Gadolinium in the Environment: A Double-Edged Sword for Plant Growth and Ecosystem Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
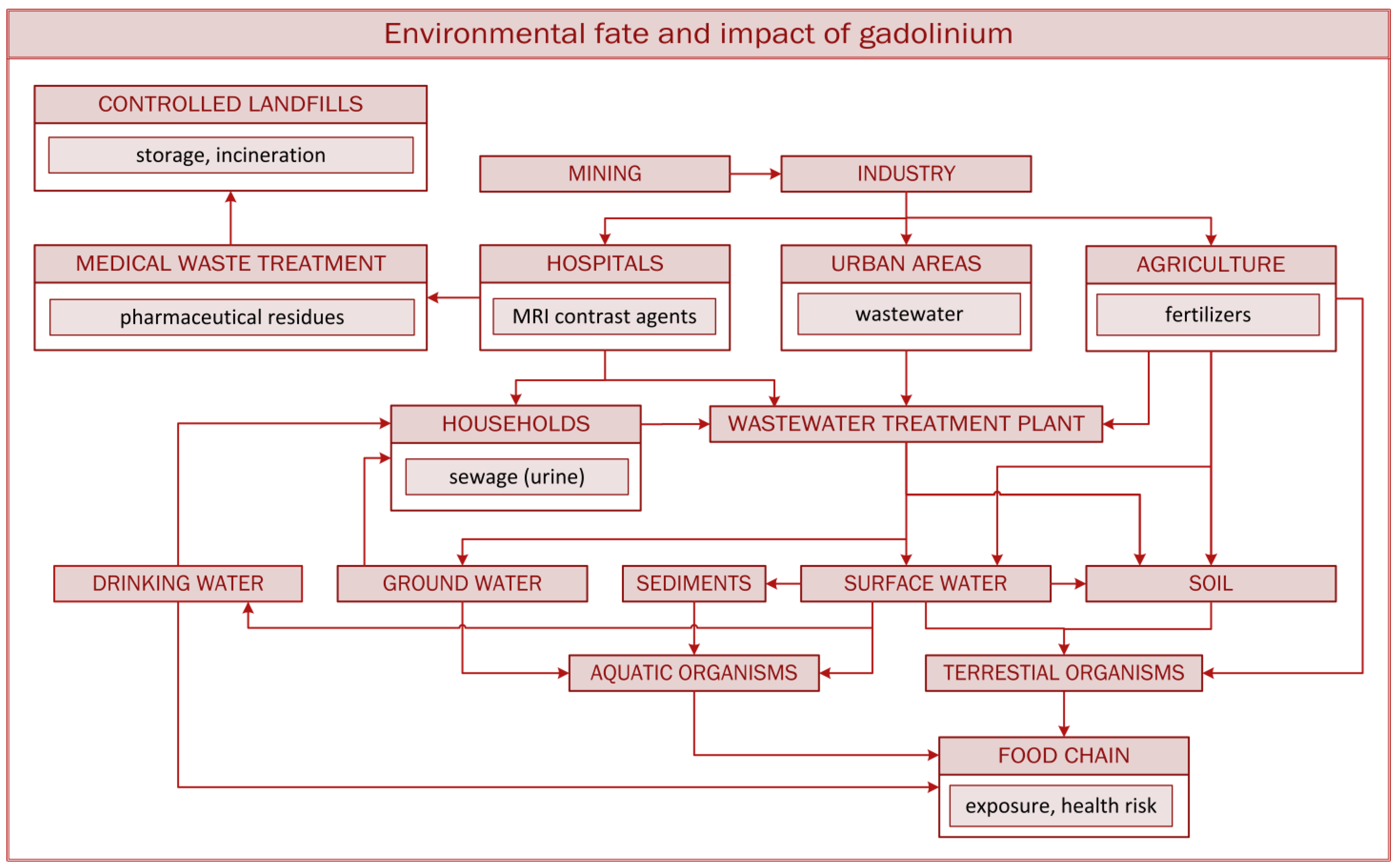
2. Gadolinium in the Environment
2.1. Sources of Contamination and Fate of Gadolinium in Soil and Water
2.2. Current Levels of Environmental Gadolinium and Trends
3. Gadolinium Uptake by Plants
4. Effects of Gadolinium on Plants
4.1. Positive Impact on Plants
4.2. Negative Impact on Plants
5. Impact of Gadolinium on Plant Stress Responses
6. Environmental and Ecological Considerations
Potential for Bioaccumulation of Gadolinium and Trophic Transfer
7. Strategies for Mitigating Environmental Exposure to Gadolinium
8. Future Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GBCA | gadolinium-based contrast agent |
| Gd(NO3)3 | gadolinium nitrate |
| Gd–BOPTA | gadobenate dimeglumine |
| Gd–BT–DO3A | gadobutrol |
| GdCl3 | gadolinium chloride |
| Gd–DOTA | gadoterate meglumine |
| Gd–DTPA | gadopentetate dimeglumine |
| Gd–DTPA–BMA | gadodiamide |
| Gd–DTPA–BMEA | gadoversetamide |
| Gd–EOB–DTPA | gadoxetate disodium |
| Gd–HP–DO3A | gadoteridol |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| REE | rare earth element |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| WWTP | wastewater treatment plant |
References
- Rogowska, J.; Olkowska, E.; Ratajczyk, W.; Wolska, L. Gadolinium as a new emerging contaminant of aquatic environments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, P.; Zhao, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.; Stagnitti, F. Biological toxicity of lanthanide elements on algae. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, M.; Metin, M.; Altay, V.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Gul, A.; Bhat, R.A.; Darvash, M.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Unal, D.; et al. Role of rare earth elements in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 41, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.J.; Carpenter, D.; Boutin, C.; Allison, J.E. Rare earth elements (REEs): Effects on germination and growth of selected crop and native plant species. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdElgawad, H.; Crecchio, C.; Nhs, M.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.A.; Malik, A.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Sulieman, S.; Shaghaleh, H.; Alyafei, M.; et al. Mitigating gadolinium toxicity in guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.) through the symbiotic associations with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: Physiological and biochemical insights. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsten-Torralba, L.R.; Magalhães, D.P.; Giese, E.C.; Nascimento, C.R.S.; Pinho, J.V.A.; Buss, D.F. Toxicity of three rare earth elements, and their combinations to algae, microcrustaceans, and fungi. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciszewska, Ż.; Gama, S.; Leśniewska, B.; Malejko, J.; Nalewajko-Sieliwoniuk, E.; Zambrzycka-Szelewa, E.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. The translocation pathways of rare earth elements from the environment to the food chain and their impact on human health. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 168, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmuc, N.R.; Dolenec, T.; Serafimovski, T.; Dolenec, M.; Vrhovnik, P. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements (REEs) in the paddy soil and rice (Oryza sativa L.) system of Kočani Field, Republic of Macedonia. Geoderma 2012, 183–184, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Guo, G. Acute toxicity of binary and ternary mixtures of La, Ce and Dy on Daphnia magna: Toxicity patterns depend on the ratios of the components and the concentration gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 956, 177305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Li, D.; Peng, A. Application of rare-earth elements in the agriculture of China and its environmental behavior in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2002, 9, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotruvo, J.A., Jr. The chemistry of lanthanides in biology: Recent discoveries, emerging principles, and technological applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, K.R.; Echaide-Aquino, F.; Huerta-Robles, A.; Valério, H.P.; Macedo-Raygoza, G.; Prado, F.M.; Medeiros, M.H.G.; Brito, H.F.; da Silva, I.G.N.; Cunha Felinto, M.C.F.; et al. Hossain, M.A., Kamiya, T., Burritt, D.J., Tran, L.