Metabolic Reprogramming of Gastric Cancer Revealed by a Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Tissue Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. LC-MS Analysis
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Network Topology Analysis Exploring Metabolic Reprogramming of GC at Different TNM Stages
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Enrolled GC Patients
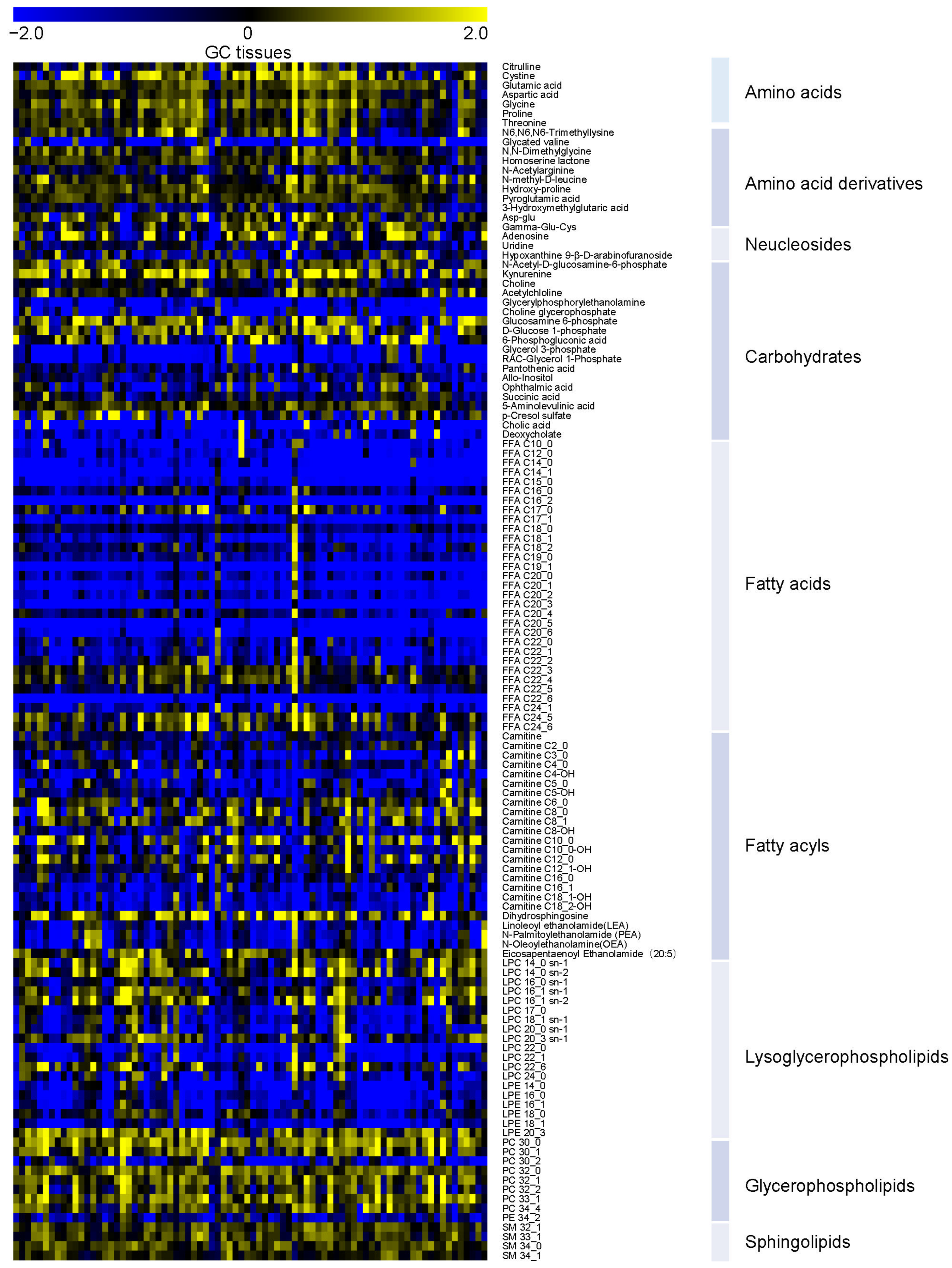
3.2. Overview of Metabolic Alterations in GC
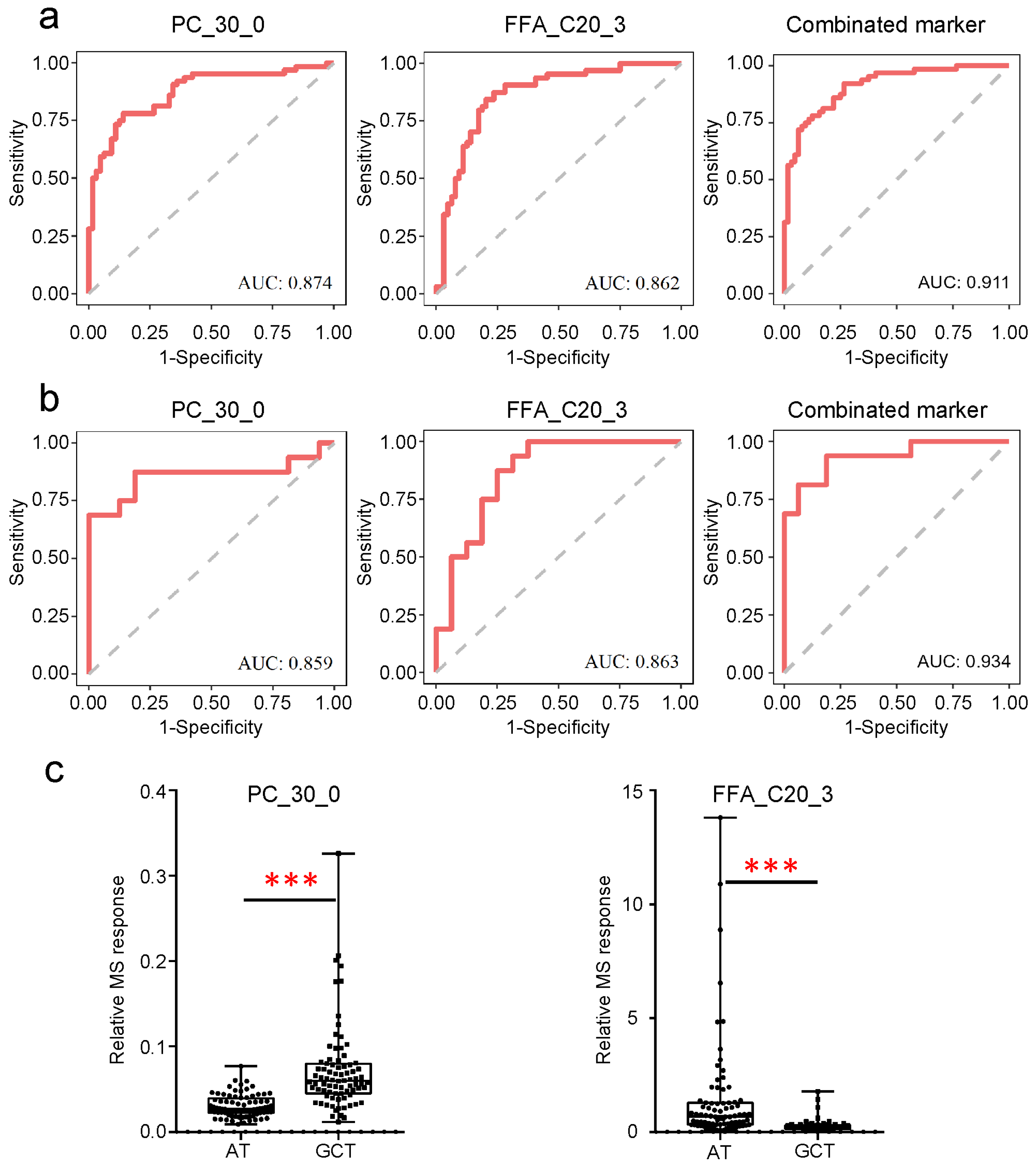
3.3. Potential Tissue Biomarkers for GC Diagnosis
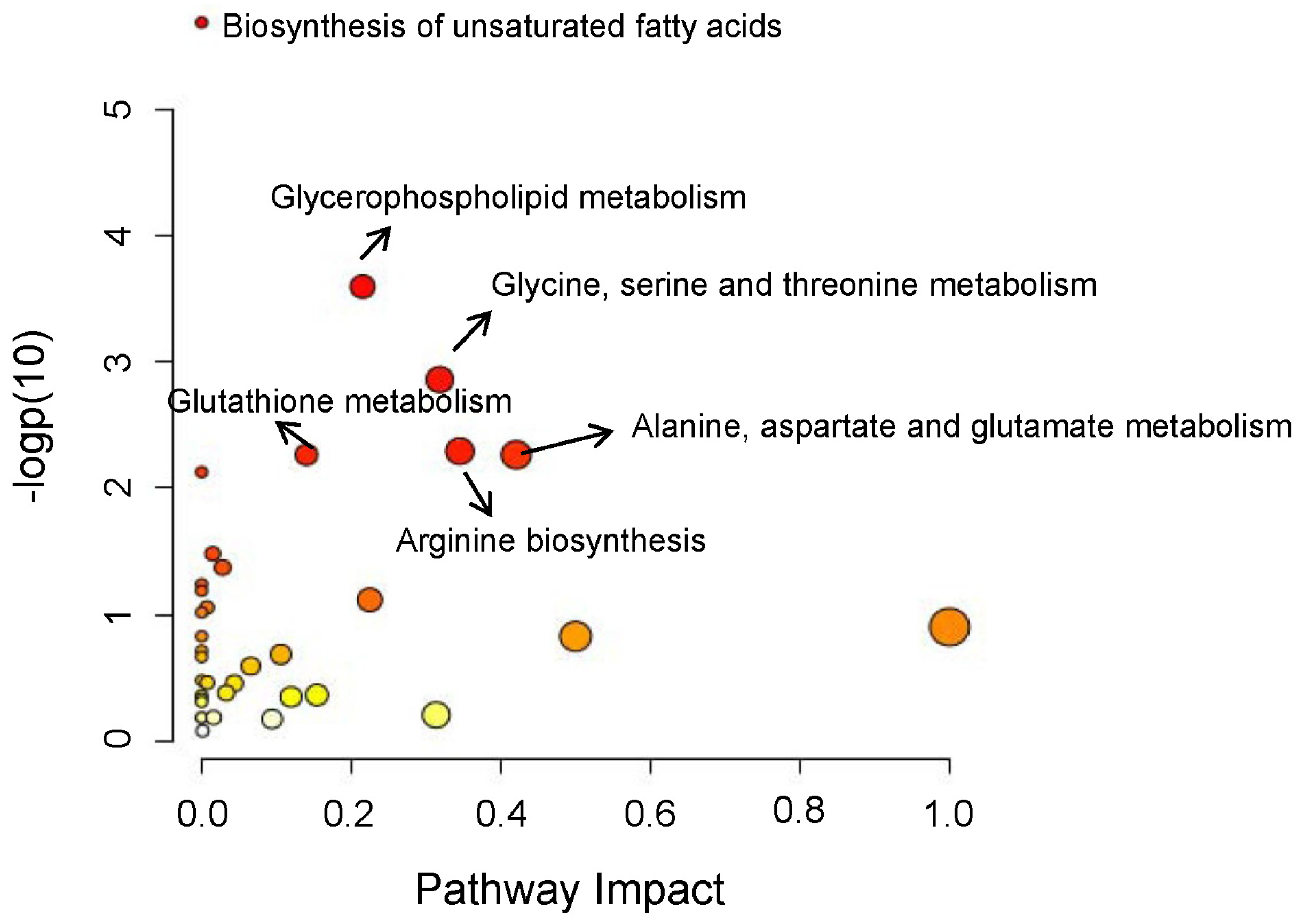
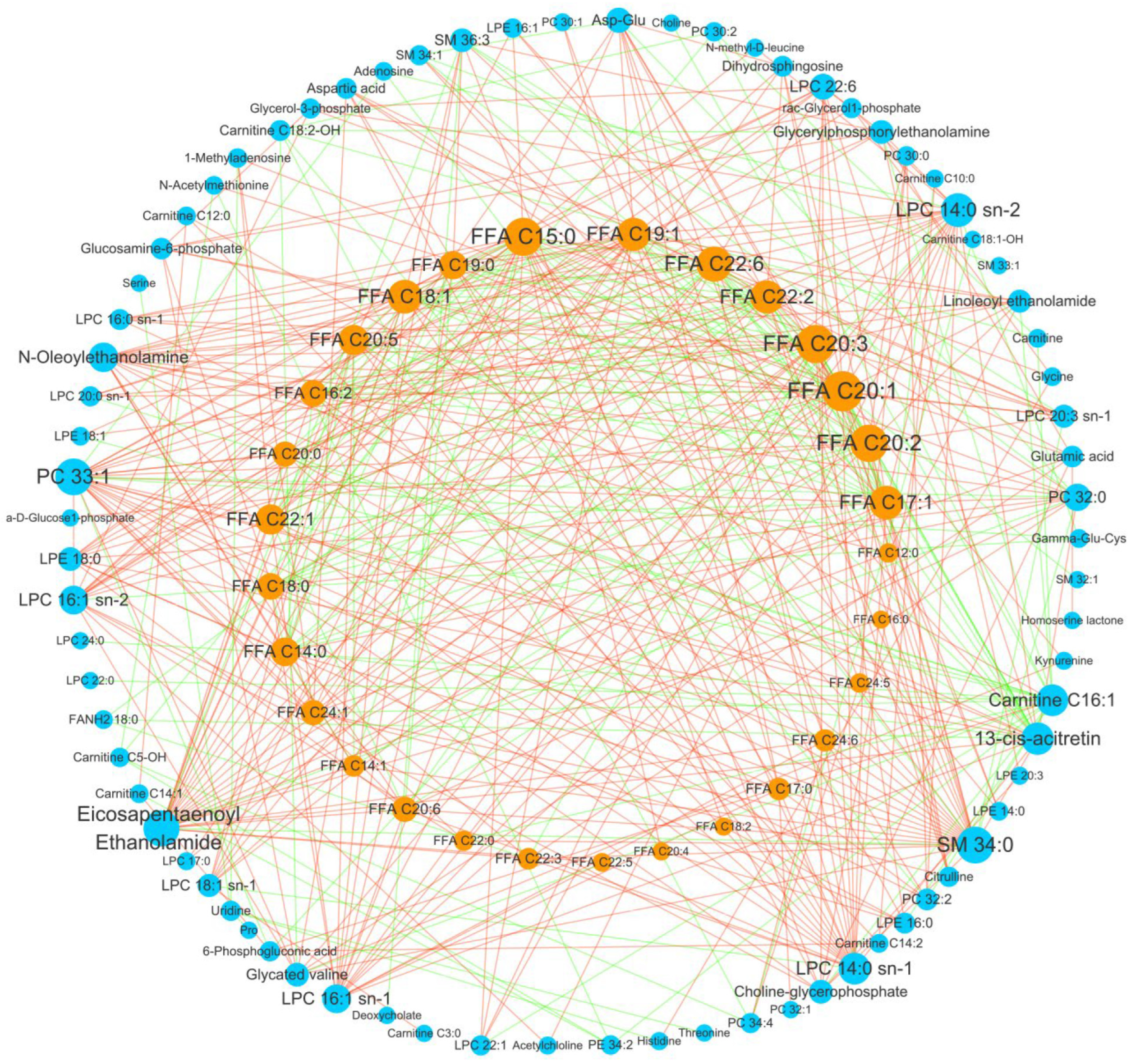
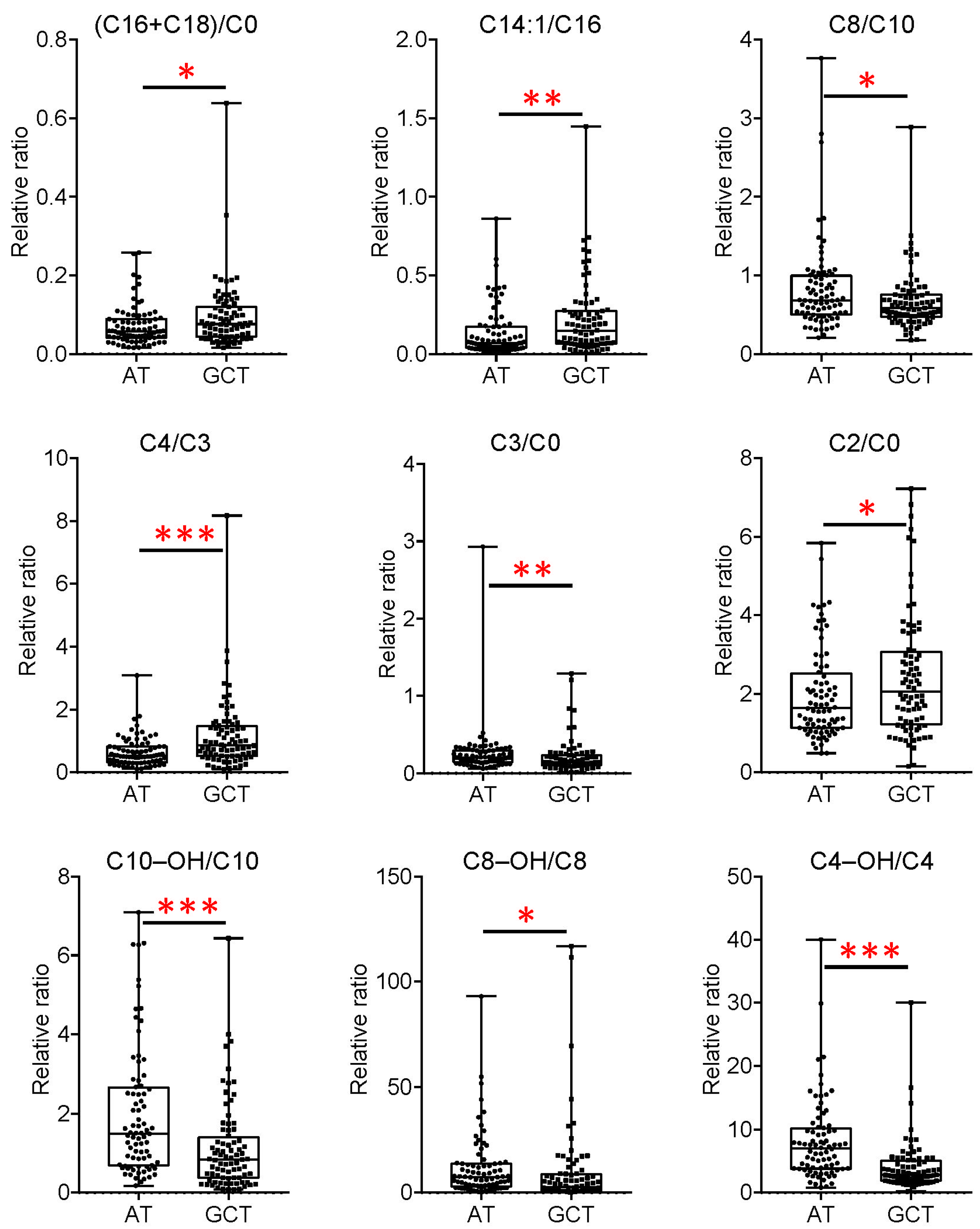
3.4. Important Fatty Acid Metabolic Reprogramming in GC
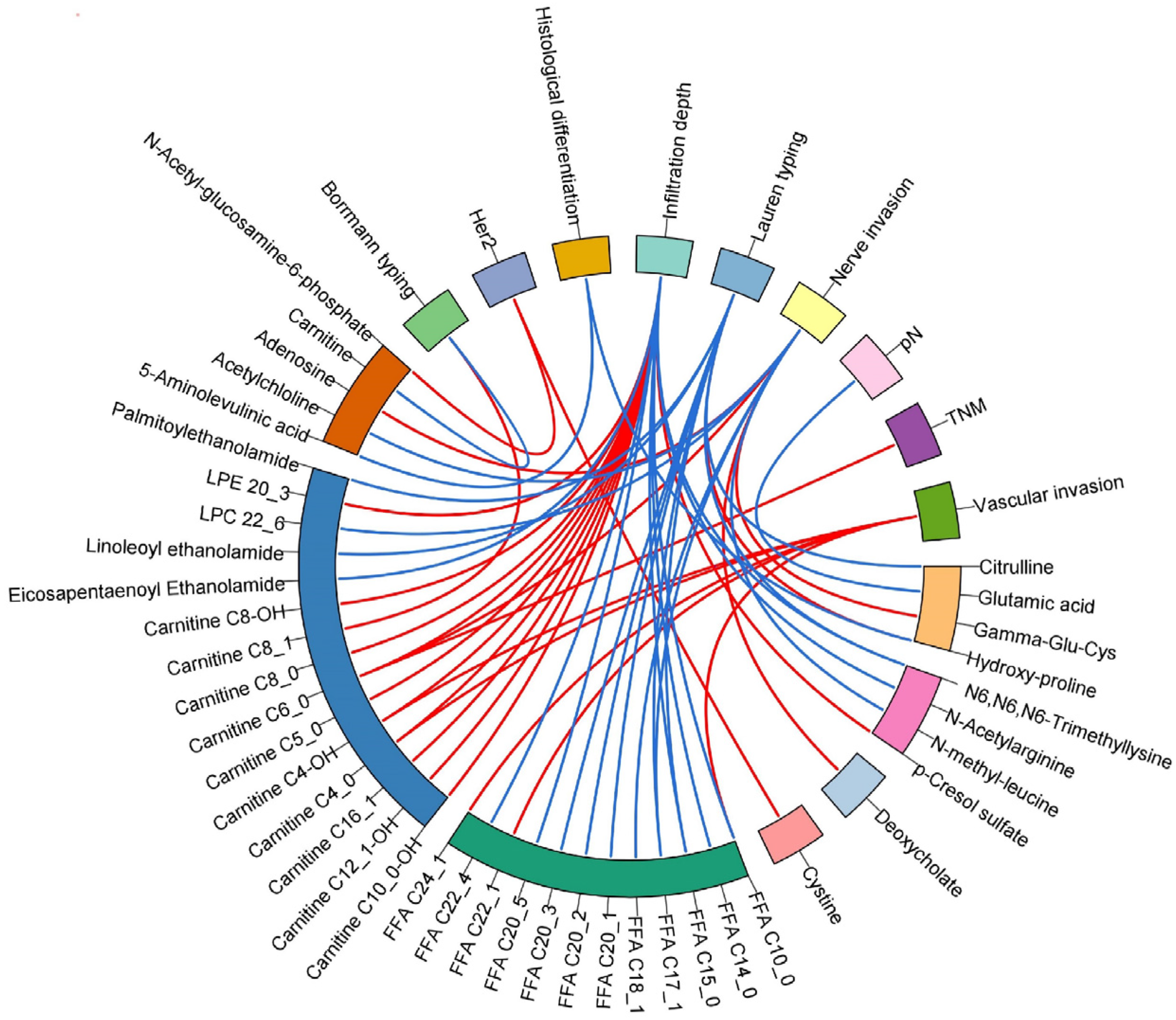
3.5. The Relationships of Clinical Prognosis Indices with Differential Metabolites in GC
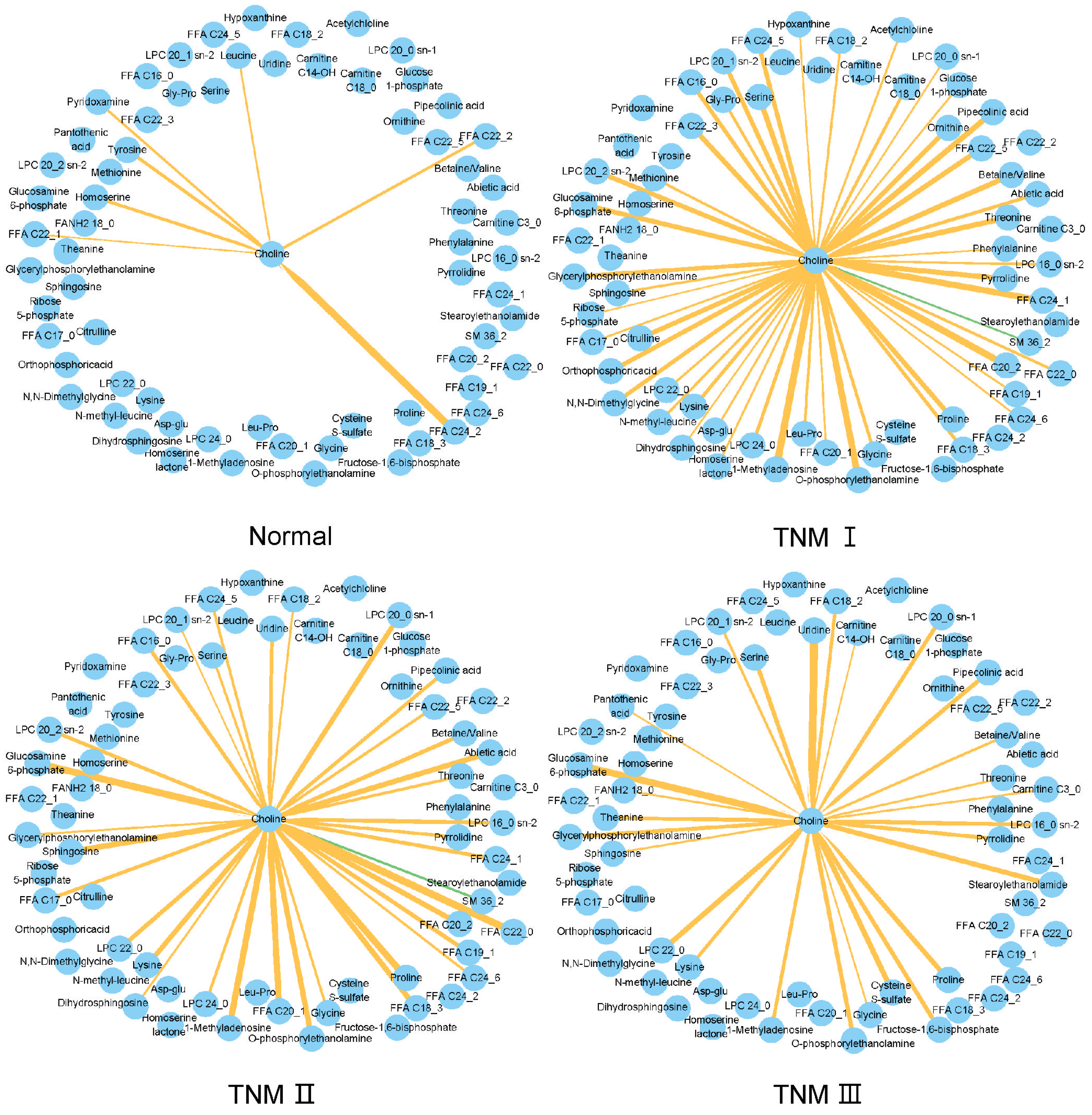
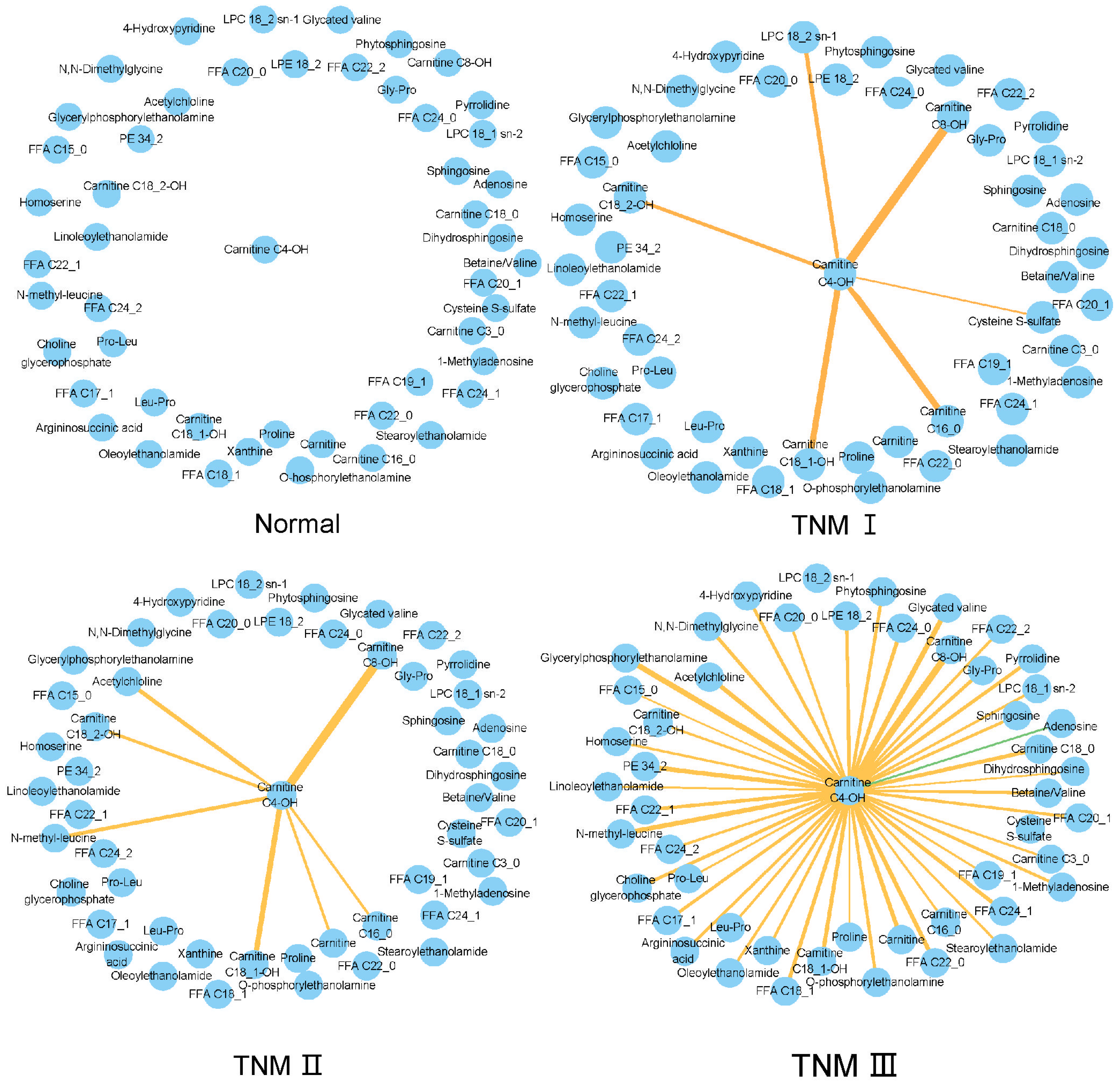
3.6. TNM-Related Metabolic Network Changes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Differential Metabolites | p-Value a | FCa (GCT/AT) | Vascular Invasion b | Nerve Invasion c | Her2 Positive d | pN e | Histological Differentiation f | WHO Histological Type g | Borrmann Typing h | Infiltration Depth i | TNM j | Lauren Typing k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-Aminolevulinic acid | *** | 1.3 | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Acetylchloline | *** | 1.4 | ― | ** | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Adenosine | *** | 2 | ― | ** | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Citrulline | * | 1.3 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * |
| Cystine | *** | 2.2 | ― | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Deoxycholate | * | 0.7 | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Gamma-Glu-Cys | * | 1.3 | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Glutamic acid | *** | 1.5 | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| Hydroxy-proline | *** | 1.4 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ** | ― | ― | ― | ― | * |
| N6,N6,N6-Trimethyllysine | *** | 1.5 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ** | ― | * |
