Lipidomic Signatures in Pediatric Metabolic Disorders
Abstract
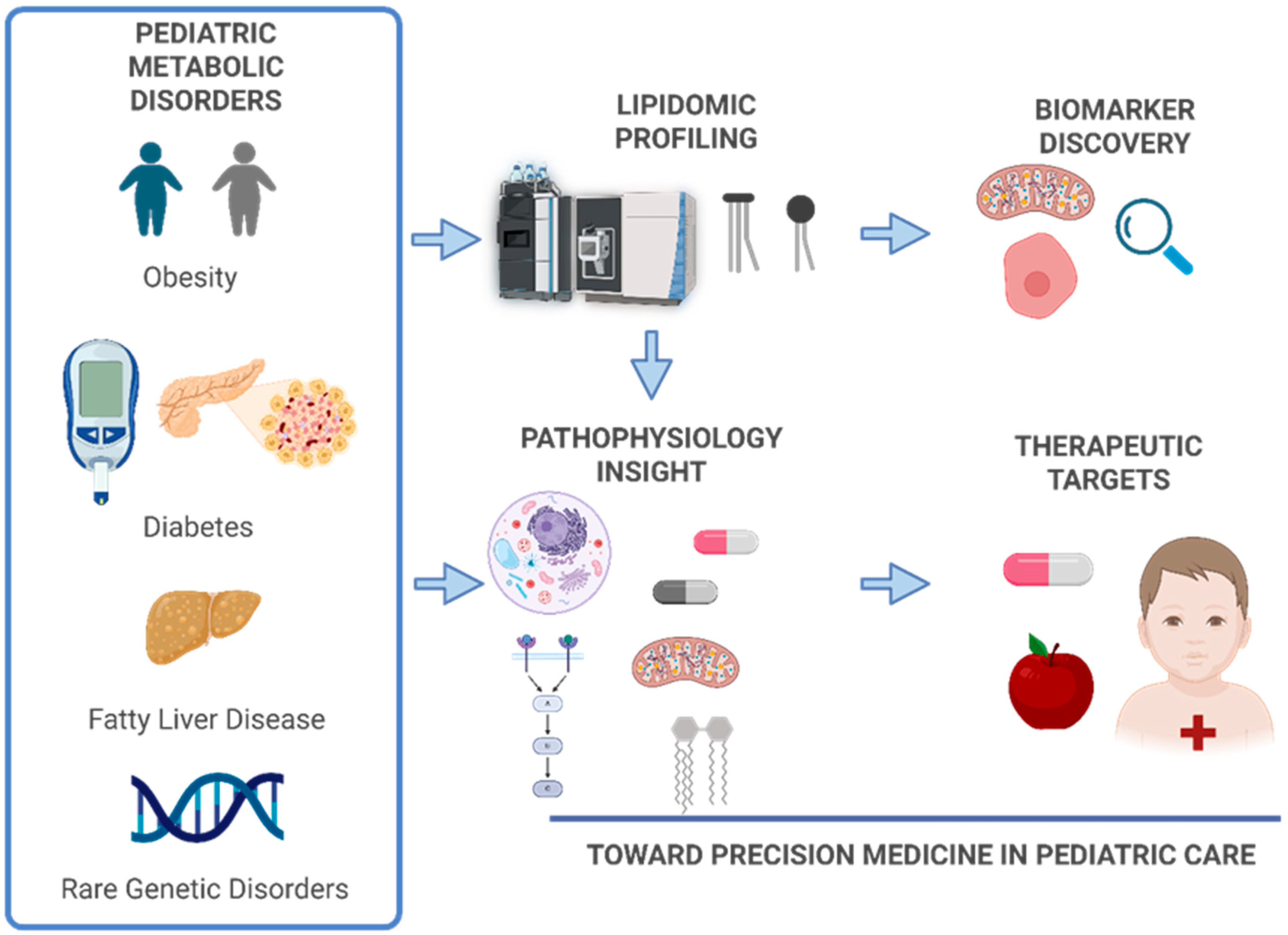
1. Introduction
2. Lipid Metabolism in Pediatric Physiology
2.1. Overview of Lipid Roles in Development
- Phospholipids: Major components of cell membranes, essential for maintaining membrane fluidity and facilitating intracellular signaling. These are particularly important during organogenesis and neural development [17].
