The Associations of Serum Folate Forms with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
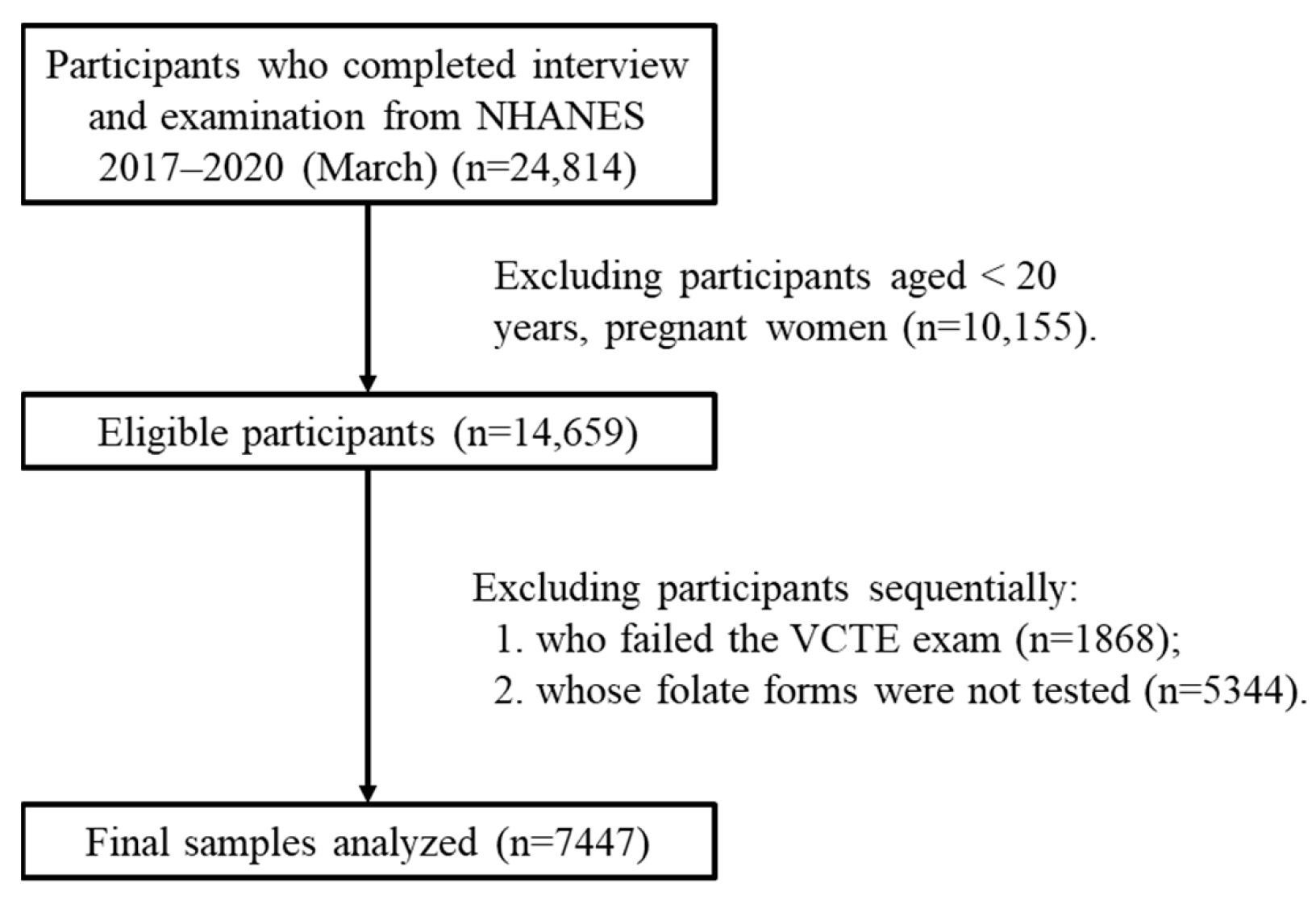
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Diagnosis of MAFLD and Liver Fibrosis
2.3. Quantification of Serum Folate Forms and Oxidative Stress
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L. From metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Controversy and consensus. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, H.; Shang, Y.; Hegmar, H.; Nasr, P. Natural history and progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Liu, C.J. Chronic hepatitis B with concurrent metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: Challenges and perspectives. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlas, T.; Weise, L.; Kuhn, S.; Krenzien, F.; Mehdorn, M.; Petroff, D.; Linder, N.; Schaudinn, A.; Busse, H.; Keim, V.; et al. Correlation of cell-free DNA plasma concentration with severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Rodríguez, A.; Vera-Barajas, A.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C.; Uribe, M.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. Looking into a new era for the approach of metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Gupta, S.; Kulshrestha, S.; Khandelwal, V.; Pandey, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, U.; Parashar, D.; Das, K. Metabolomics-Driven Biomarker Discovery for Breast Cancer Prognosis and Diagnosis. Cells 2024, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebbioso, M.; Franzone, F.; Lambiase, A.; Bonfiglio, V.; Limoli, P.G.; Artico, M.; Taurone, S.; Vingolo, E.M.; Greco, A.; Polimeni, A. Oxidative Stress Implication in Retinal Diseases-A Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Yang, H.; Lei, M.Z.; Zhu, W.P.; Su, Y.; Li, K.Y.; Zhu, W.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Qu, J.; et al. Dietary folate drives methionine metabolism to promote cancer development by stabilizing MAT IIA. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Cao, X.; Cabrera, R.M.; Ramirez, P.A.P.; Lin, Y.L.; Wlodarczyk, B.J.; Zhang, C.; Finnell, R.H.; Lei, Y. Folate regulation of planar cell polarity pathway and F-actin through folate receptor alpha. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Bartuzi, P.; Heegsma, J.; Dekker, D.; Kloosterhuis, N.; de Bruin, A.; Jonker, J.W.; van de Sluis, B.; Faber, K.N. Impaired Hepatic Vitamin A Metabolism in NAFLD Mice Leading to Vitamin A Accumulation in Hepatocytes. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 309–325.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, Q.; Yang, X. Folic Acid Reduced Triglycerides Deposition in Primary Chicken Hepatocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 13162–13172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, F.Z.