New Strategies for the Treatment of Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Abstract
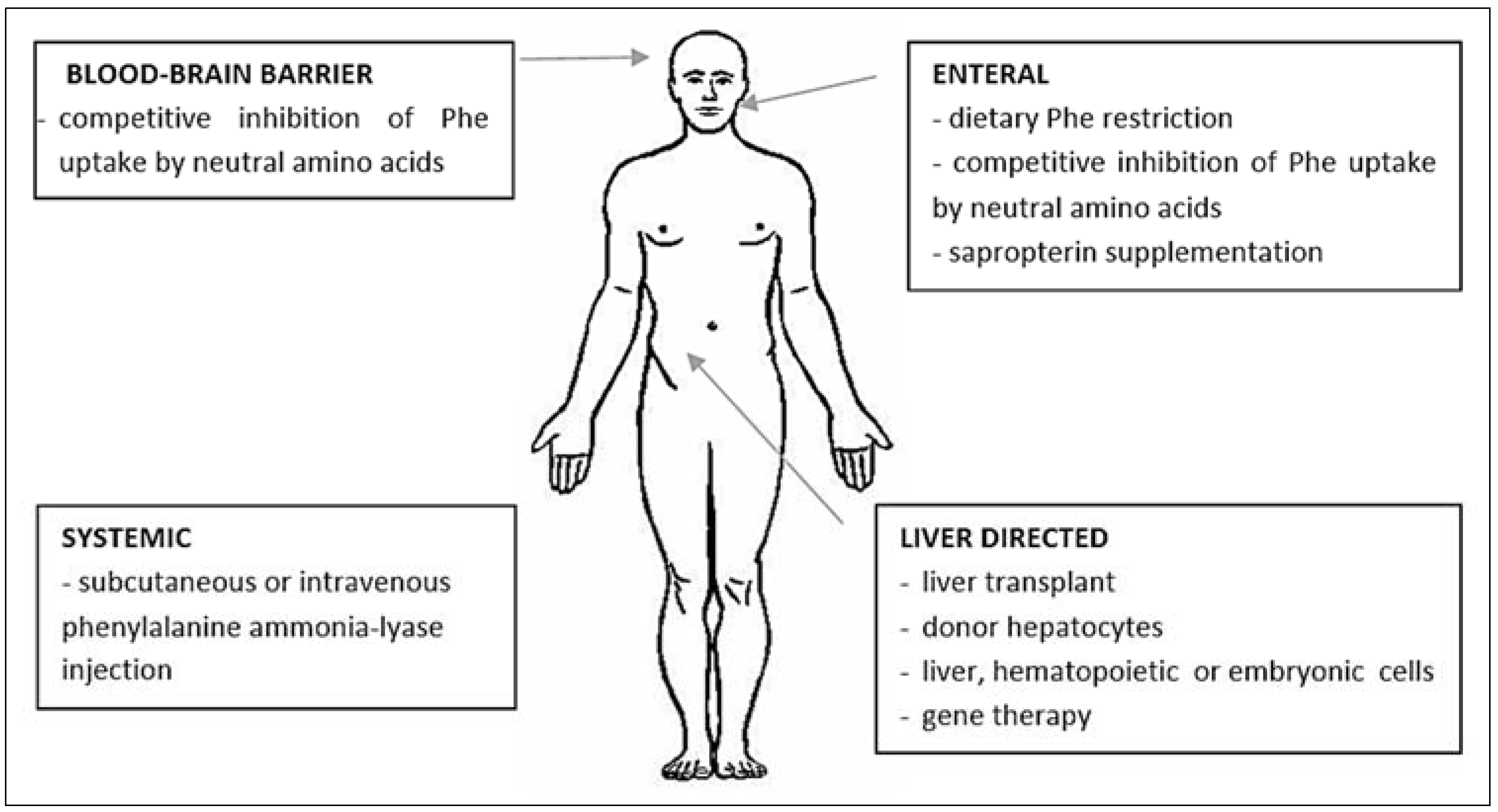
:1. Introduction
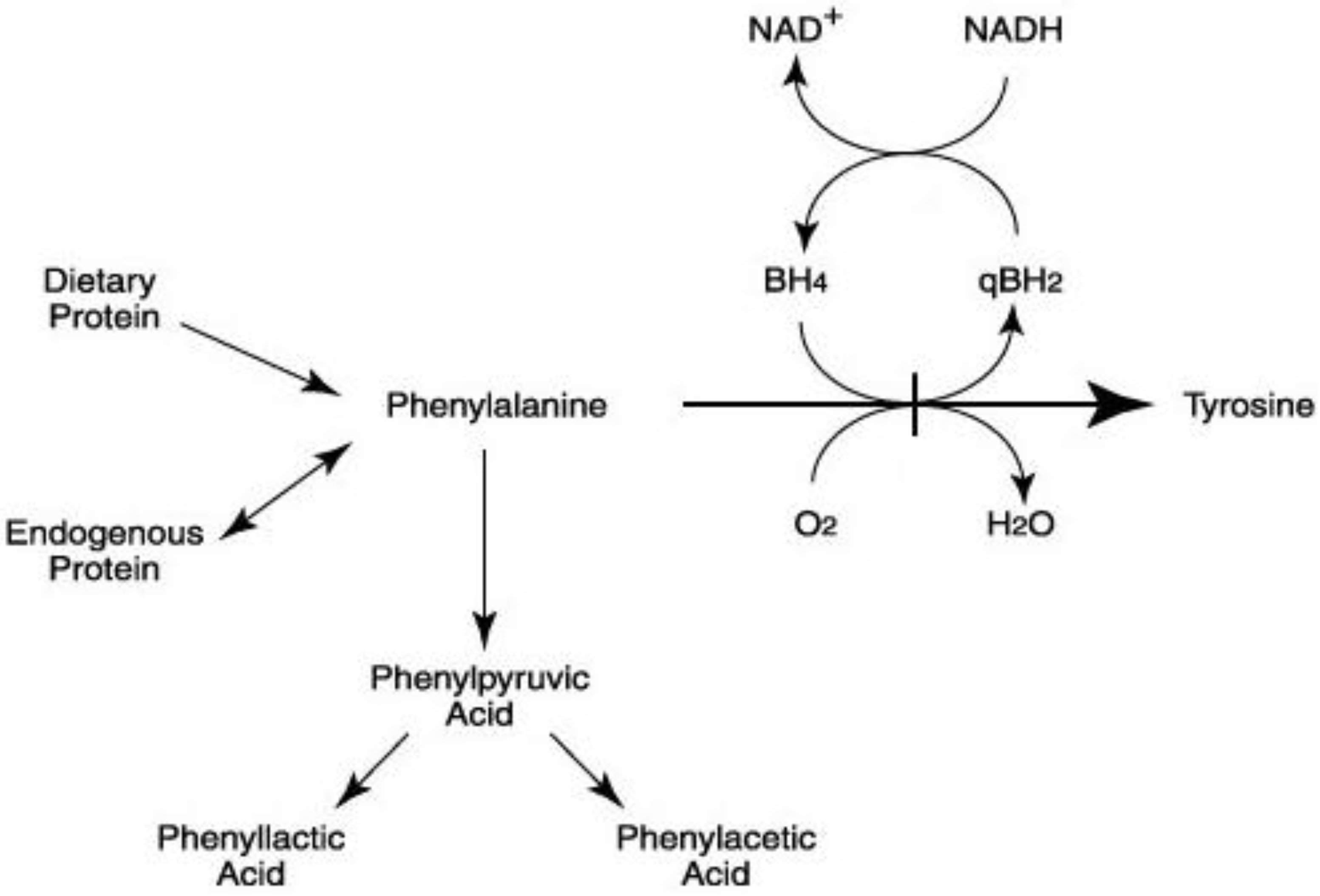
2. Dietary Treatment
3. Large Neutral Amino Acid Supplementation
4. Tetrahydropterin as Enzyme Enhancement Therapy for PKU
5. Enzyme Therapy
6. Cell Directed Therapy
7. Gene Therapy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blau, N.; van Spronsen, F.J.; Levy, H.L. Phenylketonuria. Lancet. 2010, 376, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Enns, G.M.; Koch, R.; Brumm, V.; Blakely, E.; Suter, R.; Jurecki, E. Suboptimal outcomes in patients with PKU treated early with diet alone: Revisiting the evidence. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 101, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, S.E.; Huijbregts, S.C.; de Sonneville, L.M.; White, D.A. Executive function in early-treated phenylketonuria: Profile and underlying mechanisms. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 99 (Suppl 1), S22–S32. [Google Scholar]
- Zschocke, J. Phenylketonuria mutations in Europe. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, N.; Hennermann, J.B.; Langenbeck, U.; Lichter-Konecki, U. Diagnosis, classification, and genetics of phenylketonuria and tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiencies. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, P.B.; Yannicelli, S.; Singh, R.; Mofidi, S.; Steiner, R.; de Vincentis, E.; Jurecki, E.; Bernstein, L.; Gleason, S.; Chetty, M.; Rouse, B. Nutrient intakes and physical growth of children with phenylketonuria undergoing nutrition therapy. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbelaere, D.; Michaud, L.; Debrabander, A.; Vanderbecken, S.; Gottrand, F.; Turck, D.; Farriaux, J.P. Evaluation of nutritional status and pathophysiology of growth retardation in patients with phenylketonuria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2003, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strisciuglio, P.; Concolino, D.; Moricca, M.T.; Rivalta, L.; Parlato, G. Normal serum levels of vitamin B12 and folic acid in children with phenylketonuria. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1995, 154. Article 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feillet, F.; Agostoni, C. Nutritional issues in treating phenylketonuria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Harvie, A.; McCulloch, D.L.; Demellweek, C.; Cockburn, F.; Giovannini, M.; Murray, G.; Harkness, R.A.; Riva, E. A randomized trial of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation in infants with phenylketonuria. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2006, 48, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beblo, S.; Reinhardt, H.; Demmelmair, H.; Muntau, A.C.; Koletzko, B. Effect of fish oil supplementation on fatty acid status, coordination, and fine motor skills in children with phenylketonuria. J. Pediatr. 