Breast Tissue Metabolism by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MR Methodologies to Study Breast Tissue Metabolism
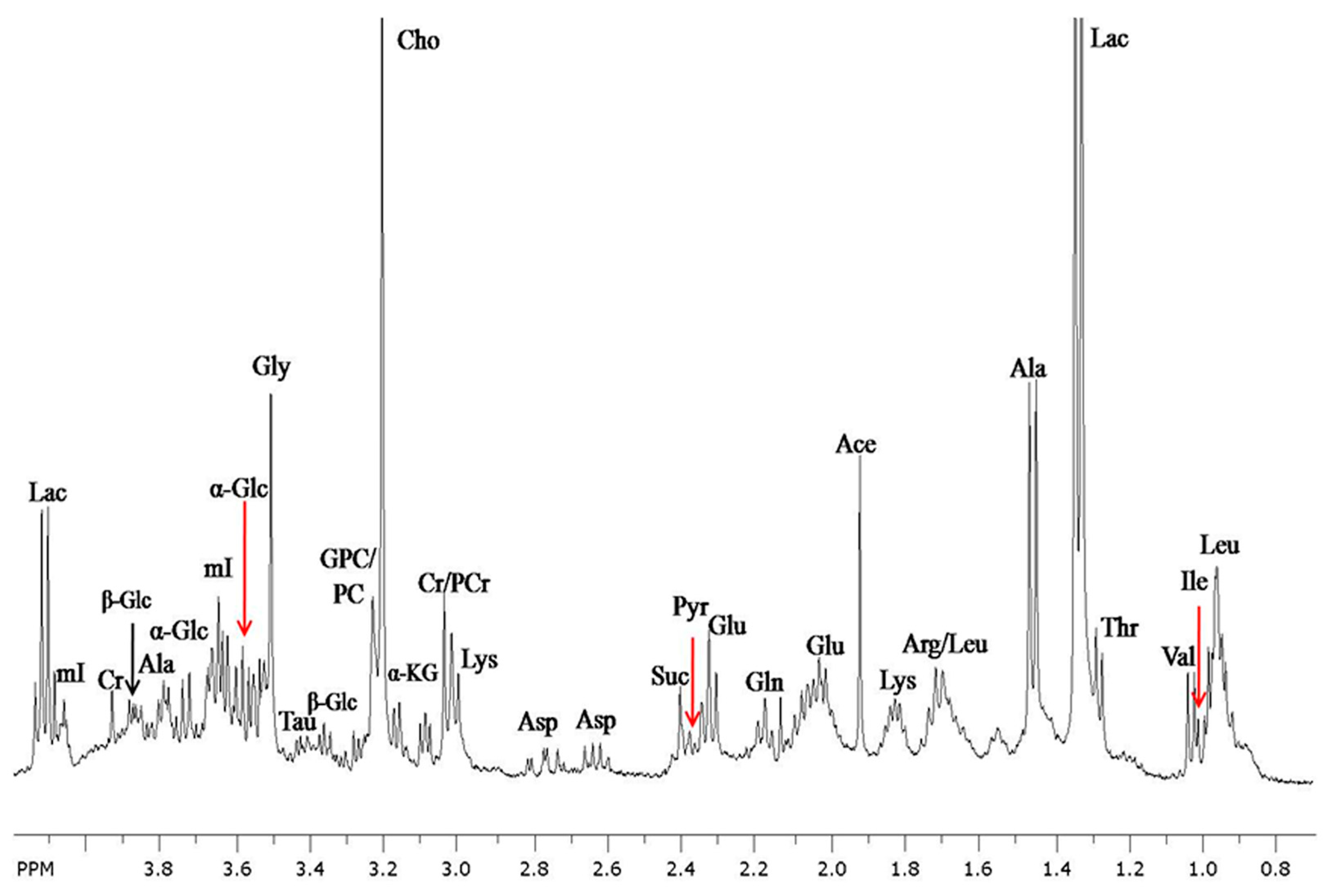
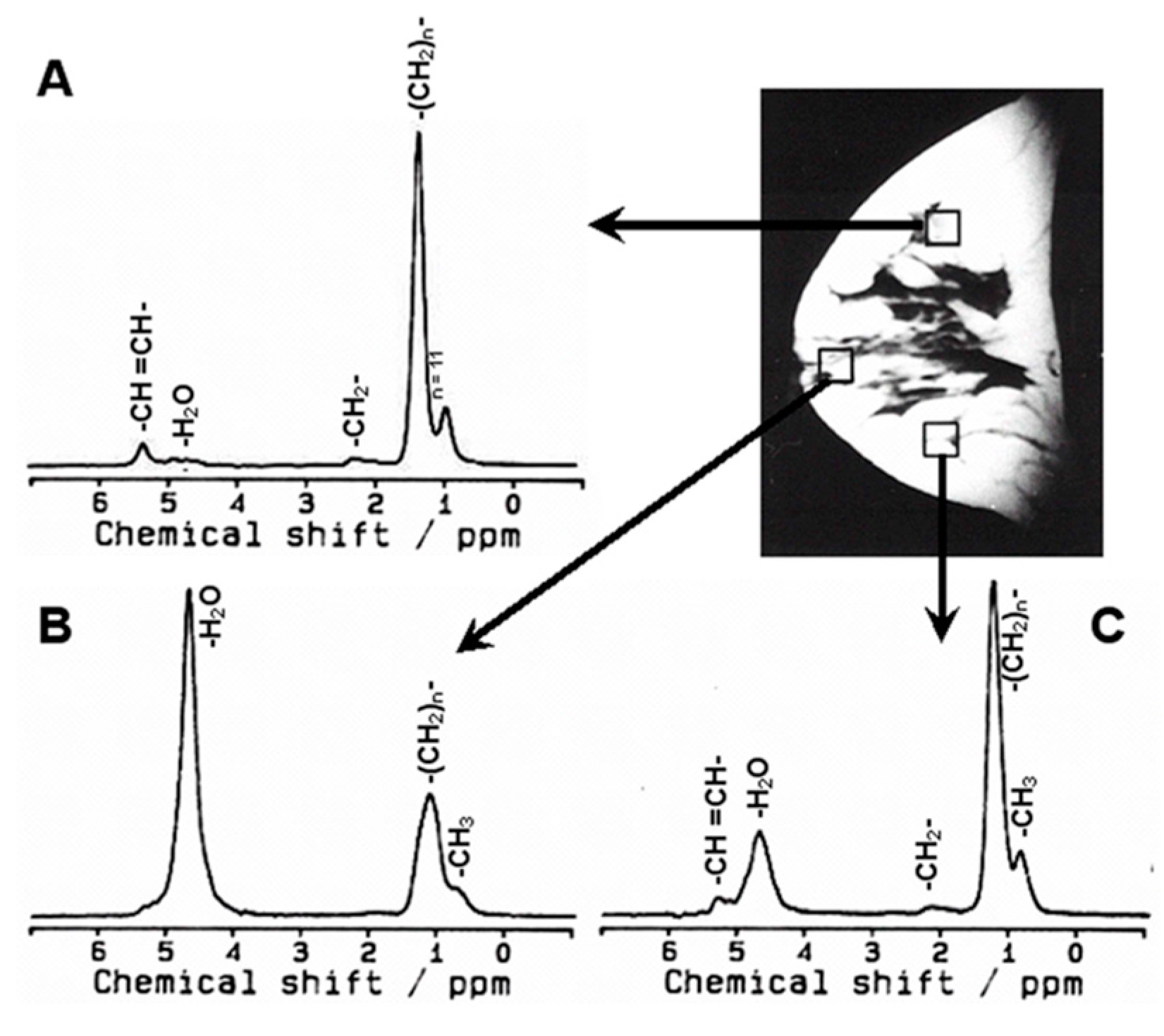
2.1. In vitro High-Resolution NMR Spectroscopy
2.2. High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HRMAS) 1H NMR Spectroscopy
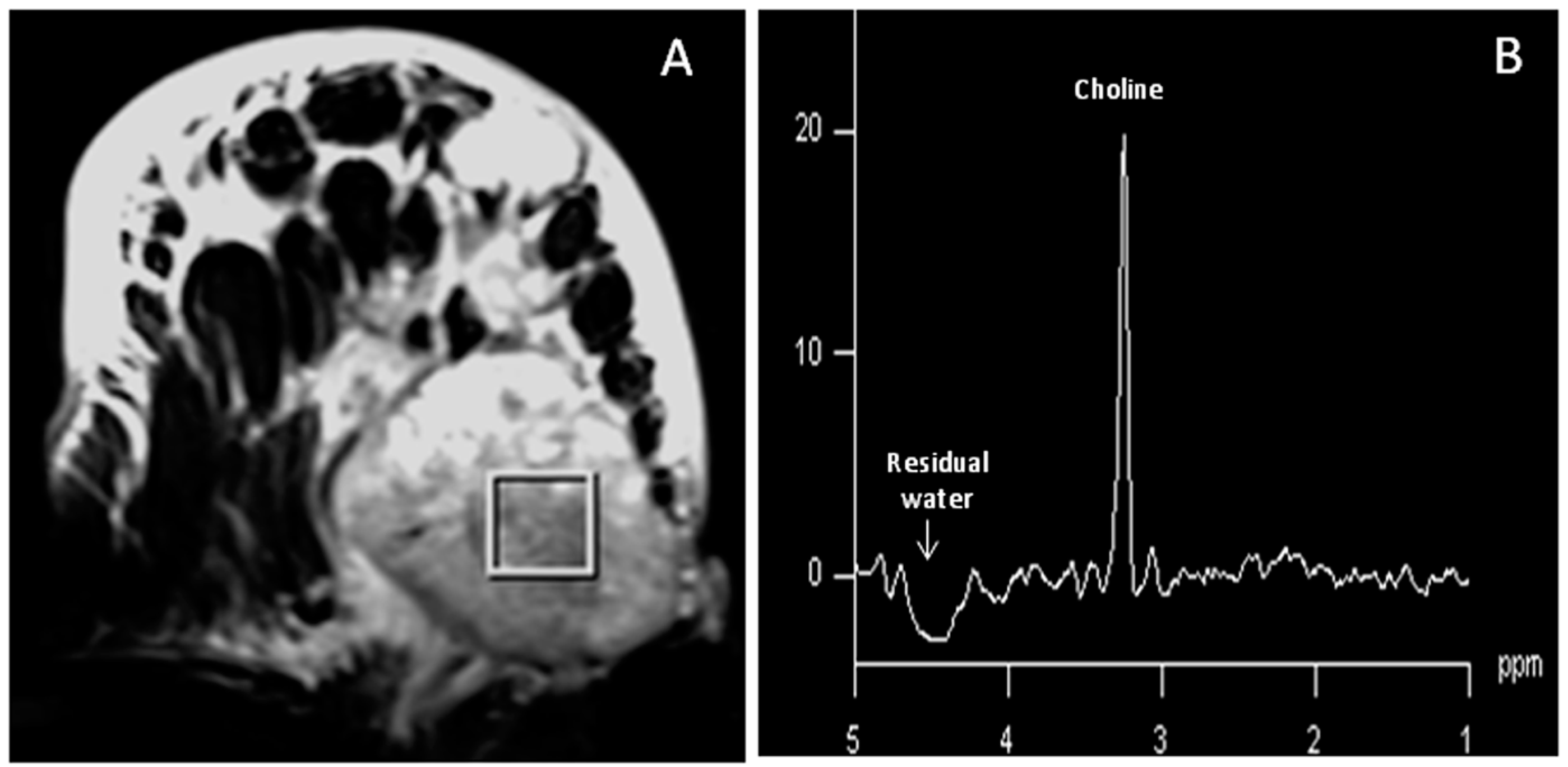
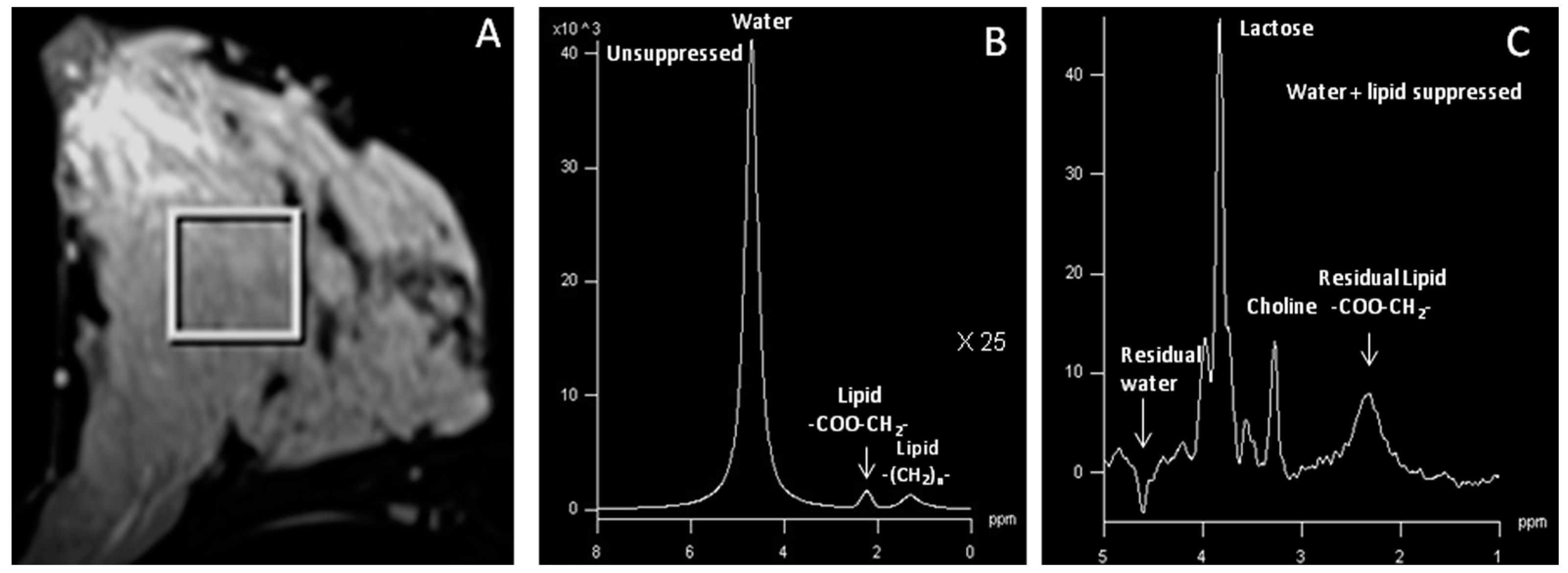
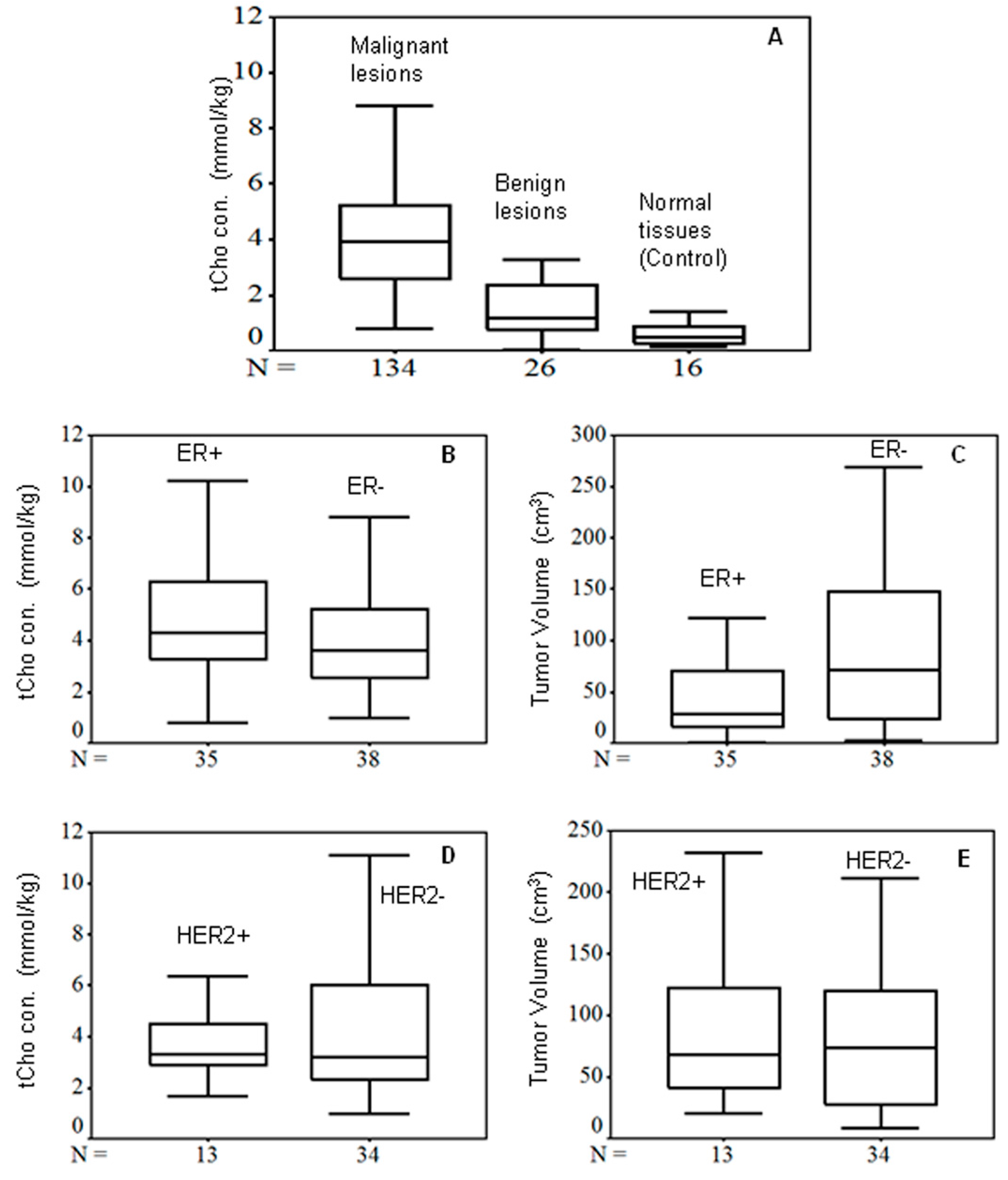
2.3. In vivo MR Spectroscopy
2.4. Hyper-Polarized NMR
2.5. 31P MR Spectroscopy
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of MRS in the Study of Tissue Metabolism
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveira, A.P.; Jewett, M.C.; Nielsen, J. From Gene Expression to Metabolic Fluxes; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppenol, W.H.; Bounds, P.L.; Dang, C.V. Otto Warburg’s contributions to current concepts of cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negendank, W. Studies of human tumors by MRS: A review. NMR Biomed. 1992, 5, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, M.O.; Verrill, M.; Glaholm, J.; Smith, T.A.D.; Collins, D.J.; Payne, G.S.; Sharp, J.C.; Ronen, S.M.; McCready, V.R.; Powles, T.J.; et al. Measurements of human breast cancer using magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a review of clinical measurements and a report of localized 31P measurements of response to treatment. NMR Biomed. 1998, 11, 314–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz-Brull, R.; Margalit, R.; Bendel, P.; Degani, H. Choline metabolism in breast cancer; 2H-, 13C- and 31P-NMR studies of cells and tumors. Magnetic Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 1998, 6, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, S.M.; Leach, M.O. Imaging biochemistry: Applications to breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2001, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podo, F.; Sardanelli, F.; Torio, E.; Canese, R.; Carpinelli, G.; Fausto, A.; Canevari, S. Abnormal choline phopholipid metabolism in breast and ovary cancer: Molecular bases for noninvasive imaging approaches. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2007, 3, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Ronen, S.M. Choline metabolism in malignant transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.D.; Döpkens, M.; Krishnamachary, B.; Vesuna, F.; Gadiya, M.M.; Lønning, P.E.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Glunde, K. Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 5 (GDPD5) expression correlates with malignant choline phospholipid metabolite profiles in human breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, G.S.; Leach, M.O. Applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in radiotherapy treatment planning. Br. J. Radiol. 2006, 79, S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Sattar, A.; Benanti, M.; Hollander, S.; Cheuck, L. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy as an imaging tool for cancer: A review of the literature. