1H NMR Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: An Example of a Possible Misinterpretation Due to Non-Adjustment of pH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Assignment of 1H NMR Signals
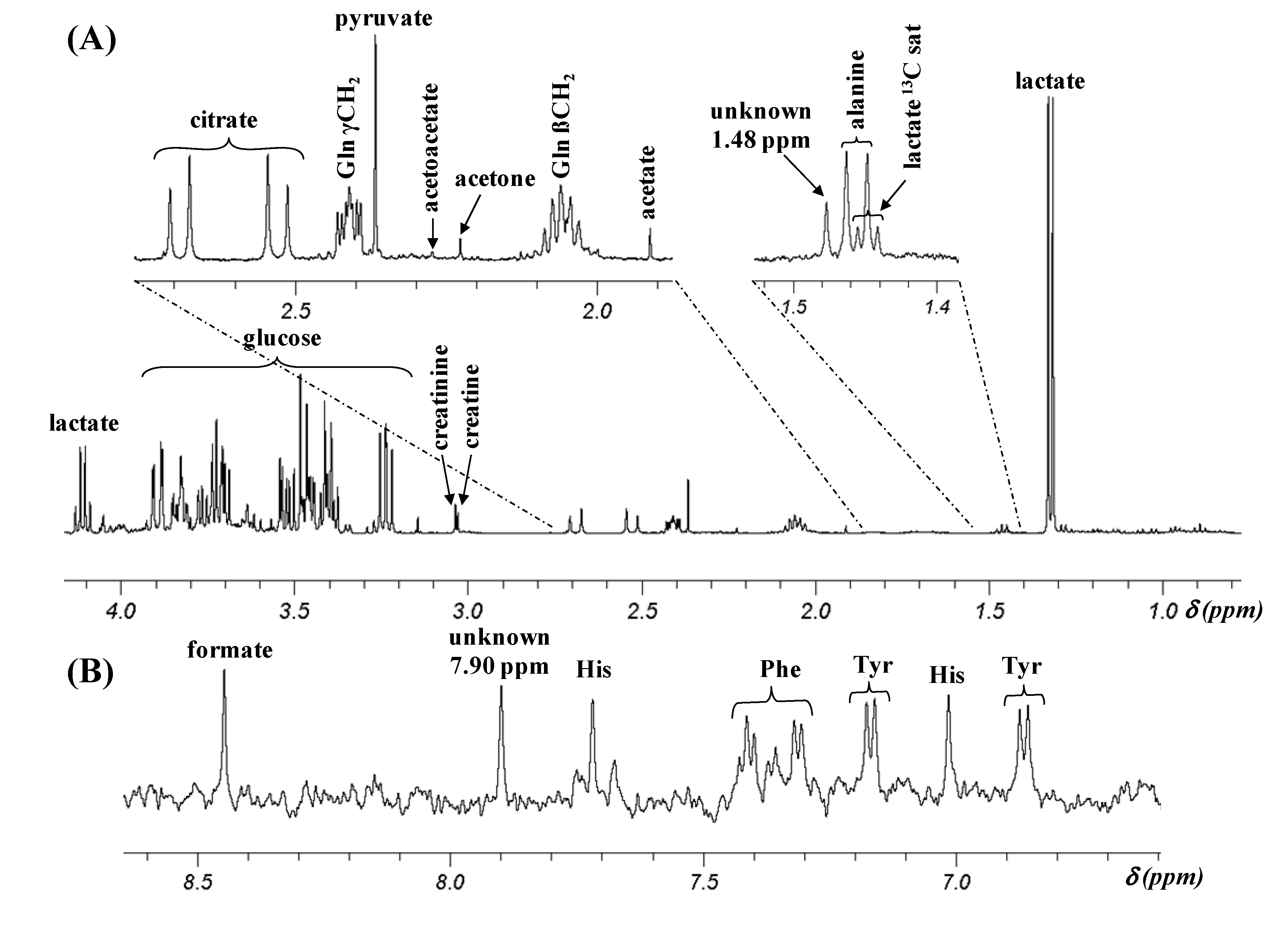

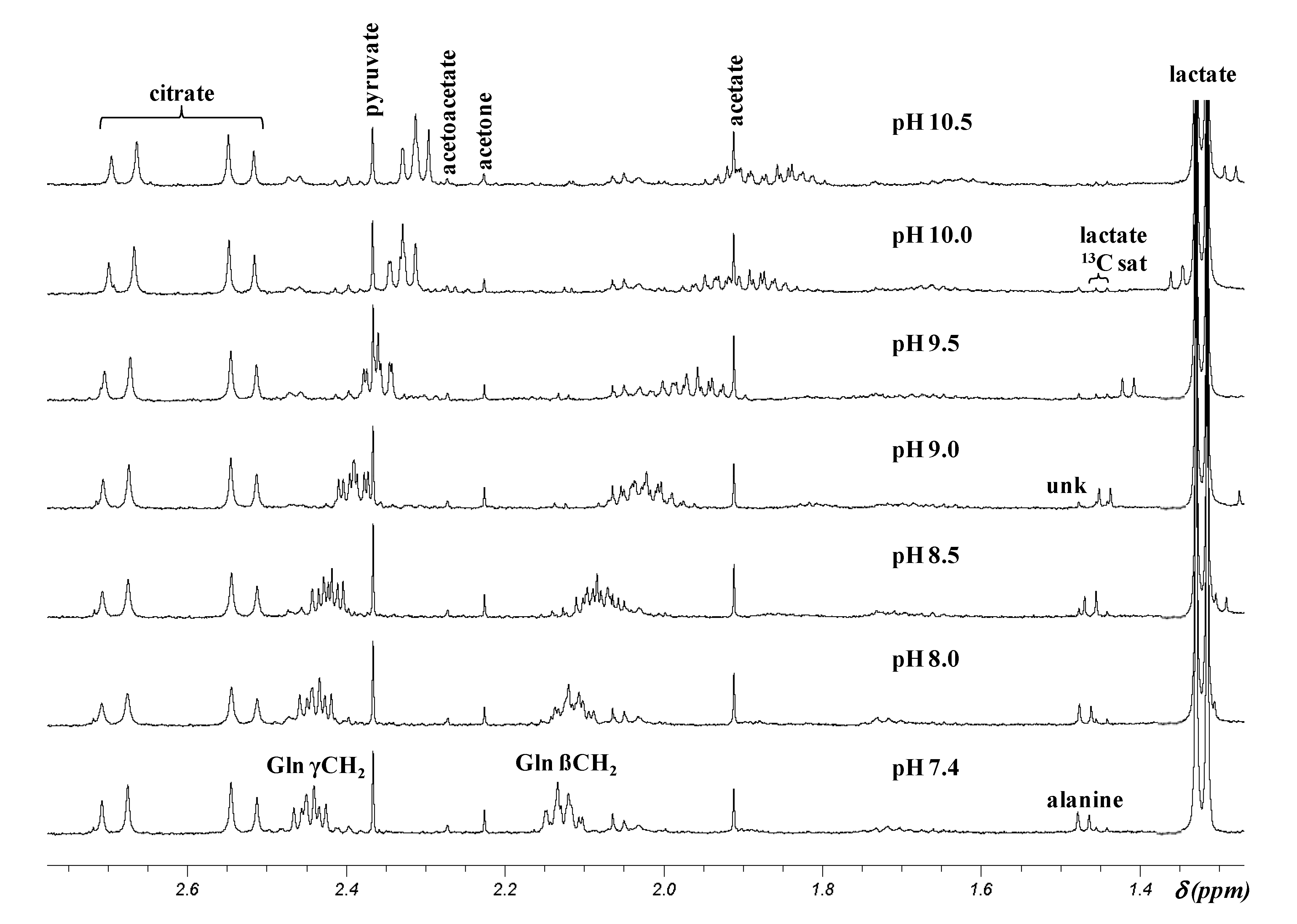
2.2. pH Dependence of 1H Chemical Shifts
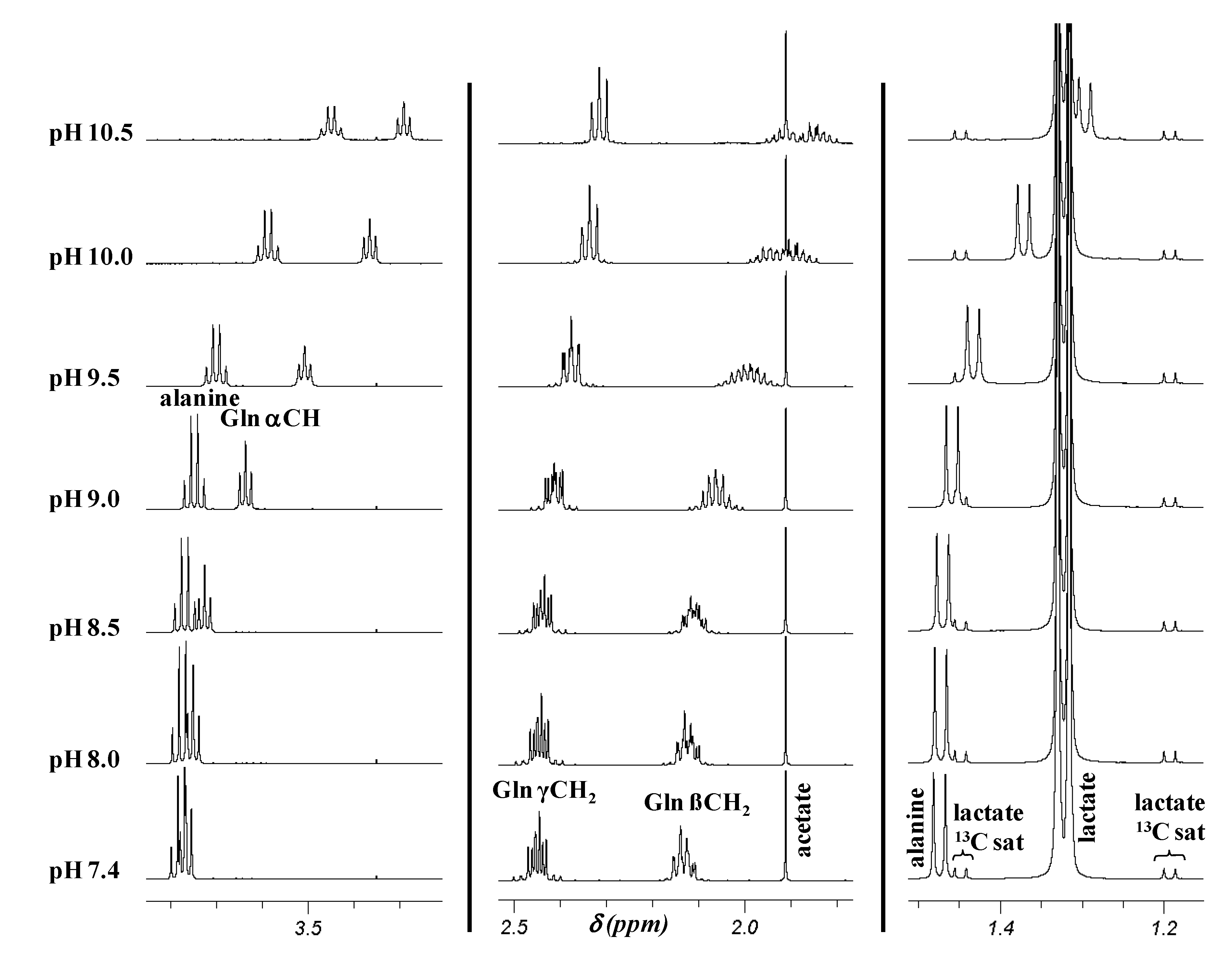
| Metabolitec | pH 7.4 a | pH 9.5 a | pH 10.5 a | Upfield shift b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In model solution | In CSF | In model solution | In CSF | In model solution | In CSF | In model solution | In CSF | |
| Acetate | ||||||||
| CH3 s | 1.91 | 1.91 | 1.91 | 1.91 | 1.91 | 1.91 | 0 | 0 |
| Alanine | ||||||||
| CH3 d | 1.47 | 1.47 | 1.43 | 1.42 | 1.30 | 1.29 | 0.17 | 0.18 |
| CH q | 3.78 | ND d | 3.70 | ND d | 3.45 | ND d | 0.33 | ND d |
| Formate | ||||||||
| CH s | 8.45 | 8.45 | 8.45 | 8.45 | 8.45 | 8.45 | 0 | 0 |
| Glutamine | ||||||||
| α CH t | 3.77 | NDd | 3.51 | ND d | 3.29 | ND d | 0.48 | / |
| β CH2 m | 2.13 | 2.13 | 1.99 | 1.98 | 1.88 | 1.87 | 0.25 | 0.26 |
| γ CH2 m | 2.45 | 2.45 | 2.37 | 2.36 | 2.31 | 2.31 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| Histidine | ||||||||
| Ar CH s | 7.05 | 7.05 | 6.98 | 6.99 | 6.92 | 6.92 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| Ar CH s | 7.77 | 7.77 | 7.69 | 7.69 | 7.67 | 7.67 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Lactate | ||||||||
| CH3 d | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.32 | 0 | 0 |
| CH q | 4.10 | 4.11 | 4.10 | 4.11 | 4.10 | 4.11 | 0 | 0 |
| Phenylalanine | ||||||||