2007, 150, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLeod, E.L.; Clayton, M.K.; van Calcar, S.C.; Ney, D.M. Breakfast with glycomacropeptide compared with amino acids suppresses plasma ghrelin levels in individuals with phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 100, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Calcar, S.C.; MacLeod, E.L.; Gleason, S.T.; Etzel, M.R.; Clayton, M.K.; Wolff, J.A.; Ney, D.M. Improved nutritional management of phenylketonuria by using a diet containing glycomacropeptide compared with amino acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.; Slover, R.; Gass, S.; Seltzer, W.K.; McCabe, L.L.; McCabe, E.R. Blood phenylalanine estimation for the patient with phenylketonuria using a portable device. Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol. 1988, 39, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, N.; Li, S.K.; Yan, G.; Kochambilli, R.P.; Papangkorn, K.; Berglund, D.; Ghanem, A.H.; Ashurst, C.L.; Ernst, S.L.; Pasquali, M.; et al. Noninvasive measurement of phenylalanine by iontophoretic extraction in patients with phenylketonuria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 910–915. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, A.L.; Roberts, R.M.; Fletcher, J.M. Dietary protein counting as an alternative way of maintaining metabolic control in phenylketonuria. JIMD Rep. 2012, 3, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harding, C.O.; Gibson, K.M. Therapeutic liver repopulation for phenylketonuria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matalon, R.; Michals-Matalon, K.; Bhatia, G.; Grechanina, E.; Novikov, P.; McDonald, J.D.; Grady, J.; Tyring, S.K.; Guttler, F. Large neutral amino acids in the treatment of phenylketonuria (PKU). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matalon, R.; Michals-Matalon, K.; Bhatia, G.; Burlina, A.B.; Burlina, A.P.; Braga, C.; Fiori, L.; Giovannini, M.; Grechanina, E.; Novikov, P.; et al. Double blind placebo control trial of large neutral amino acids in treatment of PKU: Effect on blood phenylalanine. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2007, 30, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindeler, S.; Ghosh-Jerath, S.; Thompson, S.; Rocca, A.; Joy, P.; Kemp, A.; Rae, C.; Green, K.; Wilcken, B.; Christodoulou, J. The effects of large neutral amino acid supplements in PKU: An MRS and neuropsychological study. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 91, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascucci, T.; Andolina, D.; Ventura, R.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Cabib, S. Reduced availability of brain amines during critical phases of postnatal development in a genetic mouse model of cognitive delay. Brain. Res. 2008, 27, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksma, M.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Pruim, J.; de Valk, H.W.; Paans, A.M.; van Spronsen, F.J. Phenylketonuria: High plasma phenylalanine decreases cerebral protein synthesis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 96, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concolino, D.; Mascaro, I.; Moricca, M.T.; Bonapace, G.; Matalon, K.; Patel, V.; Matalon, R.; Strisciuglio, P. Long term treatment of phenylketonuria with a new food containing LNAA. Nutrients 2014. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, K.R.; Arning, E.; Wasek, B.L.; Bottiglieri, T.; Gibson, K.M. Non-physiological amino acid (NPAA) therapy targeting brain phenylalanine reduction: Pilot studies in PAH (ENU2) mice. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, N.; Hennermann, J.B.; Langenbeck, U.; Lichter-Konecki, U. Diagnosis, classification, and genetics of phenylketonuria and tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiencies. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 104, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuzzi, V.; Pansini, M.; Sechi, E.; Chiarotti, F.; Carducci, C.; Levi, G.; Antonozzi, I. Executive function impairment in early-treated PKU subjects with normal mental development. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2004, 27, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kure, S.; Hou, D.C.; Ohura, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Suzuki, S.; Sugiyama, N.; Sakamoto, O.; Fujii, K.; Matsubara, Y.; Narisawa, K. Tetrahydrobiopterin-responsive phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. J. Pediatr. 1999, 135, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pey, A.L.; Stricher, F.; Serrano, L.; Martinez, A. Predicted effects of missense mutations on native-state stability account for phenotypic outcome in phenylketonuria, a paradigm of misfolding diseases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 1006–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerone, R.; Andria, G.; Giovannini, M.; Leuzzi, V.; Riva, E.; Burlina, A. Testing for tetrahydrobiopterin responsiveness in patients with hyperphenylalaninemia due to phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. Adv. Ther. 2013, 30, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, H.; Burton, B.; Cederbaum, S.; Scriver, C. Recommendations for evaluation of responsiveness to tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) in phenylketonuria and its use in treatment. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 92, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, N.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Demirkol, M.; Feillet, F.; Giovannini, M.; MacDonald, A.; Trefz, F.K.; van Spronsen, F.J. Optimizing the use of sapropterin (BH4) in the management of phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 96, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, P.; Thomas, J.A.; Suter, R.; Jurecki, E. Evolving patient selection and clinical benefit criteria for sapropterin dihydrochloride (Kuvan®) treatment of PKU patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 105, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blau, N.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Demirkol, M.; Feillet, F.; Giovannini, M.; MacDonald, A.; Trefz, F.-K.; van Spronsen, F. European PKU centers. Management of phenylketonuria in Europe: Survey results from 19 countries. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 99, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiege, B.; Blau, N. Assessment of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) responsiveness in phenylketonuria. J. Pediatrics 2007, 150, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, L.; Fiege, B.; Riva, E.; Giovannini, M. Incidence of BH4-responsiveness in phenylalanine-hydroxylase-deficient Italian patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, S67–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trefz, F.K.; Burton, B.K.; Longo, N.; Casanova, M.M.; Gruskin, D.J.; Dorenbaum, A.; Kakkis, E.D.; Crombez, E.A.; Grange, D.K.; Harmatz, P.; et al. Sapropterin Study Group Efficacy of sapropterin dihydrochloride in increasing phenylalanine tolerance in children with phenylketonuria: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Pediatr. 2009, 154, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambruschini, N.; Pérez-Dueñas, B.; Vilaseca, M.A.; Mas, A.; Artuch, R.; Gassió, R.; Gómez, L.; Gutiérrez, A.; Campistol, J. Clinical and nutritional evaluation of phenylketonuric patients on tetrahydrobiopterin monotherapy. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, S54–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, I.; Concolino, D.; Della Casa, R.; Nastasi, A.; Ungaro, C.; Paladino, S.; Capaldo, B.; Ruoppolo, M.; Daniele, A.; Bonapace, G.; et al. Long term follow-up of patients with hyperphenilalaninemia treated with tetrahydrobiopterin. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Longo, N.; Siriwardena, K.; Feigenbaum, A.; Dimmock, D.; Burton, B.K.; Stockler, S.; Waisbren, S.; Lang, W.; Jurecki, E.; Zhang, C.; et al. Long-term developmental progression in infants and young children taking sapropterin for phenylketonuria: A two-year analysis of safety and efficacy. Genet. Med. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, N. Sapropterin dihydrochloride for the treatment of hyperphenylalaninemias. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pey, A.L.; Ying, M.; Cremades, N.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Scherer, T.; Thöny, B.; Sancho, J.; Martinez, A. Identification of pharmacological chaperones as potential therapeutic agents to treat phenylketonuria. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 2858–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkissian, C.N.; Shao, Z.; Blain, F.; Peevers, R.; Su, H.; Heft, R.; Chang, T.M.; Scriver, C.R. A different approach to treatment of phenylketonuria: Phenylalanine degradation with recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 2339–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajro, P.; Striscìuglio, P.; Houssin, D.; Huault, G.; Laurent, J.; Alvarez, F.; Bernard, O. Correction of phenylketonuria after liver transplantation in a child with cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 29, 329–363. [Google Scholar]
