanichthanarak, K.; DeFelice, B.C.; Salemi, M.R.; Rom, W.N.; Gandara, D.R.; Phinney, B.S.; Fiehn, O.; Pass, H.; et al. Integrated Metabolomics and Proteomics Highlight Altered Nicotinamide- and Polyamine Pathways in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Kind, T.; Cajka, T.; Hazen, S.L.; Tang, W.H.W.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Irvin, M.R.; Arnett, D.K.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Systematic Error Removal Using Random Forest for Normalizing Large-Scale Untargeted Lipidomics Data. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3590–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Tsugawa, H.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Mehta, S.; Mueller, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ogiwara, A.; Meissen, J.; Showalter, M.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Identifying metabolites by integrating metabolome databases with mass spectrometry cheminformatics. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanichthanarak, K.; Fan, S.; Grapov, D.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Metabox: A Toolbox for Metabolomic Data Analysis, Interpretation and Integrative Exploration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barupal, D.K.; Haldiya, P.K.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Kind, T.; Kothari, S.L.; Pinkerton, K.E.; Fiehn, O. MetaMapp: Mapping and visualizing metabolomic data by integrating information from biochemical pathways and chemical and mass spectral similarity. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Chemical Similarity Enrichment Analysis (ChemRICH) as alternative to biochemical pathway mapping for metabolomic datasets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skogerson, K.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. The volatile compound BinBase mass spectral database. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kind, T.; Liu, K.H.; Lee, D.Y.; DeFelice, B.; Meissen, J.K.; Fiehn, O. LipidBlast in silico tandem mass spectrometry database for lipid identification. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazenovic, I.; Kind, T.; Sa, M.R.; Ji, J.; Vaniya, A.; Wancewicz, B.; Roberts, B.S.; Torbasinovic, H.; Lee, T.; Mehta, S.S.; et al. Structure Annotation of All Mass Spectra in Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Combined Targeted and Untargeted Profiling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 114, 30.4.1–30.4.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Assays | Chromatography | Mass Spectrometer | Data Processing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column | Instrument | |||
| Assay 1: - Primary | Rtx-5Sil MS column (30 m length, 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 microM 95% dimethyl 5% diphenyl polysiloxane film) | Agilent 6890 GC | Leco GCTOF Pegasus IV | ChromaTOF 4/BinBase |
| Assay 2 and 3: - Polar (ESI + and ESI − ) | Waters Acquity UPLC BEH Amide column (150 mm length × 2.1 mm i.d.; 1.7 μm particle size) | Thermo Vanquish UHPLC | Thermo Q-Exactive HF Orbitrap | NIST MS Search and R-target search |
| Assay 4 and 5: - Lipids (ESI − and ESI +) | Waters Acquity UPLC CSH C18 column (100 × 2.1 mm; 1.7 µm) | Thermo Vanquish UHPLC | Thermo Q-Exactive HF Orbitrap | NIST MS Search and R-target search |
