GC-MS-Based Endometabolome Analysis Differentiates Prostate Cancer from Normal Prostate Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
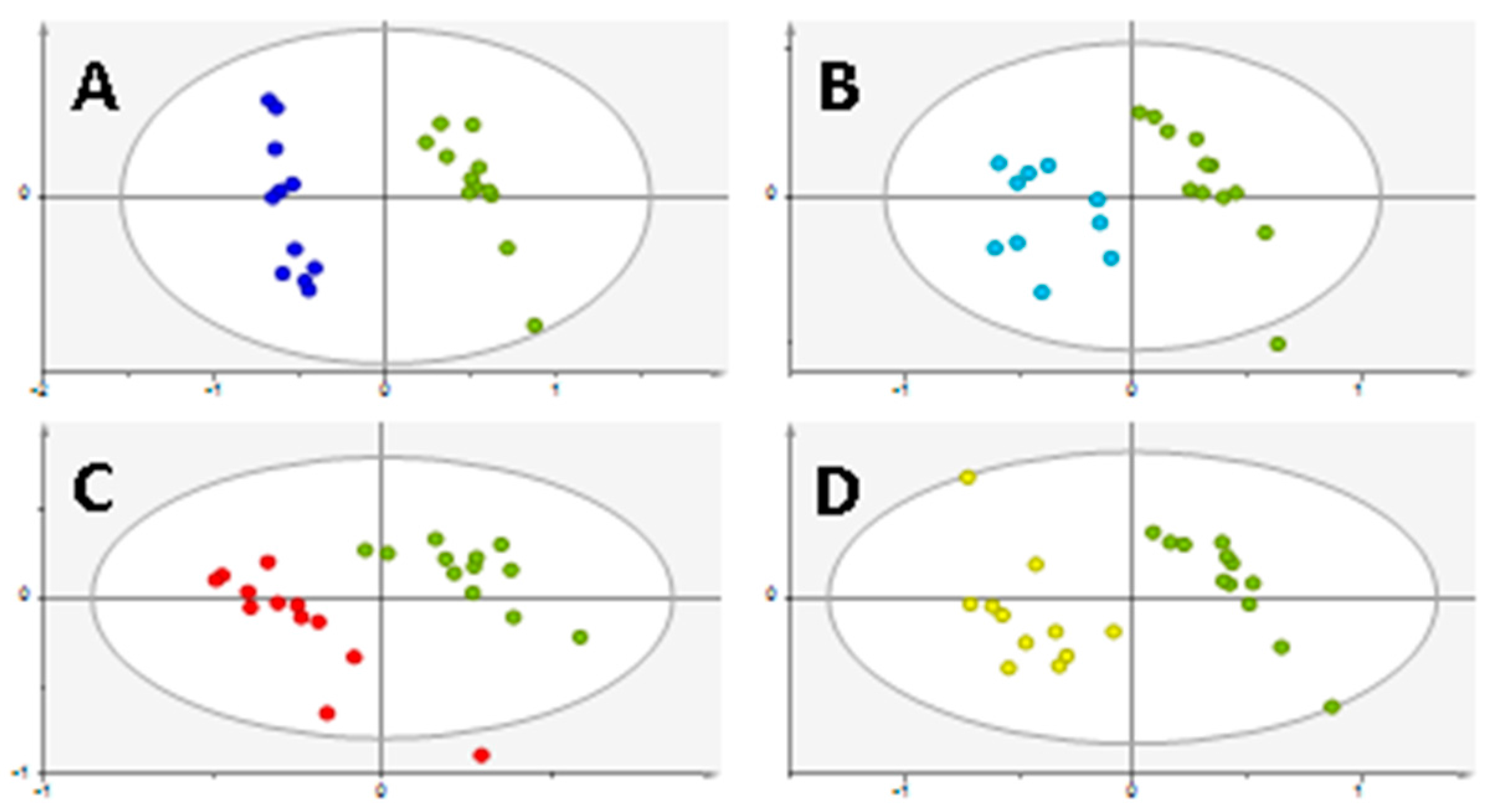
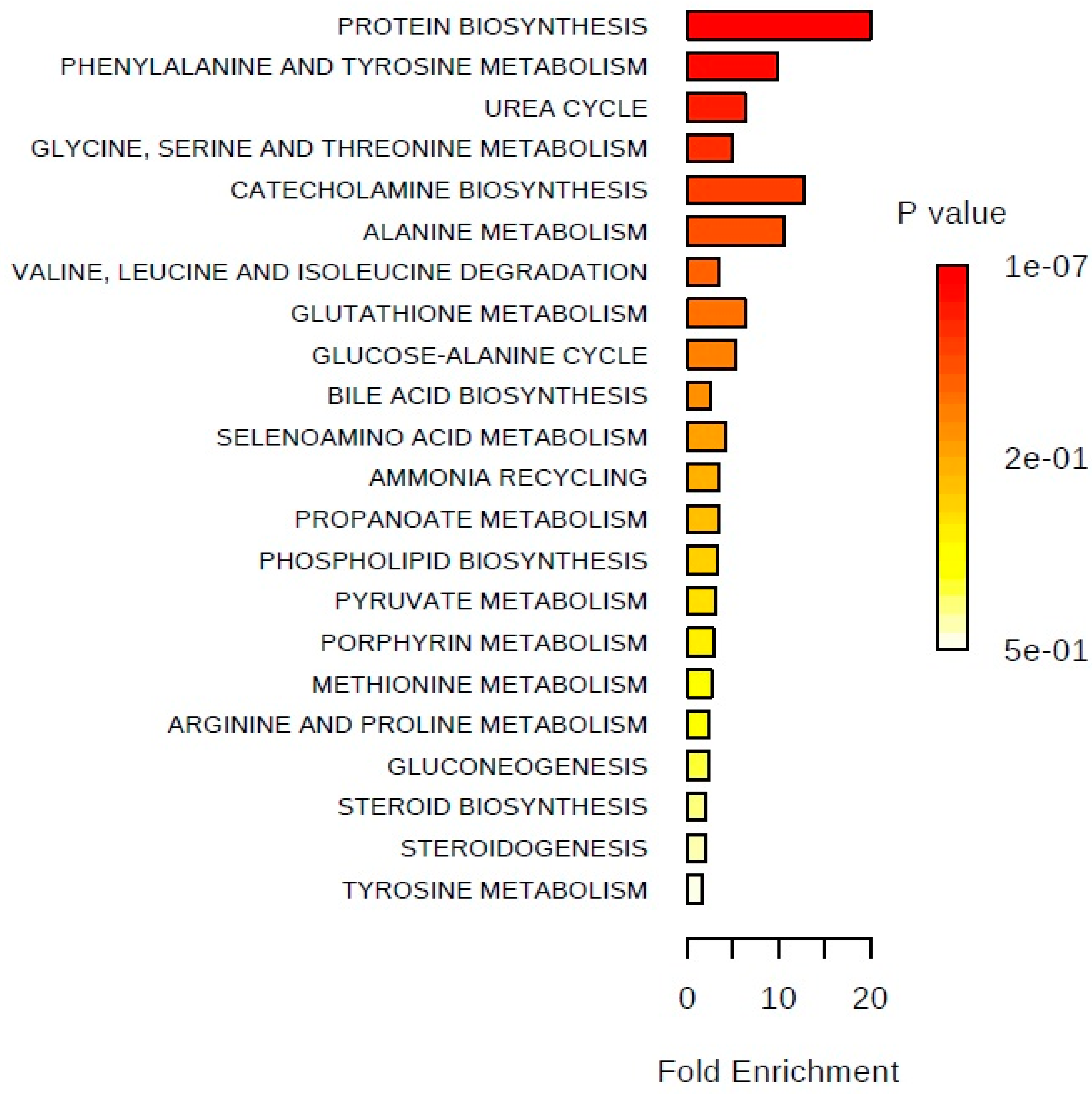
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Sample Collection
4.4. Metabolites Derivatization
4.5. GC-MS System and Data Acquisition
4.5.1. GC-MS Analysis
4.5.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rigau, M.; Olivan, M.; Garcia, M.; Sequeiros, T.; Montes, M.; Colas, E.; Llaurado, M.; Planas, J.; Torres, I.; Morote, J.; et al. The Present and Future of Prostate Cancer Urine Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12620–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decelle, E.A.; Cheng, L.L. High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning 1 h Mrs in Prostate Cancer. NMR Biomed. 2014, 27, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trock, B.J. Application of Metabolomics to Prostate Cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2011, 29, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimakakos, A.; Armakolas, A.; Koutsilieris, M. Novel Tools for Prostate Cancer Prognosis, Diagnosis, and Follow-Up. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 890697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrate, A.; Lughezzani, G.; Gadda, G.M.; Lista, G.; Kinzikeeva, E.; Fossati, N.; Larcher, A.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Mistretta, F.; Buffi, N.; et al. Clinical Use of [−2] Propsa (P2psa) and Its Derivatives (%P2psa and Prostate Health Index) for the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Review of the Literature. Korean J. Urol. 2014, 55, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, R.E.; Shariat, S.F.; Nguyen, C.V.; Farr, A.; Weinberg, A.D.; Morton, R.A.; Richardson, B.; Bernard, D.; Slawin, K.M. Variation in Prostate Specific Antigen Results from 2 Different Assay Platforms: Clinical Impact on 2304 Patients Undergoing Prostate Cancer Screening. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 2234–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, V.A.; U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Prostate Cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic Profiles Delineate Potential Role for Sarcosine in Prostate Cancer Progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.P.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Ateeq, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Athanikar, J.N.; Yocum, A.K.; Mehra, R.; Siddiqui, J.; Palapattu, G.; Wei, J.T.; et al. The Role of Sarcosine Metabolism in Prostate Cancer Progression. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Gupta, A.; Mandhani, A.; Sankhwar, S.N. Metabolomics-Derived Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: Fact or Fiction? J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDunn, J.E.; Li, Z.; Adam, K.P.; Neri, B.P.; Wolfert, R.L.; Milburn, M.V.; Lotan, Y.; Wheeler, T.M. Metabolomic Signatures of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2013, 73, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putluri, N.; Shojaie, A.; Vasu, V.T.; Nalluri, S.; Vareed, S.K.; Putluri, V.; Vivekanandan-Giri, A.; Byun, J.; Pennathur, S.; Sana, T.R.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling Reveals a Role for Androgen in Activating Amino Acid Metabolism and Methylation in Prostate Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liu, T.; Ma, C.; Xue, R.; Deng, C.; Zeng, H.; Shen, X. Gc/Ms-Based Metabolomic Approach to Validate the Role of Urinary Sarcosine and Target Biomarkers for Human Prostate Cancer by Microwave-Assisted Derivatization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzmik, F.; Stephan, C.; Lein, M.; Miller, K.; Kamlage, B.; Bethan, B.; Kristiansen, G.; Jung, K. Sarcosine in Prostate Cancer Tissue Is Not a Differential Metabolite for Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness and Biochemical Progression. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzmik, F.; Stephan, C.; Miller, K.; Schrader, M.; Erbersdobler, A.; Kristiansen, G.; Lein, M.; Jung, K. Sarcosine in Urine after Digital Rectal Examination Fails as a Marker in Prostate Cancer Detection and Identification of Aggressive Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.R.; Mde, L.B.; Carvalho, M.; de Pinho, P.G. Biomarker Discovery in Human Prostate Cancer: An Update in Metabolomics Studies. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuperlovic-Culf, M.; Barnett, D.A.; Culf, A.S.; Chute, I. Cell Culture Metabolomics: Applications and Future Directions. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halama, A. Metabolomics in Cell Culture—A Strategy to Study Crucial Metabolic Pathways in Cancer Development and the Response to Treatment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 564, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Xu, H.; Qiu, S.; Wang, X. Cell Metabolomics. OMICS 2013, 17, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshari, K.R.; Sriram, R.; van Criekinge, M.; Wilson, D.M.; Wang, Z.J.; Vigneron, D.B.; Peehl, D.M.; Kurhanewicz, J. Metabolic Reprogramming and Validation of Hyperpolarized 13c Lactate as a Prostate Cancer Biomarker Using a Human Prostate Tissue Slice Culture Bioreactor. Prostate 2013, 73, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcias, G.; Erdmann, E.; Lapouge, G.; Siebert, C.; Barthelemy, P.; Duclos, B.; Bergerat, J.P.; Ceraline, J.; Kurtz, J.E. Identification of Novel Truncated Androgen Receptor (Ar) Mutants Including Unreported Pre-Mrna Splicing Variants in the 22rv1 Hormone-Refractory Prostate Cancer (Pca) Cell Line. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. Concepts of Citrate Production and Secretion by Prostate. 