Glutamine and Albumin Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Correlated with Neurological Severity in an Experimental Model of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Timeline of the Experimental Design
Cohorts of Animals (Figure 1)
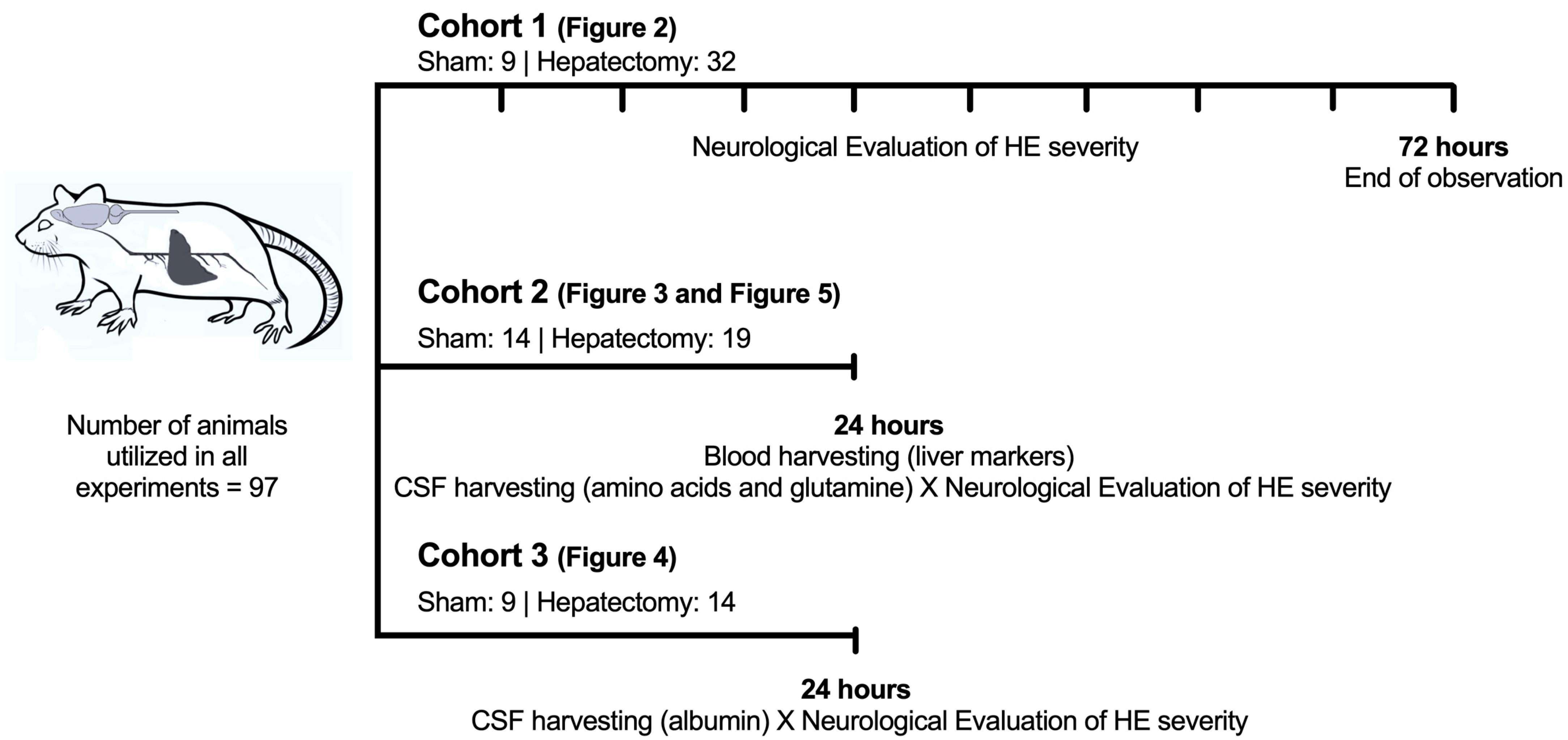
2.3. Surgical Procedure for Triggering HE
2.4. HE Neurological Severity Scale (Table 1)
2.5. Measurement of Plasma Levels of Liver Functionality Biomarkers
2.6. Measurement of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Harvest (24 h After Surgery)
2.7. Measurement of CSF Albumin Levels (24 h After Surgery)
2.8. Measurement of Amino Acid and Glutamine Levels in CSF (24 h After Surgery)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
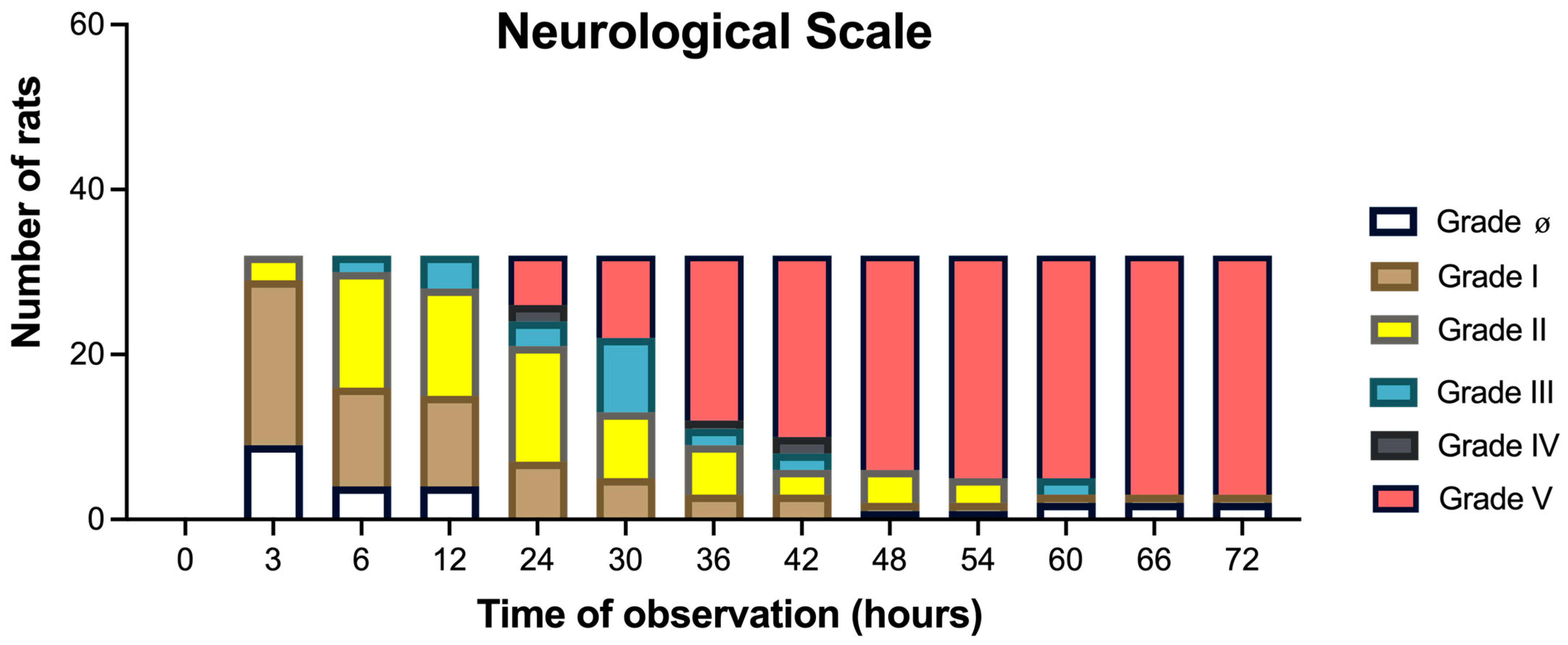
3.1. Neurological HE Severity (Grades 0 to V) Assessed for 72 H
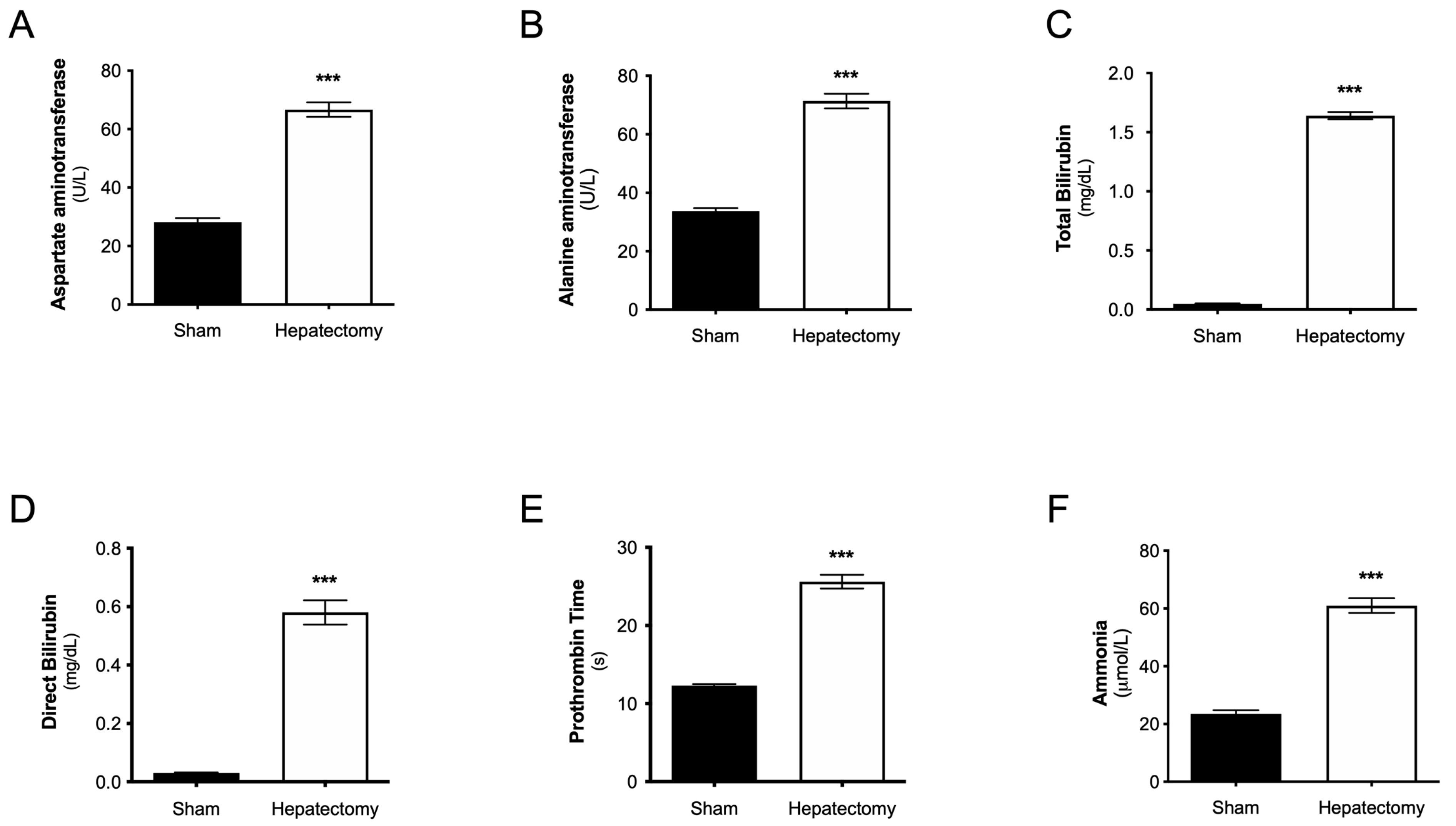
3.2. Plasma Levels of Liver Functionality Biomarkers at 24 h After Surgery
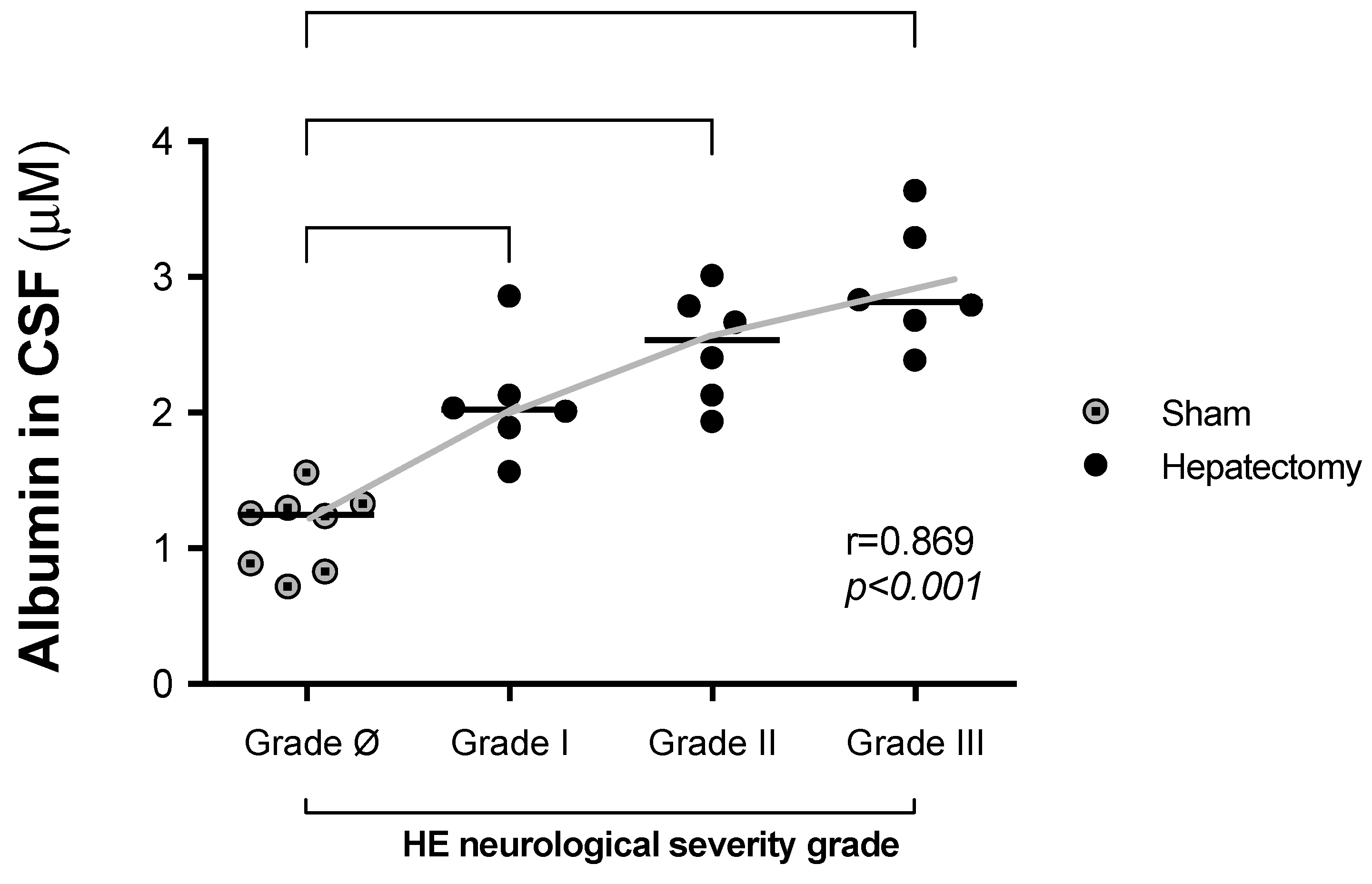
3.3. Correlations Between CSF Albumin Levels and Neurological Severity 24 h After Surgery
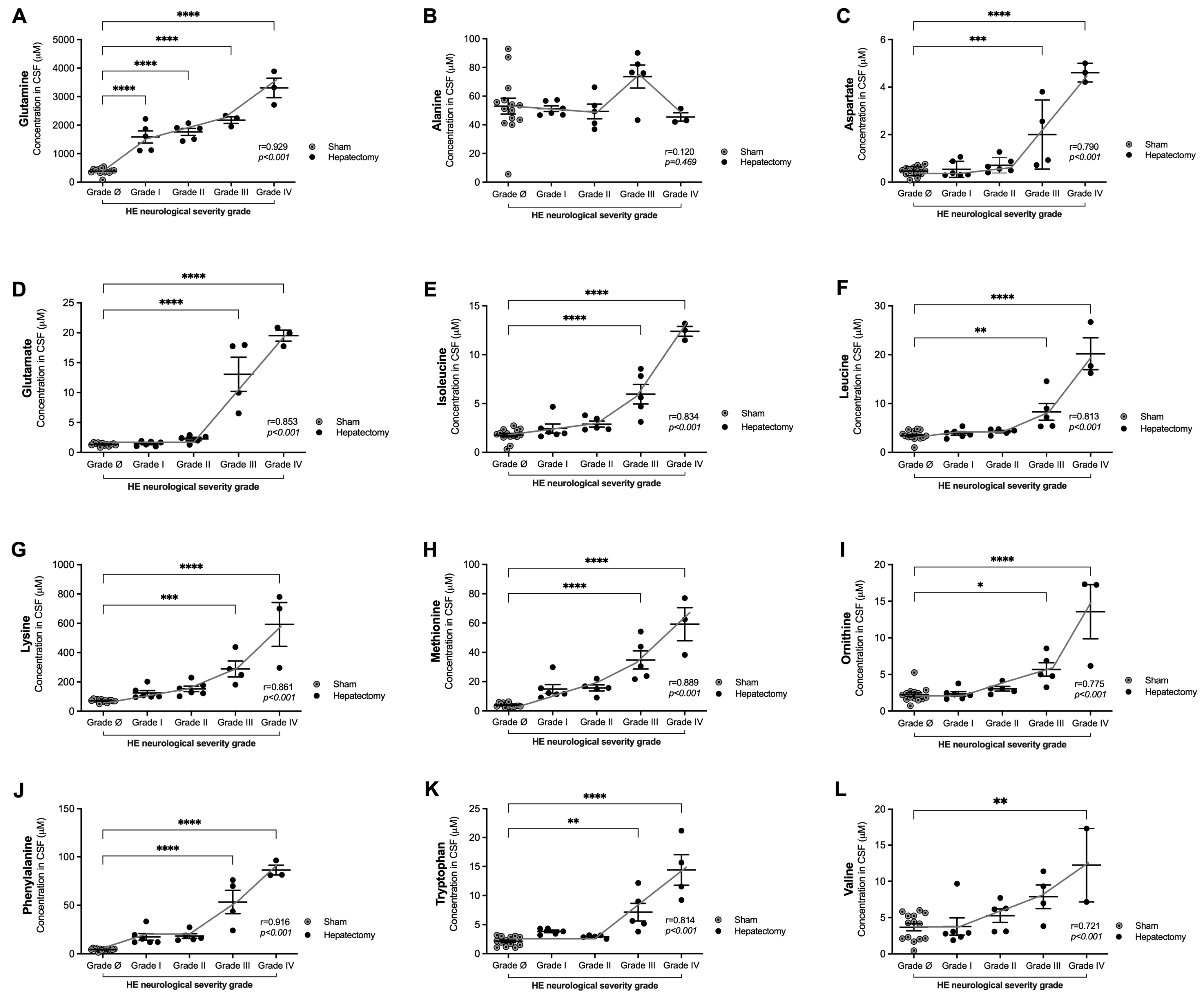
3.4. Correlations of Glutamine and Amino Acid Levels in CSF with Neurological Severity Scale Scores 24 h After Surgery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayalakshmi, V.T.; Bernal, W. Update on the management of acute liver failure. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2020, 26, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrillow, S.; Fisher, C.; Tibballs, H.; Bailey, M.; McArthur, C.; Lawson-Smith, P.; Prasad, B.; Anstey, M.; Venkatesh, B.; Dashwood, G.; et al. Coagulation abnormalities, bleeding, thrombosis, and management of patients with acute liver failure in Australia and New Zealand. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 35, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.M. Acute liver failure. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharam, A. Intensive Care Management of Acute Liver Failure: Considerations While Awaiting Liver Transplantation. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodali, S.; McGuire, B.M. Diagnosis and Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Fulminant Hepatic Failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 19, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.B.; Hoti, E.; Qasim, A.; Maguire, D.; McCormick, P.A.; Hegarty, J.E.; Geoghegan, J.G.; Traynor, O. MELD score as a prognostic model for listing acute liver failure patients for liver transplantation. Transpl. Proc. 2006, 38, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, D.; Ichai, P. Prognosis indicator in acute liver failure: Is there a place for cell death markers? J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ichai, P.; Samuel, D. Management of Fulminant Hepatitis B. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2019, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detry, O.; De Roover, A.; Honore, P.; Meurisse, M. Brain edema and intracranial hypertension in fulminant hepatic failure: Pathophysiology and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7405–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.S.; Wendon, J. Prevention and management of brain edema in patients with acute liver failure. Liver Transplant. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Study Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transplant. Soc. 2008, 14 (Suppl. S2), S90–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorg, B.; Karababa, A.; Haussinger, D. Hepatic Encephalopathy and Astrocyte Senescence. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, M.; Shigefuku, R.; Eguchi, A.; Tamai, Y.; Takei, Y. Update on blood-based biomarkers for chronic liver diseases prognosis: Literature review and institutional experience. JGH Open 2021, 5, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpurohit, S.; Musunuri, B.; Shailesh; Basthi Mohan, P.; Shetty, S. Novel Drugs for the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy: Still a Long Journey to Travel. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Vinken, M.; Jaeschke, H. Experimental models of hepatotoxicity related to acute liver failure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 290, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauli, O.; Rodrigo, R.; Boix, J.; Piedrafita, B.; Agusti, A.; Felipo, V. Acute liver failure-induced death of rats is delayed or prevented by blocking NMDA receptors in brain. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G503–G511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauli, O.; Gonzalez-Usano, A.; Cabrera-Pastor, A.; Gimenez-Garzo, C.; Lopez-Larrubia, P.; Ruiz-Sauri, A.; Hernandez-Rabaza, V.; Duszczyk, M.; Malek, M.; Lazarewicz, J.W.; et al. Blocking NMDA receptors delays death in rats with acute liver failure by dual protective mechanisms in kidney and brain. Neuromol. Med. 2014, 16, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.F.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Montagnese, S.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Vilstrup, H.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: Novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1526–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cittolin-Santos, G.F.; Guazzelli, P.A.; Nonose, Y.; Almeida, R.F.; Fontella, F.U.; Pasquetti, M.V.; Ferreira-Lima, F.J.; Lazzaroto, G.; Berlezi, R.M.; Osvaldt, A.B.; et al. Behavioral, Neurochemical and Brain Oscillation Abnormalities in an Experimental Model of Acute Liver Failure. Neuroscience 2019, 401, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefler, J.; Marfil-Garza, B.A.; Pawlick, R.L.; Freed, D.H.; Karvellas, C.J.; Bigam, D.L.; Shapiro, A.M.J. Preclinical models of acute liver failure: A comprehensive review. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helling, G.; Wahlin, S.; Smedberg, M.; Pettersson, L.; Tjader, I.; Norberg, A.; Rooyackers, O.; Wernerman, J. Plasma Glutamine Concentrations in Liver Failure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemberg, A.; Fernandez, M.A. Hepatic encephalopathy, ammonia, glutamate, glutamine and oxidative stress. Ann. Hepatol. 2009, 8, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroupina, K.; Bemeur, C.; Rose, C.F. Amino acids, ammonia, and hepatic encephalopathy. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 649, 114696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holecek, M. Ammonia and amino acid profiles in liver cirrhosis: Effects of variables leading to hepatic encephalopathy. Nutrition 2015, 31, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudalbu, C.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Brain Edema in Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2019, 9, 362–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarria, L.; Alonso, J.; Garcia-Martinez, R.; Simon-Talero, M.; Ventura-Cots, M.; Ramirez, C.; Torrens, M.; Vargas, V.; Rovira, A.; Cordoba, J. Brain magnetic resonance spectroscopy in episodic hepatic encephalopathy. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2013, 33, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, P.; Du, T.; Jiang, W.; Peng, L.; Butterworth, R.F. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and brain edema in acute liver failure: Role of glutamine redefined. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronska, M.; Albrecht, J. Alterations of blood brain barrier function in hyperammonemia: An overview. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.H.; Yamamoto, S.; Steers, J.; Sevlever, D.; Lin, W.; Shimojima, N.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Genco, P.; Golde, T.; Richelson, E.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to brain extravasation and edema in fulminant hepatic failure mice. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.H. Blood-brain barrier in acute liver failure. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; Sharifi, Y.; Jalan, R. Blood-brain barrier in liver failure: Are cracks appearing in the wall? Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2010, 30, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Sun, C.M.; Liu, P. Alterations of blood-brain barrier and associated factors in acute liver failure. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 841707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, J.; Peters, M.G. Liver disease in women: The influence of gender on epidemiology, natural history, and patient outcomes. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 9, 633–639. [Google Scholar]
