Metabolomic Analysis Revealed the Differences in Metabolites Between Three Different Sugarcane Stems and Leaves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Principal Components and Fractions of Metabolites in Different Sugarcane Varieties
2.2. Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis
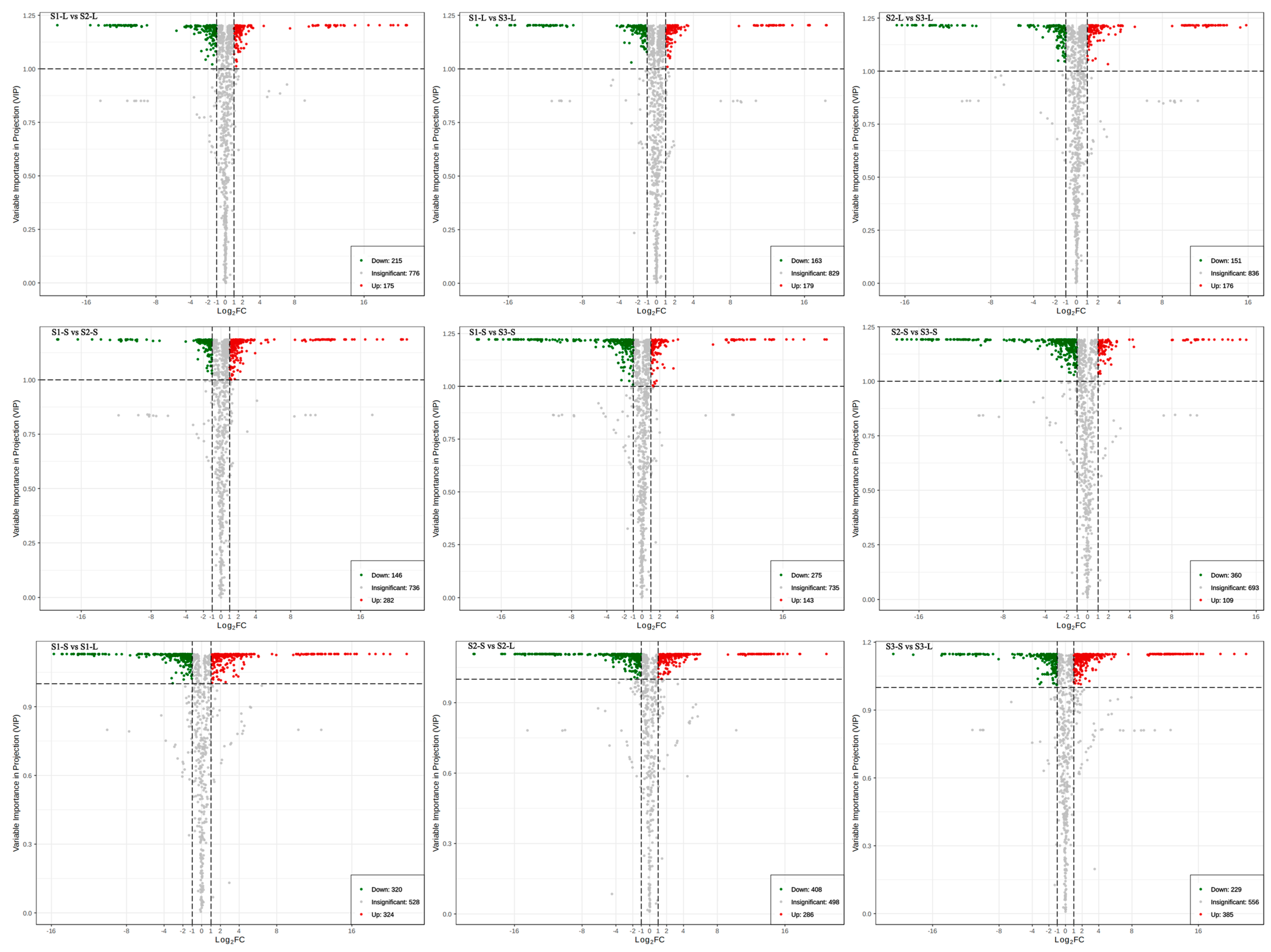
2.3. Differential Metabolite Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Top 20 Metabolites After Multiple Comparisons Across Groups
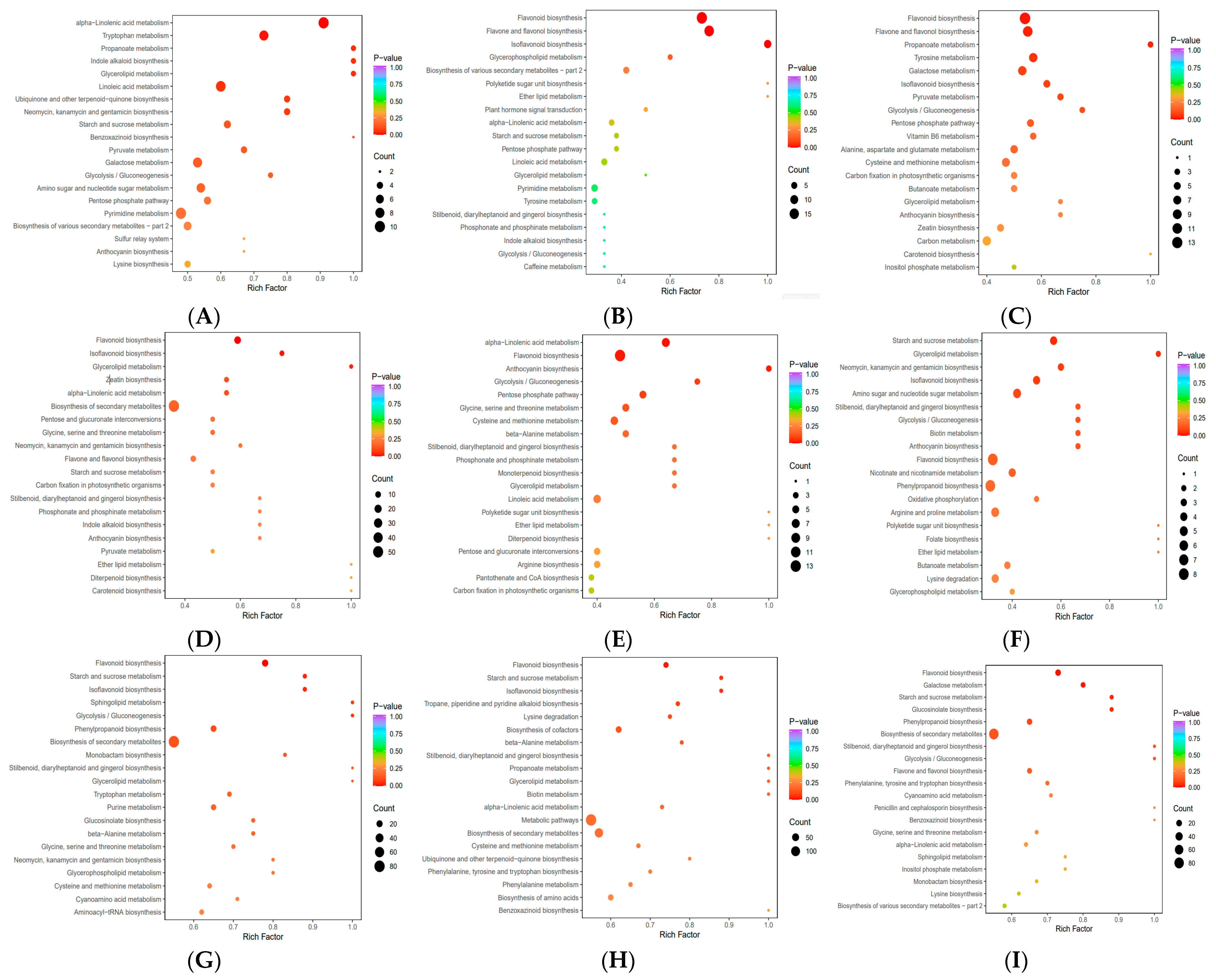
2.5. KEGG Annotation and Enrichment Analysis
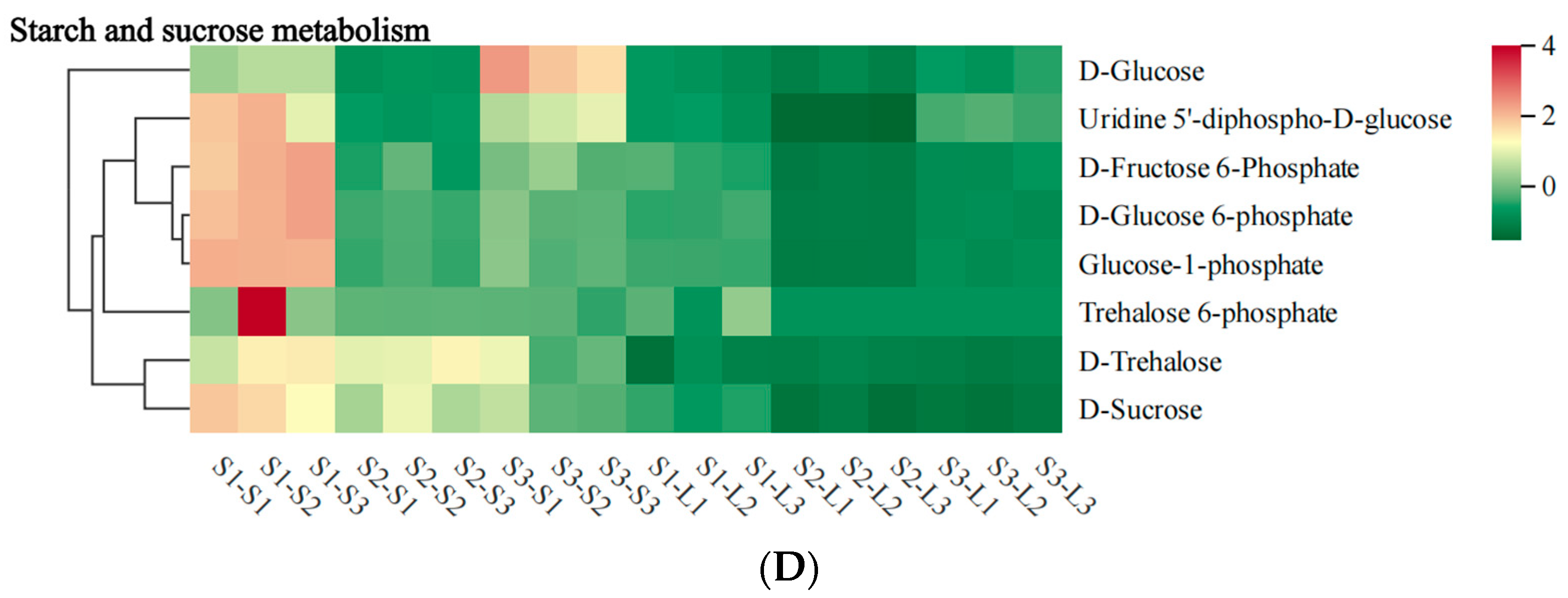
2.6. Heat Map Analysis of Metabolites in Major Metabolic Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction
4.3. UPLC Conditions
4.4. Qualitative and Quantitative Metabolite Analyses
4.5. Sample Quality Control Analysis
4.6. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hossain, M.I.; Ahmad, K.; Siddiqui, Y.; Saad, N.; Rahman, Z.; Haruna, A.O.; Bejo, S.K. Current and Prospective Strategies on Detecting and Managing Colletotrichum falcatum Causing Red Rot of Sugarcane. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.N.; Qiu, Y.S. Research on the development status of sugarcane industry in China. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2017, 44, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukam, A.; Mamphweli, S.; Reddy, P.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, O. Pre-processing of sugarcane bagasse for gasification in a downdraft biomass gasifier system: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 775–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alokika, U.; Anu, U.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Singh, B. Cellulosic and hemicellulosic fractions of sugarcane bagasse: Potential, challenges and future perspective. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Zeng, L.; Chen, P.; Liu, C. Discovery of genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis from the rind and pith of three sugarcane varieties using integrated metabolic profiling and RNA-seq analysis. BMC. Plant. Biol. 2021, 21, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Deng, J.C.; Zhao, C.C.; Zhang, J.L.; Hou, X.T. Research Progress of Chemical Components and Pharmacological Activities of Saccharum Sinensis Roxb. Leaf. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2016, 12, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Lal1, U.R.; Mukhtar, H.M.; Singh, P.S.; Shah, G.; Dhawan, R.K. Phytochemical profile of sugarcane and its potential health aspects. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, J.; Simipillai, S.S. Sugarcane in therapeutics. J. Herb. Med. Toxicol. 