A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Metabolomics Procedures
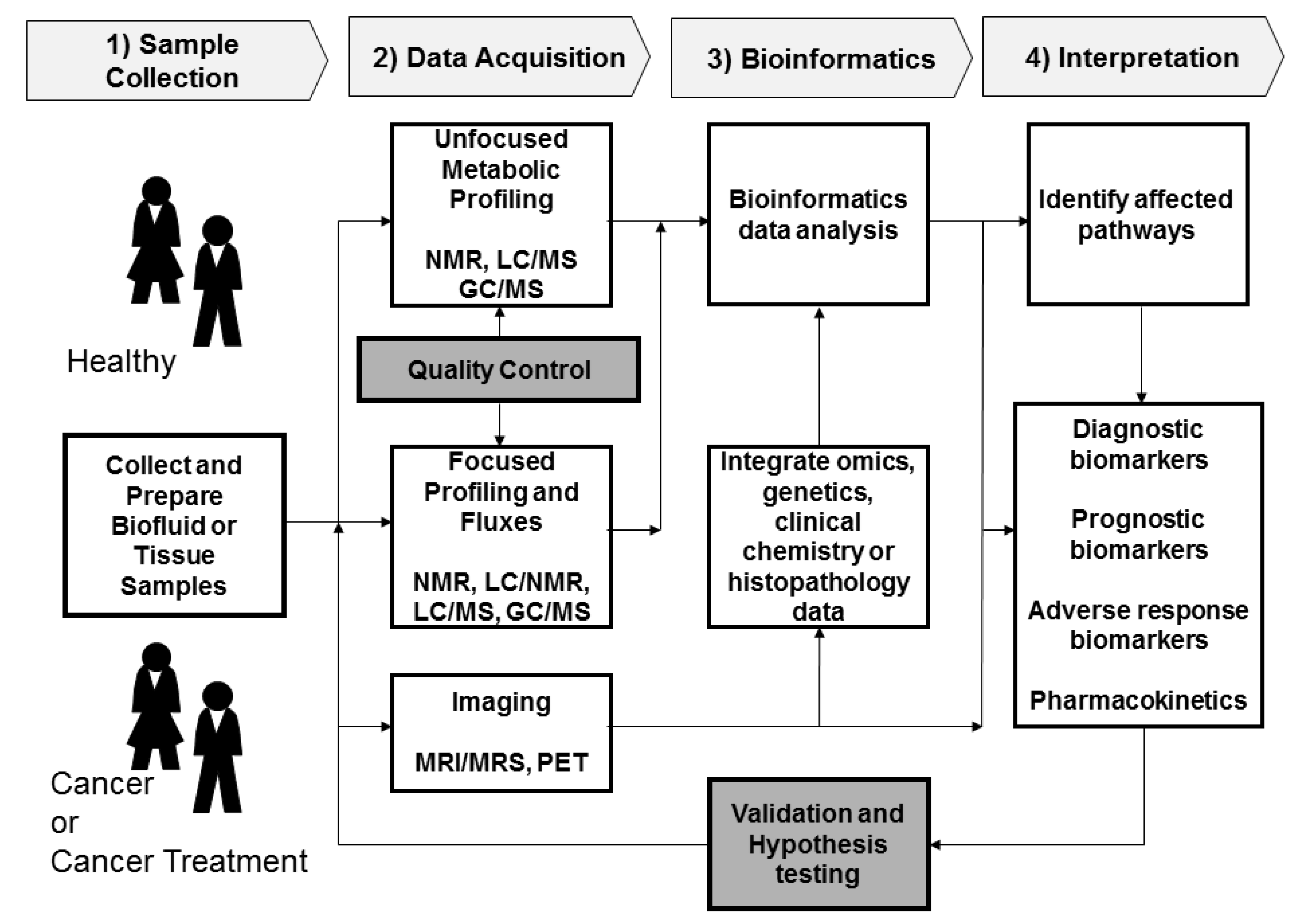
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. Sample Analysis
2.2.2. Quality Control
2.3. Data Processing and Bioinformatics
2.4. Interpretation and Validation
2.5. Challenges
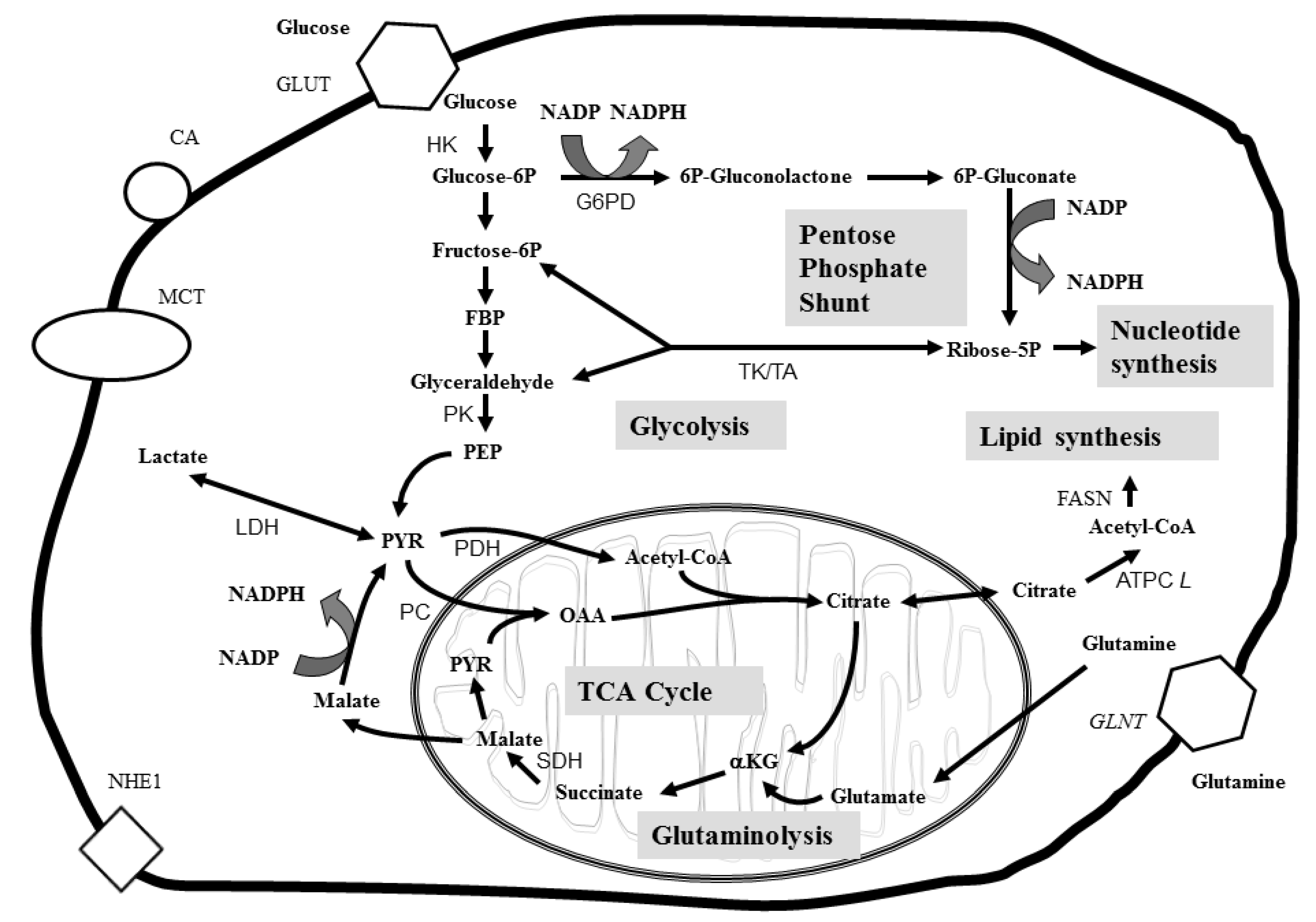
3. Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer Studies
3.1. Biomarkers of Cancer
3.2. Imaging Metabolic Biomarkers
3.3 Metabolomics and Cancer Drug Therapy
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments and Disclaimer
Conflict of Interest
References
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics—The link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, T.A.; Lindon, J.C.; Cloarec, O.; Antti, H.; Charuel, C.; Hanton, G.; Provost, J.P.; Le Net, J.L.; Baker, J.D.; Walley, R.J.; et al. Pharmaco-metabonomic phenotyping and personalized drug treatment. Nature 2006, 440, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.; Wilson, I.D.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell 2008, 134, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.L.; Shockcor, J.P. Metabolic profiles of cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Maruvada, P.; Milner, J.A. Metabolomics in biomarker discovery: Future uses for cancer prevention. Future Oncol. 2008, 4, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratlin, J.L.; Serkova, N.J.; Eckhardt, S.G. Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.W.; Lane, A.N.; Higashi, R.M. The promise of metabolomics in cancer molecular therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2004, 6, 584–592. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.L.; Griffiths, J.R. Using metabolomics to monitor anticancer drugs. Ernst Schering Found. Symp. Proc. 2007, 4, 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Heiden, M.G. Targeting cancer metabolism: A therapeutic window opens. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Kristal, B.S.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Metabolomics: A global biochemical approach to drug response and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxciol. 2008, 48, 653–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby, R.A.; Gillies, R.J. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizán, P.; Sánchez-Tena, S.; Alcarraz-Vizán, G.; Soler, M.; Messeguer, R.; Pujol, M.D.; Lee, W.-N.P.; Cascante, M. Characterization of the metabolic changes underlying growth factor angiogenic activation: Identification of new potential therapeutic targets. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, M.; Schwartz, L. The metabolic advantage of tumor cells. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weljie, A.M.; Jirik, F.R. Hypoxia-induced metabolic shifts in cancer cells: Moving beyond the Warburg effect. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Combining genomics, metabolome analysis and biochemical modeling to understand metabolic networks. Int. J. Genomics 2001, 2, 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. Metabonomics: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological nmr data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Connelly, J.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. Metabonomics: A platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Wilson, I.D. Gut microorganisms, mammalian metabolism and personalized health care. Nat. Rev. Micro. 2005, 3, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessner, U.; Luedemann, A.; Brust, D.; Fiehn, O.; Linke, T.; Willmitzer, L.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolic profiling allows comprehensive phenotyping of genetically or environmentally modified plant systems. The Plant Cell 2001, 13, 11–29. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Gross, R.W. Global analyses of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by esi mass spectrometry: A bridge to lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, M.R. Lipidomics: New tools and applications. Cell 2010, 143, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandis, A.Z.; Wenk, M.R. Lipid-based biomarkers of cancer. J. Chrom. B 2009, 877, 2830–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, L.G.; Brackett, D.J.; Harrigan, G.G. Metabolic biomarker and kinase drug target discovery in cancer using stable isotope-based dynamic metabolic profiling (sidmap). Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2003, 3, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, L.G.; Lerner, M.R.; Morgan, D.L.; Taylor, S.L.; Smith, B.J.; Postier, R.G.; Brackett, D.J. [1,2–13c2]-d-glucose profiles of the serum, liver, pancreas, and dmba-induced pancreatic tumors of rats. Pancreas 2005, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, N.L.; Fan, T.W.-H.; Higashi, R.M.; Tan, J.; Bousamra, M.; Miller, D.M. Prospects for clinical cancer metabolomics using stable isotope tracers. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-F.; Sadhukhan, S.; Tochtrop, G.P.; Brunengraber, H. Metabolomics, pathway regulation, and pathway discovery. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 23631–23635. [Google Scholar]
