Exploratory Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling in a Manganese-Exposed Parkinsonism-Affected Population in Northern Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Manganese (Mn) Concentration Data Acquisition and Data Analysis
2.4. Untargeted Metabolomic and Lipidomic Data Acquisition
2.5. Untargeted Metabolomic and Lipidomic Data Processing and Feature Retention Criteria
- •
- Level 1: Confirmed structures with MS, MS/MS, and retention time matching reference standards.
- •
- Level 2: Probable structures, where spectral evidence suggests an exact molecular identity but without confirmation by reference standards.
- •
- Level 3: Tentative candidates, where multiple potential structures exist, but insufficient evidence prevents assigning a single structure.
- •
- Level 4: Unequivocal molecular formulas, where the exact mass and isotopic patterns confirm the chemical formula, but no specific structure is proposed.
2.6. Statistical Power and Sample Size Justification
2.7. Sociodemographic Data Analysis
2.8. Metabolomic Data Analysis
2.9. Lipidomic Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Lifestyle Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Manganese Measurement Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
3.3. Machine-Learning-Based Metabolomic Exploratory Data Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) and Metabolite Associations with Disease Effect
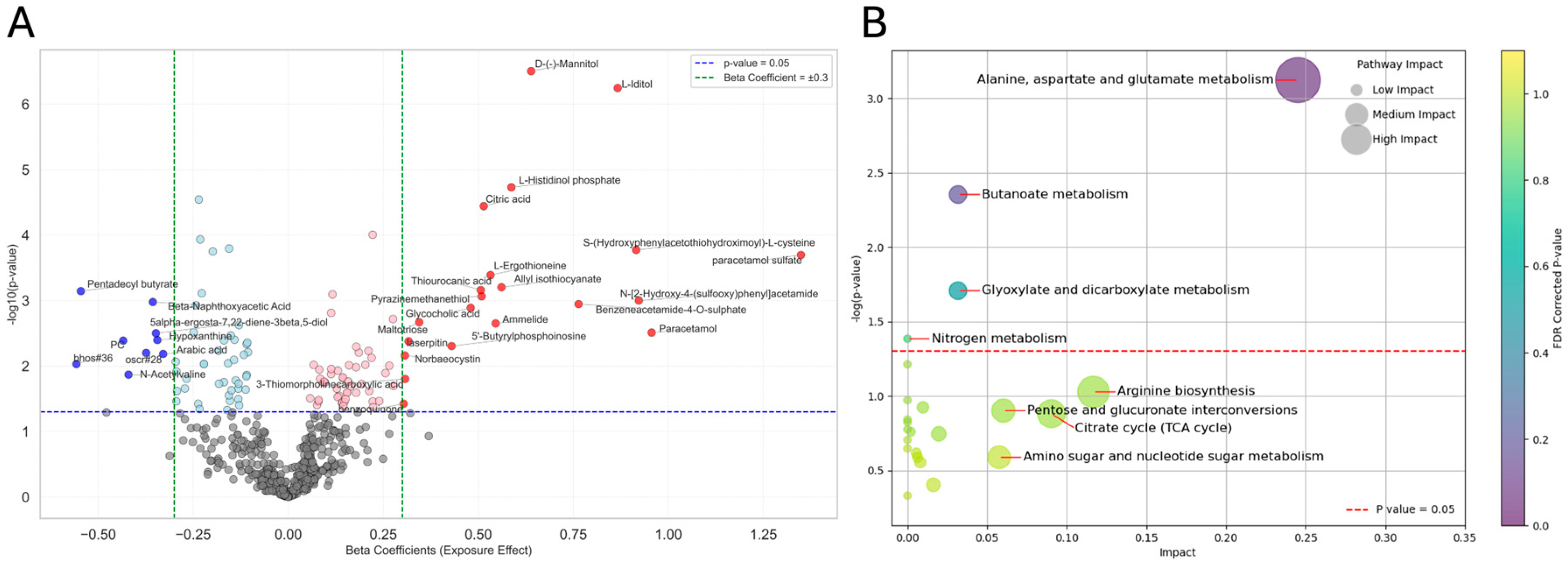
3.5. ANCOVA and Metabolite Associations with Exposure Effect
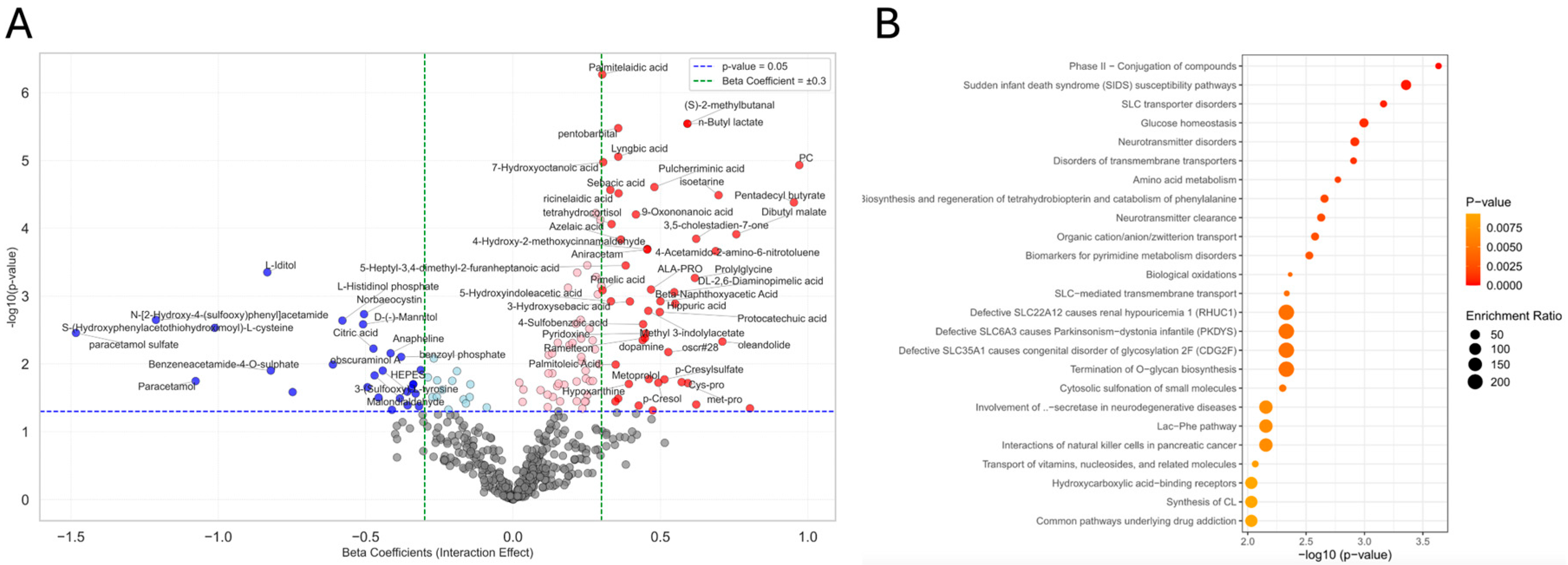
3.6. ANCOVA and Metabolite Associations with Interaction Effect
3.7. ANCOVA and Lipid Associations with Disease Effect, Exposure Effect, and Interaction Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| ANCOVA | Analysis of Covariance |
| CB1 | Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 |
| CDG2F | Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation Type 2F |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CLIA | Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FIU | Florida International University |
| GABA | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| HMDB | Human Metabolome Database |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| LIPEA | Lipid Pathway Enrichment Analysis |
| LPC | Lysophosphatidylcholine |
| MAC | Maximum Acceptable Concentration |
| Mn | Manganese |
| MnIP | Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MRL | Minimum Reporting Level |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| MSEA | Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis |
| η2p | Partial Eta Squared |
| NMDAR | N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor |
| OPA | Overrepresentation Pathway Analysis |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PD | Parkinsonism |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| QC | Quality Control |
| RaMP-DB | Relational and Pathway Database |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| S1P | Sphingosine-1-Phosphate |
| SLC | Solute Carrier |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| SMR | Standardized Morbidity Ratio |
| SP | Sphingolipid |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic Acid |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TLA | Three Letter Acronym |
| UCMR | Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule |
| UHPLC | Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| VIP | Variable Importance in Projection |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Abdelzaher, H.; Tawfik, S.M.; Nour, A.; Abdelkader, S.; Elbalkiny, S.T.; Abdelkader, M.; Abbas, W.A.; Abdelnaser, A. Climate change, human health, and the exposome: Utilizing OMIC technologies to navigate an era of uncertainty. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 973000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Yao, F.; Li, X.; Shi, C.; Zang, X.; Shu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W. Manganese Pollution and Its Remediation: A Review of Biological Removal and Promising Combination Strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. The Fourth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR 4): Data Summary; Office of Water (MS-140): Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- GOC. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document—Manganese. Water and Air Quality Bureau, Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch, Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, H.; Marushka, L.; Chan, H.M.; Batal, M.; Sadik, T.; Ing, A.; Fediuk, K.; Tikhonov, C. Metals in the drinking water of First Nations across Canada. Can. J. Public Health 2021, 112 (Suppl. S1), 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, H.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Gao, C.; Chen, T.; Feng, G.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Building Better Full Manganese-Based Cathode Materials for Next-Generation Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2023, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ryberg, M.; Yang, Y.; Feng, K.; Kara, S.; Hauschild, M.; Chen, W.-Q. Efficiency stagnation in global steel production urges joint supply- and demand-side mitigation efforts. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Dai, Q.; Gaines, L.; Hu, M.; Tukker, A.; Steubing, B. Future material demand for automotive lithium-based batteries. Commun. Mater. 2020, 1, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Villahoz, B.F.; Ponzio, R.D.; Aschner, M.; Chen, P. Signaling Pathways Involved in Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity. Cells 2023, 12, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulshreshtha, D.; Ganguly, J.; Jog, M. Manganese and Movement Disorders: A Review. J. Mov. Disord. 2021, 14, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajarillo, E.; Nyarko-Danquah, I.; Digman, A.; Multani, H.K.; Kim, S.; Gaspard, P.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. Mechanisms of manganese-induced neurotoxicity and the pursuit of neurotherapeutic strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1011947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissani, N.; Naji, Y.; Mebrouk, Y.; Chraa, M.; Ghanima, A. Parkinsonism and chronic manganese exposure: Pilot study with clinical, environmental and experimental evidence. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 3, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Albini, E.; Benedetti, L.; Borghesi, S.; Coccaglio, R.; Malara, E.C.; Parrinello, G.; Garattini, S.; Resola, S.; Alessio, L. High prevalence of Parkinsonian disorders associated to manganese exposure in the vicinities of ferroalloy industries. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2007, 50, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racette, B.A.; Nelson, G.; Dlamini, W.W.; Prathibha, P.; Turner, J.R.; Ushe, M.; Checkoway, H.; Sheppard, L.; Nielsen, S.S. Severity of parkinsonism associated with environmental manganese exposure. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, R.; Tieu, K. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism: Evidence from Epidemiological and Experimental Studies. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Aschner, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Cranmer, J.M. Neurotoxicity of manganese: Indications for future research and public health intervention from the Manganese 2016 conference. NeuroToxicology 2018, 64, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criswell, S.R.; Nielsen, S.S.; Warden, M.N.; Flores, H.P.; Lenox-Krug, J.; Racette, S.; Sheppard, L.; Checkoway, H.; Racette, B.A. MRI Signal Intensity and Parkinsonism in Manganese-Exposed Workers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 61, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Covarrubias, V.; Martínez-Martínez, E.; Del Bosque-Plata, L. The Potential of Metabolomics in Biomedical Applications. Metabolites 2022, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.G.; Lin, Y.S.; Simpson, C.D.; Shireman, L.M.; Searles Nielsen, S.; Racette, B.A.; Seixas, N. The reproducibility of urinary ions in manganese exposed workers. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 51, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, K.A.; Simpson, C.D.; Raftery, D.; Baker, M.G. Short Report: Using Targeted Urine Metabolomics to Distinguish Between Manganese Exposed and Unexposed Workers in a Small Occupational Cohort. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 666787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.D.; Duvallet, C.; Chu, N.D.; Oberst, M.K.; Murphy, M.A.; Rockafellow, I.; Sontag, D.; Alm, E.J. Predicting human health from biofluid-based metabolomics using machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, A. Small molecule metabolites: Discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Guazzetti, S.; Renzetti, S.; Broberg, K.; Caci, M.; Covolo, L.; Crippa, P.; Gelatti, U.; Hashim, D.; Oppini, M.; et al. Metal Exposure and SNCA rs356219 Polymorphism Associated With Parkinson Disease and Parkinsonism. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 556337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peli, M.; Bostick, B.C.; Barontini, S.; Lucchini, R.G.; Ranzi, R. Profiles and species of Mn, Fe and trace metals in soils near a ferromanganese plant in Bagnolo Mella (Brescia, IT). Sci. Total Env. 2021, 755 Pt 2, 143123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.R.; Litvan, I. Parkinsonian syndromes. Continuum 2013, 19, 1189–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.-P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvan, I.; Agid, Y.; Calne, D.; Campbell, G.; Dubois, B.; Duvoisin, R.C.; Goetz, C.G.; Golbe, L.I.; Grafman, J.; Growdon, J.H.; et al. Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome). Neurology 1996, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; Bak, T.H.; Bhatia, K.P.; Borroni, B.; Boxer, A.L.; Dickson, D.W.; Grossman, M.; Hallett, M.; et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration. Neurology 2013, 80, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, S.; Wenning, G.K.; Low, P.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Mathias, C.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Wood, N.W.; Colosimo, C.; Dürr, A.; Fowler, C.J.; et al. Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Neurology 2008, 71, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.M.; Romero, A.S.; Merkley, S.D.; Meyer-Hagen, J.L.; Forbes, C.; Hayek, E.E.; Sciezka, D.P.; Templeton, R.; Gonzalez-Estrella, J.; Jin, Y.; et al. In Vivo Tissue Distribution of Polystyrene or Mixed Polymer Microspheres and Metabolomic Analysis after Oral Exposure in Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2024, 132, 47005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chi, J.; LoMonaco, K.; Boon, A.; Gu, H. Recent Review on Selected Xenobiotics and Their Impacts on Gut Microbiome and Metabolome. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Li, H.; Jin, Y.; Armad, J.; Gu, H.; Mani, S.; Cui, J.Y. Maternal PBDE exposure disrupts gut microbiome and promotes hepatic proinflammatory signaling in humanized PXR-transgenic mouse offspring over time. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 194, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.E.; Sweazea, K.L.; Bowes, D.A.; Jasbi, P.; Whisner, C.M.; Sears, D.D.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Jin, Y.; Gu, H.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; et al. Gut microbiome remodeling and metabolomic profile improves in response to protein pacing with intermittent fasting versus continuous caloric restriction. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scieszka, D.P.; Garland, D.; Hunter, R.; Herbert, G.; Lucas, S.; Jin, Y.; Gu, H.; Campen, M.J.; Cannon, J.L. Multi-omic assessment shows dysregulation of pulmonary and systemic immunity to e-cigarette exposure. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying Small Molecules via High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Communicating Confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieder, C.; Frainay, C.; Poupin, N.; Rodríguez-Mier, P.; Vinson, F.; Cooke, J.; Lai, R.P.; Bundy, J.G.; Jourdan, F.; Ebbels, T. Pathway analysis in metabolomics: Recommendations for the use of over-representation analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, W.N.; Rose, F.A. Dopamine 3-O-sulphate, an end product of L-dopa metabolism in Parkinson patients. Nature 1974, 252, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leta, V.; Urso, D.; Batzu, L.; Lau, Y.H.; Mathew, D.; Boura, I.; Raeder, V.; Falup-Pecurariu, C.; Van Wamelen, D.; Ray Chaudhuri, K. Viruses, parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease: The past, present and future. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peechakara, B.V.; Gupta, M. Ampicillin/Sulbactam. In StatPearls; StatPearls PublishingCopyright © 2024; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, M.; Romero, M.-P.; Macia, A.; Valls, R.-M.; Fernández-Castillejo, S.; Solà, R.; Motilva, M.-J. Improved method for identifying and quantifying olive oil phenolic compounds and their metabolites in human plasma by microelution solid-phase extraction plate and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 4097–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewitt, P.A. Norepinephrine: The next therapeutics frontier for Parkinson's disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2012, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, A.; Santoro, C.; Poplawska-Domaszewicz, K.; Qamar, M.A.; Batzu, L.; Landolfo, S.; Rota, S.; Falup-Pecurariu, C.; Murasan, I.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Parkinson's disease and vitamins: A focus on vitamin B12. J. Neural Transm. 2024, 131, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, Y.; Erkut, C.; Pan-Montojo, F.; Boland, S.; Stewart, M.P.; Müller, D.J.; Wurst, W.; Hyman, A.A.; Kurzchalia, T.V. Products of the Parkinson's disease-related glyoxalase DJ-1, D-lactate and glycolate, support mitochondrial membrane potential and neuronal survival. Biol. Open 2014, 3, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Villa, C.; Piperi, C. Arylsulfatase A (ASA) in Parkinson’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Biomarker Potential. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figura, M.; Kuśmierska, K.; Bucior, E.; Szlufik, S.; Koziorowski, D.; Jamrozik, Z.; Janik, P. Serum amino acid profile in patients with Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem Compound Summary for CID 25010768, Tetrahomomethionine. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Tetrahomomethionine (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5282136, Lafutidine. 2025. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lafutidine (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Patel, P.; Patel, R.; Thorell, W. Mannitol; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.; Guo, Y.; Pang, M.; Huang, L.; Wang, T. Toxic and essential metals: Metabolic interactions with the gut microbiota and health implications. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1448388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, J.D.; Thongngam, M.; Kumrungsee, T. Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a potential postbiotic mediator in the gut–brain axis. Npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatha, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.; Kim, K. Association between Heavy Metal Exposure and Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of the Mechanisms Related to Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Meng, Z.; Chen, L. The SLC transporter in nutrient and metabolic sensing, regulation, and drug development. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Yaqoob, A.; Rehman, K.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A.; Al-Rashed, F.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R.; Sindhu, S. Metabolomics: A promising tool for deciphering metabolic impairment in heavy metal toxicities. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1218497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson AB, S.N. Pentobarbital. In StatPearls, 2025 Jan-ed.; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Butyl Lactate. Available online: https://www.hfpappexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=FoodSubstances&id=BUTYLLACTATE (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Administration, U.S.F.a.D. 2-Methylbutyraldehyde. Available online: https://www.hfpappexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=FoodSubstances&id=METHYLBUTYRALDEHYDE2# (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Shah, A.; Han, P.; Wong, M.-Y.; Chang, R.C.-C.; Legido-Quigley, C. Palmitate and Stearate are Increased in the Plasma in a 6-OHDA Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Metabolites 2019, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.M.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Boxall, J.A.; Balazs, N.D. Platelet trans fatty acids in relation to angiographically assessed coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 1996, 120, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, K.M.; Spiro, A., 3rd; Tucker, K.; Rush, D. Relations of vitamin B-12, vitamin B-6, folate, and homocysteine to cognitive performance in the Normative Aging Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pozo, V.A.; Tamayo-Trujillo, R.; Cadena-Ullauri, S.; Frias-Toral, E.