| N-Acetylarginine | ** | 0.8 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| N-Acetyl-glucosamine-6-phosphate | *** | 1.4 | ― | ― | ** | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| N-methyl-leucine | *** | 1.4 | ― | ** | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| p-Cresol sulfate | ** | 1.2 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| Linoleoyl ethanolamide (18_2) | *** | 0.6 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ** |
| N-Palmitoylethanolamide (16_0) | ** | 0.7 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * |
| Eicosapentaenoyl Ethanolamide (20_5) | *** | 1.4 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| LPC 22_6 | ** | 1.7 | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| LPE 20_3 | *** | 1.9 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| FFA C10_0 | *** | 0.4 | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| FFA C14_0 | *** | 0.2 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| FFA C15_0 | *** | 0.3 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ** |
| FFA C17_1 | *** | 0.3 | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ** |
| FFA C18_1 | *** | 0.4 | ― | ** | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| FFA C20_1 | *** | 0.2 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * |
| FFA C20_2 | *** | 0.4 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * |
| FFA C20_3 | *** | 0.2 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ** |
| FFA C20_5 | *** | 0.1 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| FFA C22_1 | *** | 0.4 | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| FFA C22_4 | ** | 1.2 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| FFA C24_1 | ** | 0.6 | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― |
| carnitine | *** | 0.7 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― | ― |
| carnitine C10_0-OH | * | 0.8 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| carnitine C12_1-OH | * | 0.8 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| carnitine C16_1 | ** | 0.5 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| carnitine C4_0 | * | 1 | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | *** | ― | ― |
