Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis and Bayesian Networks for Metabolomic Prediction of Childhood Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis
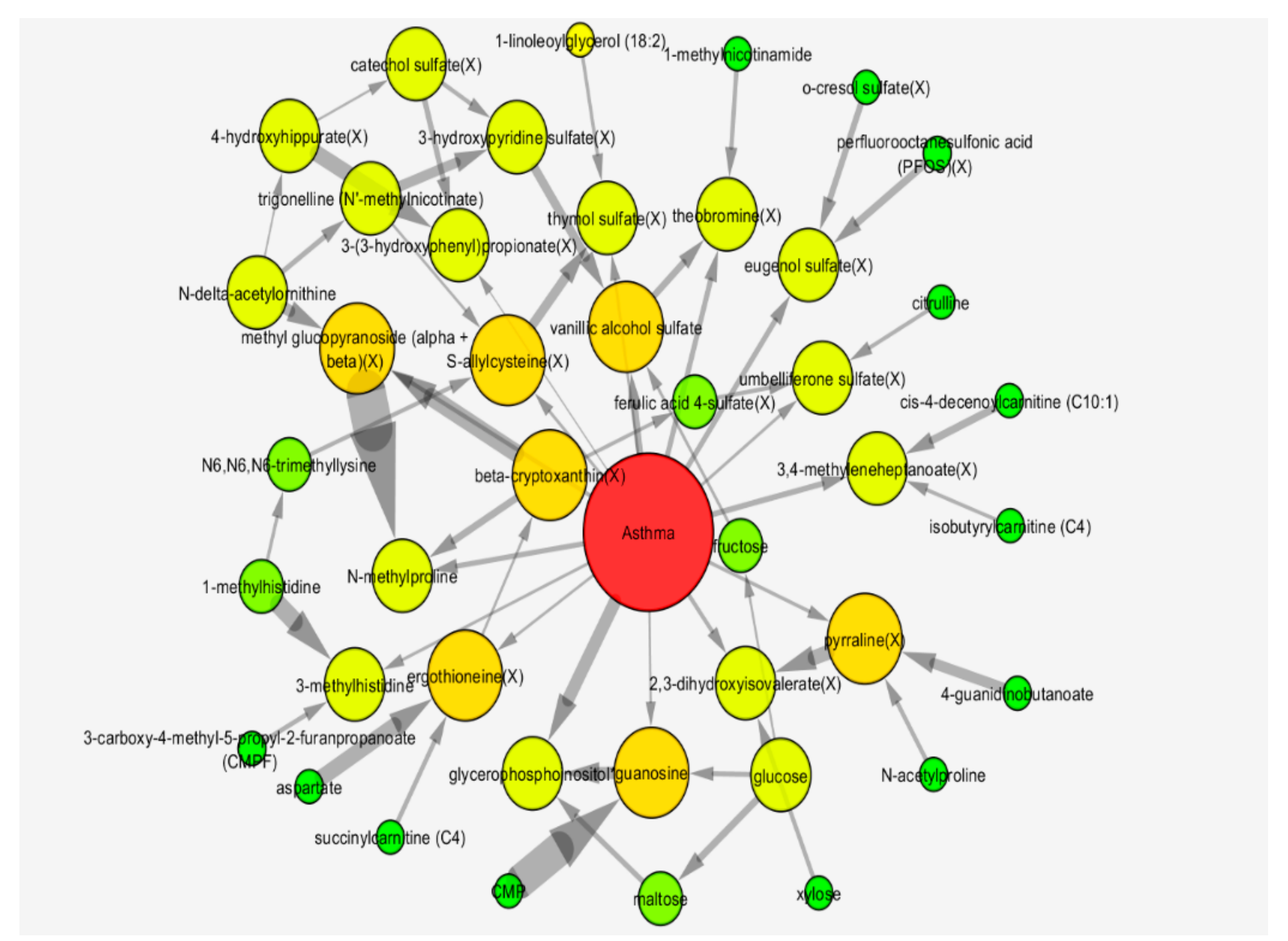
2.3. Bayesian Network Analysis
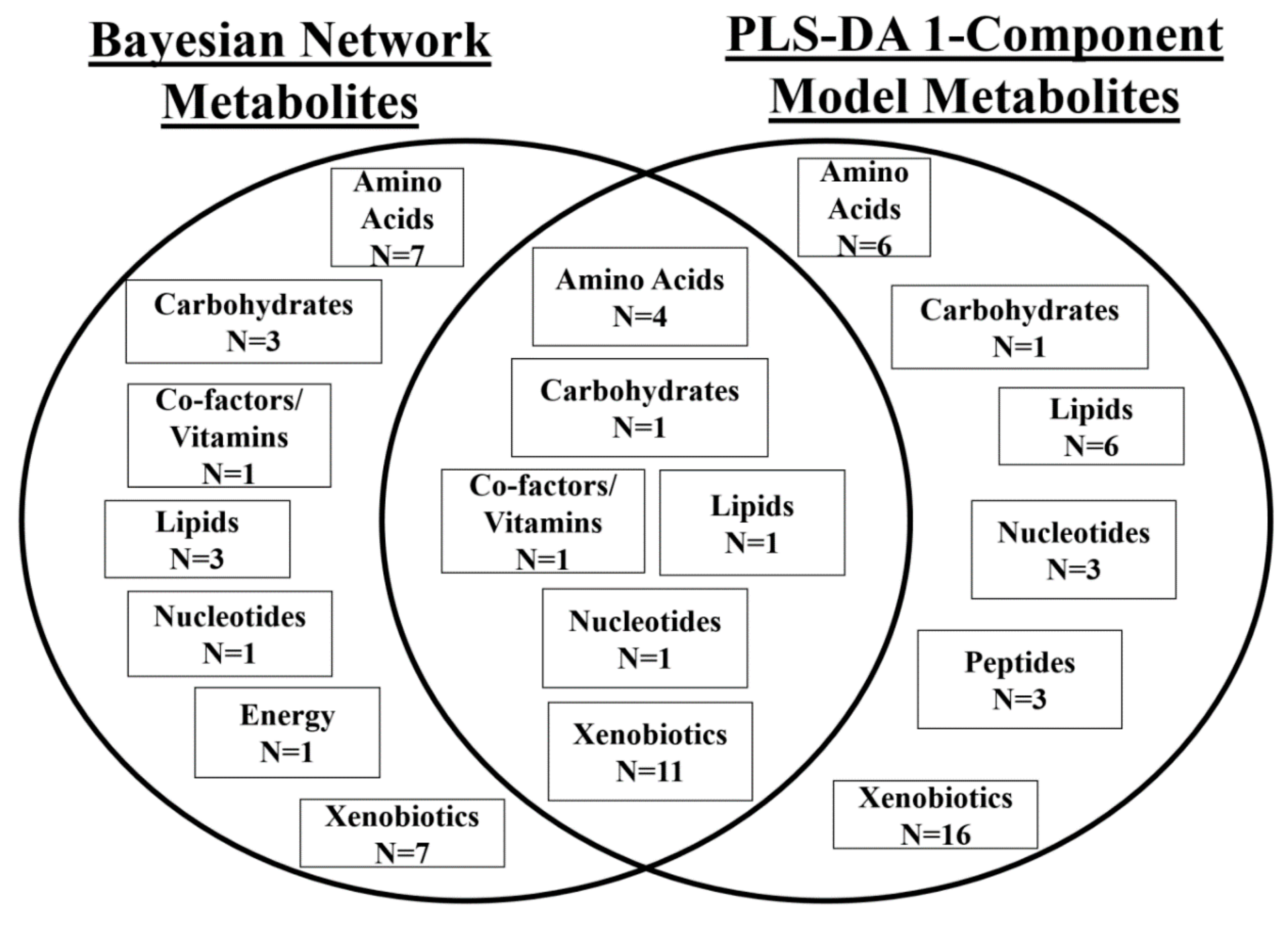
2.4. Comparison of Models
2.5. Biological Interpretation of Findings
2.5.1. PLS-DA
2.5.2. Bayesian Network Model
2.6. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Discussion
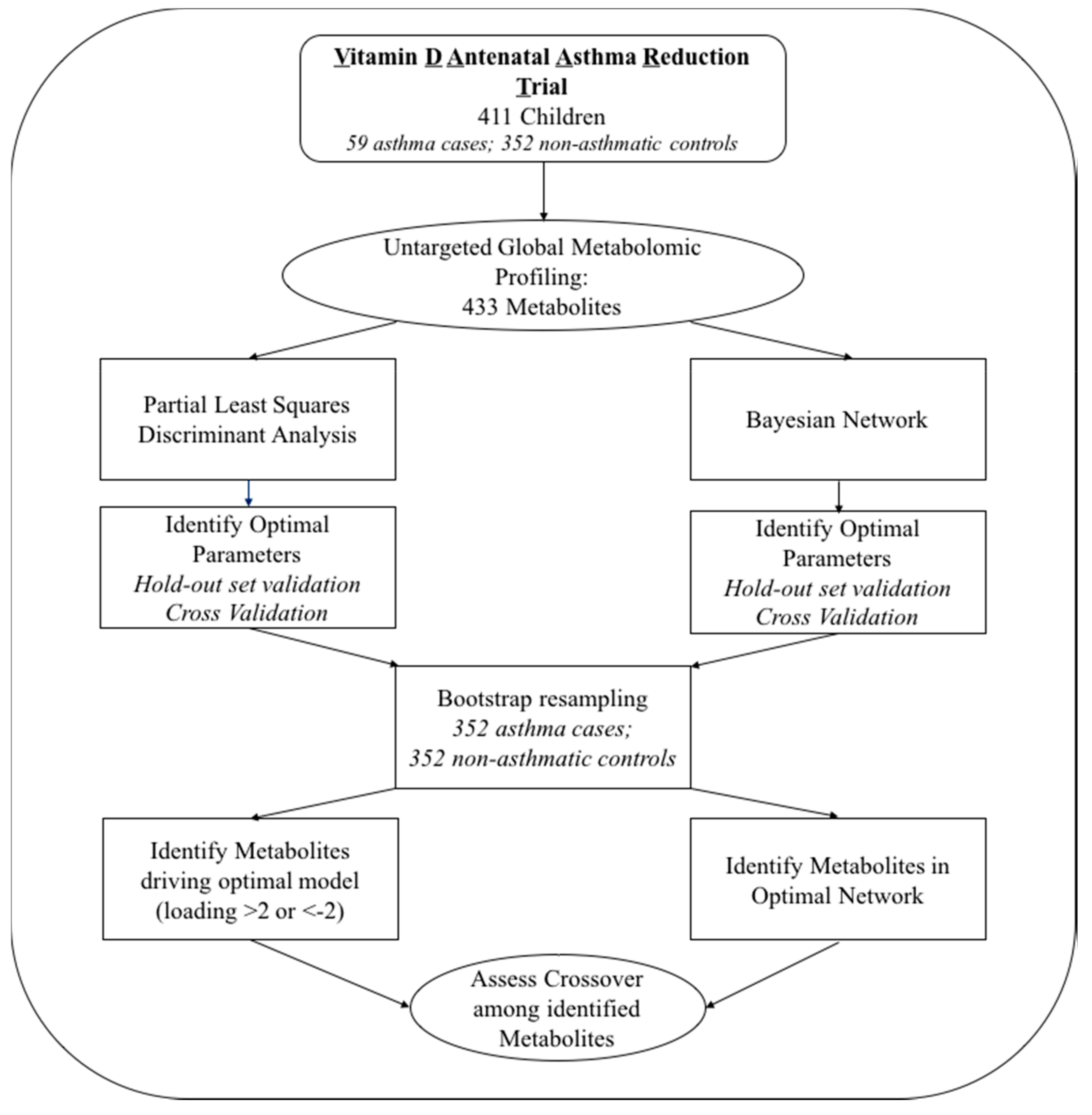
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The VDAART Clinical Trial: Study Participants
4.2. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.3.1. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis
4.3.2. Bayesian Network Analysis
4.3.3. Permutation Tests to Assess Likelihood of Overfitting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eder, W.; Ege, M.J.; von Mutius, E. The Asthma Epidemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbarao, P.; Mandhane, P.J.; Sears, M.R. Asthma: Epidemiology, etiology and risk factors. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 181, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mims, J.W. Asthma: Definitions and pathophysiology. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Wilson, I.D. Opinion: Understanding ‘global’ systems biology: Metabonomics and the continuum of metabolism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.S.; Dahlin, A.; McGeachie, M.J.; Qiu, W.; Sordillo, J.; Wan, E.S.; Wu, A.C.; Lasky-Su, J. Asthma metabolomics and the potential for integrative omics in research and the clinic. Chest 2017, 151, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garthwaite, P.H. An Interpretation of Partial Least Squares. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromski, P.S.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Xu, Y.; Correa, E.; Turner, M.L.; Goodacre, R. A tutorial review: Metabolomics and partial least squares-discriminant analysis—A marriage of convenience or a shotgun wedding. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerhuis, J.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Smit, S.; Vis, D.J.; Smilde, A.K.; van Velzen, E.J.J.; van Duijnhoven, J.P.M.; van Dorsten, F.A. Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metabolomics 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trainor, P.J.; DeFilippis, A.P.; Rai, S.N. Evaluation of Classifier Performance for Multiclass Phenotype Discrimination in Untargeted Metabolomics. Metabolites 2017, 7, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckerman, D.; Gieger, D. Learning Bayesian Networks: A unification for discrete and Gaussian domains. In Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes Factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachie, M.J.; Dahlin, A.; Qiu, W.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Savage, J.; Wu, A.C.; Wan, E.S.; Sordillo, J.E.; Al-Garawi, A.; Martinez, F.D.; et al. The metabolomics of asthma control: A promising link between genetics and disease. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2015, 3, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, A.J.; McGeachie, M.; Baron, R.M.; Gazourian, L.; Haspel, J.A.; Nakahira, K.; Fredenburgh, L.E.