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Paz-Cruz, E.; Chapela, S.; Montalván, M.; Morales-López, T.; Simancas-Racines, D.; et al. The Molecular Mechanisms of the Relationship between Insulin Resistance and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, S.; Karadimou, A.; Mulvihill, J.J.E.; Grabrucker, A.M.; Zabetakis, I. The Role of Dietary Lipids in Cognitive Health: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lope, E.G.; Loo, R.T.J.; Rauschenberger, A.; Ali, M.; Pavelka, L.; Marques, T.M.; Gomes, C.P.C.; Krüger, R.; Glaab, E. Comprehensive blood metabolomics profiling of Parkinson’s disease reveals coordinated alterations in xanthine metabolism. NPJ Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.A.; Siddique, M.M.; Wang, S.T.; Ching, J.; Shayman, J.A.; Summers, S.A. Ceramides and Glucosylceramides Are Independent Antagonists of Insulin Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidan, Y.H.; Hannun, Y.A. Translational aspects of sphingolipid metabolism. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, S.; Orsó, E.; Grandl, M.; Konovalova, T.; Liebisch, G.; Schmitz, G. Phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogens in lipid loaded human macrophages. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pralhada Rao, R.; Vaidyanathan, N.; Rengasamy, M.; Mammen Oommen, A.; Somaiya, N.; Jagannath, M.R. Sphingolipid Metabolic Pathway: An Overview of Major Roles Played in Human Diseases. J. Lipids 2013, 2013, 178910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Deng, P.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Mei, X.; Zhou, C.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Z.; Pi, H.; Wu, L.; et al. Manganese overexposure induces Parkinson-like symptoms, altered lipid signature and oxidative stress in C57BL/6 J mouse. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. A systematic review and meta-analysis of serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| N (%) or Mean (SD) | Parkinsonism (PD) Vs. Controls p-Valuea | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristiss | Parkinsonism (PD) | Controls | |||
| Exposed | Non-Exposed | Exposed | Non-Exposed | ||
| Sample Size (n=) | 23 | 26 | 25 | 23 | |
| Age (years) | 70.4 (10.8) | 66.4 (9.6) | 70.6 (12.3) | 72.4 (7.3) | p = 0.11 |
| Sex | p = 0.15 | ||||
| Male | 13 (56.5%) | 21 (80.7%) | 12 (48%) | 13 (56.5%) | |
| Female | 10 (43.4%) | 5 (19.2%) | 13 (52%) | 10 (43.4%) | |
| Coffee Consumption | p = 1.0 | ||||
| Yes | 21 (91.3%) | 25 (96.1%) | 23 (92%) | 23 (100%) | |
| No | 2 (8.6%) | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (8%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Alcohol Consumption | p = 0.40 | ||||
| Yes | 14 (60.8%) | 19 (73%) | 14 (56%) | 13 (56.5%) | |
| No | 9 (39.1%) | 7 (26.9%) | 11 (44%) | 10 (43.4%) | |
| Smoking Status | p = 0.16 | ||||
| Yes | 10 (43.4%) | 18 (69.2%) | 10 (40%) | 9 (39.1%) | |
| No | 13 (56.5%) | 8 (30.7%) | 15 (60%) | 14 (60.8%) | |
| Diabetes | p = 1.0 | ||||
| Yes | 3 (13.0%) | 6 (23.1%) | 1 (4.0%) | 7 (30.4%) | |
| No | 20 (87.0%) | 20 (76.9%) | 24 (96.0%) | 16 (69.6%) | |
| Stroke | p = 0.49 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (3.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| No | 22 (95.7%) | 25 (96.2%) | 25 (100.0%) | 23 (100.0%) | |
| Hypertension | p = 0.75 | ||||
| Yes | 13 (56.5%) | 14 (53.8%) | 13 (52.0%) | 16 (69.6%) | |
| No | 10 (43.5%) | 12 (46.2%) | 12 (48.0%) | 7 (30.4%) | |
| Leukemia | p = 0.49 | ||||
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (4.3%) | |
| No | 23 (100.0%) | 26 (100.0%) | 25 (100.0%) | 22 (95.7%) | |
| Heart Disease | p = 0.35 | ||||
| Yes | 8 (34.8%) | 5 (19.2%) | 8 (32.0%) | 10 (43.5%) | |
| No | 15 (65.2%) | 21 (80.8%) | 17 (68.0%) | 13 (56.5%) | |
| Liver Disease | p = 0.27 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (3.8%) | 5 (20.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| No | 22 (95.7%) | 25 (96.2%) | 20 (80.0%) | 23 (100.0%) | |
| Kidney Disease | p = 0.62 | ||||
