Identification of an Epoxide Metabolite of Lycopene in Human Plasma Using 13C-Labeling and QTOF-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Targeted Search for Apo-Lycopenals
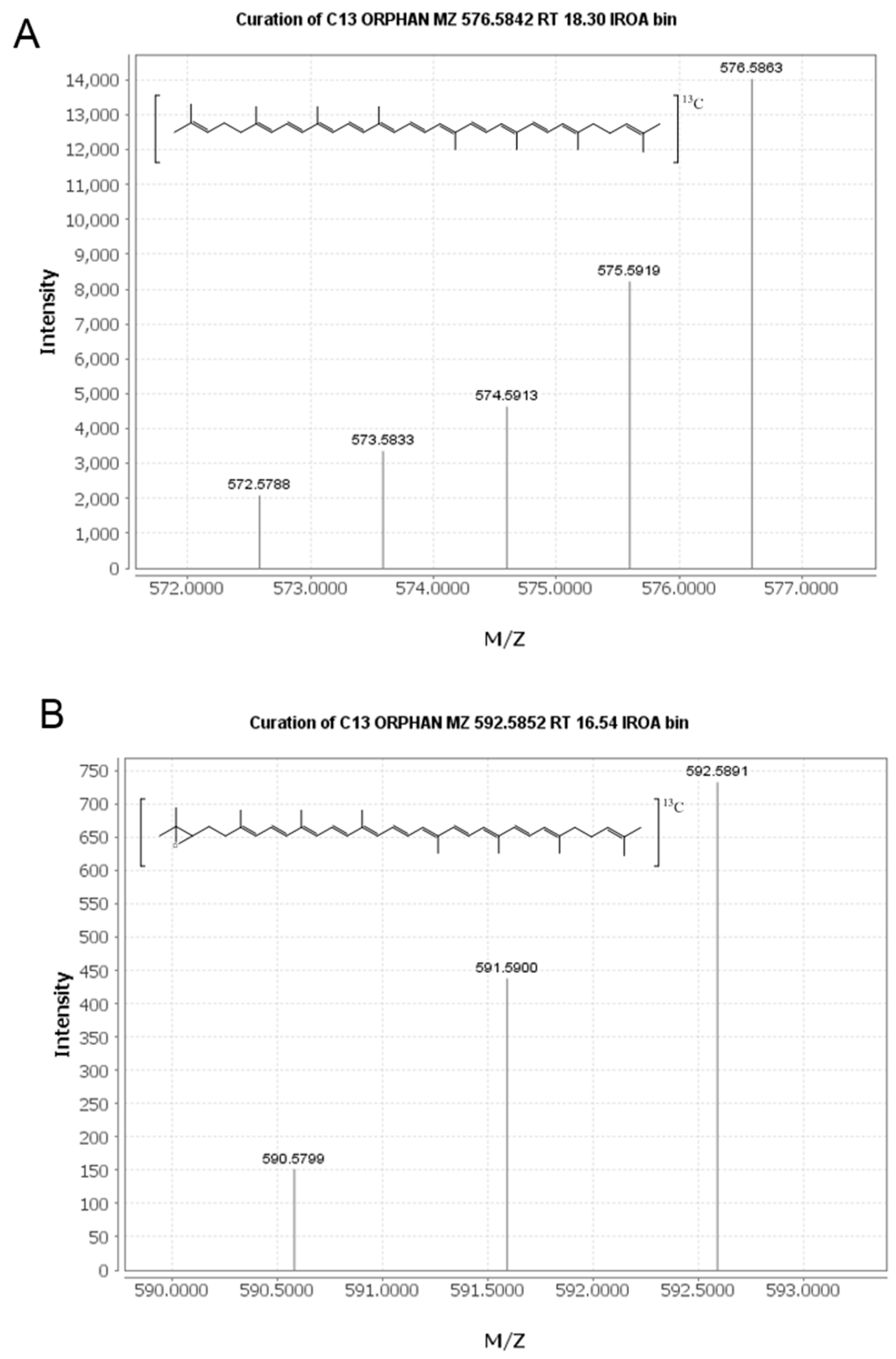
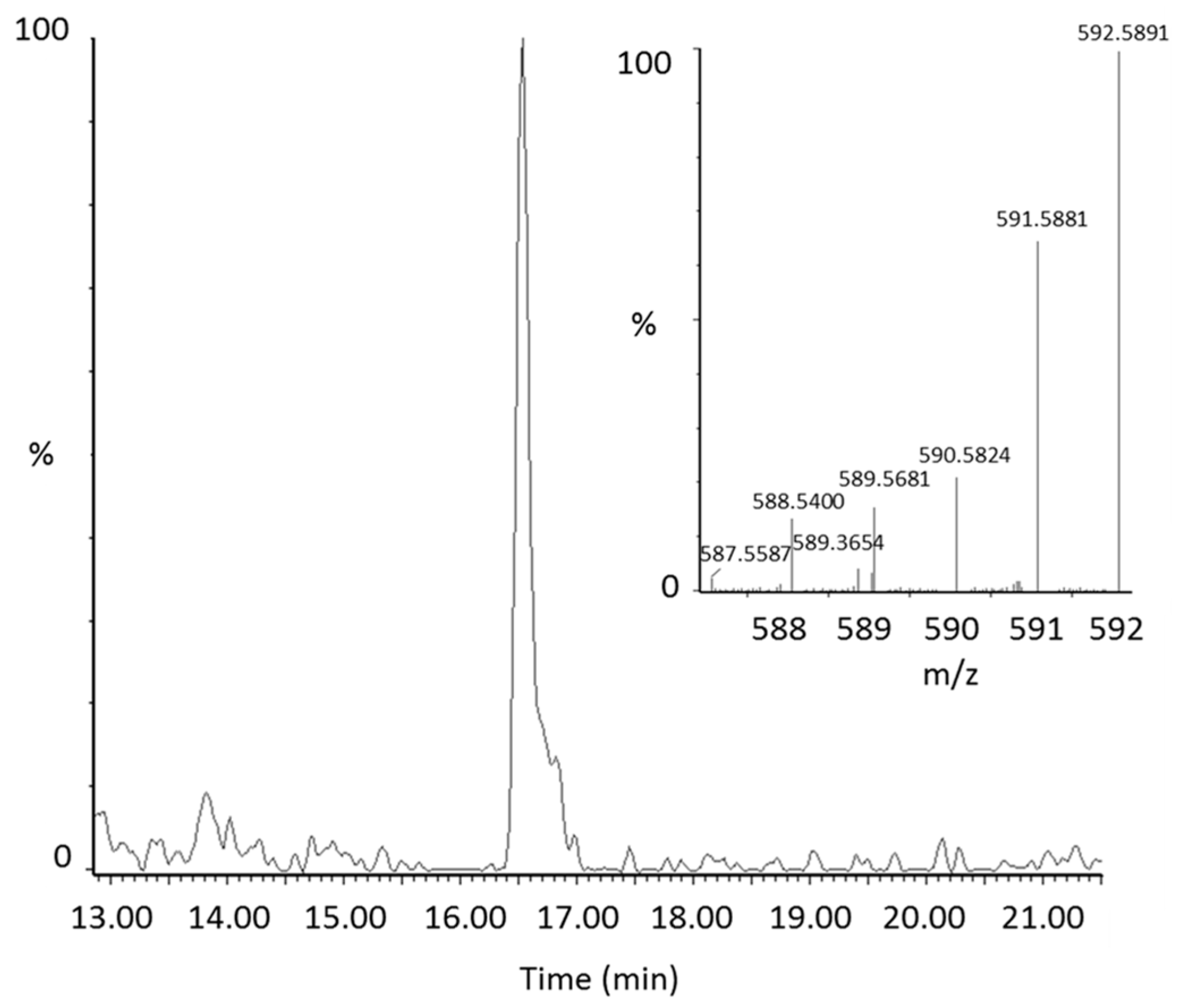
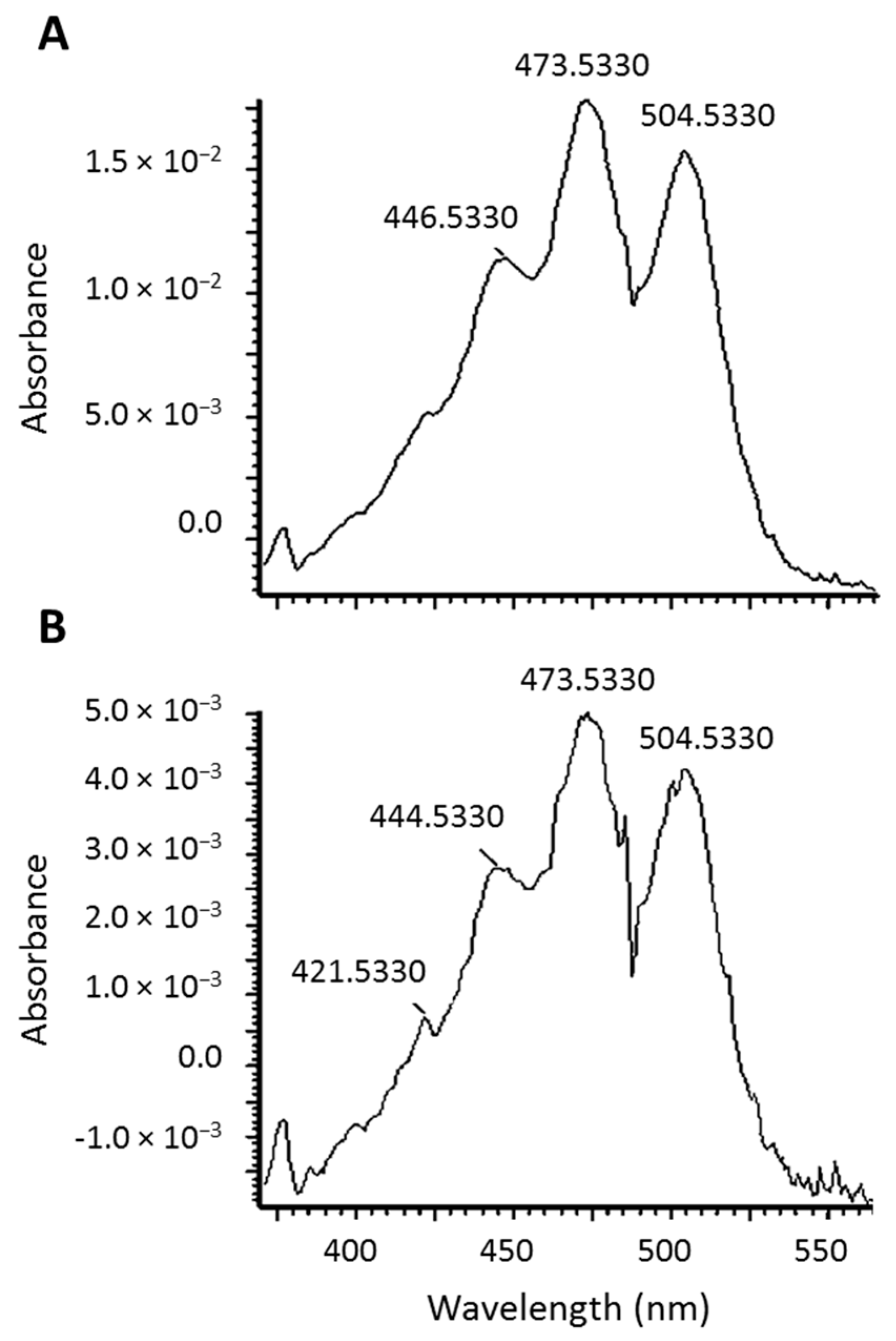
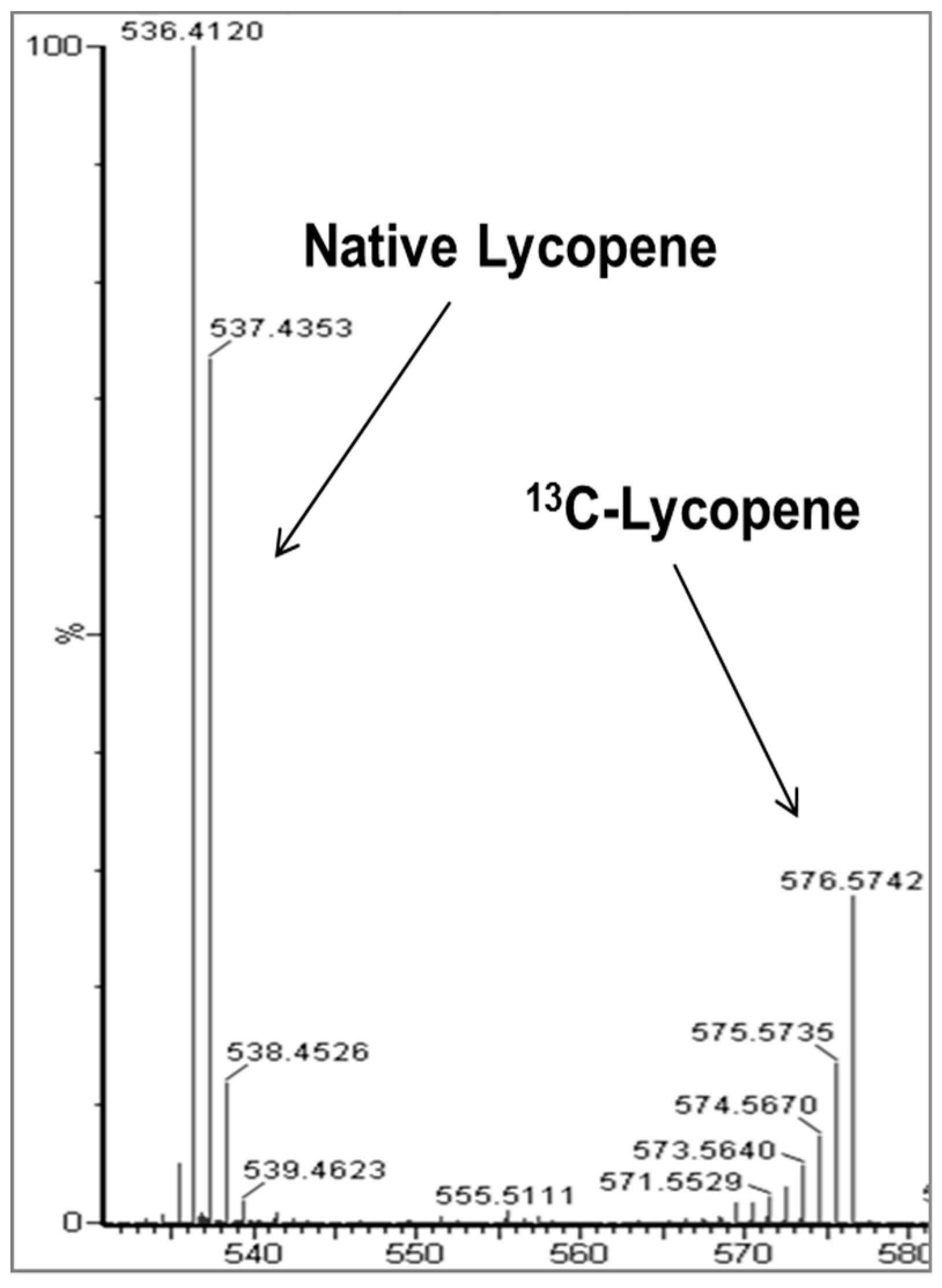
2.2. Identification of New Lycopene Metabolites
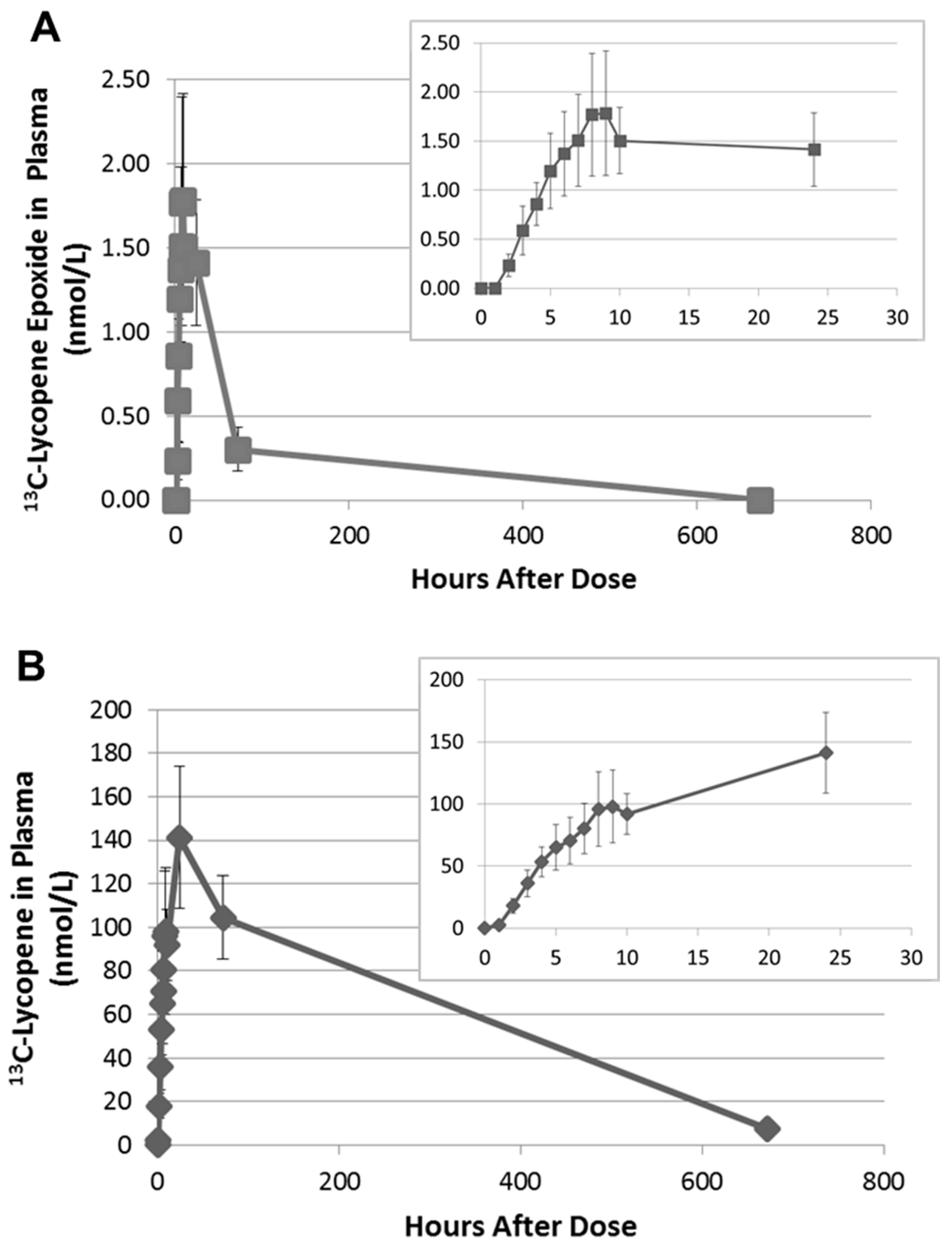
2.3. Quantitation of 13C-lycopene 1,2-Epoxide in Plasma
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Study Design
4.2. Plasma Preparation and LC-MS Analysis
4.3. Data Mining
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Key, T.J.; Appleby, P.N.; Travis, R.C.; Albanes, D.; Alberg, A.J.; Barricarte, A.; Black, A.; Boeing, H.; Bueno-De-Mesquita, H.B.; Chan, J.M.; et al. Carotenoids, retinol, tocopherols, and prostate cancer risk: Pooled analysis of 15 studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1142–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowles, J.L.; Ranard, K.M.; Applegate, C.C.; Jeon, S.; An, R.; Erdman, J.W. Processed and raw tomato consumption and risk of prostate cancer: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.-L.; Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Moran, N.E.; Cooperstone, J.L.; Erdman, J.W.; Young, G.S.; Clinton, S.K. β-carotene 9′,10′ oxygenase modulates the anticancer activity of dietary tomato or lycopene on prostate carcinogenesis in the TRAMP model. Cancer Prev. Res. 2017, 10, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boileau, T.W.-M.; Liao, Z.; Kim, S.; Lemeshow, S.; Erdman, J.W.; Clinton, S.K. Prostate carcinogenesis in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (NMU)-testosterone-treated rats fed tomato powder, lycopene, or energy-restricted diets. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinton, S.K. Lycopene: Chemistry, biology, and implications for human health and disease. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, A.; Harrison, E.H. Carotenoid metabolism in mammals, including man: Formation, occurrence, and function of apocarotenoids. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindshield, B.L.; Canene-Adams, K.; Erdman, J.W. Lycopenoids: Are lycopene metabolites bioactive? Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, A.; Hruszkewycz, D.P.; dela Sena, C.; Narayanasamy, S.; Riedl, K.M.; Kopec, R.E.; Schwartz, S.J.; Curley, R.W.; Harrison, E.H. Naturally occurring eccentric cleavage products of provitamin A β-carotene function as antagonists of retinoic acid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15886–15895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, A.; Hruszkewycz, D.P.; Curley, R.W.; Harrison, E.H. The eccentric cleavage product of β-carotene, β-apo-13-carotenone, functions as an antagonist of RXRα. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 504, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caris-Veyrat, C.; Schmid, A.; Carail, M.; Böhm, V. Cleavage products of lycopene produced by in vitro oxidations: Characterization and mechanisms of formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7318–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Nara, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Terao, J.; Nagao, A. Formation of cleavage products by autoxidation of lycopene. Lipids 2001, 36, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, R.E.; Riedl, K.M.; Harrison, E.H.; Curley, R.W.; Hruszkewycz, D.P.; Clinton, S.K.; Schwartz, S.J. Identification and quantification of apo-lycopenals in fruits, vegetables, and human plasma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaripheh, S.; Boileau, T.W.