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Raby, B.A.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. Metabolomic derangements are associated with mortality in critically ill adult patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litonjua, A.A.; Lange, N.E.; Carey, V.J.; Brown, S.; Laranjo, N.; O’Connor, G.T.; Sandel, M.; Strunk, R.C.; Bacharier, L.B.; Zeiger, R.S.; et al. The Vitamin D Antenatal Asthma Reduction Trial (VDAART): Rationale, design, and methods of a randomized, controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy for the primary prevention of asthma and allergies in children. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2014, 38, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wong, A.K.C.; Kamel, M.S. Classification of imbalanced data: A review. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2009, 23, 687–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, P.; Torgo, L.; Ribeiro, R.P. A Survey of Predictive Modeling on Imbalanced Domains. ACM Comput. Surv. 2016, 49, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, P.; Abad, M.; Ramoni, M.F. Bayesian Networks for Genomic Analysis. In Genomic Signal Processing and Statistics; Dougherty, E.R., Shmulevich, I., Chen, J., Wang, Z.J., Eds.; Hindawi Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 281–320. [Google Scholar]
- McGeachie, M.J.; Chang, H.H.; Weiss, S.T. CGBayesNets: Conditional Gaussian Bayesian network learning and inference with mixed discrete and continuous data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, G.; Jindal, S.K.; Ganguly, N.K.; Dhawan, V. Increased nitric oxide production by neutrophils in bronchial asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comhair, S.A.A.; McDunn, J.; Bennett, C.; Fettig, J.; Erzurum, S.C.; Kalhan, S.C. Metabolomic Endotype of Asthma. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.G.; Garg, M.L.; Blake, R.J.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Gibson, P.G. Airway and circulating levels of carotenoids in asthma and healthy controls. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2005, 24, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Boushey, H.A. The Microbiome in Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rymenant, E.; Abrankó, L.; Tumova, S.; Grootaert, C.; van Camp, J.; Williamson, G.; Kerimi, A. Chronic exposure to short-chain fatty acids modulates transport and metabolism of microbiome-derived phenolics in human intestinal cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 39, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, G.S.; Jung, Y.S.; Ryu, D.H.; Park, H.S.; Hwang, G.S. Serum metabolomics reveals pathways and biomarkers associated with asthma pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.V. The role of histamine in allergic diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1990, 86, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.E.; Becker, A.B.; Simons, K.J.; Gillespie, C.A. The bronchodilator effect and pharmacokinetics of theobromine in young patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1985, 76, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Huang, H.M.; Lin, C.L.; Leu, S.J.; Lee, Y.L. Ferulic Acid Induces Th1 Responses by Modulating the Function of Dendritic Cells and Ameliorates Th2-Mediated Allergic Airway Inflammation in Mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 678487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Dong, Z. Antiasthmatic Effects of Eugenol in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma by Regulation of Vitamin D3 Upregulated Protein 1/NF-κB Pathway. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.; Sorbello, V.; Ciprandi, G. FeNO as biomarker for asthma phenotyping and management. Allergy Asthma. Proc. 2015, 36, e1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, J.; Krumsiek, J.; Theis, F.J. Statistical methods for the analysis of high-throughput metabolomics data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 4, e201301009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riekeberg, E.; Powers, R. New frontiers in metabolomics: From measurement to insight. F1000Res. 2017, 6, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, J.T.S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemometr. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Marco-Ramell, A.; Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Alay, A.; Tulipani, S.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Sanchez-Pla, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Evaluation and comparison of bioinformatic tools for the enrichment analysis of metabolomics data. BMC Bioinformatics 2018, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosato, A.; Tenori, L.; Cascante, M.; de Atauri Carulla, P.R.; Martins dos Santos, V.A.P.; Saccenti, E. From correlation to causation: Analysis of metabolomics data using systems biology approaches. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fan, S.; Fiehn, O. Integrating bioinformatics approaches for a comprehensive interpretation of metabolomics datasets. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blighe, K.; Chawes, B.L.; Kelly, R.S.; Mirzakhani, H.; McGeachie, M.; Litonjua, A.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Lasky-Su, J.A. Vitamin D prenatal programming of childhood metabolomics profiles at age 3 y. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.S.; Sordillo, J.E.; Lasky-Su, J.; Dahlin, A.; Perng, W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Weiss, S.T.; Gold, D.R.; Litonjua, A.A.; Hivert, M.F.; et al. Plasma metabolite profiles in children with current asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, F.; Fawcett, T. Robust Classification for imprecise environments. Mach. Learn. 2001, 44, 203–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasko, T.A.; Bhagwat, J.G.; Zou, K.H.; Ohno-Machado, L. The use of receiver operating characteristic curves in biomedical informatics. J. Biomed. Inform. 2005, 38, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, M.; Rayens, W. Partial least squares for discrimination. J. Chemometr. 