-S.P., Fujiwara, T., Eds.; Endophytic bacteria and rare earth elements; promising candidates for nutrient use efficiency in plants. In lant Macronutrient Use Efficiency. Molecular and Genomic Perspectives in Crop Plants; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabayashi, S.; Kawane, L.; Mrabawani, N.Y.; Iwai, T.; Narukawa, T.; Tsuboi, M.; Chiba, K. Speciation analysis of gadolinium-based contrast agents using aqueous eluent-hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 222, 121531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, M.; Idée, J.-M.; Medina, C.; Robic, C.; Sabatou, M.; Corot, C. Efficiency, thermodynamic and kinetic stability of marketed gadolinium chelates and their possible clinical consequences: A critical review. Biometals 2008, 21, 469–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, Z.; Pálinkás, Z.; Uggeri, F.; Maiocchi, A.; Aime, S.; Brücher, E. Dissociation kinetics of open-chain and macrocyclic gadolinium(III)-aminopolycarboxylate complexes related to magnetic resonance imaging: Catalytic effect of endogenous ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 16426–16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraum, T.J.; Ludwig, D.R.; Bashir, M.R.; Fowler, K.J. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: A comprehensive risk assessment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, S.; Rocha, S.; Sousa, N.R.; Catarino, C.; Belo, L.; Bronze-da-Rocha, E.; Valente, M.J.; Santos-Silva, A. Toxicity mechanisms of gadolinium and gadolinium-based contrast agents—A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, K.; Reuter, S.; Elinkmann, M.; Köhrer, A.; Quarles, C.D.; Hippler, M.; Karst, U. Species-dependent uptake of gadolinium in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii algae. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idée, J.-M.; Port, M.; Robic, C.; Medina, C.; Sabatou, M.; Corot, C. Role of thermodynamic and kinetic parameters in gadolinium chelate stability. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Siebenhandl-Wolff, P.; Tranquart, F.; Jones, P.; Evans, P. Gadolinium: Pharmacokinetics and toxicity in humans and laboratory animals following contrast agent administration. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 403–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, A.; Brito, P. Stability of the macrocyclic Gd-DOTA contrast agent (DOTAREM) under different estuarine environmental conditions. Oceans 2023, 4, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Bettinelli, M.; Boffi, A.; Botta, M.; De Simone, G.; Luchinat, C.; Marengo, E.; Mei, H.; Aime, S. Rare earth elements (REE) in biology and medicine. Rend. Lincei Sci. Fis. Nat. 2020, 31, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, M.; Billotey, C.; Marty, J.-D. Gadolinium-based contrast agents: From gadolinium complexes to colloidal systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brioschi, L.; Steinmann, M.; Lucot, E.; Pierret, M.C.; Stille, P.; Prunier, J.; Badot, P.M. Transfer of rare earth elements (REE) from natural soil to plant systems: Implications for the environmental availability of anthropogenic REE. Plant Soil 2013, 366, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenishev, A.V.; Baranov, V.G.; Kuzmin, R.S.; Pokrovskiy, S.A. High temperature dilatometry of simulated oxide nuclear fuel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 130, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwasola, I.E.; Ahmad, A.L.; Shoparwe, N.F.; Ismail, S. Gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCAs): Uniqueness, aquatic toxicity concerns, and prospective remediation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 250, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, P.; Brizio, P.; Abete, M.C.; Bertoli, M.; Oss Noser, A.G.; Piazza, G.; Prearo, M.; Elia, A.C.; Pizzul, E.; Squadrone, S. Macrobenthic invertebrates as tracers of rare earth elements in freshwater watercourses. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, D.S.; Batt, A.; Scott, W.; Kim, S. Aga, D.S., Ed.; Removal of pharmaceuticals in biological wastewater treatment plants. In Fate of Pharmaceuticals in the Environment and in Water Treatment Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, J. Analysis of emerging contaminants in surface water, aquaculture ponds and wastewater treatment facilities in the Taige Canal Basin. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2023, 39, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künnemeyer, J.; Terborg, L.; Meermann, B.; Brauckmann, C.; Möller, I.; Scheffer, A.; Karst, U. Speciation analysis of gadolinium chelates in hospital effluents and wastewater treatment plant sewage by a novel HILIC/ICP-MS method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2884–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognard, J.; Barrat, J.-A.; Cotton, F.; Mian, A.; Kremer, S.; Sitoh, Y.Y.; Verclytte, S.; Loffroy, R.; Tripier, R.; Alavi, Z.; et al. A roadmap towards pollution prevention and sustainable development of gadolinium. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 48, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attrah, M.; Elmanadely, A.; Akter, D.; Rene, E.R. A review on medical waste management: Treatment, recycling, and disposal options. Environments 2022, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocka, I.A.; Rogowska, A.M.; Kostrz-Sikora, P. Investigation of anthropogenic gadolinium in tap water of polish cities: Gdańsk, Kraków, Warszawa, and Wrocław. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laczovics, A.; Csige, I.; Szabó, S.; Tóth, A.; Kálmán, F.K.; Tóth, I.; Fülöp, Z.; Berényi, E.; Braun, M. Relationship between gadolinium-based MRI contrast agent consumption and anthropogenic gadolinium in the influent of a wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Dulski, P. Transmetallation of Gd-DTPA by Cu, Y and lanthanides and its impact on the hydrosphere. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Dulski, P. Gd-DTPA in the hydrosphere: Kinetics of transmetallation by ions of rare earth elements, Y and Cu. Geochemistry 2010, 70, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telgmann, L.; Faber, H.; Jahn, S.; Melles, D.; Simon, H.; Sperling, M.; Karst, U. Identification and quantification of potential metabolites of Gd-based contrast agents by electrochemistry/separations/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1240, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brünjes, R.; Hofmann, T. Anthropogenic gadolinium in freshwater and drinking water systems. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birka, M.; Wehe, C.A.; Hachmöller, O.; Sperling, M.; Karst, U. Tracing gadolinium-based contrast agents from surface water to drinking water by means of speciation analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1440, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Herrera, L.F.; Sánchez-Calderón, L.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; López-Bucio, J. Rare earth elements lanthanum and gadolinium induce phosphate-deficiency responses in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant Soil 2012, 353, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatz, J.; Vetterlein, D.; Mattusch, J.; Otto, M.; Daus, B. The influence of gadolinium and yttrium on biomass production and nutrient balance of maize plants. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.; Ramos, S.J.; Dinali, G.S.; de Carvalho, T.S.; Martins, F.A.D.; Faquin, V.; Castro, E.M.d.; Sarkis, J.E.S.; Siqueira, J.O.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Biostimulant response of foliar application of rare earth elements on physiology, growth, and yield of rice. Plants 2024, 13, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendakovská, L.; Krejčová, A.; Weidlich, T. Sorption and biosorption of Gd-based contrast agents in the water environment. Chem. Pap. 2019, 73, 2995–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, X. Determination of trace rare earth elements in plant and soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2000, 76, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.; Tarvainen, T. Geochemical Atlas of Europe. Part 2: Interpretation of Geochemical Maps, Additional Tables, Figures, Maps, and Related Publications; Geological Survey of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Anthropogenic origin of positive gadolinium anomalies in river waters. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 143, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatje, V.; Bruland, K.W.; Flegal, A.R. Increases in anthropogenic gadolinium anomalies and rare earth element concentrations in San Francisco Bay over a 20 year record. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4159–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Ma, S. Anthropogenic gadolinium accumulation and rare earth element anomalies of the typical urban river, North China: Evidence from the three-dimensional tracing system. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2023, 7, 2511–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyris, M.; Knolle, W.; Richard, J.; Dopp, E.; von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. Reaction of gadolinium chelates with ozone and hydroxyl radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9942–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapasso, G.; Chiesa, S.; Freitas, R.; Pereira, E. What do we know about the ecotoxicological implications of the rare earth element gadolinium in aquatic ecosystems? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocka, I. Determination of rare earth elements concentrations in natural waters—A review of ICP-MS measurement approaches. Talanta 2021, 221, 121636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Fukushi, M.; Furukawa, A.; Sahoo, S.K.; Veerasamy, N.; Ichimura, K.; Kasahara, S.; Ichihara, M.; Tsukada, M.; Torii, M.; et al. Impact on gadolinium anomaly in river waters in Tokyo related to the increased number of MRI devices in use. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K.; Helmers, E. Hospital effluents as a source of gadolinium in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Bau, M.; Merschel, G.; Tepe, N. Anthropogenic gadolinium in tap water and in tap water-based beverages from fast-food franchises in six major cities in Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, H.S. Are the increasing amounts of gadolinium in surface and tap water dangerous? Acta Radiol. 2017, 58, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosjean, N.; Le Jean, M.; Berthelot, C.; Chalot, M.; Gross, E.M.; Blaudez, D. Accumulation and fractionation of rare earth elements are conserved traits in the Phytolacca genus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-S.; Laird, J.S.; Ryan, C.G.; Tang, Y.-T.; Qiu, R.-L.; Echevarria, G.; Morel, J.-L.; van der Ent, A. Rare earth elements, aluminium and silicon distribution in the fern Dicranopteris linearis revealed by μPIXE Maia analysis. Ann. Bot. 2021, 128, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Wei, Z.-G.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yang, H.-X.; Li, H.-X.; Hu, F. Effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids on gadolinium accumulation and transportation in tomato plants. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2009, 127, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezanka, T.; Kaineder, K.; Mezricky, D.; Řezanka, M.; Bišová, K.; Zachleder, V.; Vítová, M. The effect of lanthanides on photosynthesis, growth, and chlorophyll profile of the green alga Desmodesmus quadricauda. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 130, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Guo, C.; Tai, P.D.; Sun, L.Z.; Chen, Z.B. The exposure of gadolinium at environmental relevant levels induced genotoxic effects in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingott, J.; Lindner, U.; Telgmann, L.; Esteban-Fernández, D.; Jakubowski, N.; Panne, U. Gadolinium-uptake by aquatic and terrestrial organisms-distribution determined by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2016, 18, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharchaou, I.; Bahloul, F.; Fortin, C. Competition among trivalent elements (Al, Eu, Fe, Gd, Nd, Tm, and Y) for uptake in algae and applicability of the biotic ligand model. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babula, P.; Adam, V.; Opatrilova, R.; Zehnalek, J.; Havel, L.; Kizek, R. Uncommon heavy metals, metalloids and their plant toxicity: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2008, 6, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Richter, H.; Sparovek, G.; Schnug, E. Physiological and biochemical effects of rare earth elements on plants and their agricultural significance: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2004, 27, 183–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, H.; Yuan, X.; Hou, D. Effects of rare earth elements on callus growth, soluble protein content, peroxidase activity and shoot differentiation of Echinacea angustifolia cultures in vitro. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, T.; Ding, X.; Huang, X. Molecular and cellular mechanism of the effect of La(III) on horseradish peroxidase. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 15, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Jiang, N.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.D.; Lu, T.H.; Ding, X.L.; Huang, X.H. Structural basis for the decrease in the outward potassium channel current induced by lanthanum. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 15, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, L. Bioaccumulation of lanthanum and cerium and their effects on the growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Kamran, M.; Song, Q.; Zuo, B.; Jia, Z.; Han, Q. Lanthanum chloride improves maize grain yield by promoting photosynthetic characteristics, antioxidants enzymes and endogenous hormone at reproductive stages. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.S.C.; Li, X. Analysis of heavy metal contaminated soils. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2003, 7, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, A.; Spampinato, M.; Salbitani, G.; Guida, M.; Carfagna, S.; Brouziotis, A.A.; Trifuoggi, M.; Bossa, R.; Saviano, L.; Padilla Suarez, E.G.; et al. Multi-endpoint analysis of cerium and gadolinium effects after long-term exposure to Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Environments 2024, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G. Rare earth elements in soil and plant systems—A review. Plant Soil 2004, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Shi, K.; Liu, C.; Lyu, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Gadolinium accumulation, distribution, chemical forms, and influence on the growth of rice seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 179, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurtu, V.F.; Clapa, D.; Leopold, L.F.; Ranga, F.; Iancu, Ș.D.; Cadiș, A.I.; Coman, V.; Socaci, S.A.; Moț, A.C.; Coman, C. Gadolinium accumulation and toxicity on in vitro grown Stevia rebaudiana: A case-study on gadobutrol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joonas, E.; Aruoja, V.; Olli, K.; Syvertsen-Wiig, G.; Vija, H.; Kahru, A. Potency of (doped) rare earth oxide particles and their constituent metals to inhibit algal growth and induce direct toxic effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuelsoud, W.; Madany, M.M.Y.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; Korany, S.M.; Alsharef, E.; AbdElgawad, H. Alleviation of gadolinium stress on Medicago by elevated atmospheric CO2 is mediated by changes in carbohydrates, anthocyanin, and proline metabolism. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 202, 107925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, V.; Vignati, D.A.L.; Pons, M.-N.; Montarges-Pelletier, E.; Bojic, C.; Giamberini, L. Lanthanide ecotoxicity: First attempt to measure environmental risk for aquatic organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, S.; Zavanyi, G.; Koleszár, G.; del Castillo, D.; Oláh, V.; Braun, M. Phytoremediation, recovery and toxic effects of ionic gadolinium using the free-floating plant Lemna gibba. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, C. Umweltverhalten und Ökotoxikologie von Gadoliniumhaltigen Magnetresonanztomographie-Kontrastmitteln; Technischen Universität: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Plants’ response to abiotic stress: Mechanisms and strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasan, F.; Ozfidan-Konakci, C.; Yildiztugay, E.; Kucukoduk, M. Rare-earth element scandium improves stomatal regulation and enhances salt and drought stress tolerance by up-regulating antioxidant responses of Oryza sativa. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 152, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas-Rioseco, J.; Ginocchio, R.; Ortiz-Calderón, C. Increase in phytoextraction potential by genome editing and transformation: A review. Plants 2021, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, J.; van der Meer, T.; Testerink, C. How plants sense and respond to stressful environments. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1624–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotelnikova, A.D.; Rogova, O.B.; Stolbova, V.V. Lanthanides in the soil: Routes of entry, content, effect on plants, and genotoxicity (a review). Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, E.; Cui, L.; Zerges, W.; Wilkinson, K.J. Mixtures of rare earth elements show antagonistic interactions in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Lata, C. Heavy metal stress, signaling, and tolerance due to plant-associated microbes: An overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Shan, X.Q.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.N.; Pei, Z.G.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zhu, Y.G.; Wen, B. Organic acids promote the uptake of lanthanum by barley roots. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, R.H.; Liu, X.; Schijf, J. The influence of phosphate coprecipitation on rare earth distributions in natural waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 3341–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Tai, P.; Gong, Z.; Jia, C.; Liu, W. DNA damage and genetic methylation changes caused by Cd in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyad, N.S. Ahmad, M.; Alkhatib, S.G.; Hjouj, M. Gadolinium contrast agents- challenges and opportunities of a multidisciplinary approach: Literature review. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2023, 11, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, C.; Ma, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, W.; Wu, W. Exploitation alters microbial community and its co-occurrence patterns in ionic rare earth mining sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, J.; Qi, Y.; Cao, W.-W.; Liu, J.-M.; Guo, W.; Bao, Z.-H. Multiple factors influence bacterial community diversity and composition in soils with rare earth element and heavy metal co-contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, S.; Wen, Z. Soil characteristics and microbial community response in rare earth mining areas in southern Jiangxi Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 56418–56431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, H.M.; Stroomberg, G.J.; Van der Molen, A.J.; Prokop, M. Review of strategies to reduce the contamination of the water environment by gadolinium-based contrast agents. Insights Imaging 2024, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, I.; Muna, M.; Heinlaan, M.; Lukjanova, A.; Kahru, A. Potential hazard of lanthanides and lanthanide-based nanoparticles to aquatic ecosystems: Data gaps, challenges and future research needs derived from bibliometric analysis. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaux, N.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Poirier, L.; Gross, E.M.; Giamberini, L. Integrated environmental risk assessment of rare earth elements mixture on aquatic ecosystems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 974191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Xu, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, R.; Chen, Y. Geochemistry and biogeochemistry of rare earth elements in a surface environment (soil and plant) in South China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenggui, W.; Ming, Y.; Xun, Z.; Fashui, H.; Bing, L.; Ye, T.; Guiwen, Z.; Chunhua, Y. Rare earth elements in naturally grown fern Dicranopteris linearis in relation to their variation in soils in South-Jiangxi region (Southern China). Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepi, S.; Sansone, L.; Chicca, M.; Marrocchino, E.; Vaccaro, C. Distribution of rare earth elements in soil and grape berries of Vitis vinifera cv. “Glera”. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shan, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of plant availability of rare earth elements in soils by chemical fractionation and multiple regression analysis. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Xiaorong, W.; Liansheng, W.; Lemei, D.; Zhong, L.; Yijun, C. Bioconcentration of rare earth elements lanthanum, gadolinium and yttrium in algae (Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck): Influence of chemical species. Chemosphere 1997, 34, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendakovská, L.; Krejčová, A.; Černohorský, T.; Zelenková, J. Development of ICP-MS and ICP-OES methods for determination of gadolinium in samples related to hospital waste water treatment. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatz, J.; Stryhanyuk, H.; Vetterlein, D.; Musat, N.; Otto, M.; Reemtsma, T.; Richnow, H.H.; Daus, B. Location and speciation of gadolinium and yttrium in roots of Zea mays by LA-ICP-MS and ToF-SIMS. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yin, D.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Dai, L.; Chen, Y.; Cao, M. Distribution and bioavailability of rare earth elements in aquatic microcosm. Chemosphere 1999, 39, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.; Ferreira, A.; Viana, T.; Lopes, C.B.; Costa, M.; Pinto, J.; Soares, J.; Pinheiro-Torres, J.; Henriques, B.; Pereira, E. Assessment of marine macroalgae potential for gadolinium removal from contaminated aquatic systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.; Zavanyi, G.; Laczovics, A.; Berényi, E.; Szabó, S. Can aquatic macrophytes be biofilters for gadolinium based contrasting agents? Water Res. 2018, 135, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, U.; Lingott, J.; Richter, S.; Jakubowski, N.; Panne, U. Speciation of gadolinium in surface water samples and plants by hydrophilic interaction chromatography hyphenated with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minqin, R.; Xiao, C.; Yi, Z.; Hao, S.; Qingguang, R.; Yong, L.; Frank, W. Sub-100-nm STIM imaging and PIXE quantification of rare earth elements in algae cells. X-Ray Spectrom. 2013, 42, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyot, M.; Clayden, M.G.; MacMillan, G.A.; Perron, T.; Arscott-Gauvin, A. Fate and trophic transfer of rare earth elements in temperate lake food webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6009–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallares, R.M.; Li, Y.; Abergel, R.J. Understanding the biological behavior of lanthanides and actinides through omics approaches. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2023, 167, 117251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eapen, S.; D’Souza, S.F. Prospects of genetic engineering of plants for phytoremediation of toxic metals. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005, 23, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Wang, Y.; Tan, S.N.; Mohd Yusof, M.L.; Ghosh, S.; Chen, Z. Phytoremediation: A promising approach for revegetation of heavy metal-polluted land. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. EMA’s Final Opinion Confirms Restrictions on Use of Linear Gadolinium Agents in Body Scans; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/emas-final-opinion-confirms-restrictions-use-linear-gadolinium-agents-body-scans (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Kanda, T. The new restrictions on the use of linear gadolinium-based contrast agents in Japan. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2019, 18, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.D.; Grady, C.J.; Krell, K.; Strebeck, C.; Al-Hilfi, A.; Ricker, B.; Linn, M.; Xin, N.Y.; Good, N.M.; Martinez-Gomez, N.C.; et al. A novel protein for bioremediation of gadolinium waste. Protein Sci. 2025, 34, e70101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmståhl, B.; Nyman, U.; Leander, P.; Chai, C.-M.; Golman, K.; Björk, J.; Almén, T. Gadolinium contrast media are more nephrotoxic than iodine media. The importance of osmolality in direct renal artery injections. Eur. Radiol. 2006, 16, 2712–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
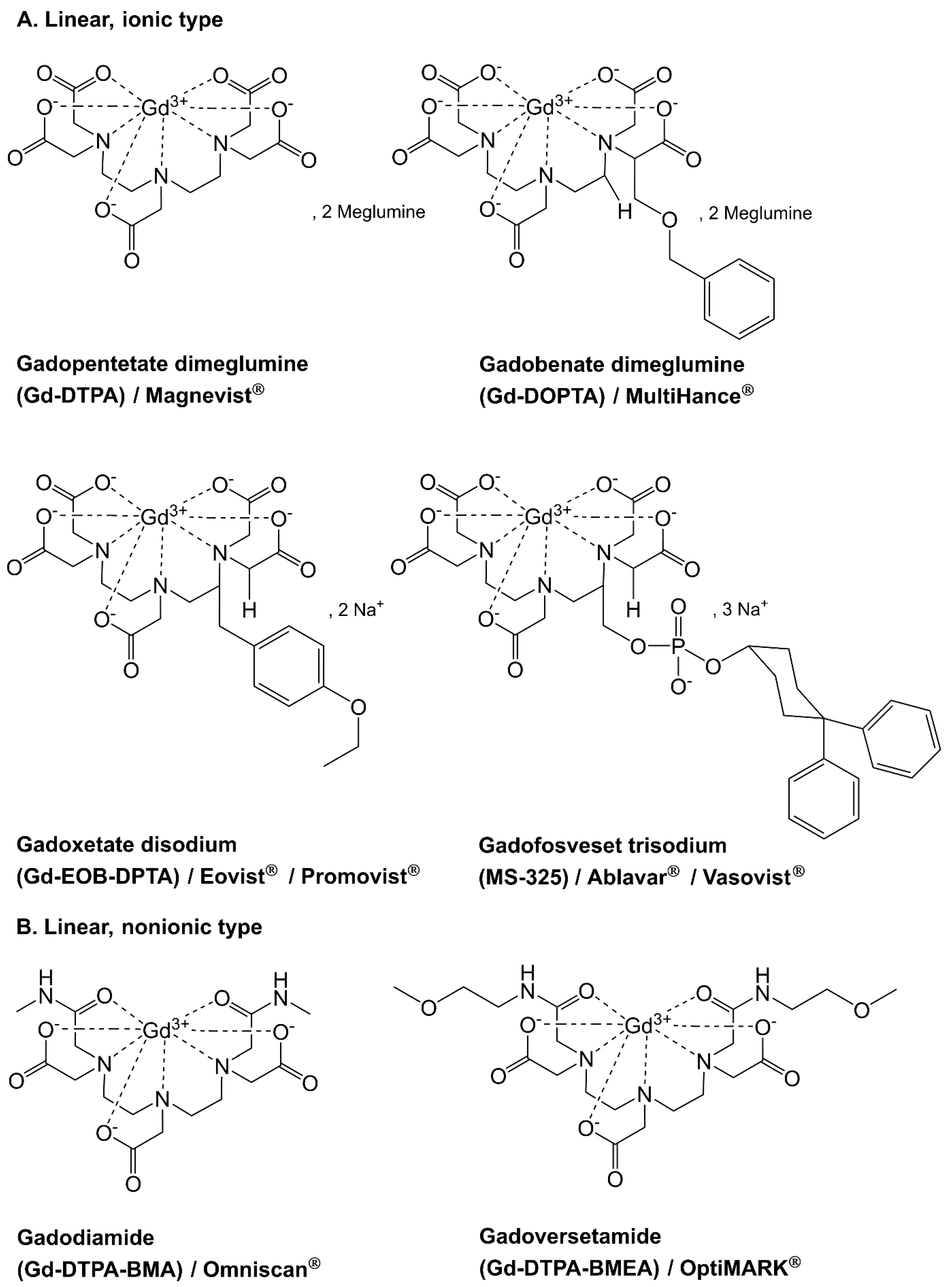
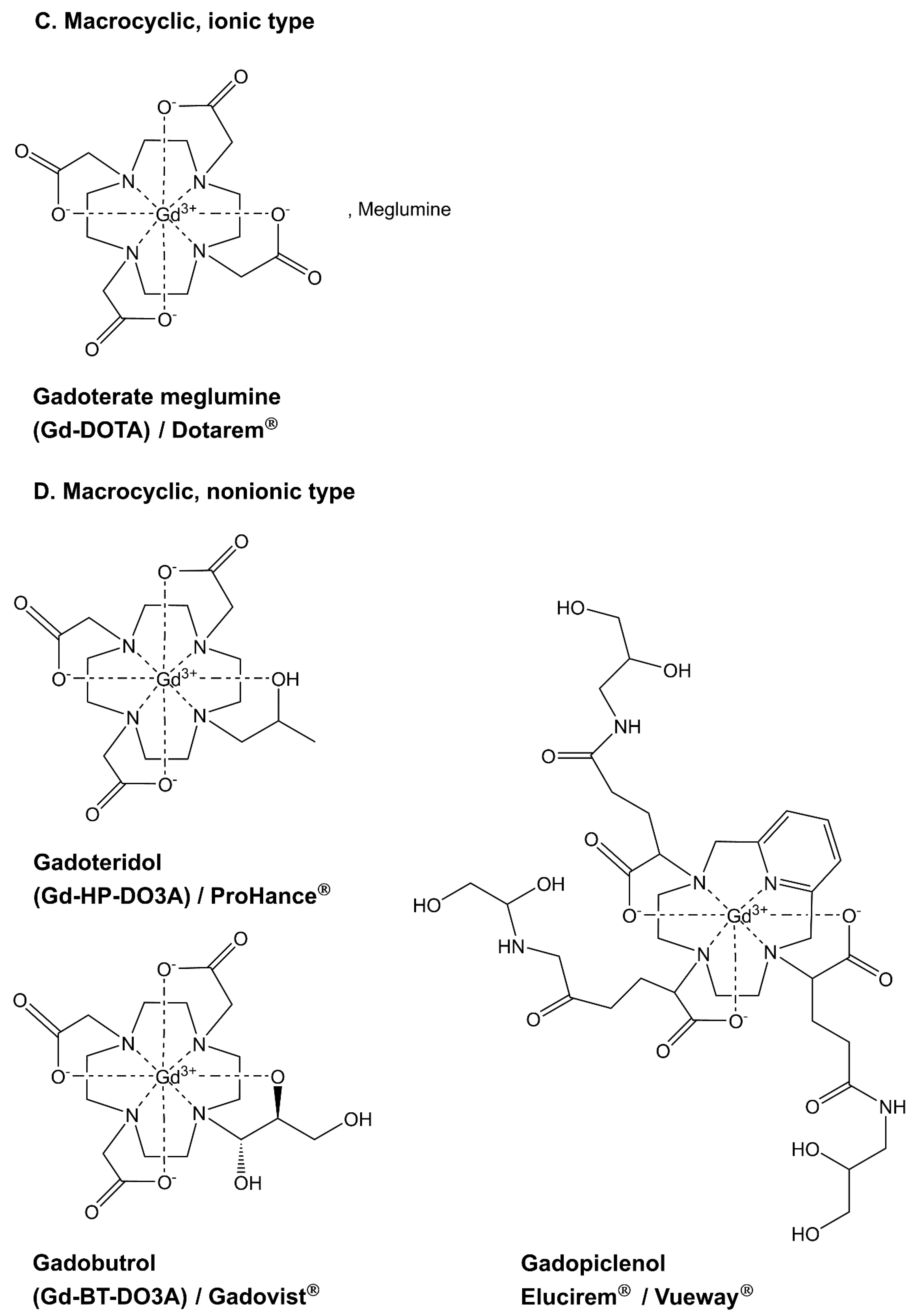

| Compound | Plant Species | EC50 [mg/L] | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gd3+ | Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata | 2.22 | González et al. [77] |
| Lemna gibba | 12.4 | Szabó et al. [78] | |
| GdCl3 | Desmodesmus subspicatus | 4.94 | Neubert [79] |
| Gd(NO3)3 | Skeletonema costatum | 10.2 | Tai et al. [2] |
| Raphidocelis subcapitata | 1.21 | Joonas et al. [75] | |
| Gd2O3 | Phaeodactylum tricornutum | 6.02 | Siciliano et al. [71] |
| Gd–DTPA | Desmodesmus subspicatus | >100 | Aga et al. [28] |
| Gd–DTPA–BMA | 20 | Neubert [79] | |
| Gd–HP–DO3A | >100 | Neubert [79] | |
| Gd–EOB–DTPA | >500 | Aga et al. [28] | |