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2006, 106, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.A.; Comstock, C.E.; Lee, C.H.; Lehman, C.D. ACR BI-RADS® magnetic resonance imaging. In ACR BI-RADS® Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; pp. 56–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, U.; Sah, R.G.; Agarwal, K.; Parshad, R.; Seenu, V.; Mathur, S.R.; Hari, S.; Jagannathan, N.R. Potential of diffusion-weighted imaging in the characterization of malignant, benign, and healthy breast tissues and molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguerol, T.M.; González, J.S.; Barbero, J.P.M.; Figueiras, R.G.; González, B.G.; Luna, A. Clinical imaging of tumor metabolism with 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2016, 24, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.; Bundy, J.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribbestad, I.S.; Petersen, S.B.; Fjøsne, H.E.; Kvinnsland, S.; Krane, J. 1H NMR spectroscopic characterization of perchloric acid extracts from breast carcinomas and non-involved breast tissue. NMR Biomed. 1994, 7, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, N.R.; Sah, R.G.; Sharma, U.; Parshad, R.; Seenu, V. Metabolic profile of human breast tissues studied by in vitro NMR spectroscopy. Proc. Intl. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 22, 1082. [Google Scholar]
- Beckonert, O.; Monnerjahn, J.; Bonk, U.; Leibfritz, D. Visualizing metabolic changes in breast-cancer tissue using 1H-NMR spectroscopy and self-organizing maps. NMR Biomed. 2003, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuss, T.L.; Cheng, L.L. Evaluation of Cancer Metabolomics using ex vivo high resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Metabolites 2016, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezabeh, T.; Ijare, O.B.; Nikulin, A.E.; Somorjai, R.L.; Smith, I.C. MRS-based Metabolomics in Cancer Research. Magn. Reson. Insights 2014, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.L.; Chang, I.W.; Smith, B.L.; González, R.G. Evaluating human breast ductal carcinomas with high-resolution magic-angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 1998, 135, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitter, B.; Sonnewald, U.; Spraul, M.; Fjösne, H.E.; Gribbestad, I.S. High-resolution magic angle spinning MRS of breast cancer tissue. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitter, B.; Lundgren, S.; Bathen, T.F.; Halgunset, J.; Fjosne, H.E.; Gribbestad, I.S. Comparison of HRMAS MR spectroscopic profiles of breast cancer tissue with clinical parameters. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathen, T.F.; Jensen, L.R.; Sitter, B.; Fjösne, H.E.; Halgunset, J.; Axelson, D.E.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Lundgren, S. MR-determined metabolic phenotype of breast cancer in prediction of lymphatic spread, grade, and hormone status. