Molybdenum-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury and Metabolic Pathway Disruption in Goat Pancreas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Managing Animals and Preparing Samples
2.2. Determination of Mineral Elements in Goat Pancreas
2.3. Detection of Antioxidant Indexes and Inflammatory Factors in Goat Pancreas
2.4. Metabolomics Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Signs of Goats
3.2. Changes in Mineral Elements in Goat Pancreas
3.3. Effects of Antioxidant Capacity in Goat Pancreas
3.4. Influences of Inflammatory Factor in Goat Pancreas
3.5. Quality Validation of Metabolomics Data
3.6. Results of Supervised Multivariate Statistical Analysis
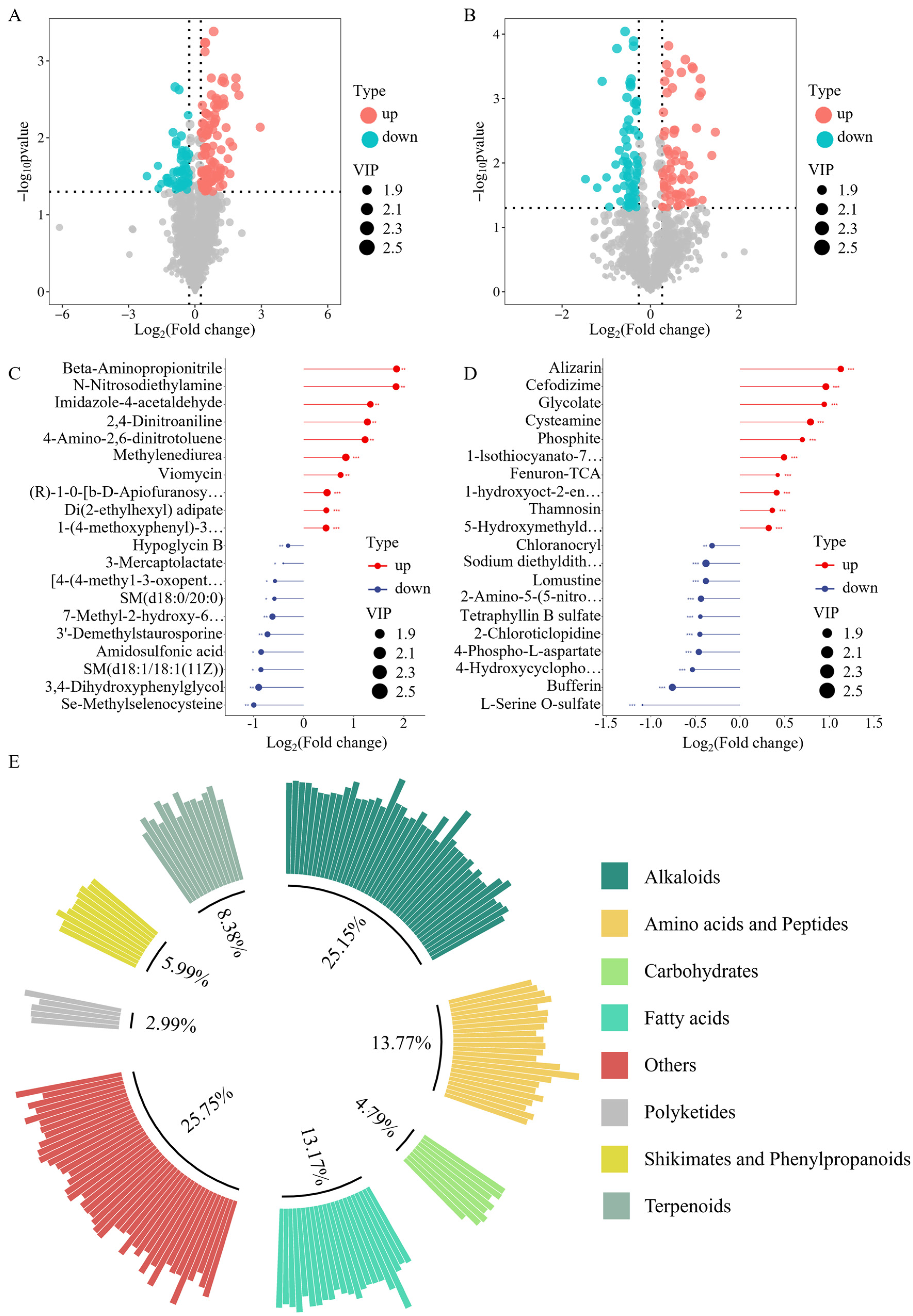
3.7. Analysis of DEMs
3.8. KEGG Metabolic Pathway Analysis of DEMs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Mo | Molybdenum |
| S | Sulfur |
| Cu | Copper |
| DEMs | Differentially expressed metabolites |
| Fe | Iron |
| Zn | Zinc |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| T-AOC | Total antioxidant capacity |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| QC | Quality control |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| TIC | Total ion chromatogram |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Jomova, K.; Makova, M.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Essential metals in health and disease. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G.; Mendel, R.R.; Ribbe, M.W. Molybdenum cofactors, enzymes and pathways. Nature 2009, 460, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Nie, G.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Dai, X.; Liao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Cao, H.; Xing, C.; et al. Molybdenum and cadmium co-induce oxidative stress and apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathway in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, A.E.; Matveeva, V.A.; Chukaeva, M.A. Development of Chemosorbent Based on Metallic Waste for Cleaning Mine Water From Molybdenum. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.L.; Montaña, F.P.; Miranda, M.; Castillo, C.; Hernández, J.; Benedito, J.L. Interactions between toxic (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) and nutritional essential (Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Se, Zn) elements in the tissues of cattle from NW Spain. Biometals 2004, 17, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorndyke, M.P.; Guimaraes, O.; Kistner, M.J.; Wagner, J.J.; Engle, T.E. Influence of molybdenum in drinking water or feed on copper metabolism in cattle—A review. Animals 2021, 11, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, L.; Kendall, N.R. Role of the rumen in copper and thiomolybdate absorption. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2011, 24, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, P.; Shen, X.; Zhao, K. Molybdenum fertilizer improved antioxidant capacity of Chinese Merino sheep under compound contamination. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, F.; Xing, C.; Hu, G.; Cao, H. Effects of different levels of molybdenum on rumen microbiota and trace elements changes in tissues from goats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 174, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.O. Molybdenum. In Veterinary Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2018; pp. 463–467. [Google Scholar]
