Combining Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) and Isotope Tagging for Off-Line LC-NMR Applications in Metabolite Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Biological Samples
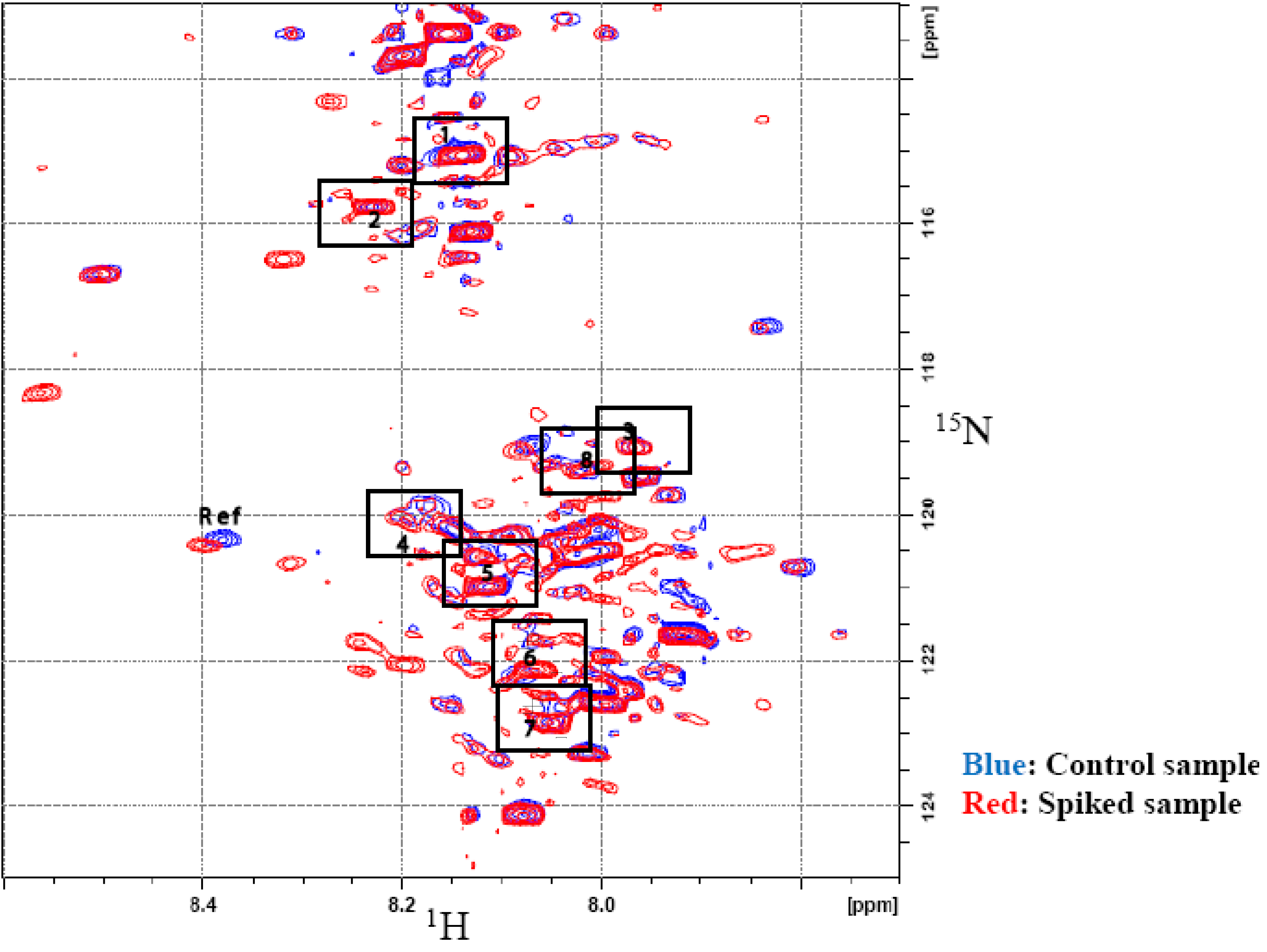
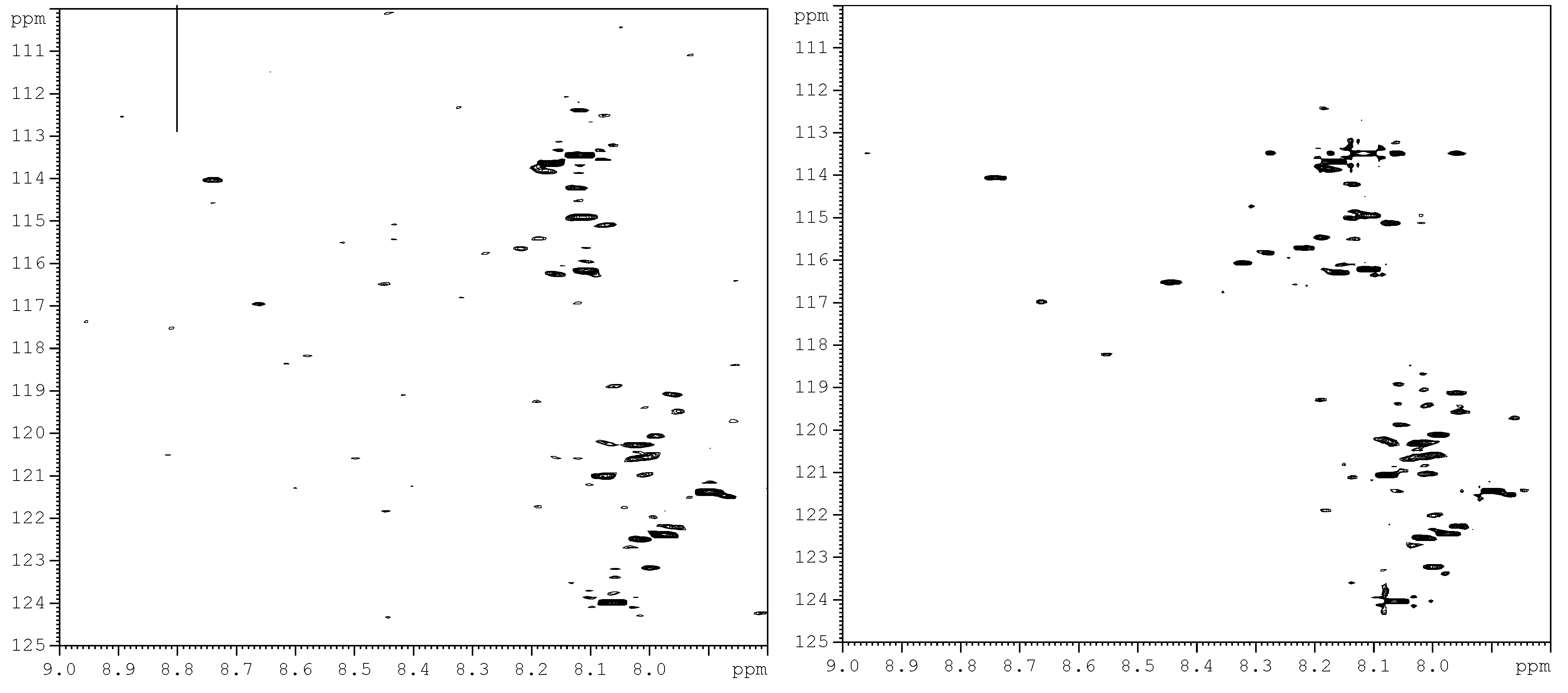
| Label | Metabolite | 1H (ppm) | 15N (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hippuric acid | 8.12 | 114.94 |
| 2 | Glutamic acid | 8.20 | 115.67 |
| 3 | Suberic acid | 8.01 | 119.34 |
| 4 | Cis-aconitic acid | 8.18 | 120.41 |
| 5 | 4-Hydroxylphenyl acetic acid | 8.10 | 120.84 |
| 6 | 3- Hydroxybutyric acid | 8.04 | 122.02 |
| 7 | Citric acid | 8.03 | 122.77 |
| 8 | Adipic acid | 8.01 | 119.34 |
| 9 | 2- Hydroxyphenyl acetic acid | 7.91 | 119.68 |
| 10 | Citraconic acid | 8.02 | 121.07 |
| 11 | Phenylacetic acid | 8.10 | 120.92 |
| 12 | L- Tartaric acid | 8.35 | 116.21 |
| 13 | β-Alanine | 8.10 | 120.07 |
2.2. 15N-Ethanolamine Tagging Procedure
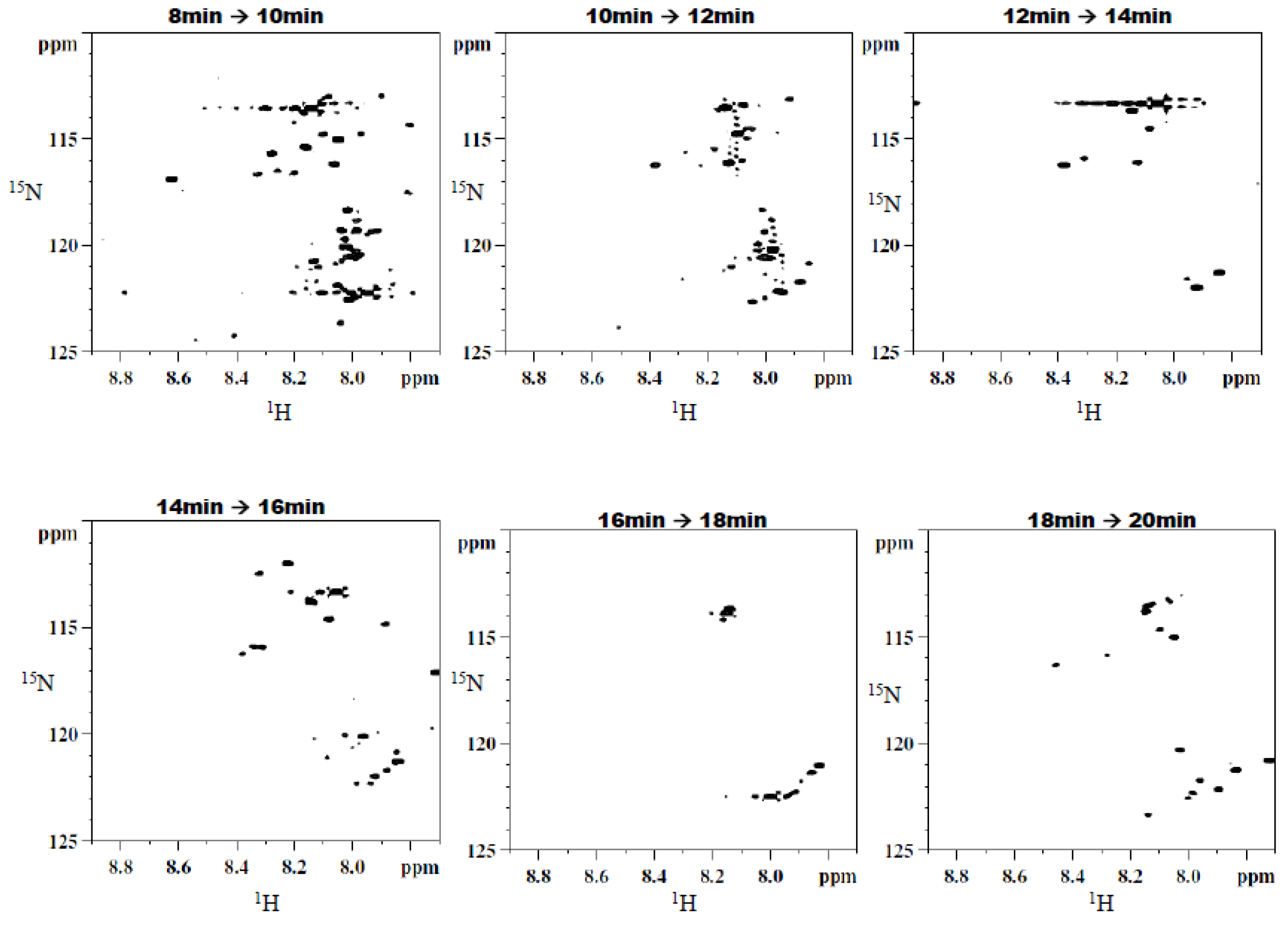
2.3. Two Dimensional HILIC Separation and Fraction Collection
2.4. NMR Spectroscopy
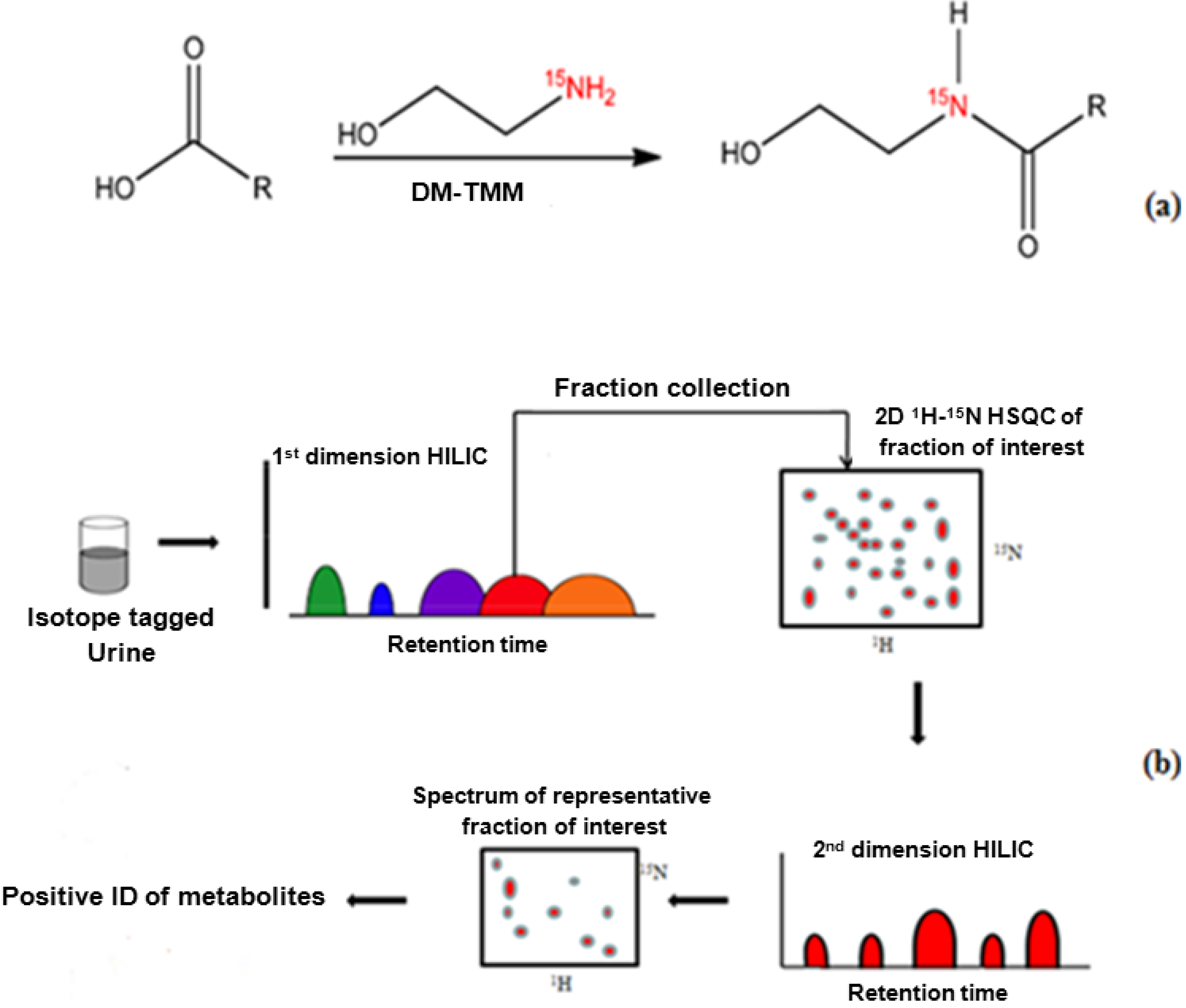
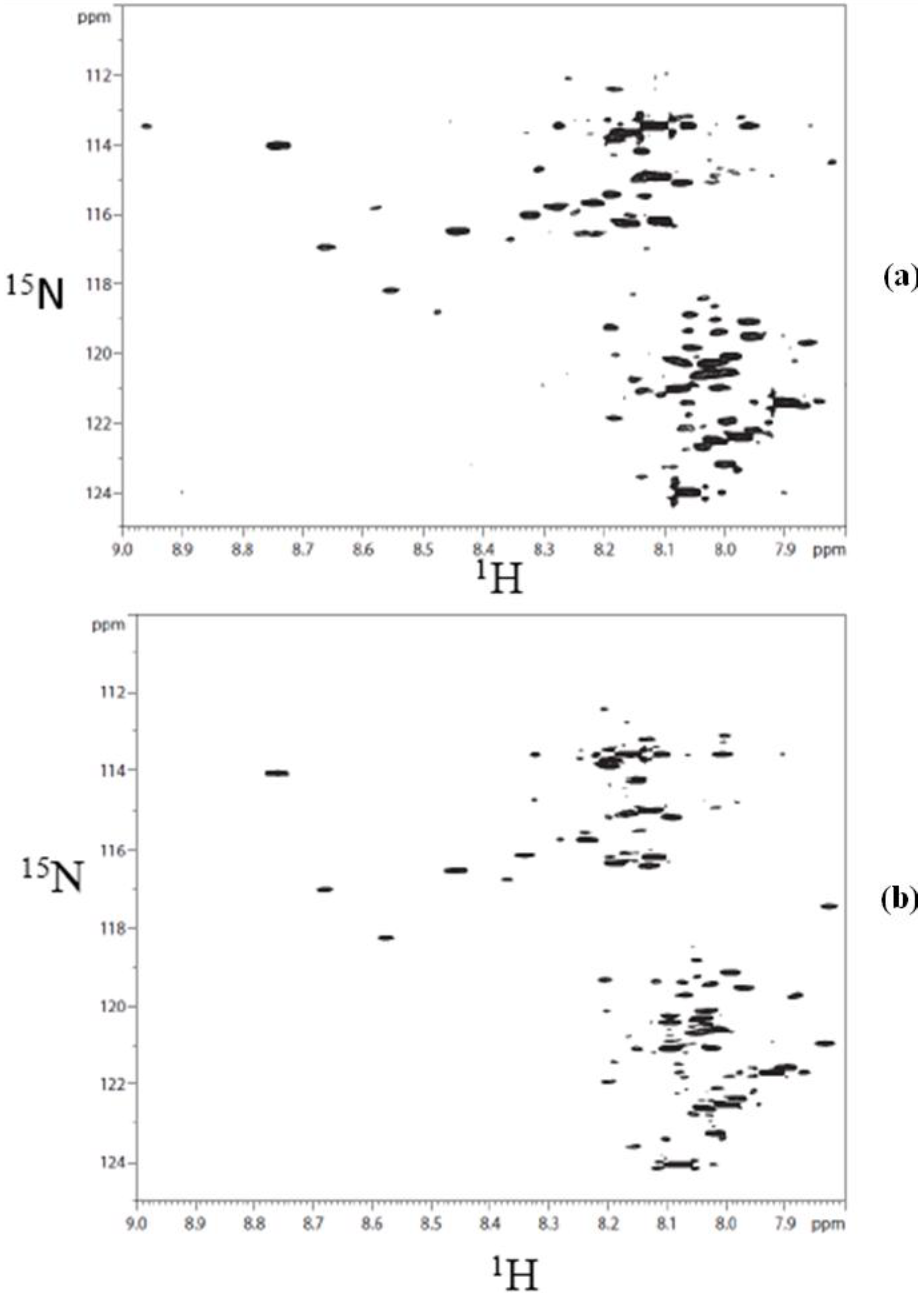
3. Results and Discussion
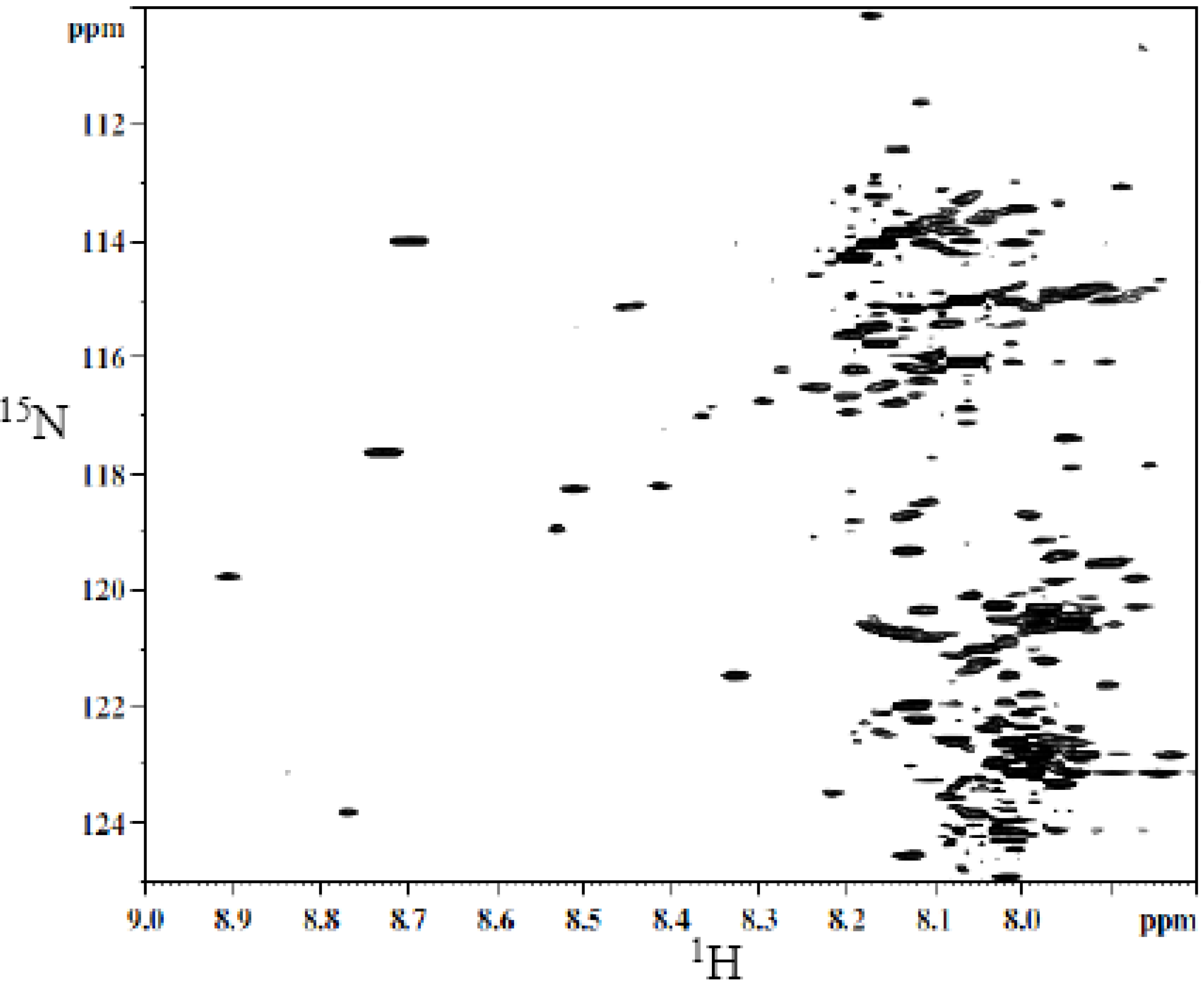
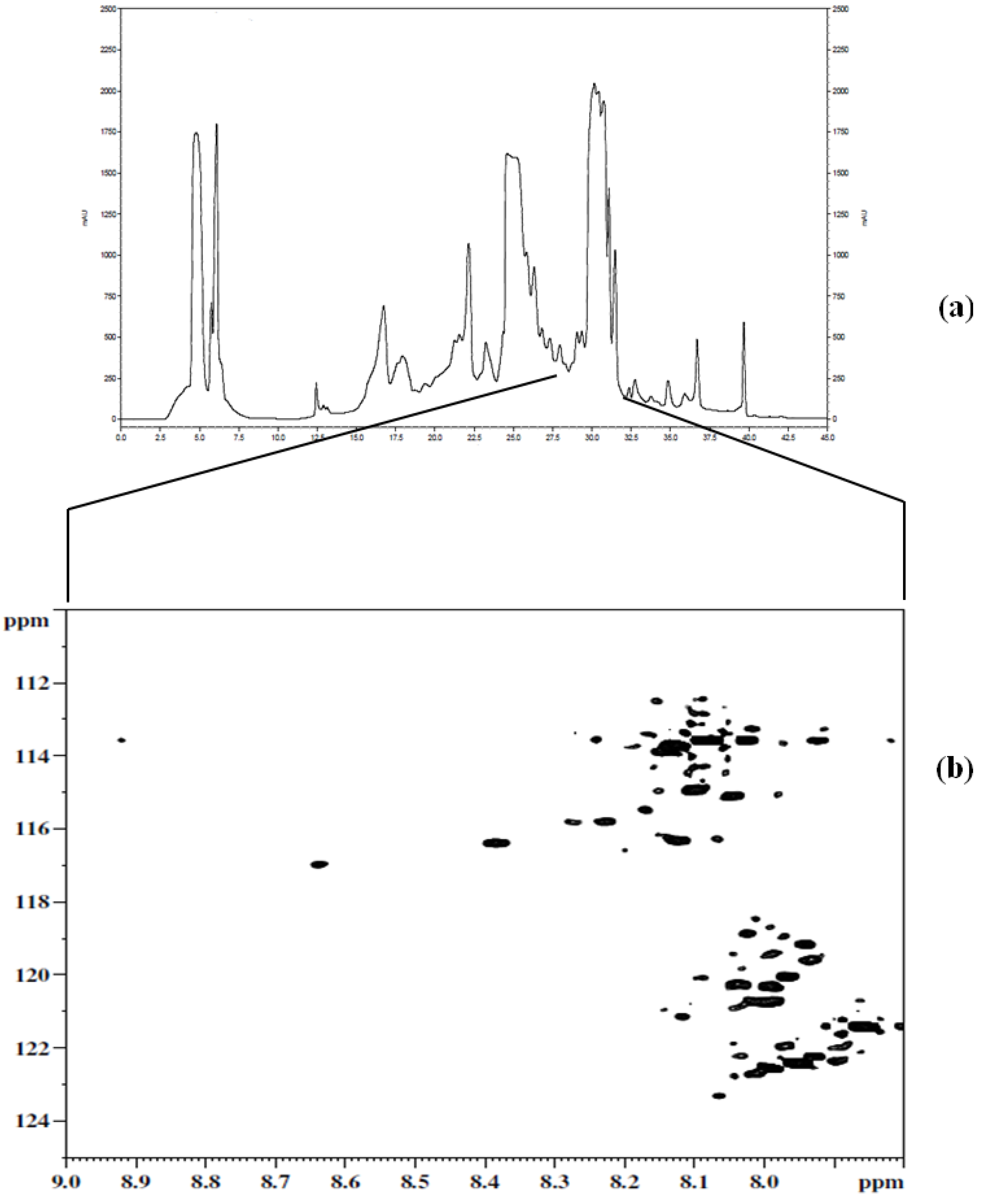
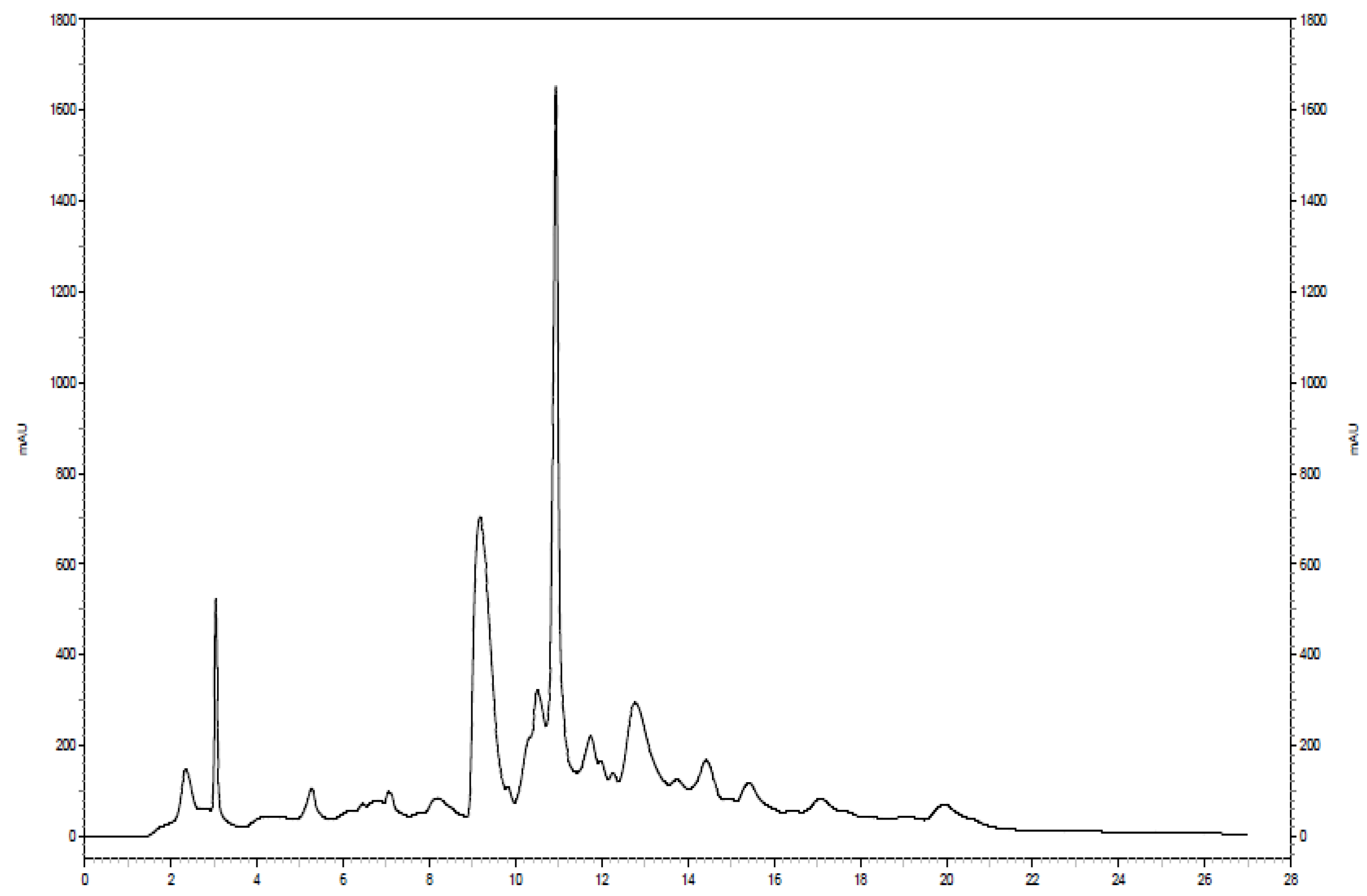
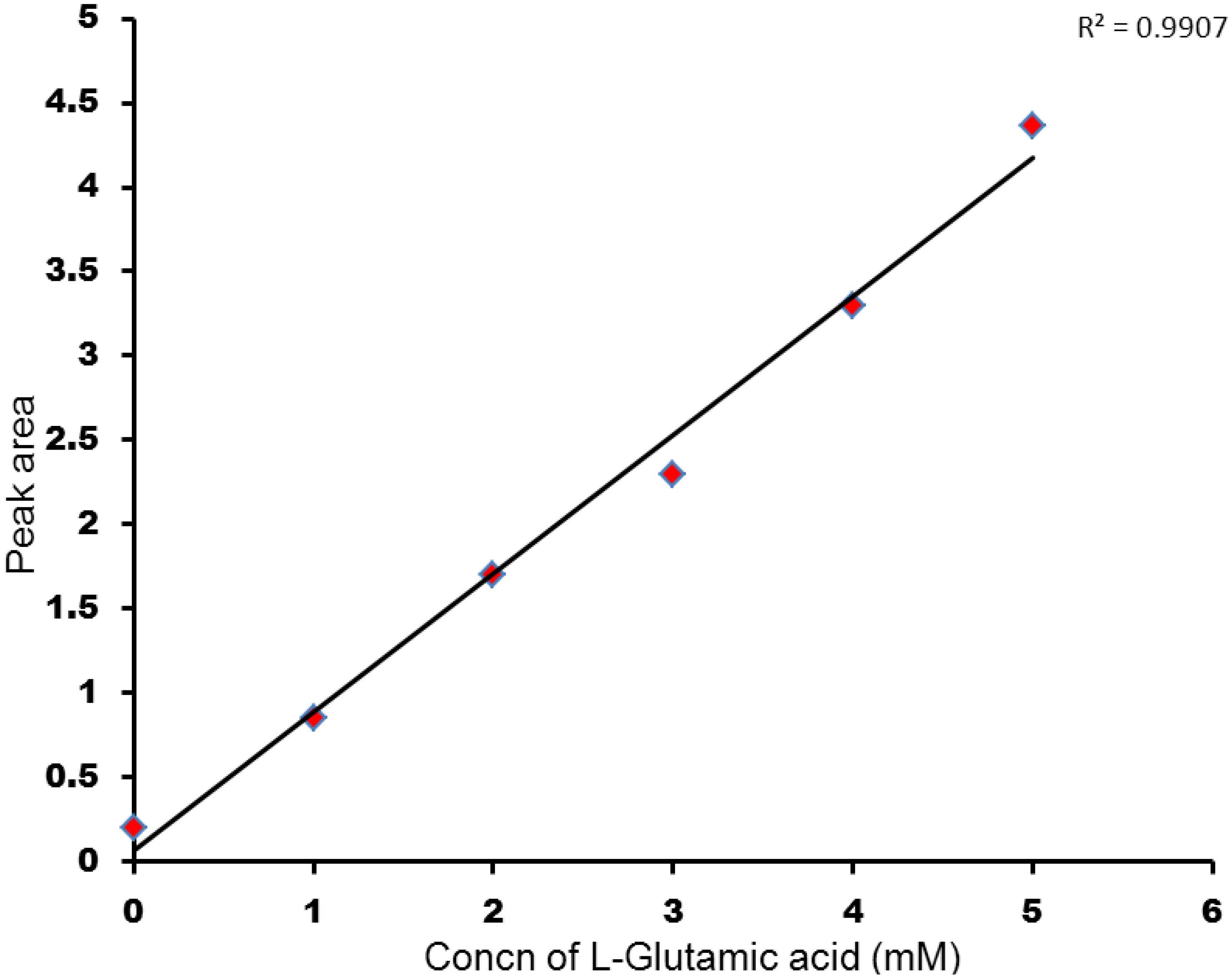
3.1. Metabolite Assignment and Quantitation by Spiking Experiments
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Nicholson, J.K.; Wilson, I.D. High resolution proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of biological fluids. Prog. NMR Spectrosc. 1989, 21, 449–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. “Metabonomics”: understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Dörmann, P.; Altmann, T.