Reduction of Dietary Fat Rescues High-Fat Diet-Induced Depressive Phenotypes and the Associated Hippocampal Astrocytic Deficits in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Feeding Regimens
2.2. Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test
2.3. Intraperitoneal Insulin Tolerance Test
2.4. Measuring Fasting Plasma Levels of Glucose and Insulin
2.5. Sucrose Preference Test
2.6. Forced Swimming Test
2.7. Tail Suspension Test
2.8. Measurement of Plasma Lipid Concentrations
2.9. Tissue Preparations
2.10. Immunoblotting
2.11. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.12. Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Analysis of Astrocytic Morphology
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
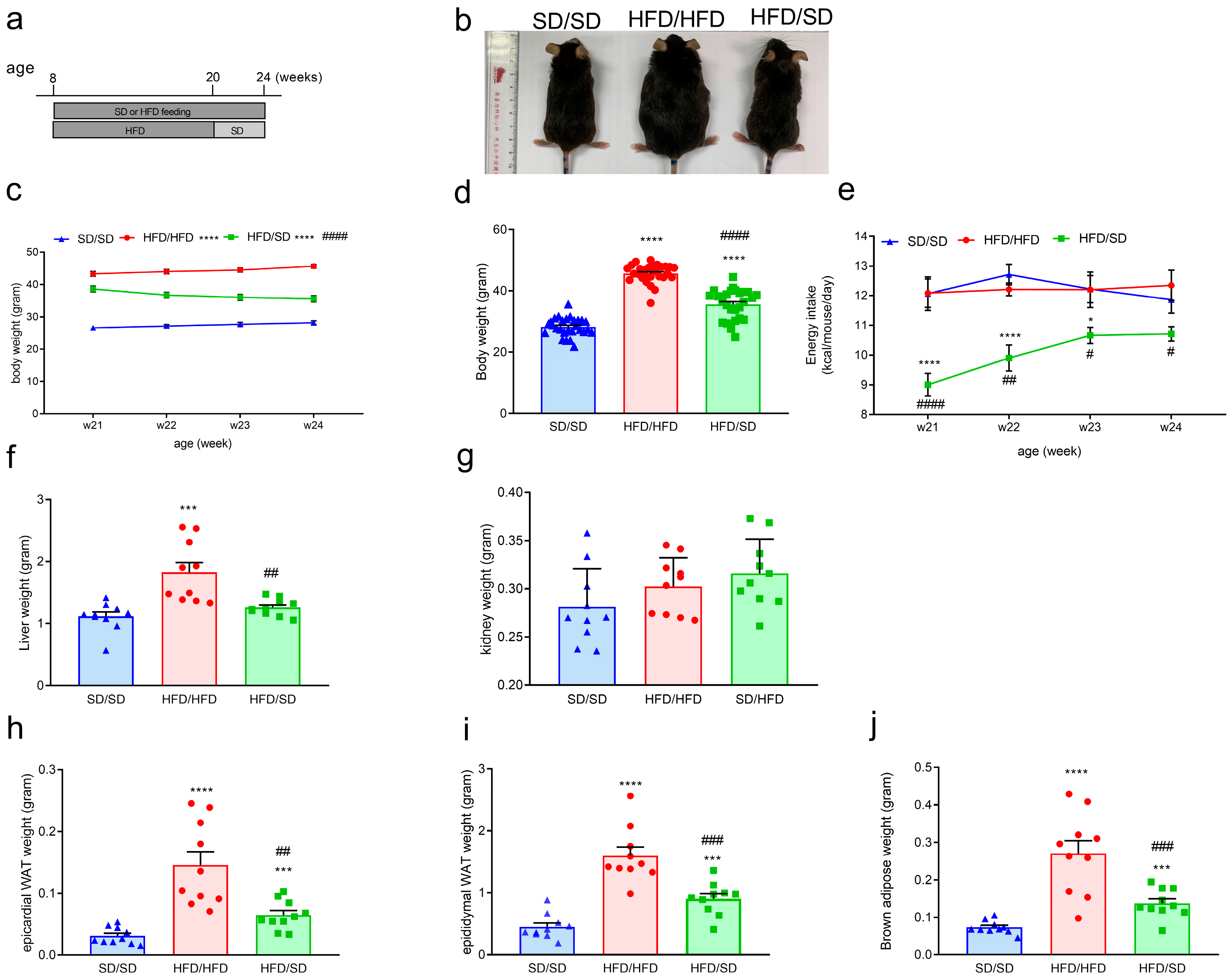
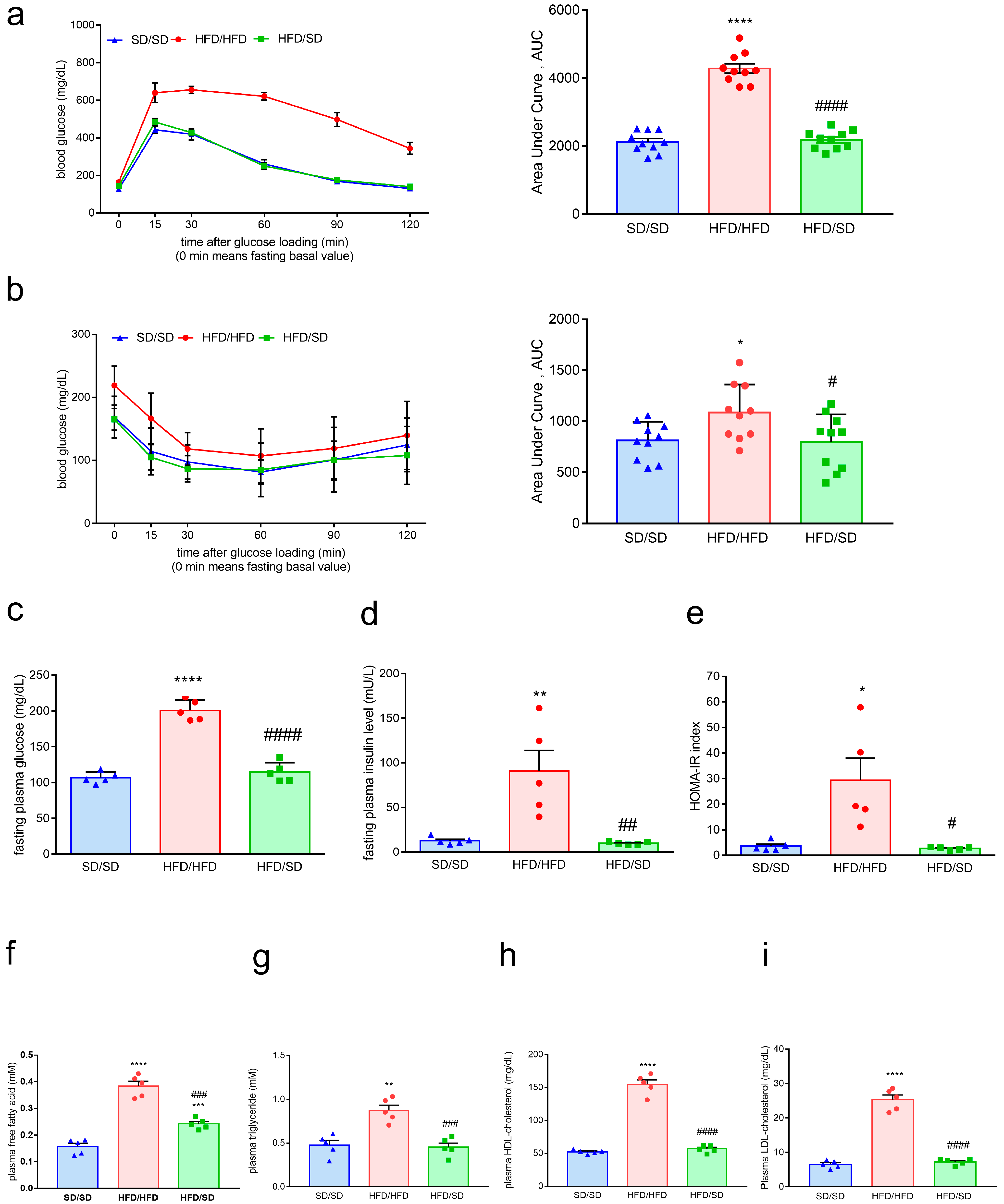
3.1. A 12-Week High-Fat Diet (HFD) Feeding Induces Obesity, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Depression-like Behaviors in Mice
3.2. Reduction of Dietary Fat Ameliorates HFD-Induced Obesity, Systemic Insulin Resistance, and Hyperlipidemia in Mice
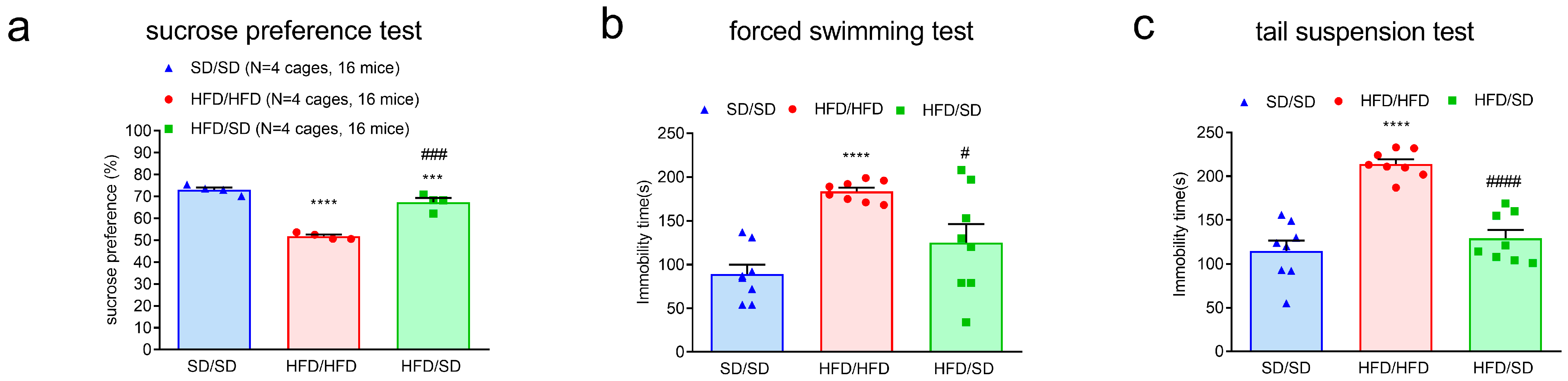
3.3. Reduction of Dietary Fat Improves HFD-Induced Depressive Phenotypes in Mice
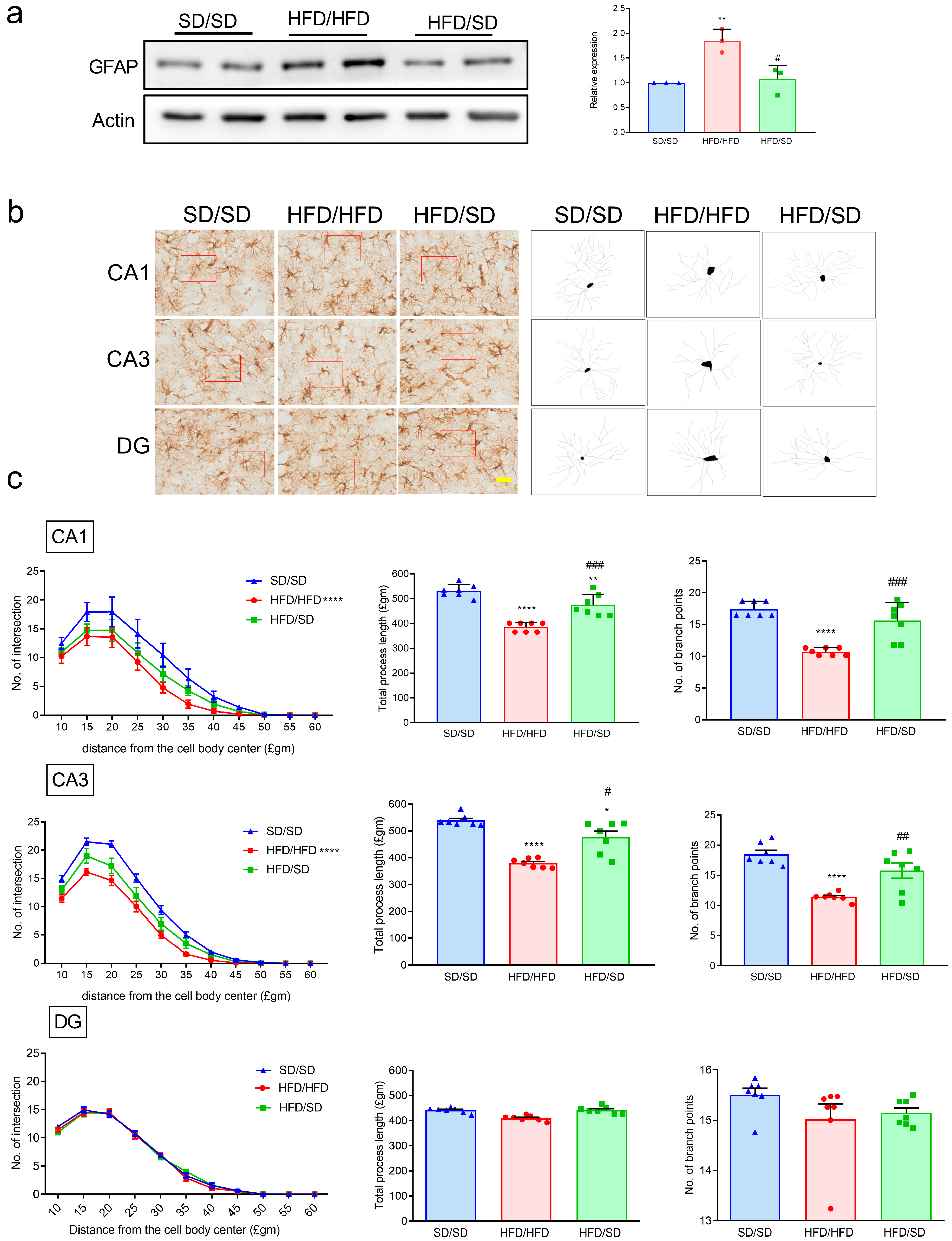
3.4. Reduction of Dietary Fat Attenuates the HFD-Induced Astrocyte Activation and Astrocytic Morphology Remodeling in the Hippocampi of Mice
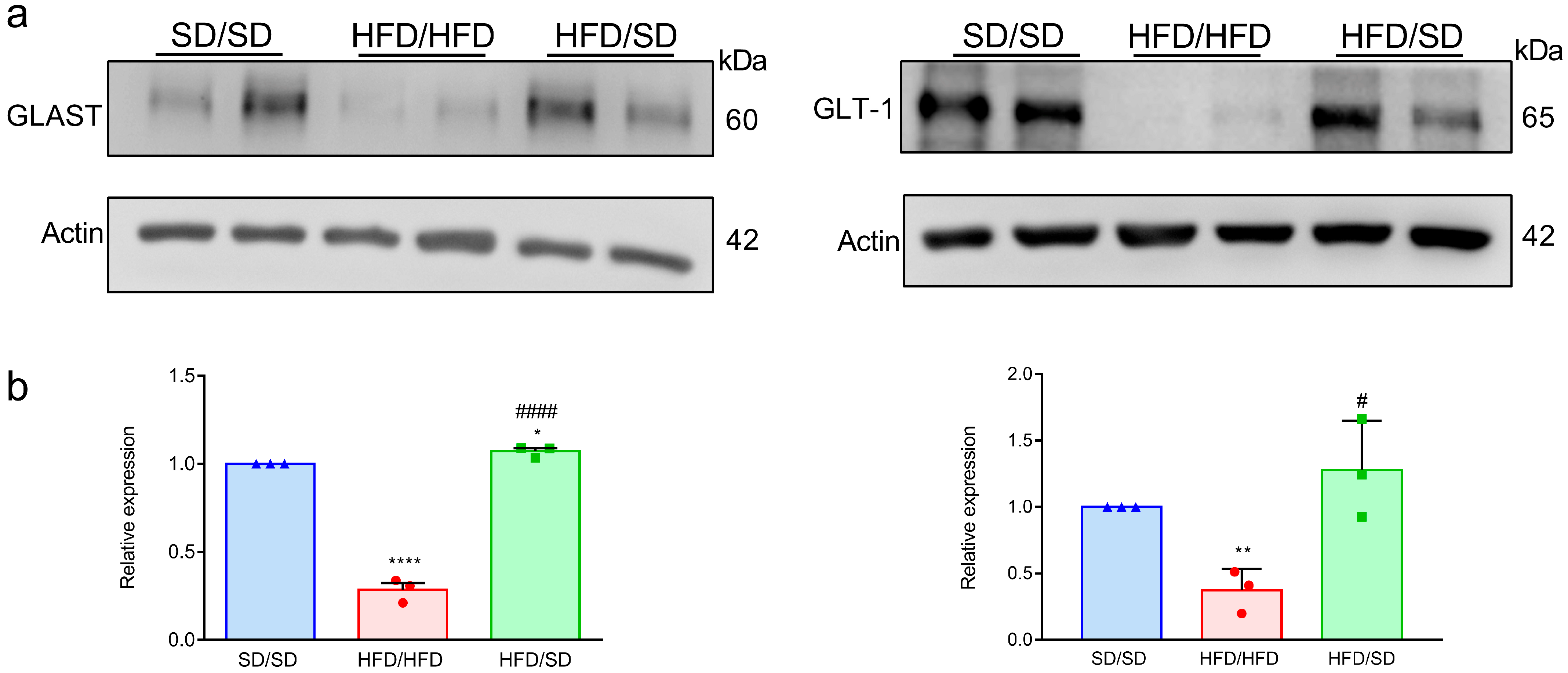
