Multiparametric Evaluation of Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Using Preclinical 7T Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rat Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Preparation
2.2. MRI Equipment
2.3. MRI Data Analysis
2.4. Blood Test
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
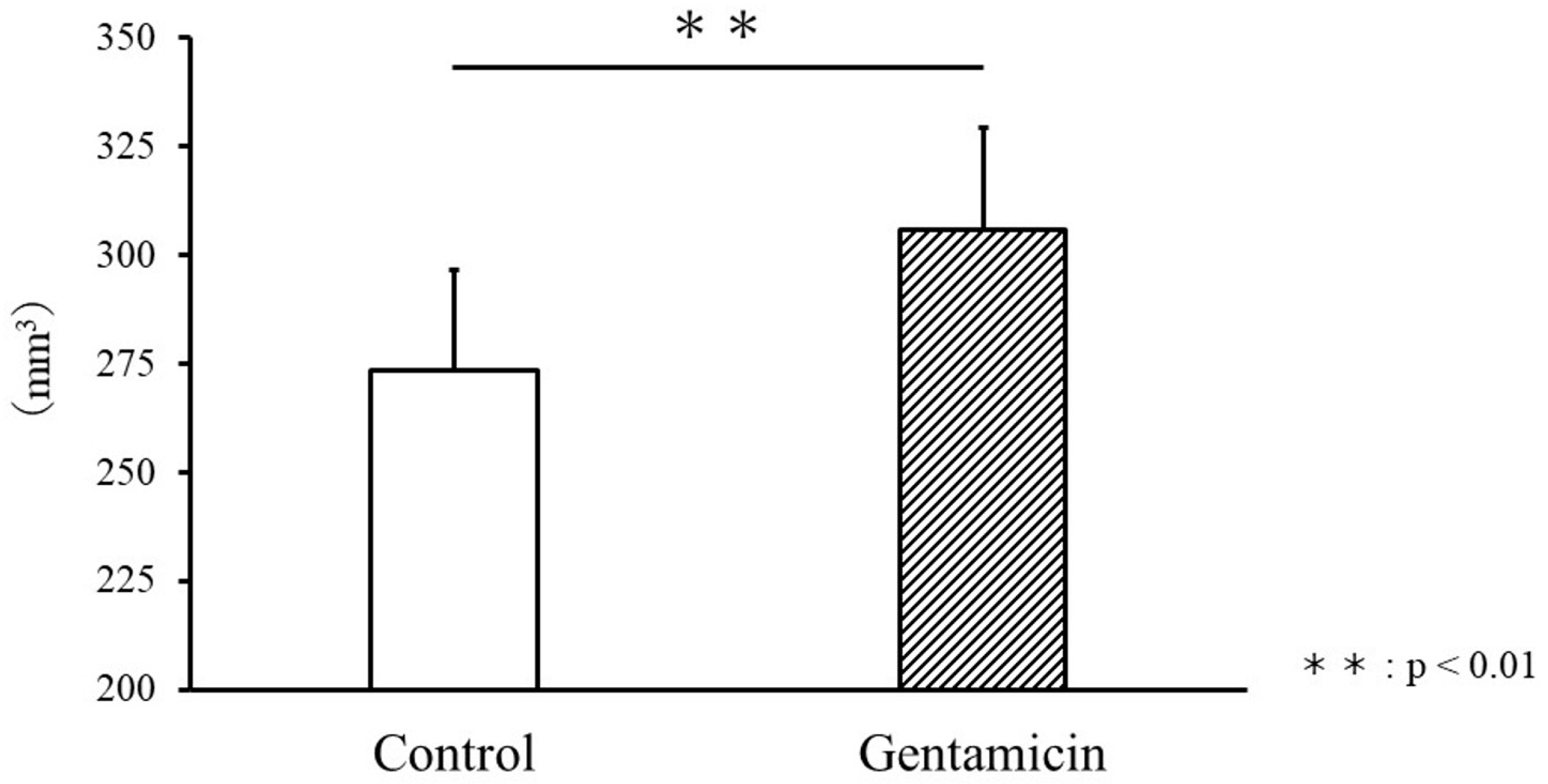
3.1. Comparison of Body Weight and Kidney Volume
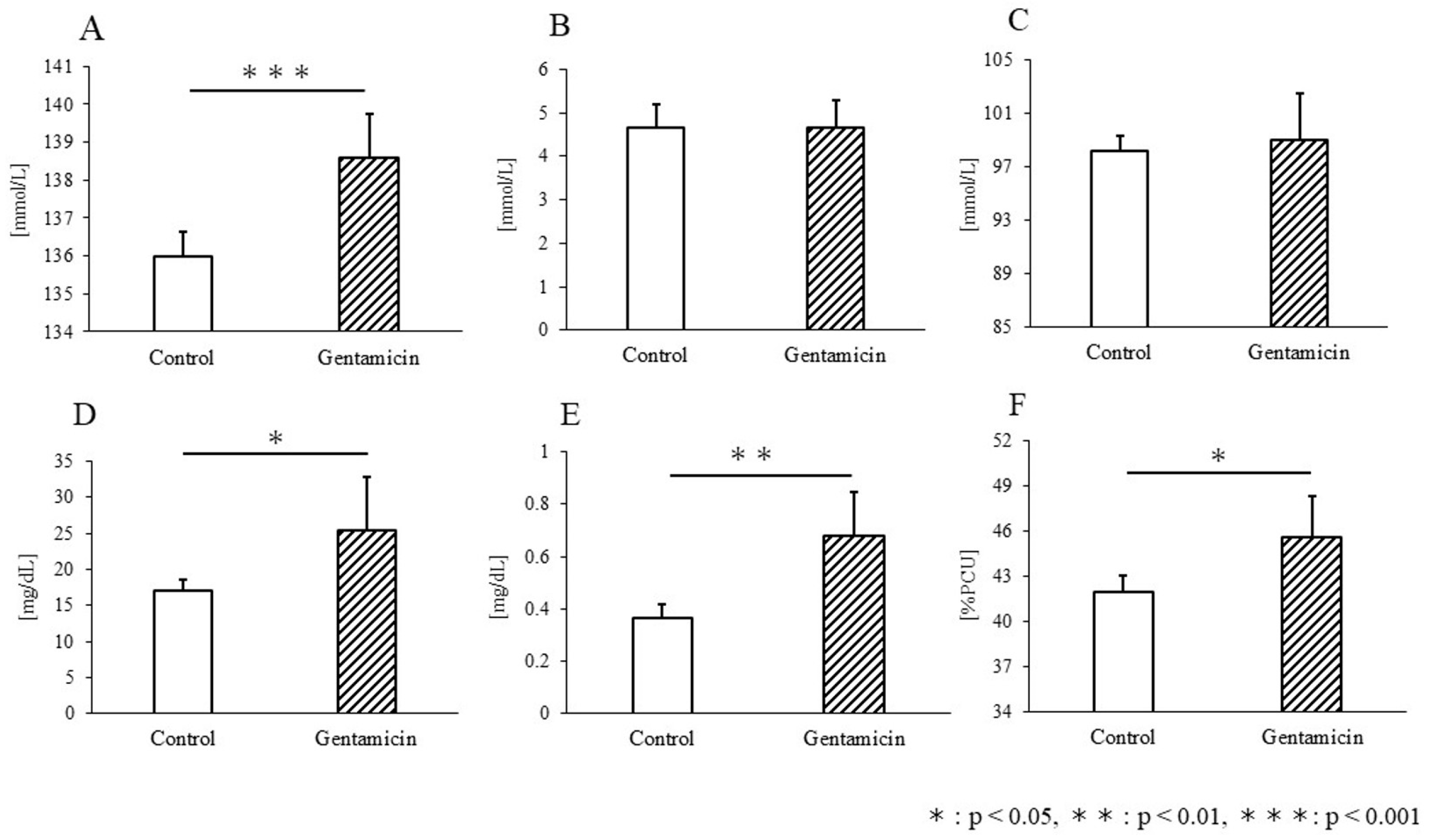
3.2. Blood Test
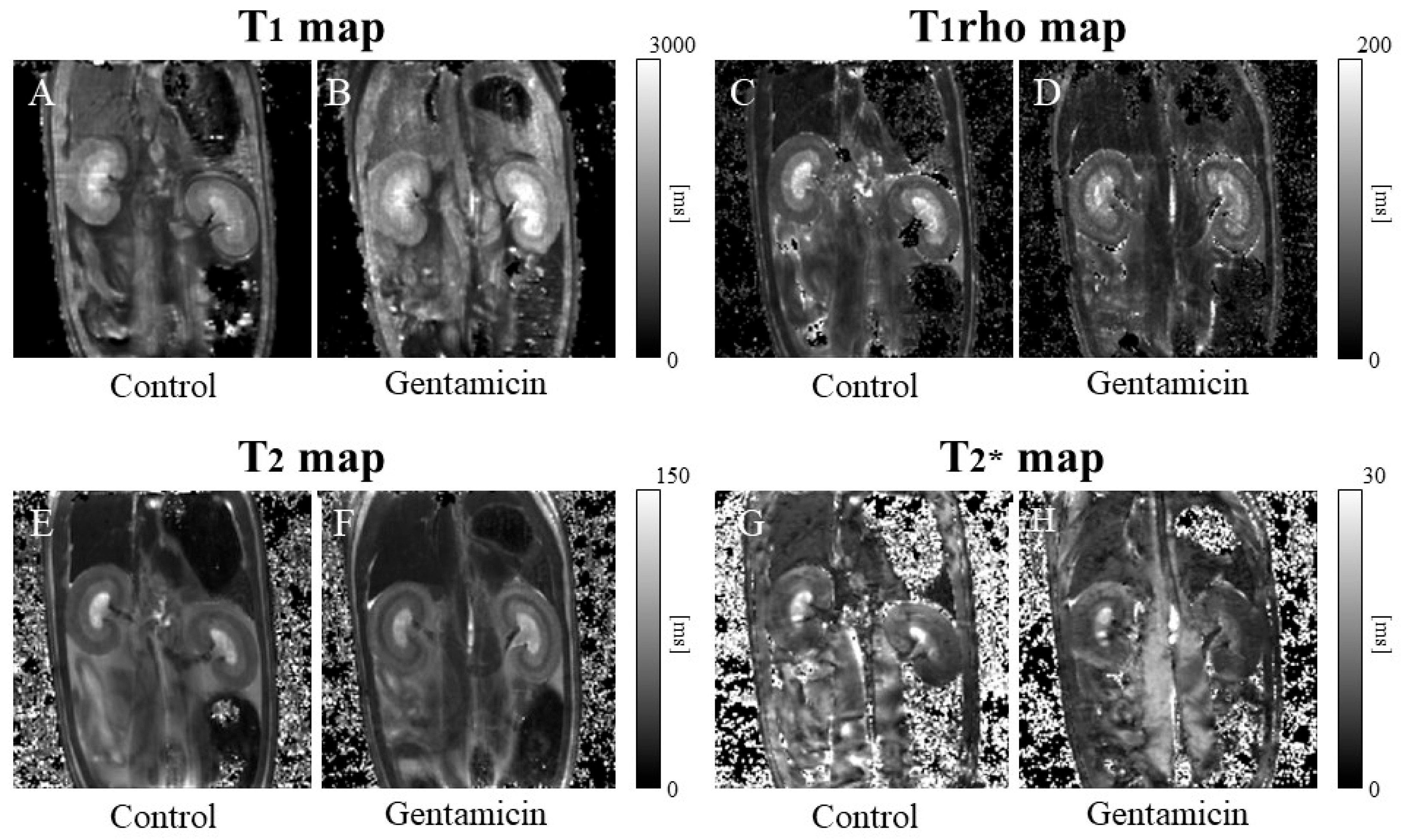
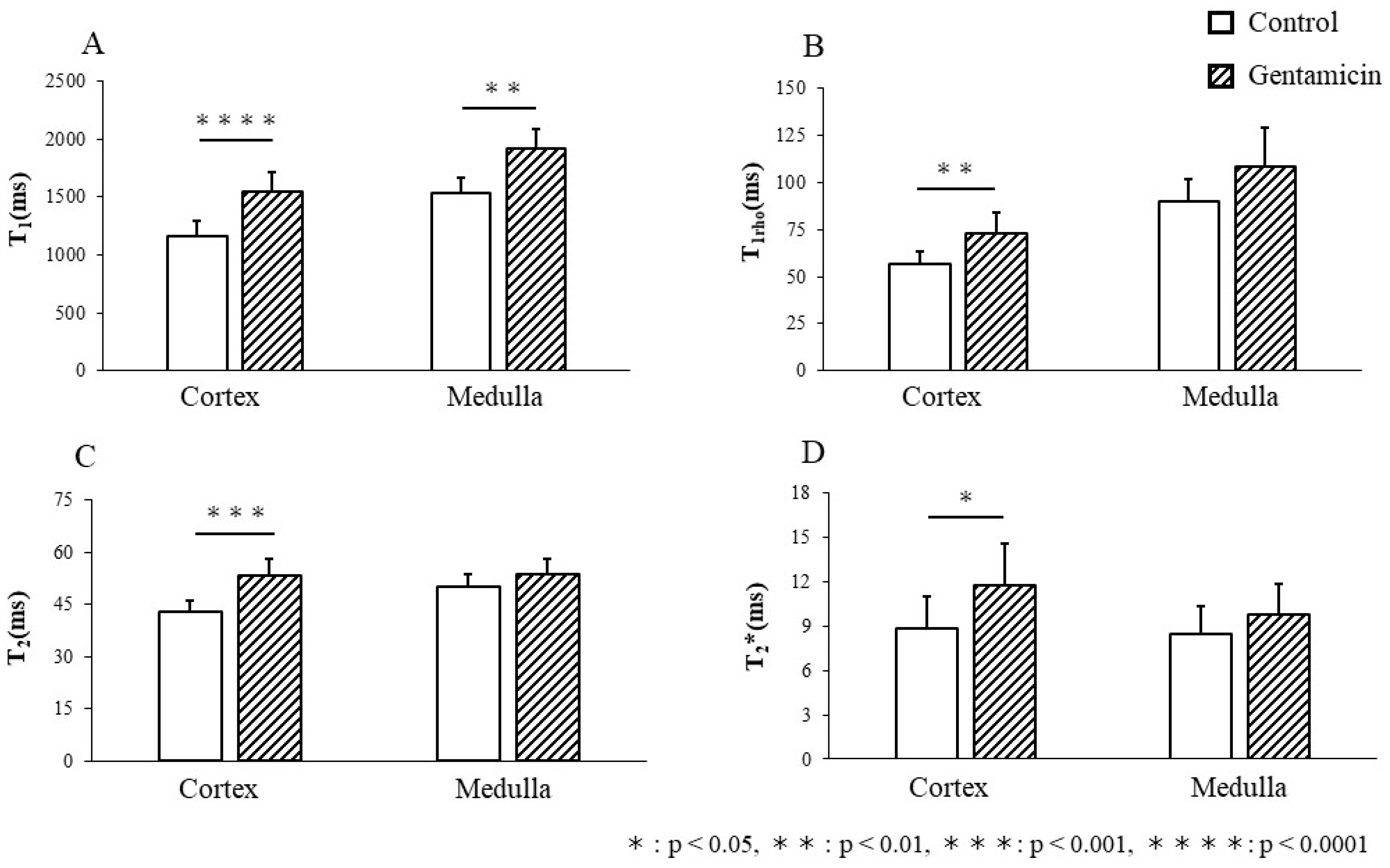
3.3. T1 Relaxation Time
3.4. T1rho Relaxation Time
3.5. T2 Relaxation Time
3.6. T2* Relaxation Time
3.7. Histological Staining
3.8. Correlation of Relaxation Time and Blood Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basile, D.P.; Anderson, M.D.; Sutton, T.A. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1303–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Ponzo, T.A.; Tang, H.; Mishra, P.K.; Macura, S.I.; Lerman, L.O. Multiparametric MRI detects longitudinal evolution of folic acid-induced nephropathy in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 315, F1252–F1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameire, N.; Biesen, W.V.; Vanholder, R. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2008, 372, 1863–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bhaduri, S.; Harwood, R.; Murray, P.; Wilm, B.; Bearon, R.; Poptani, H. Multiparametric MRI based assessment of kidney injury in a mouse model of ischemia reperfusion injury. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petejova, N.; Martinek, A.; Zadrazil, J.; Kanova, M.; Klementa, V.; Sigutova, R.; Kacirova, I.; Hrabovsky, V.; Svagera, Z.; Stejskal, D. Acute Kidney Injury in Septic Patients Treated by Selected Nephrotoxic Antibiotic Agents-Pathophysiology and Biomarkers-A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randjelovic, P.; Veljkovic, S.; Stojiljkovic, N.; Sokolovic, D.; Ilic, I. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity in animals: Current knowledge and future perspectives. EXCLI J. 2017, 16, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.T.; Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W. Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Evaluate Kidney Structure, Function, and Pathology: Moving Toward Clinical Application. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 82, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Yang, L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.; Mahmoud, H.; Cox, E.; Noble, R.; Prestwich, B.; Kasmi, I.; Taal, M.W.; Francis, S.; Selby, N.M. Multiparametric MRI assessment of renal structure and function in acute kidney injury and renal recovery. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, N.M.; Shaw, S.; Woodier, N.; Fluck, R.J.; Kolhe, N.V. Gentamicin-associated acute kidney injury. QJM 2009, 102, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, I.; Liao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Kanwar, Y.S. Modulation of gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury by myo-inositol oxygenase via the ROS/ALOX-12/12-HETE/GPR31 signaling pathway. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e155487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Jin, C.; Zhou, R.; Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Investigations on Acute and Long-Term Kidney Injury. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 59, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, D.; Hu, M.; Tang, C. Tolvaptan Improves Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2022, 2022, 7435292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Drug use and nephrotoxicity in the intensive care unit. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.C.; Ko, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Shin, N.R.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, J.C. Ameliorative effects of pine bark extract on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueper, K.; Peperhove, M.; Rong, S.; Gerstenberg, J.; Mengel, M.; Meier, M.; Gutberlet, M.; Tewes, S.; Barrmeyer, A.; Chen, R.; et al. T1-mapping for assessment of ischemia-induced acute kidney injury and prediction of chronic kidney disease in mice. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Bai, X.Y.; Sun, X.; Cai, G.; Hong, Q.; Ding, R.; Chen, X. Rapamycin protects against gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury via autophagy in mini-pig models. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Pharmacology behind Common Drug Nephrotoxicities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Drug-induced acute kidney injury: Diverse mechanisms of tubular injury. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Kusakabe, Y.; Kitamura, A.; Okada, S.; Murase, K. Protective effect of hydrogen-rich water against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats using blood oxygenation level-dependent MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2011, 10, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jin, W.W.; Huang, M.; Ji, H.; Capen, D.E.; Xia, Y.; Yuan, J.; Paunescu, T.G.; Lu, H.A.J. Gentamicin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in an Animal Model Involves Programmed Necrosis of the Collecting Duct. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2097–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brkic, B.M.; Rovcanin, B.; Stojanovic, M.; Srebro, D.; Vuckovic, S.; Savic Vujovic, K. Chloroquine Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Dose Response 2022, 20, 15593258221119871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; An, Z.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Y. Multi-Parametric MRI for Evaluating Variations in Renal Structure, Function, and Endogenous Metabolites in an Animal Model With Acute Kidney Injury Induced by Ischemia Reperfusion. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 60, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Yang, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wu, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yan, C.; Seeliger, E.; Niendorf, T.; et al. Parametric MRI Detects Aristolochic Acid Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Tomography 2022, 8, 2902–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.; Ferraro, P.M.; Naticchia, A.; Gambaro, G. Serum sodium variability and acute kidney injury: A retrospective observational cohort study on a hospitalized population. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Qin, J.; Yan, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Wu, P.Y.; Wang, X. Use of multiparametric MRI to noninvasively assess iodinated contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 114, 110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Shang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Gu, H.; Dou, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Native T1 Mapping in Assessing Kidney Fibrosis for Patients With Chronic Glomerulonephritis. Front Med. 2021, 8, 772326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, I.A.; Lamb, H.J. Clinical application and technical considerations of T(1) & T(2)(*) mapping in cardiac, liver, and renal imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, I.A.; de Boer, A.; Sharma, K.; Cox, E.F.; Lamb, H.J.; Buckley, D.L.; Bane, O.; Morris, D.M.; Prasad, P.V.; Semple, S.I.K.; et al. Consensus-based technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal T1 and T2 mapping MRI. Magma 2020, 33, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, E.F.; Buchanan, C.E.; Bradley, C.R.; Prestwich, B.; Mahmoud, H.; Taal, M.; Selby, N.M.; Francis, S.T. Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Validation, Interventions, and Alterations in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, C.E.; Mahmoud, H.; Cox, E.F.; McCulloch, T.; Prestwich, B.L.; Taal, M.W.; Selby, N.M.; Francis, S.T. Quantitative assessment of renal structural and functional changes in chronic kidney disease using multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueper, K.; Rong, S.; Gutberlet, M.; Hartung, D.; Mengel, M.; Lu, X.; Haller, H.; Wacker, F.; Meier, M.; Gueler, F. T2 relaxation time and apparent diffusion coefficient for noninvasive assessment of renal pathology after acute kidney injury in mice: Comparison with histopathology. Investig. Radiol. 2013, 48, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueper, K.; Gutberlet, M.; Brasen, J.H.; Jang, M.S.; Thorenz, A.; Chen, R.; Hertel, B.; Barrmeyer, A.; Schmidbauer, M.; Meier, M.; et al. Multiparametric Functional MRI: Non-Invasive Imaging of Inflammation and Edema Formation after Kidney Transplantation in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greite, R.; Derlin, K.; Hartung, D.; Chen, R.; Meier, M.; Gutberlet, M.; Hensen, B.; Wacker, F.; Gueler, F.; Hellms, S. Diffusion Weighted Imaging and T2 Mapping Detect Inflammatory Response in the Renal Tissue during Ischemia Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Different Mouse Strains and Predict Renal Outcome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Liang, W.; Wu, M.; Lai, C.; Mei, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Luo, L.; Quan, X. Comparison of T1 Mapping and T1rho Values with Conventional Diffusion-weighted Imaging to Assess Fibrosis in a Rat Model of Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvvuri, U.; Poptani, H.; Feldman, M.; Nadal-Desbarats, L.; Gee, M.S.; Lee, W.M.; Reddy, R.; Leigh, J.S.; Glickson, J.D. Quantitative T1rho magnetic resonance imaging of RIF-1 tumors in vivo: Detection of early response to cyclophosphamide therapy. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7747–7753. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Yuan, J.; Chu, E.S.; Go, M.Y.; Huang, H.; Ahuja, A.T.; Sung, J.J.; Yu, J. T1rho MR imaging is sensitive to evaluate liver fibrosis: An experimental study in a rat biliary duct ligation model. Radiology 2011, 259, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Ohki, A.; Shintani, Y.; Higuchi, T. Early detection of elevated lactate levels in a mitochondrial disease model using chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) at 7T-MRI. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2019, 12, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Ueda, J. Preclinical magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy in the fields of radiological technology, medical physics, and radiology. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2024, 17, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewes, S.; Gueler, F.; Chen, R.; Gutberlet, M.; Jang, M.S.; Meier, M.; Mengel, M.; Hartung, D.; Wacker, F.; Rong, S.; et al. Functional MRI for characterization of renal perfusion impairment and edema formation due to acute kidney injury in different mouse strains. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; Berchtold, L.; Moll, S.; Hadaya, K.; de Perrot, T.; Vesin, C.; Martin, P.Y.; de Seigneux, S.; Vallee, J.P. New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Index for Renal Fibrosis Assessment: A Comparison between Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and T1 Mapping with Histological Validation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, I.; Aamir, F.; Kassai, M.; Crowe, L.A.; Poletti, P.A.; Seigneux, S.; Moll, S.; Berchtold, L.; Vallee, J.P. Validation of automatically measured T1 map cortico-medullary difference (DeltaT1) for eGFR and fibrosis assessment in allograft kidneys. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Yap, J.Q.; Qian, Q. Increased mortality risk associated with serum sodium variations and borderline hypo- and hypernatremia in hospitalized adults. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, T. Association between serum sodium trajectory and mortality in patients with acute kidney injury: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Fu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hao, Q.; Bao, D.; Hou, D. Effect of curcumin on glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkaki, A.; Hoseinynejad, S.; Khombi Shooshtari, M.; Rashno, M. Synaptic plasticity and cognitive impairment consequences to acute kidney injury: Protective role of ellagic acid. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Reddy, D.; Haris, M.; Cai, K.; Rajender Reddy, K.; Hariharan, H.; Reddy, R. T1rho MRI of healthy and fibrotic human livers at 1.5 T. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, I.; Eiber, M.; Ganter, C.; Martirosian, P.; Safi, W.; Umgelter, A.; Rummeny, E.J.; Holzapfel, K. Evaluation of T1rho as a potential MR biomarker for liver cirrhosis: Comparison of healthy control subjects and patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Jung, S.I.; Moon, M.H.; Joo, K.W.; Cho, J.Y. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of chronic kidney disease: An experimental in vivo study using rat chronic kidney disease models. Acta Radiol. 2023, 64, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulow, R.D.; Boor, P. Extracellular Matrix in Kidney Fibrosis: More Than Just a Scaffold. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2019, 67, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodner, C.M.; Kudrimoti, A. Diagnosis and management of acute interstitial nephritis. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 67, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joyce, E.; Glasner, P.; Ranganathan, S.; Swiatecka-Urban, A. Tubulointerstitial nephritis: Diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijm, M.; Milani, B.; Burnier, M. Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent MRI to Assess Renal Oxygenation in Renal Diseases: Progresses and Challenges. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.; Edelman, R.R.; Epstein, F.H. Noninvasive evaluation of intrarenal oxygenation with BOLD MRI. Circulation 1996, 94, 3271–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugarten, J.; Golestaneh, L. Blood oxygenation level-dependent MRI for assessment of renal oxygenation. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc Dis. 2014, 7, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, N.M.; Francis, S.T. Assessment of Acute Kidney Injury using MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2025, 61, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlmann, A.; Hentschel, J.; Fechner, M.; Hoff, U.; Bubalo, G.; Arakelyan, K.; Cantow, K.; Seeliger, E.; Flemming, B.; Waiczies, H.; et al. High temporal resolution parametric MRI monitoring of the initial ischemia/reperfusion phase in experimental acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, J.; Xia, F.; Zhu, J.; Shen, W. Evaluation of renal cold ischemia-reperfusion injury with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging and blood oxygenation level-dependent MRI in a rat model. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1159741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabb, H.; Griffin, M.D.; McKay, D.B.; Swaminathan, S.; Pickkers, P.; Rosner, M.H.; Kellum, J.A.; Ronco, C.; Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Consensus, X.W.G. Inflammation in AKI: Current Understanding, Key Questions, and Knowledge Gaps. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| (A) | ||||
