Rapid, Reproducible, Quantifiable NMR Metabolomics: Methanol and Methanol: Chloroform Precipitation for Removal of Macromolecules in Serum and Whole Blood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
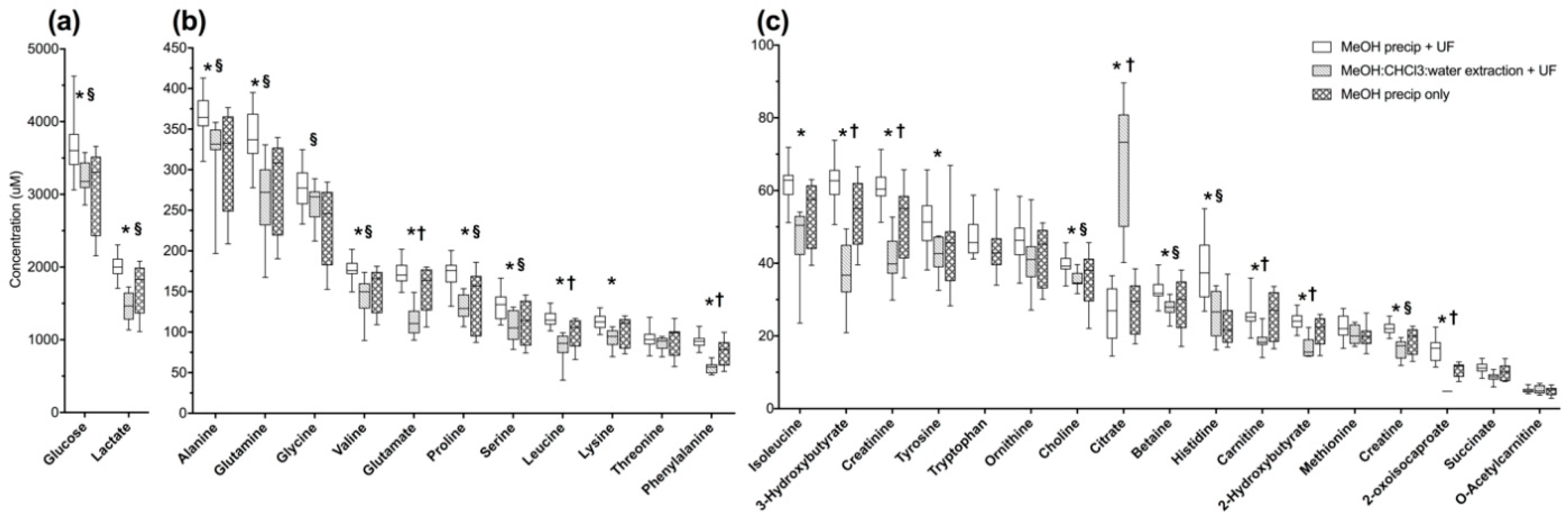
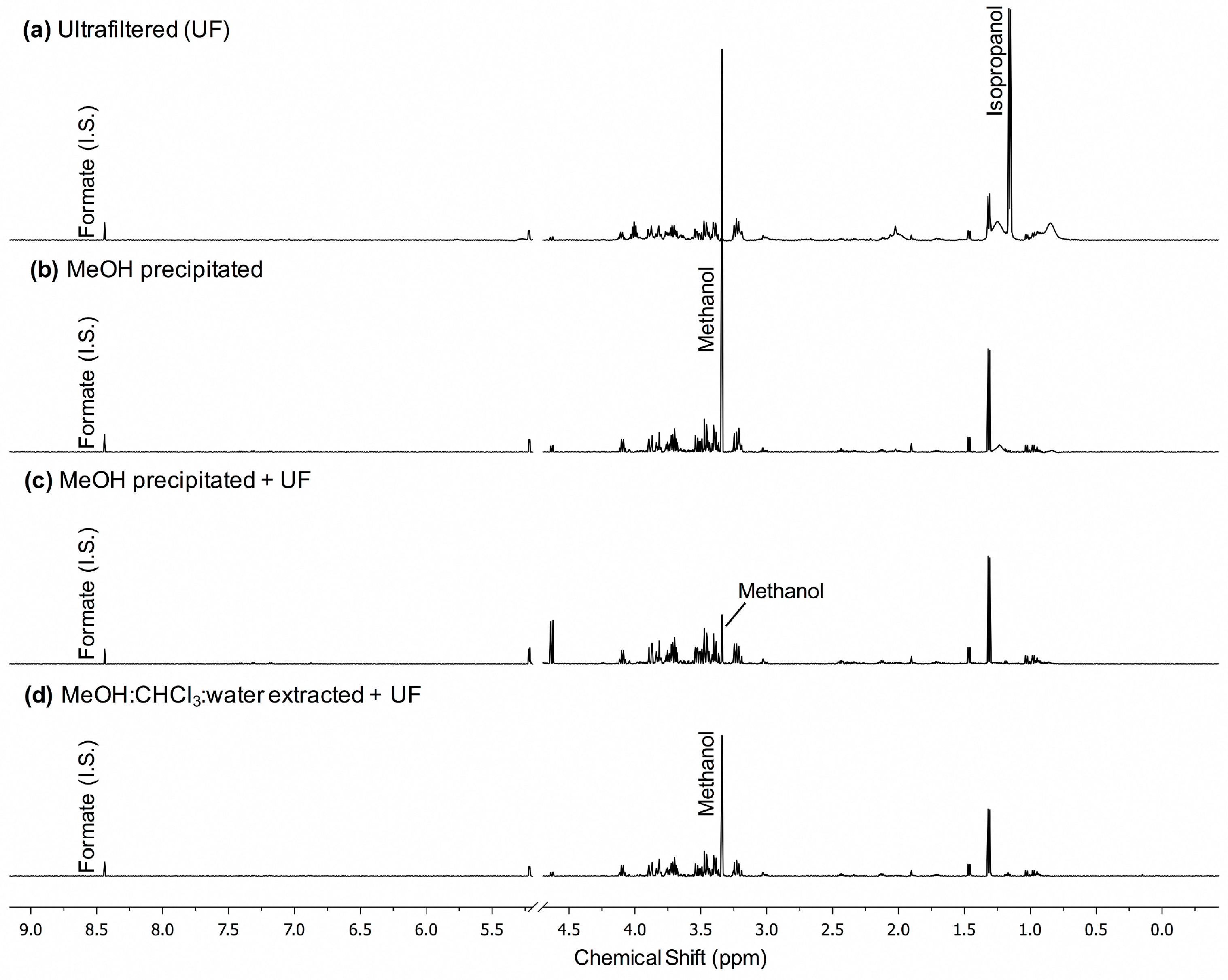
2.1. MeOH Pecipitation with Ultrafiltration Has Better Metabolite Recovery and Lower Variance than Other Methods of Macromolecule Removal in Normal Pooled Human Serum
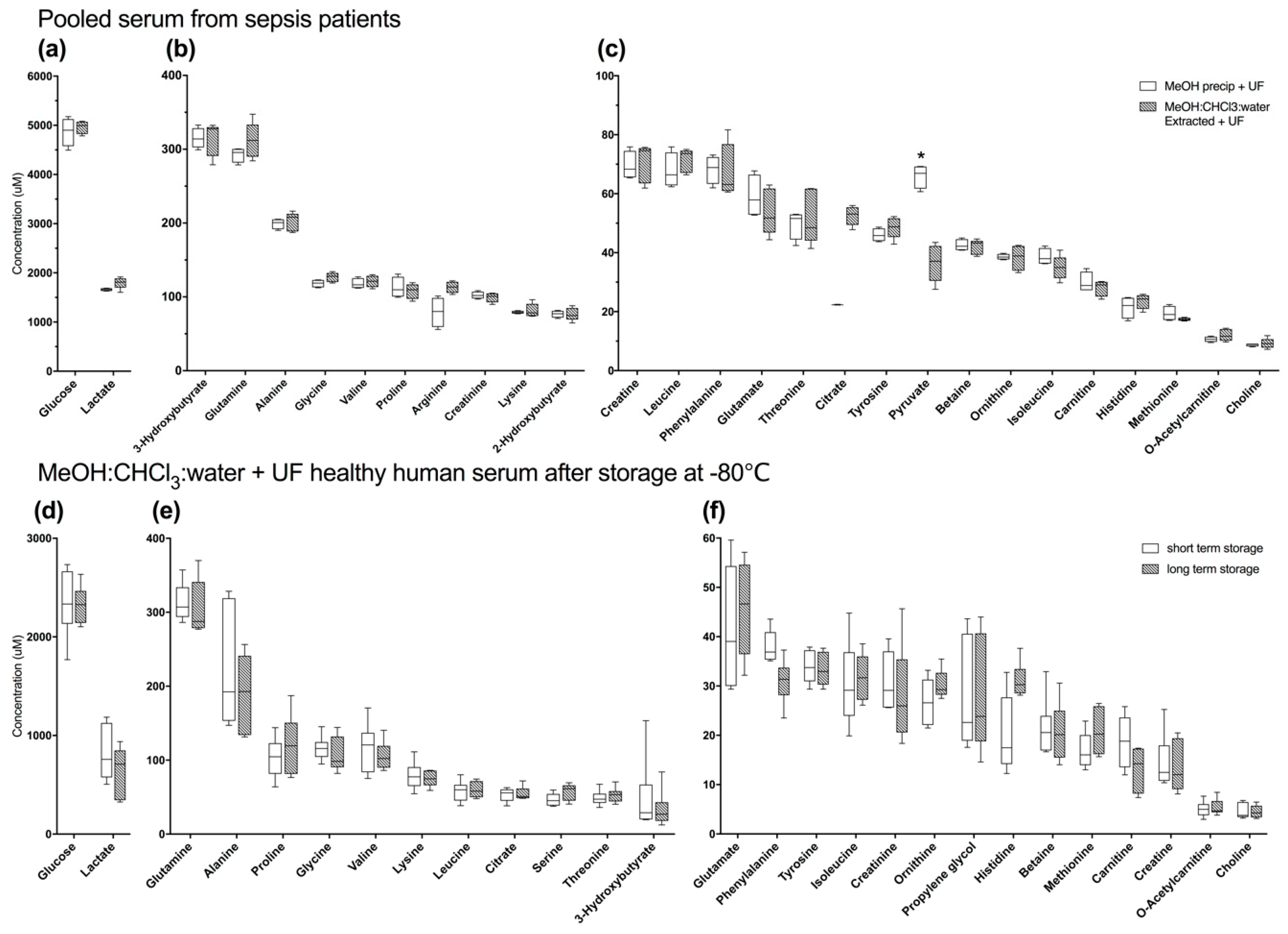
2.2. Differences in Efficacy of MeOH Precipitation with Ultrafiltration in Healthy Pooled Serum and Pooled Serum from Patients with Sepsis are not Due to Effects of Long-Term Storage (−80 °C)
2.2.1. Methanol Precipitation with Ultrafiltration is Not Clearly Superior to Alternate Methods in Pooled Human Serum from Sepsis Patients
2.2.2. Long-Term Storage at −80 °C does Not Alter the Serum Metabolome
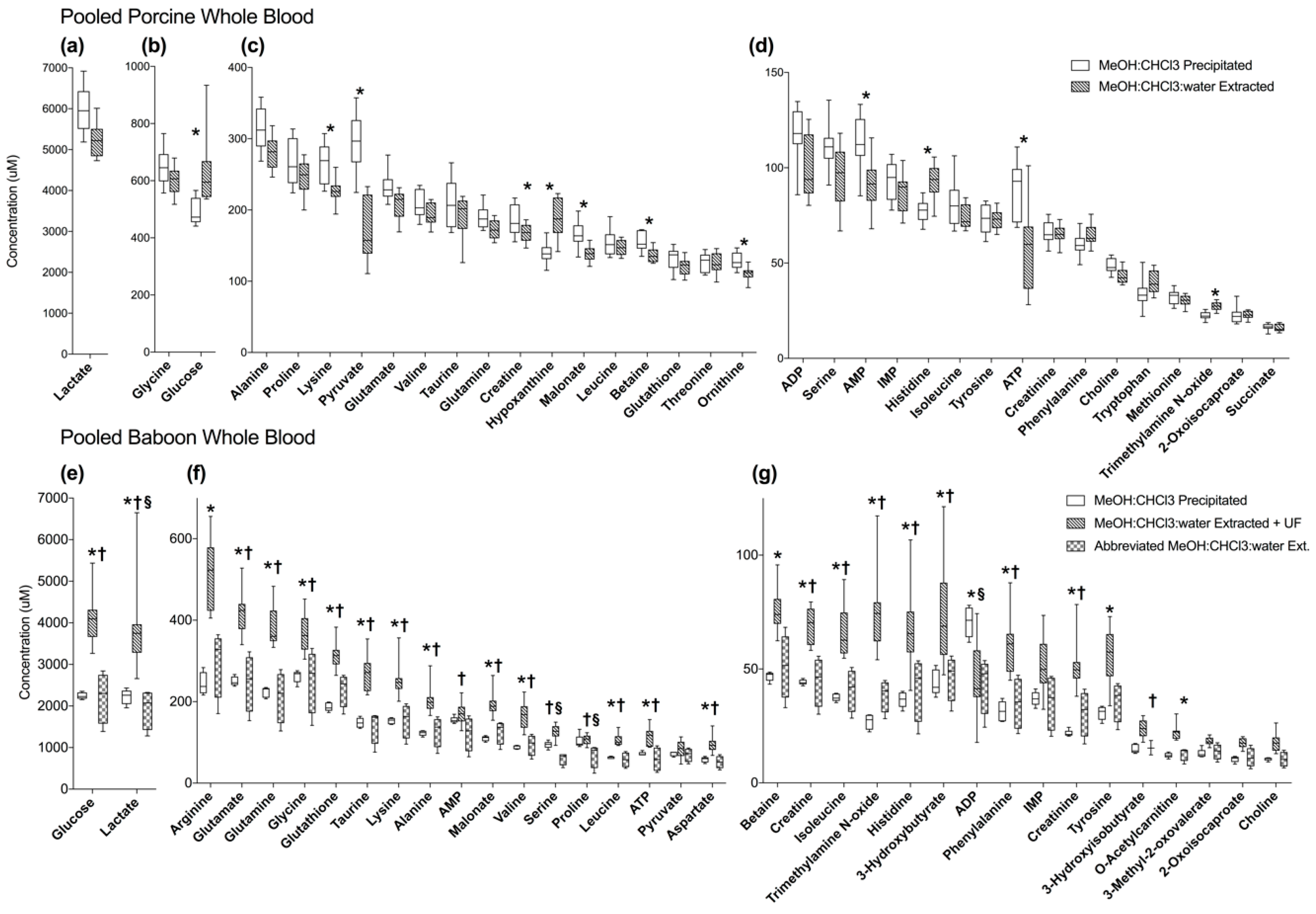
2.3. MeOH:CHCl3:Water Extraction and MeOH:CHCl3 Precipitation of Pooled Porcine Whole Blood Yield Similar Metabolite Recovery and Variance
2.4. MeOH:CHCl3 Precipitation Reduces Variance in Baboon Whole Blood Compared to MeOH:CHcl3:Water Extractions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Ultrafiltration
4.3. Methanol Precipitations (MeOH ppt)
4.4. Methanol:Chloroform:Water Extractions (MeOH:CHCl3:Water Ext)
4.5. Abbreviated Methanol:Chloroform:Water Extractions (MeOH:CHCl3:Water Ext) of WB
4.6. Methanol Chloroform Precipitation (MeOH:CHCl3ppt)
4.7. 1d-1H NMR
4.8. Test of Long-Term Storage on Human Serum