- Beger, R.; Hansen, D.; Schnackenberg, L.; Cross, B.; Fatollahi, J.; Lagunero, F.T.; Sarnyai, Z.; Boros, L. Single valproic acid treatment inhibits glycogen and rna ribose turnover while disrupting glucose-derived cholesterol synthesis in liver as revealed by the [u-13C6]-d-glucose tracer in mice. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, L.G.; Lee, W.-N.P.; Cascante, M. Imatinib and chronic-phase leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boros, L.G. Metabolic targeted therapy of cancer: Current tracer technologies and future drug design strategies in the old metabolic network. Metabolomics 2005, 1, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance for industry pharmacogenomic data submissions. US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2006.
- Beger, R.; Colatsky, T. Metabolomics data and the biomarker qualification process. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.; Nicholls, A.; Daykin, C.; Heald, S.; Keun, H.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; Griffiths, J.; Cheng, L.; Rocca-Serra, P.; Rubtsov, D.; et al. Standard reporting requirements for biological samples in metabolomics experiments: Mammalian/in vivo experiments. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beger, R.; Beale, M.H.; Daykin, C.; Fan, T.W.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsov, D.; Jenkins, H.; Ludwig, C.; Easton, J.; Viant, M.; Günther, U.; Griffin, J.; Hardy, N. Proposed reporting requirements for the description of nmr-based metabolomics experiments. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodacre, R.; Baker, D.J.; Beger, R.; Bessant, C.; Broadhurst, D.; Connor, S.; Capuani, G.; Craig, A.; Ebbels, T.; Kell, D.B.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, S.; Weiss, R.H. Urine metabolomics for kidney cancer detection and biomarker discovery. Urol. Oncol. 2011, 29, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamas, M.; Dunn, W.B.; Neyes, L.; Goodacre, R. The role of metabolites and metabolomics in clinically applicable biomarkers of disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Serkova, N.; Glunde, K. Metabolomics of cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 250, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protocols 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Ellis, D.I. Metabolomics: Current analytical platforms and methodologies. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.G. Metabonomics in toxicology: A review. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 85, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, E.M.; Wilson, I.D. Analytical strategies in metabonomics. J. Prot. Res. 2007, 6, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychogios, N.; Hau, D.; Peng, J.; Guo, A.; Mandal, R.; Bouatra, S.; Sinelnikov, I.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Eisner, R.; Gautam, B.; et al. The human serum metabolome. PLoS One 2011, 6, e16957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, T.; Major, H.; Plumb, R.; Wilson, A.J.; Wilson, I.D. A pragmatic and readily implemented quality control strategy for HPLC-MS and GC-MS-based metabonomic analysis. Analyst 2006, 131, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Wilson, I.D.; Nicholls, A.W.; Broadhurst, D. The importance of experimental design and qc samples in large-scale and ms-driven untargeted metabolomic studies of humans. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 2249–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, D.; Kell, D. Statistical strategies for avoiding false discoveries in metabolomics and related experiments. Metabolomics 2006, 2, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reily, M.D.; Robosky, L.C.; Manning, M.L.; Butler, A.; Baker, J.D.; Winters, R.T. Dftmp, an NMR reagent for assessing the near-neutral pH of biological samples. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12360–12361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saude, E.; Sykes, B. Urine stability for metabolomic studies: Effects of preparation and storage. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katajamaa, M.; Orešič, M. Data processing for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. J. Chrom. A 2007, 1158, 318–328. [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan, A.; Avizonis, D.; German, J.B.; Slupsky, C.M. Software tools for NMR metabolomics. eMagRes. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto, M.; Kawakami, M.; Robert, M.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Bioinformatics tools for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data processing and analysis. Curr. Bioinformatics 2012, 7, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Fonville, J.M.; Richards, S.E.; Barton, R.H.; Boulange, C.L.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Dumas, M.-E. The evolution of partial least squares models and related chemometric approaches in metabonomics and metabolic phenotyping. J. Chemometrics 2010, 24, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, R.; Lundstedt, T.; Trygg, J. Chemometrics in metabolomics—a review in human disease diagnosis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 659, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Knox, C.; Guo, A.C.; Eisner, R.; Young, N.; Gautam, B.; Hau, D.D.; Psychogios, N.; Dong, E.; Bouatra, S.; et al. Hmdb: A knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucl. Acids Res. 2009, 37, D603–D610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S.; et al. Hmdb: The human metabolome database. Nucl. Acids Res. 2007, 35, D521–D526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopka, J.; Schauer, N.; Krueger, S.; Birkemeyer, C.; Usadel, B.; Bergmuller, E.; Dormann, P.; Weckwerth, W.; Gibon, Y.; Stitt, M.; et al. Gmd@csb.Db: The golm metabolome database. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; O’Maille, G.; Want, E.J.; Qin, C.; Trauger, S.A.; Brandon, T.R.; Custodio, D.E.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. Metlin—a metabolite mass spectral database. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Brown, A.; Dennis, E.A.; Glass, C.K.; Merrill, A.H.; Murphy, R.C.; Raetz, C.R.H.; Russell, D.W.; et al. Lmsd: Lipid maps structure database. Nucl. Acids Res. 2007, 35, D527–D532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blekherman, G.; Laubenbacher, R.; Cortes, D.F.; Mendes, P.; Torti, F.M.; Akman, S.; Torti, S.V.; Shulaev, V. Bioinformatics tools for cancer metabolomics. Metabolomics 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Richardson, A.D.; Smith, J.W.; Osterman, A. Comparative metabolomics of breast cancer. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2007, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, A.; Fan, T.-M.; Bousamra, M.; Higashi, R.; Yan, J.; Miller, D. Stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (sirm) in cancer research with clinical application to nonsmall cell lung cancer. OMICS 2011, 15, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamas, M.; Dunn, W.; Neyses, L.; Goodacre, R. The role of metabolites and metabolomics in clinically applicable biomarkers of disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheis, K.; Laurie, D.; Andriamandroso, C.; Arber, N.; Badimon, L.; Benain, X.; Bendjama, K.; Clavier, I.; Colman, P.; Firat, H.; et al. A generic operational strategy to qualify translational safety biomarkers. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Patterson, A.D.; Krausz, K.W.; Lanz, C.; Kang, D.W.; Luecke, H.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Idle, J.R. Radiation metabolomics. 4. UPLC-ESI-QTOFMS-based metabolomics for urinary biomarker discovery in gamma-irradiated rats. Radiation Res. 2011, 175, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coy, S.L.; Cheema, A.K.; Tyburski, J.B.; Laiakis, E.C.; Collins, S.P.; Fornace, A.J. Radiation metabolomics and its potential in biodosimetry. Int. J Rad. Bio. 2011, 87, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, T.; Ardeshirpour, F.; Asher, S.; Winnike, J.; Yin, X.; George, J.; Guttridge, D.; He, W.; Wysong, A.; Willis, M.; et al. Metabolomic analysis of cancer cachexia reveals distinct lipid and glucose alterations. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, T.; Shelton, L. Cancer as a metabolic disease. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-w.; Dang, C.V. Cancer's molecular sweet tooth and the Warburg effect. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8927–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; McDunn, J.; Gunst, P.; Smith, E.; Milburn, M.; Troyer, D.; Lawton, K. Cancer detection and biopsy classification using concurrent histopathological and metabolomic analysis of core biopsies. Genome Medicine 2012, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nishiumi, S.; Ikeda, A.; Yoshie, T.; Sakai, A.; Matsubara, A.; Izumi, Y.; Tsumura, H.; Tsuda, M.; Nishisaki, H.; et al. A novel serum metabolomics-based diagnostic approach to pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, A.; Nishiumi, S.; Shinohara, M.; Yoshie, T.; Hatano, N.; Okuno, T.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E.; Takenawa, T.; Azuma, T.; et al. Serum metabolomics as a novel diagnostic approach for gastrointestinal cancer. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odunsi, K.; Wollman, R.M.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Hutson, A.; McCann, S.E.; Tammela, J.; Geisler, J.P.; Miller, G.; Sellers, T.; Cliby, W.; et al. Detection of epithelial ovarian cancer using 1H-nmr-based metabonomics. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osl, M.; Drreiseitl, S.; Pfeifer, B.; Weinberger, K.; Klocker, H.; Bartsch, G.; Schafer, G.; Tilg, B.; Graber, A. A new rule-based algorithm for identifying metabolic markers in prostate cancer using tandem mass spectrometry. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2908–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P. C-myc suppression of mir-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, L.F.; Shen, P.; Wang, S.F. Analysis of serum metabolome of patients with breast cancer by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Zhejiang Da Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2009, 38, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Beger, R.; Schnackenberg, L.; Holland, R.; Li, D.; Dragan, Y. Metabonomic models of human pancreatic cancer using 1d proton nmr spectra of lipids in plasma. Metabolomics 2006, 2, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.K.; Wei, B.J.; Lin, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.T.; Zhang, W.D. A metabonomic approach to the diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma, oral clichen planus and oral leukoplakia. Oral Oncol. 2008, 44, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Coates, J.; Bowles, T.; McNerney, G.; Sutcliffe, J.; Jung, I.; Gandour-Edwaeds, R.; Chuang, F.; Bold, R.; Kung, H. Arginine deiminase as a novel therapy for prostate cancer induces autophary and caspase-independent apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.; Chung, B.C.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, D. Combining tissue transcriptomics and urine metabolomics for breast cancer biomarker identification. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3151–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, S.; Weiss, R.H. Urine metabolomics for kidney cancer detection and biomarker discovery. Metabolomics 2011, 29, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, D.; Carbognani, P.; Corradi, M.; Goldoni, M.; Acampa, O.; Balbi, B.; Bianchi, L.; Rusca, M.; Mutti, A. Exhaled volatile organic compounds in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Cross sectional and nested short-term follow-up study. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Ditkoff, B.A.; Fisher, P.; Greenberg, J.; Gunawardena, R.; Kwon, C.S.; Tietje, O.; Wong, C. Prediction of breast cancer using volatile biomarkers in the breath. Breast Cancer Res. 2006, 99, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiumi, S.; Shinohara, M.; Ikeda, A.; Yoshie, T.; Hatano, N.; Kakuyama, S.; Mizuno, S.; Sanuki, T.; Kutsumi, H.; Fukusaki, E.; et al. Serum metabolomics as a novel diagnostic approach for pancreatic cancer. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Dang, C.V. Cancer’s molecular sweet tooth and the Warburg effect. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8927–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, I.F.; Rotin, D. Acid ph in tumors and its potential for therapeutic exploitation. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 4373–4384. [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik, P.C.; Loftfield, R.B.; Stephenson, M.L.; Steele, J.M. Studies on the carbohydrate and protein metabolism of the rat hepatoma. Cancer Res. 1951, 11, 592–602. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, W.; Yang, T. Identification of possible biomarkers for breast cancer from free fatty acid profiles determined by GC/MS and multivariate statistical analysis. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, K.; Hwang, B.J.; Dewi, R.E.; Ou, L.; Twaddel, W.; Fang, H.-b.; Vafai, S.B.; Vazquez, F.; Puigserver, P.; Boros, L.; et al. Pgc1a promotes tumor growth by inducing gene expression programs supporting lipogenesis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6888–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V. Glutaminolysis: Supplying carbon or nitrogen or both for cancer cells? Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3884–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, A.; Cantley, L.C.; Pandolfi, P.P. Cancer metabolism: Fatty acid oxidation in the limelight. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeehan, W.L. Glycolysis, glutaminolysis and cell proliferation. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 1982, 6, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreadith, R.W.; Lehninger, A.L. The pathways of glutamate and glutamine oxidation by tumor cell mitochondria. Role of mitochondrial nad(p)+-dependent malic enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 6215–6221. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Yoseph, O.; Badar-Goffer, R.S.; Morris, P.G.; Bachelard, H.S. Glycerol 3-phosphate and lactate as indicators of the cerebral cytoplasmic redox state in severe and mild hypoxia respectively: A 13C- and 31P N. M. R. Study. Biochem. J. 1993, 291, 915–919. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, J.R.; Stubbs, M. Opportunities for studying cancer by metabolomics: Preliminary observations on tumors deficient in hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2003, 43, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, W.; Waszczuk-Jankowska, M.; Kaliszan, R.; Markuszewski, M.J. The state-of-the-art determination of urinary nucleosides using chromatographic techniques “Hyphenated” With advanced bioinformatics methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 410, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Zambonin, C.G.; Aresta, A.; Palmisano, F.; Specchia, G.; Liso, V. Liquid chromatography determination of urinary 5-methyl-2'-deoxycytidine and psuedouridine as potential biomarkers for leukaemia. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasco, A.J.; Rey, F.; Reynaud, C.; Bobin, Y.L.; Clavel, M.; Niveleau, A. Breast cancer prognostic significance of some modified urinary nucleosides. Cancer Lett. 1996, 108, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Kong, H.W.; Xiong, J.H.; Lv, S.; Xu, G.W. Clinical significance and prognostic value of urinary nucleosides in breast cancer patients. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.M.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, M.H.; Jung, B.H.; Lee, J.; Kong, G.; Nam, S.J.; Kim, S.; Bai, S.W.; Chung, B.C. Mass spectrometry based metabolomic approaches in urinary biomarker study of women's cancers. Clin. Chem. Acta 2009, 400, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.J.; Feng, B.; Kong, H.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Lv, S.; Zheng, M.H.; Xu, G.W. Urinary nucleosides as biological markers for patients with colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3871–3876. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xu, G.; Zheng, Y.; Kong, H.; Pang, T.; Lv, S.; Yang, Q. Diagnosis of liver cancer using hplc-based metabonomics avoiding false-positive result from hepatitis and hepatocirrhosis diseases. J. Chrom. B 2004, 813, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.E. Oxidation of C14-labeled carbohydrate intermediates in tumor and normal tissue. Cancer Res. 1951, 11, 571–584. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerstaff, E.; Pflug, B.R.; Nelson, J.B.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Detection of increased choline compounds with proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy subsequent to malignant transformation of human prostatic epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3599–3603. [Google Scholar]