2010, 4, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, A.; Girón, L.M.; Alvarado, S.R.; Torres, M.F. Screening of antimicrobial activity of plants popularly used in Guatemala for the treatment of dermatomucosal diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1987, 20, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, S. The antibiotic activity and mechanisms of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) bagasse extract against food-borne pathogens. Food. Chem. 2015, 185, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, I.D.; Baker, J.M.; Ward, J.L.; Beale, M.H.; Creste, S.; Cavalheiro, A.J. Metabolite profiling of sugarcane genotypes and identification of flavonoidglycosides and phenolic acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4198–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Su, J.P.; Fang, F.X.; Tang, Y.; Huang, X.F. Extraction and isolation of Polysaccharide from sugarcane leaves and its antitumor effect in vitro. J. Clin. Ration. Drug. Use 2012, 5, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.Y.; Xian, W.; Liang, Q.; Su, S.Q.; Yang, R.Z. Extraction and antioxidant activity of ploysaccharide from sugarcane leaves. Acta. Southwest. Chin. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 25, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Shen, J.F.; Zhao, M.M. Antioxidant and antitumor activities ofpolyphenol compounds from sugarcane top. Sci. Technol. Food. Ind. 2015, 36, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.J.; Ana, L.O.; Sílvia, S.P.; Pintado, M.; Madureira, A.R. Potential of sugarcane extracts as cosmetic and skincare ingredients. Ind. Crop Prod. 2021, 169, 113625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.J.; Liu, J.M.; Zhang, R.T.; Wang, D.Q.; Xu, Y.Y. Main components in different varieties of Xihuangcao by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and UPLC-DAD. Chin. J. Chin. Materia Med. 2022, 47, 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.N.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, F.S.; Fan, Q.; Luo, J.; AN, P.K.; Zhang, Y.L.; LI, Q.; Peng, T. Metabonomics analysis on different varieties of angelica sinensis based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2020, 26, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yang, D.; Liu, S.S.; Teng, F.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Xu, G.B.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, Z.M.; Chen, L.M.; et al. Comparison of chemical components between aerial and underground parts of Coptis chinensis based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS E technology. Chin. J. Chin. Materia Med. 2022, 47, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.P.; Chen, Z.T.; Yu, P.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Duh, P.D. Identification of bioactive compounds and comparison of apoptosis induction of there varieties of sugarcane leaves. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, M.D.; Stojanovska, L.; Feehan, J.; Nurgali, K.; Donald, E.L.; Plebanski, M. Anti-cancer effects of polyphenol-rich sugarcane extract. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucio-Noble, D.; Kautto, L.; Krisp, C.; Ball, M.S.; Molloy, M.S. Polyphenol extracts from dried sugarcane inhibit inflammatory mediators in an in vitro colon cancer model. J. Proteom. 