| Assay 6 and 7: - Bile acids/steroids and Oxylipins | Waters Acquity BEH C18 column (1.7 µm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm) | Waters ACQUITY UPLC I-Class system | Sciex 6500+ QTRAP hybrid | MultiQuant 3.0.2 (AB Sciex) |
| NCBI Gene ID | Gene Symbol | IMPC Line | Gene Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 235661 | Dync1li1 | K2P2 | Dynein Cytoplasmic 1 Light Intermediate Chain 1 |
| 71742 | Ulk3 | K2P2 | unc-51-like kinase 3 |
| 14380 | G6pd2 | KOMP2 | Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 |
| 29875 | Iqgap1 | KOMP2 | IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1 |
| 23980 | Pebp1 | KOMP2 | phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein 1 |
| 30939 | Pttg1 | KOMP2 | pituitary tumor-transforming gene 1 |
| 11947 | Atp5b | NorCOMM2 | ATP synthase, H+ transporting mitochondrial F1 complex, beta subunit |
| 11972 | Atp6v0d1 | NorCOMM2 | ATPase H+ Transporting lysosomal V0 Subunit D1 |
| 12567 | Cdk4 | NorCOMM2 | Cyclin Dependent Kinase 4 |
| 13361 | Dhfr | NorCOMM2 | Dihydrofolate reductase |
| 68421 | Lmbrd1 | NorCOMM2 | LMBR1 domain containing 1 |
| 18005 | Nek2 | NorCOMM2 | NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related expressed kinase 2 |
| 67963 | Npc2 | NorCOMM2 | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2 |
| 19193 | Pipox | NorCOMM2 | Pipecolic acid oxidase |
| 19877 | Rock1 | NorCOMM2 | Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 |
| 269378 | Ahcy | NorCOMM2 | S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase |
| 232345 | A2m | NorCOMM2 | alpha-2-macroglobulin |
| 230558 | C8a | NorCOMM2 | complement component 8, alpha polypeptide |
| 14420 | Galc | NorCOMM2 | galactosylceramidase |
| 26384 | Gnpda1 | NorCOMM2 | glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 |
| 15926 | Idh1 | NorCOMM2 | isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| 67096 | Mmachc | NorCOMM2 | methylmalonic aciduria cblC type, with homocystinuria |
| 17855 | Mvk | NorCOMM2 | mevalonate kinase |
| 76293 | Mfap4 | NorCOMM2 | microfibrillar-associated protein 4 |
| 54128 | Pmm2 | NorCOMM2 | phosphomannomutase 2 |
| 16922 | Phyh | NorCOMM2 | phytanoyl- CoA hydroxylase |
| 18817 | Plk1 | NorCOMM2 | polo-like kinase 1, serine/threonine protein kinase |
| 19248 | Ptpn12 | NorCOMM2 | protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 12 |
| 24068 | Sra1 | NorCOMM2 | steroid receptor RNA activator 1 |
| 22631 | Ywhaz | NorCOMM2 | tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein |
| Assay | Internal Standard Name | m/z Value | Retention Time (min) | Relative Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSHNEG | FA (16:0)-d3 | 258.2515 | 2.3 | 8% |
| CSHNEG | CUDA iSTD | 339.2653 | 0.5 | 10% |
| CSHNEG | MAG (17:0/0:0/0:0) | 403.3066 | 3.0 | 9% |
| CSHNEG | LPE (17:1) | 464.2782 | 1.2 | 17% |
| CSHNEG | LPC (17:0) | 568.362 | 1.7 | 8% |
| CSHNEG | Ceramide (d18:1/17:0) | 610.5416 | 5.9 | 14% |
| CSHNEG | PC (12:0/13:0) | 694.4665 | 3.5 | 8% |
| CSHNEG | PE (17:0/17:0) | 718.5392 | 6.2 | 11% |
| CSHNEG | PG (17:0/17:0) | 749.5338 | 4.9 | 14% |
| CSHNEG | SM (d18:1/17:0) | 775.5971 | 5.3 | 52% |
| CSHPOS | LPC(17:0) | 510.3554 | 1.7 | 5% |
| CSHPOS | PC(12:0/13:0) | 636.4599 | 3.5 | 6% |
| CSHPOS | Cer(d18:1/17:0) | 552.535 | 5.8 | 7% |
| CSHPOS | SM(d18:1/17:0) | 717.5905 | 5.0 | 7% |
| CSHPOS | PE(17:0/17:0) | 720.5538 | 6.2 | 7% |
| CSHPOS | CUDA | 341.2799 | 0.7 | 8% |
| CSHPOS | LPE(17:1) | 466.2928 | 1.2 | 8% |
| CSHPOS | MG(17:0/0:0/0:0) | 367.2819 | 3.0 | 9% |
| CSHPOS | CE(22:1) | 729.652 | 11.5 | 10% |