- Adamus, J.P.; Ruszczyńska, A.; Wyczałkowska-Tomasik, A. Molybdenum’s role as an essential element in enzymes catabolizing redox reactions: A review. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Xing, C.; Huang, A.; Zhuang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G.; Mao, Y.; Cao, H. Molybdenum induces mitochondrial oxidative damage in kidney of goats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 197, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Nie, G.; Hu, R.; Wang, C.; Xing, C.; Li, G.; Hu, G.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C. Inhibition of autophagy aggravates molybdenum-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by aggravating oxidative stress in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.Y.; Yen, C.C.; Lee, K.I.; Su, C.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Hsieh, S.S.; Ueng, K.C.; Huang, C.F. Molybdenum induces pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis via interdependent of JNK and AMPK activation-regulated mitochondria-dependent and ER stress-triggered pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 294, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Cao, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, A.; Zhang, J. Effect of different levels of molybdenum on serum free radical metabolism in goats. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 33, 918–922. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Ali, T.; Chen, R.; Hu, G.; Zhuang, Y.; Luo, J.; Cao, H.; Han, B. In vivo studies of molybdenum-induced apoptosis in kidney cells of caprine. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 165, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; MA, S.; Shen, Y.; LI, S.; Wang, H. Effects of molybdenum on rumen pathophysiology and digestive enzymes of sheep. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2022, 43, 72–76+78–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, K.L.; Olson, K.C.; Wright, C.L.; Austin, K.J.; Johnson, P.S.; Cammack, K.M. Effects of supplemental molybdenum on animal performance, liver copper concentrations, ruminal hydrogen sulfide concentrations, and the appearance of sulfur and molybdenum toxicity in steers receiving fiber-based diets1. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 5005–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olesti, E.; González-Ruiz, V.; Wilks, M.F.; Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S. Approaches in metabolomics for regulatory toxicology applications. Analyst 2021, 146, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Cox, M.J.; Runau, F. Molecular advances in pancreatic cancer: A genomic, proteomic and metabolomic approach. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 5171–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shen, X. Multi-omics insights into the mechanisms of muscle damage induced by molybdenum exposure in goats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 299, 118373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, G.; Huo, T. Metabolic characteristics related to the hazardous effects of environmental arsenic on humans: A metabolomic review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Melton, D.A. Pancreas regeneration. Nature 2018, 557, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisbeck, M.F.; Siemion, R.S.; Smith, M.A. Modest copper supplementation blocks molybdenosis in cattle. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2006, 18, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majak, W.; Steinke, D.; Lysyk, T.; Ogilvie, K.; McGillivray, J. Efficacy of copper supplementation in the prevention of molybdenosis in cattle. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 59, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, R.S.; López, S.; Montanholi, Y.R.; Smith, B.; Haas, L.S.; Miller, S.P.; France, J. A meta-analysis of the effects of dietary copper, molybdenum, and sulfur on plasma and liver copper, weight gain, and feed conversion in growing-finishing cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5714–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffany, M.E.; Mcdowell, L.R.; O’Connor, G.A.; Martin, F.G.; Wilkinson, N.S.; Percival, S.S.; Rabiansky, P.A. Effects of residual and reapplied biosolids on performance and mineral status of grazing beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryssen, V.; Stielau, W.J. Effect of different levels of dietary molybdenum on copper and Mo metabolism in sheep fed on high levels of Cu. Br. J. Nutr. 1981, 45, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative stress. Annu. Rev. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Shen, X. Multi-omics reveals the hepatic metabolic mechanism of neurological symptoms caused by selenium exposure in Przewalski’s gazelle (Procapra przewalskii). Environ. Pollut. 2025, 375, 126341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Regenstein, J.M.; Xie, D.; Lu, W.; Ren, X.; Yuan, J.; Mao, L. The oxidative stress and antioxidant responses of Litopenaeus vannamei to low temperature and air exposure. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Bi, M.; Yang, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, G.; Zhang, Z. Cadmium exposure triggers oxidative stress, necroptosis, Th1/Th2 imbalance and promotes inflammation through the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway in swine small intestine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Zhou, P.; Shen, X. Abnormal Phenylalanine Metabolism of Procapra przewalskii in Chronic Selenosis in Selenium-Enriched Habitats. Metabolites 2023, 13, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, S.G.; Beguesse, K.A.; Min, B.R. Effect of high molybdenum diet on copper status, growth performance, blood metabolites, select liver and kidney minerals, and immune responses of boer crosses. Animals 2024, 14, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Tang, M.; Mu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Liao, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C. Oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the adverse effects of cadmium exposure on all-cause and cause-specific mortality in patients with diabetes and prediabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.-A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, X.; Teng, X. Cadmium-induced oxidative stress and immunosuppression mediated mitochondrial apoptosis via JNK-FoxO3a-PUMA pathway in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Gills. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 233, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraerts, S.L.; Heylen, E.; De Keersmaecker, K.; Kampen, K.R. The ins and outs of serine and glycine metabolism in cancer. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A.; Simon, M.C. Glutathione metabolism in cancer progression and treatment resistance. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, P.; Huang, R.; Zhou, X. Oxidation Resistance of the sulfur amino acids: Methionine and cysteine. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9584932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.A.; Lee, W.; Cowell, T.L.; Wells, T.M.; Weissbach, H.; Kantorow, M. Silencing of the methionine sulfoxide reductase A gene results in loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and increased ROS production in human lens cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yermolaieva, O.; Xu, R.; Schinstock, C.; Brot, N.; Weissbach, H.; Heinemann, S.H.; Hoshi, T. Methionine sulfoxide reductase a protects neuronal cells against brief hypoxia/reoxygenation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.A.K.; Huang, P.; Liu, G.; Ren, W.; Teklebrh, T.; Yan, W.; Zhou, X.; Yin, Y. Hyperhomocysteinemia and cardiovascular disease in animal model. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, G. Antioxidant effects of sulfur-containing amino acids. Yonsei Med. J. 2004, 45, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaloo, A.; Reid, M.; Forrester, T.; Heird, W.C.; Jahoor, F. Cysteine supplementation improves the erythrocyte glutathione synthesis rate in children with severe edematous malnutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ren, W.; Yang, G.; Duan, J.; Huang, X.; Fang, R.