Metabolomics and Cytokine Signatures in COVID-19: Uncovering Immunometabolism in Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Patients’ Enrollment
2.2. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy (LC-MS)-Based Metabolomics Analysis
2.3. Cytokines Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Cytokine Profiling of COVID Patients
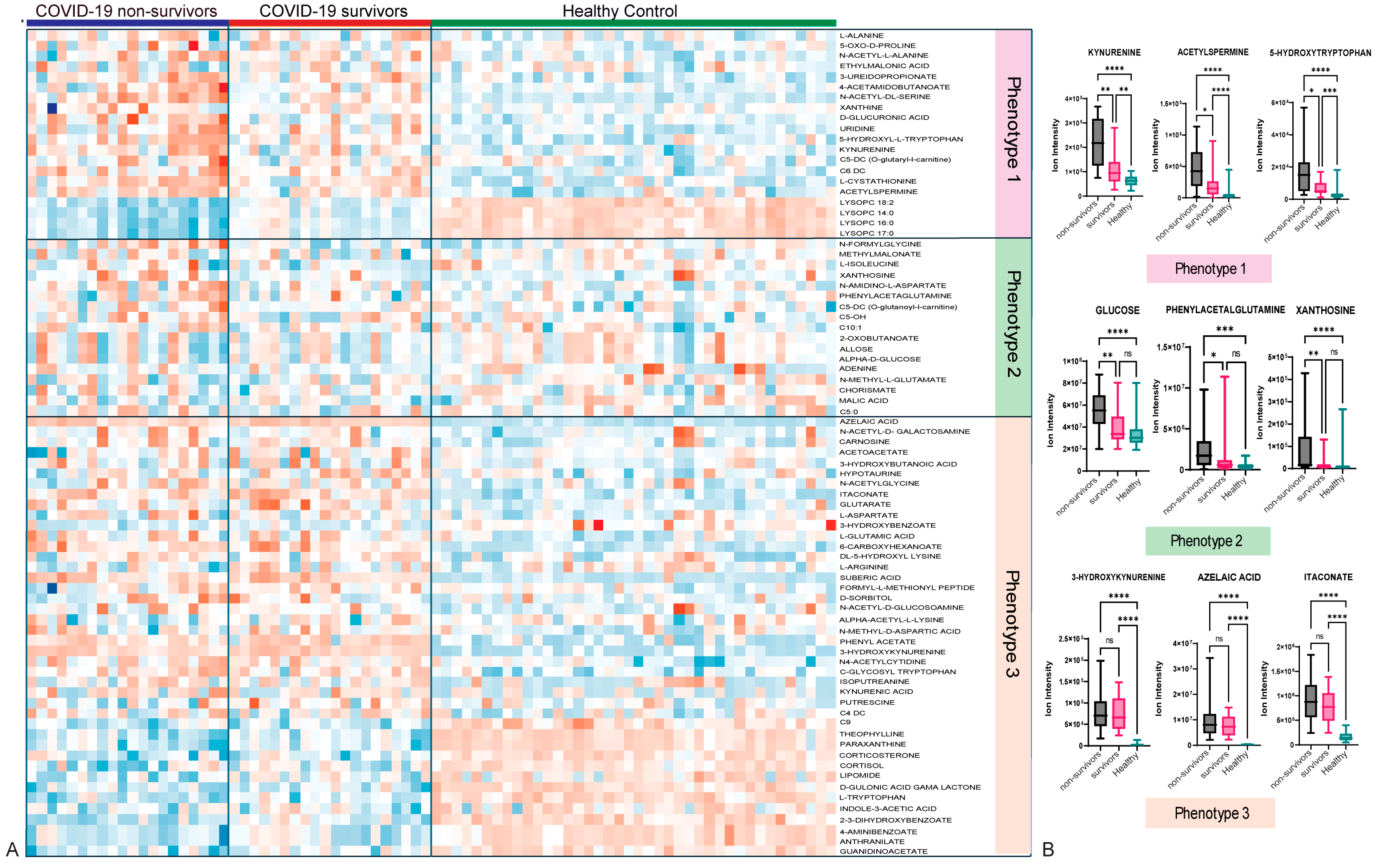
3.3. Metabolomic Profiling Showed Three Main Metabolic Phenotypes in Patients with COVID-19 Compared with Those in HCs
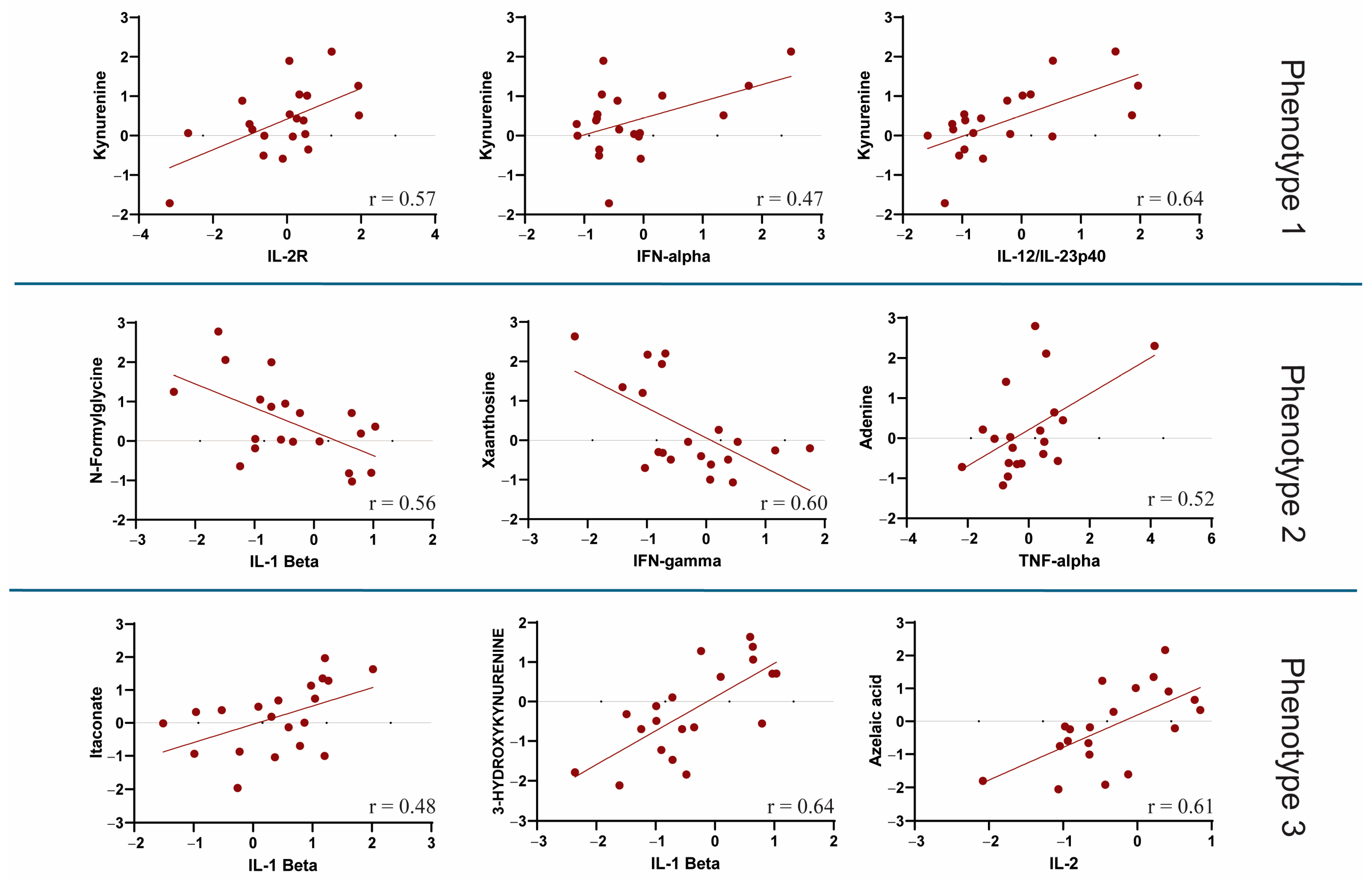
3.4. Correlation Between Metabolic Phenotypes 1–3 and Cytokine Profiling
3.5. Metabolomics and Patients’ Demographics, Clinical Data, and Comorbidities
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Kumar, A.; Narayan, R.K.; Prasoon, P.; Kumari, C.; Kaur, G.; Kumar, S.; Kulandhasamy, M.; Sesham, K.; Pareek, V.; Faiq, M.A.; et al. COVID-19 Mechanisms in the Human Body-What We Know So Far. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 693938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, E.; Canonica, G.W.; Moretta, L. COVID-19: Unanswered questions on immune response and pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Nie, M.; Pang, H.; Wang, B.; Hu, J.; Meng, X.; Li, K.; Ran, X.; Long, Q.; Deng, H.; et al. Integrated cytokine and metabolite analysis reveals immunometabolic reprogramming in COVID-19 patients with therapeutic implications. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyton, R.J.; Altmann, D.M. The immunology of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: What are the key questions? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Schulze, M.B. Global pandemics interconnected—obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangge, H.; Kneihsl, M.; Schnedl, W.; Sendlhofer, G.; Curcio, F.; Domenis, R. Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2-Questions and Experiences. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vabret, N.; Britton, G.J.; Gruber, C.; Hegde, S.; Kim, J.; Kuksin, M.; Levantovsky, R.; Malle, L.; Moreira, A.; Park, M.D.; et al. Immunology of COVID-19: Current State of the Science. Immunity 2020, 52, 910–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: A key role for monocytes and macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codo, A.C.; Davanzo, G.G.; Monteiro, L.B.; de Brito Monteiro, L.; de Souza, G.F.; Muraro, S.P.; Virgilio-da-Silva, J.V.; Prodonoff, J.S.; Carregari, V.C.; de Biagi Junior, C.A.; et al. Elevated Glucose Levels Favor SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Monocyte Response through a HIF-1α/Glycolysis-Dependent Axis. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 437–446.e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, T.; Stefanoni, D.; Reisz, J.A.; Nemkov, T.; Bertolone, L.; Francis, R.O.; Hudson, K.E.; Zimring, J.C.; Hansen, K.C.; Hod, E.A.; et al. COVID-19 infection alters kynurenine and fatty acid metabolism, correlating with IL-6 levels and renal status. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e140327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J.; HLH Across Speciality Collaboration. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.; Krammer, F.; Iwasaki, A. The first 12 months of COVID-19: A timeline of immunological insights. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Minn, D.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.K. Inflammatory Markers and Cytokines in Moderate and Critical Cases of COVID-19. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Pan, H.; Li, R.; He, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L. Increased Circulating Cytokines Have a Role in COVID-19 Severity and Death With a More Pronounced Effect in Males: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 802228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.S.; Haider Kazmi, S.J.; Khan, N.A.; Akram, M.; Hassan, M.; Rasheed, U.; Ahmed Khan, S. Poor Prognostic Biochemical Markers Predicting Fatalities Caused by COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Study From a Developing Country. Cureus 2020, 12, e9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fialek, B.; Pruc, M.; Smereka, J.; Jas, R.; Rahnama-Hezavah, M.; Denegri, A.; Szarpak, A.; Jaguszewski, M.J.; Peacock, F.W.; Szarpak, L. Diagnostic value of lactate dehydrogenase in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiol. J. 2022, 29, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, M.D.; Sowell, R.T.; Kaech, S.M.; Pearce, E.L. Metabolic Instruction of Immunity. Cell 2017, 169, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Pearce, E.J. Immunometabolism governs dendritic cell and macrophage function. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 213, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannahill, G.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Adamik, J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; McGettrick, A.F.; Goel, G.; Frezza, C.; Bernard, N.J.; Kelly, B.; Foley, N.H.; et al. Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1β through HIF-1α. Nature 2013, 496, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, A.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peace, C.G.; O’Neill, L.A. The role of itaconate in host defense and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e148548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, W. Targeting Arginine in COVID-19-Induced Immunopathology and Vasculopathy. Metabolites 2022, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindelar, M.; Stancliffe, E.; Schwaiger-Haber, M.; Anbukumar, D.S.; Adkins-Travis, K.; Goss, C.W.; O’Halloran, J.A.; Mudd, P.A.; Liu, W.C.; Albrecht, R.A. Longitudinal metabolomics of human plasma reveals prognostic markers of COVID-19 disease severity. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 00369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of COVID-19 Patient Sera. Cell 2020, 182, 59–72.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Farha, M.; Thanaraj, T.A.; Qaddoumi, M.G.; Hashem, A.; Abubaker, J.; Al-Mulla, F. The Role of Lipid Metabolism in COVID-19 Virus Infection and as a Drug Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A. An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the De Ritis Ratio and Disease Severity and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19. Life 2023, 13, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overmyer, K.A.; Shishkova, E.; Miller, I.J.; Balnis, J.; Bernstein, M.N.; Peters-Clarke, T.M.; Meyer, J.G.; Quan, Q.; Muehlbauer, L.K.; Trujillo, E.A.; et al. Large-Scale Multi-omic Analysis of COVID-19 Severity. Cell Syst. 2021, 12, 23–40.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, J.S. A metabolic handbook for the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasquin, M.F.; Melamud, E.; Rabinowitz, J.D. LC-MS Data Processing with MAVEN: A Metabolomic Analysis and Visualization Engine. In Current Protocols in Bioinformatics; Baxevanis, A.D., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 14.11.1–14.11.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoei, M.M.; Hashemi Shahraki, A.; Santos, K.; Holt, G.; Mirsaeidi, M. Investigating Metabolic Phenotypes for Sarcoidosis Diagnosis and Exploring Immunometabolic Profiles to Unravel Disease Mechanisms. Metabolites 2025, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Kumar, S.; Sehgal, R.; George, S.; Gupta, R.; Poddar, S.; Jha, A.; Pathak, S. El-MAVEN: A Fast, Robust, aCorrectednd User-Friendly Mass Spectrometry Data Processing Engine for Metabolomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1978, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, X.; Xiang, Y.; Gutierrez-Castrellon, P.; Ma, X. Inflammatory pathways in COVID-19: Mechanism and therapeutic interventions. MedComm 2022, 3, e154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabara, S.M.; Serdan, T.D.A.; Gorjao, R.; Masi, L.N.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; Covas, D.T.; Curi, R.; Durigon, E.L. SARS-COV-2 Variants: Differences and Potential of Immune Evasion. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 781429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.A.C.; Rodrigues, L.E.; Alecrim-Zeza, A.L.; de Araújo Ferreira, L.; Trettel, C.D.S.; Gimenes, G.M.; da Silva, A.F.; Sousa-Filho, C.P.B.; Serdan, T.D.A.; Levada-Pires, A.C.; et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in tissue-specific metabolic modulation by SARS-CoV-2. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1037467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Shu, T.; Yang, X.; Song, J.X.; Zhang, M.; Yao, C.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. Plasma metabolomic and lipidomic alterations associated with COVID-19. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Thomas, T.; Akpan, I.J.; Reisz, J.A.; Cendali, F.I.; Gamboni, F.; Nemkov, T.; Thangaraju, K.; Katneni, U.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Biological and Clinical Factors Contributing to the Metabolic Heterogeneity of Hospitalized Patients with and without COVID-19. Cells 2021, 10, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, L.F. Immune Response, Inflammation, and the Clinical Spectrum of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, F.C.; Virseda-Berdices, A.; Resino, S.; Ryan, P.; Martínez-González, O.; Peréz-García, F.; Martin-Vicente, M.; Brochado-Kith, O.; Blancas, R.; Bartolome-Sánchez, S.; et al. Metabolic Profiling at COVID-19 Onset Shows Disease Severity and Sex-Specific Dysregulation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.S.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Wei, X.; Gong, K.; Li, Z.; Yao, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.; et al. Identification of serum metabolites enhancing inflammatory responses in COVID-19. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; He, X.; Deng, M.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Elevation of Serum Cytokine Profiles and Liver Metabolomic Normalization in Early Convalescence of COVID-19 Patients. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 626633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, D.; Lu, S.; Qiu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Tan, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.; et al. Plasma metabolome and cytokine profile reveal glycylproline modulating antibody fading in convalescent COVID-19 patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117089119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binayke, A.; Zaheer, A.; Dandotiya, J.; Gupta, S.K.; Mani, S.; Tripathy, M.R.; Madan, U.; Shrivastava, T.; Kumar, Y.; Pandey, A.K.; et al. Proinflammatory innate cytokines and metabolomic signatures predict T cell response in active COVID-19. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, N.G.; Gray, N.; Kimhofer, T.; Boughton, B.; Gay, M.; Yang, R.; Morillon, A.C.; Chin, S.T.; Ryan, M.; Begum, S.; et al. Systemic Perturbations in Amine and Kynurenine Metabolism Associated with Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Inflammatory Cytokine Responses. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 2796–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Kim, D.J.; Takahashi, T.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Yan, H.; Ma, S.; Rattray, N.J.W.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Israelow, B.; Klein, J.; et al. Kynurenic acid may underlie sex-specific immune responses to COVID-19. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eabf8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, S.; Nitschke, P.; Kimhofer, T.; Coudert, J.D.; Begum, S.; Bong, S.H.; Richards, T.; Edgar, D.; Raby, E.; Spraul, M.; et al. NMR Spectroscopic Windows on the Systemic Effects of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Plasma Lipoproteins and Metabolites in Relation to Circulating Cytokines. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 1382–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössler, T.; Berezhnoy, G.; Singh, Y.; Cannet, C.; Reinsperger, T.; Schäfer, H.; Spraul, M.; Kneilling, M.; Merle, U.; Trautwein, C. Quantitative Serum NMR Spectroscopy Stratifies COVID-19 Patients and Sheds Light on Interfaces of Host Metabolism and the Immune Response with Cytokines and Clinical Parameters. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendeiro, A.F.; Vorkas, C.K.; Krumsiek, J.; Singh, H.K.; Kapadia, S.N.; Cappelli, L.V.; Cacciapuoti, M.T.; Inghirami, G.; Elemento, O.; Salvatore, M. Metabolic and Immune Markers for Precise Monitoring of COVID-19 Severity and Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 809937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, S.; Madonna, G.; Di Gennaro, E.; Capone, F.; Bagnara, P.; Capone, M.; Sale, S.; Nicastro, C.; Atripaldi, L.; Fiorentino, G.; et al. New Insights into the Identification of Metabolites and Cytokines Predictive of Outcome for Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection Showed Similarity with Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kzhyshkowska, J.; Venketaraman, V.; Escobedo, G. Editorial: Community series in immunometabolic mechanisms underlying the severity of COVID-19, volume II. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1221642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudiansyah, M.; Jasim, S.A.; Mohammad Pour, Z.G.; Athar, S.S.; Jeda, A.S.; Doewes, R.I.; Jalil, A.T.; Bokov, D.O.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Noroozbeygi, M.; et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) update: From metabolic reprogramming to immunometabolism. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 4611–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hora, S.; Pahwa, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Saxena, A.; Kashyap, M.; Sevak, J.K.; Singh, R.; Javed, M.; Yadav, P.; Kale, P.; et al. Metabolic alterations unravel the maternofetal immune responses with disease severity in pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e29257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciarambino, T.; Para, O.; Giordano, M. Immune system and COVID-19 by sex differences and age. Womens Health 2021, 17, 17455065211022262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghare Naz, M.S.; Banaei, M.; Dashti, S.; Tehrani, F.R. An overview of sex hormones in relation to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Future Virol. 2021, 16, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escarcega, R.D.; Honarpisheh, P.; Colpo, G.D.; Ahnstedt, H.W.; Couture, L.; Juneja, S.; Torres, G.; Ortiz, G.J.; Sollome, J.; Tabor, N.; et al. Sex differences in global metabolomic profiles of COVID-19 patients. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patients Characteristics | Alive (n = 20) | Death (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (Male/Female) | 10/10 | 10/10 | 1.000 |