2018, 177, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.G. Strategic significance and basic ideas of Medicinal Research on crop waste. Guangxi. Trad. Chin. Med. 2010, 33, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Imm, J.Y. Antiobesity effect of tricin, a methylated cereal flavone, in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9989–9994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.Z.; Chan, Y.W.; Ho, W.S. Identification and growth inhibitory activity of the chemical constituents from Imperata cylindrical aerial part ethyl acetate extract. Molecules 2018, 23, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; Bang, M.H.; Jo, S.K.; Jhee, K.H.; Yang, S.A. Protection against UVB-induced damages in human dermal fibroblasts: Efficacy of tricin isolated from enzyme-treated Zizania latifolia extract. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.L.; Shen, N.; Yuan, X.; Dang, J.; Shao, Y.; Mei, L.J. Two-dimensional chromatography based on on-line HPLC-DPPH bioactivityguided assay for the preparative isolation of analogue antioxidant compound from Arenaria kansuensis. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1046, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.G.; Yan, Z.; He, H.J. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of luteolin in-vivo. J. Guangdong. Med. Coll. 2009, 27, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.Q. Effect of luteolin on blood lipid, blood glucose and oxidative stress index of hyperlipidemia rats. Acta Chin. Med. 2014, 29, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.B.; Wang, W.J.; Xu, C.; Xie, Y.J.; Wang, X.R.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, J.M.; Huang, M.; Xie, C.; Liu, P.; et al. Luteolin and its derivative apigenin suppress the inducible PD-L1 expression to improve anti-tumor immunity in KRAS-mutant lung cancer. Cancer. Lett. 2021, 515, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Gao, X.; Sun, T.; YU, L.; Guo, Y.; Hong, W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, M. The antimicrobial activity of luteolin against four bacteriainvitro. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 37, 1558–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, K. Luteolin inhibits herpes simplex virus 1 infection by activating cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase-mediated antiviral innate immunity. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, A.A.; Chen, S.Z.; Ren, L.B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Pei, T.L.; Jia, B.; Gong, D.Y. Luteolin Inhibited the Self-Renewal and Altered the Polarization of Primary Alveolar Macrophages. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2022, 18, 3517020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari-Garageshlaghi, F.; Hashtarkhani, F.; Sor-aya, H.; Malekinejad, H. Quercetin protectded from aluminum phosphide-induced acute and subacute cardio-and hepatotoxicity in Rats. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 3513–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Zhou, D.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; He, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Quercetin suppresses human glioblastoma migration and invasion via GSK3β/β-catenin/ZEBI signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 963614. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Nikitkova, A.; Abdelsalam, H.; Li, J.Y.; Xiao, H. Activity of quercetin and kemferol against Streptococcus mutans biofilm. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2019, 98, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Assessing the anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin using network pharmacology and in vitro experiments. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ji, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Shin, D.H.; Park, H.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, I.K.; Yun, B.S.; Jeong, T.S. Soy leaf extract containing kaempferol glycosides and pheophorbides improves glucose homeostasis by enhancing pancreatic β-cell function and suppressing hepatic lipid accumulation in db/db mice. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2015, 63, 7198–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Guo, Y.Y.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, F.Y.; Liu, B.; Shen, C.S. Kaempferol potentiates the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to erlotinib via inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and epidermal growth factor receptor. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1587–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, X.R.; Yang, Z.H.; Suo, F.Y.; Yao, S.K. An exploration on mechanisms of Qinggan Huayu Granule in treating liver cancer based on network pharmacology. Chin. Trad. Herb. Drug. 2021, 52, 2039–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, X.H.; Sun, Z.; Bao, X.Y.; Xue, L.P.; Xu, Z.M.; Dong, P.F.; Xia, J.L. Study on the mechanism of Shenkang injection in the treatment of chronic renal failure based on the strategy of “Network pharmacology-Molecular docking-Key target validation”. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarero, S.; Cañas, A.I.; Nousiainen, P.; Record, E.; Lomascolo, A.; MartÍnez, M.J.; Martínez, Á.T. P-hydroxycinnamic acids as natural mediators for laccase oxidation of recalcitrant compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6703–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.O.; Min, K.J.; Kwon, T.K.; Um, B.H.; Moreau, R.A.; Choi, S.W. Anti-inflammatory activity of hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives isolated from corn bran in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated raw 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pragasam, S.J.; Venkatesan, V.; Rasool, M. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effect of p-coumaric acid, a common dietary polyphenol on experimental inflammation in rats. Inflammation 2013, 36, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzaiene, N.N.; Jaziri, S.K.; Kovacic, H.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Ghedira, K.; Luis, J. The effects of caffeic, coumaric and ferulic acids on proliferation, superoxide production, adhesion and migration of human tumor cells in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 766, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.A.; Kang, S.I.; Shin, H.S.