1. Metabolic Relationships. Prostate 1991, 18, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, L.C.; Franklin, R.B. Prostatic Fluid Electrolyte Composition for the Screening of Prostate Cancer: A Potential Solution to a Major Problem. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2009, 12, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pertega-Gomes, N.; Baltazar, F. Lactate Transporters in the Context of Prostate Cancer Metabolism: What Do We Know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18333–18348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramautar, R.; Berger, R.; van der Greef, J.; Hankemeier, T. Human Metabolomics: Strategies to Understand Biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarelli, G.; Rutigliano, M.; Galleggiante, V.; Giglio, A.; Palazzo, S.; Ferro, M.; Simone, C.; Bettocchi, C.; Battaglia, M.; Ditonno, P. Metabolomic Profiling for the Identification of Novel Diagnostic Markers in Prostate Cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hardie, R.A.; Hoy, A.J.; van Geldermalsen, M.; Gao, D.; Fazli, L.; Sadowski, M.C.; Balaban, S.; Schreuder, M.; Nagarajah, R.; et al. Targeting Asct2-Mediated Glutamine Uptake Blocks Prostate Cancer Growth and Tumour Development. J. Pathol. 2015, 236, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struck-Lewicka, W.; Kordalewska, M.; Bujak, R.; Mpanga, A.Y.; Markuszewski, M.; Jacyna, J.; Matuszewski, M.; Kaliszan, R.; Markuszewski, M.J. Urine Metabolic Fingerprinting Using Lc-Ms and Gc-Ms Reveals Metabolite Changes in Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 111, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufe, D.W. Mucins in Cancer: Function, Prognosis and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernei, N.; Heger, Z.; Gumulec, J.; Zitka, O.; Masarik, M.; Babula, P.; Eckschlager, T.; Stiborova, M.; Kizek, R.; Adam, V. Sarcosine as a Potential Prostate Cancer Biomarker—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13893–13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Song, R.; Ma, C.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, P.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Lu, X.; et al. Discovery and Validation of Potential Urinary Biomarkers for Bladder Cancer Diagnosis Using a Pseudotargeted Gc-Ms Metabolomics Method. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20719–20728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, Y.; Higashiyama, M.; Gochi, A.; Akaike, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Miura, T.; Saruki, N.; Bando, E.; Kimura, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Plasma Free Amino Acid Profiling of Five Types of Cancer Patients and Its Application for Early Detection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teahan, O.; Bevan, C.L.; Waxman, J.; Keun, H.C. Metabolic Signatures of Malignant Progression in Prostate Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eley, H.L.; Russell, S.T.; Baxter, J.H.; Mukerji, P.; Tisdale, M.J. Signaling Pathways Initiated by Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate to Attenuate the Depression of Protein Synthesis in Skeletal Muscle in Response to Cachectic Stimuli. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E923–E931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Reszka, R.; Kamlage, B.; Bethan, B.; Stephan, C.; Lein, M.; Kristiansen, G. Tissue Metabolite Profiling Identifies Differentiating and Prognostic Biomarkers for Prostate Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2914–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thysell, E.; Surowiec, I.; Hornberg, E.; Crnalic, S.; Widmark, A.; Johansson, A.I.; Stattin, P.; Bergh, A.; Moritz, T.; Antti, H.; et al. Metabolomic Characterization of Human Prostate Cancer Bone Metastases Reveals Increased Levels of Cholesterol. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A.B.; Fink, C.S.; Williams, H.; Kim, U. In Vitro and in Vivo (Scid Mice) Effects of Phytosterols on the Growth and Dissemination of Human Prostate Cancer Pc-3 Cells. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2001, 10, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Mao, J.; Ai, J.; Deng, Y.; Roth, M.R.; Pound, C.; Henegar, J.; Welti, R.; Bigler, S.A. Identification of Plasma Lipid Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer by Lipidomics and Bioinformatics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, M.G.; Keshari, K.R.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Simko, J.P.; Shinohara, K.; Carroll, P.R.; Zektzer, A.S.; Kurhanewicz, J. Quantification of Choline- and Ethanolamine-Containing Metabolites in Human Prostate Tissues Using 1 h Hr-Mas Total Correlation Spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintz, A.; Wang, L.; Ponde, D.E. Comparison of Radiolabeled Choline and Ethanolamine as Probe for Cancer Detection. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. Hmdb: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Knox, C.; Guo, A.C.; Eisner, R.; Young, N.; Gautam, B.; Hau, D.D.; Psychogios, N.; Dong, E.; Bouatra, S.; et al. Hmdb: A Knowledgebase for the Human Metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D603–D610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. Hmdb 3.0—The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, X.; Jones, C.M.; Long, T.Q.; Monge, M.E.; Zhou, M.; Walker, L.D.; Mezencev, R.; Gray, A.; McDonald, J.F.; Fernandez, F.M. Feasibility of Detecting Prostate Cancer by Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Serum Metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3444–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saylor, P.J.; Karoly, E.D.; Smith, M.R. Prospective Study of Changes in the Metabolomic Profiles of Men During Their First Three Months of Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, F.L.; Allen, N.E.; Appleby, P.N.; Overvad, K.; Aardestrup, I.V.; Johnsen, N.F.; Tjonneland, A.; Linseisen, J.; Kaaks, R.; Boeing, H.; et al. Fatty Acid Composition of Plasma Phospholipids and Risk of Prostate Cancer in a Case-Control Analysis Nested within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Msea: A Web-Based Tool to Identify Biologically Meaningful Patterns in Quantitative Metabolomic Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W71–W77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, D.M.; Vinholes, J.; de Pinho, P.G.; Valentao, P.; Mouga, T.; Teixeira, N.; Andrade, P.B. A Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Multi-Target Method for the Simultaneous Analysis of Three Classes of Metabolites in Marine Organisms. Talanta 2012, 100, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, A.; Ferrarini, A.; Rey-Stolle, F.; Garcia, A.; Barbas, C. From Sample Treatment to Biomarker Discovery: A Tutorial for Untargeted Metabolomics Based on Gc-(Ei)-Q-Ms. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 900, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Oresic, M. Mzmine 2: Modular Framework for Processing, Visualizing, and Analyzing Mass Spectrometry-Based Molecular Profile Data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berben, L.; Sereika, S.M.; Engberg, S. Effect Size Estimation: Methods and Examples. Int. J. Nurs Stud. 2012, 49, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aickin, M.; Gensler, H. Adjusting for Multiple Testing When Reporting Research Results: The Bonferroni vs. Holm Methods. Am. J. Public Health 1996, 86, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Wilson, M.; Wishart, D.S. Translational Biomarker Discovery in Clinical Metabolomics: An Introductory Tutorial. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Chemical Name (IUPAC) or Common Name | 22RV1 vs. PNT2 | PC3 vs. PNT2 | DU145 vs. PNT2 | LNCaP vs. PNT2 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p Value | Variation ± Uncertainty | ES ± ESSE | AUC | p Value | Variation ± Uncertainty | ES ± ESSE | AUC | p Value | Variation ± Uncertainty | ES ± ESSE | AUC | p Value | Variation ± Uncertainty | ES ± ESSE | AUC | |
| Amino acids | ||||||||||||||||
| L-Alanine | 0.0034 | ↓ 24.92 ± 8.48 | ↓ 1.18 ± 0.90 | 0.85 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 53.75 ± 8.88 | ↓ 3.26 ± 1.20 | 0.98 | 0.0171 | ↓ 24.11 ± 9.88 | ↓ 1.13 ± 0.85 | 0.77 | ||||
| Glycine | 0.0004 P | ↑ 335.89 ± 27.22 | ↑ 1.99 ± 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.0015 | ↑ 111.09 ± 27.01 | ↑ 1.35 ± 0.93 | 0.88 | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | 0.0042 | ↑ 118.14 ± 20.13 | ↑ 1.57 ± 0.91 | 0.86 | |
| Sarcosine (N-methylglycine) | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | |||||||||||||
