Comparative Analysis of Metabolite Changes in Huangjiu During Different Aging Periods Using HRMS Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Analysis of Metabolites
2.2.1. UPLC Conditions
2.2.2. Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling
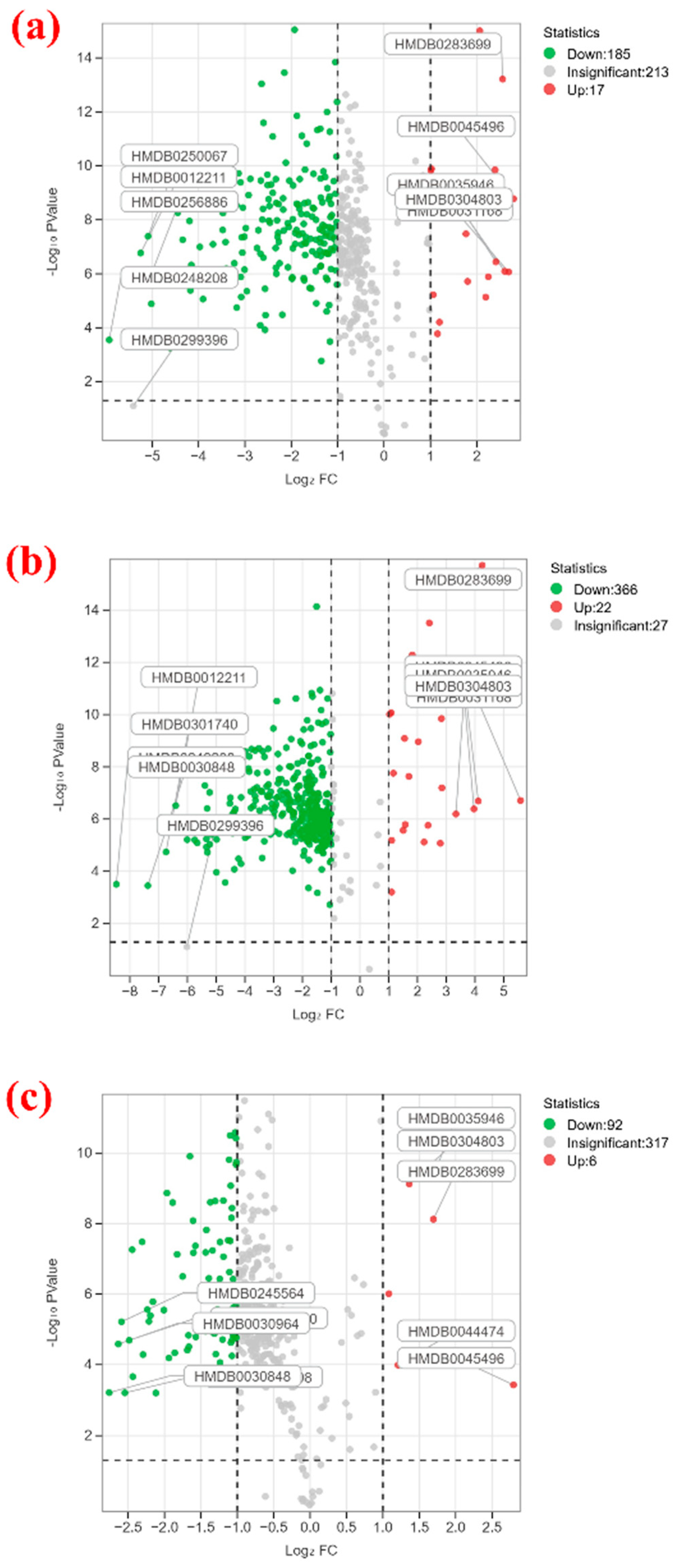
3.2. Analysis of Differential Metabolites
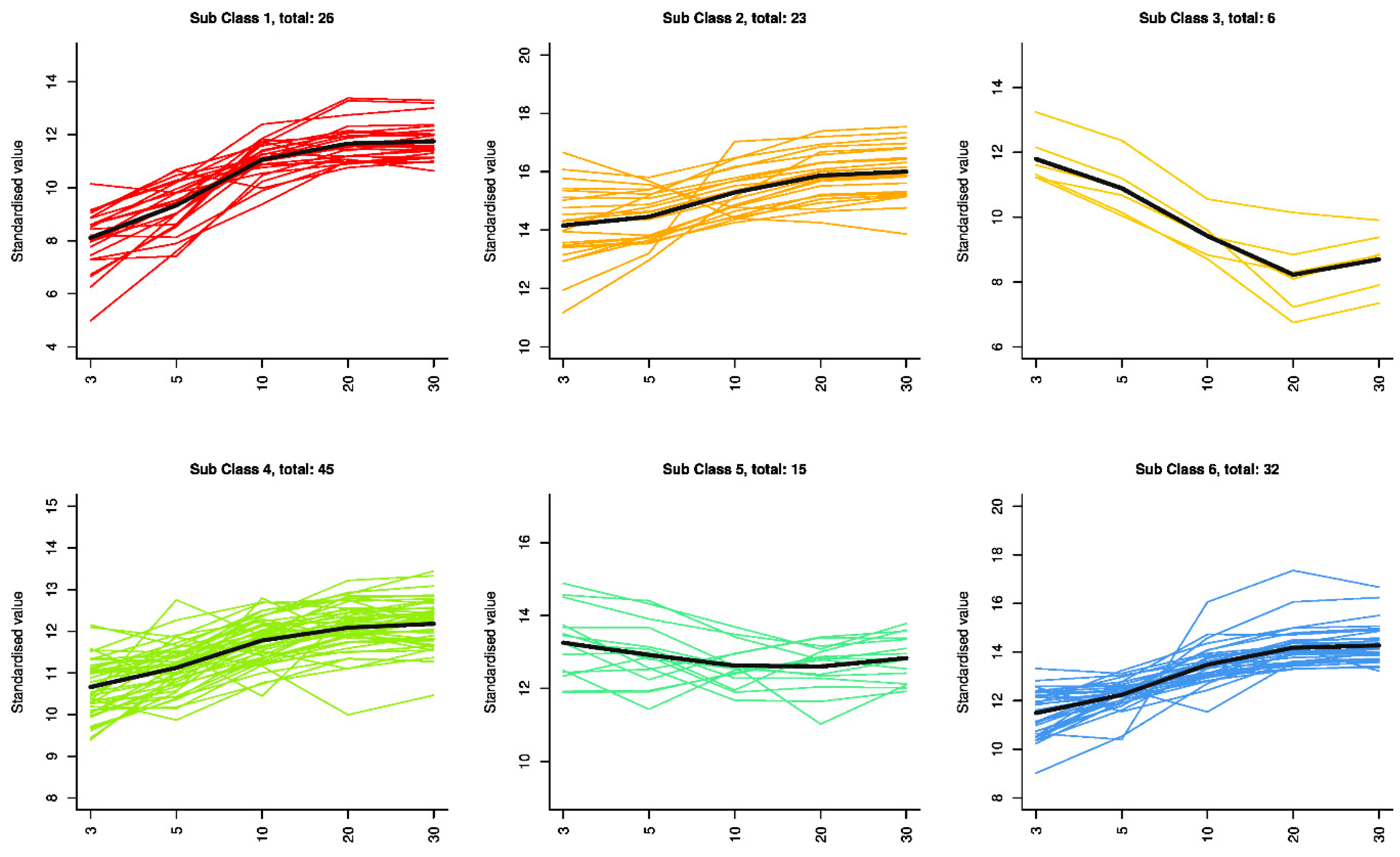
3.3. Prediction of Characteristic Metabolites of Huangjiu Aging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, S.F.; Zeng, W.Z.; Fang, F.; Zhou, J.W.; Du, G.C. The microbiome of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu). Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, E.B.; Long, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.M.; Jin, Z.Y.; Jiao, A.Q. Characterization of volatile flavor compounds in Chinese rice wine fermented from enzymatic extruded rice. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C1476–C1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.Y.; Lee, R.; Huang, J.J.; Yang, J.P.; Henning, S.M.; Hong, X.T.; Heber, D.; Li, Z.P. Quantification of bioactive constituents and antioxidant activity of Chinese yellow wine. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Ma, X.L.; Sun, H.J. Antifatigue and antiaging effects of Chinese rice wine in mice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Song, J.Y.; Zhou, J.D.; Lin, H.; Wu, Z.A.; Liu, N.; Xie, W.Q.; Guo, H.Y.; Chi, J.F. Functional components of Chinese rice wine can ameliorate diabetic cardiomyopathy through the modulation of autophagy, apoptosis, gut microbiota, and metabolites. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 940663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.D.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.H.; Zhao, W.H.; Liu, G.L.; Qian, M.; Li, X.L.; Wang, H. Structural characterization, antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of a polysaccharide from a traditional Chinese rice wine, Guangdong Hakka Huangjiu. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Xia, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Ni, B.; Ni, L.; Wang, G.Q.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; et al. Enhancement of the aromatic alcohols and health properties of Chinese rice wine by using a potentially probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae BR14. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 181, 114748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Hou, L.Z.; Gao, J.; Li, D.F.; Tian, Z.L.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.Z.; Li, S.Y. Metabolomics approaches for the comprehensive evaluation of fermented foods: A review. Foods 2021, 10, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.; Zhao, H.P.; Yin, Z.Y.; Dong, H.Y.; Chu, X.M.; Meng, X.L.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.H. Application and prospect of metabolomics-related technologies in food inspection. Food Res. Int. 2023, 171, 113071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Seo, S.H.; Kim, E.J.; Byun, S.; Na, C.S.; Son, H.S. Changes of microbial community and metabolite in kimchi inoculated with different microbial community starters. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Singh, D.; Lee, C.H. Integrated Metabolomics and Volatolomics for Comparative Evaluation of Fermented Soy Products. Foods 2021, 10, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.R.; Feng, J.; Zhou, R.; Ma, M. Integrated metabolomics and high-throughput sequencing to explore the dynamic correlations between flavor related metabolites and bacterial succession in the process of Mongolian cheese production. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Teng, J.W.; Huang, L.; Wei, B.Y.; Xia, N. Determination of the variations in the metabolic profile and sensory quality of Liupao tea during fermentation through UHPLC–HR–MS metabolomics. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabago, M.K.A.G.; Calingacion, M.N.; Garcia, J. Recent advances in NMR-based metabolomics of alcoholic beverages. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 2, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, D.J.; Kerr, E.D.; Schenk, G.; Schulz, B.L. Metabolomics of non-Saccharomyces yeasts in fermented beverages. Beverages 2022, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, H.J.; Lee, N.R.; Yang, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, C.H. Qualitative and Quantitative Metabolite Comparison of Korean Traditional Alcoholic Beverages: Takju, Yakju, and Traditional-Soju. Foods 2024, 13, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.L.; Ji, Z.W.; Liu, S.P.; Han, X.; Zheng, F.P.; Mao, J. Characterization of the volatile compounds of huangjiu using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry (GC× GC-TOFMS). J. Food Process Pres. 2019, 43, e14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Meng, K.; Zheng, H.J.; Yu, H.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Lin, Z.C.; Xie, G.F. Metabolites comparison in post-fermentation stage of manual (mechanized) Chinese Huangjiu (yellow rice wine) based on GC–MS metabolomics. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, C.J.; Gao, X.L.; Kang, Y.L.; Huang, M.Q.; Wu, J.H.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, H.H.; Zhang, Y.Y. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Huangjiu from northern China by sensory-directed flavor analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.R.; Wang, Y.P.; Cui, F.; Yin, S.P.; Hu, F.D. The Formation, influencing factors, efficacy, and analytical techniques of flavor substances in Huangjiu. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.Q.; Huang, M.Q.; Sun, B.G.; Ren, F.Z.; Wu, J.H.; Meng, N.; Zhang, J.L. Identification of nonvolatile chemical constituents in Chinese Huangjiu using widely targeted metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.L.; Xu, Y. Identification of Low Molecular Weight Peptides in Chinese Rice Wine (Huang Jiu) by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Inst. Brew. 2011, 117, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Hu, W.Y.; Xia, Y.J.; Mu, Z.Y.; Tao, L.R.; Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Ni, B.; Ai, L.Z. Flavor formation in Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): Impacts of the flavor-active microorganisms, raw materials, and fermentation technology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.M. Age-dependent characterization of volatile organic compounds and age discrimination in Chinese rice wine using an untargeted GC/MS-based metabolomic approach. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, J.N.; Li, H.X.; Ma, Y.; Pu, Z.E.; Li, L.; Huang, L.B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.Q.; Jiang, G.F.; et al. Based on electronic nose and multi-omics, investigate the dynamic changes of volatile and non-volatile organic compounds in waxy wheat Baijiu from different years. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, D.; Chen, C.; Ge, C.; Tian, H. Exploring microbial dynamics and metabolic pathways shaping flavor profiles in Huangjiu through metagenomic analysis. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Qian, M.C. Aroma characterization of Chinese rice wine by gas chromatography–olfactometry, chemical quantitative analysis, and aroma reconstitution. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11295–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Reddy, A.V.B. Recent advances on anticancer activity of coumarin derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2022, 5, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkina, L.G. Phenylpropanoids as naturally occurring antioxidants: From plant defense to human health. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 53, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sá, R.D.D.E.; Andrade, L.N.; de Oliveira, R.D.B.; de Sousa, D.P. A review on anti-inflammatory activity of phenylpropanoids found in essential oils. Molecules 2014, 19, 1459–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zou, M.X.; Tang, C.; Ao, H.Y.; He, L.P.; Qiu, S.Y.; Li, C. The insights into sour flavor and organic acids in alcoholic beverages. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitzer, J.; Steiner, K.; Schmid, C.; Schein, V.K.; Prause, C.; Kniely, C.; Reif, M.; Geier, M.; Pietrich, E.; Reiter, T.; et al. Racemization-free and scalable amidation of l-proline in organic media using ammonia and a biocatalyst only. Green. Chem. 2022, 24, 5171–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.R.; Chen, J.