Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for SFTS: Insights into Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
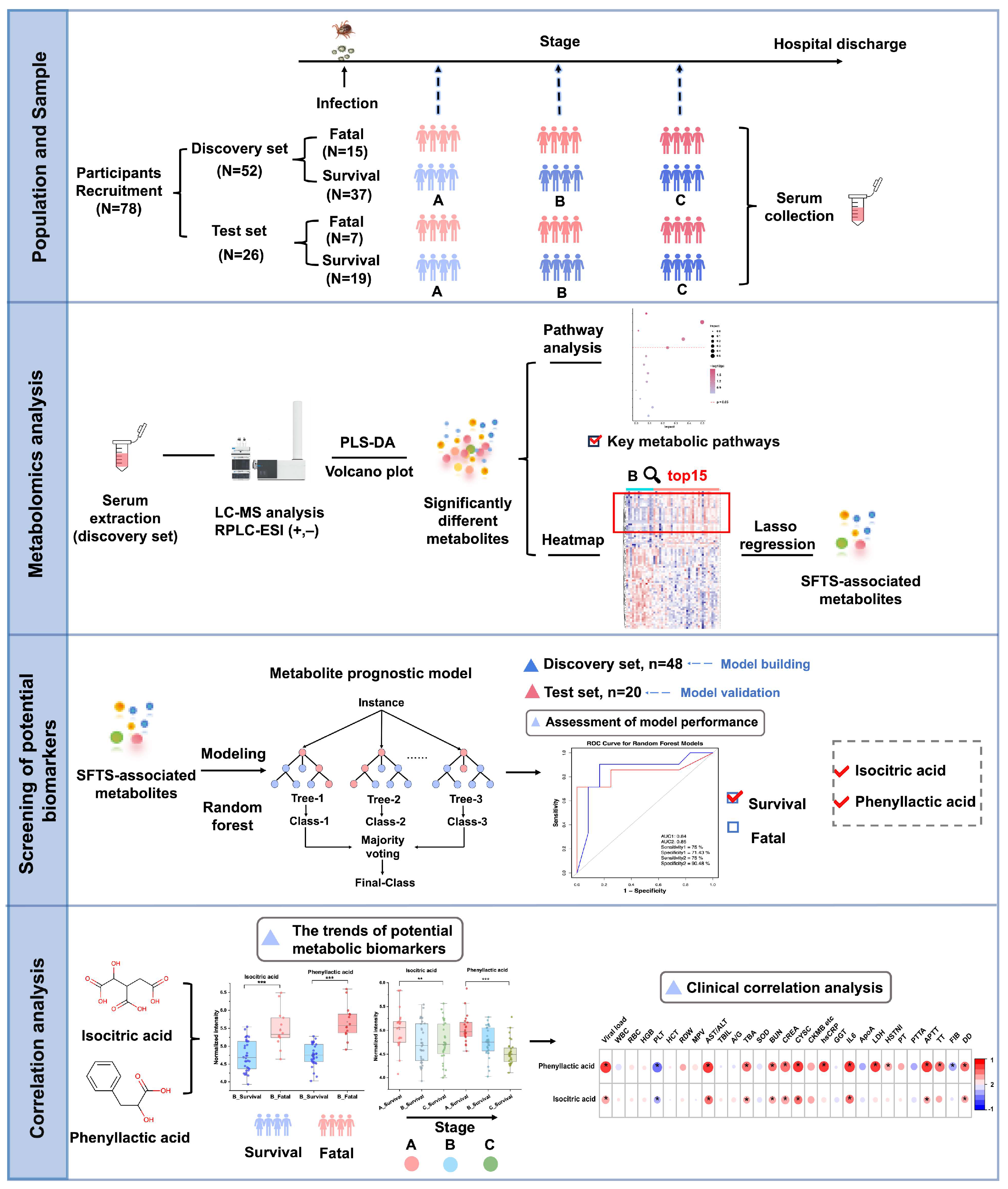
2.1. Study Population Information
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Criteria for Staging Bunyavirus Patients
2.4. Serum Sample Collection and Preparation
2.5. LC-MS Analysis
2.6. Data Processing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
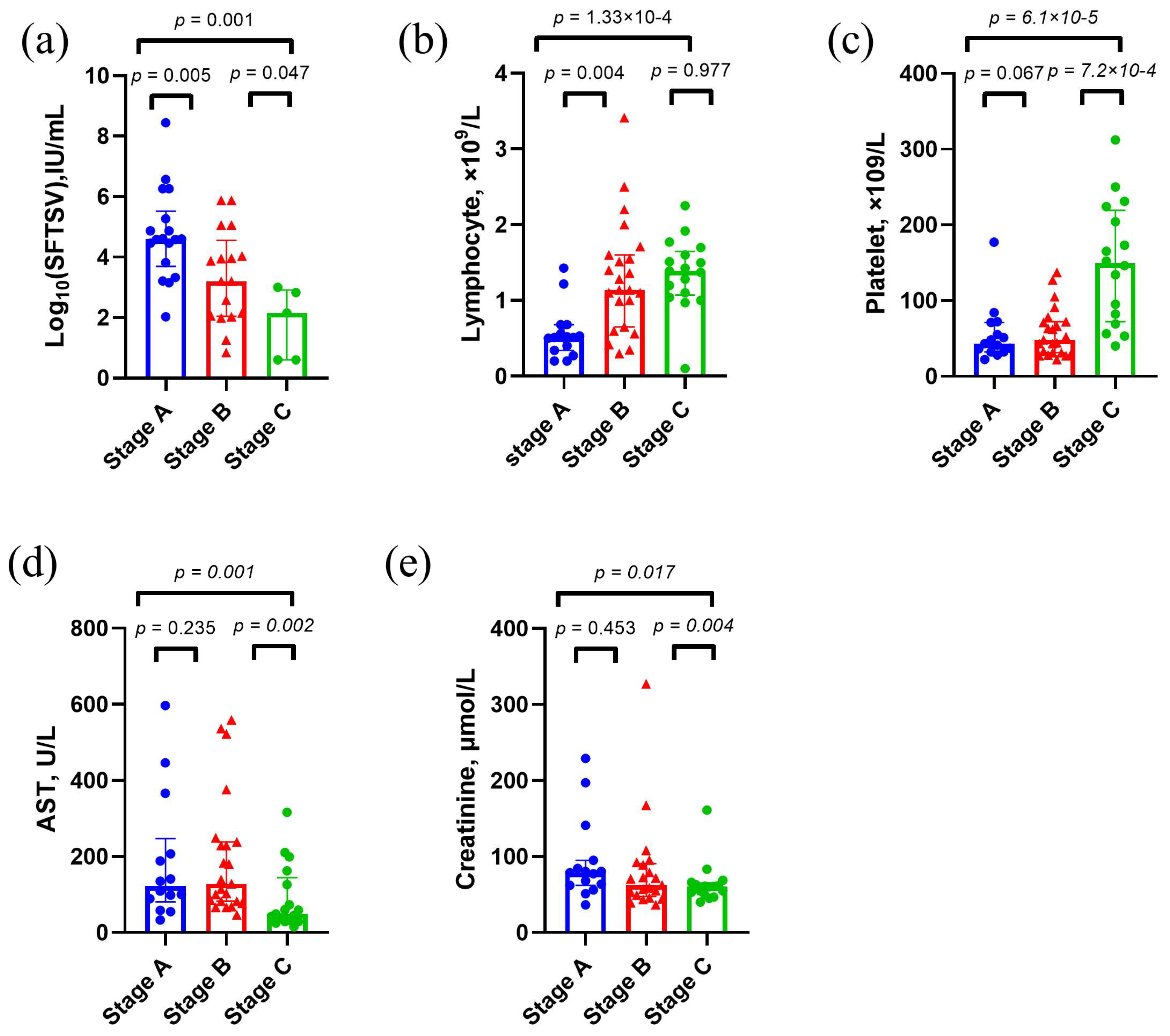
3.1. Clinical Features of Study Population
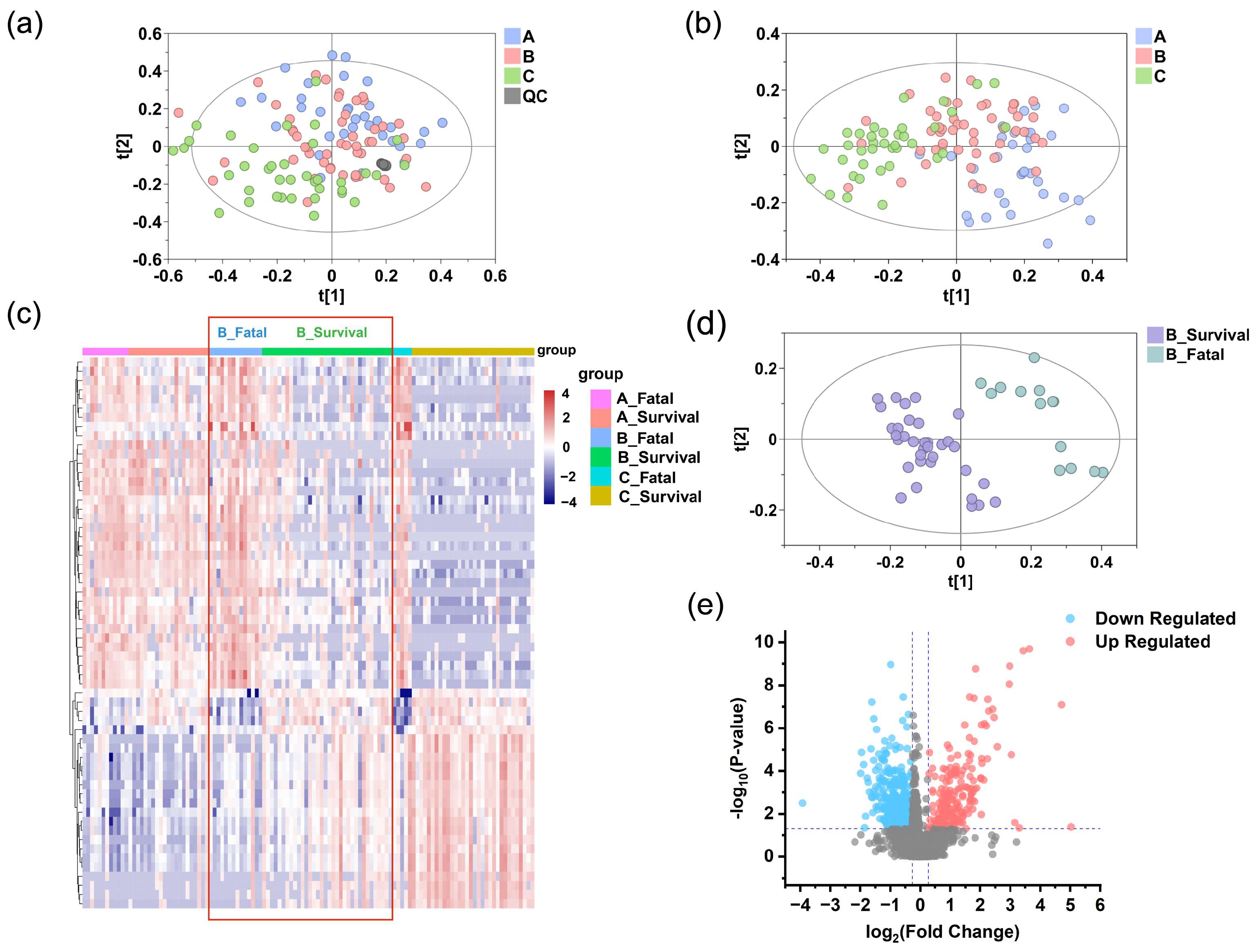
3.2. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Patients with Severe Fever with SFTS
3.3. Exploratory Analysis of Grouping
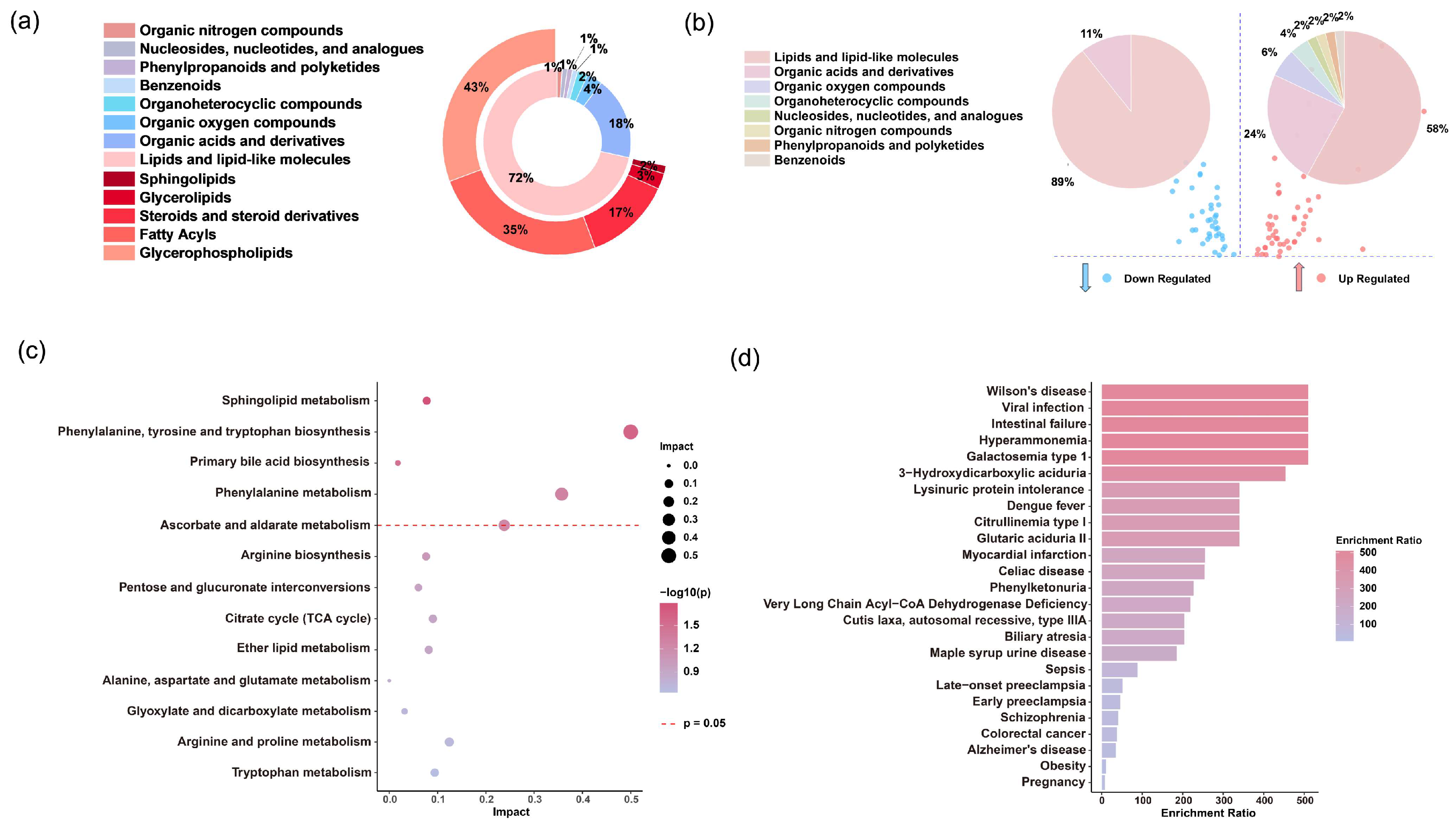
3.4. Significantly Altered Differential Metabolites
3.5. Selection and Evaluation of Potential Biomarkers
3.6. Correlation Analysis with Clinical Information
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; He, B.; Huang, S.Y.; Wei, F.; Zhu, X.Q. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Cao, P.; Lu, J. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: A highly lethal bunyavirus. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lu, Q.-B.; Xing, B.; Zhang, S.-F.; Liu, K.; Du, J.; Li, X.-K.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.-D.; Wang, L.-Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical features of laboratory-diagnosed severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011–2017, a prospective observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Maeda, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ishido, A.; Shigeoka, T.; Tominaga, T.; Kamei, T.; Honda, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Sakai, T.; et al. The first identification and retrospective study of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Yi, J.; Kim, G.; Choi, S.J.; Jun, K.I.; Kim, N.-H.; Choe, P.G.; Kim, N.-J.; Lee, J.-K.; Oh, M. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.J.; Liang, M.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.D.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Zhan, F.; Song, Y.; Guo, D. Current status of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Liu, Q. The changing epidemiological characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011-2016. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chai, C.; Wang, C.; Amer, S.; Lv, H.; He, H.; Sun, J.; Lin, J. Systematic review of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: Virology, epidemiology, and clinical characteristics. Rev. Med. Virol. 