- Waxman, D.J.; Holloway, M.G. Sex differences in the expression of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detry, O.; Gaspar, Y.; Cheramy-Bien, J.P.; Drion, P.; Meurisse, M.; Defraigne, J.O. A modified surgical model of fulminant hepatic failure in the rat. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 181, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzelli, P.A.; Cittolin-Santos, G.F.; Meira-Martins, L.A.; Grings, M.; Nonose, Y.; Lazzarotto, G.S.; Nogara, D.; da Silva, J.S.; Fontella, F.U.; Wajner, M.; et al. Acute Liver Failure Induces Glial Reactivity, Oxidative Stress and Impairs Brain Energy Metabolism in Rats. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, J.P.; Best, J.; Benko, T.; Bockhorn, M.; Gu, Y.; Niehues, E.M.; Bucchi, A.; Benedetto-Castro, E.M.; Gerken, G.; Rauen, U.; et al. Extent of liver resection modulates the activation of transcription factors and the production of cytokines involved in liver regeneration. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 7093–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El’chaninov, A.V.; Fatkhudinov, T.K.; Arutyunyan, I.V.; Makarov, A.V.; Usman, N.Y.; Mikhailova, L.P.; Lokhonina, A.V.; Botchey, V.M.; Glinkina, V.V.; Bol’shakova, G.B. Dynamics of Expression of Cytokine Genes and Macrophage Content in the Lungs and Kidneys after Subtotal Hepatectomy in Rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 165, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrahimov, N.; Dirsch, O.; Broelsch, C.; Dahmen, U. Marginal hepatectomy in the rat: From anatomy to surgery. Ann. Surg. 2006, 244, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieling, C.O.; Backes, A.N.; Maurer, R.L.; Cruz, C.U.; Osvaldt, A.B.; Silveira, T.R.; Matte Uda, S. The effects of anesthetic regimen in 90% hepatectomy in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2012, 27, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rohlfing, A.K.; Trescher, K.; Hahnel, J.; Muller, C.; Hildebrandt, J.P. Partial hepatectomy in rats results in immediate down-regulation of p27Kip1 in residual liver tissue by transcriptional and post-translational processes. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauli, O.; Llansola, M.; Agusti, A.; Rodrigo, R.; Hernandez-Rabaza, V.; Rodrigues, T.B.; Lopez-Larrubia, P.; Cerdan, S.; Felipo, V. Cerebral oedema is not responsible for motor or cognitive deficits in rats with hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cittolin-Santos, G.F.; de Assis, A.M.; Guazzelli, P.A.; Paniz, L.G.; da Silva, J.S.; Calcagnotto, M.E.; Hansel, G.; Zenki, K.C.; Kalinine, E.; Duarte, M.M.; et al. Guanosine Exerts Neuroprotective Effect in an Experimental Model of Acute Ammonia Intoxication. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, M.H.; Marsden, C.A. Amino acids and small peptides. In HPLC of Small Peptides; Lim, C.F., Ed.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; pp. 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Turell, L.; Botti, H.; Bonilla, L.; Torres, M.J.; Schopfer, F.; Freeman, B.A.; Armas, L.; Ricciardi, A.; Alvarez, B.; Radi, R. HPLC separation of human serum albumin isoforms based on their isoelectric points. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 944, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunchorntavakul, C.; Reddy, K.R. Acute Liver Failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 769–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, J.E.; McKiernan, P.; Squires, R.H. Acute Liver Failure: An Update. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 773–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, V.; Nanchal, R.; Karvellas, C.J. Pathophysiology of Acute Liver Failure. Nutr. Clin. Pr. 2020, 35, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: The concept of synergism revisited. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montana, V.; Verkhratsky, A.; Parpura, V. Pathological role for exocytotic glutamate release from astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 12, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjihambi, A.; Arias, N.; Sheikh, M.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: A critical current review. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouri, S.; Tripon, S.; Rudler, M.; Mallet, M.; Mayaux, J.; Thabut, D.; Weiss, N. FOUR score, a reliable score for assessing overt hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients. Neurocrit. Care 2015, 22, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Rao, K.V.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: The trojan horse hypothesis revisited. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranah, T.H.; Paolino, A.; Shawcross, D.L. Pathophysiological mechanisms of hepatic encephalopathy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 5, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, M.; Albrecht, J.; Popek, M. Dysregulation of Astrocytic Glutamine Transport in Acute Hyperammonemic Brain Edema. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 874750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumani, H.; Huss, A.; Bachhuber, F. The cerebrospinal fluid and barriers—Anatomic and physiologic considerations. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 146, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, K.; Okita, K.; Suzuki, K.; Sato, I.; Fujisawa, M.; Yoshiji, H. Association between serum albumin and cognitive dysfunction in hepatic encephalopathy: An exploratory data analysis. JGH Open 2021, 5, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Zielinska, M.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine as a mediator of ammonia neurotoxicity: A critical appraisal. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussinger, D.; Schliess, F. Pathogenetic mechanisms of hepatic encephalopathy. Gut 2008, 57, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Neurological Grades | Hepatic Encephalopathy Neurological Scale for Rats |
|---|---|
| ø | Freely moving and exploring the home cage. No reflex alterations. |
| I | No spontaneous exploratory activity. Righting reflex present. Researcher is not able to place the animal on its back. Corneal reflex preserved. |
| II | No spontaneous exploratory activity. Researcher is not able to place the animal on its back, but the animal is able to return to normal position within 3 s. Corneal reflex preserved. |