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Chiu, H.F.; Wu, M.J.; Wu, Y.C. Bioactive acetogenins from the seeds of Annona atemoya. Phytochemistry 1999, 51, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Q.; Li, S.Y.; Lv, J.M.; Gao, H.; Chen, G.D.; Awakawa, T.; Abe, I.; Yao, X.S.; Hu, D. Biosynthesis of clinically used antibiotic fusidic acid and identification of two short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases with converse stereoselectivity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Kuruvilla, K.M. Cinnamon. Handbook of Herbs and Spices; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 182–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hiley, C.R.; Hoi, P.M. Oleamide: A fatty acid amide signaling molecule in the cardiovascular system? Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2007, 25, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, H.M.J. Spices and Condiments I. In Volatile Compounds in Foods and Beverages; Maarse, H., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 411–447. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhuang, Y.B.; Liu, T. Discovery of glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of ligupurpuroside B. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 7851–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncar, M.; Jakovljevic, M.; Subaric, D.; Pavlic, M.; Sluzek, V.B.; Cindric, I.; Molnar, M. Coumarins in food and methods of their determination. Foods 2020, 9, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, Y.; Li, W.M.; Guo, H.B.; Zhang, X.M.; Caiyin, Q.; Yuan, Y. Dynamic profiling of metabolite changes and health-promoting functions in ‘yuling paste’ during nine steaming and nine sun-drying processes. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Aging Period | Significant Metabolites |
|---|---|
| 3-year | L-Prolinamide N-docosahexaenoyl Methionine Artemoin A Leu-Arg-Asn-Arg 3-keto Fusidic acid |
| 5-year | Cincassiol B Alpha-linolenoyl ethanolamide Leucyl-Lysine |
| 10-year | CDP-DG (R)-1-O-[b-D-Glucopyranosyl-(1- > 6)-b-D-glucopyranoside]-1,3-octanediol |
| 20-year | Oleamide Salvinolone Ginsenoyne A |
| 30-year | Cinnamylideneacetone Osmanthuside A N-lauroyl histidine Vitamin A2 Coumarin Palmitic amide |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
E, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H. Comparative Analysis of Metabolite Changes in Huangjiu During Different Aging Periods Using HRMS Metabolomics. Metabolites 2025, 15, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050298
E Y, Wang Z, Guo H. Comparative Analysis of Metabolite Changes in Huangjiu During Different Aging Periods Using HRMS Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2025; 15(5):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050298
Chicago/Turabian StyleE, Yue, Zhuang Wang, and Hongbin Guo. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Metabolite Changes in Huangjiu During Different Aging Periods Using HRMS Metabolomics" Metabolites 15, no. 5: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050298
APA StyleE, Y., Wang, Z., & Guo, H. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Metabolite Changes in Huangjiu During Different Aging Periods Using HRMS Metabolomics. Metabolites, 15(5), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15050298