- Glunde, K.; Jie, C.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Molecular causes of the aberrant choline phospholipid metabolism in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilvo, M.; Denkert, C.; Lehtinen, L.; Müller, B.; Brockmöller, S.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Budczies, J.; Bucher, E.; Yetukuri, L.; Castillo, S.; et al. Novel theranostic opportunities offered by characterization of altered membrane lipid metabolism in breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3236–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cai, X.; Zhao, L.; Xue, X.; Zou, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X. Lysophosphatidylcholine profiling of plasma: Discrimination of isomers and discovery of lung cancer biomarkers. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.D.; Maurhofer, O.; Beyoğlu, D.; Lanz, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Pabst, T.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Dufour, J.-F.o.; Idle, J.R. Aberrant lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by plasma metabolomics and lipid profiling. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6590–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleh, M.; Pozlep, B.; Mlakar, A.; Meden-Vrtovec, H.; Zupanic-Kralj, L. Determination of serum lysophosphatidic acid as a potential biomarker for ovarian cancer. J. Chrom. B 2007, 858, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, M.D.; Hayre, N.; Saito, J.; Saunier, B.; Schuppert, F.; Burch, H.; Bernet, V.; Burman, K.D.; Kohn, L.D.; Saji, M. Overexpression and overactivation of akt in thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6105–6111. [Google Scholar]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-akt pathway in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandis, A.Z.; Wenk, M.R. Lipid-based biomarkers for cancer. J. Chrom. B 2009, 877, 2830–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddoughi, S.A.; Song, P.; Ogretmen, B. Roles of bioactive sphingolipids and cancer biology and therapeutics. Subcell. Biochem. 2008, 49, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, V.E.; Hobson, J.P.; Murthy, S.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase type 1 promotes estrogen-dependent tumorigenesis of breast cancer mcf-7 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 281, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Maceyka, M.; Hait, N.C.; Paugh, S.W.; Sankala, H.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase 1 is required for migration, proliferation and survival of mcf-7 human breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5313–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poullet, J.-B.; Martinez-Bisbal, M.; Valverde, D.; Monleon, D.; Celda, B.; Arus, C.; Van Huffel, S. Quantification and classification of high-resolution magic angle spinning data for brain tumor diagnosis. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2007, 5407–5410. [Google Scholar]
- Tessem, M.B. Evaluation of lactate and alanine as metabolic biomarkers of prostate cancer using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy of biopsy tissues. J Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitter, B.; Sonnewald, U.; Spraul, M.; Fjösne, H.E.; Gribbestad, I.S. High-resolution magic angle spinning mrs of breast cancer tissue. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Davies, N.P.; Brunder, M.-A.; McConville, C.; Grundy, R.G.; Peet, A.C. High resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR of childhood brain and nervous system tumors. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somashekar, B.S.; Kamarajan, P.; Danciu, T.; Kapila, Y.L.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Ramamoorthy, A. Magic angle spinning NMR-based metabolic profiling of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma tissues. J. Prot. Res. 2011, 10, 5232–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, K.; Stattin, Pär.; Stenlund, H.; Riklund, K.; Gröbner, G.; Bergh, A. 1H hrmas nmr derived bio-markers related to tumor grade, tumor cell fraction, and cell proliferation in prostate tissue samples. Biomarker Insights 2011, 6, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.L.; Burns, M.A.; Taylor, J.L.; He, W.; Halpern, E.F.; McDougal, W.S.; Wu, C.-L. Metabolic characterization of human prostate cancer with tissue magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3030–3034. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.C.Y.; Koh, P.K.; Mal, M.; Cheah, P.Y.; Eu, K.W.; Backshall, A.; Cavill, R.; Nicholson, J.K.; Keun, H.C. Metabolic profiling of human colorectal cancer using high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS NMR) spectroscopy and gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS). J. Prot. Res. 2008, 8, 352–361. [Google Scholar]
