Current Applications of Metabolomics in Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
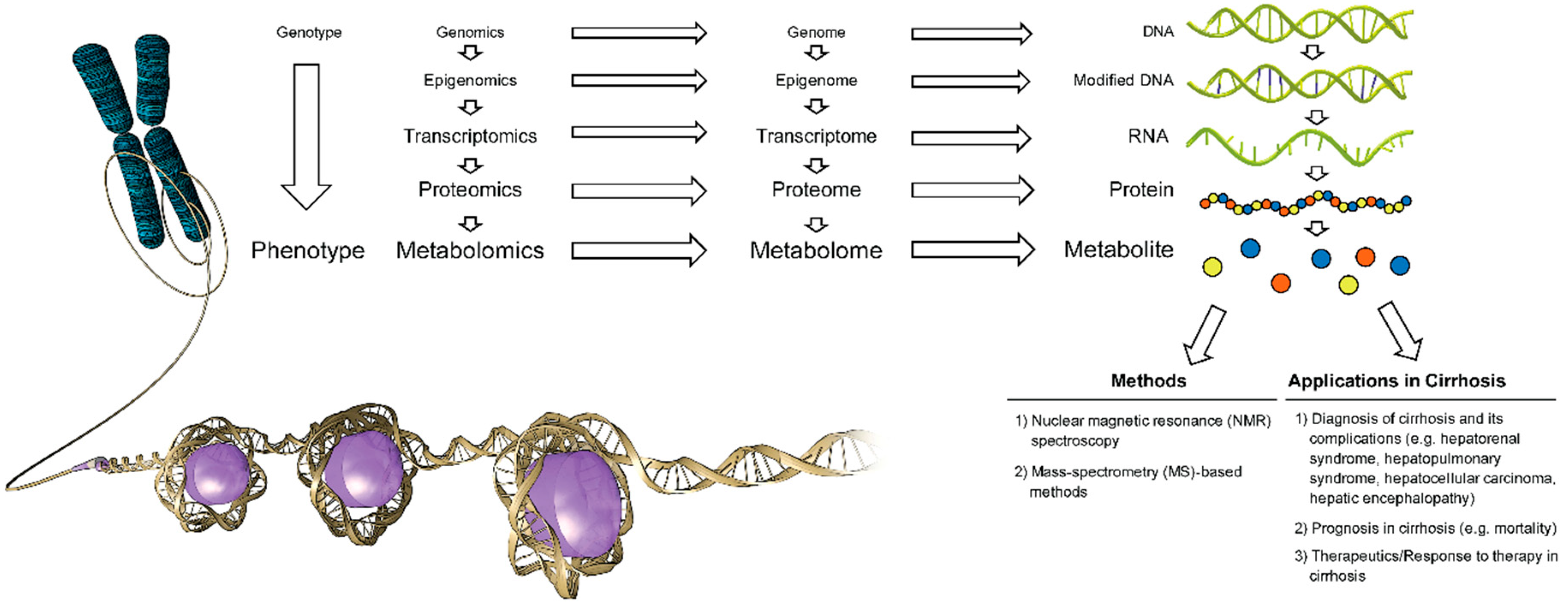
1.1. Metabolomics, Metabolome, Metabolite
1.2. Major Analytical Techniques in Metabolite Detection, Quantitation and Data Analysis
1.3. Metabolomics in Cirrhosis
2. Current Applications of Metabolomics in Cirrhosis
2.1. Differentiation between Patients with Cirrhosis and Healthy Controls
2.2. Differentiation between Decompensated Cirrhosis and Compensated Cirrhosis
2.3. Differentiation between Severe Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis and Alcoholic Cirrhosis
2.4. Differentiation between Cirrhosis Secondary to Alcoholic Hepatitis and Acute Decompensated Cirrhosis Secondary to Non-Alcohol Related Etiologies
2.5. Differentiation between Hepatitis B Cirrhosis and Alcoholic Cirrhosis
2.6. Differentiation between Acute on Chronic Liver Failure and Chronic Liver Failure
2.7. Metabolomic Signature of Hepatorenal Dysfunction and Glomerular Filtration Rate in Patients with Cirrhosis
2.8. Metabolomic Profile in Patients with Cirrhosis and Minimal (Covert) Hepatic Encephalopathy
2.9. Metabolomic Profile in Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy
2.10. Impact of Lactobacillus GG and Rifaximin on Metabolome in Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy
2.11. Metabolomic Profile in Hepatopulmonary Syndrome
2.12. Metabolomic Profile in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
2.13. Mortality without Liver Transplantation
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosures
References
- Kalim, S.; Rhee, E.P. An overview of renal metabolomics. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.H.; Kim, K. Metabolomics in the study of kidney diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 8, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emwas, A.H. The strengths and weaknesses of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry with particular focus on metabolomics research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1277, 161–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Huhman, D.V.; Sumner, L.W. Mass spectrometry strategies in metabolomics. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25435–25442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, J.; Krumsiek, J.; Theis, F.J. Statistical methods for the analysis of high-throughput metabolomics data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 4, e201301009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.X.; Chen, T.L.; Li, M.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Cui, G.H.; Zhao, A.H.; Jia, W.; Huang, L.Q.; Qi, X.Q. Use of the metabolomics approach to characterize Chinese medicinal material Huangqi. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chance, M.R. Pathway analyses and understanding disease associations. Curr. Genet. Med. Rep. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.W.; Tu, Z.G.; Peng, W.J.; Wang, L.X.; Ou-Yang, X.; Cai, A.J.; Dai, Y. 1H NMR-based serum metabolic profiling in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Tu, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, L.; Peng, W.; Cai, A.; Dai, Y. Comparison of the metabolic profiling of hepatitis B virus-infected cirrhosis and alcoholic cirrhosis patients by using 1H NMR-based metabonomics. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Cong, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Lin, D. Application of 1H NMR-based metabonomics in the study of metabolic profiling of human hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbin, I.R.; Ryner, L.N.; Singh, H.; Minuk, G.Y. Quantitative hepatic phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G379–G384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchetto, D.M.; Tschanz, C.; Bjornsson, T.D. Decreased rate of creatinine production in patients with hepatic disease: Implications for estimation of creatinine clearance. Ther. Drug Monit. 