| Gd–BT–DO3A | 937 | Aga et al. [28] |
| Compound | Exposure Concentration [mg/L; µg/g *] | Concentration in Dry Weight Sample [µg/g] | Plant Species | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gadolinium | 5.6–8.2 * | 0.065–0.07 | Camelia sinensis | Cao et al. [44] | |
| 0.16 | Brassica juncea | ||||
| 0.28 roots 0.13 stems 0.21 leaves 0.015 fruits | Capsicum annuum | ||||
| 1.32–7.14 * | 0.118–2.87 | Eucalyptus globulus | Miao et al. [97] | ||
| 4.61–32.8 | Dicranopteris dichotoma | ||||
| 0.205–0.734 | Pinus massoniana | ||||
| 0.189 | Phodomyrtus tomentosa | ||||
| 0.296 | Lophatherum gracile | ||||
| 2.52 | Casuarina equisetifolia | ||||
| 2.70–147 * | 1.44–85 stems 0.65–3.14 petioles 13.3–76.9 laminas | Dicranopteris linearis | Zhenggui et al. [98] | ||
| 3.07–6.84 * | 0.020–0.065 juice 0.097–0.322 solid | Vitis vinifera | Pepi et al. [99] | ||
| 3.46–5.33 * | <0.00115 grains 0.00591 stems 0.0305 leaves 0.146 roots | Zea mays | Li et al. [100] | ||
| <0.00115 grains 0.018 stems 0.0391 leaves 0.932 roots | Oryza sativa | ||||
| Gd3+ | 0–20 | 0–1439 | Lemna gibba | Szabó et al. [78] | |
| 1 | 6360 | Chlorella vulgaris | Hao et al. [101] | ||
| GdCl3 | 3.14 | 500 × 10−7 ng/cell lysate 130 × 10−6 ng/cell residue | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Sommer et al. [18] | |
| Gd(NO3)3 | 1.57–31.5 | 67.3–253 roots 2.19–2.73 shoots | Arabidopsis thaliana | Liu et al. [60] | |
| 0.1 medium 0.0021–0.00273 MRI 0.00143–0.00273 WWTP | 68.3–83.2 medium 4.73–5.22 MRI 3.49–5.23 WWTP | Chlorella kessleri | Bendakovská et al. [102] | ||
| 10 | 217 | Zea mays | Saatz et al. [103] | ||
| 0.002–0.1 | 1–80 | Chlorella kessleri | Bendakovská et al. [102] | ||
| Gd2O3 | 1.00 | 104 | Sperollela polyrrhiza | Yang et al. [104] | |
| 0.01–0.5 | 14–696 | Ulva lactuca | Ferreira et al. [105] | ||
| 0.01–0.5 | 17.1–602 | Gracilaria sp. | |||
| 0.01–0.5 | 2.40–220 | Fucus spiralis | |||
| Gd2O3 + organic ligands | 1.00 | (CIT) | 3160 | Chlorella vulgaris | Hao et al. [101] |
| (NTA) | 3120 | ||||
| (EDTA) | 380 | ||||
| Gd–DTPA | 5.56 | 5.6 × 10−8 ng/cell lysate 11 × 10−8 ng/cell residue | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Sommer et al. [18] | |
| Gd–DTPA–BMA | 7.86 | 9.6 × 10−8 ng/cell lysate 17 × 10−8 ng/cell residue | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | ||
| 0.256 | 138 | Ceratophyllum demersum | Braun et al. [106] | ||
| 0.256 | 39 | Lemna gibba | |||
| Gd–DOTA | 5.91 | <LOD | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Sommer et al. [18] | |
| 0.256 | 39 | Lemna gibba | Braun et al. [106] | ||
| 0.256 | 59 | Ceratophyllum demersum | |||
| 1 | 1–1.1 | Lepidium sativum | Lindner et al. [107] | ||
| 0.002–0.1 | 0.8–30 | Chlorella kessleri | Bendakovská et al. [102] | ||
| Gd–BT–DO3A | 7.48 | 0.59 × 10−8 ng/cell lysate 0.29 × 10−8 ng/cell residue | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | Sommer et al. [18] | |
| 1 | 1–1.2 | Lepidium sativum | Lindner et al. [107] | ||
| 6.05–1814 | 7.88–744 | Stevia rebaudiana | Scurtu et al. [74] | ||
| Gd–BOPTA | 1 | 1 stems 2 roots 10 leaves | Lepidium sativum | Lindner et al. [107] | |
| 0.002–0.02 | 1–40 | Chlorella kessleri | Bendakovská et al. [102] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomczuk, M.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B.; Bajguz, A. Gadolinium in the Environment: A Double-Edged Sword for Plant Growth and Ecosystem Stability. Metabolites 2025, 15, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060415
Tomczuk M, Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz B, Bajguz A. Gadolinium in the Environment: A Double-Edged Sword for Plant Growth and Ecosystem Stability. Metabolites. 2025; 15(6):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060415
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomczuk, Marlena, Beata Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, and Andrzej Bajguz. 2025. "Gadolinium in the Environment: A Double-Edged Sword for Plant Growth and Ecosystem Stability" Metabolites 15, no. 6: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060415
APA StyleTomczuk, M., Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B., & Bajguz, A. (2025). Gadolinium in the Environment: A Double-Edged Sword for Plant Growth and Ecosystem Stability. Metabolites, 15(6), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060415