| ortho CH m | 7.33 | 7.33 | 7.31 | 7.30 | 7.29 | 7.29 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| para CH m | 7.37 | 7.37 | 7.34 | 7.33 | 7.31 | 7.31 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| meta CH m | 7.42 | 7.42 | 7.40 | 7.40 | 7.38 | 7.38 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Tyrosine | ||||||||
| Ar CH app d | 6.89 | 6.89 | 6.83 | 6.83 | 6.70 | 6.69 | 0.19 | 0.20 |
| Ar CH app d | 7.19 | 7.19 | 7.14 | 7.15 | 7.06 | 7.05 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
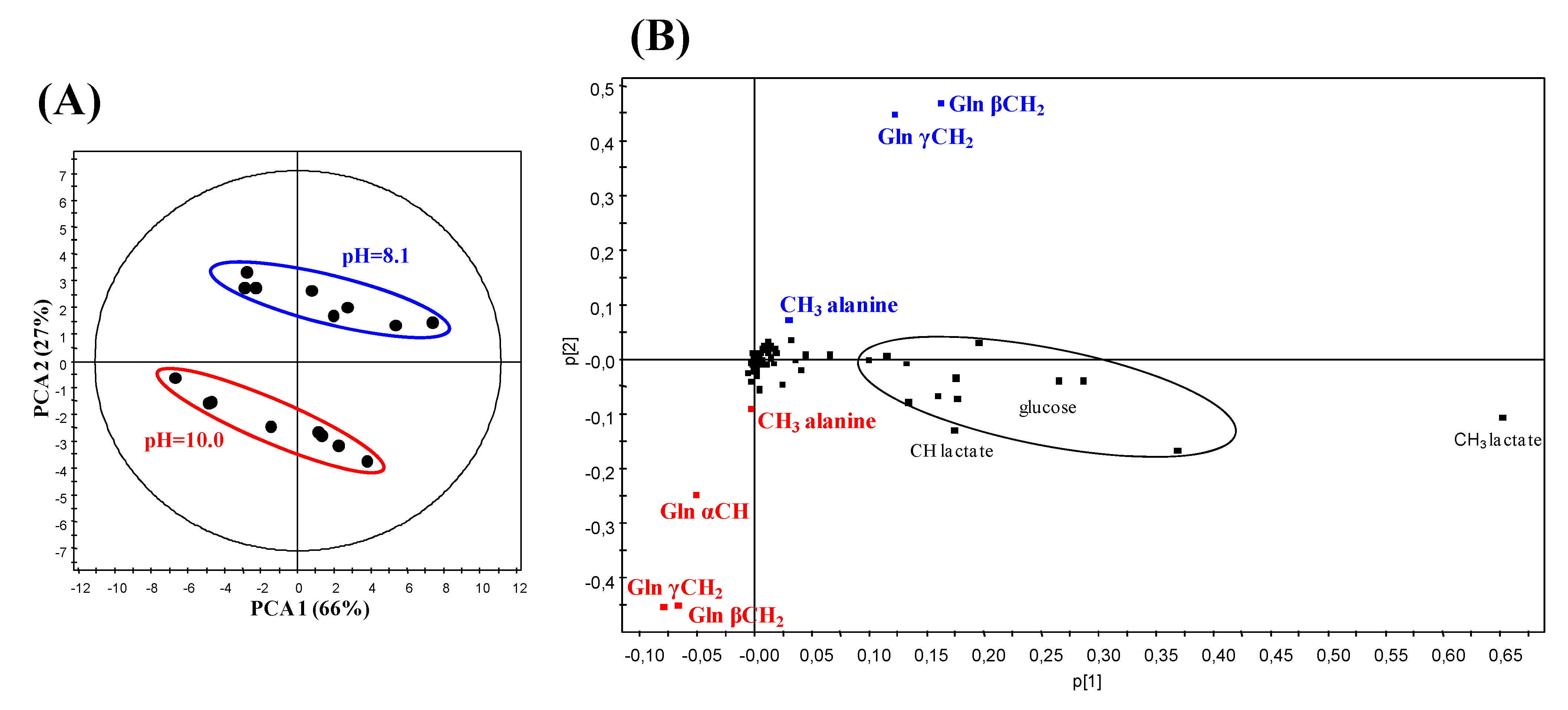
2.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of the 1H NMR Data from CSF Samples at Two Different pH
2.4. Effect of pH on the δ of the Resonances Proposed as Biomarkers by Kork et al.
2.5. Quantification of Some CSF Metabolites Discussed in this Study
| Metabolite | AD patients | Control | p-value a | Literature value in normal CSF (μM) [18] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± sd (μM) | Mean ± sd (μM) | |||
| Acetate | 57 ± 23 | 47 ± 32 | 0.21 | 58 ± 27 b |
| Alanine | 48 ± 18 | 46 ± 17 | 0.55 | 46 ± 27 b |
| Formate | 28 ± 10 | 43 ± 15 | 0.01 | 32 ± 16 b |
| Glutamine | 532 ± 67 | 543 ± 137 | 0.51 | 398 ± 150 b,c |
| Histidine | 14 ± 3 | 13 ± 3 | 0.73 | 15 ± 8 b,c |
| Phenylalanine | 15 ± 4 | 15 ± 5 | 0.73 | 15 ± 8 b,c |
| Tyrosine | 11 ± 3 | 12 ± 5 | 0.73 | 12 ± 9 b |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Patients and CSF Sampling
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Preparation of CSF Samples and Model Solutions
3.3.1. CSF Samples
3.3.2. Model Solutions
3.4. 1H NMR Spectra Recording Conditions