| T1 map | T1rho map | T2 map | T2* map | |
| Na | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.46 | 0.12 |
| K | −0.19 | −0.43 | −0.41 | −0.34 |
| Cl | 0.27 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.49 |
| BUN | 0.68 | 0.57 | 0.59 | 0.45 |
| Crea | 0.70 | 0.45 | 0.46 | 0.25 |
| Hct | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.17 |
| (B) | ||||
| T1 map | T1rho map | T2 map | T2* map | |
| Na | 0.43 | 0.27 | 0.59 | −0.05 |
| K | −0.31 | −0.44 | −0.47 | −0.33 |
| Cl | 0.24 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.39 |
| BUN | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.31 |
| Crea | 0.41 | 0.22 | −0.01 | 0.10 |
| Hct | 0.65 | 0.47 | 0.19 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natsuyama, T.; Ueda, J.; Yabata, I.; Sawaya, R.; Itagaki, K.; Saito, S. Multiparametric Evaluation of Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Using Preclinical 7T Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rat Models. Metabolites 2025, 15, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090593
Natsuyama T, Ueda J, Yabata I, Sawaya R, Itagaki K, Saito S. Multiparametric Evaluation of Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Using Preclinical 7T Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rat Models. Metabolites. 2025; 15(9):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090593
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatsuyama, Tomohiro, Junpei Ueda, Isamu Yabata, Reika Sawaya, Koji Itagaki, and Shigeyoshi Saito. 2025. "Multiparametric Evaluation of Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Using Preclinical 7T Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rat Models" Metabolites 15, no. 9: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090593
APA StyleNatsuyama, T., Ueda, J., Yabata, I., Sawaya, R., Itagaki, K., & Saito, S. (2025). Multiparametric Evaluation of Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Using Preclinical 7T Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rat Models. Metabolites, 15(9), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15090593






