High-Coverage Profiling of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Using Bromine Isotope Labeling and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Stock Solutions and Calibrators
2.3. Sampling and Sample Preparation
2.4. Establishment of Quantitative Structure–Retention Relationship (QSRR) Model
2.5. UPLC-HRMS Analysis
2.6. Performance Evaluation of the Method
2.7. Data Processing
2.8. Strategy for Screening and Annotating Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
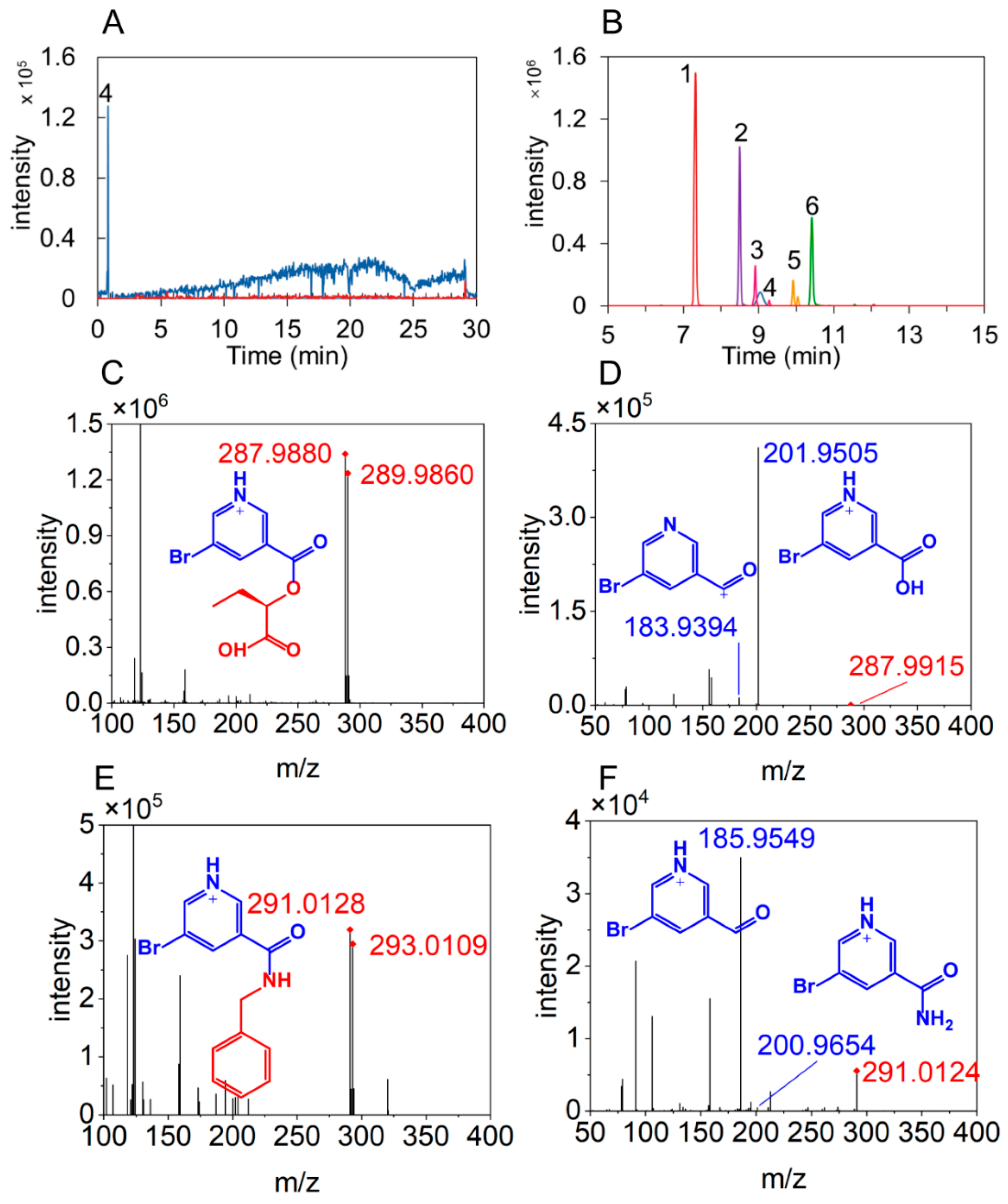
3.1. Characteristics of LC and MS of BrNC-Labeled Compounds
3.2. Optimization of Sample Preparation Conditions
3.3. Prediction of Retention Times
3.4. Method Validation
3.5. Annotation of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu
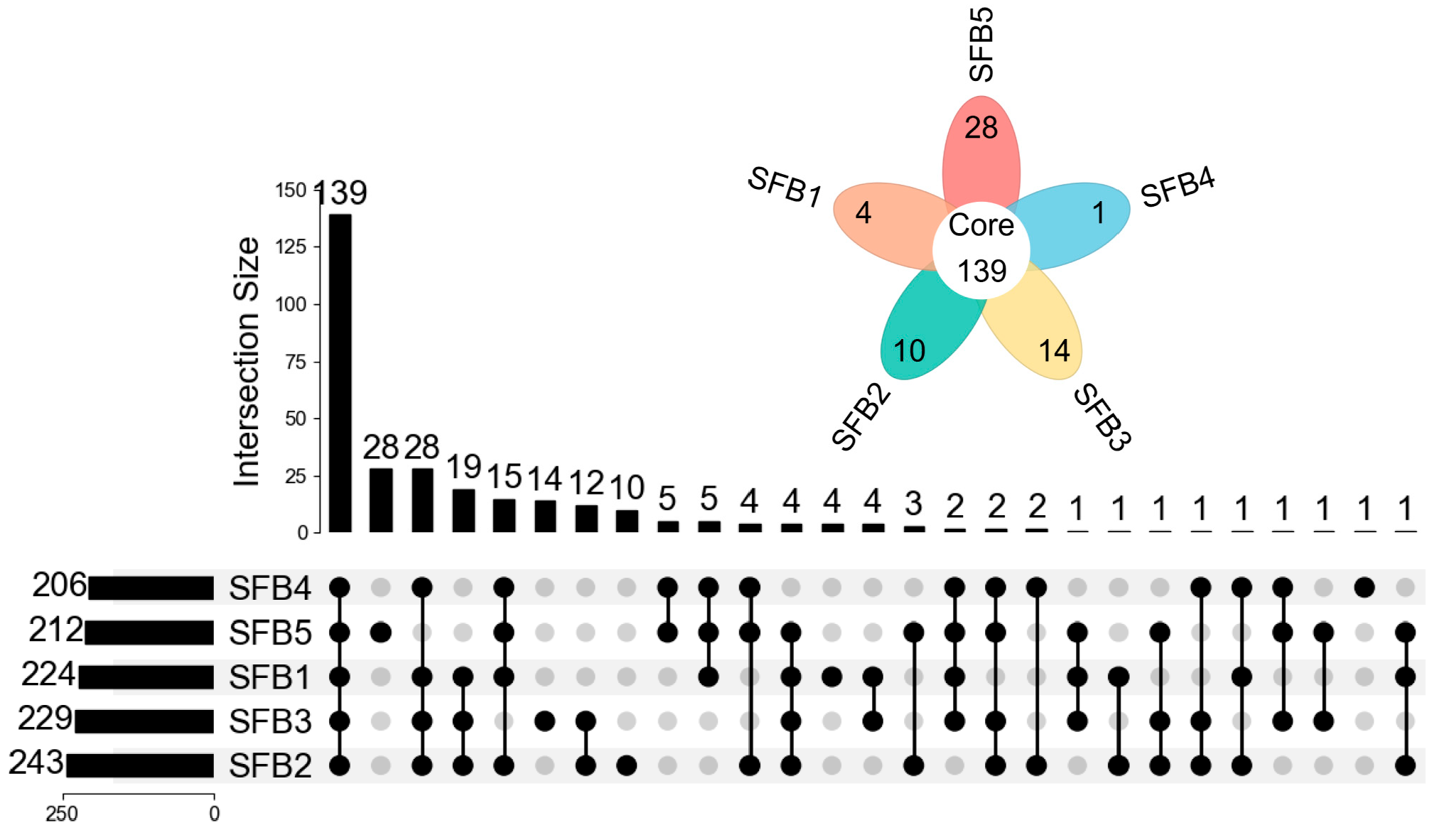
3.6. Comparison of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Different Grades of Baijiu
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Wei, J.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S. Rapid identification of Chinese Sauce liquor from different fermentation positions with FT-IR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 883–884, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Qin, D.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Zheng, F.; Sun, B. Why the key aroma compound of soy sauce aroma type baijiu has not been revealed yet? Lwt 2022, 154, 112735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Yang, J.G.; Zhao, Q.S.; Zhang, K.Z.; Su, C. Research Progress on Flavor Compounds and Microorganisms of Maotai Flavor Baijiu. J. Food Sci. 2018, 84, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chai, L.-J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.-J.; Lu, Z.-M.; Wang, S.-T.; Shen, C.-H.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Changes in flavor profile of sauce-flavor baijiu: Perceptual interactions between 1-propanol and aroma compounds. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, S.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Li, A.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Sun, B. Determination of 6 Phenols in 103 Kinds of Chinese Baijiu by GC-MS/SIM. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 19, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Fan, Z.; Du, A.; Shi, L.; Ren, J. Characterisation of key odorants causing honey aroma in Feng-flavour Baijiu during the 17-year ageing process by multivariate analysis combined with foodomics. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, A.; Mackie, P.M.; Phan, L.T.; Mirabel, R.; Smith, A.R.; Miller, E.; Franks, S.; Syed, O.; Riaz, T.; Law, B.K.; et al. Who Knew? Dopamine Transporter Activity Is Critical in Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Cells 2023, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, Z.