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, R.K.; Behar, K.L. Quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy of blood plasma metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2100–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkova, N.J.; Niemann, C.U. Pattern recognition and biomarker validation using quantitative 1H-NMR-based metabolomics. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2006, 6, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.W.-M.; Lane, A.N. Structure-based profiling of metabolites and isotopomers by NMR. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2008, 52, 69–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S. Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Barbas, C.; Raftery, D. Correlative and quantitative 1H-NMR-based metabolomics reveals specific metabolic pathway disturbances in diabetic rats. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 383, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A.N.; Zhang, S.; Haiwei, G.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, D.; Raftery, D. Metabolomics-based methods for early disease diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Connely, J.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. Metabonomics: A platform for studying drug toxicity and gene function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Maruvada, P.; Milner, J.A. Metabolomics in biomarker discovery: Future uses for cancer prevention. Future Oncol. 2008, 4, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cevallos-Cevallos, J.M.; Reyes-De-Corcuero, J.I.; Etxeberria, E.; Danyluka, M.D.; Rodrick, G. Metabolomic analysis in food science: A review. Trends Food. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, D.A. Enzymes, metabolites and fluxes. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghatelian, A.; Cravatt, B.F. Global strategies to integrate the proteome and metabolome. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assfalg, M.; Bertini, I.; Colangiuli, D.; Luchinat, C.; Schäfer, H.; Schütz, B.; Spraul, M. Evidence of different metabolic phenotypes in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Greef, J.; Smilde, A.K. Symbiosis of chemometrics and metabolomics: Past, present and future. J. Chemomet. 2005, 19, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Spectroscopic and statistical techniques for information recovery in metabonomics and metabolomics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 1, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spraul, M.; Freund, A.S.; Nast, R.E.; Withers, R.S.; Maas, W.E.; Corcoran, O. Advancing NMR sensitivity for LC-NMR-MS using a cryoflow probe: Application to the analysis of acetaminophen metabolites in urine. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, I.D.; Park, G.H.K.; Kc, R.; Tobias, B.; Raftery, D. Design and Construction of a Microcoil NMR Probe for the Routine Analysis of 20 µL Samples. Concepts Magn. Reson. 2008, 33B, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kc, R.; Gowda, Y.N.; Djukovic, D.; Henry, I.D.; Park, G.H.J.; Raftery, D. Susceptibility-matched plugs for microcoil NMR probes. J. Mag. Reson. 