-M.; Lila, M.A.; Erdman, J.W. [14C]-lycopene and [14C]-labeled polar products are differentially distributed in tissues of F344 rats prefed lycopene. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 4189–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.E.; Clinton, S.K.; Erdman, J.W. Differential bioavailability, clearance, and tissue distribution of the acyclic tomato carotenoids lycopene and phytoene in mongolian gerbils. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1920–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.B.; Vuong, L.T.; Ruckle, J.; Synal, H.A.; Schulze-Konig, T.; Wertz, K.; Rumbeli, R.; Liberman, R.G.; Skipper, P.L.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; et al. Lycopene bioavailability and metabolism in humans: An accelerator mass spectrometry study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleshman, M.K.; Riedl, K.M.; Novotny, J.A.; Schwartz, S.J.; Harrison, E.H. An LC/MS method for d8-β-carotene and d4-retinyl esters: β-carotene absorption and its conversion to vitamin A in humans. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurilich, A.C.; Britz, S.J.; Clevidence, B.A.; Novotny, J.A. Isotopic labeling and LC-APCI-MS quantification for investigating absorption of carotenoids and phylloquinone from kale (Brassica oleracea). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4877–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.E.; Cichon, M.J.; Riedl, K.M.; Grainger, E.M.; Schwartz, S.J.; Novotny, J.A.; Erdman, J.W.; Clinton, S.K. Compartmental and noncompartmental modeling of 13C-lycopene absorption, isomerization, and distribution kinetics in healthy adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.E.; Novotny, J.A.; Cichon, M.J.; Riedl, K.M.; Rogers, R.B.; Grainger, E.M.; Schwartz, S.J.; Erdman, J.W.; Clinton, S.K. Absorption and distribution kinetics of the 13C-labeled tomato carotenoid phytoene in healthy adults. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachik, F.; Steck, A.; Niggli, U.A.; Pfander, H. Partial synthesis and structural elucidation of the oxidative metabolites of lycopene identified in tomato paste, tomato juice, and human serum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4874–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadante, A.Z.; Egeland, E.S. Carotenoids Handbook; Britton, G., Liaaen-Jensen, S., Pfander, H., Eds.; Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khachik, F.; Goli, M.B.; Beecher, G.R.; Holden, J.; Lusby, W.R.; Tenorio, M.D.; Barrera, M.R. Effect of food preparation on qualitative and quantitative distribution of major carotenoid constituents of tomatoes and several green vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, C.H. Chemical Derivatization: Microscale Tests for the Presence of Common Functional Groups in Carotenoids. In Carotenoids Volume 1A: Isolation and Analysis; Britton, G., Liaaen-Jensen, S., Pfander, H., Eds.; Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 1995; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Khachik, F.; Spangler, C.J.; Smith, J.C.; Canfield, L.M.; Steck, A.; Pfander, H. Identification, quantification, and relative concentrations of carotenoids and their metabolites in human milk and serum. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachik, F.; Pfander, H.; Traber, B. Proposed mechanisms for the formation of synthetic and naturally occurring metabolites of lycopene in tomato products and human serum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4885–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, G.; Goodwin, T.W. Carotene epoxides from the Delta tomato mutant. Phytochemistry 1975, 14, 2530–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonucci, L.H.; Holden, J.M.; Beecher, G.R.; Khachik, F.; Davis, C.S.; Mulokozi, G. Carotenoid content of thermally processed tomato-based food products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.B.; Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. Lycopene epoxides and apo-lycopenals formed by chemical reactions and autoxidation in model systems and processed foods. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C674–C682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichon, M.J.; Riedl, K.M.; Schwartz, S.J. A metabolomic evaluation of the phytochemical composition of tomato juices being used in human clinical trials. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.W.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Epoxide hydrolases: Their roles and interactions with lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2005, 44, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, A.B.; Olson, J.A. Xanthophyll epoxides, unlike beta-carotene monoepoxides, are not detectibly absorbed by humans. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 3212–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, A.B. Intestinal absorption of epoxy-beta-carotenes by humans. Biochem. J. 1999, 339, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duitsman, P.K.; Barua, A.B.; Becker, B.; Olson, J.A. Effects of epoxycarotenoids, beta-carotene, and retinoic acid on the differentiation and viability of the leukemia cell line NB4 in vitro. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1999, 69, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Node, K.; Huo, Y.; Ruan, X.; Yang, B.; Spiecker, M.; Ley, K.; Zeldin, D.C.; Liao, J.K. Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science 1999, 285, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.; Vito, S.; Inceoglu, B.; Hammock, B.D. The role of long chain fatty acids and their epoxide metabolites in nociceptive signaling. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2014, 113–115, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, K.M.; Yang, W.; Gross, G.J.; Campbell, W.B. Roles of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in vascular regulation and cardiac preconditioning. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2007, 50, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Panigrahy, D.; Mahakian, L.M.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.-Y.; Stephen Lee, K.S.; Wettersten, H.I.; Ulu, A.; Hu, X.; Tam, S.; et al. Epoxy metabolites of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) inhibit angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6530–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.E.; Rogers, R.B.; Lu, C.-H.; Conlon, L.E.; Lila, M.A.; Clinton, S.K.; Erdman, J.W. Biosynthesis of highly enriched 13C-lycopene for human metabolic studies using repeated batch tomato cell culturing with 13C-glucose. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goltz, S.R.; Campbell, W.W.; Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Failla, M.L.; Ferruzzi, M.G. Meal triacylglycerol profile modulates postprandial absorption of carotenoids in humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unlu, N.Z.; Bohn, T.; Clinton, S.K.; Schwartz, S.J. Carotenoid absorption from salad and salsa by humans is enhanced by the addition of avocado or avocado oil. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, W.S.; Zhou, Y.; Crane, A.; Dixon, P.; Quadt, F.; Flendrig, L.M. Modeling the dose effects of soybean oil in salad dressing on carotenoid and fat-soluble vitamin bioavailability in salad vegetables. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cichon, M.J.; Moran, N.E.; Riedl, K.M.; Schwartz, S.J.; Clinton, S.K. Identification of an Epoxide Metabolite of Lycopene in Human Plasma Using 13C-Labeling and QTOF-MS. Metabolites 2018, 8, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010024
Cichon MJ, Moran NE, Riedl KM, Schwartz SJ, Clinton SK. Identification of an Epoxide Metabolite of Lycopene in Human Plasma Using 13C-Labeling and QTOF-MS. Metabolites. 2018; 8(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCichon, Morgan J., Nancy E. Moran, Ken M. Riedl, Steven J. Schwartz, and Steven K. Clinton. 2018. "Identification of an Epoxide Metabolite of Lycopene in Human Plasma Using 13C-Labeling and QTOF-MS" Metabolites 8, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010024
APA StyleCichon, M. J., Moran, N. E., Riedl, K. M., Schwartz, S. J., & Clinton, S. K. (2018). Identification of an Epoxide Metabolite of Lycopene in Human Plasma Using 13C-Labeling and QTOF-MS. Metabolites, 8(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8010024