2003, 17, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, T.; Martens, H.; Sæbø, S.; Warringer, J.; Snipen, L. A Partial Least Squares based algorithm for parsimonious variable selection. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, S. SIMPLS: An Alternative Approach to Partial Least Squares Regression. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 1993, 18, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.F.; Herskovits, E. A Bayesian method for the induction of probabilistic networks from data. Mach. Learn. 1992, 9, 309–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Controls (n = 352) | Cases (n = 59) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |||
| Gender | Male | 183 | 52.0% | 36 | 61.0% | 0.208 |
| Female | 169 | 48.0% | 23 | 39.0% | ||
| Race | White | 119 | 33.8% | 15 | 25.4% | 0.003 |
| Black | 159 | 45.2% | 40 | 67.8% | ||
| Other | 74 | 21.0% | 4 | 6.8% | ||
| Treatment Group | Placebo | 182 | 51.7% | 28 | 47.5% | 0.576 |
| Intervention | 170 | 48.3% | 31 | 52.5% | ||
| BMI | Mean (SD) | 16.6 (2.1) | 17.1 (1.9) | 0.063 | ||
| Metabolite | Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | HMDB ID | Loading |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| glycochenodeoxycholate sulfate | Lipid | Primary Bile Acid Metabolism | −9.12 | |
| stachydrine | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB04827 | −6.41 |
| N-methylproline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | −6.31 | |
| glycolithocholate sulfate | Lipid | Secondary Bile Acid Metabolism | HMDB02639 | −4.87 |
| methyl glucopyranoside (alpha + beta) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | −4.54 | |
| theobromine | Xenobiotics | Xanthine Metabolism | HMDB02825 | −4.44 |
| cysteine s-sulfate | Amino Acid | Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism | HMDB00731 | −4.23 |
| 4-vinylguaiacol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | −4.14 | |
| taurolithocholate 3-sulfate | Lipid | Secondary Bile Acid Metabolism | HMDB02580 | −4.12 |
| 3-hydroxyhippurate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB06116 | −3.72 |
| 2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB12141 | −3.34 |
| 4-methylcatechol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | −3.33 | |
| vanillic alcohol sulfate | Amino Acid | Tyrosine Metabolism | −3.25 | |
| 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB00375 | −3.21 |
| p-cresol-glucuronide | Amino Acid | Tyrosine Metabolism | HMDB11686 | −3.2 |
| CMP | Nucleotide | Pyrimidine Metabolism, Cytidine containing | HMDB00095 | −3.16 |
| indolepropionate | Amino Acid | Tryptophan Metabolism | HMDB02302 | −3.11 |
| beta-cryptoxanthin | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB33844 | −3.08 |
| xylose | Carbohydrate | Pentose Metabolism | HMDB00098 | −3.05 |
| tauro-beta-muricholate | Lipid | Primary Bile Acid Metabolism | HMDB00932 | −3.04 |
| 5-hydroxyindoleacetate | Amino Acid | Tryptophan Metabolism | HMDB00763 | −2.93 |
| gamma-glutamylglutamate | Peptide | Gamma-glutamyl Amino Acid | HMDB11737 | −2.87 |
| ferulic acid 4-sulfate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB29200 | −2.8 |
| cinnamoylglycine | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB11621 | −2.71 |