2014, 24, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kato, H.; Yamagishi, T.; Shimada, T.; Matsui, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurosu, T.; Shimojima, M.; Morikawa, S.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Japan, 2013–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, Q.-B.; Cui, N.; Li, H.; Wang, L.-Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, Z.-D.; Wang, B.-J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; et al. Case-fatality ratio and effectiveness of ribavirin therapy among hospitalized patients in China who had severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Hu, X.-N.; Ma, H.; Du, Y.-H.; Kang, K.; You, A.-G.; Wang, H.-F.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.-M.; Dumler, J.S.; et al. Detection of new bunyavirus RNA by reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.H.; Cheon, H.-S.; Park, S.-J.; Lloren, K.K.S.; Ahn, S.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, W.-S.; Yu, M.-A.; Kwon, H.-I.; Kwon, J.-J.; et al. Simple, Rapid and sensitive portable molecular diagnosis of SFTS virus using reverse transcriptional loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.W.; Kim, D.; Yun, N.; Kim, D.M. Clinical update of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Viruses 2021, 13, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y. Antiviral treatment options for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome infections. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 1805–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Altamirano, M.M.B.; Kolstoe, S.E.; Sánchez-García, F.J. Virus control of cell metabolism for replication and evasion of host immune responses. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenreich, W.; Rudel, T.; Heesemann, J.; Goebel, W. How viral and intracellular bacterial pathogens reprogram the metabolism of host cells to allow their intracellular replication. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Keshari, K.R. Metabolic analysis as a driver for discovery, diagnosis, and therapy. Cell 2022, 185, 2678–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Lee, Y.H.; Thein, T.L.; Fang, J.; Pang, J.; Ooi, E.E.; Leo, Y.S.; Ong, C.N.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Serum metabolomics reveals serotonin as a predictor of severe dengue in the early phase of dengue fever. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounta, V.; Liu, Y.; Cheyne, A.; Larrouy-Maumus, G. Metabolomics in infectious diseases and drug discovery. Mol. Omics. 2021, 17, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindelar, M.; Stancliffe, E.; Schwaiger-Haber, M.; Anbukumar, D.S.; Adkins-Travis, K.; Goss, C.W.; O’halloran, J.A.; Mudd, P.A.; Liu, W.-C.; Albrecht, R.A.; et al. Longitudinal metabolomics of human plasma reveals prognostic markers of COVID-19 disease severity. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-K.; Lu, Q.-B.; Chen, W.-W.; Xu, W.; Liu, R.; Zhang, S.-F.; Du, J.; Li, H.; Yao, K.; Zhai, D.; et al. Arginine deficiency is involved in thrombocytopenia and immunosuppression in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.-X.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, T.-T.; Cui, N.; Du, J.; Liu, W.; Lu, Q.-B. Metabolic alterations in urine among the patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnosis and treatment scheme for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (2023 edition). Chin. J. Infect. Control 2024, 23, 918–920.
- Hao, J.-D.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-Z.; An, N.; Bai, P.-R.; Zhu, Q.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q. Novel peak shift correction method based on the retention index for peak alignment in untargeted metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 13330–13337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFelice, B.C.; Mehta, S.S.; Samra, S.; Čajka, T.; Wancewicz, B.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Fiehn, O. Mass spectral feature list optimizer (MS-FLO): A tool to minimize false positive peak reports in untargeted liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy (LC-MS) data processing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3250–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, S.; Bobeldijk, I.; Verheij, E.R.; Ramaker, R.; Kochhar, S.; Macdonald, I.A.; van Ommen, B.; Smilde, A.K. Large-scale human metabolomics studies: a strategy for data (pre-) processing and validation. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Rai, A.; Saito, K.; Nakabayashi, R. Metabolomics and complementary techniques to investigate the plant phytochemical cosmos. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 1729–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; Fenner, K.; Ruff, M.; Singer, H.P.; Hollender, J. Identifying small molecules via high resolution mass spectrometry: Communicating confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Song, P.; Li, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. A scoring model for predicting prognosis of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xue, X.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.; Chen, Z. A model based on meta-analysis to evaluate poor prognosis of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1307960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, M.-F.; Jin, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, C.-B.; Li, C.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Bian, P.-F.; et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, S.; Ran, R.; Li, A.; Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S.; et al. A longitudinal sampling study of transcriptomic and epigenetic profiles in patients with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; He, Y.-W.; Dai, Y.-A.; Xiong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, D.-J.; Li, J.; Sun, Q.; Luo, X.-L.; Cheng, Y.-L.; et al. Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel bunyavirus in China: Pathogenesis and correlates of fatal outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Wei, X.; Yuan, H.; Xu, X.; Liang, H.; Wen, H. Clinical laboratory parameters and fatality of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhan, F.; Wang, X.; Liang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, S.; Guan, X.; Huo, X.; Li, C.; et al. Host cytokine storm is associated with disease severity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, R.J.W.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Netea, M.G. Cellular metabolism of myeloid cells in sepsis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-K.; Zhang, S.-F.; Xu, W.; Xing, B.; Lu, Q.-B.; Zhang, P.-H.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.-C.; Chen, W.-W.; et al. Vascular endothelial injury in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome caused by the novel bunyavirus. Virology 2018, 520, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frej, C.; Linder, A.; Happonen, K.E.; Taylor, F.B.; Lupu, F.; Dahlbäck, B. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and its carrier apolipoprotein M in human sepsis and in Escherichia coli sepsis in baboons. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Fernando, S.; Fernando, R.H.; Wickramasinghe, N.; Shyamali, N.L.A.; Ogg, G.S.; Malavige, G.N. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in acute dengue infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangerle, R.; Kurz, K.; Neurauter, G.; Kitchen, M.; Sarcletti, M.; Fuchs, D. Increased blood phenylalanine to tyrosine ratio in HIV-1 infection and correction following effective antiretroviral therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atila, A.; Alay, H.; Yaman, M.E.; Akman, T.C.; Cadirci, E.; Bayrak, B.; Celik, S.; Atila, N.E.; Yaganoglu, A.M.; Kadioglu, Y.; et al. The serum amino acid profile in COVID-19. Amino. Acids. 2021, 53, 1569–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Duan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; et al. Metabolomic analysis of the effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment on rats with sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Jin, C.; Zhu, L.; Liang, M.; Li, C.; Cardona, C.J.; Li, D.; Xing, Z. Host responses and regulation by NFκB signaling in the liver and liver epithelial cells infected with a novel tick-borne bunyavirus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Yue, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Cui, N.; Yuan, C.; Li, J.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila protects mice against an emerging tick-borne viral pathogen. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and metabolomic characterization of COVID-19 patient sera. Cell 2020, 182, 59–72.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Gong, Y.; Mai, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, X.; Wan, X.; Xie, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Clinical and antibody characteristics reveal diverse signatures of severe and non-severe SARS-CoV-2 patients. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Pellicciari, R.; Pruzanski, M.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K. Targeting bile-acid signalling for metabolic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylemon, P.B.; Zhou, H.; Pandak, W.M.; Ren, S.; Gil, G.; Dent, P. Bile acids as regulatory molecules. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z. Bile acids and coronavirus disease 2019. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.S.; Al-kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Youssef, F.S.; El-Sherbeni, S.A.; Negm, W.A. A perspective study of the possible impact of obeticholic acid against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.H.; Park, T.; Park, Y.Y.; Huh, J.W.; Lim, C.