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhang, R.N.; Pan, Q.; Gong, Z.Z.; Sun, C.; Fan, J.G. Folic acid attenuates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis via deacetylase SIRT1-dependent restoration of PPARα. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2203–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Singh, B.K.; Zhou, J.; Tikno, K.; Widjaja, A.; Sandireddy, R.; Arul, K.; Abdul Ghani, S.A.B.; Bee, G.G.B.; Wong, K.A.; et al. Vitamin B12 and folate decrease inflammation and fibrosis in NASH by preventing syntaxin 17 homocysteinylation. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ye, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Associations of different serum folate forms with indices of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and advanced fibrosis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 17, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCHS. About the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; NCHS: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2017.
- NCHS. Information for Participants. Informed Consent; NCHS: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020.
- Zhao, H.; Kang, X. Associations of Depression Score with Dialkyl Phosphate Metabolites in Urine: A Cross-Sectional Study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Gurusamy, K.S.; Ntaoula, S.; Cholongitas, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Burroughs, A.K. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Ong, M.F.; Martens, S.; Sarrazin, C.; Bojunga, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Herrmann, E. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: A meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Tu, X.; Duan, W. Associations of depression score with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis. J. Affect Disord. 2023, 334, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilis, P.; Vordoni, A.; Kalaitzidis, R.G. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017–2020: Epidemiology, Clinical Correlates, and the Role of Diagnostic Scores. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, P.F.; Korevaar, T.I.M.; Mustieles, V.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Messerlian, C. Relationship between Blood Trihalomethane Concentrations and Serum Thyroid Function Measures in U.S. Adults. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14087–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazili, Z.; Whitehead, R.D., Jr.; Paladugula, N.; Pfeiffer, C.M. A high-throughput LC-MS/MS method suitable for population biomonitoring measures five serum folate vitamers and one oxidation product. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4549–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCHS. 2005–2006 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies. Volatile Organice Compounds—Blood and Related Questionnaire Items (VOCWB_D); NCHS: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2011.