- Brindle, K. New approaches for imaging tumour responses to treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, H.; Langhans, J.; Ebert, M.; Beger, H.G.; Stollfuss, J.; Reske, S.N.; Büchler, M.W. Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer by 2 [18-F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography. Gut 1995, 36, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöttgen, C.; Levegrün, S.; Theegarten, D.; Marnitz, S.; Grehl, S.; Pink, R.; Eberhardt, W.; Stamatis, G.; Gauler, T.; Antoch, G.; et al. Value of 18f-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography in non-small-cell lung cancer for prediction of pathologic response and times to relapse after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadin, I.S.; McIntosh, A.; Meisamy, S.; Corum, C.; Snyder, A.L.S.; Powell, N.J.; Nelson, M.T.; Yee, D.; Garwood, M.; Bolan, P.J. Metabolite quantification and high-field mrs in breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towner, R.A.; Foley, L.M.; Painter, D.M. Hepatocarcinogenesis tumor grading correlated within vivo image-guided 1H-nmr spectroscopy in a rat model. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 207 (Suppl2), 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, P.; Coakley, F.; Kurhanewicz, J. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of prostate cancer. Rev. Urol. 2006, 8, S4–S10. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, H.; Guo, J.; Matoba, M.; Higashi, K.; Tonami, H.; Nagao, Y. Lactate, choline, and creatine levels measured by vitro 1H-MRS as prognostic parameters in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M. Advanced imaging techniques in brain tumors. Cancer Imaging 2009, 9, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkbey, B.; Aras, Ö.; Karabulut, N.; Tuncay Turgut, A.; Akpinar, E.; Alibek, S.; Pang, Y.; Ertürk, S.; El Khouli, R.; Bluemke, D.; et al. Diffusion-weighted mri for detecting and monitoring cancer: A review of current applications in body imaging. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 18, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Türkbey, B.; Thomasson, D.; Bernardo, M.; Choyke, P.L. The role of dynamic contrast-enhanced mri in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 16, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- DeMartini, W.; Lehman, C.; Partridge, S. Breast mri for cancer detection and characterization: A review of evidence-based clinical applications. Acad, Radiol. 2008, 15, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, E.; Messersmith, H.; Causer, P.; Eisen, A.; Shumak, R.; Plewes, D. Systematic review: Using magnetic resonance imaging to screen women at high risk for breast cancer. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartella, L.; Huang, W. Proton (1H) MR spectroscopy of the breast. Radiographics 2007, 27, S241–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, C.; Bollen, A.W.; Noworolski, S.M.; McDermott, M.W.; Barbaro, N.M.; Day, M.R.; Henry, R.G.; Chang, S.M.; Dillon, W.P.; Nelson, S.J.; et al. Preoperative proton mr spectroscopic imaging of brain tumors: Correlation with histopathologic analysis of resection specimens. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 604–612. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, M.; Shukla-Dave, A.; Bjartell, A.; Touijer, K.; Sciarra, A.; Bastian, P.J.; Stief, C.; Hricak, H.; Graser, A. Functional magnetic resonance imaging in prostrate cancer. Europ. Urol. 2009, 55, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alusta, P.; Im, I.; Pearce, B.A.; Beger, R.D.; Kretzer, R.M.; Buzatu, D.A.; Wilkes, J.G. Improving proton mr spectroscopy of brain tissue for noninvasive diagnostics. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 32, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elion, G.B.; Singer, S.; Hitchings, G.H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives: Viii. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J. Biol. Chem. 1954, 208, 477–488. [Google Scholar]