-M.; Koh, Y.; Song, D.-K.; Hong, S.-B. Clinical significance of enzymatic lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) assay data in patients with sepsis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautbauer, S.; Eisinger, K.; Wiest, R.; Liebisch, G.; Buechler, C. Systemic saturated lysophosphatidylcholine is associated with hepatic function in patients with liver cirrhosis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2016, 124, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.T.; Ramesh, T.; Toh, X.R.; Nguyen, L.N. Emerging roles of lysophospholipids in health and disease. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2020, 80, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuplez, E.; Marsche, G. An updated review of pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of plasma lysophosphatidylcholines in the vascular system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcic, S.; Holzer, M.; Pasterk, L.; Knuplez, E.; Eichmann, T.O.; Frank, S.; Zimmermann, R.; Schicho, R.; Heinemann, A.; Marsche, G. Secretory phospholipase A2 modified HDL rapidly and potently suppresses platelet activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.-M.; Liu, H.-Y.; An, N.; Li, A.-L.; Li, J.; Wang, S.-J.; Yang, G.; Duan, Y.-W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for SFTS: Insights into Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes. Metabolites 2025, 15, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040228
Zhu Z-M, Liu H-Y, An N, Li A-L, Li J, Wang S-J, Yang G, Duan Y-W, Yang Y, Zhang M, et al. Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for SFTS: Insights into Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040228
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhuo-Min, Huan-Yu Liu, Na An, An-Ling Li, Jia Li, Sai-Jun Wang, Gui Yang, Yong-Wei Duan, Ying Yang, Mei Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for SFTS: Insights into Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040228
APA StyleZhu, Z.-M., Liu, H.-Y., An, N., Li, A.-L., Li, J., Wang, S.-J., Yang, G., Duan, Y.-W., Yang, Y., Zhang, M., Zhu, Q.-F., Liu, S.-M., & Feng, Y.-Q. (2025). Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Prognostic Biomarkers for SFTS: Insights into Disease Severity and Clinical Outcomes. Metabolites, 15(4), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040228