- Ong, K.L.; Allison, M.A.; Cheung, B.M.; Wu, B.J.; Barter, P.J.; Rye, K.A. Trends in C-reactive protein levels in US adults from 1999 to 2010. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1430–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Fei, Y.; Yuan, L.; Li, K.; Xu, Q.; Cao, X.; Su, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of the mediating role of BMI in associations of different folate forms with hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis in adolescents in the USA: Results from the NHANES 2017-2018. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1273580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniz, C.; Bertinato, J.F.; Lucena, M.R.; De Carli, E.; Amorim, P.M.D.S.; Gomes, G.W.; Palchetti, C.Z.; Figueiredo, M.S.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Fazili, Z.; et al. A Daily Dose of 5 mg Folic Acid for 90 Days Is Associated with Increased Serum Unmetabolized Folic Acid and Reduced Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity in Healthy Brazilian Adults. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tun, H.M.; Zhang, D.; Chau, H.T.; Huang, F.Y.; Kwok, H.; Wong, D.K.; Mak, L.Y.; Yuen, M.F.; Seto, W.K. Alleviation of Hepatic Steatosis: Dithizone-Related Gut Microbiome Restoration During Paneth Cell Dysfunction. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 813783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, R.P.; Kelly, K.B.; Al Rajabi, A.; Jacobs, R.L. Novel insights on interactions between folate and lipid metabolism. Biofactors 2014, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Gallego-Escuredo, J.M.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Domingo, P.; Moncada, R.; Valentí, V.; Salvador, J.; Giralt, M.; Villarroya, F.; et al. FGF19 and FGF21 serum concentrations in human obesity and type 2 diabetes behave differently after diet- or surgically-induced weight loss. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Huo, J.; Huang, J.; Shangguan, S.; Li, S.; Zou, J.; Bao, Y.; et al. The effect of folic acid deficiency on FGF pathway via Brachyury regulation in neural tube defects. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4688–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, L.K.; Wu, N.; Wang, P.; Hwang, S.Y.; Siow, O.K. Folic acid supplementation attenuates high fat diet induced hepatic oxidative stress via regulation of NADPH oxidase. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 90, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sid, V.; Wu, N.; Sarna, L.K.; Siow, Y.L.; House, J.D.; O, K. Folic acid supplementation during high-fat diet feeding restores AMPK activation via an AMP-LKB1-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R1215-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, M.; Huang, L.; Yang, J.; Chiang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: A next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcena-Varela, M.; Colyn, L.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G. Epigenetic Mechanisms in Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation During Liver Fibrosis and Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepfish, M.; Gross, T.; Vugman, M.; Afratis, N.A.; Havusha-Laufer, S.; Brazowski, E.; Solomonov, I.; Varol, C.; Sagi, I. LOXL2 Inhibition Paves the Way for Macrophage-Mediated Collagen Degradation in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, A.; Qi, T. Diagnostic significance of serum type IV collagen (IVC) combined with aspartate aminotransferase (AST)/alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ratio in liver fibrosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LLOD (nmol/L) | |