- Sphingolipids: Involved in cell signaling, membrane stability, and the formation of the myelin sheath. These lipids are critical for proper neurodevelopment and are often implicated in neurological manifestations of metabolic disorders [18].
- Triglycerides: Serve as the primary form of energy storage. In children, triglycerides are mobilized during periods of fasting, illness, and rapid growth to meet increased energy demands [19].
- Fatty Acids: Act as substrates for β-oxidation and are precursors for bioactive lipid mediators such as eicosanoids. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFAs), including DHA and AA, are essential for brain and retinal development in early life [22].
- Lipoproteins and lipid transport: These are complexes of lipids and proteins that transport hydrophobic lipid molecules through the bloodstream [23]. Their composition and concentration vary with age, sex, and pubertal status [24]. Lipoproteins are crucial for delivering lipids to developing tissues and are increasingly studied as carriers of disease-specific lipidomic signatures in pediatric populations.
2.2. Age-Related Variability in Lipid Profiles
2.3. Implications for Lipidomic Research
3. Lipidomic Technologies and Methodologies
3.1. Analytical Platforms
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Data Acquisition and Processing
- Peak Detection: Identifies signal peaks corresponding to lipid ions in the spectra.
- Peak Alignment: Corrects for retention time shifts across samples to ensure consistent comparison.
- Normalization: Adjusts for technical variability (e.g., batch effects, instrument drift) using internal standards or statistical methods.
- Lipid Identification: Matches detected features to known lipid species using spectral libraries and databases such as LIPID MAPS (Lipid Metabolites and Pathways Strategy), HMDB (Human Metabolome Database), LipidBlast and MS-DIAL for in silico fragmentation and annotation.
- Quantification: Can be relative (based on ion intensity) or absolute (using calibration curves and internal standards).
3.4. Strengths and Limitations
4. Lipidomic Alterations in Common Pediatric Metabolic Disorders
4.1. Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
4.1.1. Lipidomic Signatures in Pediatric Obesity
4.1.2. Metabolically Healthy vs. Unhealthy Obesity
4.1.3. Clinical Implications and Future Directions
4.2. Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
4.3. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
4.4. Inborn Errors of Metabolism (IEMs)
4.5. Rare and Undiagnosed Disorders
5. Lipidomics and the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis
6. Lipidomics and Mental Health in Children
7. Lipidomics in Pediatric Oncology
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PMDs | Pediatric metabolic disorders |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| LC-PUFAs | Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| FAMEs | Fatty acid methyl esters |
| IMS | Ion mobility spectrometry |
| RT | Retention time |
| TOF | Time of flight |
| HMDB | Human Metabolome Database |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| SFAs | Saturated fatty acids |
| MHO | Metabolically healthy obesity |
| MUO | Metabolically unhealthy obesity |
| BCAAs | Branched-chain amino acids |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| DNL | De novo lipogenesis |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
| IEM | Inborn Errors of Metabolism |
| ERT | Enzyme replacement therapy |
| SRT | Substrate reduction therapy |
| FAODs | Fatty acid oxidation defects |
| CPT | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase |
| VLCAD | Very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase |
| ZSDs | Zellweger spectrum disorders |
| NALD | Neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy |
| CA | Cholic acid |
| CDCA | Chenodeoxycholic acid |
| DHCA | 3α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholestanoic acid |
| THCA | 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholestanoic acid |
| VLCFAs | Very-long-chain fatty acids |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| ADHD | Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder |
| BD | Bipolar disorder |
| SCZ | Schizophrenia |
| TAGs | Triacylglycerols |
References