- Eavri, R.; Lorberboum-Galski, H. A novel approach for enzyme replacement therapy. The use of phenylalanine hydroxylase-based fusion proteins for the treatment of phenylketonuria. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23402–23409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez, A.; Wang, L.; Straub, M.; Patch, M.G.; Stevens, R.C. Toward PKU enzyme replacement therapy: PEGylation with activity retention for three forms of recombinant phenylalanine hydroxylase. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkissian, C.N.; Gámez, A. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase, enzyme substitution therapy for phenylketonuria, where are we now? Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, S22–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, N.; Harding, C.O.; Burton, B.K.; Grange, D.K.; Vockley, J.; Wasserstein, M.; Rice, G.M.; Dorenbaum, A.; Neuenburg, J.K.; Musson, D.G.; et al. Single-dose, subcutaneous recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase conjugated with polyethylene glycol in adult patients with phenylketonuria: An open-label, multicentre, phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet. 2014, 84, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.S.; Wang, L.; Sarkissian, C.N.; Gámez, A.; Scriver, C.R.; Stevens, R.C. Converting an injectable protein therapeutic into an oral form: Phenylalanine ammonia lyase for phenylketonuria. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2010, 99, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, C.O. Progress toward cell-directed therapy for phenylketonuria. Clin. Genet. 2008, 74, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enns, G.M.; Millan, M.T. Cell-based therapies for metabolic liver disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 95, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Georgiev, P.; Thöny, B. Administration-route and gender-independent long-term therapeutic correction of phenylketonuria (PKU) in a mouse model by recombinant adeno-associated virus 8 pseudo typed vector-mediated gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebuffat, A.; Harding, C.O.; Ding, Z.; Thöny, B. Comparison of adeno-associated virus pseudotype1, 2, and 8 vectors administered by intramuscular injection in the treatment of murine phenylketonuria. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, I.E.; Cunningham, S.C.; Logan, G.J.; Christodoulou, J. Potential of AAV vectors in the treatment of metabolic disease. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, G.; Reichardt, J.; Christodoulou, J. In vitro read-through of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) nonsense mutations using aminoglycosides: A potential therapy for phenylketonuria. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strisciuglio, P.; Concolino, D. New Strategies for the Treatment of Phenylketonuria (PKU). Metabolites 2014, 4, 1007-1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4041007
Strisciuglio P, Concolino D. New Strategies for the Treatment of Phenylketonuria (PKU). Metabolites. 2014; 4(4):1007-1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4041007
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrisciuglio, Pietro, and Daniela Concolino. 2014. "New Strategies for the Treatment of Phenylketonuria (PKU)" Metabolites 4, no. 4: 1007-1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4041007
APA StyleStrisciuglio, P., & Concolino, D. (2014). New Strategies for the Treatment of Phenylketonuria (PKU). Metabolites, 4(4), 1007-1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4041007