3.5. Reduction of Dietary Fat Reverses the HFD-Downregulated Astrocytic Neuroplasticity-Related Proteins in the Hippocampi of Mice
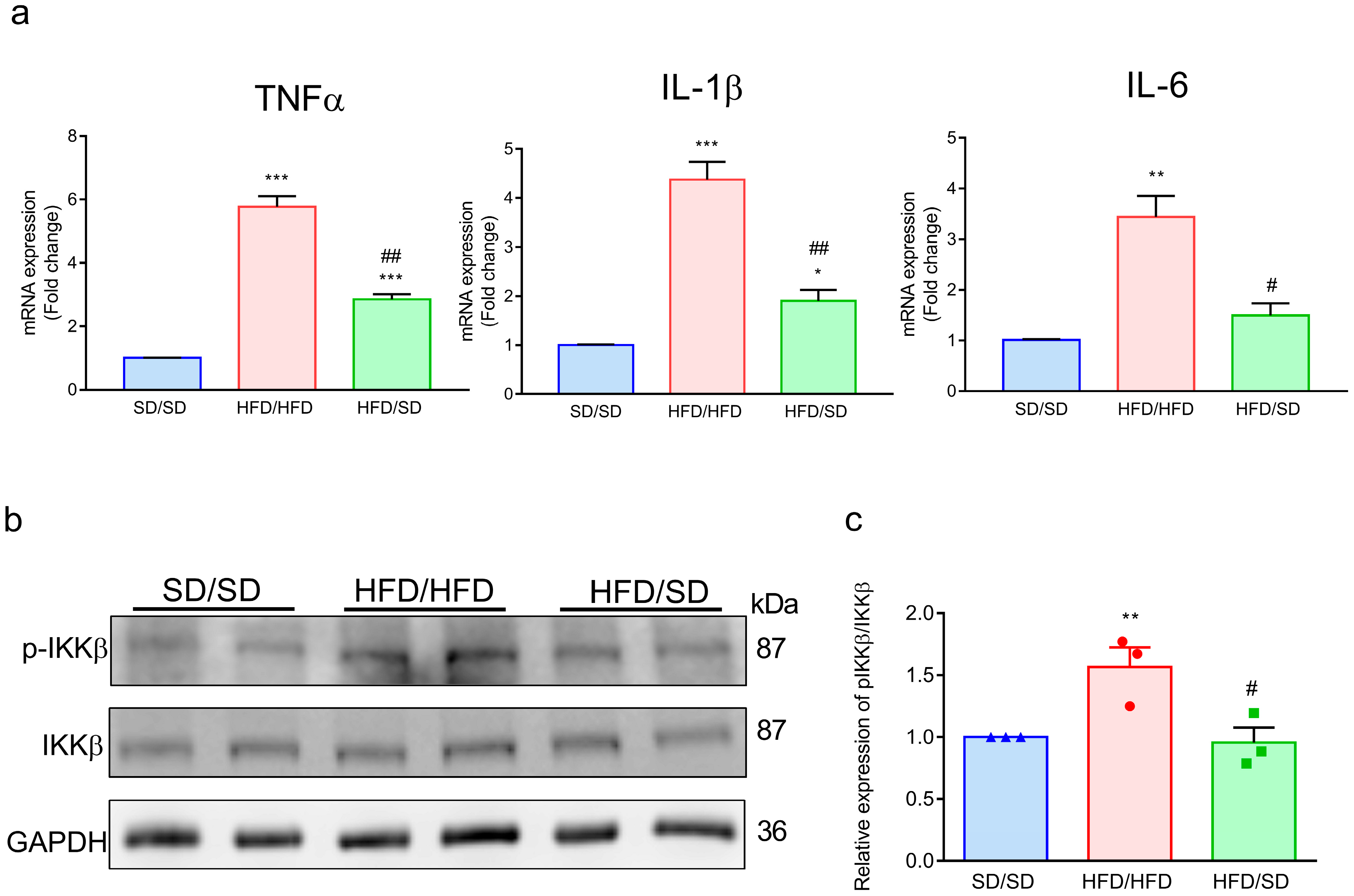
3.6. Reduction of Dietary Fat Abolishes the HFD-Induced Inflammatory Factors in the Ventral Hippocampus of Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaborators GBDO; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Wadden, T.A. Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Management of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasin, D.S.; Sarvet, A.L.; Meyers, J.L.; Saha, T.D.; Ruan, W.J.; Stohl, M.; Grant, B.F. Epidemiology of Adult DSM-5 Major Depressive Disorder and Its Specifiers in the United States. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, L.A.; Brody, D.J. Depression and obesity in the U.S. adult household population, 2005–2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2014, 167, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Simmons, W.K.; van Rossum, E.F.C.; Penninx, B.W. Depression and obesity: Evidence of shared biological mechanisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppino, F.S.; de Wit, L.M.; Bouvy, P.F.; Stijnen, T.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W.; Zitman, F.G. Overweight, obesity, and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, M.; Hakansson-Ovesjo, M.L.; Misane, I.; Ogren, S.O.; Meister, B. Decreased 5-HT transporter mRNA in neurons of the dorsal raphe nucleus and behavioral depression in the obese leptin-deficient ob/ob mouse. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 81, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Tsai, S.F.; Chen, P.C.; Kuo, Y.M.; Chen, Y.W. Pioglitazone rescues high-fat diet-induced depression-like phenotypes and hippocampal astrocytic deficits in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.F.; Wu, H.T.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Yu, M.; Wang, T.F.; Wu, S.Y.; Tzeng, S.F.; Kuo, Y.M. High-fat diet suppresses the astrocytic process arborization and downregulates the glial glutamate transporters in the hippocampus of mice. Brain Res. 2018, 1700, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkowska, G.; Stockmeier, C.A. Astrocyte pathology in major depressive disorder: Insights from human postmortem brain tissue. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, J.A.; O’Neill, K.; Milner, J.; Mahajan, G.J.; Lawrence, T.J.; May, W.L.; Miguel-Hidalgo, J.; Rajkowska, G.; Stockmeier, C.A. Density of GFAP-immunoreactive astrocytes is decreased in left hippocampi in major depressive disorder. Neuroscience 2016, 316, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banasr, M.; Duman, R.S. Glial loss in the prefrontal cortex is sufficient to induce depressive-like behaviors. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, C.T.; Araujo, E.P.; Bordin, S.; Ashimine, R.; Zollner, R.L.; Boschero, A.C.; Saad, A.C.B.; Velloso, L.A. Consumption of a fat-rich diet activates a proinflammatory response and induces insulin resistance in the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 4192–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, T.W.; Mletzko, T.C.; Alagbe, O.; Musselman, D.L.