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Qian, M.C. Volatile Analysis of Wuliangye Baijiu by LiChrolut EN SPE Fractionation Coupled with Comprehensive GC×GC-TOFMS. Molecules 2022, 27, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Yan, G.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, J.; Han, L. A Novel Data Fusion Strategy of GC-MS and 1H NMR Spectra for the Identification of Different Vintages of Maotai-flavor Baijiu. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2024, 72, 14865–14873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Fan, Z.; Du, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shi, Q.; Shi, L.; Chu, X. Recent advances in Baijiu analysis by chromatography based technology–A review. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, B.; Xie, K.; Cao, R.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y. Characterization of the content characteristics of pyrazines and volatile phenols in Chinese Baijiu Daqu by QuEChERS-UPLC-MS/MS approach. Food Res. Int. 2025, 204, 115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Li, Y.; Du, A.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Shi, L.; Luo, C.; Feng, K.; Chang, J.; Chu, X. Foodomics analysis of natural aging and gamma irradiation maturation in Chinese distilled Baijiu by UPLC-Orbitrap-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösl, M.; Dunkel, A.; Hartl, D.; Dollinger, A.; Spaccasassi, A.; Stark, T.D.; Dawid, C.; Hofmann, T.F. Toward High-Throughput Analysis of Aroma Compounds Using Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Screening of Key Food Odorants in Various Foods. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 8622–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, L. Differential 12C/13C-Isotope Dansylation Labeling and Fast Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry for Absolute and Relative Quantification of the Metabolome. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3919–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, C.-F.; Zhu, Q.-F.; Chen, Y.-Y.; He, D.-X.; Feng, Y.-Q. Screening and Identification of Epoxy/Dihydroxy-Oxylipins by Chemical Labeling-Assisted Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9904–9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Gao, M.; Sun, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Xu, F. Discovery of Acylated Glycine and Alanine by Integrating Chemical Derivatization-Based LC-MS/MS and Knowledge-Driven Prediction. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 18957–18966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-E.; Zhu, S.; Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, X.