Disorders of Iron Metabolism: A “Sharp Edge” of Deoxynivalenol-Induced Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Grouping and Sampling
2.2. Liver Function Assessment
2.3. Liver Histomorphology Analysis
2.4. Liver Fe2+ Content
2.5. Measurement of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Indicators
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Immunofluorescence Double Staining
2.8. Western Blotting Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. DON-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
3.2. DON-Induced Changes in Liver Oxidative Stress-Related Indices in Mice
3.3. DON-Induced Ferroptosis Signature Pathway and mRNA Expression Levels of Nrf2 and Its Downstream Pathways in Mouse Livers
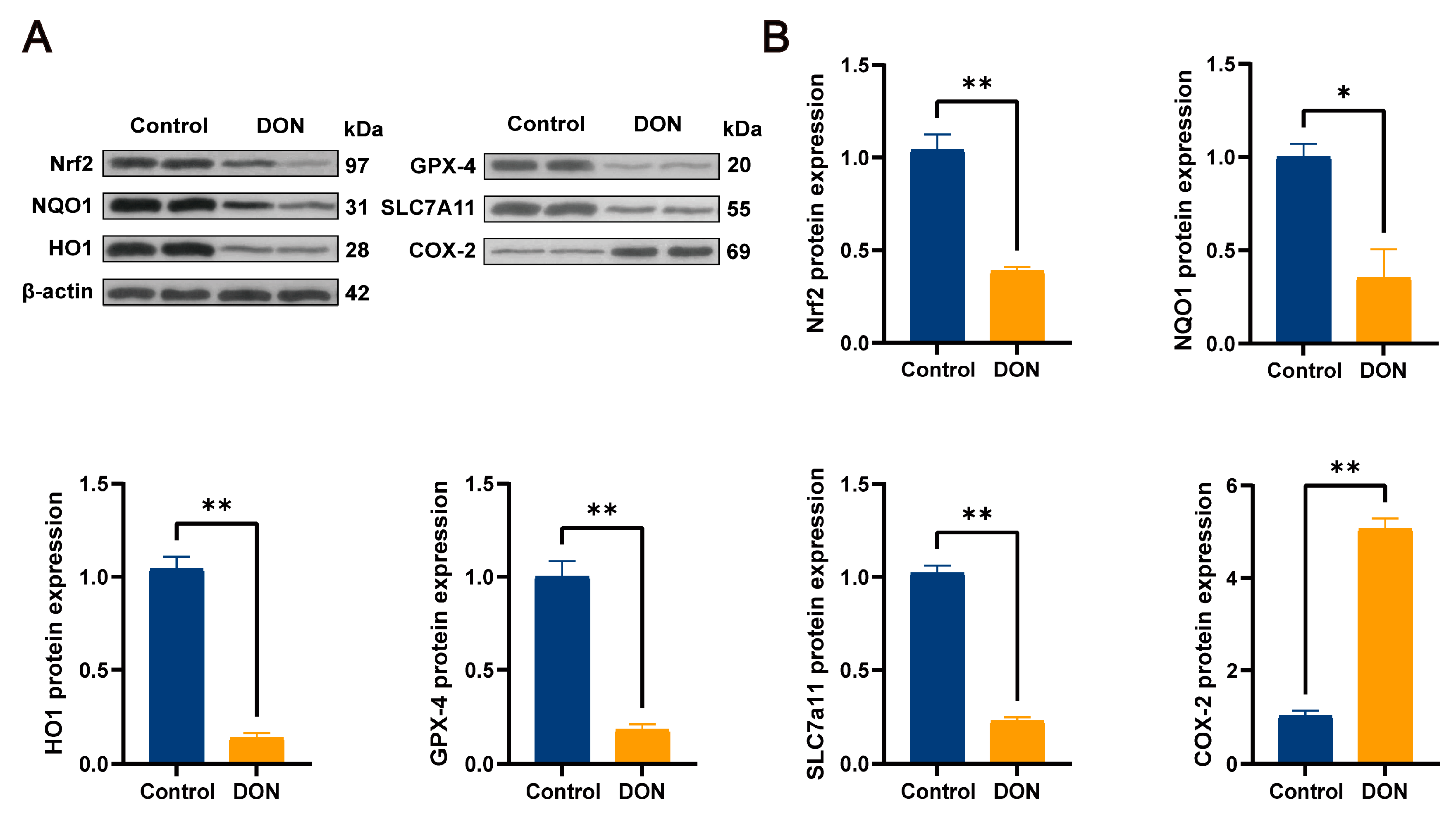
3.4. DON-Induced Ferroptosis Signature Pathway and Protein Expression Levels of Nrf2 and Its Downstream Pathways in Mouse Livers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DON | Deoxynivalenol |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| CAT | Catalase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| T-AOC | Total antioxidant capacity |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase |
| NQO1 | Quinone oxidoreductase 1 |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| SLC7a11 | Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 |
| DON-GlcA | DON-glucuronide |
| UGT | UDP-Glycosyltransferase |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| PG | Prostaglandins |
| AA | Acid |
| PTGS2 | Prostaglandin–endoperoxide synthase 2 |
References
- Cavret, S.; Lecoeur, S. Fusariotoxin transfer in animal. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liao, Y.; Peng, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Nüssler, A.K.; Shi, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, W. Food raw materials and food production occurrences of deoxynivalenol in different regions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.S.; Roux, J.; Mounien, L.; Dallaporta, M.; Troadec, J.D. Advances in deoxynivalenol toxicity mechanisms: The brain as a target. Toxins 2012, 4, 1120–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J.J. Deoxynivalenol: Mechanisms of action, human exposure, and toxicological relevance. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, M.; Momonaka, Y.; Yokose, C.; Tadaishi, M.; Shimizu, M.; Yamane, T.; Oishi, Y.; Kobayashi-Hattori, K. Anorexic action of deoxynivalenol in hypothalamus and intestine. Toxicon 2016, 118, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Peng, Z.; Liao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Qin, C.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Cai, Q.; et al. Deoxynivalenol-induced oxidative stress and Nrf2 translocation in maternal liver on gestation day 12.5 d and 18.5 d. Toxicon 2019, 161, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Favero, G.; Woelflingseder, L.; Braun, D.; Puntscher, H.; Kütt, M.L.; Dellafiora, L.; Warth, B.; Pahlke, G.; Dall’Asta, C.; Adam, G.; et al. Response of intestinal HT-29 cells to the trichothecene mycotoxin deoxynivalenol and its sulfated conjugates. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 295, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.; Tan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, G. Hazard assessment of the health effects of deoxynivalenol. J. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Sun, L.H.; Wang, X. Cytochrome P450 enzymes mediated by DNA methylation is involved in deoxynivalenol-induced hepatoxicity in piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Chen, L.; Nüssler, A.K.; Liu, L.; Yang, W. Current sights for mechanisms of deoxynivalenol-induced hepatotoxicity and prospective views for future scientific research: A mini review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Mo, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Karrow, N.A.; Wu, H.; Sun, L. Ferroptosis is involved in deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal damage in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Huang, T.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Deoxynivalenol induces testicular ferroptosis by regulating the Nrf2/System Xc−/GPX4 axis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 175, 113730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Ruan, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, H. Ferritinophagy is critical for deoxynivalenol-induced liver injury in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 6660–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Lin, L.; Li, P.; Tian, H.; Shen, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Tang, C. Selenomethionine protects the liver from dietary deoxynivalenol exposure via Nrf2/PPARγ-GPX4-ferroptosis pathway in mice. Toxicology 2024, 501, 153689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, M.; Martí-Bonmatí, L.; Porto, G.; Silva, S.; Guimarães, S.; Alberich-Bayarri, Á.; Vizcaíno, J.; Miranda, H.P. Tissue iron quantification in chronic liver diseases using MRI shows a relationship between iron accumulation in liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 215.e1–215.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.J.; Velardi, E.; Shono, Y.; Argyropoulos, K.V.; Holland, A.M.; Smith, O.M.; Yim, N.L.; Rao, U.K.; Kreines, F.M.; Lieberman, S.R.; et al. Nrf2 regulates CD4+ T cell–induced acute graft-versus-host disease in mice. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2018, 132, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, M.; Castro-Portuguez, R.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 23, 101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Ma, K.; Ren, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Shan, A. Dihydroartemisinin alleviates deoxynivalenol induced liver apoptosis and inflammation in piglets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelstraete, W.; Devreese, M.; Croubels, S. Comparative toxicokinetics of Fusarium mycotoxins in pigs and humans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazar, S.; Omurtag, G.Z. Fumonisins, trichothecenes and zearalenone in cereals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2062–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthey, F.A.; Wolf-Hall, C.E.; Yalla, S.; Vijayakumar, C.; Carlson, D. Microbial loads, mycotoxins, and quality of durum wheat from the 2001 harvest of the northern plains region of the United States. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardivel, C.; Airault, C.; Djelloul, M.; Guillebaud, F.; Barbouche, R.; Troadec, J.D.; Gaigé, S.; Dallaporta, M. The food born mycotoxin deoxynivalenol induces low-grade inflammation in mice in the absence of observed-adverse effects. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Liao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Qin, C.; Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Hu, J.; Li, D.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 regulates autophagy through carbon–oxygen to alleviate deoxynivalenol-induced hepatic damage. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.; Prasse, K.; Mahaffey, E. Veterinary Laboratory Medicine: Clinical Pathology; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, J.; Ratner, M.; Shaw, M.; Bailey, W.; Schomaker, S. The current state of serum biomarkers of hepatotoxicity. Toxicology 2008, 245, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Shen, T.; Ding, Q.; Lv, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, K.; Yan, L.; Song, S. Zearalenone induces ROS-mediated mitochondrial damage in porcine IPEC-J2 cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, H.; Zong, Q.; Ahmed, A.A.; Bao, W.; Liu, H.Y.; Cai, D. Lactoferrin relieves Deoxynivalenol-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response by modulating the Nrf2/MAPK pathways in the liver. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8182–8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D. GPX4 in cell death, autophagy, and disease. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2621–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2054–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, F.; Kroemer, G.; Klionsky, D.J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yu, K.; Yu, H.; Wang, P.; Song, M.; Xiu, C.; Li, Y. Lycopene relieves AFB1-induced liver injury through enhancing hepatic antioxidation and detoxification potential with Nrf2 activation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 39, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, T.L.; Rupasinghe, H.V.; Dellaire, G.; Xu, Z. Regulation of Nrf2/ARE pathway by dietary flavonoids: A friend or foe for cancer management? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mine, Y.; Young, D.; Yang, C. Antioxidative stress effect of phosphoserine dimers is mediated via activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, I.-G.; Shin, D.-H.; Kang, K.-S.; Kwak, M.-K. Involvement of Nrf2-GSH signaling in TGFβ1-stimulated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition changes in rat renal tubular cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2015, 38, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, L.; Yuan, S.; Zhuang, X.; Qiao, T.; He, J. Ferroptosis inhibitor alleviates Radiation-induced lung fibrosis (RILF) via down-regulation of TGF-β1. J. Inflamm. 2019, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagallier, C.; Avry, F.; Touchefeu, Y.; Buron, F.; Routier, S.; Chérel, M.; Arlicot, N. Development of PET radioligands targeting COX-2 for colorectal cancer staging, a review of in vitro and preclinical imaging studies. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 675209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Niu, C.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, S.; Liu, D. Hyperoxia-activated Nrf2 regulates ferroptosis in intestinal epithelial cells and intervenes in inflammatory reaction through COX-2/PGE2/EP2 pathway. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, H.; Cui, Y.; Hua, Z.; Deng, Y.; Deng, H.; Deng, J. Disorders of Iron Metabolism: A “Sharp Edge” of Deoxynivalenol-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Metabolites 2025, 15, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030165
Guan H, Cui Y, Hua Z, Deng Y, Deng H, Deng J. Disorders of Iron Metabolism: A “Sharp Edge” of Deoxynivalenol-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Metabolites. 2025; 15(3):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030165
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Haoyue, Yujing Cui, Zixuan Hua, Youtian Deng, Huidan Deng, and Junliang Deng. 2025. "Disorders of Iron Metabolism: A “Sharp Edge” of Deoxynivalenol-Induced Hepatotoxicity" Metabolites 15, no. 3: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030165
APA StyleGuan, H., Cui, Y., Hua, Z., Deng, Y., Deng, H., & Deng, J. (2025). Disorders of Iron Metabolism: A “Sharp Edge” of Deoxynivalenol-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Metabolites, 15(3), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030165