| III | No spontaneous exploratory activity. Loss of righting reflex–animal is not able to return to normal position. Corneal reflex preserved. |
| IV | No spontaneous exploratory activity or locomotion. Loss of reflexes and no response to pain stimuli. |
| V | Death |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guazzelli, P.A.; Fachim, F.d.S.; Travassos, A.S.; Schaukoski, C.C.; Ferreira, P.C.L.; Fontella, F.U.; de Bastiani, M.A.; de Assis, A.M.; Souza, D.O. Glutamine and Albumin Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Correlated with Neurological Severity in an Experimental Model of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy. Metabolites 2025, 15, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090598
Guazzelli PA, Fachim FdS, Travassos AS, Schaukoski CC, Ferreira PCL, Fontella FU, de Bastiani MA, de Assis AM, Souza DO. Glutamine and Albumin Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Correlated with Neurological Severity in an Experimental Model of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090598
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuazzelli, Pedro Arend, Felipe dos Santos Fachim, Anderson Santos Travassos, Caroline Casagrande Schaukoski, Pâmela Cristina Lukasewicz Ferreira, Fernanda Uruth Fontella, Marco Antônio de Bastiani, Adriano Martimbianco de Assis, and Diogo Onofre Souza. 2025. "Glutamine and Albumin Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Correlated with Neurological Severity in an Experimental Model of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090598
APA StyleGuazzelli, P. A., Fachim, F. d. S., Travassos, A. S., Schaukoski, C. C., Ferreira, P. C. L., Fontella, F. U., de Bastiani, M. A., de Assis, A. M., & Souza, D. O. (2025). Glutamine and Albumin Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid Are Correlated with Neurological Severity in an Experimental Model of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy. Metabolites, 15(9), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090598