| carnitine C4-OH | *** | 0.4 | ** | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| carnitine C5_0 | ** | 0.7 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ** | ― | ― |
| carnitine C6_0 | * | 1.4 | ― | * | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | *** | * | ― |
| carnitine C8_0 | * | 1.8 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
| carnitine C8_1 | ** | 1.3 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― | ― |
| carnitine C8-OH | *** | 0.6 | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | ― | * | ― | ― |
Appendix B
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer Statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Segers, S.; Blaser, M.J. Association between Helicobacter pylori and mortality in the NHANES III study. Gut 2013, 62, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, P.; Valderrama, M.V.; Bravo, J.; Quest, A.F.G. Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: Adaptive Cellular Mechanisms Involved in Disease Progression. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, G.; Axon, A. Role of bacterial overgrowth in the stomach as an additional risk factor for gastritis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17 (Suppl. B), 13B–17B. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, M.; Kochi, M.; Takayama, T. Recent advances in chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer in Japan. Surg. Today 2010, 40, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Jung, Y.; Bang, E.J.; Cho, S.-i.; Jang, Y.-J.; Kwak, J.-M.; Ryu, D.H.; Park, S.; Hwang, G.-S. Noninvasive Diagnosis and Evaluation of Curative Surgery for Gastric Cancer by Using NMR-based Metabolomic Profiling. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, S736–S742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasechnikov, V.; Chukov, S.; Fedorov, E.; Kikuste, I.; Leja, M. Gastric cancer: Prevention, screening and early diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 13842–13862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necula, L.; Matei, L.; Dragu, D.; Neagu, A.; Mambet, C.; Nedeianu, S.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Chivu-Economescu, M. Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudino, W.M.; Quattrone, A.; Biganzoli, L.; Pestrin, M.; Bertini, I.; Di Leo, A. Metabolomics: Available results, current research projects in breast cancer, and future applications. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2840–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Thompson, C.B. The Emerging Hallmarks of Cancer Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Zhu, J.; Thompson, C.B. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, M.; Nozawa, H. Hallmarks of Cancer: After the next generation. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 885. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, D.R.; Patel, R.; Kirsch, D.G.; Lewis, C.A.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Locasale, J.W. Metabolomics in cancer research and emerging applications in clinical oncology. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 333–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursu, S.; Ciocan, A.; Ursu, C.P.; Gherman, C.D.; Ciocan, R.A.; Pop, R.S.; Spârchez, Z.; Zaharie, F.; Al Hajjar, N. Role of Metabolomics in Pathogenesis and Prompt Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer Metastasis-A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.Y.; Zhou, L.Y. Gastric cancer: Metabolic and metabolomics perspectives. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoi, M.; Britz-McKibbin, P. New Advances in Tissue Metabolomics: A Review. Metabolites 2021, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Dang, T.; Qin, W.; Teng, L.; Ye, J.; Jiang, H. Interactions between gastric microbiota and metabolites in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, S.; Irino, T.; Kusuhara, M.; Makuuchi, R.; Yamakawa, Y.; Tokunaga, M.; Tanizawa, Y.; Bando, E.; Kawamura, T.; Kami, K.; et al. Metabolomic profiling of gastric cancer tissues identified potential biomarkers for predicting peritoneal recurrence. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Ye, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H. 1H NMR metabolic profiling of gastric cancer patients with lymph node metastasis. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.-L.; Wu, X.-B.; Wang, H.-S.; Liu, Z.-H.; Li, Y.; Diao, D.-C.; Chen, H.-L.; Peng, J.-S. Tissue metabolomic fingerprinting reveals metabolic disorders associated with human gastric cancer morbidity. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xue, R.; Tang, Z.; Deng, C.; Liu, T.; Zeng, H.; Sun, Y.; Shen, X. Metabolomic investigation of gastric cancer tissue using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aa, J.; Yu, L.; Sun, M.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Cao, B.; Shi, J.; Xu, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, J.; et al. Metabolic features of the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer and the link to the systemic macroenvironment. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Deng, P.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Jie, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.-L. Tissue metabolic profiling of human gastric cancer assessed by 1H NMR. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, K.; Wu, G.; Zhang, W.; Ma, P.; Feng, S. Tissue-based metabolomics reveals metabolic signatures and major metabolic pathways of gastric cancer with help of transcriptomic data from TCGA. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Keum, B.; Kim, H.J.; Chun, H.J.; Park, Y.H. Gastric Cancer and Intestinal Metaplasia: Differential Metabolic Landscapes and New Pathways to Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; You, W.; Pan, K.; Li, W. A systematic review of metabolomic profiling of gastric cancer and esophageal cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftabi, Y.; Soleymani, J.; Jouyban, A. Efficacy of Analytical Technologies in Metabolomics Studies of the Gastrointestinal Cancers. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Breitkopf, S.B.; Yang, X.; Asara, J.M. A positive/negative ion-switching, targeted mass spectrometry-based metabolomics platform for bodily fluids, cells, and fresh and fixed tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Suo, F.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Gou, L.; Gu, M.; Xu, G. Development of a fast and robust liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolomics analysis method for neonatal dried blood spots. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 230, 115383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, A.; Lu, X.; Zhao, C.; Hu, C.