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Miller Heim, C.M. Increased stress-induced inflammatory responses in male patients with major depression and increased early life stress. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.T.; Li, H.J.; Zhou, T.F.; Zhou, A.C.; Zhong, Z.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Yuan, L.L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Luan, D.; et al. Antidepressant-like effects of helicid on a chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression rat model: Inhibiting the IKK/IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB pathway through NCALD to reduce inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 93, 107165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.T.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, P.S.; Chiu, W.T.; Kuo, Y.M.; Tzeng, S.F. Inhibitory Effects of Trifluoperazine on Peripheral Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression and Hypothalamic Microglia Activation in Obese Mice Induced by Chronic Feeding With High-Fat-Diet. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 752771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.T.; Tsai, S.F.; Wu, H.T.; Huang, H.Y.; Hsieh, H.H.; Kuo, Y.M.; Chen, P.S.; Yang, C.S.; Tzeng, S.F. Chronic exposure to high fat diet triggers myelin disruption and interleukin-33 upregulation in hypothalamus. BMC Neurosci. 2019, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Bayghen, E.; Ortega, A. Glial glutamate transporters: New actors in brain signaling. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, A.; Burke, S.; Thompson, R.C.; Bunney, W.; Myers, R.M., Jr.; Schatzberg, A.; Akil, H.; Watson, S.J. Glutamate transporters: A key piece in the glutamate puzzle of major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, A.; Prevot, V. When Size Matters: How Astrocytic Processes Shape Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 995–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Chen, L.; Ouyang, L.; Gu, L.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q. Hippocampal astrocyte atrophy in a mouse depression model induced by corticosterone is reversed by fluoxetine instead of benzodiazepine diazepam. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklas, B.J.; Ambrosius, W.; Messier, S.P.; Miller, G.D.; Penninx, B.W.; Loeser, R.F.; Palla, S.; Bleecker, E.; Pahor, M. Diet-induced weight loss, exercise, and chronic inflammation in older, obese adults: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, M.S.; Matz, P.E.; Jorge, M.A. Obesity-depression associations in the population. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 53, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hryhorczuk, C.; Sharma, S.; Fulton, S.E. Metabolic disturbances connecting obesity and depression. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wang, H. Cytokines mediated inflammation and decreased neurogenesis in animal models of depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raison, C.L.; Capuron, L.; Miller, A.H. Cytokines sing the blues: Inflammation and the pathogenesis of depression. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosari-Nasab, M.; Shokouhi, G.; Ghorbanihaghjo, A.; Abbasi, M.M.; Salari, A.A. Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of Silymarin compared to diazepam and fluoxetine in a mouse model of mild traumatic brain injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 338, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Reichel, J.M.; Han, C.; Zuniga-Hertz, J.P.; Cai, D. Astrocytic Process Plasticity and IKKbeta/NF-kappaB in Central Control of Blood Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Body Weight. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1091–1102.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folie, S.; Radlinger, B.; Goebel, G.; Salzmann, K.; Staudacher, G.; Ress, C.; Tilg, H.; Kaser, S. Changing the dietary composition improves inflammation but not adipocyte thermogenesis in diet-induced obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 99, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemot-Legris, O.; Masquelier, J.; Everard, A.; Cani, P.D.; Alhouayek, M.; Muccioli, G.G. High-fat diet feeding differentially affects the development of inflammation in the central nervous system. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gzielo, K.; Kielbinski, M.; Ploszaj, J.; Janeczko, K.; Gazdzinski, S.P.; Setkowicz, Z. Long-Term Consumption of High-Fat Diet in Rats: Effects on Microglial and Astrocytic Morphology and Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 83–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, V.; Valladolid-Acebes, I.; Hernandez-Nuno, F.; Merino, B.; Del Olmo, N.; Chowen, J.A.; Ruiz-Gayo, M. Morphological changes in glial fibrillary acidic protein immunopositive astrocytes in the hippocampus of dietary-induced obese mice. Neuroreport 2014, 25, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keaton, S.A.; Madaj, Z.B.; Heilman, P.; Smart, L.; Grit, J.; Gibbons, R.; Postolache, T.T.; Roaten, K.; Achtyes, E.D.; Brundin, L. An inflammatory profile linked to increased suicide risk. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 247, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, H.; Davies, A.M. Regulation of neural process growth, elaboration and structural plasticity by NF-kappaB. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviedes, A.; Lafourcade, C.; Soto, C.; Wyneken, U. BDNF/NF-kappaB Signaling in the Neurobiology of Depression. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3154–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linde, J.A.; Simon, G.E.; Ludman, E.J.; Ichikawa, L.E.; Operskalski, B.H.; Arterburn, D.; Rohde, P.; Finch, E.A.; Jeffery, R.W. A