| Age | 73 ± 11.4 | 70 ± 12.5 | 0.549 |
| Ethnicity (Hispanic/Non-Hispanic) | 16/4 | 18/2 | 0.428 |
| Race (White/Black) | 18/2 | 17/3 | 0.501 |
| Obesity (Yes/No) | 2/18 | 6/14 | 0.235 |
| Chronic Diseases (Yes/No) | 16/4 | 16/4 | 1.000 |
| Diabetes (Yes/No) | 3/17 | 7/13 | 0.137 |
| Hypertension (Yes/No) | 56/48 | 28/11 | 0.039 |
| Infectious Diseases (Yes/No) | 13/93 | 4/35 | 0.497 |
| Immunodeficiencies (Yes/No) | 15/92 | 8/31 | 0.239 |
| Pneumonia (Yes/No) | 13/7 | 19/1 | 0.055 |
| Intubation/endotracheal tubes (Yes/No) | 5/15 | 14/6 | <0.0001 |
| Bipap (Yes/No) | 4/16 | 8/12 | 0.011 |
| PT (24/48 after COVID infection) | 15.2 ± 2.1 | 16.2 ± 5.6 | 0.491 |
| PPT (24/48 after COVID infection) | 35.7 ± 10.3 | 35.2 ± 9.7 | 0.904 |
| INR | 1.2 ± 0.20 | 1.32 ± 0.64 | 0.475 |
| Respiratory rate | 18.7 ± 4.2 | 26.2 ± 6.6 | <0.0001 |
| Tidal volume | 357.5 ± 60.1 | 405.5 ± 39.3 | 0.149 |
| PEEP cm/H2O | 11.0 ± 1.41 | 11.8 ± 2.7 | 0.682 |
| PaO2 | 113.0 ± 59.3 | 87.5 ± 43.5 | 0.226 |
| FiO2 | 56.0 ± 30.7 | 75.3 ± 25.9 | 0.105 |
| PF-ratio | 247.3 ± 141.0 | 135.0 ± 79.0 | 0.016 |
| P/F ratio (<100, 100–200, >201) | 2, 1, 4 | 9, 5, 4 | 0.002 |
| Oxygen-dependent (<6 L O2) (Yes/No) | 10/10 | 4/16 | 0.006 |
| ICU admission (Yes/No) | 3/17 | 19/1 | <0.0001 |
| ARDS (Yes/No) | 3/17 | 19/1 | <0.0001 |
| ICU length of stay | 3.00 ± 3.01 | 16.8 ± 15.1 | 0.182 |
| Length of stay to discharge or death | 11.2 ± 8.7 | 16.5 ± 11.6 | 0.123 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banoei, M.M.; Hashemi Shahraki, A.; Santos, K.; Holt, G.; Mirsaeidi, M. Metabolomics and Cytokine Signatures in COVID-19: Uncovering Immunometabolism in Pathogenesis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090608
Banoei MM, Hashemi Shahraki A, Santos K, Holt G, Mirsaeidi M. Metabolomics and Cytokine Signatures in COVID-19: Uncovering Immunometabolism in Pathogenesis. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):608. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090608
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanoei, Mohammad Mehdi, Abdulrazagh Hashemi Shahraki, Kayo Santos, Gregory Holt, and Mehdi Mirsaeidi. 2025. "Metabolomics and Cytokine Signatures in COVID-19: Uncovering Immunometabolism in Pathogenesis" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090608
APA StyleBanoei, M. M., Hashemi Shahraki, A., Santos, K., Holt, G., & Mirsaeidi, M. (2025). Metabolomics and Cytokine Signatures in COVID-19: Uncovering Immunometabolism in Pathogenesis. Metabolites, 15(9), 608. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090608