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Hou, X.; et al. Comprehensive Strategy to Construct In-House Database for Accurate and Batch Identification of Small Molecular Metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7635–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, A.T.; Katsyv, I.; Song, W.-M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, B. DGCA: A comprehensive R package for Differential Gene Correlation Analysis. BMC Syst. Biol. 2016, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Nilsson, R.; Sharma, S.; Madhusudhan, N.; Kitami, T.; Souza, A.L.; Kafri, R.; Kirschner, M.W.; Clish, C.B.; Mootha, V.K. Metabolite Profiling Identifies a Key Role for Glycine in Rapid Cancer Cell Proliferation. Science 2012, 336, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phang, J.M.; Donald, S.P.; Pandhare, J.; Liu, Y. The metabolism of proline, a stress substrate, modulates carcinogenic pathways. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, B.J.; Stine, Z.E.; Dang, C.V. From Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Wang, A.; Chen, X.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, Y. Microbial-Related Metabolites May Be Involved in Eight Major Biological Processes and Represent Potential Diagnostic Markers in Gastric Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Li, C.F.; Song, Y.M.; Yan, Z.K. Inhibition of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A-induced fatty acid oxidation suppresses cell progression in gastric cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 696, 108664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puca, F.; Yu, F.; Bartolacci, C.; Pettazzoni, P.; Carugo, A.; Huang-Hobbs, E.; Liu, J.T.; Zanca, C.; Carbone, F.; Del Poggetto, E.; et al. Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Protects Mitochondria from Lipid Peroxidation in Glioblastoma. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2904–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.P.Y.; Yeung, C.L.S.; Tey, S.K.; Mao, X.W.; Wong, S.W.K.; Ng, T.H.; Ko, F.C.F.; Kwong, E.M.L.; Tang, A.H.N.; Ng, I.O.L.; et al. Suppression of ACADM-Mediated Fatty Acid Oxidation Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Aberrant CAV1/SREBP1 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3679–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.H.; Gu, H.T.; Zhang, K.D.; Guo, Z.