- Yauch, R.L.; Settleman, J. Recent advances in pathway-targeted cancer drug therapies emerging from cancer genome analysis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2012, 22, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, D.A.; Duran, R.V.; Gottlieb, E. Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.H.; Kim, K. Metabolomics in the study of kidney diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayet-Robert, M.; Morvan, D.; Chollet, P.; Barthomeuf, C. Pharmacometabolomics of docetaxel-treated human mcf7 breast cancer cells provides evidence of varying cellular responses at high and low doses. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 120, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backshall, A.; Sharma, R.; Clarke, S.J.; Keun, H.C. Pharmacometabonomic profiling as a predictor of toxicity in pateints with inoperable colorectal cancer treated with capecitabine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3019–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evelhoch, J.; Garwood, M.; Vigneron, D.; Knopp, M.; Sullivan, D.; Menkens, A.; Clarke, L.; Liu, G. Expanding the use of magnetic resonance in the assessment of tumor response to therapy: Workshop report. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7041–7044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerhouni, E.A.; Sanders, C.A.; von Eschenbach, A.C. The biomarkers consortium: Public and private sectors working in partnership to improve the public health. The Oncologist 2007, 12, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodsaid, F.M.; Mendrick, D.L. Translational medicine and the value of biomarker qualification. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 47ps44–47ps44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muirhead, L.J.; Kinross, J.; FitzMaurice, T.S.; Takats, Z.; Darzi, A.; Nicholson, J.K. Surgical systems biology and personalized longitudinal phenotyping in critical care. Pers. Med. 2012, 9, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.M.; Darzi, A.W.; Takats, z.; Lindon, J.C. Metabolic phenotyping in clinical and surgical environments. Nature 2012, 491, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, J.; Szaniszlo, T.; Schaefer, K.-C.; Denes, J.; Lopata, A.; Godorhazy, L.; Szalay, D.; Balogh, L.; Sasi-Szabo, L.; Toth, M.; et al. Identification of biological tissues by rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7343–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oermann, E.K.; Wu, J.; Guan, K.-L.; Xiong, Y. Alterations of metabolic genes and metabolites in cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Happel, C.; Manna, S.; Acquaah-Mensah, G.; Carratero, J.; Kumar, S.; Nasipuri, P.; Krausz, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Ruby Dewi, R.; et al. Nrf2 regulates mir-1 and mir-206 to drive tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Bertilsson, H.; Tessem, M.-B.; Flatberg, A.; Viset, T.; Gribbestad, I.; Angelsen, A.; Halgunset, J. Changes in gene transcription underlying the aberrant citrate and choline metabolism in human prostate cancer samples. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3261–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantalainen, M.; Cloarec, O.; Beckonert, O.; Wilson, I.D.; Jackson, D.; Tonge, R.; Rowlinson, R.; Rayner, S.; Nickson, J.; Wilkinson, R.W.; et al. Statistically integrated metabonomic—Proteomic studies on a human prostate cancer xenograft model in mice. J. Prot. Res. 2006, 5, 2642–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Qin, H. An integrated proteomics and metabolomics approach for defining oncofetal biomarkers in the colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuperlovic-Culf, M.; Ferguson, D.; Culf, A.; Morin, P.; Touaibia, M. 1H nmr metabolomics analysis of glioblastoma subtypes: Correlation between metabolomics and gene expression characteristics. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20164–20175. [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart, A.D.; Beebe, K.; Milburn, M. Metabolomics as a key integrator for "Omic" advancement of personalized medicine and future therapies. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2012, 5, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Beger, R.D. A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer. Metabolites 2013, 3, 552-574. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030552
Beger RD. A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer. Metabolites. 2013; 3(3):552-574. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030552
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeger, Richard D. 2013. "A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer" Metabolites 3, no. 3: 552-574. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030552
APA StyleBeger, R. D. (2013). A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer. Metabolites, 3(3), 552-574. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030552