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, H.C.; Kim, S.J. P-Coumaric acid modulates glucose and lipid metabolism via AMP-activated protein kinase in L6 skeletal muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 432, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Zhu, X.L.; Li, W.C.; Xu, W.R.; Li, X.J. Research progress on the pharmacological effects of caffeic acid and its derivatives, caffeic acid phenethyl ester. Chin. Pharm. J. 2013, 48, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.H.; Ou-yang, J.P. Pharmacological actions of sodium ferulate in cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Drug. Rev. 2005, 23, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taofiq, O.; Gonz’alez-Param’as, A.M.; Martins, A.; Barreiro, M.F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Mushrooms extracts and compounds in cosmetics, cosmeceuticals and nutricosmetics-a review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 90, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleno, S.A.; Martins, A.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Bioactivity of phenolic acids: Metabolites versus parent compounds: A review. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taofiq, O.; Gonz’alez-Param’as, A.M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; McPhee, D.J. Hydroxycinnamic acids and their derivatives: Cosmeceutical significance, challenges and future perspectives, a review. Molecules 2017, 22, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Petrillo, A.; Gonz’alez-Param’as, A.M.; Era, B.; Medda, R.; Pintus, F.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Fais, A. Tyrosinase inhibition and antioxidant properties of Asphodelus microcarpus extracts. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, S.; Lin, F.; Xie, Y.; An, J.; Wang, S. Paeonia × suffruticosa Andrews leaf extract and its main component apigenin 7-O-glucoside ameliorate hyperuricemia by inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity and regulating renal urate transporters. Phytomedicine 2023, 118, 154957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Zeng, X.; Li, H.; Li, J. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside alleviates trimethyltin chloride-induced neurodegeneration by maintaining glutamate homeostasis through modulation of the gut microbiota. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.F.; Xu, H.X.; Yin, Z.P.; Chen, J.G.; Zhang, Q.F. The combination effects of quercetin on starch and digestive enzymes reduce postprandial blood glucose in rats. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Xiao, S.; Lv, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wei, D. Metabolic Engineering of Filamentous Fungus Trichoderma reesei for Itaconic Acid Production. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 4716–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yin, H. The Flavonoid Biosynthesis Network in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wu, Q.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Lu, W.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Dissection of genetic architecture for desirable traits in sugarcane by integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 136009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hua, X.