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Wei, Q.Y.; Weng, L.; Han, X.; Lv, Y.; Cao, M.; et al. Exosomal ACADM sensitizes gemcitabine-resistance through modulating fatty acid metabolism and ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, U.; Davis, E.M.; LeBeau, M.M.; Stoffel, W. Human mitochondrial enoyl-CoA hydratase gene (ECHS1): Structural organization and assignment to chromosome 10q26.2-q26.3. Genomics 1997, 40, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.S.; Gao, P.; Dai, Y.C.; Xie, J.P.; Zeng, W.; Lian, Q.N. Attenuation of enoyl coenzyme A hydratase short chain 1 expression in gastric cancer cells inhibits cell proliferation and migration in vitro. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2014, 19, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ediriweera, M.K.; To, N.B.; Lim, Y.; Cho, S.K. Odd-chain fatty acids as novel histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) inhibitors. Biochimie 2021, 186, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glunde, K.; Penet, M.-F.; Jiang, L.; Jacobs, M.A.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Choline metabolism-based molecular diagnosis of cancer: An update. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Ronen, S.M. Choline metabolism in malignant transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Peiris-Pages, M.; Pestell, R.G.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Cancer metabolism: A therapeutic perspective. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Aa, J.; Xu, J.; Sun, M.; Qian, S.; Cheng, L.; Yang, S.; Shi, R. Metabolomic phenotype of gastric cancer and precancerous stages based on gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.N.; Lee, H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, S.; Kim, J.J. Screening for Early Gastric Cancer Using a Noninvasive Urine Metabolomics Approach. Cancers 2020, 12, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Characteristics of GC Patients (n = 80) | Number or Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Gender (No.) (male/female) | 62/18 |
| Age (years) | 66.0 ± 8.3 |