| tryptophan betaine | Amino Acid | Tryptophan Metabolism | HMDB61115 | −2.7 |
| 1,2,3-benzenetriol sulfate (2) | Xenobiotics | Chemical | −2.66 | |
| catechol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB59724 | −2.65 |
| quinate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB03072 | −2.62 |
| inosine 5’-monophosphate (IMP) | Nucleotide | Purine Metabolism, (Hypo)Xanthine/Inosine containing | HMDB00175 | −2.59 |
| gamma-glutamylvaline | Peptide | Gamma-glutamyl Amino Acid | HMDB11172 | −2.58 |
| ergothioneine | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB03045 | −2.49 |
| ribitol | Carbohydrate | Pentose Metabolism | HMDB00508 | −2.49 |
| glycerophosphoinositol | Lipid | Phospholipid Metabolism | −2.49 | |
| umbelliferone sulfate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | −2.43 | |
| pyrraline | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB33143 | −2.4 |
| 4-acetylphenyl sulfate | Xenobiotics | Drug | −2.37 | |
| gamma-glutamylisoleucine | Peptide | Gamma-glutamyl Amino Acid | HMDB11170 | −2.36 |
| N-acetylproline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | −2.34 | |
| 3-methoxycatechol sulfate (1) | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | −2.32 | |
| 4-vinylphenol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB04072 | −2.29 |
| sphinganine | Lipid | Sphingolipid Metabolism | HMDB00269 | −2.29 |
| hydantoin-5-propionic acid | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | HMDB01212 | −2.23 |
| trigonelline (N’-methylnicotinate) | Cofactors and Vitamins | Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism | HMDB00875 | −2.19 |
| O-methylcatechol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB60013 | −2.18 |
| 4-allylphenol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | −2.16 | |
| 2-aminophenol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Chemical | HMDB61116 | −2.14 |
| citrulline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | HMDB00904 | −2.13 |
| uridine 3’-monophosphate (3’-UMP) | Nucleotide | Pyrimidine Metabolism, Uracil containing | −2.09 | |
| 3-methyl catechol sulfate (1) | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | −2.09 | |
| 3-hydroxypyridine sulfate | Xenobiotics | Chemical | −2.06 | |
| isoursodeoxycholate | Lipid | Secondary Bile Acid Metabolism | HMDB00686 | −2.05 |
| propyl 4-hydroxybenzoate sulfate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | 2.18 | |
| 2’-O-methylcytidine | Nucleotide | Pyrimidine Metabolism, Cytidine containing | 2.33 | |
| methyl-4-hydroxybenzoate sulfate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | 2.37 |
| Metabolite | Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | HMDB ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-linoleoylglycerol (18:2) | Lipid | Monoacylglycerol | |
| 1-methylhistidine | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | HMDB00001 |
| 1-methylnicotinamide | Cofactors and Vitamins | Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism | HMDB00699 |
| 2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB12141 |