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 104, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Song, Y.; Cho, N.; Chang, J.M.; Koo, H.R.; Yi, A.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Moon, W.K. An HR-MAS MR metabolomics study on breast tissues obtained with core needle biopsy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Baek, H.M.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.J.; Youk, J.H.; Moon, H.J.; Kim, E.K.; Nam, Y.K. Magnetic resonance metabolic profiling of breast cancer tissue obtained with core needle biopsy for predicting pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giskeødegård, G.F.; Grinde, M.T.; Sitter, B.; Axelson, D.E.; Lundgren, S.; Fjøsne, H.E.; Dahl, S.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Bathen, T.F. Multivariate modeling and prediction of breast cancer prognostic factors using MR metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giskeødegård, G.F.; Lundgren, S.; Sitter, B.; Fjøsne, H.E.; Postma, G.; Buydens, L.M.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Bathen, T.F. Lactate and glycine-potential MR biomarkers of prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, K.M.; Dewhirst, M.W. Tumor metabolism of lactate: the influence and therapeutic potential for MCT and CD147 regulation. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotnda, P.; Wu, D.; Swanson, A.M. Hypoxic tumors and their effect on immune cells and cancer therapy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 651, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburg, O. On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science 1956, 124, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 22, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Katz-Brull, R.; Seger, D.; Rivenson-Segal, D.; Rushkin, E.; Degani, H. Metabolic markers of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moestue, S.; Borgan, E.; Huuse, E.; Lindholm, E.; Sitter, B.; Børresen-Dale, A.; Engebraaten, O.; Mælandsmo, G.; Gribbestad, I. Distinct choline metabolic profiles are associated with differences in gene expression for basal like and luminal-like breast cancer xenograft models. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumors. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzendrowskyj, T.E.; Noyszewski, E.A.; Beers, J.; Bolinger, L. Lipid composition changes in normal breast throughout the menstrual cycle. Magnetic Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 1997, 5, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Kumar, M.; Sah, R.G.; Jagannathan, N.R. Study of normal breast tissue by in vivo volume localized proton MR spectroscopy (MRS): Variation of water-fat (W/F) ratio in relation to the heterogeneity of the breast and the menstrual cycle. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 27, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coum, A.; Ouldamer, L.; Noury, F.; Barantin, L.; Saint-Hilaire, A.; Vilde, A.; Bougnoux, P.; Gambarota, G. In vivo MR spectroscopy of human breast tissue: Quantification of fatty acid composition at clinical field strength (3 T). Magnetic Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2016, 29, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graaf, R.A.; Klomp, D.W.; Luijten, P.R.; Boer, V.O. Intramolecular zero-quantum-coherence 2D NMR spectroscopy of lipids in the human breast at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijens, P.E.; Wijrdeman, H.K.; Moerland, M.A.; Bakker, C.J.; Vermeulen, J.W.; Luyten, P.R. Human breast cancer in vivo: H-1 and P-31 MR spectroscopy at 1.5 T. Radiology 1988, 169, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvistad, K.A.; Bakken, I.J.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Ehrnholm, B.; Lundgren, S.; Fjøsne, H.E.; Haraldseth, O. Characterization of neoplastic and normal human breast tissues with in vivo 1H MR Spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1999, 10, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebuck, J.R.; Cecil, K.M.; Schnall, M.D.; Lenkinski, R.E. Human breast lesions: Characterization with proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 1998, 209, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, D.K.; Cheung, H.S.; Tse, G.M. Human breast lesions: Characterization with contrast-enhanced in vivo proton MR spectroscopy—Initial results. Radiology 2001, 220, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecil, K.M.; Schnall, M.D.; Siegelman, E.S.; Lenkinski, R.E. The evaluation of human breast lesions with magnetic resonance imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2001, 68, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, N.R.; Kumar, M.; Seenu, V.; Coshic, O.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Julka, P.K.; Srivastava, A.; Rath, G.K. Evaluation of total choline from in vivo volume localized proton MR spectroscopy and its response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz-Brull, R.; Lavin, P.T.; Lenkinski, R.E. Clinical utility of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in characterizing breast lesions. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, R.G.; Sharma, U.; Parshad, R.; Seenu, V.; Mathur, S.R.; Jagannathan, N.R. Association of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status with total choline concentration and tumor volume in breast cancer patients: An MRI and in vivo proton MRS study. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Cohen, J.S. Phospholipid metabolites as indicators of cancer cell function. NMR Biomed. 1992, 5, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glunde, K.; Jie, C.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Molecular causes of the aberrant choline phospholipid metabolism in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podo, F. Tumour phospholipid metabolism. NMR Biomed. 1999, 12, 413–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboagye, E.O.