Sphingolipid Metabolism Perturbations in Rett Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Participants and Clinical Data
2.2. Metabolic Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analyses
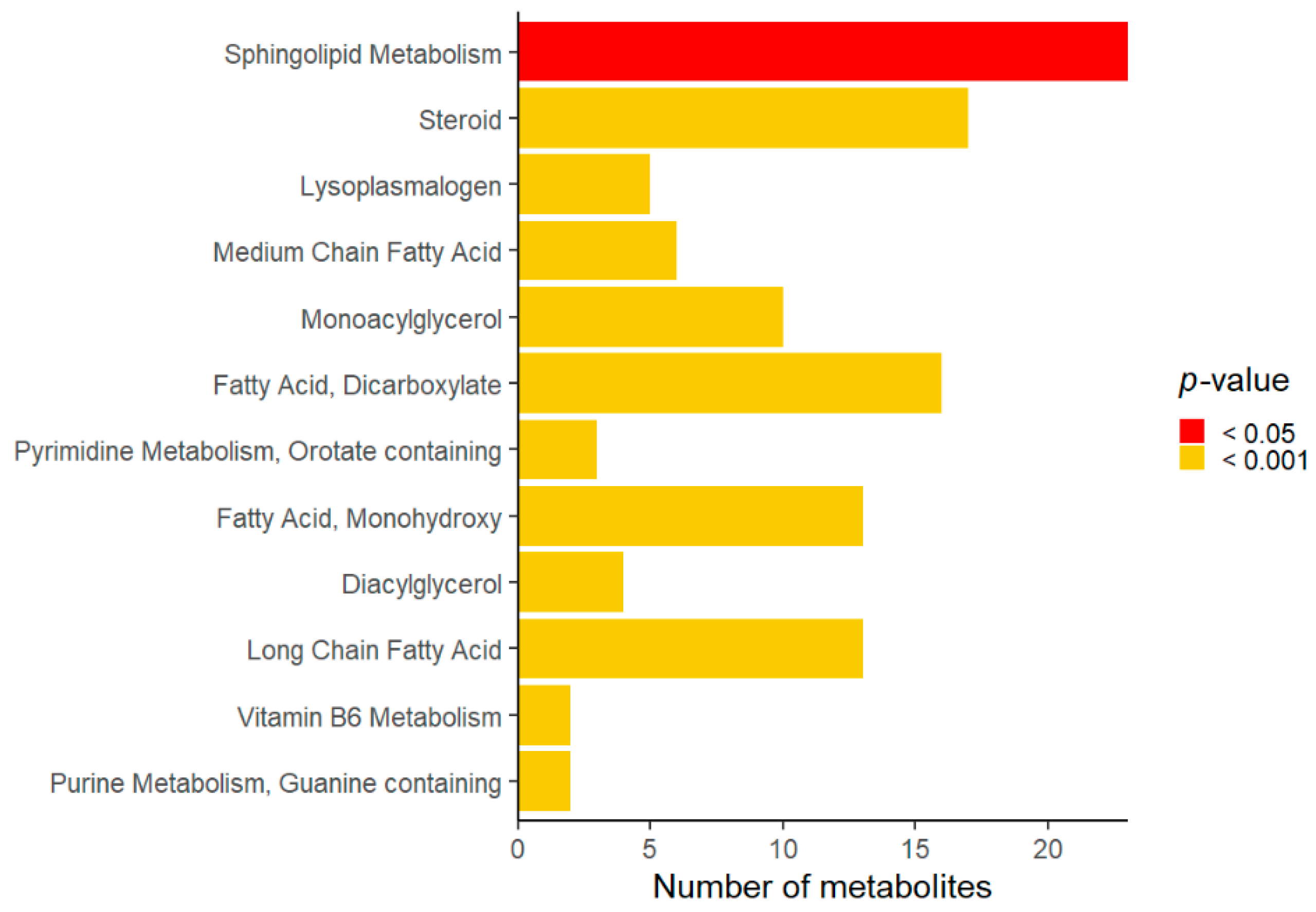
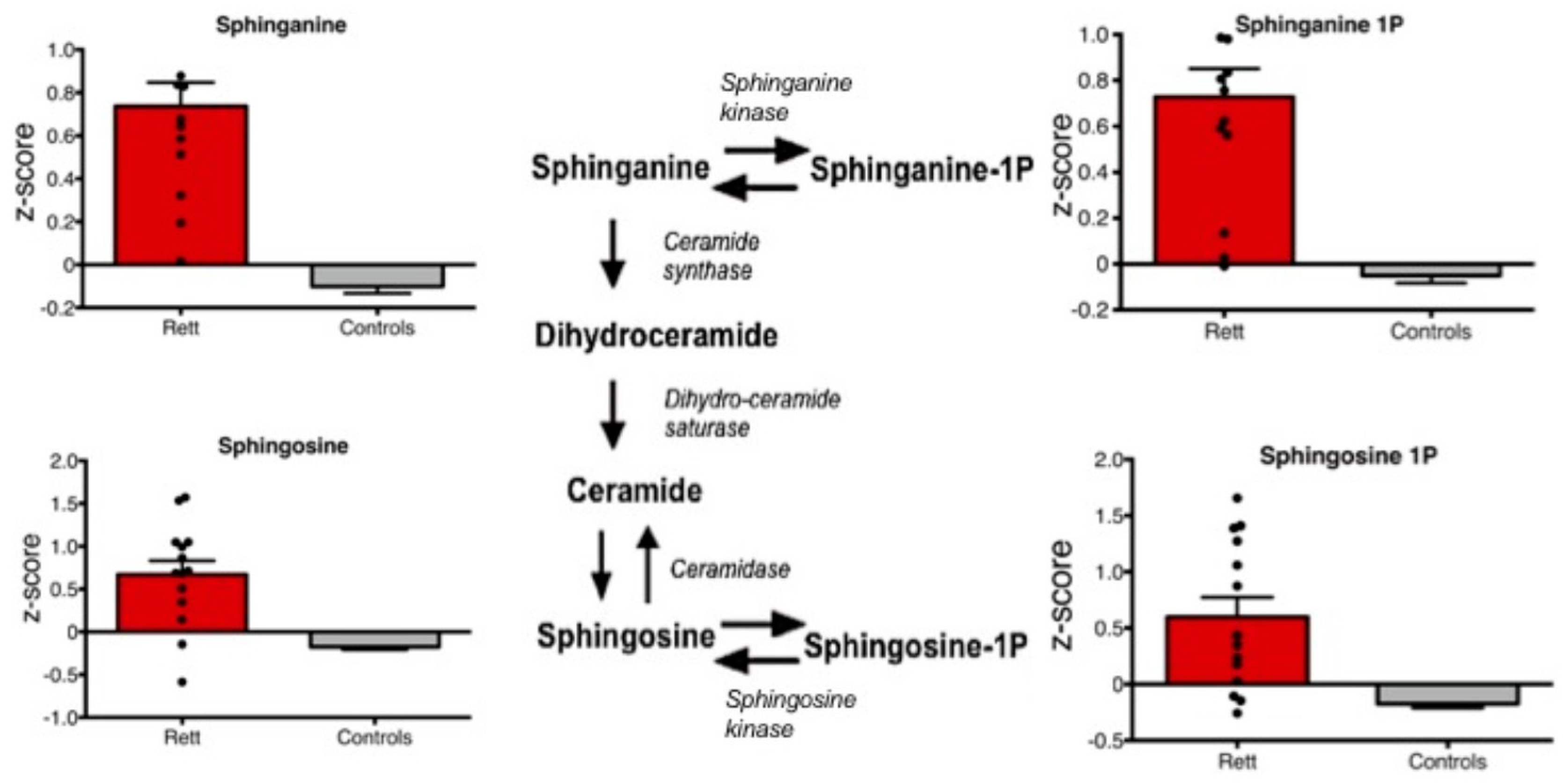
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, M.J.; Kennedy, A.D.; Eckhart, A.D.; Burrage, L.C.; Wulff, J.E.; Miller, L.A.D.; Milburn, M.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Beaudet, A.L.; Sun, Q.; et al. Untargeted metabolomic analysis for the clinical screening of inborn errors of metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donti, T.R.; Cappuccio, G.; Hubert, L.; Neira, J.; Atwal, P.S.; Miller, M.J.; Cardon, A.L.; Sutton, V.R.; Porter, B.E.; Baumer, F.M.; et al. Diagnosis of adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency by metabolomic profiling in plasma reveals a phenotypic spectrum. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2016, 8, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, G.; Pinelli, M.; Alagia, M.; Donti, T.; Day-Salvatore, D.-L.; Veggiotti, P.; De Giorgis, V.; Lunghi, S.; Vari, M.S.; Striano, P.; et al. Biochemical phenotyping unravels novel metabolic abnormalities and potential biomarkers associated with treatment of GLUT1 deficiency with ketogenic diet. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaving, L.S.; Ellaway, C.J.; Gécz, J.; Christodoulou, J. Rett syndrome: Clinical review and genetic update. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Castro, J.; Sur, M. Rett syndrome: Genes, synapses, circuits, and therapeutics. Front. Psychiatry 2012, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, R.E.; Van den Veyver, I.B.; Wan, M.; Tran, C.Q.; Francke, U.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, S.L.; Christodoulou, J. Rett syndrome: New clinical and molecular insights. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 14, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J.; Abdala Sheikh, A.P. A perspective on ‘cure’ for Rett syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchovecky, C.M.; Turley, S.D.; Brown, H.M.; Kyle, S.M.; McDonald, J.G.; Liu, B.; Pieper, A.A.; Huang, W.; Katz, D.M.; Russell, D.W.; et al. A suppressor screen in Mecp2 mutant mice implicates cholesterol metabolism in Rett syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.B.; Lee, H.-S.; Smith, L.W.; Cheng, P.; Percy, A.K.; Glaze, D.G.; Neul, J.L.; Motil, K.J.; Barrish, J.O.; Skinner, S.A.; et al. Clinical severity and quality of life in children and adolescents with Rett syndrome. Neurology 2011, 77, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.M.; DeHaven, C.D.; Barrett, T.; Mitchell, M.; Milgram, E. Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6656–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashi, N.; Justice, M.J. Treating Rett syndrome: From mouse models to human therapies. Mamm Genome 2019, 30, 90–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel Ciernia, A.; Yasui, D.H.; Pride, M.C.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Noronha, A.B.; Chang, A.; Knotts, T.A.; Rutkowsky, J.R.; Ramsey, J.J.; Crawley, J.N.; et al. MeCP2 isoform e1 mutant mice recapitulate motor and metabolic phenotypes of Rett syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 4077–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squillaro, T.; Alessio, N.; Capasso, S.; Di Bernardo, G.; Melone, M.A.B.; Peluso, G.; Galderisi, U. Senescence Phenomena and Metabolic Alteration in Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segatto, M.; Trapani, L.; Di Tunno, I.; Sticozzi, C.; Valacchi, G.; Hayek, J.; Pallottini, V. Cholesterol metabolism is altered in Rett syndrome: A study on plasma and primary cultured fibroblasts derived from patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouro, F.M.; Miranda-Lourenço, C.; Sebastião, A.M.; Diógenes, M.J. From Cannabinoids and Neurosteroids to Statins and the Ketogenic Diet: New Therapeutic Avenues in Rett Syndrome? Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhaber, G.M.; Riemann, E.; Baumeister, F.A.M. Ketogenic diet in Rett syndrome. J. Child. Neurol. 2003, 18, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, E.W.M.; Marcy, G.; Yoon, S.-I.; Ma, D.; Rosales, F.J.; Augustine, G.J.; Goh, E.L.K. Choline Ameliorates Disease Phenotypes in Human iPSC Models of Rett Syndrome. NeuroMolecular Med. 2016, 18, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, M.; Gao, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Xia, W.; Wu, S.; Sumner, S.J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Potential serum biomarkers from a metabolomics study of autism. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2016, 41, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pardo, A.; Maglione, V. Sphingolipid Metabolism: A New Therapeutic Opportunity for Brain Degenerative Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deogracias, R.; Yazdani, M.; Dekkers, M.P.J.; Guy, J.; Ionescu, M.C.S.; Vogt, K.E.; Barde, Y.-A. Fingolimod, a sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor modulator, increases BDNF levels and improves symptoms of a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14230–14235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Subject | Age (years) | MECP2 Variant a | Seizures | Drugs | Clinical Severity Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | c.1116_1201del86 | - | Vitamin D | 6 |
| 2 | 13 | c.455C>G (p.Pro152Arg) | + | Clonazepam, Carbamazepine, Acetazolamide, Lansoprazole, Vitamin D | 58 |
| 3 | 12 | c.455C>G (p.Pro152Arg) | + | Carbamazepine, Lansoprazole | 57 |
| 4 | 10 | c.1164_1189del26 | - | N-acetyl-cysteine | 6 |
| 5 | 16 | c.908_1143del236+1159-1170del12 | - | Carbamazepine, Insulin | 48 |