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ming, R.; Zhang, J. Evolutionary expansion and functional divergence of sugar transporters in saccharum (S. spontaneum and S. officinarum). Plant J. 2021, 105, 884–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alseekh, S.; Aharoni, A.; Brotman, Y.; Contrepois, K.; D’Auria, J.; Ewald, J.; Ewald, J.C.; Fraser, P.D.; Giavalisco, P.; Hall, R.D.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: A guide for annotation, quan-tification and best reporting practices. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Li, R.; Ren, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, D.; Luo, Y. A comparative metabolomics study of flavonoids in sweet potato with different flesh colors (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam). Food Chem. 2018, 260, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Clowers, B.H.; Moore, R.J.; Zink, E.M. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, XCMS, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Song, Y.; He, J.; Sun, J.; Bai, J.; An, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhan, Q.; Abliz, Z. RRLC-MS/MS-based metabonomics combined with in-depth analysis of metabolic correlation network: Finding potential biomarkers for breast cancer. Analyst 2009, 134, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Xia, J.G. MetaboAnalystR: An R package for flexible and reproducible analysis of metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4313–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, H.J.; Williams, R.; Wilson, A.J.; Wilson, I.D. A metabonomic analysis of plasma from Zucker rat strains using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and pattern recognition. Rapid. Commun. Mass. Sp. 2006, 20, 3295–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, E.A.; Roux, A.; Xu, Y.; Ezan, E.; Junot, C. Analysis of the Human Adult Urinary Metabolome Variations with Age, Body Mass Index, and Gender by Implementing a Comprehensive Workflow for Univariate and OPLS Statistical Analyses. J. Proteome. Res. 2015, 14, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; He, L.; Li, F. Metabolomic Analysis Revealed the Differences in Metabolites Between Three Different Sugarcane Stems and Leaves. Metabolites 2025, 15, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050327
Lou H, Xie L, Wang X, Li X, He L, Li F. Metabolomic Analysis Revealed the Differences in Metabolites Between Three Different Sugarcane Stems and Leaves. Metabolites. 2025; 15(5):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050327
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Hongbo, Linyan Xie, Xianhong Wang, Xianli Li, Lilian He, and Fusheng Li. 2025. "Metabolomic Analysis Revealed the Differences in Metabolites Between Three Different Sugarcane Stems and Leaves" Metabolites 15, no. 5: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050327
APA StyleLou, H., Xie, L., Wang, X., Li, X., He, L., & Li, F. (2025). Metabolomic Analysis Revealed the Differences in Metabolites Between Three Different Sugarcane Stems and Leaves. Metabolites, 15(5), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050327





