Multiple Hits on Cerebral Folate, Tetrahydrobiopterin and Dopamine Metabolism in the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disorder: A Limited Study of Post-Mortem Human Brain Tissues
Abstract
1. Introduction
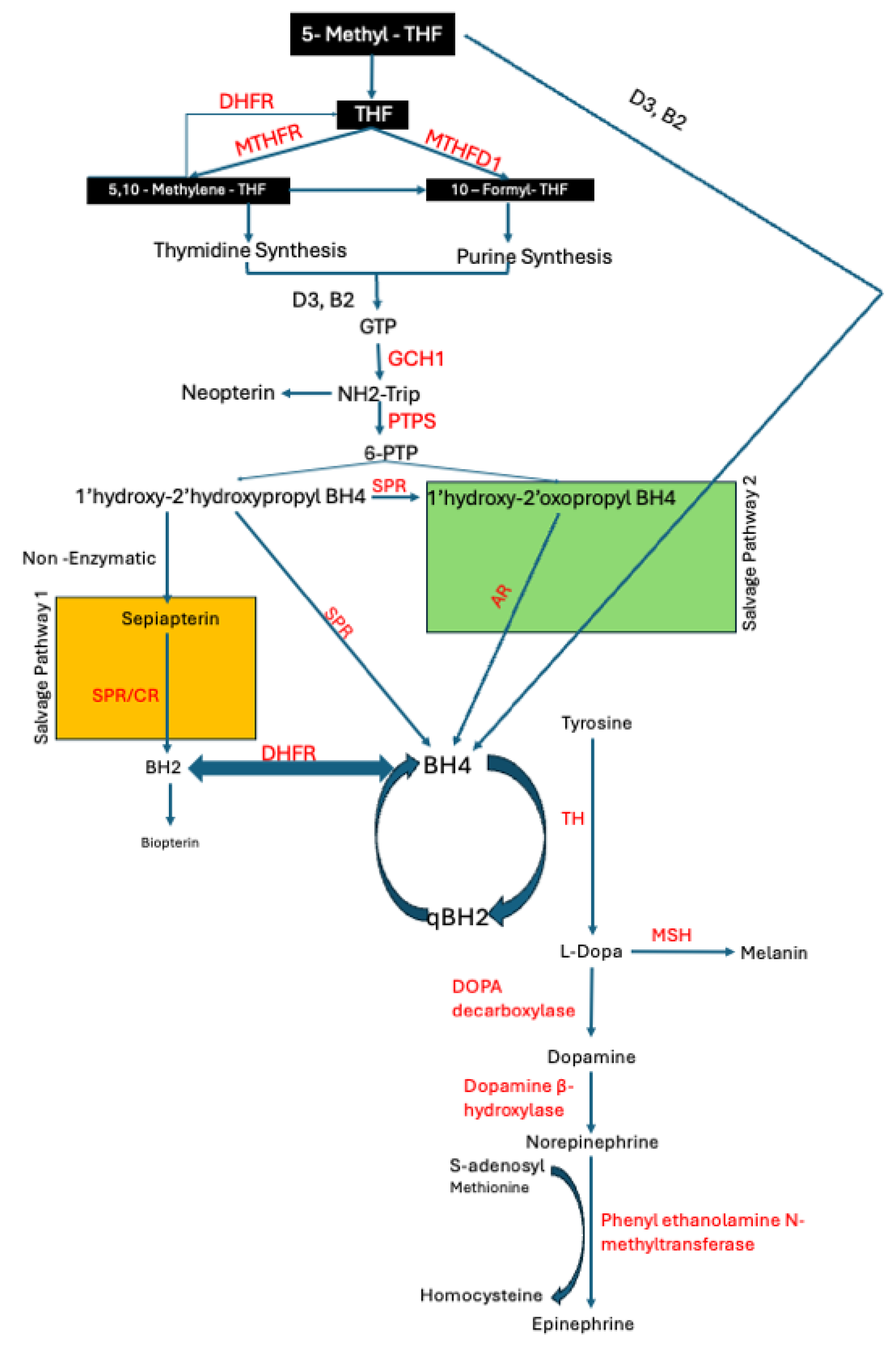
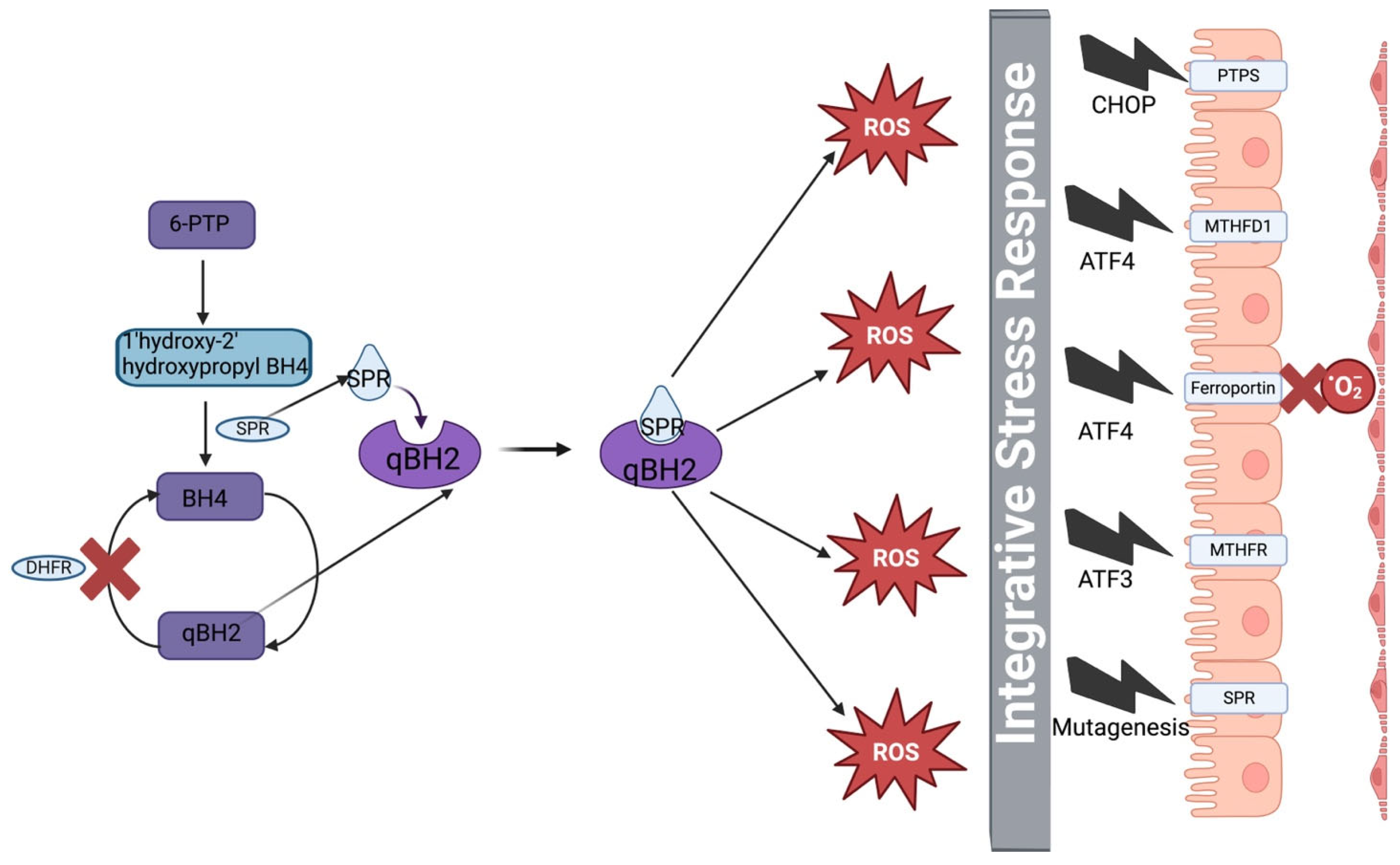
1.1. BH4 Deficiency in PD
1.2. Dopamine Synthesis and ROS-Induced Neurodegeneration
1.3. Iron Dysregulation and Its Contribution to Oxidative Stress
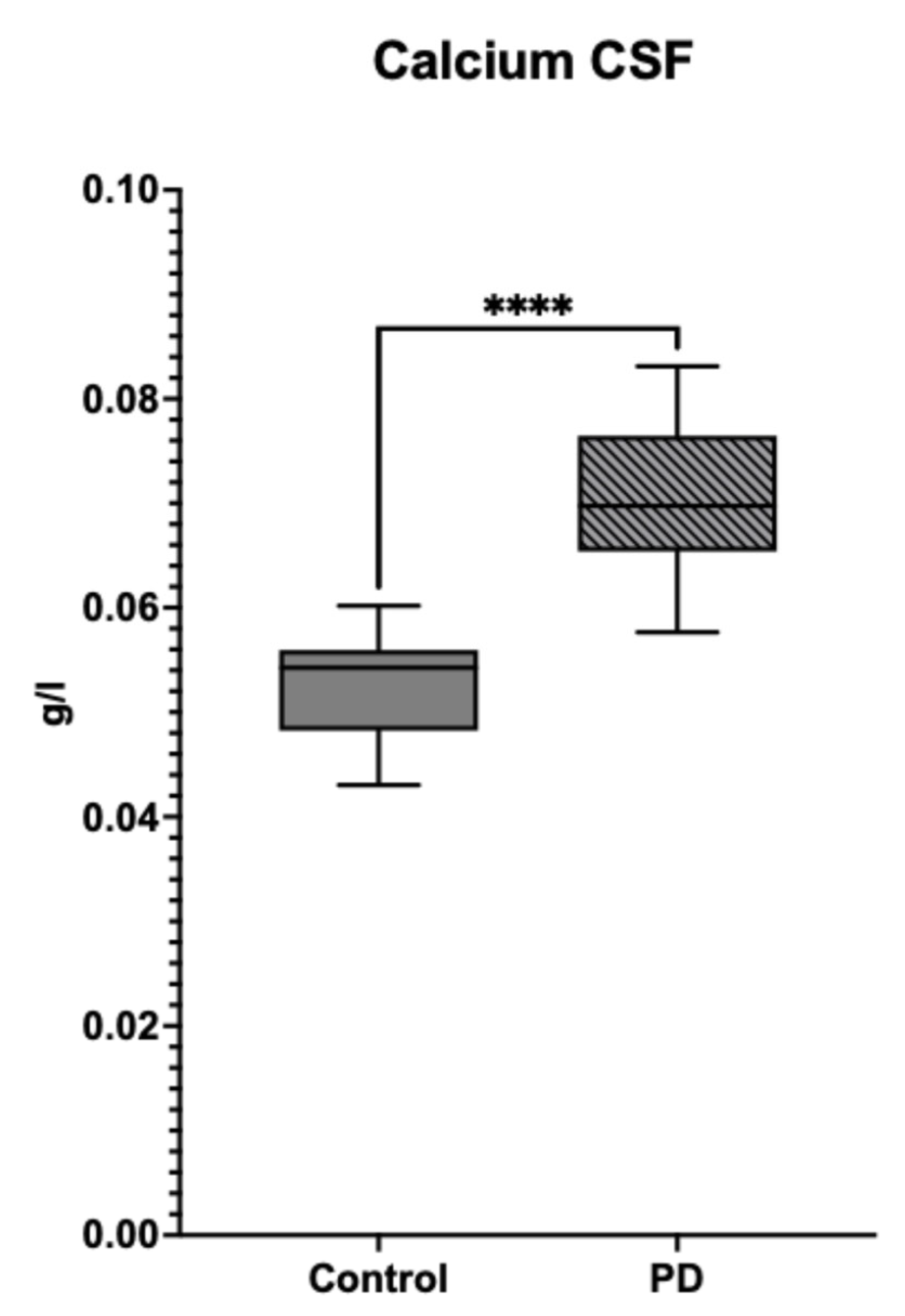
1.4. Role of Calcium in Lewy Body Formation
1.5. Aims and Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Western Blots and Dot Blots
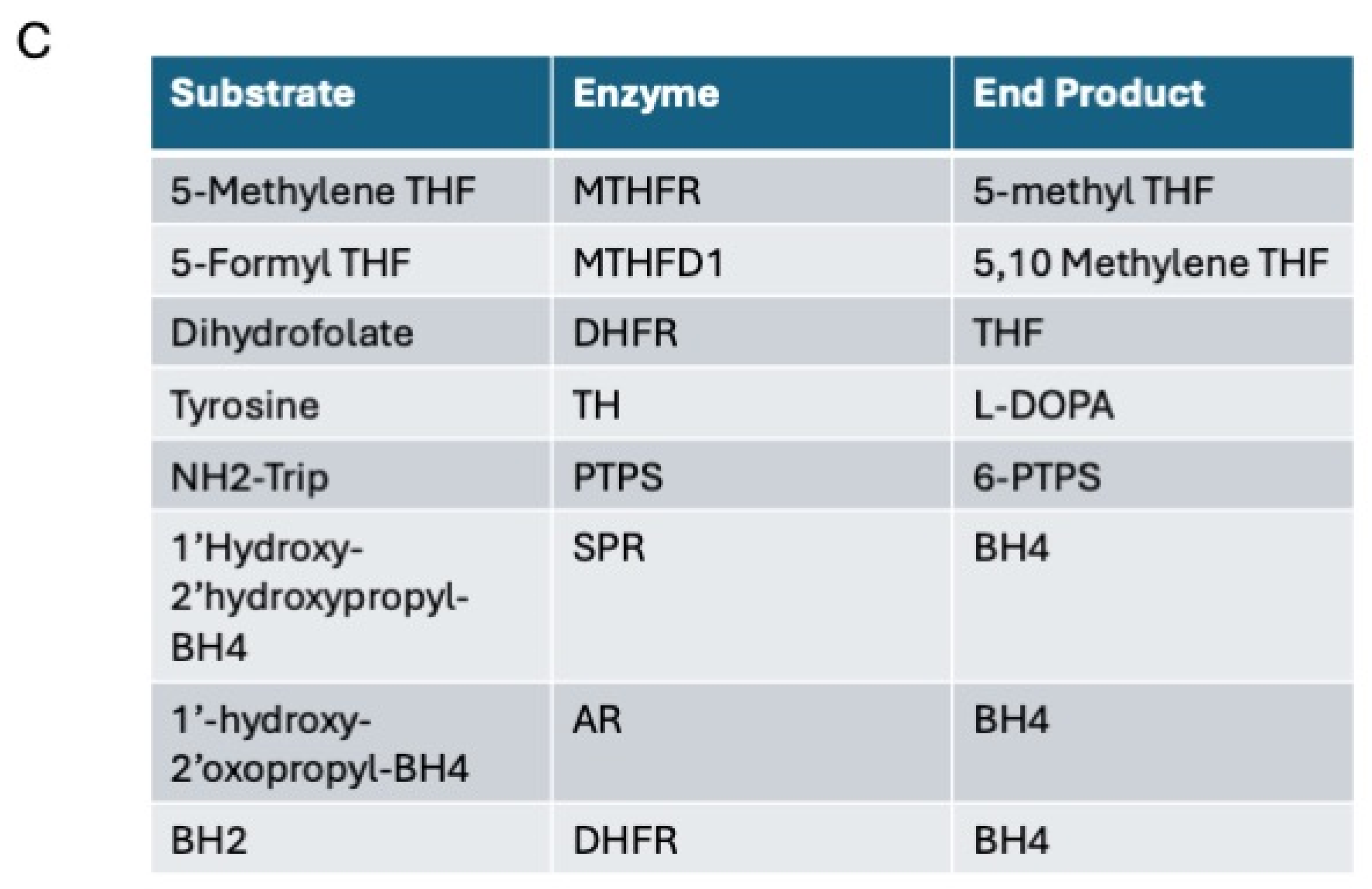
2.3. Enzymatic Assays
2.4. Hydrogen Peroxide Quantification:
2.5. Calcium Quantification
2.6. Parkinson’s Patient Involvement Focus Group
3. Results
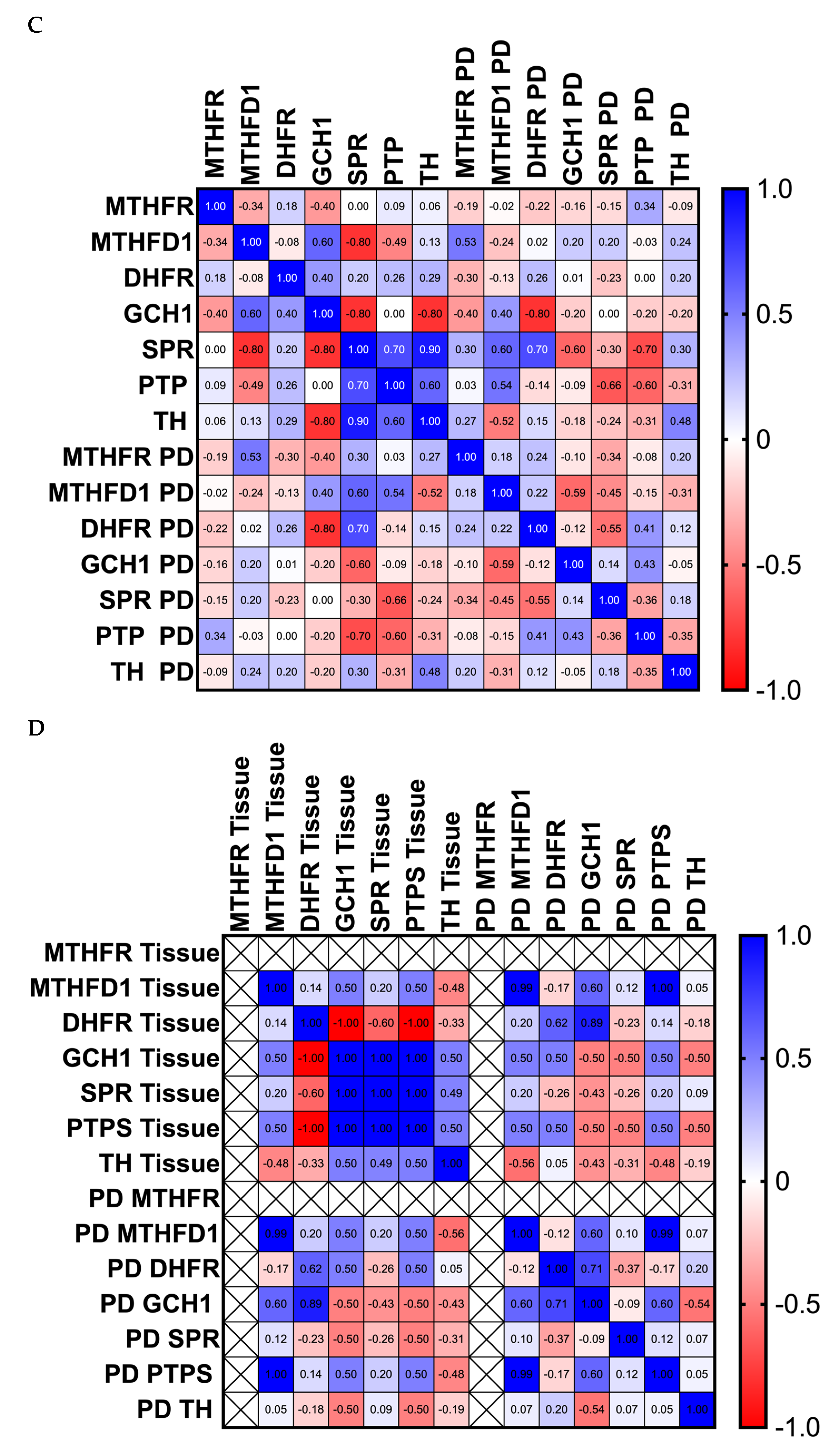
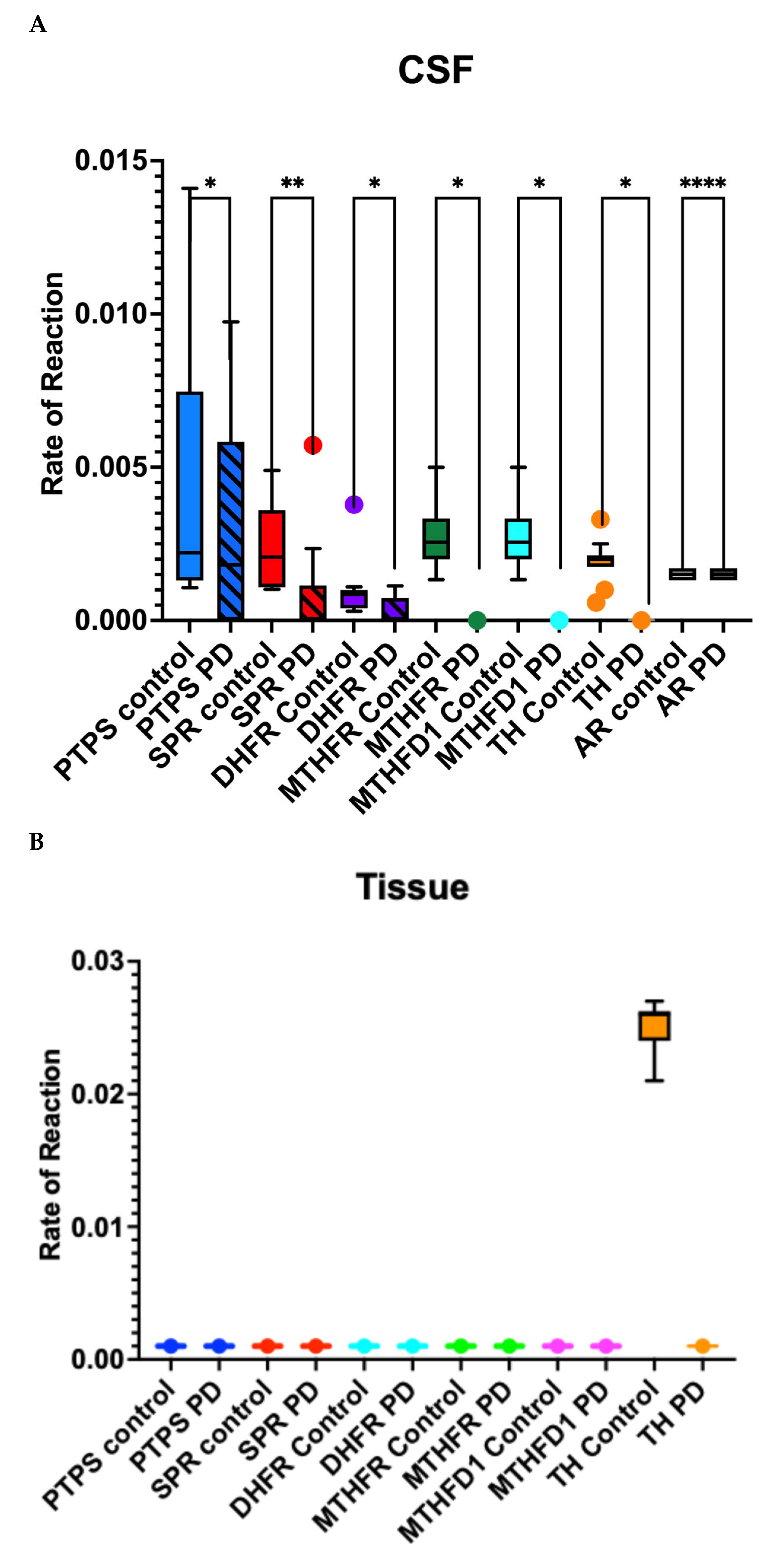
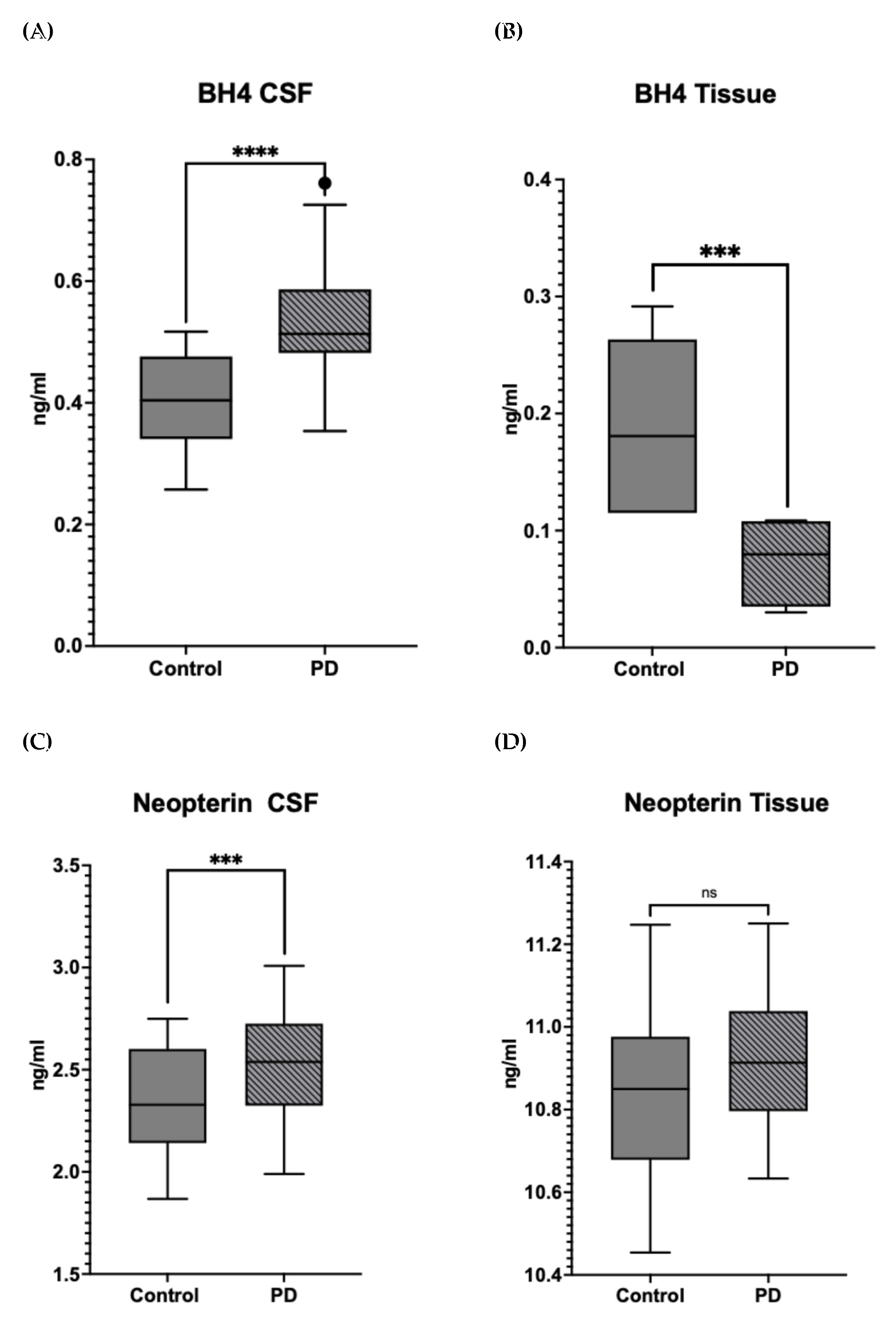
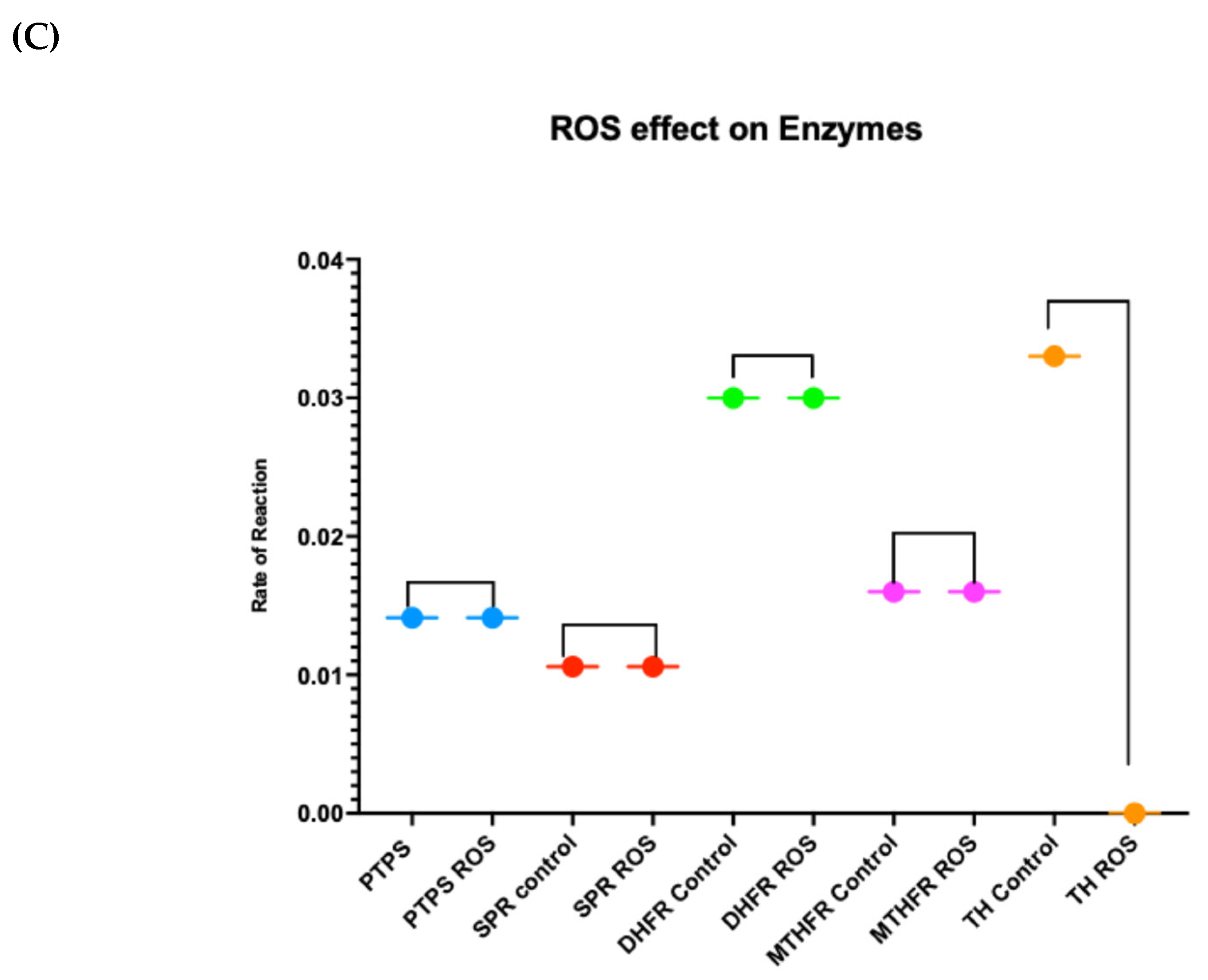
3.1. Differences in the Level and Activity of Key Folate and BH4 Enzymes in PD Samples
3.2. Effects of Folate Metabolism on PD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Parkinson’s Disorder |
| GCH1 | GTP-CYCLOHYDROXYLASE 1 |
| SPR | SEPIAPTERIN REDUCTASE |
| TH | TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE |
| MAOA | MONOAMINE OXIDASE A |
| NOS | NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE |
| ROS | REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES |
| BH4 | TETRAHYDROBIPTERIN |
| MTHFR | METHYL TETRAHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE |
| MTHFD1 | METHYLENE TETRAHYDROFOLATE DEHYDROGENASE 1 |
| DHFR | DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE |
| CSF | CEREBROSPINAL FLUID |
| NADPH | NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE |
| PTPS | PYRUVOYL TETRAHYDROPTERIN SYNTASE |
| CP | CHOROID PLEXUS |
| SHMT | SERINE HYDROXYMETHYL TRANSFERASE |
| 5-MTHF | 5-METHYL TETRAHYDROFOLATE |
| BH2 | DIHYDROBIOPTERIN |
| AR | ALPHA REDUCTASE |
| CBR | CARBONYL REDUCTASE |
| TCA | TRICARBOXYL ACID CYCLE |
| THF | TETRAHYDROFOLATE |
| ENT2 | Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 2 |
| ATP | ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE |
References
- Alexander, G.E. Biology of Parkinson’s disease: Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of a multisystem neurodegenerative disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 6, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, A.; Saleem, S.; Akhtar, A.; Ashraf, S.; Ahmed, M.F. Juvenile Parkinson Disease. Cureus 2019, 11, e5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, R.C.; Gorman, M.P.; Lim, M. Autoimmune encephalitis in children: Clinical phenomenology, therapeutics, and emerging challenges. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbin, O.; Montgomery, E.B. Challenges for future theories of Parkinson pathophysiology. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 177, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foffani, G.; Obeso, J.A. A Cortical Pathogenic Theory of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuron. 2018, 99, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchine, J.; McConnell, H. CSF as a Reflection of Cerebral Metabolism. In Cerebrospinal Fluid in Neurology and Psychiatry; McConnell, H., Bianchine, J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kira, R.; Ohga, S.; Takada, H.; Gondo, K.; Mihara, F.; Hara, T. MR choroid plexus sign of iron overload. Neurology 2000, 55, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissing, I.C.; Güttler, F.; Pakkenberg, H.; Lou, H.; Gerdes, A.M.; Lykkelund, C.; Rasmussen, V. Tetrahydrobiopterin and Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1989, 79, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanet, H.; Capuron, L.; Castanon, N.; Calon, F.; Vancassel, S. Tetrahydrobioterin (BH4) Pathway: From Metabolism to Neuropsychiatry. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 591–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lee, S.; Cho, S.-R. Juvenile Parkinsonism with PARK2 Gene Mutation Misdiagnosed as Dopa-responsive Dystonia: A Case Report. Brain Neurorehabil. 2020, 13, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.; Todisco, M.; Zappia, M.; Pacchetti, C.; Fasano, A. Parkinsonism and cerebrospinal fluid disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 433, 120019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostile, G.; Fasano, A.; Zappia, M. Parkinsonism in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Is it time for defining a clinical tetrad? Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 5201–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molde, K.; Söderström, L.; Laurell, K. Parkinsonian symptoms in normal pressure hydrocephalus: A population-based study. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.; Gulyani, S.; Manthripragada, L.; Luciano, M.; Moghekar, A.; Yasar, S. Evaluation of the effect comorbid Parkinson syndrome on normal pressure hydrocephalus assessment. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 207, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Gu, L.; Liu, P.; Cao, J.; Zhang, S. The Critical Role of Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) Metabolism in Modulating Radiosensitivity: BH4/NOS Axis as an Angel or a Devil. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 720632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyland, K.; Surtees, R.A.; Heales, S.J.; Bowron, A.; Howells, D.W.; Smith, I. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of pterins and metabolites of serotonin and dopamine in a pediatric reference population. Pediatr. Res. 1993, 34, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, E.; Channon, K.M. The role of tetrahydrobiopterin in inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 108, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, M.; Latremoliere, A.; Woolf, C.J. Analgesia by inhibiting tetrahydrobiopterin synthesis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, L.; Capel, A.V.; Doddaballapur, D.; Miyan, J. Accumulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid, Ventricular Enlargement, and Cerebral Folate Metabolic Errors Unify a Diverse Group of Neuropsychiatric Conditions Affecting Adult Neocortical Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spix, T.; Gittis, A. Debunking an old theory. eLife 2020, 9, e62694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haavik, J.; Toska, K. Tyrosine hydroxylase and Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 1998, 16, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, L.M.; Sullivan, P.; Dunn, A.R.; Bermejo, M.K.; Fu, R.; Masoud, S.T.; Gregersen, E.; Urs, N.M.; Nazari, R.; Jensen, P.H.; et al. Enhanced tyrosine hydroxylase activity induces oxidative stress, causes accumulation of autotoxic catecholamine metabolites, and augments amphetamine effects in vivo. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 960–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blesa, J.; Trigo-Damas, I.; Quiroga-Varela, A.; Jackson-Lewis, V.R. Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, D.M.; Yorgason, J.T.; Perez, A.W.; Schilaty, N.D.; Williams, B.M.; Watt, R.K.; Steffensen, S.C. Spontaneous Formation of Melanin from Dopamine in the Presence of Iron. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.M.; Kaplan, J. Ferroportin-mediated iron transport: Expression and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routhe, L.J.; Thomsen, M.S.; Moos, T. The Significance of the Choroid Plexus for Cerebral Iron Homeostasis. In Role of the Choroid Plexus in Health and Disease; Praetorius, J., Blazer-Yost, B., Damkier, H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Lorenzo, S.; Ferreira Francisco, D.M.; Vos, R.; van het Hof, B.; Rijnsburger, M.; Schroten, H.; Ishikawa, H.; Beaino, W.; Bruggmann, R.; Kooij, G.; et al. Altered secretory and neuroprotective function of the choroid plexus in progressive multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Gholam Azad, M.; Dharmasivam, M.; Richardson, V.; Quinn, R.J.; Feng, Y.; Pountney, D.L.; Tonissen, K.F.; Mellick, G.D.; Yanatori, I.; et al. Parkinson’s disease: Alterations in iron and redox biology as a key to unlock therapeutic strategies. Redox Biol. 2021, 41, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Ding, C.C.; Sun, T.; Wu, J.; Chen, K.Y.; Zhou, P.; Chi, J.T. The regulation of ferroptosis by MESH1 through the activation of the integrative stress response. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, J.; Crosbourne, I.; Roberge, C.L.; Bossardi-Ramos, R.; Warren, J.S.A.; Matteson, K.; Wang, L.; Jourd’heuil, F.; Borisov, S.M.; Bresnahan, E.; et al. DMT1-dependent endosome-mitochondria interactions regulate mitochondrial iron translocation and metastatic outgrowth. Oncogene 2024, 43, 650–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.T.; Huang, Y.