2010, 205, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kc, R.; Henry, I.D.; Park, G.H.J.; Aghdasi, A.; Raftery, D. New Solenoidal Microcoil NMR Probe Using Zero-Susceptibility Wire. Concepts Mag. Reson. B 2010, 37B, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kc, R.; Henry, I.D.; Park, G.H.J.; Raftery, D. Design and Construction of a versatile dual volume heteronuclear double resonance microcoil NMR probe. J. Mag. Reson. 2009, 197, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, G.; Duarte, I.F.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Carreira, I.M.; Couciero, A.B.; Domingiues, M.; Spraul, L.; Tseng, L.; Gil, A.M. Metabolite profiling of human amniotic fluid by hyphenated nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6085–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah-Amponsah, E.; Shanaiah, N.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Owusu-Sarfo, K.; Ye, T.; Raftery, D. Identification of 4-deoxythreonic acid present in human urine by combining HPLC and NMR techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukovic, D.; Appiah-Amponsah, E.; Shanaiah, N.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Henry, I.; Everly, M.; Tobias, B.; Raftery, D. Ibuprofen metabolite profiling using a combination of SPE/column-trapping and HPLC-micro-coil NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Ji, C.; Li, L. Stable-isotope dimethylation labeling combined with LC-ESI MS for quantification of amine-containing metabolites in biological samples. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8631–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelmann, U.G.; Bjørnsdottir, I.; Shockor, J.P.; Hansen, S.H.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Directly coupled HPLC-NMR and HPLC-MS approaches for the rapid characterisation of drug metabolites in urine: Application to the human metabolism of naproxen. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 24, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, K.; Nieder, M.; Bayer, E.; Spraul, M. Continuous-flow nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Chrom. A 1985, 346, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvit, C.; Shapiro, G.; Bohlen, J.M.; Parella, T. Technical aspects of an efficient multiple solvent suppression pulse sequence. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1999, 37, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogg, R.J.; Kingsley, P.B.; Taylor, J.S. WET, a T1- and B1-insensitive water-suppression method for in vivo localized 1H-NMR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. B 1994, 104, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.L.; Mao, X.A.; Ye, C.H.; Huang, H.; Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Improved WATERGATE pulse sequence for solvent suppression in NMR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 1998, 132, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.D.; Meng, X.; Donovan, K.J.; Shaka, A.J. SOGGY: Solvent-optimized double gradient spectroscopy for water suppression. A comparison with some existing techniques. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 184, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallcombe, S.H. Solvent suppression with symmetrically-shifted pulses. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 4776–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiago, V.M.; Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Zhang, S.; Shanaiah, N.; Clark, J.; Raftery, D. Use of EDTA to Minimize Ionic Strength Dependent Frequency Shifts in the 1H NMR Spectra of Urine. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weljie, A.M.; Newton, J.; Mercier, P.; Carlson, E.; Slupsky, C.M. Targeted profiling: Quantitative analysis of 1H-NMR metabolomics data. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4430–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spraul, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Wilson, I.; Lenz, E.; Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Coupling of HPLC with 19F- and 1H-NMR spectroscopy to investigate the human urinary excretion of flurbiprofen metabolites. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1993, 11, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanaiah, N.; De Silva, A.M.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, M.; Hainline, B.E.; Raftery, D. Class Selection of Amino Acid Metabolites in Body Fluids Using Chemical Derivatization and Their 13C NMR Detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 11540–11544. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, A.M.; Shanaiah, N.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Rosa-Pérez, K.; Hanson, B.A.; Raftery, D. Application of 31P NMR Spectroscopy and Chemical Derivatization Formetabolite Profiling of Lipophilic Compounds in Human Serum. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, 574–580. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, T.; Mo, H.; Shanaiah, N.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Zhang, S.; Raftery, D. Chemoselective 15N Tag for Sensitive and High-Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Profiling of the Carboxyl-Containing Metabolome. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4882–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Tayyari, F.; Ye, T.; Suryani, Y.; Wei, S.; Shanaiah, N.; Raftery, D. Quantitative Analysis of Blood Plasma Metabolites Using Isotope Enhanced NMR Methods. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8983–8990. [Google Scholar]
- Tolstikov, V.V.; Fiehn, O. Analysis of highly polar compounds of plant origin: Combination of hydrophilic interaction chromatography and electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 301, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godejohann, M. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectroscopy—A new approach for the separation and identification of extremely polar analytes in bodyfluids. J. Chrom. A 2007, 1156, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kunishima, M.; Kawachi, C.; Monta, J.; Terao, K.; Iwasaki, F.; Tani, S. 4-(4, 6-dimethoxy-1, 3, 5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methyl-morpholinium chloride: An efficient condensing agent leading to the formation of amides and esters. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13159–13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunishima, M.; Kawachi, C.; Hioki, K.; Terao, K.; Tani, S. Formation of carboxamides by direct condensation of carboxylic acids and amines in alcohols using a new alcohol- and water-soluble condensing agent: DMT-MM. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; van der Giet, M.; Jankowski, V.; Schmidt, S.; Hemeier, M.; Mahn, B.; Giebing, G.; Tolle, M.; Luftmann, H.; Schluter, H.; et al. Increased plasma phenylacetic acid in patients with end-stage renal failure inhibits iNOS expression. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 112, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, T.; Korson, M.S.; Sakamoto, M.; Evans, J.E. A GC/MS/MS screening method for multiple organic acidemias from urine specimens. Clin. Chim. Acta 1999, 283, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Material

© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Appiah-Amponsah, E.; Owusu-Sarfo, K.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Ye, T.; Raftery, D. Combining Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) and Isotope Tagging for Off-Line LC-NMR Applications in Metabolite Analysis. Metabolites 2013, 3, 575-591. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030575
Appiah-Amponsah E, Owusu-Sarfo K, Gowda GAN, Ye T, Raftery D. Combining Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) and Isotope Tagging for Off-Line LC-NMR Applications in Metabolite Analysis. Metabolites. 2013; 3(3):575-591. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030575
Chicago/Turabian StyleAppiah-Amponsah, Emmanuel, Kwadwo Owusu-Sarfo, G.A. Nagana Gowda, Tao Ye, and Daniel Raftery. 2013. "Combining Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) and Isotope Tagging for Off-Line LC-NMR Applications in Metabolite Analysis" Metabolites 3, no. 3: 575-591. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030575
APA StyleAppiah-Amponsah, E., Owusu-Sarfo, K., Gowda, G. A. N., Ye, T., & Raftery, D. (2013). Combining Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) and Isotope Tagging for Off-Line LC-NMR Applications in Metabolite Analysis. Metabolites, 3(3), 575-591. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo3030575