| 6 | 15 | c.763C>T (p.Arg255Ter) | + | Valproate, Lamotrigine, Melatonin | 47 |
| 7 | 7 | c.1151_1352del202 | + | Vitamin D | 28 |
| 8 | 11 | c.397C>T (p.Arg133Cys) | + | Valproate | 36 |
| 9 | 3 | c.502C>T (p.Arg168Ter) | - | Carnitine | 48 |
| 10 | 17 | c.763C>T (p.Arg255Ter) | - | Carbamazepine | 43 |
| 11 | 29 | c.808C>T (p.Arg270Ter) | - | Carnitine, Carbamazepine, Pentoxifylline, Chlorpromazine | 37 |
| 12 | 13 | c.502C>T (p.Arg168Ter) | - | Valproate | 12 |
| 13 | 21 | c.397C>T (p.Arg133Cys) | - | Valproate, Topiramate, Prazosin | 12 |
| 14 | 29 | c.473C>T (p.Thr158Met) | - | Phenobarbital | 16 |
| Super-Pathway | Compounds in Super-Pathway |
|---|---|
| Lipid | 305 *** |
| Amino Acid | 147 ** |
| Cofactor and Vitamin | 17 * |
| Xenobiotics | 71 |
| Energy | 8 |
| Peptide | 34 |
| Carbohydrate | 22 |
| Nucleotide | 28 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cappuccio, G.; Donti, T.; Pinelli, M.; Bernardo, P.; Bravaccio, C.; Elsea, S.H.; Brunetti-Pierri, N. Sphingolipid Metabolism Perturbations in Rett Syndrome. Metabolites 2019, 9, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100221
Cappuccio G, Donti T, Pinelli M, Bernardo P, Bravaccio C, Elsea SH, Brunetti-Pierri N. Sphingolipid Metabolism Perturbations in Rett Syndrome. Metabolites. 2019; 9(10):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100221
Chicago/Turabian StyleCappuccio, Gerarda, Taraka Donti, Michele Pinelli, Pia Bernardo, Carmela Bravaccio, Sarah H. Elsea, and Nicola Brunetti-Pierri. 2019. "Sphingolipid Metabolism Perturbations in Rett Syndrome" Metabolites 9, no. 10: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100221
APA StyleCappuccio, G., Donti, T., Pinelli, M., Bernardo, P., Bravaccio, C., Elsea, S. H., & Brunetti-Pierri, N. (2019). Sphingolipid Metabolism Perturbations in Rett Syndrome. Metabolites, 9(10), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100221