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Chiou, H.-Y.; Chan, L.; Chien, L.-N. Newly Diagnosed Anemia Increases Risk of Parkinson’s disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, E.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H. ER Stress-Mediated Signaling: Action Potential and Ca(2+) as Key Players. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Calcium and neurodegeneration. Aging Cell 2007, 6, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, E.M.; Carmen, V.; Camandola, S. Physiology and pathology of calcium signaling in the brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenschläger, J.; Stephens, A.D.; Fusco, G.; Ströhl, F.; Curry, N.; Zacharopoulou, M.; Michel, C.H.; Laine, R.; Nespovitaya, N.; Fantham, M.; et al. C-terminal calcium binding of α-synuclein modulates synaptic vesicle interaction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihán, P.; Carreras-Sureda, A.; Hetz, C. BCL-2 family: Integrating stress responses at the ER to control cell demise. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, M.J.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D908-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyhan, W.L. Disorders of purine and pyrimidine metabolism. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2005, 86, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Lecca, D.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Ceruti, S. Pathophysiological Role of Purines and Pyrimidines in Neurodevelopment: Unveiling New Pharmacological Approaches to Congenital Brain Diseases. Exp. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2017, 8, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, R.; Shen, S.; Tian, Y.; Burton, C.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chang, C.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Metabolomics Approach Reveals Integrated Metabolic Network Associated with Serotonin Deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazielle, N.; Ghersi-Egea, J.-F. Choroid Plexus in the Central Nervous System: Biology and Physiopathology. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 59, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, M.M.; Nelson, A.B. Circuit Mechanisms of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuron 2019, 101, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, S.D.F.; Villalobos, A.R. GSH and Zinc Supplementation Attenuate Cadmium-Induced Cellular Stress and Stimulation of Choline Uptake in Cultured Neonatal Rat Choroid Plexus Epithelia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Jan, Y.H.; Gray, J.P.; Mishin, V.; Heck, D.E.; Laskin, D.L.; Laskin, J.D. Sepiapterin reductase mediates chemical redox cycling in lung epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19221–19237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calakos, N.; Caffall, Z.F. The integrated stress response pathway and neuromodulator signaling in the brain: Lessons learned from dystonia. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e177833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, A.; Krukowski, K.; Jopson, T.; Zhu, P.J.; Costa-Mattioli, M.; Walter, P.; Rosi, S. Inhibition of the integrated stress response reverses cognitive deficits after traumatic brain injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6420–E6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, H.D. The integrated stress response in metabolic adaptation. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; An, Y.A.; Luo, X.; Deng, Y.; Gillette, T.G.; Scherer, P.E.; Wang, Z.V. Integrated Stress Response Couples Mitochondrial Protein Translation With Oxidative Stress Control. Circulation 2021, 144, 1500–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakos-Zebrucka, K.; Koryga, I.; Mnich, K.; Ljujic, M.; Samali, A.; Gorman, A.M. The integrated stress response. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1374–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Pung, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Meza, M.; Toro, L.; Cai, H. Sepiapterin reductase regulation of endothelial tetrahydrobiopterin and nitric oxide bioavailability. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H331–H339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, C.F. Laboratory Diagnosis of Vitamin B12 and Folate Deficiency: A Guide for the Primary Care Physician. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Liu, G.; Sun, L.; Ding, J. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1 making molecular inroads into the differential vulnerability of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuron subtypes in Parkinson’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2014, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Meléndez-Flores, J.D.; Millán-Alanís, J.M.; de León-Gutiérrez, H.; Rojo-Garza, S.S.; Álvarez-Villalobos, N.A.; Estrada-Bellmann, I. Association of anemia with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review with meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Rev. Mex. Neurociencia 2023, 24, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linscheid, P.; Schaffner, A.; Schoedon, G. Modulation of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase mRNA Stability by Tetrahydrobiopterin in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 243, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekaik, H.; Blaudin de Thé, F.X.; Prochiantz, A.; Fuchs, J.; Joshi, R.L. Dissecting the role of Engrailed in adult dopaminergic neurons—Insights into Parkinson disease pathogenesis. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 3786–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, M.; Malave, L.; Castello, J.; Flajolet, M.; Cenci, M.A.; Friedman, E.; Rebholz, H. CK2 Oppositely Modulates l-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia via Striatal Projection Neurons Expressing D1 or D2 Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11930–11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingle, S.K.; Tumane, R.G.; Jawade, A.A. Neopterin: Biomarker of cell-mediated immunity and potent usage as biomarker in silicosis and other occupational diseases. Indian. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008, 12, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, S. Chapter 3—More than a drainage fluid: The role of CSF in signaling in the brain and other effects on brain tissue. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 146, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortenlöf, N.; Vallius, S.; Karlsson, H.; Ekström, C.; Kristiansson, A.; Holmqvist, B.; Pankratova, S.; Barton, N.; Ley, D.; Gram, M. Choroid plexus extracellular vesicle transport of blood-borne insulin-like growth factor 1 to the hippocampus of the immature brain. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Symptom | Deficiency |
|---|---|
| Change in taste | Zinc and vitamin B |
| Anemia | Folate and B12 |
| Fatigue | Folate/adrenaline |
| Hair loss | Vitamin D and zinc |
| Hearing loss | MTHFD1 and MTHFR |
| Temperature regulation | Low B12, folate and C, changes to ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus |
| Clammy skin | Adrenaline |
| Incontinence | Calcium increase and folate deficiency |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doddaballapur, D.B.; Heyes, D.J.; Miyan, J.A. Multiple Hits on Cerebral Folate, Tetrahydrobiopterin and Dopamine Metabolism in the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disorder: A Limited Study of Post-Mortem Human Brain Tissues. Metabolites 2025, 15, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050307
Doddaballapur DB, Heyes DJ, Miyan JA. Multiple Hits on Cerebral Folate, Tetrahydrobiopterin and Dopamine Metabolism in the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disorder: A Limited Study of Post-Mortem Human Brain Tissues. Metabolites. 2025; 15(5):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050307
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoddaballapur, Dhruti Balakrishna, Derren J. Heyes, and Jaleel A. Miyan. 2025. "Multiple Hits on Cerebral Folate, Tetrahydrobiopterin and Dopamine Metabolism in the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disorder: A Limited Study of Post-Mortem Human Brain Tissues" Metabolites 15, no. 5: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050307
APA StyleDoddaballapur, D. B., Heyes, D. J., & Miyan, J. A. (2025). Multiple Hits on Cerebral Folate, Tetrahydrobiopterin and Dopamine Metabolism in the Pathophysiology of Parkinson’s Disorder: A Limited Study of Post-Mortem Human Brain Tissues. Metabolites, 15(5), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050307