1983, 5, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Furube, M.; Hirano, S.; Takatori, K.; Iida, K.; Kajiwara, M. Evaluation of 13C-phenylalanine and 13C-tyrosine breath tests for the measurement of hepatocyte functional capacity in patients with liver cirrhosis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachakonda, V.; Gabbert, C.; Raina, A.; Bell, L.N.; Cooper, S.; Malik, S.; Behari, J. Serum metabolomic profiling in acute alcoholic hepatitis identifies multiple dysregulated pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascha, M.; Wang, Z.; Ascha, M.S.; Dweik, R.; Zein, N.N.; Grove, D.; Brown, J.M.; Marshall, S.; Lopez, R.; Hanouneh, I.A. Metabolomics studies identify novel diagnostic and prognostic indicators in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amathieu, R.; Triba, M.N.; Nahon, P.; Bouchemal, N.; Kamoun, W.; Haouache, H.; Trinchet, J.C.; Savarin, P.; Le Moyec, L.; Dhonneur, G. Serum 1H-NMR metabolomic fingerprints of acute-on-chronic liver failure in intensive care unit patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindikoglu, A.L.; Opekun, A.R.; Putluri, N.; Devaraj, S.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Vierling, J.M.; Goss, J.A.; Rana, A.; Sood, G.K.; Jalal, P.K.; et al. Unique metabolomic signature associated with hepatorenal dysfunction and mortality in cirrhosis. Transl. Res. 2018, 195, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, B.; Montoliu, C.; MacIntyre, D.A.; Serra, M.A.; Wassel, A.; Jover, M.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Rodrigo, J.M.; Pineda-Lucena, A.; Felipo, V. Serum metabolic signature of minimal hepatic encephalopathy by 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 5180–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Hirano, H.; Yano, Y.; Momose, K.; Yoshida, M.; Azuma, T. Serum level of taurine would be associated with the amelioration of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, N.; Barbier Saint Hilaire, P.; Colsch, B.; Isnard, F.; Attala, S.; Schaefer, A.; Amador, M.D.; Rudler, M.; Lamari, F.; Sedel, F.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolomics highlights dysregulation of energy metabolism in overt hepatic encephalopathy. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Sanyal, A.J.; Puri, P.; Sterling, R.K.; Luketic, V.; Stravitz, R.T.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Fuchs, M.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Lactobacillus GG modulates gut microbiome, metabolome and endotoxemia in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Sterling, R.K.; Stravitz, R.T.; Fuchs, M.; Ridlon, J.M.; Daita, K.; Monteith, P.; et al. Modulation of the metabiome by rifaximin in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronnemaa, E.; Zethelius, B.; Vessby, B.; Lannfelt, L.; Byberg, L.; Kilander, L. Serum fatty-acid composition and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A longitudinal population-based study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, K.A.; Martin, A.; Joseph, J.A. Essential fatty acids and the brain: Possible health implications. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2000, 18, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, K.M.; Forde, K.A.; Krok, K.; Patel, M.; Lin, G.; Oh, J.K.; Mottram, C.; Scanlon, P.D.; Batra, S.; Goldberg, D.S.; et al. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling in Hepatopulmonary Syndrome. Hepatology 2015, 62, 927A–928A. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Nie, X.; Feng, X.; Chen, W.; Yue, Y.; Tang, H.; Deng, F. Metabonomic studies of human hepatocellular carcinoma using high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy in conjunction with multivariate data analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2605–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, A.D.; Maurhofer, O.; Beyoglu, D.; Lanz, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Pabst, T.