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kork, F.; Holthues, J.; Hellweg, R.; Jankowski, V.; Tepel, M.; Öhring, R.; Heuser, I.; Bierbrauer, J.; Peters, O.; Schlattmann, P.; et al. A possible new diagnostic biomarker in early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2009, 6, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kork, F.; Gentsch, A.; Holthues, J.; Hellweg, R.; Jankowski, V.; Tepel, M.; Zidek, W.; Jankowski, J. A biomarker for severity of Alzheimer’s disease: 1H-NMR resonances in cerebrospinal fluid correlate with performance in mini-mental-state-exam. Biomarkers 2012, 17, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wevers, R.A.; Engelke, U.; Wendel, U.; de Jong, J.G.N.; Gabreëls, F.J.M.; Heerschap, A. Standardized method for high-resolution 1H-NMR of cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 744–751. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, N.W.; Viola, A.; Malikova, I.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Ranjeva, J.P.; Pelletier, J.; Cozzone, P.J. A branched-chain organic acid linked to multiple sclerosis: First identification by NMR spectroscopy of CSF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2007, 354, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. Hmdb 3.0-The human metabolome database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunniffe, J.G.; Whitby-Strevens, S.; Wilcox, M.H. Effect of pH changes in cerebrospinal fluid specimens on bacterial survival and antigen test results. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 49, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuolikainen, A.; Hedenström, M.; Moritz, T.; Marklund, S.L.; Antti, H.; Andersen, P.M. Optimization of procedures for collecting and storing of CSF for studying the metabolome in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawn, J.R.; Ekhator, N.N.; Geracioti, T.D., Jr. In-use stability of monoamine metabolites in human cerebrospinal fluid. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 760, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, H.; Corcia, P.; Moreau, C.; Veau, S.; Fournier, C.; Vourc’h, P.; Emond, P.; Gordon, P.; Pradat, P.F.; Praline, J.; et al. 1H-NMR-based metabolomic profiling of CSF in early amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13223. [Google Scholar]
- Maillet, S.; Vion-Dury, J.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Nicoli, F.; Lutz, N.W.; Viout, P.; Cozzone, P.J. Experimental protocol for clinical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid by high resolution proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Brain Res. Protoc. 1998, 3, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteh, A.N.; Harrington, R.J.; Tsai, A.; Liao, P.; Harrington, M.G. Free amino acid and dipeptide changes in the body fluids from Alzheimer's disease subjects. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, C.; Berndt, P.; Busch, K.; Schmitz, O.; Wiemer, J.; Most, V.; Hampel, H.; Kastler, J.; Senn, H. Metabolite profiling of Alzheimer’s disease cerebrospinal fluid. PLoS One 2012, 7, e31501. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, Y.; Oishi, M.; Hara, M.; Takasu, T. Amino acid concentration in dementia of the Alzheimer type and multi-infarct dementia. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1996, 26, 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- D’Aniello, A.; Fisher, G.; Migliaccio, N.; Cammisa, G.; D’Aniello, E.; Spinelli, P. Amino acids and transaminases activity in ventricular CSF and in brain of normal and Alzheimer patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 388, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoli, F.; Vion-Dury, J.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Maillet, S.; Gastaut, J.L.; Cozzone, P.J. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolic profiles in multiple sclerosis and degenerative dementias obtained by high resolution proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 1996, 319, 622–631. [Google Scholar]
- Stoop, M.P.; Coulier, L.; Rosenling, T.; Shi, S.; Smolinska, A.M.; Buydens, L.; Ampt, K.; Stingl, C.; Dane, A.; Muilwijk, B.; et al. Quantitative proteomics and metabolomics analysis of normal human cerebrospinal fluid samples. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2010, 9, 2063–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Lewis, M.J.; Morrissey, J.A.; Flegel, M.D.; Jeroncic, K.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, D.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; Tzur, D.; et al. The human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 871, 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, R.; Guo, A.C.; Chaudhary, K.K.; Liu, P.; Yallou, F.S.; Dong, E.; Aziat, F.; Wishart, D.S. Multi-platform characterization of the human cerebrospinal fluid metabolome: a comprehensive and quantitative update. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, C.; Simó, C.