| CSHPOS | DG(12:0/12:0/0:0) | 474.4153 | 4.2 | 12% |
| CSHPOS | Cholesterol d7 | 376.3955 | 4.7 | 12% |
| CSHPOS | DG(18:1/2:0/0:0) | 416.3371 | 3.2 | 17% |
| CSHPOS | TAG d5(17:0/17:1/17:0) | 874.7882 | 10.9 | 20% |
| CSHPOS | Sphingosine(d17:1) | 286.2741 | 1.1 | 21% |
| HILICNEG | 15N2-l-Arginine | 175.0974 | 9.41 | 22% |
| HILICNEG | CUDA | 339.2642 | 1.1 | 11% |
| HILICNEG | D3-Creatinine | 115.0694 | 4.71 | 12% |
| HILICNEG | D3-dl-Alanine | 91.0581 | 7.97 | 19% |
| HILICNEG | D3-dl-Aspartic acid | 135.048 | 9.09 | 27% |
| HILICNEG | D3-dl-Glutamic acid | 149.0636 | 8.65 | 27% |
| HILICNEG | D5-l-Glutamine | 150.0922 | 8.46 | 20% |
| HILICNEG | Val-Tyr-Val | 378.2023 | 6.79 | 9% |
| HILICPOS | 15N2-l-Arginine | 177.113 | 9.53 | 9% |
| HILICPOS | CUDA | 341.2799 | 1.16 | 11% |
| HILICPOS | D3-1-Methylnicotinamide | 140.0898 | 6.25 | 5% |
| HILICPOS | D3-AC(2:0) | 207.1419 | 7.21 | 7% |
| HILICPOS | D3-Creatine | 135.0956 | 8.15 | 9% |
| HILICPOS | D3-Creatinine | 117.085 | 4.95 | 4% |
| HILICPOS | D3-dl-Alanine | 93.0738 | 8.17 | 8% |
| HILICPOS | D3-dl-Aspartic acid | 137.0636 | 9.34 | 9% |
| HILICPOS | D3-dl-Glutamic acid | 151.0793 | 8.85 | 7% |
| HILICPOS | D3-Histamine, N-methyl- | 129.1214 | 7.35 | 20% |
| HILICPOS | D3-l-Carnitine | 165.1313 | 7.83 | 6% |
| HILICPOS | D5-l-Glutamine | 152.1078 | 8.67 | 11% |
| HILICPOS | D9-Betaine | 127.1427 | 7.25 | 13% |
| HILICPOS | D9-Butyrobetaine | 155.174 | 7.83 | 6% |
| HILICPOS | D9-Choline | 113.1635 | 5.18 | 6% |
| HILICPOS | D9-Crotonobetaine | 153.1584 | 7.86 | 9% |
| HILICPOS | D9-TMAO | 85.1322 | 5.57 | 8% |
| HILICPOS | Val-Tyr-Val | 380.218 | 6.95 | 24% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barupal, D.K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, T.; Fan, S.; Roberts, B.S.; Fitzgerald, P.; Wancewicz, B.; Valdiviez, L.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Byram, G.; et al. A Comprehensive Plasma Metabolomics Dataset for a Cohort of Mouse Knockouts within the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium. Metabolites 2019, 9, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050101
Barupal DK, Zhang Y, Shen T, Fan S, Roberts BS, Fitzgerald P, Wancewicz B, Valdiviez L, Wohlgemuth G, Byram G, et al. A Comprehensive Plasma Metabolomics Dataset for a Cohort of Mouse Knockouts within the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium. Metabolites. 2019; 9(5):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050101
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarupal, Dinesh K., Ying Zhang, Tong Shen, Sili Fan, Bryan S. Roberts, Patrick Fitzgerald, Benjamin Wancewicz, Luis Valdiviez, Gert Wohlgemuth, Gregory Byram, and et al. 2019. "A Comprehensive Plasma Metabolomics Dataset for a Cohort of Mouse Knockouts within the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium" Metabolites 9, no. 5: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050101
APA StyleBarupal, D. K., Zhang, Y., Shen, T., Fan, S., Roberts, B. S., Fitzgerald, P., Wancewicz, B., Valdiviez, L., Wohlgemuth, G., Byram, G., Choy, Y. Y., Haffner, B., Showalter, M. R., Vaniya, A., Bloszies, C. S., Folz, J. S., Kind, T., Flenniken, A. M., McKerlie, C., ... Fiehn, O. (2019). A Comprehensive Plasma Metabolomics Dataset for a Cohort of Mouse Knockouts within the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium. Metabolites, 9(5), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050101