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Dufour, J.F.; Idle, J.R. Aberrant lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by plasma metabolomics and lipid profiling. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6590–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhail, M.J.; Shawcross, D.L.; Lewis, M.R.; Coltart, I.; Want, E.J.; Antoniades, C.G.; Veselkov, K.; Triantafyllou, E.; Patel, V.; Pop, O.; et al. Multivariate metabotyping of plasma predicts survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, N.; Gao, L.; Xu, Y.J.; Huang, C.; Yu, K.; Ling, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; et al. Acetylcarnitine Is a Candidate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Risino, C.; Gargante, M.P.; Oreste, G.; Barone, G.; Tomasello, A.V.; Costanzo, M.; Cannizzaro, M.A. Decrease of serum carnitine levels in patients with or without gastrointestinal cancer cachexia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 4541–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinci, E.; Rampello, E.; Zanoli, L.; Oreste, G.; Pistone, G.; Malaguarnera, M. Serum carnitine levels in patients with tumoral cachexia. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 16, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatikos, G.; Schoell, N.; Ferreiros, N.; Bon, D.; Herrmann, E.; Farnik, H.; Koberle, V.; Piiper, A.; Zeuzem, S.; Kronenberger, B.; et al. Serum sphingolipidomic analyses reveal an upregulation of C16-ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18095–18105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soga, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Honma, M.; Mori, M.; Igarashi, K.; Kashikura, K.; Ikeda, S.; Hirayama, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Serum metabolomics reveals gamma-glutamyl dipeptides as biomarkers for discrimination among different forms of liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatikos, G.; Ferreiros, N.; Waidmann, O.; Bon, D.; Schroeter, S.; Koch, A.; Herrmann, E.; Zeuzem, S.; Kronenberger, B.; Pfeilschifter, J. Serum Sphingolipid Variations Associate with Hepatic Decompensation and Survival in Patients with Cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotte, J.P. Biological functions of sphingomyelins. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Gillevet, P.M.; Patel, N.R.; Ahluwalia, V.; Ridlon, J.M.; Kettenmann, B.; Schubert, C.M.; Sikaroodi, M.; Heuman, D.M.; Crossey, M.M.; et al. A longitudinal systems biology analysis of lactulose withdrawal in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2012, 27, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.N.; Dong, S.; Wei, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Su, S.B. Metabolomic mechanisms of gypenoside against liver fibrosis in rats: An integrative analysis of proteomics and metabolomics data. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iebba, V.; Guerrieri, F.; Di Gregorio, V.; Levrero, M.; Gagliardi, A.; Santangelo, F.; Sobolev, A.P.; Circi, S.; Giannelli, V.; Mannina, L.; et al. Combining amplicon sequencing and metabolomics in cirrhotic patients highlights distinctive microbiota features involved in bacterial translocation, systemic inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressom, H.W.; Di Poto, C.; Ferrarini, A.; Yunli, H.; Nezami Ranjbar, M.R.; Ehwang, S.; Varghese, R.S.; Minkun, W.; Shiyue, Z.; Rui, Z.; et al. Multi-omic approaches for characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2016, 2016, 3437–3440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Mass Spectrometry | NMR Spectroscopy |
|---|---|
| More sensitivity | Less sensitivity |
| Requires a smaller amount of sample | Requires more samples |
| Destructive to the sample | Non-destructive to the sample |
| Various ionization techniques applied to detect a greater number of metabolites | Single method applied |
| All elemental composition | Proton, carbon, phosphorus |