-E.; Liu, H. 8-Plex stable isotope labeling absolute quantitation strategy combined with dual-targeted recognizing function material for simultaneous separation and determination of glucosylsphingosine and galactosylsphingosine in human plasma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1124, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, T.; Wu, Y.; Tang, C.; Lin, G.; Li, L. DnsID in MyCompoundID for Rapid Identification of Dansylated Amine- and Phenol-Containing Metabolites in LC–MS-Based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9838–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Zhu, Q.-F.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Xiong, C.-F.; Hu, Y.-N.; Feng, Y.-Q. Integration of Chemical Derivatization and in-Source Fragmentation Mass Spectrometry for High-Coverage Profiling of Submetabolomes. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 11321–11328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, B.C.; Catrow, J.L.; Maschek, J.A.; Cox, J.E. QSRR Automator: A Tool for Automating Retention Time Prediction in Lipidomics and Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Allen, D.; Tian, S.; Oler, E.; Gautam, V.; Greiner, R.; O Metz, T.; Wishart, D.S. CFM-ID 4.0–a web server for accurate MS-based metabolite identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W165–W174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Han, W.; Chan, W.; Li, L. Metabolomic Coverage of Chemical-Group-Submetabolome Analysis: Group Classification and Four-Channel Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12108–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhart, A.E.; Booth, P.-P.M.; Simcox, K.M.; Ramos, B.A.; Kennedy, R.T. Systematic evaluation of benzoylation for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of different analyte classes. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1722, 464872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.-Y.; Xiao, X.; Peng, R.; Le, J.; Wang, H.-B.; Wang, S.-T. Rapid Derivatization of Phenolic and Oxime Hydroxyl with Isonicotinoyl Chloride under Aqueous Conditions and Its Application in LC–MS/MS Profiling Multiclass Steroids. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 17980–17987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Prior, Á.; Bermúdez-Oria, A.; Millán-Linares, M.d.C.; Fernández-Bolaños, J.; Espejo-Calvo, J.A.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity of Hydroxytyrosol and 3,4-Dihydroxyphenyglycol Purified from Table Olive Effluents. Foods 2021, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Si, C.; Sun, X.; Zhong, Q.; Yang, S. An Exploration of Pepino (Solanum muricatum) Flavor Compounds Using Machine Learning Combined with Metabolomics and Sensory Evaluation. Foods 2022, 11, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takao, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Yamada, T.; Goshima, T.; Isogai, A.; Sueno, K.; Fujii, T.; Akao, T. Characteristic features of the unique house sake yeast strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae Km67 used for industrial sake brewing. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajanikar, R.V.; Nataraj, B.H.; Naithani, H.; Ali, S.A.; Panjagari, N.R.; Behare, P.V. Phenyllactic acid: A green compound for food biopreservation. Food Control. 2021, 128, 108184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ramirez, M.; Cerezo, A.B.; Valero, E.; Troncoso, A.M.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C. From tyrosine to hydroxytyrosol: A pathway involving biologically active compounds and their determination in wines by ultra performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 9399–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; You, Y.; Du, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Suo, H.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, J. Metagenomic analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum DACN768 inoculation effects on volatile flavor compounds, microbial succession, and flavor metabolic network in suansun. Food Res. Int. 2025, 199, 115382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zheng, F.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Hu, C.; Ma, M.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. Untargeted and quantitative analyses of amine and phenol compounds in Baijiu via chemical isotope labeling. Explor. Foods Foodomics 2023, 1, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, T.; Jiang, L.; Shang, Y.; You, X.; Hu, F.; Yu, D.; Liu, X.; Wan, B.; et al. High-Coverage Profiling of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Using Bromine Isotope Labeling and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2025, 15, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070464
Wang Z, Sun Y, Chen T, Jiang L, Shang Y, You X, Hu F, Yu D, Liu X, Wan B, et al. High-Coverage Profiling of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Using Bromine Isotope Labeling and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites. 2025; 15(7):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070464
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zixuan, Youlan Sun, Tiantian Chen, Lili Jiang, Yuhao Shang, Xiaolong You, Feng Hu, Di Yu, Xinyu Liu, Bo Wan, and et al. 2025. "High-Coverage Profiling of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Using Bromine Isotope Labeling and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Metabolites 15, no. 7: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070464
APA StyleWang, Z., Sun, Y., Chen, T., Jiang, L., Shang, Y., You, X., Hu, F., Yu, D., Liu, X., Wan, B., Hu, C., & Xu, G. (2025). High-Coverage Profiling of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Using Bromine Isotope Labeling and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites, 15(7), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070464









