Reference Intervals of Serum Metabolites and Lipids of a Healthy Chinese Population Determined by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
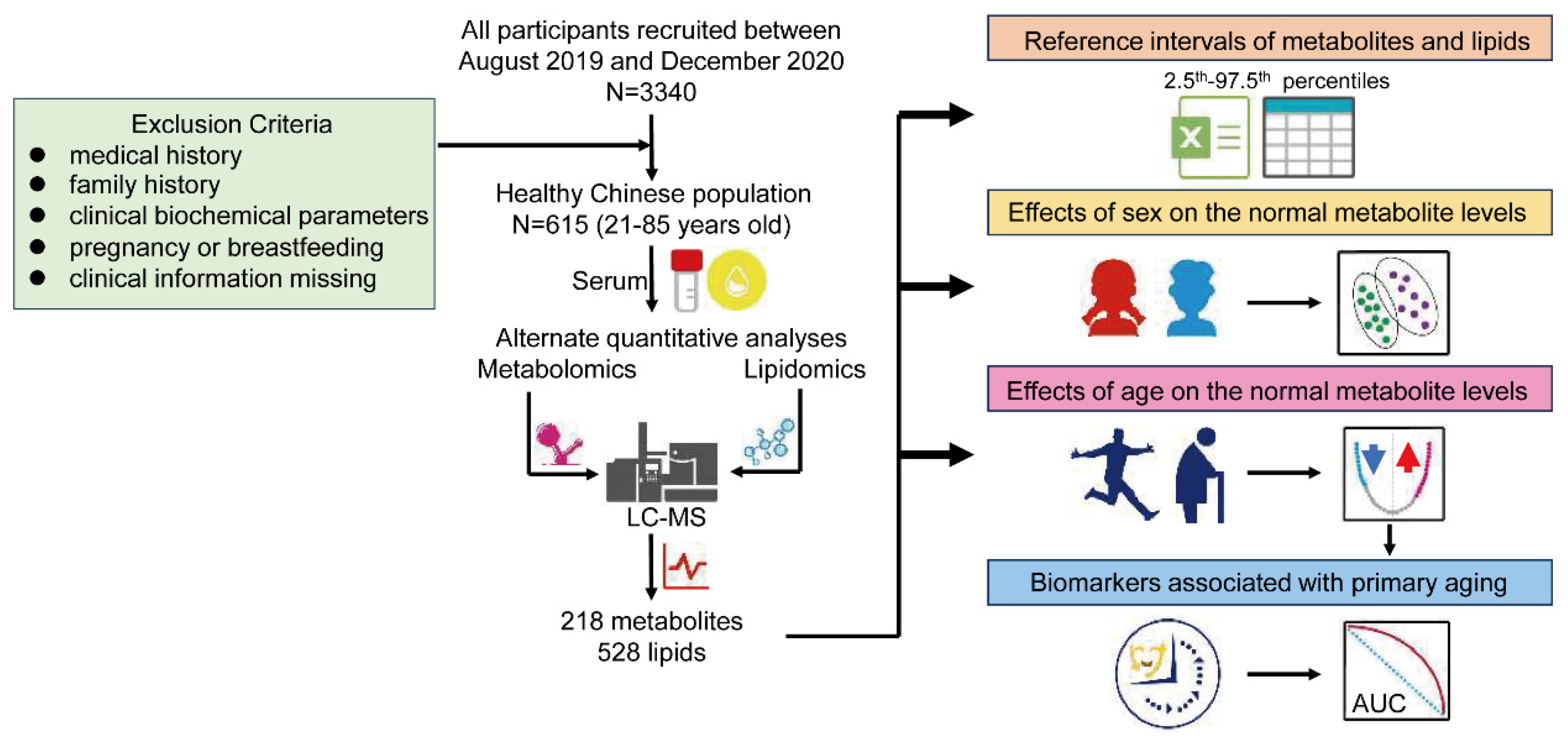
