Lysophosphatidylinositol Signalling and Metabolic Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lysophosphatidylinositol
3. GPR55
3.1. Structure and Distribution
3.2. GPR55 Signalling
4. LPI/GPR55 Signalling and Physiological Function
4.1. Metabolism
4.2. Endothelial Cells and Vasculature
4.3. Gastrointestinal Functions
4.4. Central and Peripheral Nervous System
4.5. Nociception and Inflammation
4.6. Bone
5. LPI/GPR55 Axis and Disease
5.1. Obesity and Type-2 Diabetes
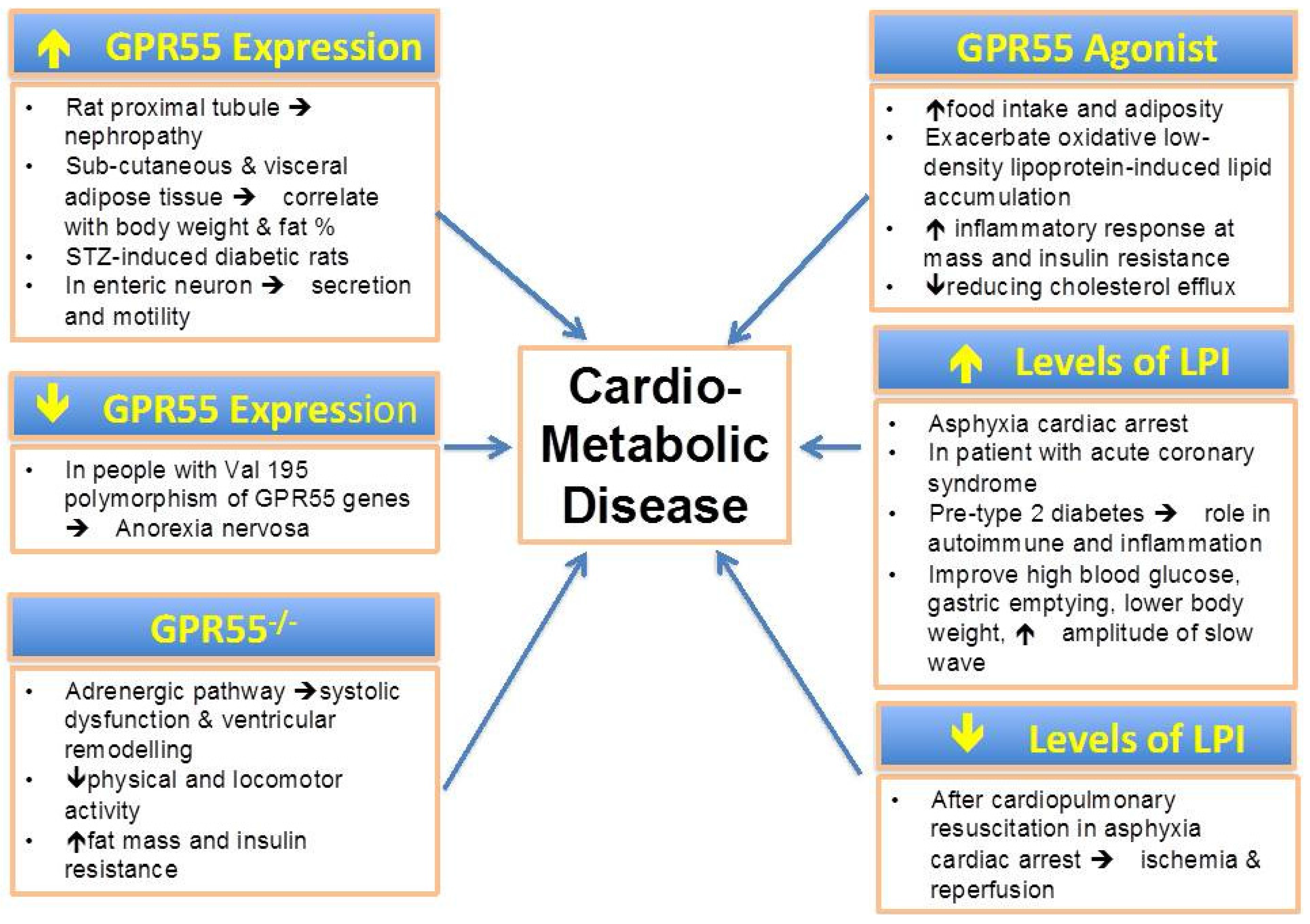
5.2. Cardiovascular Disease
5.3. Cancer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckel, R.H.; Alberti, K.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The Metabolic Syndrome. Lancet 2010, 375, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Olson, P.; Evans, R.M. Minireview: Lipid Metabolism, Metabolic Diseases, and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.J.W.; Chun, J. Lysophospholipids and Their Receptors in the Central Nervous System. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigyi, G. New Trends in Lysophospholipid Research. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Chun, J. Lysophospholipid Receptors in Drug Discovery. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 333, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro, R.; Falasca, M. Lysophosphatidylinositol Signalling: New Wine from an Old Bottle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Catalán, V.; Whyte, L.; Díaz-Arteaga, A.; Vázquez-Martínez, R.; Rotellar, F.; Guzmán, R.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Pulido, M.R.; Russell, W.R.; et al. The L-α-Lysophosphatidylinositol/GPR55 System and its Potential Role in Human Obesity. Diabetes 2012, 61, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbernon, M.; Whyte, L.; Diaz-Arteaga, A.; Russell, W.R.; Moreno, N.R.; Vazquez, M.J.; Gonzalez, C.R.; Díaz-Ruiz, A.; Lopez, M.; Malagón, M.M.; et al. Regulation of GPR55 in Rat White Adipose Tissue and Serum LPI by Nutritional Status, Gestation, Gender and Pituitary Factors. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 383, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, S.A. Lysophosphatidylinositol, but not Lysophosphatidic Acid Stimulates Insulin Release. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 138, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, S. Mobilization of Cellular Ca2+ by Lysophospholipids in Rat Islets of Langerhans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 968, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falasca, M.; Corda, D. Elevated Levels and Mitogenic Activity of Lysophosphatidylinositol in K-ras-transformed Epithelial Cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 221, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falasca, M.; Siletta, M.; Carvelli, A.; di Francesco, A.; Fusco, A.; Ramakrishna, V.; Corda, D. Signalling Pathways Involved in the Mitogenic Action of Lysophosphatidylinositol. Oncogene 1995, 10, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falasca, M.; Lurisci, C.; Carvelli, A.; Sacchetti, A.; Corda, D. Release of the Mitogen Lysophosphatidylinositol from H-Ras-transformed Fibroblasts; A Possible Mechanism of Autocrine Control of Cell Proliferation. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henstridge, C.M.; Balenga, N.A.B.; Kargl, J.; Andradas, C.; Brown, A.J.; Irving, A.; Sanchez, C.; Waldhoer, M. Minireview: Recent Developments in the Physiology and Pathology of the Lysophosphatidylinositol-sensitive Receptor GPR55. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Nakajima, K.; Yamashita, A.; Kishimoto, S.; Sugiura, T. Identification of GPR55 as a Lysophosphatidylinositol Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 362, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.A. L-α-lysophosphatidylinositol Meets GPR55: A Deadly Relationship. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Zerbo, S.Y.; Rafacho, A.; Díaz-Arteaga, A.; Suárez, J.; Quesada, I.; Imbernon, M.; Ross, R.A.; Dieguez, C.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Nogueiras, R.; et al. A Role for the Putative Cannabinoid Receptor GPR55 in the Islets of Langerhans. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 211, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.-T.; Yeo, J.-F.; Farooqui, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Chen, P.; Ong, W.-Y. Differential Effects of Lysophospholipids on Exocytosis in Rat PC12 Cells. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, A.I.; Malli, R.; Graier, W.F. The GPR55 Agonist Lysophosphatidylinositol Directly Activates Intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ Channels. Cardiovascular Phys. 2011, 262, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danthi, S.; Enyeart, J.A.; Enyeart, J.J. Modulation of Native TREK-1 and Kv1.4 K+ Channels by Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Lysophospholipids. J. Membr. Biol. 2003, 195, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monet, M.; Gkika, D.; Lehen’kyi, V.; Pourtier, A.; Abeele, F.V.; Bidaux, G.; Juvin, V.; Rassendren, F.; Humez, S.; Prevarsakaya, N. Lysophospholipids Stimulate Prostate Cancer Cell Migration via TRPV2 Channel Activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Cell Res. 2009, 1793, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawzdargo, M.; Nguyen, T.; Lee, D.K.; Lynch, K.R.; Cheng, R.; Heng, H.H.Q.; George, S.R.; O’Dowd, B.F. Identification and Cloning of Three Novel Human G protein-coupled receptor Genes GPR52, Psi GPR53 and GPR55: GPR55 is Extensively Expressed in Human Brain. Mol. Brain Res. 1999, 64, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Wise, A. Identification of Modulators of GPR55 Activity. U.S. Patent 10/275,200, 19 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ryberg, E.; Larsson, N.; Sjögren, S.; Hjorth, S.; Hermansson, N.O.; Leonova, J.; Elebring, T.; Nilsson, K.; Drmota, T.; Greasley, P.J. The Orphan Receptor GPR55 is a Novel Cannabinoid Receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro, R.; Maffucci, T.; Falasca, M. The Putative Cannabinoid Receptor GPR55 Defines a Novel Autocrine Loop in Cancer Cell Proliferation. Oncogene 2011, 30, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andradas, C.; Caffarel, M.M.; Pérez-Gómez, E.; Salazar, M.; Lorente, M.; Velasco, G.; Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, C. The Orphan G Protein-coupled Receptor GPR55 Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation via ERK. Oncogene 2011, 30, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, L.A.; Roelofs, A.J.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Mowat, L.; Simpson, D.G.; Irving, A.J.; Rogers, M.J.; Rajnicek, A.M.; Ross, R.A. A Role for L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol and GPR55 in the Modulation of Migration, Orientation and Polarization of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, E.P.; Andradas, C.; Flores, J.; Quantanilla, M.; Pamamio, J.; Guzman, M.; Sanchez, C. The Orphan Receptor GPR55 Drives Skin Carcinogenesis and is Upregulated in Human Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Oncogene 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Henstridge, C.M.; Balenga, N.A.B.; Ford, L.A.; Ross, R.A.; Waldhoer, M.; Irving, A.J. The GPR55 Ligand L-alpha-Lysophosphatidylinositol Promotes RhoA-dependent Ca2+ Signaling and NFAT Activation. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Jensen, J.B.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lu, H.-C.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. GPR55 is a Cannabinoid Receptor that Increases Intracellular Calcium and Inhibits M Current. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Toshida, T.; Maruyama, K.; Nakajima, K.; Yamashita, A.; Sugiura, T. 2-Arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoinositol: A Possible Natural Ligand for GPR55. J. Biochem. 