An Update on the Metabolic Roles of Carbonic Anhydrases in the Model Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Aspects of Carbonic Anhydrases
2.1. Carbonic Anhydrases in Photosynthetic Organisms
2.2. Carbonic Anhydrases in Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
2.1.1. α-Carbonic Anhydrase 1
2.1.2. α-Carbonic Anhydrase 2
2.1.3. α-Carbonic Anhydrase 3
2.1.4. β-Carbonic Anhydrase 4
2.1.5. β-Carbonic Anhydrase 5
2.1.6. β-Carbonic Anhydrase 6
2.1.7. β-Carbonic Anhydrase 7
2.1.8. β-Carbonic Anhydrase 8
2.1.9. β-Carbonic Anhydrase 9
2.1.10. Limiting CO2 Inducible-B Protein/β-Carbonic Anhydrase Family
2.1.11. γ-Carbonic Anhydrases
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; AlOthman, Z.; Osman, S.M.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Biochemical characterization of recombinant beta-carbonic anhydrase (PgiCAb) identified in the genome of the oral pathogenic bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. The eta-class carbonic anhydrases as drug targets for antimalarial agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, V.M.; Kaufman, G.K.; Urbach, A.R.; Gitlin, I.; Gudiksen, K.L.; Weibel, D.B.; Whitesides, G.M. Carbonic anhydrase as a model for biophysical and physical-organic studies of proteins and protein-ligand binding. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 946–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikutani, S.; Nakajima, K.; Nagasato, C.; Tsuji, Y.; Miyatake, A.; Matsuda, Y. Thylakoid luminal theta-carbonic anhydrase critical for growth and photosynthesis in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9828–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. An overview of the alpha-, beta- and gamma-carbonic anhydrases from Bacteria: Can bacterial carbonic anhydrases shed new light on evolution of bacteria? J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floryszak-Wieczorek, J.; Arasimowicz-Jelonek, M. The multifunctional face of plant carbonic anhydrase. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 11, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. An overview of the bacterial carbonic anhydrases. Metabolites 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMario, R.J.; Clayton, H.; Mukherjee, A.; Ludwig, M.; Moroney, J.V. Plant carbonic anhydrases: Structures, locations, evolution, and physiological roles. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Sun, J.; Wunder, T.; Tang, D.; Cousins, A.B.; Sze, S.K.; Mueller-Cajar, O.; Gao, Y.G. Structural insights into the LCIB protein family reveals a new group of beta-carbonic anhydrases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14716–14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindskog, S. Structure and mechanism of carbonic anhydrase. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 74, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroney, J.V.; Ma, Y.; Frey, W.D.; Fusilier, K.A.; Pham, T.T.; Simms, T.A.; DiMario, R.J.; Yang, J.; Mukherjee, B. The carbonic anhydrase isoforms of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Intracellular location, expression, and physiological roles. Photosynth. Res. 2011, 109, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, D.T.; Franklin, L.A.; Samuelsson, G.; Badger, M.R. The Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cia3 mutant lacking a thylakoid lumen-localized carbonic anhydrase is limited by CO2 supply to rubisco and not photosystem II function in vivo. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinder, L.C.M.; Chen, C.; Leib, R.D.; Patena, W.; Blum, S.R.; Rodman, M.; Ramundo, S.; Adams, C.M.; Jonikas, M.C. A spatial interactome reveals the protein organization of the algal CO2-concentrating mechanism. Cell 2017, 171, 133–147.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, C.V.; Chapman, K.D. Biochemical and molecular inhibition of plastidial carbonic anhydrase reduces the incorporation of acetate into lipids in cotton embryos and tobacco cell suspensions and leaves. Plant Physiol. 2002, 128, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R.P. Multiple roles of carbonic anhydrase in cellular transport and metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1996, 58, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geers, C.; Gros, G. Carbon dioxide transport and carbonic anhydrase in blood and muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 681–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, D.; Yang, S.; Cui, Q. Proton transfer function of carbonic anhydrase: Insights from QM/MM simulations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Taraphder, S. Role of protein motions on proton transfer pathways in human carbonic anhydrase II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missner, A.; Kugler, P.; Saparov, S.M.; Sommer, K.; Mathai, J.C.; Zeidel, M.L.; Pohl, P. Carbon dioxide transport through membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25340–25347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkkila, S.; Parkkila, A.K.; Rajaniemi, H.; Shah, G.N.; Grubb, J.H.; Waheed, A.; Sly, W.S. Expression of membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase XIV on neurons and axons in mouse and human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Catalytic and inhibition mechanisms, distribution and physiological roles. In Carbonic Anhydrase: Its Inhibitors and Activators; Supuran, C.T., Scozzafava, A., Conway, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chegwidden, W.R.; Dodgson, S.J.; Spencer, I.M. The Roles of Carbonic Anhydrase in Metabolism, Cell Growth and Cancer in Animals; Chegwidden, W.R., Carter, N.D., Edwards, Y.H., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 90, pp. 343–363. [Google Scholar]
- Woolley, P. Models for metal ion function in carbonic anhydrase. Nature 1975, 258, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esbaugh, A.J.; Tufts, B.L. The structure and function of carbonic anhydrase isozymes in the respiratory system of vertebrates. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2006, 154, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodgson, S.J.; Forster, R.E., 2nd. Carbonic anhydrase: Inhibition results in decreased urea production by hepatocytes. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 60, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, C.V.; Schraer, H.; Anderson, R.E.; Cao, H. Current studies on the location and function of carbonic anhydrase in osteoclasts. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1984, 429, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R.P. The function of invertebrate carbonic anhydrase in ion transport. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1984, 429, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Song, B.; Morel, F.M. Diversity of the cadmium-containing carbonic anhydrase in marine diatoms and natural waters. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMario, R.J.; Machingura, M.C.; Waldrop, G.L.; Moroney, J.V. The many types of carbonic anhydrases in photosynthetic organisms. Plant Sci. 2018, 268, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewett-Emmett, D. Evolution and Distribution of the Carbonic Anhydrase Gene Families; Chegwidden, W.R., Carter, N.D., Edwards, Y.H., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 90, pp. 29–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Feng, L.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Shi, Y.; Morel, F.M. Structure and metal exchange in the cadmium carbonic anhydrase of marine diatoms. Nature 2008, 452, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.S.; Jakubzick, C.; Whittam, T.S.; Ferry, J.G. Carbonic anhydrase is an ancient enzyme widespread in prokaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 15184–15189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.B.; Lane, T.W.; Morel, F.M.M. Carbonic anhydrase in the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.R.; Zheng, H.; Shoemaker, D.; Rodriguez, J.; Read, B.A.; Wahlund, T.M. Identification and preliminary characterization of two cDNAs encoding unique carbonic anhydrases from the marine alga Emiliania huxleyi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5500–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, G.; Di Fiore, A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. The zinc coordination pattern in the eta-carbonic anhydrase from Plasmodium falciparum is different from all other carbonic anhydrase genetic families. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangani, S.; Hakansson, K. Crystallographic studies of the binding of protonated and unprotonated inhibitors to carbonic anhydrase using hydrogen sulphide and nitrate anions. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 210, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, D.; Kim, C.U.; Tu, C.; Robbins, A.H.; Gruner, S.M.; Silverman, D.N.; McKenna, R. Structural and kinetic effects on changes in the CO2 binding pocket of human carbonic anhydrase II. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 9156–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronk, J.D.; Rowlett, R.S.; Zhang, K.Y.; Tu, C.; Endrizzi, J.A.; Lee, J.; Gareiss, P.C.; Preiss, J.R. Identification of a novel noncatalytic bicarbonate binding site in eubacterial beta-carbonic anhydrase. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 4351–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, T.M.; Alber, B.E.; Kisker, C.; Ferry, J.G.; Rees, D.C. A closer look at the active site of gamma-class carbonic anhydrases: High-resolution crystallographic studies of the carbonic anhydrase from Methanosarcina thermophila. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 9222–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisker, C.; Schindelin, H.; Alber, B.E.; Ferry, J.G.; Rees, D.C. A left-hand beta-helix revealed by the crystal structure of a carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, R.; Margaria, R.; Meldrum, N.; Roughton, F. The CO2 catalyst present in blood. J. Physiol. 1932, 75, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum, N.; Roughton, F. Some properties of carbonic anhydrase, the CO2 enzyme present in blood. J. Physiol. 1932, 75, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Aspatwar, A.; Tolvanen, M.E.; Parkkila, S. Phylogeny and expression of carbonic anhydrase-related proteins. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neish, A.C. Studies on chloroplasts: Their chemical composition and the distribution of certain metabolites between the chloroplasts and the remainder of the leaf. Biochem. J. 1939, 33, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Bacterial carbonic anhydrases as drug targets: Toward novel antibiotics? Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, E.H.; McLendon, G.L.; Morel, F.M.; Lane, T.W.; Prince, R.C.; Pickering, I.J.; George, G.N. The active site structure of Thalassiosira weissflogii carbonic anhydrase 1. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 12128–12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez Covarrubias, A.; Larsson, A.M.; Hogbom, M.; Lindberg, J.; Bergfors, T.; Björkelid, C.; Mowbray, S.L.; Unge, T.; Jones, T.A. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18782–18789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimber, M.S.; Pai, E.F. The active site architecture of Pisum sativum beta-carbonic anhydrase is a mirror image of that of alpha-carbonic anhydrases. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.S.; Cosper, N.J.; Stalhandske, C.; Scott, R.A.; Ferry, J.G. Structural and kinetic characterization of an archaeal beta-class carbonic anhydrase. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 6605–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strop, P.; Smith, K.S.; Iverson, T.M.; Ferry, J.G.; Rees, D.C. Crystal structure of the “cab”-type beta class carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10299–10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bury-Mone, S.; Mendz, G.L.; Ball, G.E.; Thibonnier, M.; Stingl, K.; Ecobichon, C.; Avé, P.; Huerre, M.; Labigne, A.; Thiberge, J.M.; et al. Roles of alpha and beta carbonic anhydrases of Helicobacter pylori in the urease-dependent response to acidity and in colonization of the murine gastric mucosa. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, S.J.; Bermudez, L.E. Identification of Bicarbonate as a Trigger and Genes Involved with Extracellular DNA Export in Mycobacterial Biofilms. mBio 2016, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.K.; Colvin, C.J.; Needle, D.B.; Mba Medie, F.; Champion, P.A.; Abramovitch, R.B. The Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor Ethoxzolamide Inhibits the Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR Regulon and Esx-1 Secretion and Attenuates Virulence. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4436–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, G.; Perales, M.; Fornasari, M.S.; Colaneri, A.; Gonzalez-Schain, N.; Gomez-Casati, D.; Zimmermann, S.; Brennicke, A.; Araya, A.; Ferry, J.G.; et al. Gamma carbonic anhydrases in plant mitochondria. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 55, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alber, B.E.; Ferry, J.G. A carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6909–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macauley, S.R.; Zimmerman, S.A.; Apolinario, E.E.; Evilia, C.; Hou, Y.M.; Ferry, J.G.; Sowers, K.R. The archetype gamma-class carbonic anhydrase, Cam, contains iron when synthesized in vivo. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alber, B.E.; Colangelo, C.M.; Dong, J.; Stalhandske, C.M.; Baird, T.T.; Tu, C.; Fierke, C.A.; Silverman, D.N.; Scott, R.A.; Ferry, J.G. Kinetic and spectroscopic characterization of the gamma-carbonic anhydrase from the methanoarchaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 13119–13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, S.A.; Ferry, J.G. Proposal for a hydrogen bond network in the active site of the prototypic gamma-class carbonic anhydrase. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 5149–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinn, P.J.; Morel, F.M. Expression and regulation of carbonic anhydrases in the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana and in natural phytoplankton assemblages from Great Bay, New Jersey. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterio, V.; Langella, E.; Viparelli, F.; Vullo, D.; Ascione, G.; Dathan, N.A.; Morel, F.M.; Supuran, C.T.; De Simone, G.; Monti, S.M. Structural and inhibition insights into carbonic anhydrase CDCA1 from the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, K.L.; Castel, S.E.; de Araujo, C.; Espie, G.S.; Kimber, M.S. Structural basis of the oxidative activation of the carboxysomal gamma-carbonic anhydrase, CcmM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2455–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, G.D.; Howitt, SM.; Harrison, K.; Badger, M.R. Analysis of a genomic DNA region from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC7942 involved in carboxysome assembly and function. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 2871–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuzawa, H.; Fujiwara, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Dionisio-Sese, M.L.; Miyachi, S. cDNA cloning, sequence, and expression of carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Regulation by environmental CO2 concentration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4383–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, S.; Fukuzawa, H.; Tachiki, A.; Miyachi, S. Structure and differential expression of two genes encoding carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9779–9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnell, J.N.; Gibbs, M.J.; Mason, J.G. Spinach chloroplastic carbonic anhydrase: Nucleotide sequence analysis of cDNA. Plant Physiol. 1990, 92, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T.W.; Browse, J.A.; Volokita, M.; Bartlett, S.G. Spinach carbonic anhydrase primary structure deduced from the sequence of a cDNA clone. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 5414–5417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roeske, C.A.; Ogren, W.L. Nucleotide sequence of pea cDNA encoding chloroplast carbonic anhydrase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mitra, M.; Mason, C.; Lato, S.M.; Ynalvez, R.A.; Xiao, Y.; Moroney, J.V. The carbonic anhydrase gene families of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Can. J. Bot. 2005, 83, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardol, P.; Gonzalez-Halphen, D.; Reyes-Prieto, A.; Baurain, D.; Matagne, R.F.; Remacle, C. The mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation proteome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii deduced from the Genome Sequencing Project. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, G.D.; Badger, M.R.; Woodger, F.J.; Long, B.M. Advances in understanding the cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating-mechanism, CCM, functional components, Ci transporters, diversity, genetic regulation and prospects for engineering into plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 1441–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toguri, T.; Muto, S.; Miyachi, S. Biosynthesis and intracellular processing of carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 158, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucho, K.; Yoshioka, S.; Taniguchi, F.; Ohyama, K.; Fukuzawa, H. Cis-acting elements and DNA-binding proteins involved in CO2-responsive transcriptional activation of Cah1 encoding a periplasmic carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucho, K.; Ohyama, K.; Fukuzawa, H. CO2-responsive transcriptional regulation of CAH1 encoding carbonic anhydrase is mediated by enhancer and silencer regions in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Juvale, P.S.; Wagner, R.L.; Spalding, M.H. Opportunistic proteolytic processing of carbonic anhydrase 1 from Chlamydomonas in Arabidopsis reveals a novel route for protein maturation. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2339–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ishida, S.; Muto, S.; Miyachi, S. Structural analysis of periplasmic carbonic anhydrase 1 of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 214, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamo, T.; Shimogawara, K.; Fukuzawa, H.; Muto, S.; Miyachi, S. Subunit constitution of carbonic anhydrase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 192, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, S.; Taniguchi, F.; Miura, K.; Inoue, T.; Yamano, T.; Fukuzawa, H. The novel Myb transcription factor LCR1 regulates the CO2-responsive gene Cah1, encoding a periplasmic carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachiki, A.; Fukuzawa, H.; Miyachi, S. Characterization of carbonic anhydrase isozyme CA2, which is the CAH2 gene product, in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1992, 56, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, M.; Moroney, J.V. Partial, characterization of a new isoenzyme of carbonic anhydrase isolated from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9719–9723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, J.; Clarke, A.K.; Chen, Z.Y.; Hugghins, S.Y.; Park, Y.I.; Husic, H.D.; Moroney, J.V.; Samuelsson, G. A novel alpha-type carbonic anhydrase associated with the thylakoid membrane in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is required for growth at ambient CO2. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Funke, R.P.; Kovar, J.L.; Weeks, D.P. Intracellular carbonic anhydrase is essential to photosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii at atmospheric levels of CO2: Demonstration via genomic complementation of the high-CO2-requiring mutant ca-1. Plant Physiol. 1997, 114, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, J.; Hiltonen, T.; Husic, H.D.; Ramazanov, Z.; Samuelsson, G. Intracellular carbonic anhydrase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1995, 109, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Rivero, A.; Shutova, T.; Roman, M.J.; Villarejo, A.; Martinez, F. Phosphorylation controls the localization and activation of the lumenal carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.I.; Karlsson, J.; Rojdestvenski, I.; Pronina, N.; Klimov, V.; Oquist, G.; Samuelsson, G. Role of a novel photosystem II-associated carbonic anhydrase in photosynthetic carbon assimilation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. FEBS Lett. 1999, 444, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlloch, R.; Shevela, D.; Hainzl, T.; Grundstrom, C.; Shutova, T.; Messinger, J.; Samuelsson, G.; Sauer-Eriksson, A.E. Crystal structure and functional characterization of photosystem II-associated carbonic anhydrase CAH3 in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinetova, M.A.; Kupriyanova, E.V.; Markelova, A.G.