randomized controlled trial of behavioral weight loss treatment versus combined weight loss/depression treatment among women with comorbid obesity and depression. Ann. Behav. Med. 2011, 41, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, K.-P.; Chao, H.-H.; Hsu, C.-J.; Tsai, S.-F.; Chiu, Y.-J.; Kuo, Y.-M.; Chen, Y.-W. Reduction of Dietary Fat Rescues High-Fat Diet-Induced Depressive Phenotypes and the Associated Hippocampal Astrocytic Deficits in Mice. Metabolites 2025, 15, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070485
Cheng K-P, Chao H-H, Hsu C-J, Tsai S-F, Chiu Y-J, Kuo Y-M, Chen Y-W. Reduction of Dietary Fat Rescues High-Fat Diet-Induced Depressive Phenotypes and the Associated Hippocampal Astrocytic Deficits in Mice. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070485
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Kai-Pi, Hsin-Hao Chao, Chin-Ju Hsu, Sheng-Feng Tsai, Yen-Ju Chiu, Yu-Min Kuo, and Yun-Wen Chen. 2025. "Reduction of Dietary Fat Rescues High-Fat Diet-Induced Depressive Phenotypes and the Associated Hippocampal Astrocytic Deficits in Mice" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070485
APA StyleCheng, K.-P., Chao, H.-H., Hsu, C.-J., Tsai, S.-F., Chiu, Y.-J., Kuo, Y.-M., & Chen, Y.-W. (2025). Reduction of Dietary Fat Rescues High-Fat Diet-Induced Depressive Phenotypes and the Associated Hippocampal Astrocytic Deficits in Mice. Metabolites, 15(7), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070485