| Less expensive | More expensive |
| Difficult to measure polymers | Great advantage for polymer analysis |
| Less reproducible | More reproducible |
| Equipment requires smaller space | Equipment requires larger space |
| Applications | Representative Metabolites * | Representative Studies | Technique Used | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increased ** | Decreased ** | |||
| Differentiation Between Patients with Cirrhosis ** and Healthy Controls | Blood acetate, α-ketoglutarate, glycerol, glutamine, 1-methylhistidine, N-acetylglycoproteins, phenylalanine, pyruvate, taurine, tyrosine, hepatic phosphomonoester/phosphodiester ratio | Blood acetoacetate, choline, isoleucine, LDL, leucine, unsaturated lipid, valine, VLDL, hepatic tissue beta-ATP | Gao et al. (2009) [11], Corbin et al. (2004) [12] | 1H NMR-spectroscopy, quantitative hepatic phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| Differentiation Between Decompensated Cirrhosis ** and Compensated Cirrhosis | Blood alanine, creatine, glutamate, glutamine, histidine, lysine, phenylalanine, pyruvate, succinate | Blood acetone, LDL, VLDL, hepatic tissue beta-ATP | Qi et al. (2012) [9], Corbin et al. (2004) [12] | 1H NMR-spectroscopy, quantitative hepatic phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| Differentiation Between Severe Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis ** and Alcoholic Cirrhosis | Blood glucuronate, biliverdin, erythronate, methionine, lactate, cortisol, N-acetyltryptophan, symmetric dimethylarginine | Blood choline, glycerophosphocholine (GPC), glycerol-3-phosphate, ascorbate, serotonin, isoleucine, leucine, valine, deoxycholate, glycodeoxycholate | Rachakonda et al. (2014) [15] | MS |
| Differentiation Between Hepatitis B Cirrhosis ** and Alcoholic Cirrhosis | Blood creatine, isobutyrate | Blood acetoacetate, glutamate, glutamine | Qi et al. (2012) [10] | 1H NMR-spectroscopy |
| Differentiation Between Cirrhosis Secondary to Alcoholic Hepatitis ** and Acute Decompensated Cirrhosis Secondary to Non-Alcohol Related Etiologies | Blood betaine, citrulline, creatinine, phenylalanine, homocitrulline, tyrosine, octenoyl-carnitine, symmetric dimethylarginine | Ascha et al. (2016) [16] | MS | |
| Differentiation Between Acute on Chronic Liver Failure ** and Chronic Liver Failure | Blood creatinine, glutamate, glutamine, ketone bodies (hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate), pyruvate, lactate, phenylalanine and tyrosine | Blood HDL | Amathieu et al. (2014) [17] | 1H NMR-spectroscopy |
| Metabolomic Signature of Hepatorenal Dysfunction in Cirrhosis (Differentiation Between High Liver and Kidney Disease Severity ** and Low Liver and Kidney Disease Severity) | The top 10 among 34 blood metabolites based on fold increase included 4-acetamidobutanoate, trans-aconitate, 1-methylhistidine, glucuronate, N4-acetylcytidine, 3-ureidopropionate, 3-methoxytyramine sulfate, cytidine, S-adenosylhomocysteine, myo-inositol | Mindikoglu et al. (2017) [18] | MS | |
| Metabolomic Signature of Reduced Glomerular Filtration Rate | The top 10 among 34 blood metabolites based on R-square included erythronate, N6-carbamoylthreonyladenosine, 1-methylhistidine, pseudouridine, N-acetylserine, creatinine, 7-methylguanine, N2–N2-dimethylguanosine, C-glycosyltryptophan, myo-inositol | Mindikoglu et al. (2018) [18] | MS | |
| Minimal (Covert) Hepatic Encephalopathy | Blood glucose, glycerol, lactate, methionine, trimethylamine-N-oxide | Acetoacetate, alanine, alpha-acid glycoproteins, branched chain amino acids, choline, glycine, and lipid moiety, taurine | Jimenez et al. (2010) [19], Saito et al. (2016) [20] | 1H NMR-spectroscopy, MS |
| Differentiation Between Subjects with Hepatic Encephalopathy ** and Controls without Neurological Disease | Cerebrospinal fluid glutamine, glutamate, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, formyl-methionine, N4-acetylcytidine | Cerebrospinal fluid taurine | Weiss et al. [21] | MS |