| 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionate (X) | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB00375 |
| 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoate (CMPF) | Lipid | Fatty Acid, Dicarboxylate | HMDB61112 |
| 3-hydroxypyridine sulfate (X) | Xenobiotics | Chemical | |
| 3-methylhistidine | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | HMDB00479 |
| 3,4-methyleneheptanoate (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | |
| 4-guanidinobutanoate | Amino Acid | Guanidino and Acetamido Metabolism | HMDB03464 |
| 4-hydroxyhippurate (X) | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB13678 |
| aspartate | Amino Acid | Alanine and Aspartate Metabolism | HMDB00191 |
| beta-cryptoxanthin (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB33844 |
| catechol sulfate (X) | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB59724 |
| cis-4-decenoylcarnitine (C10:1) | Lipid | Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine) | |
| citrulline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | HMDB00904 |
| CMP | Nucleotide | Pyrimidine Metabolism, Cytidine containing | HMDB00095 |
| Ergothioneine (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB03045 |
| eugenol sulfate (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | |
| ferulic acid 4-sulfate (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB29200 |
| fructose | Carbohydrate | Fructose, Mannose and Galactose Metabolism | HMDB00660 |
| glucose | Carbohydrate | Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, and Pyruvate Metabolism | HMDB00122 |
| glycerophosphoinositol | Lipid | Phospholipid Metabolism | |
| guanosine | Nucleotide | Purine Metabolism, Guanine containing | HMDB00133 |
| isobutyrylcarnitine (C4) | Amino Acid | Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine Metabolism | HMDB00736 |
| maltose | Carbohydrate | Glycogen Metabolism | HMDB00163 |
| methyl glucopyranoside (alpha + beta) (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | |
| N-acetylproline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | |
| N-delta-acetylornithine | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | |
| N-methylproline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | |
| N6,N6,N6-trimethyllysine | Amino Acid | Lysine Metabolism | HMDB01325 |
| o-cresol sulfate (X) | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | |
| perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) (X) | Xenobiotics | Chemical | HMDB59586 |
| Pyrraline (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB33143 |
| S-allylcysteine (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB34323 |
| succinylcarnitine (C4) | Energy | TCA Cycle | HMDB61717 |
| Theobromine (X) | Xenobiotics | Xanthine Metabolism | HMDB02825 |
| thymol sulfate (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB01878 |
| trigonelline (N’-methylnicotinate) | Cofactors and Vitamins | Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism | HMDB00875 |
| umbelliferone sulfate (X) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | |
| vanillic alcohol sulfate | Amino Acid | Tyrosine Metabolism | |
| xylose | Carbohydrate | Pentose Metabolism | HMDB00098 |