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. L-Cysteine metabolism and its nutritional implications. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Tremaroli, V. Therapeutic Potential of Butyrate for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 761834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, C.C.; Kien, C.L.; Bouthillier, L.; Levy, E. Short-Chain Fatty Acids: Ready for Prime Time? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2006, 21, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, K.; de Vos, P.; Priebe, M.G. Butyrate and other short-chain fatty acids as modulators of immunity: What relevance for health? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga-Ramos, A.; Barba-Ostria, C.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Guamán, L.P. Protective role of butyrate in obesity and diabetes: New insights. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1067647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, R.Q.; Karpowicz, S.J. Reaction of hypotaurine or taurine with superoxide produces the organic peroxysulfonic acid peroxytaurine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Ge, X.; Ding, H.; Jiang, H.; Christensen, B.M.; Li, J. Role of glutamate decarboxylase-like protein 1 (GADL1) in taurine biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40898–40906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Guerrero, S.; Guardo-Maya, S.; Medina-Rincón, G.J.; Orrego-González, E.E.; Cabezas-Pérez, R.; González-Reyes, R.E. Taurine and astrocytes: A homeostatic and neuroprotective relationship. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 937789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.W.; Jong, C.J.; Ito, T.; Azuma, J. Role of taurine in the pathologies of MELAS and MERRF. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, J.; Liebisch, G. Application of stable isotopes to investigate the metabolism of fatty acids, glycerophospholipid and sphingolipid species. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 54, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, J.; Tomé, D.; Schmidely, P.; Demersay, T.-C.; Azzout-Marniche, D. Histidine: A systematic review on metabolism and physiological effects in human and different animal species. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Histidine in Health and Disease: Metabolism, Physiological Importance, and Use as a Supplement. Nutrients 2020, 12, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombley, P.Q.; Horning, M.S.; Blakemore, L.J. Interactions between carnosine and zinc and copper: Implications for neuromodulation and neuroprotection. Biochemistry 2000, 65, 807–816. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Ran, Y.; Shen, X. Molybdenum-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury and Metabolic Pathway Disruption in Goat Pancreas. Metabolites 2025, 15, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080541
Li L, Ran Y, Shen X. Molybdenum-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury and Metabolic Pathway Disruption in Goat Pancreas. Metabolites. 2025; 15(8):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080541
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Longfei, Yang Ran, and Xiaoyun Shen. 2025. "Molybdenum-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury and Metabolic Pathway Disruption in Goat Pancreas" Metabolites 15, no. 8: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080541
APA StyleLi, L., Ran, Y., & Shen, X. (2025). Molybdenum-Induced Oxidative and Inflammatory Injury and Metabolic Pathway Disruption in Goat Pancreas. Metabolites, 15(8), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15080541