| Impact of Lactobacillus GG on Metabolome in Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy | Blood hydroxylamine and benzoic acid | Blood isoleucine, threonine, methionine, urine metabolites including glycodeoxycholic acid, phophatidylcholines, vitamin C, riboflavin metabolites | Bajaj et al. (2014) [22] | MS |
| Impact of Rifaximin on Metabolome in Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy | Blood myristic acid, caprylic acid, palmitic acid, succinic acid, fructose | Blood lipopolysaccharides | Bajaj et al. (2013) [23] | MS |
| Hepatopulmonary Syndrome | Blood primary and secondary bile acids, bilirubin, biliverdin, endothelin, fatty acids, nitric oxide synthase signaling regulators, sphingosine metabolites, urobilinogen | Blood monoglycerol | Fallon et al. (2015) [26] | MS |
| Differentiation Between Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) ** and HCC-Free Hepatic Tissue | Hepatic alanine, choline, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, lactate, leucine, and phosphorylethanolamine | Hepatic glucose, glycogen, and triglyceride, acetylcarnitine | Yang et al. (2007) [27], Lu et al. (2016) | 1H NMR-spectroscopy, MS |
| Differentiation Between High-Grade HCC ** and Low-Grade HCC | Hepatic alanine, choline, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, lactate, leucine, and phosphorylethanolamine | Hepatic glucose, glycerophophocholine, glycogen, phosphocholine, and triglycerides | Yang et al. (2007) [27] | 1H NMR-spectroscopy |
| Differentiation Between Cirrhosis with HCC ** and Cirrhosis without HCC | Blood bilirubin, biliverdin, γ-glutamyl dipeptides (γ-Glu-Ala, γ-Glu-Citrulline, γ-Glu-Thr, and γ-Glu-Phe), long chain (C16–C20) and very long chain (≥C24) ceramides, sphingosine, sphinganine-1-phosphate and sphingosine-1-phosphate | Several blood lysophosphocholines | Patterson et al. (2011) [28], Soga et al. (2011) [34], Grammatikos et al. (2016) [33] | MS |
| Differentiation Between Subjects with HCC ** and Healthy Subjects | Blood glycodeoxycholic acid, deoxycholic acid 3-sulfate, acetate, α-ketoglutarate, glycerol, 1-methylhistidine, n-acetylglycoproteins, phenylalanine, pyruvate, tyrosine | Several blood lysophosphocholines, acetoacetate, choline, certain lipids (LDL, VLDL, unsaturated lipid), and valine | Patterson et al. (2011) [28], Gao et al. (2009) [11] | 1H NMR-spectroscopy, MS |
| Increased Mortality without Liver Transplantation | Blood S-adenosylhomocysteine, glucuronate, trans-aconitate, 3-ureidopropionate, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate, 3-methoxytyramine sulfate, arabitol/xylitol, N-formylmethionine, phenyllactate and 7-methylguanine, tyrosine | Several blood sphingomyelins, glycerophosphocholines, glycerophosphoethanolamines, lysophophatidylcholines, phosphatidylcholines, long and very long chain ceramides (e.g., C24-ceramide) | Mindikoglu et al. (2018) [18], McPhail et al. (2016) [29], Grammatikos et al. (2015) [35], Ascha et al. (2016) [16] | MS, 1H NMR-spectroscopy |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, V.; Putluri, N.; Sreekumar, A.; Mindikoglu, A.L. Current Applications of Metabolomics in Cirrhosis. Metabolites 2018, 8, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040067
Khan V, Putluri N, Sreekumar A, Mindikoglu AL. Current Applications of Metabolomics in Cirrhosis. Metabolites. 2018; 8(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040067
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Vinshi, Nagireddy Putluri, Arun Sreekumar, and Ayse L. Mindikoglu. 2018. "Current Applications of Metabolomics in Cirrhosis" Metabolites 8, no. 4: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040067
APA StyleKhan, V., Putluri, N., Sreekumar, A., & Mindikoglu, A. L. (2018). Current Applications of Metabolomics in Cirrhosis. Metabolites, 8(4), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040067