| β-Alanine | <0.0001 P | ↓ 83.07 ± 21.15 | ↓ 2.52 ± 1.07 | 0.99 | 0.0066 | ↑ 78.49 ± 18.46 | ↑ 1.43 ± 0.94 | 0.84 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 729.64 ± 20.99 | ↑ 2.95 ± 1.14 | 1 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 87.83 ± 21.39 | ↓ 2.73 ± 1.12 | 1 |
| L-Valine | <0.0001 P | ↓ 92.03 ± 12.16 | ↓ 5.20 ± 1.70 | 1 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 62.12 ± 15.18 | ↓ 2.40 ± 1.10 | 0.97 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 58.58 ± 11.82 | ↓ 2.76 ± 1.10 | 0.97 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 71.40 ± 10.70 | ↓ 3.92 ± 1.38 | 1 |
| L-Leucine | <0.0001 P | ↓ 72.24 ± 10.06 | ↓ 4.29 ± 1.47 | 1 | 0.0420 | ↓ 25.18 ± 12.60 | ↓ 1.00 ± 0.88 | 0.75 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 45.52 ± 10.07 | ↓ 2.97 ± 1.16 | 0.95 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 51.55 ± 9.06 | ↓ 2.97 ± 1.16 | 0.98 |
| L-Proline | >0.05 | ↑ 21.11 ± 17.59 | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | ||||
| L-Threonine | 0.0187 | ↓ 37.40 ± 17.94 | ↓ 1.02 ± 0.84 | 0.79 | 0.0104 | ↓ 39.33 ± 16.31 | ↓ 1.18 ± 0.90 | 0.79 | 0.0499 | ↓ 26.44 ± 13.94 | ↓ 0.86 ± 0.81 | 0.0445 | ↓ 27.58 ± 14.13 | ↓ 0.88 ± 0.82 | 0.75 | |
| L-Aspartic acid | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | >0.05 | ↓ 25.32 ± 22.20 | ↓ | ||||
| L-Glutamine | <0.0001 P | ↑ 122.44 ± 13.48 | ↑ 2.36 ± 1.04 | 0.95 | >0.05 | ↑ 35.65 ± 19.27 | ↑ | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | <0.0001 P | ↑ 108.67 ± 12.83 | ↑ 2.29 ± 1.03 | 0.92 | ||
| Phenylalanine | 0.0075 | ↑ 29.96 ± 8.45 | ↑ 1.23 ± 0.87 | 1 | 0.0056 | ↓ 35.65 ± 13.25 | ↓ 1.34 ± 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.0447 | ↓ 20.14 ± 10.71 | ↓ | 0.0036 | ↓ 42.45 ± 13.45 | ↓ 1.59 ± 0.91 | 0.85 | |
| L-Tyrosine | 0.0002 P | ↑ 43.50 ± 7.52 | ↑ 1.92 ± 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.0322 | ↑ 27.81 ± 10.49 | ↑ 1.04 ± 0.89 | 0.73 | 0.0406 | ↓ 20.27 ± 8.09 | ↓ 0.90 ± 0.81 | 0.76 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 44.38 ± 9.74 | ↓ 2.28 ± 1.03 | 0.93 |
| Sugars | ||||||||||||||||
| Sorbose | <0.0001 P | ↓ 73.09 ± 10.30 | ↓ 4.22 ± 1.45 | 1 | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | 0.0009 P | ↓ 37.57 ± 11.50 | ↓ 1.59 ± 0.89 | 0.86 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 64.31 ± 10.68 | ↓ 3.41 ± 1.26 | 1 | |
| Organic acids derivatives | ||||||||||||||||
| Lactic Acid | <0.0001 P | ↓ 84.79 ± 7.44 | ↓ 7.43 ± 2.29 | 1 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 31.78 ± 6.23 | ↓ 2.38 ± 1.10 | 0.96 | 0.0213 | ↓ 18.06 ± 7.62 | ↓ 1.03 ± 0.85 | 0.81 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 55.39 ± 7.88 | ↓ 3.83 ± 1.36 | 1 |
| 3-Hydroxy-propionic acid | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | |||||||||||||
| 2-Butenoic acid | >0.05 | ↑ 29.61 ± 20.94 | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ 28.98 ± 11.45 | ↑ | <0.0001 P | ↑ 130.36 ± 12.10 | ↑ 2.57 ± 1.06 | 0.99 | >0.05 | ↑ 20.13 ± 14.41 | ↑ | |||