2.2. Study Cohort and Approval
2.3. Metabolome and Lipidome Extractions and RPLC-MS Analysis
2.4. Pre-Processing of Data and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
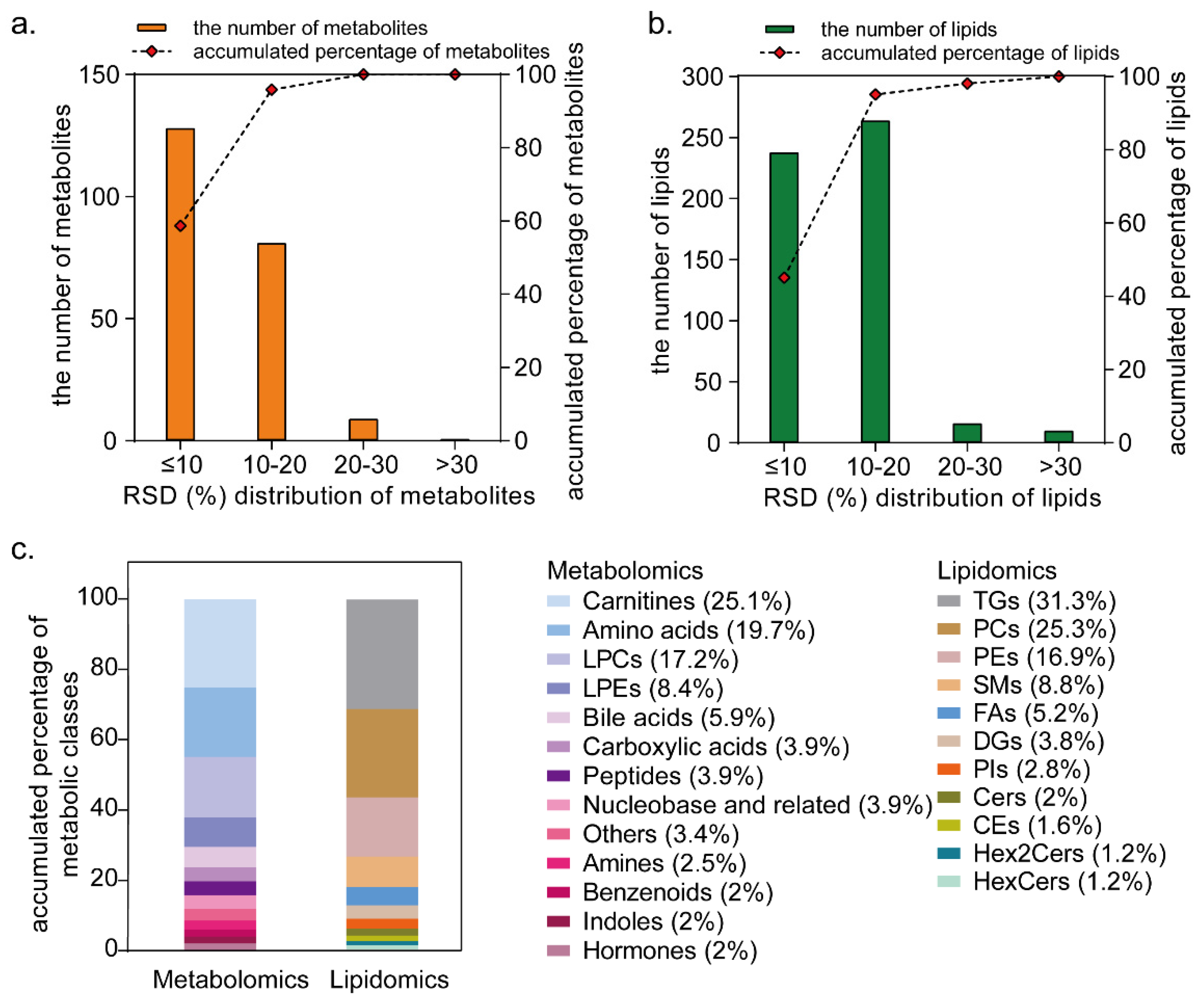