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Malignant transformation alters membrane choline phospholipid metabolism of human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronen, S.M.; Jackson, L.E.; Beloueche, M.; Leach, M.O. Magnetic resonance detects changes in phosphocholine associated with Ras activation and inhibition in NIH 3T3 cells. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, R.G.; Agarwal, K.; Sharma, U.; Parshad, R.; Seenu, V.; Jagannathan, N.R. Characterization of malignant breast tissue of breast cancer patients and the normal breast tissue of healthy lactating women volunteers using diffusion MRI and in vivo 1H MR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanwell, P.; Gluch, L.; Clark, D.; Tomanek, B.; Baker, L.; Giuffrè, B.; Lean, C.; Malycha, P.; Mountford, C. Specificity of choline metabolites for in vivo diagnosis of breast cancer using 1H MRS at 1.5 T. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, P.J.; Henry, P.G.; Baker, E.H.; Meisamy, S.; Garwood, M. Measurement and correction of respiration-induced B0 variations in breast 1H MRS at 4 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 52, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.B.; Brennan, S.B.; Ishill, N.M.; Morris, E.A.; Liberman, L.; Dershaw, D.D.; Bartella, L.; Koutcher, J.A.; Huang, W. Diagnostic usefulness of water-to-fat ratio and choline concentration in malignant and benign breast lesions and normal breast parenchyma: An in vivo 1H MRS study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, H.M.; Su, M.Y.; Yu, H.; Mehta, R.; Nalcioglu, O. Quantification of choline-containing compounds in malignant breast tumors by 1H MR spectroscopy using water as an internal reference at 1.5 T. Magnetic Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2006, 19, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrius, M.D.; Pijnappel, R.M.; van der Weide Jansen, M.C.; Jansen, L.; Kappert, P.; Oudkerk, M.; Sijens, P.E. The added value of quantitative multi-voxel MR spectroscopy in breast magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Mehta, R.S.; Baek, H.M.; Nie, K.; Liu, H.; Lin, M.Q.; Yu, H.J.; Nalcioglu, O.; Su, M.Y. Clinical characteristics and biomarkers of breast cancer associated with choline concentration measured by 1H MR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, H.M.; Yu, H.J.; Chen, J.H.; Nalcioglu, O.; Su, M.Y. Quantitative correlation between 1H MR spectroscopy and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of human breast cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 26, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltzer, P.A.; Dietzel, M. Breast lesions: Diagnosis by using proton MR spectroscopy at 1.5 and 3.0 T-systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 2013, 3, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongzhi, C.; Li, X. Differential diagnosis between malignant and benign breast lesions using single voxel proton MRS: A meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xu, L.; Yao, W.; Wan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xin, S.X. In vivo post-contrast 1HMRS evaluation of malignant and benign breast lesions: A meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.J.; Song, H.S.; Chen, L.H. 1H-MRS evaluation of breast lesions by using total choline signal-to-noise ratio as an indicator of malignancy: A meta-analysis. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardanelli, F.; Carbonaro, L.A.; Montemezzi, S.; Cavedon, C.; Trimboli, R.M. Clinical breast MR using MRS or DWI: Who Is the Winner? Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, U.; Baek, H.M.; Su, M.Y.; Jagannathan, N.R. In vivo 1H MRS in the assessment of the therapeutic response of breast cancer patients. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolan, P.J.; Kim, E.; Herman, B.A.; Newstead, G.M.; Rosen, M.A.; Schnall, M.D.; Pisano, E.D.; Weatherall, P.T.; Morris, E.A.; Lehman, C.D.; et al. Spectroscopy of breast cancer for assessing early treatment response: Results from the ACRIN 6657 MRS trial. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, E.; Caramujo, M.J.; Cecchetti, S.; Spadaro, F.; Carpinelli, G.; Canese, R.; Podo, F. Key players in choline metabolic reprogramming in triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, R.K.; Bissell, M.J. Tissue architecture and breast cancer: The role of extracellular matrix and steroid hormones. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2000, 7, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazi, M.M.; Trivedi, T.I.; Kobawala, T.P.; Ghosh, N.R. The Potential of Wnt signaling pathway in cancer: A focus on breast cancer. Cancer Transl. Med. 2016, 2, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, A.; Papanikolaou, A. Cyclin D1 in breast cancer pathogenesis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4215–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, R.L.; Musgrove, E.A. Cyclin D1 and mammary carcinoma: New insights from transgenic mouse models. Br. Caner Res. 2002, 4, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Hariprasad, G.; Rani, K.; Sharma, U.; Mathur, S.R.; Seenu, V.; Parshad, R.; Jagannathan, N.R. Is there an association between enhanced choline and β-catenin pathway in breast cancer? A pilot study by MR Spectroscopy and ELISA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glunde, K.; Jiang, L.; Moestue, S.A.; Gribbestad, I.S. MRS and MRSI guidance in molecular medicine: Targeting and monitoring of choline and glucose metabolism in cancer. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Wildes, F.; Takagi, T.; Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. The tumor microenvironment modulates choline and lipid metabolism. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindle, K.M.; Bohndiek, S.E.; Gallagher, F.A.; Kettunen, M.I. Tumor imaging using hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrao, E.M.; Brindle, K.M. Potential clinical roles for metabolic imaging with hyperpolarized [1-13C] pyruvate. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar Butt, S.; Søgaard, L.V.; Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Lauritzen, M.H.; Engelholm, L.H.; Paulson, O.B.; Mirza, O.; Holck, S.; Magnusson, P.; Åkeson, P. Monitoring mammary tumor progression and effect of tamoxifen treatment in MMTV-PymT using MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy with hyperpolarized [1-13C] pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 1, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shestov, A.A.; Lee, S.C.; Nath, K.; Guo, L.; Nelson, D.S.; Roman, J.C.; Leeper, D.B.; Wasik, M.A.; Blair, I.A.; Glickson, J.D. 13C MRS and LC–MS flux analysis of tumor intermediary metabolism. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, G.R.; Philip, R.; Tan, Y.H. Analysis of cellular phosphoproteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: Applications for cell signaling in normal and cancer cells. Electrophoresis 1994, 15, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, T.E.; Kasimos, J.N.; Vroom, T.; de Bree, E.; Iwata, J.L.; de Graaf, P.W.; Glonek, T. Malignant breast tumor phospholipid profiles using 31P magnetic resonance. Cancer Lett. 2002, 25, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, G.S.; Dowsett, M.; Leach, M.O. Hormone-dependent metabolic changes in the normal breast monitored noninvasively by 31P magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy. Breast 1994, 3, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Park, J.H. Human in vivo 31P MR spectroscopy of benign and malignant breast tumors. Korean J. Radiol. 2001, 2, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehouwer, B.L.; van der Kemp, W.J.; Luijten, P.R.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Veldhuis, W.B.; Wijnen, J.P.; Klomp, D.W. 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the breast and the influence of the menstrual cycle. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 3, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlebnikov, V.; Wijnen, J.; van der Kemp, W.J.M.; Klomp, D.W.J. 31P MRSI studies in patients with cancer. Annu. Rep. NMR. Spectrosc. 2016, 87, 319–368. [Google Scholar]
- Klomp, D.W.; van de Bank, B.L.; Raaijmakers, A.; Korteweg, M.A.; Possanzini, C.; Boer, V.O.; van de Berg, C.A.; van der Bosch, M.A.; Luijten, P.R. 31P MRSI and 1H MRS at 7 T: Initial results in human breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2011, 10, 1337–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnen, J.P.; Jiang, L.; Greenwood, T.R.; van der Kemp, W.J.; Klomp, D.W.; Glunde, K. 1H/31P polarization transfer at 9.4 Tesla for improved specificity of detecting phosphomonoesters and phosphodiesters in breast tumor models. PLoS ONE 2014, 7, e102256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnen, J.P.; Klomp, D.W.; Nabuurs, C.I.; de Graaf, R.A.; van Kalleveen, I.M.; van der Kemp, W.J.; Luijten, P.R.; Kruit, M.C.; Webb, A.; Kan, H.E.; et al. Proton observed phosphorus editing (POPE) for in vivo detection of phospholipid metabolites. NMR Biomed. 2016, 9, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kemp, W.J.; Stehouwer, B.L.; Boer, V.O.; Luijten, P.R.; Klomp, D.W.; Wijnen, J.P. Proton and phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the healthy human breast at 7 T. NMR Biomed. 