| Yes | 2 (8.7%) | 1 (3.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (4.3%) | |
| No | 21 (91.3%) | 25 (96.2%) | 25 (100.0%) | 22 (95.7%) | |
| Thyroid Disease | p = 0.68 | ||||
| Yes | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (3.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (13.0%) | |
| No | 22 (95.7%) | 25 (96.2%) | 25 (100.0%) | 20 (87.0%) | |
| Geographical Site | |||||
| Bagnolo Mella | 2 (8.6%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Garda Lake | 0 (0%) | 15 (57.6%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (21.7%) | |
| Val Camonica | 21 (91.3%) | 0 (0%) | 24 (96%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Brescia City | 0 (0%) | 11 (42.3%) | 0 (0%) | 18 (78.2%) | |
| Group | N | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Min | Max | Parkinsonism (PD) Vs. Controls p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinsonism (PD) | 32 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 1.55 | 0.75 | 0.6 | 3.5 | 0.001 |
| Control | 46 | 1.12 | 0.46 | 1.02 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 2.77 |
| Variable | β Coefficient | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Blood Mn (µg/dL) | 0.88 | 2.42 | 1.13–5.17 | 0.022 |
| Omic | Disease Effect | Exposure Effect | Interaction Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolomics | 3-sulfoxy-L-tyrosineosine | glycocholic acid | palmitelaidic acid |
| formiminoglutamic acid | butanoate | vitamin B6 metabolism | |
| glyoxylic acid | glutamate | glucose homeostasis | |
| amino acid metabolism | alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism | amino acid metabolism | |
| citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | butanoate metabolism | SLC transporters disorders | |
| SLC-mediated transmembrane transport | |||
| Lipidomics | triacylglycerols | ceramides | phosphatidylethanolamines |
| ferroptosis | ferroptosis | ||
| endocannabinoid signaling | endocannabinoid signaling | ||
| sphingolipid metabolism and signaling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewis, F.; Shoieb, D.; Azmoun, S.; Colicino, E.; Jin, Y.; Chi, J.; Krishnamurthy, H.; Placidi, D.; Padovani, A.; Pilotto, A.; et al. Exploratory Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling in a Manganese-Exposed Parkinsonism-Affected Population in Northern Italy. Metabolites 2025, 15, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070487
Lewis F, Shoieb D, Azmoun S, Colicino E, Jin Y, Chi J, Krishnamurthy H, Placidi D, Padovani A, Pilotto A, et al. Exploratory Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling in a Manganese-Exposed Parkinsonism-Affected Population in Northern Italy. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070487
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewis, Freeman, Daniel Shoieb, Somaiyeh Azmoun, Elena Colicino, Yan Jin, Jinhua Chi, Hari Krishnamurthy, Donatella Placidi, Alessandro Padovani, Andrea Pilotto, and et al. 2025. "Exploratory Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling in a Manganese-Exposed Parkinsonism-Affected Population in Northern Italy" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070487
APA StyleLewis, F., Shoieb, D., Azmoun, S., Colicino, E., Jin, Y., Chi, J., Krishnamurthy, H., Placidi, D., Padovani, A., Pilotto, A., Pepe, F., Tula, M., Crippa, P., Wang, X., Gu, H., & Lucchini, R. (2025). Exploratory Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiling in a Manganese-Exposed Parkinsonism-Affected Population in Northern Italy. Metabolites, 15(7), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070487