| 3-Hydroxy-isovaleric acid | <0.0001 P | ↑ 802.11 ± 48.46 | ↑ 1.84 ± 1.00 | 1 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 789.83 ± 18.65 | ↑ 3.37 ± 1.23 | 1 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 3161.67 ± 34.43 | ↑ 2.40 ± 1.04 | 1 | ||||
| Toluic acid | >0.05 | ↓ 16.04 ± 10.59 | ↓ | |||||||||||||
| Galacturonic acid | >0.05 | ↑ 115.65 ± 78.05 | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | ||||
| Fatty acids | ||||||||||||||||
| Tridecanoic acid | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ 63.28 ± 58.62 | ↑ | ||||||||||
| Palmitic Acid | >0.05 | ↓ 13.54 ± 6.80 | ↓ 0.86 ± 0.83 | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | 0.0424 | ↑ 21.27 ± 8.34 | ↑ 0.95 ± 0.84 | 0.78 | |||
| 9-Hexadecenoic acid (palmitoleic acid) | <0.0001 P | ↑ 284.2 ± 18.01 | ↑ 2.81 ± 1.13 | 1 | 0.0048 | ↑ 85.75 ± 23.12 | ↑ 1.02 ± 0.83 | 0.83 | ||||||||
| 13-Octadecenoic acid | <0.0001 P | ↑ 560.66 ± 18.06 | ↑ 3.54 ± 1.29 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Steroids | ||||||||||||||||
| Cholesterol | 0.0004 P | ↑ 110.4 ± 15.40 | ↑ 1.96 ± 0.97 | 0.91 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 65.91 ± 7.57 | ↑ 3.01 ± 1.23 | 0.99 | >0.05 | ↑ 20.85 ± 12.10 | ↑ | 0.0004 P | ↑ 73.42 ± 14.39 | ↑ 1.58 ± 0.91 | 0.91 | |
| Others | ||||||||||||||||
| Ethanolamine | <0.0001 P | ↓ 97.18 ± 18.37 | ↓ 3.80 ± 1.35 | 1 | 0.0052 | ↓ 54.13 ± 21.78 | ↓ 1.41 ± 0.93 | 0.83 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 80.14 ± 18.04 | ↓ 2.92 ± 1.31 | 0.99 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 89.19 ± 17.26 | ↓ 3.47 ± 1.28 | 1 |
| Urea | 0.0002 P | ↓ 36.52 ± 9.04 | ↓ 1.93 ± 0.97 | 0.92 | <0.0001p | ↓ 45.10 ± 9.41 | ↓ 2.36 ± 1.09 | 0.97 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 47.59 ± 9.66 | ↓ 2.31 ± 1.01 | 0.97 | >0.05 | ↑ 8.39 ± 7.20 | ↑ | |
| Glycerol | >0.05 | ↑ 32.43 ± 19.85 | ↑ | 0.0005 P | ↓ 60.06 ± 18.39 | ↓ 1.84 ± 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.0004 P | ↓ 58.18 ± 15.77 | ↓ 1.97 ± 0.97 | 0.98 | |||||
| Creatinine | >0.05 | ↓ 51.11 ± 46.5 | ↓ | |||||||||||||
| Methyl 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-3-O-methyl-a-d-galactopyrano-side | >0.05 | ↑ 196.92 ± 50.03 | ↑ 1.05 ± 0.89 | 0.0037 | ↑ 88.07 ± 16.92 | ↑ 1.42 ± 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.0050 | ↑ 374.03 ± 5.88 | ↑ 1.57 ± 0.91 | 0.89 | |||||
| Unknowns | ||||||||||||||||
| Unknown 1 | >0.05 | ↑ 69.09 ± 27.41 | ↑ 0.90 ± 0.87 | 0.0001 P | ↓ 70.35 ± 22.44 | ↓ 1.82 ± 0.94 | 0.94 | |||||||||
| Unknown 2 | 0.0309 | ↑ 55.75 ± 17.47 | ↑ 1.04 ± 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.0006 P | ↓ 44.67 ± 12.70 | ↓ 1.67 ± 0.97 | 0.69 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 56.86 ± 15.31 | ↓ 2.05 ± 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.0321 | ↑ 93.47 ± 25.21 | ↑ 1.07 ± 0.84 | 0.70 |
| Unknown 3 | >0.05 | ↓ 54.68 ± 39.46 | ↓ | >0.05 | ↓ 37.52 ± 36.65 | ↓ | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | >0.05 | ↓ 40.90 ± 32.77 | ↓ | ||||