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Pronina, N.A. Identification and functional role of the carbonic anhydrase Cah3 in thylakoid membranes of pyrenoid of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1817, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, M.; Norici, A.; Forssen, M.; Eriksson, M.; Raven, J.A. An anaplerotic role for mitochondrial carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 2126–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villand, P.; Eriksson, M.; Samuelsson, G. Carbon dioxide and light regulation of promoters controlling the expression of mitochondrial carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochem. J. 1997, 327, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eriksson, M.; Karlsson, J.; Ramazanov, Z.; Gardestrom, P.; Samuelsson, G. Discovery of an algal mitochondrial carbonic anhydrase: Molecular cloning and characterization of a low-CO2-induced polypeptide in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12031–12034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ynalvez, R.A.; Xiao, Y.; Ward, A.S.; Cunnusamy, K.; Moroney, J.V. Identification and characterization of two closely related beta-carbonic anhydrases from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 133, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardol, P.; Vanrobaeys, F.; Devreese, B.; Van Beeumen, J.; Matagne, R.F.; Remacle, C. Higher plant-like subunit composition of mitochondrial complex I from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: 31 conserved components among eukaryotes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1658, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.R.; Berry, J.A.; Togasaki, R.K.; Grossman, A.R. Identification of Extracellular Carbonic Anhydrase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1984, 76, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarejo, A.; Shutova, T.; Moskvin, O.; Forssen, M.; Klimov, V.V.; Samuelsson, G. A photosystem II-associated carbonic anhydrase regulates the efficiency of photosynthetic oxygen evolution. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutova, T.; Kenneweg, H.; Buchta, J.; Nikitina, J.; Terentyev, V.; Chernyshov, S.; Andersson, B.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Klimov, V.V.; Dau, H.; et al. The photosystem II-associated Cah3 in Chlamydomonas enhances the O2 evolution rate by proton removal. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, M.; Lato, S.M.; Ynalvez, R.A.; Xiao, Y.; Moroney, J.V. Identification of a new chloroplast carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Stessman, D.J.; Spalding, M.H. The CO2 concentrating mechanism and photosynthetic carbon assimilation in limiting CO2: How Chlamydomonas works against the gradient. Plant J. 2015, 82, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, G.D.; Badger, M.R. Expression of Human Carbonic Anhydrase in the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC7942 Creates a High CO2-Requiring Phenotype: Evidence for a Central Role for Carboxysomes in the CO2 Concentrating Mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1989, 91, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.I.; Kim, J.Y. Quantitative analysis of the chemotaxis of a green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, to bicarbonate using diffusion-based microfluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 014121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Boisson-Dernier, A.; Israelsson-Nordstrom, M.; Bohmer, M.; Xue, S.; Ries, A.; Godoski, J.; Kuhn, J.M.; Schroeder, J.I. Carbonic anhydrases are upstream regulators of CO2-controlled stomatal movements in guard cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromm, S.; Braun, H.P.; Peterhansel, C. Mitochondrial gamma carbonic anhydrases are required for complex I assembly and plant reproductive development. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
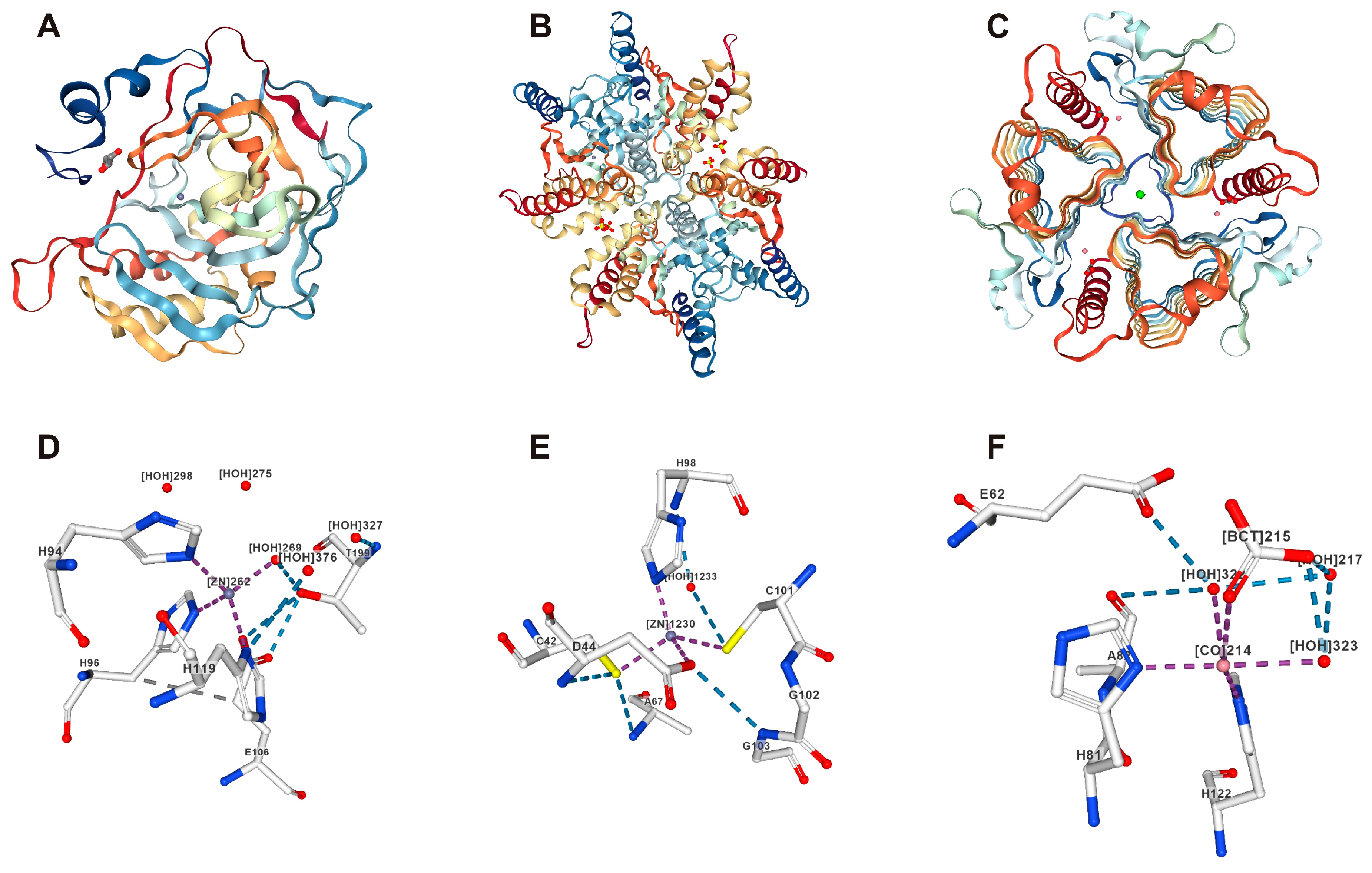
| CAs | Enzyme | Metal Ion | Organisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | Monomeric, dimeric | Zn2+ | Animals, prokaryotes, fungi, and plants | [8,32] |
| β | Multimeric | Zn2+ | Plants, bacteria, and fungi | [8,32] |
| γ | Trimeric | Zn2+ or Fe, Co | Plants, archaea, fungi, and bacteria | [33,34] |
| ζ | Monomeric | Cd or Zn | Marine diatoms | [30,33,34] |
| δ | Monomeric | Co | Marine diatoms | [30,35,36] |
| η | Monomeric | Zn2+ | Plasmodium spp. | [1,37] |
| θ | Monomeric | Zn2+ | Marine diatoms | [4,9,10] |
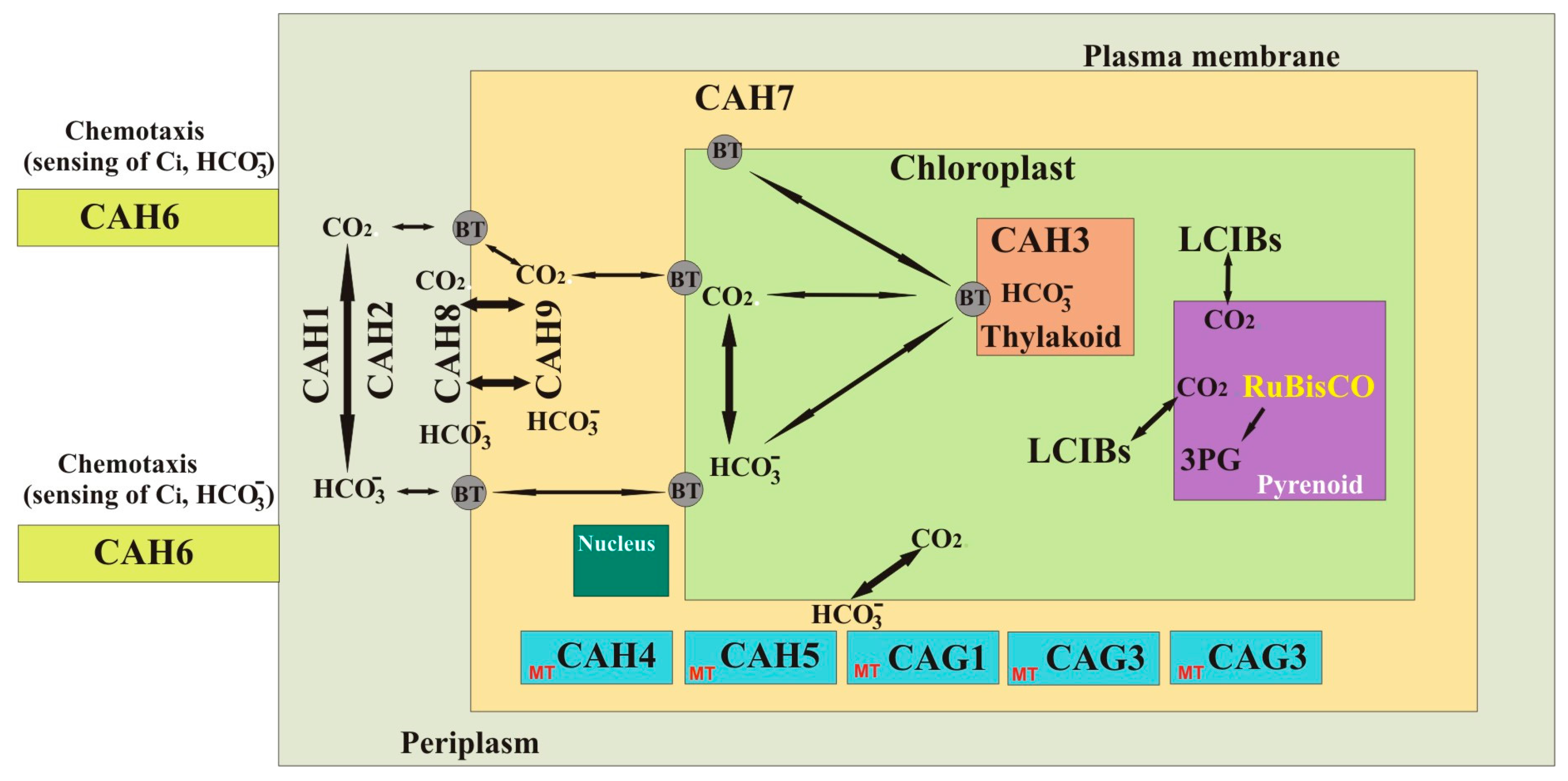
| CA Protein | Chr | Gene Family | MW (kDa) | Location | Known/Predicted Physiological Roles of the CAs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAH1 a | 4 | α | 78 | Periplasm/late secretory pathway | Supply of Ci in low CO2 | [66,73,74,75,76,77,78,79] |
| CAH2 a | 4 | 84 | Periplasm/late secretory pathway | Supply of Ci in high CO2 | [14,66,80,81] | |
| CAH3 a | 9 | 29.5 | Chloroplasts | Growth in low CO2 | [14,82,83,84,85,86,87,88] | |
| CAH4 *,a | 5 | β | 21 | Mitochondria | - | [14,89,90,91] |
| CAH5 *,a | 5 | 21 | Mitochondria | - | [14,40,41,42] | |
| CAH6 a | 12 | 31 | Flagella | CCM | [14] | |
| CAH7 b | 13 | 35.79 | Periplasm? | - | [92] | |
| CAH8 a | 9 | 35.79 | Periplasm | - | [92] | |
| CAH9 a | 5 | 13.06 | Cytosol | - | [14] | |
| LCIB1 b | 48 c | Chloroplasts | CO2, uptake, CCM | [10] | ||
| LCIB2 b | 48 c | Chloroplasts | CO2, uptake, CCM | [10] | ||
| LCIB3 b | 48 c | Chloroplasts | CO2, uptake, CCM | [10] | ||
| CAG1 b | 9 | γ | 24.29 | Mitochondria | Transport of mitochondrial CO2 to chloroplasts | [14,70,71,93] |
| CAG2 b | 6 | 31.17 | Mitochondria | Transport of mitochondrial CO2 to chloroplasts | [14,71,72,93] | |
| CAG3 b | 12 | 32.69 | Mitochondria | Transport of mitochondrial CO2 to chloroplasts | [14,71,72,93] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aspatwar, A.; Haapanen, S.; Parkkila, S. An Update on the Metabolic Roles of Carbonic Anhydrases in the Model Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metabolites 2018, 8, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010022
Aspatwar A, Haapanen S, Parkkila S. An Update on the Metabolic Roles of Carbonic Anhydrases in the Model Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metabolites. 2018; 8(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleAspatwar, Ashok, Susanna Haapanen, and Seppo Parkkila. 2018. "An Update on the Metabolic Roles of Carbonic Anhydrases in the Model Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii" Metabolites 8, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010022
APA StyleAspatwar, A., Haapanen, S., & Parkkila, S. (2018). An Update on the Metabolic Roles of Carbonic Anhydrases in the Model Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metabolites, 8(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010022