|---|---|
| serum 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-mTHF) | 0.13 |
| serum folic acid | 0.14 |
| serum 5-formyltetrahydrofolate (5-fTHF) | 0.20 |
| serum tetrahydrofolate (THF) | 0.25 |
| serum 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate (5,10-mTHF) | 0.20 |
| serum MeFox | 0.10 |
| Characteristics | Total (n = 7447) | Hepatic Fibrosis (n = 746) | p a | MAFLD (n = 3840) | p b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age (year) | 48 ± 17 | 55 ± 15 | <0.001 | 51 ± 16 | <0.001 |
| 20–39, % | 36.5 | 18.9 | 27.9 | ||
| 40–59, % | 33.2 | 37.1 | 37.6 | ||
| ≥60, % | 30.3 | 44.0 | 34.5 | ||
| gender, female (%) | 60.2 | 48.8 | <0.001 | 56.0 | <0.001 |
| race/ethnicity (%) | 0.004 | <0.001 | |||
| mexican american | 13.1 | 14.6 | 16.3 | ||
| other hispanic | 9.9 | 11.0 | 10.2 | ||
| non-hispanic white | 33.9 | 36.9 | 35.1 | ||
| non-hispanic black | 24.9 | 24.1 | 23.2 | ||
| other race | 18.2 | 13.4 | 15.3 | ||
| education (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| less than high school | 17.8 | 20.9 | 18.2 | ||
| high school or equivalent | 23.5 | 24.5 | 24.1 | ||
| college or above | 33.5 | 37.1 | 34.9 | ||
| unknown | 25.1 | 17.4 | 22.8 | ||
| PIR (%) | 0.162 | 0.035 | |||
| ≤1 | 19.7 | 20.1 | 18.7 | ||
| 1–3 | 42.4 | 45.3 | 43.8 | ||
| >3 | 37.9 | 34.6 | 37.5 | ||
| BMI (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| underweight | 5.0 | 2.6 | n.a. | ||
| normal weight | 22.3 | 8.5 | 1.7 | ||
| overweight | 30.9 | 17.2 | 34.2 | ||
| obese | 41.8 | 71.8 | 64.1 | ||
| waist circumference (cm) | 99.82 ± 17.34 | 115.83 ± 19.81 | <0.001 | 109.83 ± 14.62 | <0.001 |
| smoking (%) | 0.078 | <0.001 | |||
| never | 55.2 | 59.6 | 61.9 | ||
| current | 44.8 | 40.4 | 38.1 | ||
| drinking (%) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| never | 19.5 | 26.1 | 21.5 | ||
| sometimes | 59.6 | 56.6 | 58.4 | ||
| often | 21.0 | 17.3 | 20.1 | ||
| hepatitis B (%) | 0.9 | 1.7 | <0.001 | 1.1 | 0.074 |
| hepatitis C (%) | 1.6 | 5.0 | <0.001 | 1.7 | 0.742 |
| diabetes mellitus (%) | 15.2 | 37.0 | <0.001 | 24.3 | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 21.21 ± 15.59 | 30.70 ± 25.74 | <0.001 | 24.36 ± 17.67 | <0.001 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 29.63 ± 45.72 | 56.53 ± 110.63 | <0.001 | 34.34 ± 39.37 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.11 ± 8.04 | 5.74 ± 8.68 | <0.001 | 5.18 ± 9.13 | <0.001 |
| CAP (dB/m) | 261.60 ± 62.16 | 307.43 ± 61.85 | <0.001 | 307.47 ± 40.52 | <0.001 |
| LSM (kPa) | 5.86 ± 5.01 | 14.83 ± 12.14 | <0.001 | 6.58 ± 5.48 | <0.001 |
| Hepatic Fibrosis (95% CI, %) | MAFLD (95% CI, %) | |
|---|---|---|
| total estimation | 10.0 (9.3–10.7) | 51.6 (50.4–52.7) |
| gender | ||
| male | 5.4 (4.9–5.9) | 31.9 (30.6–33.2) |
| female | 5.2 (4.6–5.7) | 37.3 (36.1–38.6) |
| race/ethnicity | ||
| mexican american | 1.6 (1.3–1.9) | 14.8 (13.7–15.8) |
| other hispanic | 1.2 (0.9–1.5) | 9.8 (8.9–10.7) |
| non-hispanic white | 3.9 (3.5–4.4) | 27.2 (26.0–28.4) |
| non-hispanic black | 2.6 (2.2–3.0) | 19.8 (18.6–20.9) |
| other race | 1.5 (1.2–1.8) | 14.0 (12.9–15.0) |
| PIR | ||