| Body mass index (BMI) | 25.6 ± 22.4 |
| Hypertension (no/yes) | 54/26 |
| Diabetes mellitus (no/yes) | 69/11 |
| Cholecystolithiasis (no/yes) | 74/6 |
| Smoking (no/yes) | 35/45 |
| Drinking (no/yes) | 52/28 |
| WHO histological classification (adenocarcinoma/signet ring cell carcinoma/mucinous adenocarcinoma) | 47/19/14 |
| Tumor differentiation (low/low–medium/medium/medium–high/high/mixed/unknown) | 29/26/12/6/0/2/5 |
| Borrmann typing (1/2/3/4/unknown) | 4/41/31/2/2 |
| Infiltration depth (mucosa (lamina propria, muscularis mucosa, and submucosa/muscularis propria/subserosa/serosa and extra serous organ) | 8/13/23/36 |
| Lauren typing (intestinal/mixed/diffuse/unknown) | 21/21/30/8 |
| Nerve invasion (No/yes/unknown) | 32/42/6 |
| Vascular invasion (no/yes/unknown) | 46/28/6 |
| pN (0/1/2/3) | 27/15/17/21 |
| pM (No/Yes) | 76/4 |
| TNM stage (I/II/III/IV) | 13/24/39/4 |
| Her2 (negative/positive) | 65/15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Su, B.; Shan, Z.; Gao, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Yuan, S.; Sun, S.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of Gastric Cancer Revealed by a Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Study. Metabolites 2025, 15, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040222
Zhou L, Su B, Shan Z, Gao Z, Guo X, Wang W, Wang X, Sun W, Yuan S, Sun S, et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of Gastric Cancer Revealed by a Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Study. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040222
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Lina, Benzhe Su, Zexing Shan, Zhenbo Gao, Xingyu Guo, Weiwei Wang, Xiaolin Wang, Wenli Sun, Shuai Yuan, Shulan Sun, and et al. 2025. "Metabolic Reprogramming of Gastric Cancer Revealed by a Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Study" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040222
APA StyleZhou, L., Su, B., Shan, Z., Gao, Z., Guo, X., Wang, W., Wang, X., Sun, W., Yuan, S., Sun, S., Zhang, J., Xu, G., & Lin, X. (2025). Metabolic Reprogramming of Gastric Cancer Revealed by a Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Study. Metabolites, 15(4), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040222