4.9. Data/Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.C.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; et al. The Human Serum Metabolome. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.W.M.; Lane, A.N. Applications of NMR spectroscopy to systems biochemistry. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2016, 92–93, 18–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barding, G.A.; Salditos, R.; Larive, C.K. Quantitative NMR for bioanalysis and metabolomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, K.A.; Younger, J.G.; McHugh, C.; Yeomans, L.; Finkel, M.A.; Puskarich, M.A.; Jones, A.E.; Trexel, J.; Karnovsky, A. Whole Blood Reveals More Metabolic Detail of the Human Metabolome than Serum as Measured by (1)H-NMR Spectroscopy: Implications for Sepsis Metabolomics. Shock (Augusta Ga.) 2015, 44, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheedy, J.R.; Ebeling, P.R.; Cooley, P.R.; McConville, M.J. A sample preparation protocol for 1H nuclear magnetic resonance studies of water-soluble metabolites in blood and urine. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 398, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daykin, C.A.; Foxall, P.J.D.; Connor, S.C.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. The Comparison of Plasma Deproteinization Methods for the Detection of Low-Molecular-Weight Metabolites by 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 304, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, N.G.A.; Raftery, D. Recent Advances in NMR-Based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 490–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serkova, N.; Klawitter, J.; Niemann, C.U. Organ-specific response to inhibition of mitochondrial metabolism by cyclosporine in the rat. Transpl. Int. 2003, 16, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trexel, J.; Yoon, G.S.; Keswani, R.K.; McHugh, C.; Yeomans, L.; Vitvitsky, V.; Banerjee, R.; Sud, S.; Sun, Y.; Rosania, G.R.; et al. Macrophage-Mediated Clofazimine Sequestration Is Accompanied by a Shift in Host Energy Metabolism. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 106, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Vosegaard, T.; Guo, Z. Applications of nuclear magnetic resonance in lipid analyses: An emerging powerful tool for lipidomics studies. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 68, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanbakhsh, S.; Liu, P.; Bjorndahl, T.C.; Mandal, R.; Grant, J.R.; Wilson, M.; Eisner, R.; Sinelnikov, I.; Hu, X.; Luchinat, C.; et al. Accurate, fully-automated NMR spectral profiling for metabolomics. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, N.G.A.; Raftery, D. Quantitating Metabolites in Protein Precipitated Serum Using NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5433–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, P.; Lewis, M.J.; Chang, D.; Baker, D.; Wishart, D.S. Towards automatic metabolomic profiling of high-resolution one-dimensional proton NMR spectra. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 49, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, N.G.A.; Gowda, Y.Y.N.; Raftery, D. Expanding the Limits of Human Blood Metabolite Quantitation Using NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2014, 87, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emwas, A.-H.; Luchinat, C.; Turano, P.; Tenori, L.; Roy, R.; Salek, R.M.; Ryan, D.; Merzaban, J.S.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Zeri, A.C.; et al. Standardizing the experimental conditions for using urine in NMR-based metabolomic studies with a particular focus on diagnostic studies: A review. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 872–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandes, V.V.; Barbas, C.; Dudzik, D. A review of blood sample handling and pre-processing for metabolomics studies. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Xi, C.; Zhang, R.; Song, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Bi, X.; Abliz, Z. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry-Based Plasma Metabonomics Delineate the Effect of Metabolites’ Stability on Reliability of Potential Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2606–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Peter, A.; Franken, H.; Zhao, X.; Neukamm, S.S.; Rosenbaum, L.; Lucio, M.; Zell, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Xu, G.; et al. Preanalytical aspects and sample quality assessment in metabolomics studies of human blood. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuckovic, D. Current trends and challenges in sample preparation for global metabolomics using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1523–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, N.G.A.; Raftery, D. Whole Blood Metabolomics by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Provides a New Opportunity to Evaluate Coenzymes and Antioxidants. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4620–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymani, J.; Jouyban-Gharamaleki, V.; Jouyban-Gharamaleki, K.; Acree, W.E., Jr.; Kenndler, E.; Jouyban, A. Solubility of trisodium citrate in water + methanol mixtures at various temperatures. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabi, M.; Keller, M.D.; Jonsson, N.N. NMR-based metabonomics of bovine blood: An investigation into the effects of long term storage on plasma samples. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Galhano, E.; Pita, C.; Almeida, M.d.C.; Carreira, I.M.; Gil, A.M.Y. Human plasma stability during handling and storage: Impact on NMR metabolomics. Analyst 2014, 139, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roessl, U.; Leitgeb, S.; Nidetzky, B. Protein freeze concentration and micro-segregation analysed in a temperature-controlled freeze container. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 6, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebels, D.G.A.J.; Georgiadis, P.; Keun, H.C.; Athersuch, T.J.; Vineis, P.; Vermeulen, R.; Portengen, L.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Hallmans, G.; Palli, D.; et al. Performance in Omics Analyses of Blood Samples in Long-Term Storage: Opportunities for the Exploitation of Existing Biobanks in Environmental Health Research. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weljie, A.M.; Bondareva, A.; Zang, P.; Jirik, F.R. 1H NMR metabolomics identification of markers of hypoxia-induced metabolic shifts in a breast cancer model system. J. Biomol. NMR 2011, 49, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiziani, S.; Emwas, A.-H.; Lodi, A.; Ludwig, C.; Bunce, C.M.; Viant, M.R.; Gunther, U.L. Optimized metabolite extraction from blood serum for 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 377, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuhadar, S.; Koseoglu, M.; Atay, A.; Dirican, A. The effect of storage time and freeze-thaw cycles on the stability of serum samples. Biochem. Med. 2013, 23, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.L.; Yasui, Y.; Li, C.I.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Lampe, P.D. Impact of freeze-thaw cycles and storage time on plasma samples used in mass spectrometry based biomarker discovery projects. Cancer Inform. 2005, 1, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, P.; McKay, R.T.; Finkel, M.; Karnovsky, A.; Woehler, S.; Lewis, M.J.; Chang, D.; Stringer, K.A. Signal intensities derived from different NMR probes and parameters contribute to variations in quantification of metabolites. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 for Comprehensive Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 55, 11–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McHugh, C.E.; Flott, T.L.; Schooff, C.R.; Smiley, Z.; Puskarich, M.A.; Myers, D.D.; Younger, J.G.; Jones, A.E.; Stringer, K.A. Rapid, Reproducible, Quantifiable NMR Metabolomics: Methanol and Methanol: Chloroform Precipitation for Removal of Macromolecules in Serum and Whole Blood. Metabolites 2018, 8, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040093
McHugh CE, Flott TL, Schooff CR, Smiley Z, Puskarich MA, Myers DD, Younger JG, Jones AE, Stringer KA. Rapid, Reproducible, Quantifiable NMR Metabolomics: Methanol and Methanol: Chloroform Precipitation for Removal of Macromolecules in Serum and Whole Blood. Metabolites. 2018; 8(4):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040093
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcHugh, Cora E., Thomas L. Flott, Casey R. Schooff, Zyad Smiley, Michael A. Puskarich, Daniel D. Myers, John G. Younger, Alan E. Jones, and Kathleen A. Stringer. 2018. "Rapid, Reproducible, Quantifiable NMR Metabolomics: Methanol and Methanol: Chloroform Precipitation for Removal of Macromolecules in Serum and Whole Blood" Metabolites 8, no. 4: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040093
APA StyleMcHugh, C. E., Flott, T. L., Schooff, C. R., Smiley, Z., Puskarich, M. A., Myers, D. D., Younger, J. G., Jones, A. E., & Stringer, K. A. (2018). Rapid, Reproducible, Quantifiable NMR Metabolomics: Methanol and Methanol: Chloroform Precipitation for Removal of Macromolecules in Serum and Whole Blood. Metabolites, 8(4), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040093