| Metabolite | Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | HMDB ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| vanillic alcohol sulfate | Amino Acid | Tyrosine Metabolism | |
| citrulline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | HMDB00904 |
| N-acetylproline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | |
| N-methylproline | Amino Acid | Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism | |
| xylose | Carbohydrate | Pentose Metabolism | HMDB00098 |
| trigonelline (N’-methylnicotinate) | Cofactors and Vitamins | Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism | HMDB00875 |
| Glycerophosphoinositol | Lipid | Phospholipid Metabolism | |
| CMP | Nucleotide | Pyrimidine Metabolism, Cytidine containing | HMDB00095 |
| 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB00375 |
| catechol sulfate | Xenobiotics | Benzoate Metabolism | HMDB59724 |
| 2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB12141 |
| beta-cryptoxanthin | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB33844 |
| ergothioneine | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB03045 |
| ferulic acid 4-sulfate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB29200 |
| methyl glucopyranoside (alpha + beta) | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | |
| pyrraline | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | HMDB33143 |
| umbelliferone sulfate | Xenobiotics | Food Component/Plant | |
| theobromine | Xenobiotics | Xanthine Metabolism | HMDB02825 |
| 3-hydroxypyridine sulfate | Xenobiotics | Chemical |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kelly, R.S.; McGeachie, M.J.; Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Kachroo, P.; Chu, S.H.; Virkud, Y.V.; Huang, M.; Litonjua, A.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Lasky-Su, J. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis and Bayesian Networks for Metabolomic Prediction of Childhood Asthma. Metabolites 2018, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040068
Kelly RS, McGeachie MJ, Lee-Sarwar KA, Kachroo P, Chu SH, Virkud YV, Huang M, Litonjua AA, Weiss ST, Lasky-Su J. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis and Bayesian Networks for Metabolomic Prediction of Childhood Asthma. Metabolites. 2018; 8(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040068
Chicago/Turabian StyleKelly, Rachel S., Michael J. McGeachie, Kathleen A. Lee-Sarwar, Priyadarshini Kachroo, Su H. Chu, Yamini V. Virkud, Mengna Huang, Augusto A. Litonjua, Scott T. Weiss, and Jessica Lasky-Su. 2018. "Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis and Bayesian Networks for Metabolomic Prediction of Childhood Asthma" Metabolites 8, no. 4: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040068
APA StyleKelly, R. S., McGeachie, M. J., Lee-Sarwar, K. A., Kachroo, P., Chu, S. H., Virkud, Y. V., Huang, M., Litonjua, A. A., Weiss, S. T., & Lasky-Su, J. (2018). Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis and Bayesian Networks for Metabolomic Prediction of Childhood Asthma. Metabolites, 8(4), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040068