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O.; Kivipelto, M.; Cedazo-Mínguez, A.; Cifuentes, A. A new metabolomic workflow for early detection of Alzheimer's disease. J. Chromatogr. A. 2013, 1302, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz, T.; Balayssac, S.; Gilard, V.; Martino, R.; Vincent, C.; Pariente, J.; Malet-Martino, M. 1H NMR Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: An Example of a Possible Misinterpretation Due to Non-Adjustment of pH. Metabolites 2014, 4, 115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4010115
Cruz T, Balayssac S, Gilard V, Martino R, Vincent C, Pariente J, Malet-Martino M. 1H NMR Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: An Example of a Possible Misinterpretation Due to Non-Adjustment of pH. Metabolites. 2014; 4(1):115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4010115
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz, Thomas, Stéphane Balayssac, Véronique Gilard, Robert Martino, Christian Vincent, Jérémie Pariente, and Myriam Malet-Martino. 2014. "1H NMR Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: An Example of a Possible Misinterpretation Due to Non-Adjustment of pH" Metabolites 4, no. 1: 115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4010115
APA StyleCruz, T., Balayssac, S., Gilard, V., Martino, R., Vincent, C., Pariente, J., & Malet-Martino, M. (2014). 1H NMR Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid from Alzheimer’s Disease Patients: An Example of a Possible Misinterpretation Due to Non-Adjustment of pH. Metabolites, 4(1), 115-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo4010115