2009, 145, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldeck-Weiermair, M.; Zoratti, C.; Osibow, K.; Balenga, N.A.B.; Goessnitzer, E.; Waldhoer, M.; Malli, R.; Graier, W.F. Integrin Clustering Enables Anandamide-induced Ca2+ Signaling in Endothelial Cells via GPR55 by Protection Against CB1-receptor-Triggered Repression. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1704–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, Y.; Maceyka, M.; Spiegel, S.; Chun, J. Lysophospholipid Receptor Nomenclature Review: IUPHAR Review 8. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3575–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Marzo, V.; di Elphick, M.R.; Greasley, P.J.; Hansen, H.S.; Kunos, G. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid Receptors and Their Ligands: Beyond CB 1 and CB 2. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 588–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, Y.; Ueno, S.; Yanagihata, Y.; Nakahata, N. Lysophosphatidylinositol Causes Neurite Retraction via GPR55, G13 and RhoA in PC12 Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Oka, S.; Tanikawa, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Sugiura, T. The Actions and Metabolism of Lysophosphatidylinositol, an Endogenous Agonist for GPR55. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013, 107, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsikorou, E.; Madrigal, K.E.; Hurst, D.P.; Sharir, H.; Lynch, D.L.; Heynen-Genel, S.; Milan, L.B.; Chung, T.D.Y.; Seltzman, H.H.; Bai, Y.; et al. Identification of the GPR55 Agonist Binding Site Using a Novel Set of High-Potency GPR55 Selective Ligands. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5633–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henstridge, C.M.; Balenga, N.A.; Schroder, R.; Kargl, J.K.; Platzer, W.; Martini, L.; Arthur, S.; Penman, J.; Whistler, J.L.; Kostenis, E.; et al. GPR55 Ligands Promote Receptor Coupling to Multiple Signalling Pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y. Approaches of Targeting Rho GTPases in Cancer Drug Discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKillop, A.M.; Moran, B.M.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A.; Flatt, P.R. Evaluation of the Insulin Releasing and antihyperglycaemic Activities of GPR55 Lipid Agonists Using Clonal Beta-cells, Isolated Pancreatic Islets and Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlSuleimani, Y.M.; Hiley, C.R. The GPR55 Agonist Lysophosphatidylinositol Mediates Vasorelaxation of the Rat Mesenteric Resistance Artery and Induces Calcium Release in Rat Mesenteric Artery Endothelial Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, D.G.; Behm, D.J.; Walker, D.J.; Ao, Z.; Shapland, E.M.; Daniels, D.A.; Riddick, M.; Dowell, S.; Staton, P.C.; Green, P.; et al. The Novel Endocannabinoid Receptor GPR55 is Activated by Atypical Cannabinoids but Does Not Mediate Their Vasodilator Effects. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargl, J.; Brown, A.J.; Andersen, L.; Dorn, G.; Schicho, R.; Waldhoer, M.; Heinemann, A. A Selective Antagonist Reveals a Potential Role of G protein-coupled Receptor 55 in Platelet and Endothelial Cell Function. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schicho, R.; Storr, M. A Potential Role for GPR55 in Gastrointestinal Functions. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stančić, A.; Jandl, K.; Hasenöhrl, C.; Reichmann, F.; Marsche, G.; Schuligoi, R.; Heinemann, A.; Storr, M.; Schicho, R. The GPR55 Antagonist CID16020046 Protects Against Intestinal Inflammation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, P.J.; Barlow, C.K.; Mellett, N.A.; Mundra, P.A.; Bonham, M.P.; Larsen, A.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Sinclair, A.; Nestel, P.J.; Wong, G. Postprandial Plasma Phospholipids in Men Are Influenced by the Source of Dietary Fat. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soga, T.; Ohishi, T.; Matsui, T.; Saito, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Takasaki, J.; Matsumoto, S.-I.; Kamohara, M.; Hiyama, H.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Lysophosphatidylcholine Enhances Glucose-dependent Insulin Secretion via an Orphan G-protein-coupled Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.S.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Holst, J.J.; Schwartz, T.W. GPR119 as a Fat Sensor. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietr, M.; Kozela, E.; Levy, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Lin, Y.H.; Stella, N.; Vogel, Z.; Juknat, A. Differential Changes in GPR55 During Microglial Cell Activation. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deliu, E.; Sperow, M.; Console-Bram, L.; Carter, R.L.; Tilley, D.G.; Kalamarides, D.J.; Kirby, L.G.; Brailoiu, G.C.; Brailoiu, E.; Benamar, K.; et al. The Lysophosphatidylinositol Receptor GPR55 Modulates Pain Perception in the Periaqueductal Gray. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, G.R.; Lichtman, A.; Dewey, W.L.; Akbarali, H.I. Evidence for the Putative Cannabinoid Receptor (GPR55)-mediated Inhibitory Effects on Intestinal Contractility in Mice. Pharmacology 2012, 90, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, D.M.; Park, S.J.; Valinsky, W.C.; Beyak, M.J. Impaired Intestinal Afferent Nerve Satiety Signalling and Vagal Afferent Excitability in Diet Induced Obesity in the Mouse. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 2857–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. The Vagus Nerve and the Inflammatory Reflex-linking Immunity and Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staton, P.C.; Hatcher, J.P.; Walker, D.J.; Morrison, A.D.; Shapland, E.M.; Hughes, J.P.; Chong, E.; Mander, P.K.; Green, P.J.; Billinton, A.; et al. The Putative Cannabinoid Receptor GPR55 Plays a Role in Mechanical Hyperalgesia Associated with Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. Pain 2008, 139, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltzer, Z.; Dubner, R.; Shir, Y. A Novel Behavioral Model of Neuropathic Pain Disorders Produced in Rats by Partial Sciatic Nerve Injury. Pain 1990, 43, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, M.; Bosisio, D.; Polentarutti, N.; D’amico, G.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Mancinelli, R.; van’t Veer, C.; Penton-Rol, G.; Ruco, L.P.; Allavena, P.; et al. Differential Expression and Regulation of Toll-like Receptors (TLR) in Human Leukocytes: Selective Expression of TLR3 in Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5998–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, L.S.; Ryberg, E.; Sims, N.A.; Ridge, S.A.; Mackie, K.; Greasley, P.J.; Ross, R.A.; Rogers, M.J. The Putative Cannabinoid Receptor GPR55 Affects Osteoclast Function in Vitro and Bone Mass in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16511–16516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmuhl, E.; Ramer, R.; Salamon, A.; Peters, K.; Hinz, B. Increase of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration by Cannabidiol via Activation of p42/44 MAPK. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, H.; Onaivi, E.S.; Horiuchi, Y.; Imai, K.; Komaki, G.; Ishikawa, T.; Suzuki, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Ando, T.; Higuchi, S.; et al. Functional Polymorphism in the GPR55 Gene is Associated with Anorexia Nervosa. Synapse 2011, 65, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Arteaga, A.; Vázquez, M.J.; Vazquez-Martínez, R.; Pulido, M.R.; Suarez, J.; Velásquez, D.A.; López, M.; Ross, R.A.; de Fonseca, F.R.; Bermudez-Silva, F.J.; et al. The Atypical Cannabinoid O-1602 Stimulates Food Intake and Adiposity in Rats. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, A.; Jh, L.; Cs, W.; Wei, Q.; Pradhan, G.; Yafi, M.; Hc, L. Deletion of G-protein Coupled Receptor 55 Promotes Obesity by Reducing Physical Activity. Int J. Obes. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Fichna, J.; Schicho, R.; Saur, D.; Bashashati, M.; Mackie, K.; Li, Y.; Zimmer, A.; Göke, B.; Sharkey, K.; et al. A Role for O-1602 and G protein-Coupled Receptor GPR55 in the Control of Colonic Motility in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.H.; Wei, D.D.; Wang, H.C.; Wang, B.; Bai, C.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, G.E.; Li, H.P.; Ren, X.Q. Role of Orphan G protein-coupled Receptor 55 in Diabetic Gastroparesis in Mice. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2014, 66, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jenkin, K.; McAinch, A.J.; Zhang, Y.; Kelly, D.J.; Hryciw, D.H. Elevated Cannabinoid Receptor 1 and G protein-coupled Receptor 55 Expression in Proximal Tubule Cells and Whole Kidney Exposed to Diabetic Conditions. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 42, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgaard, A.J.; Weir, J.M.; de Souza, D.P.; Tull, D.; Haase, C.; Meikle, P.J.; Pociot, F. Lipidomic and Metabolomic Characterization of a Genetically Modified Mouse Model of the Early Stages of Human Type 1 Diabetes Pathogenesis. Metabolomics 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.K.; Hector, E.E.; Andréasson, A.-C.; Jönsson-Rylander, A.-C.; Wainwright, C.L. GPR55 Deletion in Mice Leads to Age-Related Ventricular Dysfunction and Impaired Adrenoceptor-mediated Inotropic Responses. PLoS ONE 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lampe, J.; Yin, T.; Shinozaki, K.; Becker, L. Phospholipid Alterations in the Brain and Heart in a Rat Model of Asphyxia-Induced Cardiac Arrest and Cardiopulmonary Bypass Resuscitation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 408, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurano, M.; Suzuki, A.; Inoue, A.; Tokuhara, Y.; Kano, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Igarashi, K.; Ohkawa, R.; Nakamura, K.; Dohi, T.; et al. Possible Involvement of Minor Lysophospholipids in the Increase in Plasma Lysophosphatidic Acid in Acute Coronary Syndrome. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanuti, M.; Talamonti, E.; Maccarrone, M.; Chiurchiù, V. Activation of GPR55 Receptors Exacerbates OxLDL-induced Lipid Accumulation and Inflammatory Responses, While Reducing Cholesterol Efflux from Human Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falasca, M.; Ferro, R. Role of the Lysophosphatidylinositol/GPR55 Axis in Cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruban, E.L.; Ferro, R.; Arifin, S.A.; Falasca, M. Lysophosphatidylinositol: A novel link between ABC transporters and G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simcocks, A.C.; O’Keefe, L.; Jenkin, K.A.; Mathai, M.L.; Hryciw, D.H.; McAinch, A.J. A Potential Role for GPR55 in the Regulation of Energy Homeostasis. Drug Discov. Today 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Song, S.; Jones, P.M.; Persaud, S.J. GPR55: From Orphan to Metabolic Regulator? Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 145, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arifin, S.A.; Falasca, M. Lysophosphatidylinositol Signalling and Metabolic Diseases. Metabolites 2016, 6, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6010006
Arifin SA, Falasca M. Lysophosphatidylinositol Signalling and Metabolic Diseases. Metabolites. 2016; 6(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleArifin, Syamsul A., and Marco Falasca. 2016. "Lysophosphatidylinositol Signalling and Metabolic Diseases" Metabolites 6, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6010006
APA StyleArifin, S. A., & Falasca, M. (2016). Lysophosphatidylinositol Signalling and Metabolic Diseases. Metabolites, 6(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo6010006