- Hoffman, D.J.; Powell, T.L.; Barrett, E.S.; Hardy, D.B. Developmental origins of metabolic diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 739–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suarez, V.J.; Martin-Rodriguez, A.; Redondo-Florez, L.; Lopez-Mora, C.; Yanez-Sepulveda, R.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. New Insights and Potential Therapeutic Interventions in Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.A.; Marnett, L.J. Introduction to lipid biochemistry, metabolism, and signaling. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5817–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Xiao, F.; Bhusal, C.K.; Sabapathy, P.C.; Segal, R.; Chen, J.; Bai, X. Lipids dysregulation in diseases: Core concepts, targets and treatment strategies. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurowski, K.; Kochan, K.; Walczak, J.; Baranska, M.; Piekoszewski, W.; Buszewski, B. Analytical Techniques in Lipidomics: State of the Art. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 418–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandl-Lang, M.; Plecko, B.; Kofeler, H. Lipidomics-Paving the Road towards Better Insight and Precision Medicine in Rare Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutaki, D.; Stefanou, G.; Genitsaridi, S.M.; Ramouzi, E.; Kyrkili, A.; Kontogianni, M.D.; Kokkou, E.; Giannopoulou, E.; Kassari, P.; Charmandari, E. Exploring Metabolic Signatures: Unraveling the Association with Obesity in Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, L.J.; Krogvold, L.; Hasselby, J.P.; Kaur, S.; Claessens, L.A.; Russell, M.A.; Mathews, C.E.; Hanssen, K.F.; Morgan, N.G.; Koeleman, B.P.C.; et al. Abnormal islet sphingolipid metabolism in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamari, F.; Mochel, F.; Sedel, F.; Saudubray, J.M. Disorders of phospholipids, sphingolipids and fatty acids biosynthesis: Toward a new category of inherited metabolic diseases. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez Reyes, C.D.; Alejo-Jacuinde, G.; Perez Sanchez, B.; Chavez Reyes, J.; Onigbinde, S.; Mogut, D.; Hernandez-Jasso, I.; Calderon-Vallejo, D.; Quintanar, J.L.; Mechref, Y. Multi Omics Applications in Biological Systems. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 5777–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Thomson, D.; Seto, I.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Curtis, S.; Constantin, E.; Batmanabane, G.; Hartling, L.; Klassen, T.; et al. Standard 6: Age groups for pediatric trials. Pediatrics 2012, 129, S153–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemela, P.S.; Castillo, S.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Oresic, M. Bioinformatics and computational methods for lipidomics. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 2855–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.N. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the growth and development of the brain and memory. Nutrition 2003, 19, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.; Franco, L.; Regal, P.; Lamas, A.; Cepeda, A.; Fente, C. Breast Milk: A Source of Functional Compounds with Potential Application in Nutrition and Therapy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, J.B. Dietary lipids from an evolutionary perspective: Sources, structures and functions. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2011, 7, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.W. Advances in Understanding of the Role of Lipid Metabolism in Aging. Cells 2021, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divecha, N.; Irvine, R.F. Phospholipid signaling. Cell 1995, 80, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussani, P.; Prinetti, A.; Tringali, C. The role of Sphingolipids in myelination and myelin stability and their involvement in childhood and adult demyelinating disorders. J. Neurochem. 2021, 156, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLelland, G.L.; Lopez-Osias, M.; Verzijl, C.R.C.; Ellenbroek, B.D.; Oliveira, R.A.; Boon, N.J.; Dekker, M.; van den Hengel, L.G.; Ali, R.; Janssen, H.; et al. Identification of an alternative triglyceride biosynthesis pathway. Nature 2023, 621, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I. Cholesterol in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L. Steroid hormone synthesis in mitochondria. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2013, 379, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambold, A.S.; Cohen, S.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Fatty acid trafficking in starved cells: Regulation by lipid droplet lipolysis, autophagy, and mitochondrial fusion dynamics. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.H.; Gatta, A.T.; Levine, T.P. Lipid transfer proteins: The lipid commute via shuttles, bridges and tubes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, C.J.; Janssen, I. Distribution of lipoproteins by age and gender in adolescents. Circulation 2006, 114, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.R.; Greer, F.R.; Committee on Nutrition. Lipid screening and cardiovascular health in childhood. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, H.B.; Olshansky, G.; Smith, A.A.T.; Giles, C.; Huynh, K.; Cinel, M.; Mellett, N.A.; Cadby, G.; Hung, J.; Hui, J.; et al. High-coverage plasma lipidomics reveals novel sex-specific lipidomic fingerprints of age and BMI: Evidence from two large population cohort studies. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornburg, D.; Wu, S.; Moqri, M.; Zhou, X.; Contrepois, K.; Bararpour, N.; Traber, G.M.; Su, B.; Metwally, A.A.; Avina, M.; et al. Dynamic lipidome alterations associated with human health, disease and ageing. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1578–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anh, N.K.; Thu, N.Q.; Tien, N.T.N.; Long, N.P.; Nguyen, H.T. Advancements in Mass Spectrometry-Based Targeted Metabolomics and Lipidomics: Implications for Clinical Research. Molecules 2024, 29, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narvaez-Rivas, M.; Zhang, Q. Comprehensive untargeted lipidomic analysis using core-shell C30 particle column and high field orbitrap mass spectrometer. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1440, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, J.; Scherer, M.; Schmitz, G.; Liebisch, G. A rapid GC-MS method for quantification of positional and geometric isomers of fatty acid methyl esters. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 897, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.F. Mass spectrometry-based shotgun lipidomics—A critical review from the technical point of view. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6387–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, R.; Baker, D.; Schwitter, C.; Neuhaus, S.; Hauptmann, T.; Post, J.M.; Kramer, S.; Bindila, L. Four-dimensional trapped ion mobility spectrometry lipidomics for high throughput clinical profiling of human blood samples. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zullig, T.; Trotzmuller, M.; Kofeler, H.C. Lipidomics from sample preparation to data analysis: A primer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvaez-Rivas, M.; Setchell, K.D.R.; Galandi, S.L.; Zhao, X.; Iqbal, N.T.; Ahmed, S.; Iqbal, J.; Syed, S.; Ali, S.A.; Moore, S.R. Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency Associates with Growth Faltering and Environmental Enteric Dysfunction in Children. Metabolites 2023, 13, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, E.M.; Xu, L.Y. Guide to Metabolomics Analysis: A Bioinformatics Workflow. Metabolites 2022, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nishida, K.; Harayama, T.; Todoroki, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Oka, T.; et al. MS-DIAL 5 multimodal mass spectrometry data mining unveils lipidome complexities. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Qian, Y.; Pan, B.; Ge, L.; Wang, Q.; Ding, G.; Wang, J. Global Trends and Future Prospects of Child Nutrition: A Bibliometric Analysis of Highly Cited Papers. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 633525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansra, A.R.; Lakkunarajah, S.; Jay, M.S. Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: A Review. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 581461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, C.M.; Gil-Campos, M.; Canete, R.; Gil, A. Alterations in plasma and tissue lipids associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Clin. Sci. 2008, 114, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauschert, S.; Uhl, O.; Koletzko, B.; Kirchberg, F.; Mori, T.A.; Huang, R.C.; Beilin, L.J.; Hellmuth, C.; Oddy, W.H. Lipidomics Reveals Associations of Phospholipids With Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Young Adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvado, L.; Coll, T.; Gomez-Foix, A.M.; Salmeron, E.; Barroso, E.; Palomer, X.; Vazquez-Carrera, M. Oleate prevents saturated-fatty-acid-induced ER stress, inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells through an AMPK-dependent mechanism. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, M.C.; McSorley, E.M.; Mulhern, M.S.; Strain, J.J.; van Wijngaarden, E.; Yeates, A.J. Influence of fatty acid desaturase (FADS) genotype on maternal and child polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) status and child health outcomes: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska, N.; Bobrus-Chociej, A.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Tarasow, E.; Wojtkowska, M.; Chabowski, A.; Lebensztejn, D.M. Increased serum concentration of ceramides in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratford, S.; Hoehn, K.L.; Liu, F.; Summers, S.A. Regulation of insulin action by ceramide: Dual mechanisms linking ceramide accumulation to the inhibition of Akt/protein kinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36608–36615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjos, S.; Feiteira, E.; Cerveira, F.; Melo, T.; Reboredo, A.; Colombo, S.; Dantas, R.; Costa, E.; Moreira, A.; Santos, S.; et al. Lipidomics Reveals Similar Changes in Serum Phospholipid Signatures of Overweight and Obese Pediatric Subjects. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 3174–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Allen, T.M.; Umeda, M.; Jewell, L.; Mason, A.; Vance, D.E. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, T.; Collins, C.E.; Garg, M.L. Omega-3 index, obesity and insulin resistance in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, e532–e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sulek, K.; Stinson, S.E.; Holm, L.A.; Kim, M.; Trost, K.; Hooshmand, K.; Lund, M.A.V.; Fonvig, C.E.; Juel, H.B.; et al. Lipid profiling identifies modifiable signatures of cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents with obesity. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.Z.W.; Shie, Y.H.; Piyasanka, S.R.; Kioh, D.Y.Q.; Sng, A.A.; Lee, B.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Chan, E.C.Y.; Ooi, D.S.Q. Metabolome alterations in pediatric metabolically unhealthy obesity are primarily linked to abnormal glucose homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Gong, Z.; Sun, J.; Shen, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Huo, J. Integrating Metabolomics and Gut Microbiota to Identify Key Biomarkers and Regulatory Pathways Underlying Metabolic Heterogeneity in Childhood Obesity. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson Svard, A.; Kaur, S.; Trost, K.; Suvitaival, T.; Lernmark, A.; Maziarz, M.; Pociot, F.; Overgaard, A.J.; DiPi, S.S.G. Characterization of plasma lipidomics in adolescent subjects with increased risk for type 1 diabetes in the DiPiS cohort. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, G.; Huang, K.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, M.; Hao, X.; Ni, Y.; Fu, J. Metabolomics and Lipidomics Studies in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes: Biomarker Discovery for the Early Diagnosis and Prognosis. Pediatr. Diabetes 2023, 2023, 6003102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgul-Convey, E. Sphingolipids in Type 1 Diabetes: Focus on Beta-Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, L. Lipid metabolism in type 1 diabetes mellitus: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 999108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, D.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; Larsson, H.E.; Hyotylainen, T.; Ivarsson, S.A.; Lernmark, A.; Oresic, M.; DiPi, S.S.G. Decreased cord-blood phospholipids in young age-at-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3951–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuplez, E.; Marsche, G. An Updated Review of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Plasma Lysophosphatidylcholines in the Vascular System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Godinez, S.; de la Garza, A.L.; Tamez-Rivera, O.; Senes-Guerrero, C.; Carrizales-Sanchez, A.K.; Garcia-Rivas, G.; Hernandez-Brenes, C. Lipidomic signatures linked to gut microbiota alterations in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Zhou, Y.; Sadevirta, S.; Leivonen, M.; Arola, J.; Oresic, M.; Hyotylainen, T.; Yki-Jarvinen, H. Hepatic ceramides dissociate steatosis and insulin resistance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.P.; Nakamura, M.; Clarke, S.D. Cloning, expression, and fatty acid regulation of the human delta-5 desaturase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37335–37339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.P.; Nakamura, M.T.; Clarke, S.D. Cloning, expression, and nutritional regulation of the mammalian Delta-6 desaturase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, D.A.; Murata, N. Structure and expression of fatty acid desaturases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1394, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocher, D.R.; Leaver, M.J.; Hodgson, P.A. Recent advances in the biochemistry and molecular biology of fatty acyl desaturases. Prog. Lipid Res. 1998, 37, 73–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.S.; Toke, D.A.; Mandala, S.; Martin, C.E. ELO2 and ELO3, homologues of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ELO1 gene, function in fatty acid elongation and are required for sphingolipid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 17376–17384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirica, B.M. Use of Biomarkers in Predicting the Onset, Monitoring the Progression, and Risk Stratification for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.; Masoodi, S.R.; Mir, S.A.; Nabi, M.; Ghazanfar, K.; Ganai, B.A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: From a metabolic disorder to an inflammatory condition. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barranco-Altirriba, M.; Alonso, N.; Weber, R.J.M.; Lloyd, G.R.; Hernandez, M.; Yanes, O.; Capellades, J.; Jankevics, A.; Winder, C.; Falguera, M.; et al. Lipidome characterisation and sex-specific differences in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizo-Roca, D.; Henderson, J.D.; Zierath, J.R. Metabolomics in cardiometabolic diseases: Key biomarkers and therapeutic implications for insulin resistance and diabetes. J. Intern. Med. 2025, 297, 584–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, P.J.; Wong, G.; Barlow, C.K.; Kingwell, B.A. Lipidomics: Potential role in risk prediction and therapeutic monitoring for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 143, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaca-Tabaszewska, M.; Bogusiewicz, J.; Bojko, B. Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling of Gliomas-A New Direction in Personalized Therapies. Cancers 2022, 14, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sessa, A.; Riccio, S.; Pirozzi, E.; Verde, M.; Passaro, A.P.; Umano, G.R.; Guarino, S.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E.; Marzuillo, P. Advances in paediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Role of lipidomics. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3815–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.P.; Jenkins, B.; Furse, S.; Snowden, S.G.; Alisi, A.; Draijer, L.G.; Karnebeek, K.; Kelly, D.A.; Koot, B.G.; Mosca, A.; et al. Comparison of the Lipidomic Signature of Fatty Liver in Children and Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 74, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draijer, L.G.; Froon-Torenstra, D.; van Weeghel, M.; Vaz, F.M.; Bohte, A.E.; Holleboom, A.G.; Benninga, M.A.; Koot, B.G.P. Lipidomics in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Exploring Serum Lipids as Biomarkers for Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, S.; Melone, R.; Vitulano, C.; Guida, P.; Maddaluno, I.; Guarino, S.; Marzuillo, P.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E.; Di Sessa, A. Advances in pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: From genetics to lipidomics. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2022, 11, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoodi, M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Hyotylainen, T.; Arretxe, E.; Alonso, C.; Gaggini, M.; Brosnan, J.; Anstee, Q.M.; Millet, O.; Ortiz, P.; et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics in NAFLD: Biomarkers and non-invasive diagnostic tests. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 835–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.T.; Showalter, M.R.; Fiehn, O. Inborn Errors of Metabolism in the Era of Untargeted Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, N.U.; Saith, A.; Ruan, A.; Yang, R.; Burton, A.; Mistry, P.K. Eliglustat substrate reduction therapy in children with Gaucher disease type 1. Front. Pediatr. 2025, 13, 1543136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, M.M.; Pohl-Worgall, T.; Deckelbaum, R.J.; Simpson, W.; Mendelson, D.; Desnick, R.J.; Schuchman, E.H.; Wasserstein, M.P. Lipid abnormalities in children with types A and B Niemann Pick disease. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, J.D.; Mataraso, S.J.; Holzapfel, L.F.; Maric, I.; Kasowski, M.M.; Martin, C.R.; Long, J.Z.; Stevenson, D.K.; Shaw, G.M.; Stanford Metabolic Health, C. Applications of Metabolomics and Lipidomics in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Neoreviews 2025, 26, e100–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, K.; Pras-Raves, M.L.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Vervaart, M.A.T.; Luyf, A.C.M.; van Kampen, A.H.C.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Waterham, H.R.; Vaz, F.M. Plasma lipidomics as a diagnostic tool for peroxisomal disorders. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Narvaez Rivas, M.; Setchell, K.D.R. Tandem mass spectrometry of serum cholestanoic (C(27)) acids—Typical concentration ranges and application to the study of peroxisomal biogenesis disorders. J. Mass. Spectrom. Adv. Clin. Lab. 2024, 34, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangler, M.F.; Hubert, L.; Donti, T.R.; Ventura, M.J.; Miller, M.J.; Braverman, N.; Gawron, K.; Bose, M.; Moser, A.B.; Jones, R.O.; et al. A metabolomic map of Zellweger spectrum disorders reveals novel disease biomarkers. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Biase, I.; Tortorelli, S.; Kratz, L.; Steinberg, S.J.; Cusmano-Ozog, K.; Braverman, N.; Committee, A.L.Q.A. Laboratory diagnosis of disorders of peroxisomal biogenesis and function: A technical standard of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, G.A.; Giugliani, R.; Guffon, N.; Jones, S.A.; Mengel, E.; Scarpa, M.; Witters, P.; Yarramaneni, A.; Li, J.; Armstrong, N.M.; et al. Long-term safety and clinical outcomes of olipudase alfa enzyme replacement therapy in pediatric patients with acid sphingomyelinase deficiency: Two-year results. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, J.E.; Stratton, K.G.; Zink, E.M.; Kim, Y.M.; Bloodsworth, K.J.; Monroe, M.E.; Undiagnosed Diseases, N.; Waters, K.M.; Webb-Robertson, B.M.; Koeller, D.M.; et al. A resource of lipidomics and metabolomics data from individuals with undiagnosed diseases. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, A.; Gorla, G.; Carrozzini, T.; Bersano, A.; Gatti, L.; Pollaci, G. Lipidomic Approaches in Common and Rare Cerebrovascular Diseases: The Discovery of Unconventional Lipids as Novel Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Hock, D.H.; Pitt, J.; Thorburn, D.R.; Stroud, D.A.; Christodoulou, J. Review: Utility of mass spectrometry in rare disease research and diagnosis. npj Genom. Med. 2025, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: The implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yao, J.; Yang, C.; Yu, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; He, N. Gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids act as mediators of the gut-liver-brain axis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2025, 40, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Khachatryan, L.G.; Younis, N.K.; Mustafa, M.A.; Ahmad, N.; Athab, Z.H.; Polyanskaya, A.V.; Kasanave, E.V.; Mirzaei, R.; Karampoor, S. Microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids in pediatric health and diseases: From gut development to neuroprotection. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1456793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, K.; Liang, L.; Yang, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, T.; Fan, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of the gut microbiota and metabolites in children with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. mSystems 2025, 10, e0114824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, R.; Basak, S.; Das, R.K.; Banerjee, A.; Paul, S.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Roles of the gut microbiota in human neurodevelopment and adult brain disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1446700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Xie, Y.; Yi, L.; Cheng, W.; Jia, H.; Shi, W.; Liu, Q.; Fang, L.; Xue, S.; Liu, D.; et al. Bile acids affect intestinal barrier function through FXR and TGR5. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1607899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkuwaiti, S.H.; Skrabulyte-Barbulescu, J.; Yassin, L.K.; Almazrouei, S.; Aldhaheri, D.; Alderei, M.; BaniYas, S.; Alshamsi, S.H.; Alnuaimi, A.; Saeed, S.; et al. Harnessing the microbiota-gut-brain axis to prevent and treat pediatric neurodevelopmental disorders: Translational insights and strategies. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, M. Essential fatty acids and the brain. Can. J. Psychiatry 2003, 48, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ansary, A.; Chirumbolo, S.; Bhat, R.S.; Dadar, M.; Ibrahim, E.M.; Bjorklund, G. The Role of Lipidomics in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Predescu, E.; Vaidean, T.; Rapciuc, A.M.; Sipos, R. Metabolomic Markers in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) among Children and Adolescents-A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castor, K.; Dawlaty, J.; Arakaki, X.; Gross, N.; Woldeamanuel, Y.W.; Harrington, M.G.; Cowan, R.P.; Fonteh, A.N. Plasma Lipolysis and Changes in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Signaling Lipids Reveal Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Migraine. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 691733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, A.A.; Farooqui, T. Phospholipids, Sphingolipids, and Cholesterol-Derived Lipid Mediators and Their Role in Neurological Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesti, M.N.; Arena, J.F.; Del Casale, A.; Gentile, G.; Borro, M.; Parmigiani, G.; Simmaco, M.; Guariglia, C.; Ferracuti, S. Lipidomics and genomics in mental health: Insights into major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, E.F.; Ramsden, C.E.; Sherazy, M.S.; Gelenberg, A.J.; Davis, J.M.; Rapoport, S.I. Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Bipolar Disorder: A Review of Biomarker and Treatment Studies. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, e1301–e1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, D.; Benyamin, B.; Lee, S.H.; Hypponen, E. A Metabolome-Wide Mendelian Randomization Study Identifies Dysregulated Arachidonic Acid Synthesis as a Potential Causal Risk Factor for Bipolar Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 96, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Alvarez-Mon, M.A.; Garcia-Montero, C.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; Monserrat, J.; Martinez-Rozas, L.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, R.; Alvarez-Mon, M.; Lahera, G. Microbiota-gut-brain axis mechanisms in the complex network of bipolar disorders: Potential clinical implications and translational opportunities. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2645–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, S.; Xue, J.; Gao, T.; Li, X.; Zhai, Z.; Lu, C.; Dong, Y.; Zhuo, K.; Xiang, Q.; et al. Identifying serum lipidomic signatures related to prognosis in first-episode schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2025, 25, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.X.; Huang, W.; Shi, X.J.; Du, Y.; Liang, J.Q.; Fang, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Cheng, Y. Dysregulation of Serum Exosomal Lipid Metabolism in Schizophrenia: A Biomarker Perspective. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 3556–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, C.; Sweers, K.; Frajerman, A.; Bergaoui, H.; Ferreri, F.; Delva, C.; Lapidus, N.; Lamaziere, A.; Roiser, J.P.; De Hert, M.; et al. Membrane lipidomics in schizophrenia patients: A correlational study with clinical and cognitive manifestations. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Zaytseva, Y.Y.; Deng, P.; Wang, L. LC-MS analysis of serum lipidomic and metabolomic signatures in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2025, 51, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Bao, L. Plasma lipidomics profiling to identify signatures of pediatric medulloblastoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2025; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolman, M.; Kiyota, T.; Belgadi, S.A.; Fujita, N.; Fiorante, A.; Ramaswamy, V.; Daniels, C.; Rutka, J.T.; McIntosh, C.; Munoz, D.G.; et al. Lipidomic-Based Approach to 10 s Classification of Major Pediatric Brain Cancer Types with Picosecond Infrared Laser Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sun, J.; Sun, R.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. Integral-Omics: Serial Extraction and Profiling of Metabolome, Lipidome, Genome, Transcriptome, Whole Proteome and Phosphoproteome Using Biopsy Tissue. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lipid Class | Primary Functions | Relevance in Pediatric Physiology |
|---|---|---|
| Phospholipids | Structural components of cell membranes; involved in membrane fluidity and signaling | Crucial for organ development, especially the brain and lungs |
| Sphingolipids | Cell signaling, membrane stability, and myelin sheath formation | Essential for neurodevelopment and nerve conduction |
| Triglycerides | Major energy storage molecules | Provide energy during fasting, illness, and rapid growth phases |
| Cholesterol | Precursor for steroid hormones, vitamin D, and bile acids; membrane structure | Supports hormonal development and digestion; vital for brain and adrenal function |
| Fatty Acids | Energy substrates; precursors for signaling molecules (e.g., eicosanoids) | Long-chain PUFAs (e.g., DHA, AA) are critical for brain and retinal development |
| Lipoproteins | Transport lipids in the bloodstream | Vary with age and puberty; important for lipid delivery to growing tissues |
| Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|
| High sensitivity and specificity | Ion suppression and matrix effects |
| Broad coverage of lipid classes | Requires extensive standardization |
| Suitable for both targeted and untargeted analysis | Complex data interpretation |
| Potential for high-throughput screening | Limited pediatric reference databases |
| Feature | Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) | Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogenesis | Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic β-cells | Insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction, often linked to poor nutrition and obesity |
| Key Lipidomic Changes |
|
|
| Biomarker Potential | Early indicators of autoimmune activity and β-cell stress | Correlation with glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and disease severity |
| Clinical Implications |
| Same as T1D, with emphasis on distinguishing T2D from obesity and predicting rapid progression |
| Future Directions | Longitudinal studies, integration with immunologic/genomic data, predictive modeling | Same as T1D |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Narvaez-Rivas, M.; Setchell, K.D.R. Lipidomic Signatures in Pediatric Metabolic Disorders. Metabolites 2026, 16, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010033
Narvaez-Rivas M, Setchell KDR. Lipidomic Signatures in Pediatric Metabolic Disorders. Metabolites. 2026; 16(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarvaez-Rivas, Monica, and Kenneth D. R. Setchell. 2026. "Lipidomic Signatures in Pediatric Metabolic Disorders" Metabolites 16, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010033
APA StyleNarvaez-Rivas, M., & Setchell, K. D. R. (2026). Lipidomic Signatures in Pediatric Metabolic Disorders. Metabolites, 16(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo16010033