2017, 2, e3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, A.M.; Veldhuis, W.B.; Menke-Pluijmers, M.B.; van der Kemp, W.J.; van der Velden, T.A.; Kock, M.C.; Westenend, P.J.; Klomp, D.W.; Gilhuijs, K.G. Multiparametric MRI with dynamic contrast enhancement, diffusion-weighted imaging, and 31-Phosphorus spectroscopy at 7 T for characterization of breast cancer. Investig. Radiol. 2015, 11, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kemp, W.J.; Stehouwer, B.L.; Luijten, P.R.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Klomp, D.W. Detection of alterations in membrane metabolism during neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer using phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 7 Tesla. Springerplus 2014, 3, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danishad, K.K.; Sharma, U.; Sah, R.G.; Seenu, V.; Parshad, R.; Jagannathan, N.R. Assessment of therapeutic response of locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) monitored using sequential magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haddadin, I.S.; McIntosh, A.; Meisamy, S.; Corum, C.; Styczynski Snyder, A.L.; Powell, N.J.; Nelson, M.T.; Yee, D.; Garwood, M.; Bolan, P.J. Metabolite quantification and high-field MRS in breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloueche-Babari, M.; Chung, Y.L.; Al-Saffar, N.M.; Falck-Miniotis, M.; Leach, M.O. Metabolic assessment of the action of targeted cancer therapeutics using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glunde, K.; Ackerstaff, E.; Mori, N.; Jacobs, M.A.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Choline phospholipid metabolism in cancer: Consequences for molecular pharmaceutical interventions. Mol. Pharm. 2006, 3, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtscherand, I.M.; Holtas, S. Proton MR spectroscopy in clinical routine. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 13, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, T.R. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic evaluation of brain tumor metabolism. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jagannathan, N.R.; Sharma, U. Breast Tissue Metabolism by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Metabolites 2017, 7, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7020025
Jagannathan NR, Sharma U. Breast Tissue Metabolism by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Metabolites. 2017; 7(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleJagannathan, Naranamangalam R., and Uma Sharma. 2017. "Breast Tissue Metabolism by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy" Metabolites 7, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7020025
APA StyleJagannathan, N. R., & Sharma, U. (2017). Breast Tissue Metabolism by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Metabolites, 7(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7020025