| Unknown 4 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 182.71 ± 16.77 | ↑ 2.97 ± 1.22 | 1 | 0.0018 | ↑ 82.93 ± 11.28 | ↑ 2.05 ± 0.97 | 0.86 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 64.27 ± 7.16 | ↑ 2.80 ± 1.13 | 0.95 | ||||
| Unknown 5 | >0.05 | ↑ 47.15 ± 41.17 | ↑ | |||||||||||||
| Unknown 6 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 222.97 ± 14.87 | ↑ 3.03 ± 1.17 | 1 | 0.0008 P | ↑ 132.53 ± 18.38 | ↑ 2.18 ± 1.06 | 0.95 | 0.0078 | ↑ 70.10 ± 16.23 | ↑ 1.26 ± 0.85 | 0.83 | ||||
| Unknown 7 | >0.05 | ↓ | ↓ | >0.05 | ↑ 63.22 ± 58.62 | ↑ | ||||||||||
| Unknown 8 | 0.0002 P | ↑ 71.71 ± 10.89 | ↑ 1.91 ± 0.94 | 0.93 | ||||||||||||
| Unknown 9 | 0.0106 | ↑ 25.74 ± 8.04 | ↑ 1.16 ± 0.85 | 0.81 | >0.05 | ↓ 16.43 ± 9.53 | ↓ | 0.0014 | ↑ 27.91 ± 7.39 | ↑ 1.31 ± 0.87 | 0.87 | >0.05 | ↑ 15.5 ± 7.07 | ↑ | ||
| Unknown 10 | 0.0252 | ↑ 24.74 ± 8.62 | ↑ 1.04 ± 0.84 | 0.79 | 0.0032 | ↓ 29.52 ± 9.79 | ↓ 1.48 ± 0.94 | 0.90 | >0.05 | ↑ 11.09 ± 7.51 | ↑ | 0.0256 | ↑ 20.39 ± 7.37 | ↑ 1.02 ± 0.84 | 0.76 | |
| Unknown 11 | <0.0001 P | ↑ 147.83 ± 10.00 | ↑ 3.53 ± 1.29 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Unknown 12 | >0.05 | ↑ 25.39 ± 16.87 | ↑ | |||||||||||||
| Unknown 13 | <0.0001 P | ↓ 56.54 ± 9.08 | ↓ 3.52 ± 1.35 | 0.99 | ||||||||||||
| Unknown 14 | >0.05 | ↑ | ↑ | |||||||||||||
| Unknown | <0.0001 P | ↑ 326.66 ± 19.57 | ↑ 2.50 ± 1.04 | 0.96 | ||||||||||||
| Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|
| 22RV1 vs. PNT2 | 100% | 100% |
| PC3 vs. PNT2 | 100% | 100% |
| DU145 vs. PNT2 | 100% | 100% |
| LNCaP vs. PNT2 | 97% | 100% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima, A.R.; Araújo, A.M.; Pinto, J.; Jerónimo, C.; Henrique, R.; Bastos, M.D.L.; Carvalho, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. GC-MS-Based Endometabolome Analysis Differentiates Prostate Cancer from Normal Prostate Cells. Metabolites 2018, 8, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010023
Lima AR, Araújo AM, Pinto J, Jerónimo C, Henrique R, Bastos MDL, Carvalho M, Guedes de Pinho P. GC-MS-Based Endometabolome Analysis Differentiates Prostate Cancer from Normal Prostate Cells. Metabolites. 2018; 8(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima, Ana Rita, Ana Margarida Araújo, Joana Pinto, Carmen Jerónimo, Rui Henrique, Maria De Lourdes Bastos, Márcia Carvalho, and Paula Guedes de Pinho. 2018. "GC-MS-Based Endometabolome Analysis Differentiates Prostate Cancer from Normal Prostate Cells" Metabolites 8, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010023
APA StyleLima, A. R., Araújo, A. M., Pinto, J., Jerónimo, C., Henrique, R., Bastos, M. D. L., Carvalho, M., & Guedes de Pinho, P. (2018). GC-MS-Based Endometabolome Analysis Differentiates Prostate Cancer from Normal Prostate Cells. Metabolites, 8(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010023