| ≤1 | 1.9 (1.6–2.2) | 14.9 (13.9–16.0) |
| 1–3 | 4.2 (3.7–4.7) | 29.1 (27.8–30.3) |
| >3 | 3.2 (2.8–3.7) | 26.0 (24.8–27.2) |
| BMI | ||
| underweight | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | n.a. |
| normal weight | 0.9 (0.7–1.1) | 1.8 (1.3–2.2) |
| overweight | 1.8 (1.5–2.2) | 26.6 (25.4–27.8) |
| obese | 7.3 (6.7–7.9) | 40.5 (39.3–41.7) |
| smoking | 2.1 (1.8–2.4) | 14.6 (13.5–15.7) |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| hepatic fibrosis | ||||||
| 5-mTHF | 0.98 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 | 0.98 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 |
| folic acid | 0.89 (0.85–0.93) | <0.001 | 0.91 (0.87–0.95) | <0.001 | 0.94 (0.89–1.00) | 0.043 |
| 5-fTHF | 0.37 (0.01–10.77) | 0.560 | 0.43 (0.02–9.31) | 0.587 | 0.09 (0.00–666.60) | 0.599 |
| THF | 3.03 (2.41–3.80) | <0.001 | 2.40 (1.91–3.02) | <0.001 | 2.41 (1.65–3.52) | <0.001 |
| 5,10-mTHF | 2.47 (0.54–11.32) | 0.246 | 2.83 (0.61–13.08) | 0.184 | 2.04 (0.21–20.21) | 0.542 |
| MeFox | 1.05 (1.02–1.09) | 0.002 | 1.04 (1.00–1.07) | 0.045 | 0.99 (0.92–1.08) | 0.880 |
| MAFLD | ||||||
| 5-mTHF | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 0.005 |
| folic acid | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.054 | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.102 | 0.98 (0.95–1.01) | 0.260 |
| 5-fTHF | 0.03 (0.00–7.99) | 0.215 | 0.01 (0.00–3.60) | 0.127 | 0.00 (0.00–1.70) | 0.067 |
| THF | 2.68 (2.06–3.49) | <0.001 | 2.50 (1.92–3.26) | <0.001 | 1.76 (1.27–2.43) | 0.001 |
| 5,10-mTHF | 0.69 (0.14–3.35) | 0.644 | 0.71 (0.15–3.46) | 0.670 | 2.55 (0.34–19.12) | 0.362 |
| MeFox | 1.06 (1.00–1.12) | 0.035 | 1.04 (0.99–1.10) | 0.147 | 0.98 (0.91–1.05) | 0.487 |
| Folate Forms (nmol/L) | Total (n = 7447) | Hepatic Fibrosis (n = 746) | p a | MAFLD (n = 3840) | p b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-mTHF | 30.90 (21.10, 46.60) | 30.40 (21.00, 43.50) | 0.091 | 29.95 (20.50, 45.70) | <0.001 |
| folic acid | 0.60 (0.46, 0.89) | 0.61 (0.48, 0.90) | 0.415 | 0.61 (0.46, 0.90) | 0.123 |
| 5-fTHF | 0.14 (0.14, 0.14) | 0.14 (0.14, 0.14) | 0.815 | 0.14 (0.14, 0.14) | 0.438 |
| THF | 0.66 (0.47, 0.92) | 0.76 (0.52, 1.04) | <0.001 | 0.70 (0.50, 0.96) | <0.001 |
| 5,10-mTHF | 0.14 (0.14, 0.14) | 0.14 (0.14, 0.14) | 0.072 | 0.14 (0.14, 0.14) | <0.001 |
| MeFox | 1.23 (0.76, 2.10) | 1.45 (0.90, 2.49) | <0.001 | 1.31 (0.80, 2.24) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Fan, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kang, X. The Associations of Serum Folate Forms with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolites 2025, 15, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060370
Zhao H, Fan W, Yan Y, Liu Y, Kang X. The Associations of Serum Folate Forms with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolites. 2025; 15(6):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060370
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hai, Wei Fan, Yan Yan, Yuxing Liu, and Xuejun Kang. 2025. "The Associations of Serum Folate Forms with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study" Metabolites 15, no. 6: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060370
APA StyleZhao, H., Fan, W., Yan, Y., Liu, Y., & Kang, X. (2025). The Associations of Serum Folate Forms with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolites, 15(6), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15060370