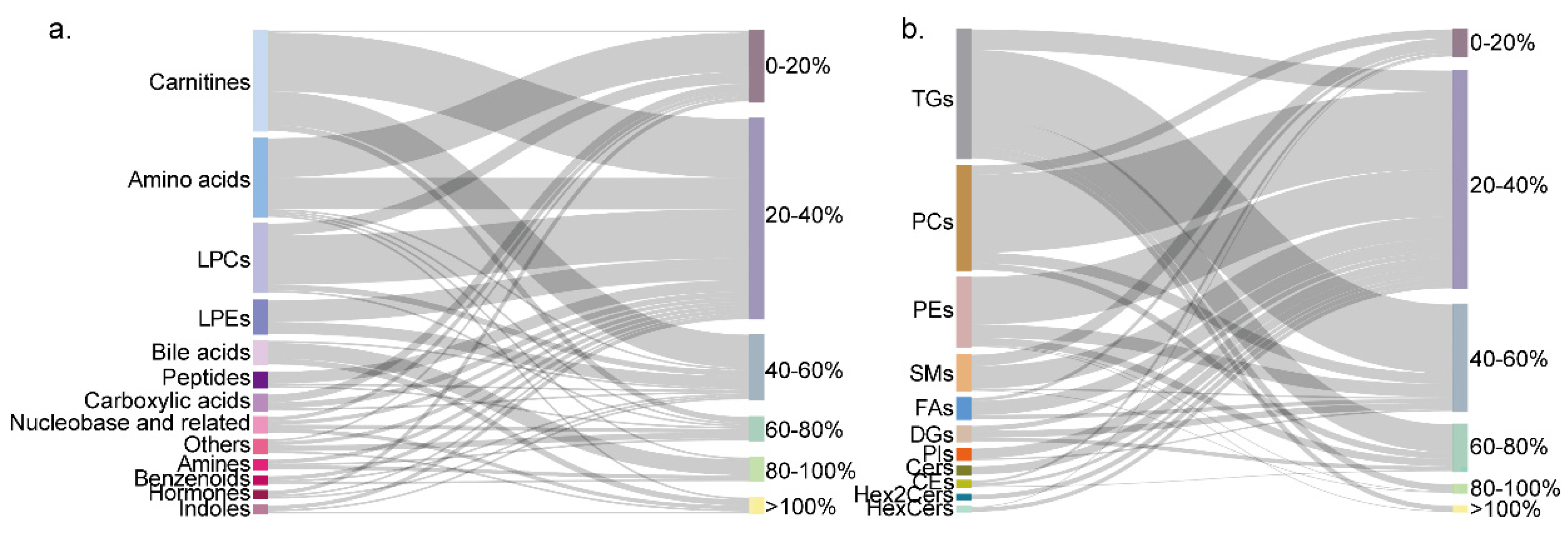
3.1. Targeted Metabolome and Lipidome Profiling
3.2. Establishment of Reference Intervals for Metabolites and Lipids
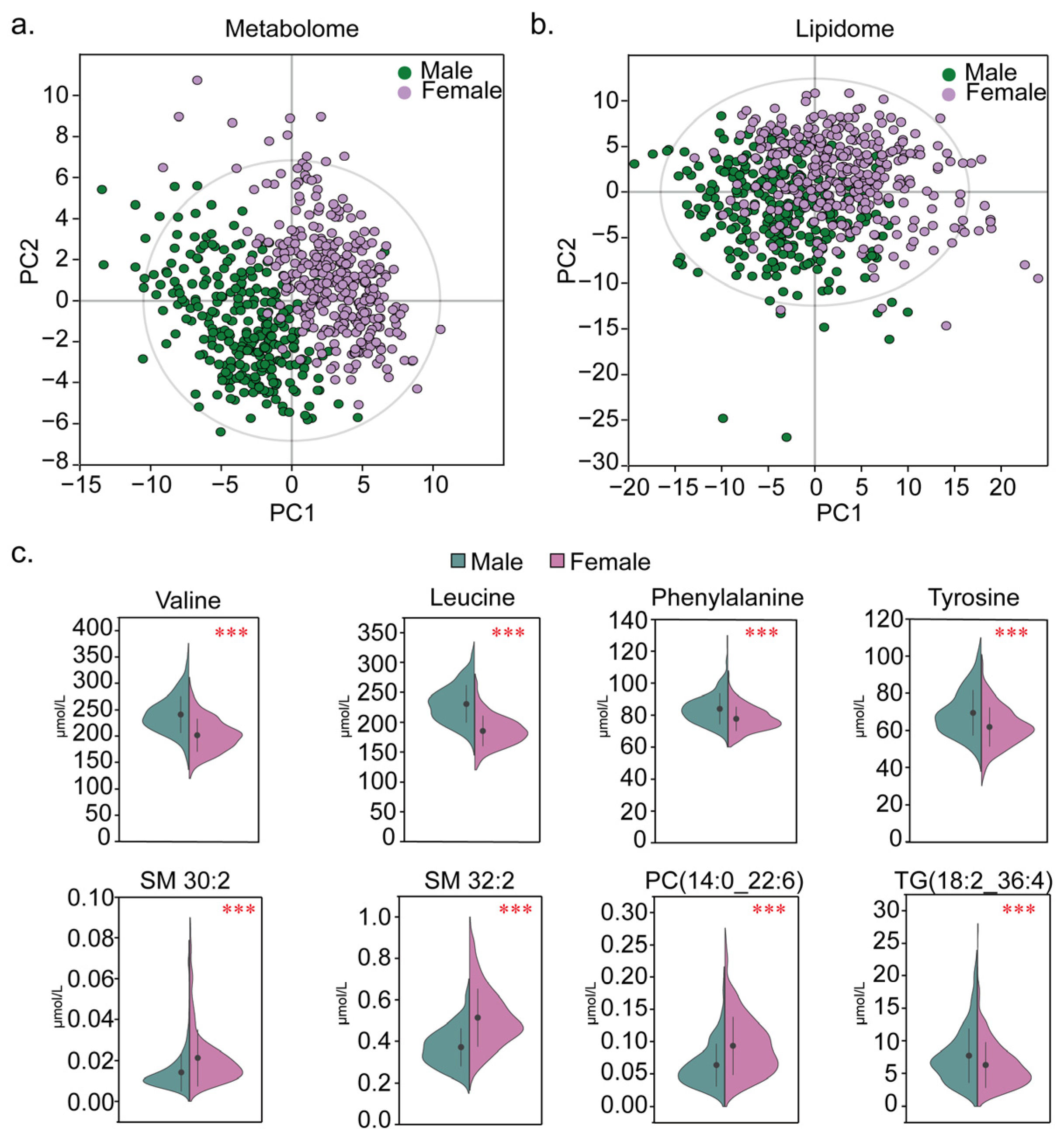
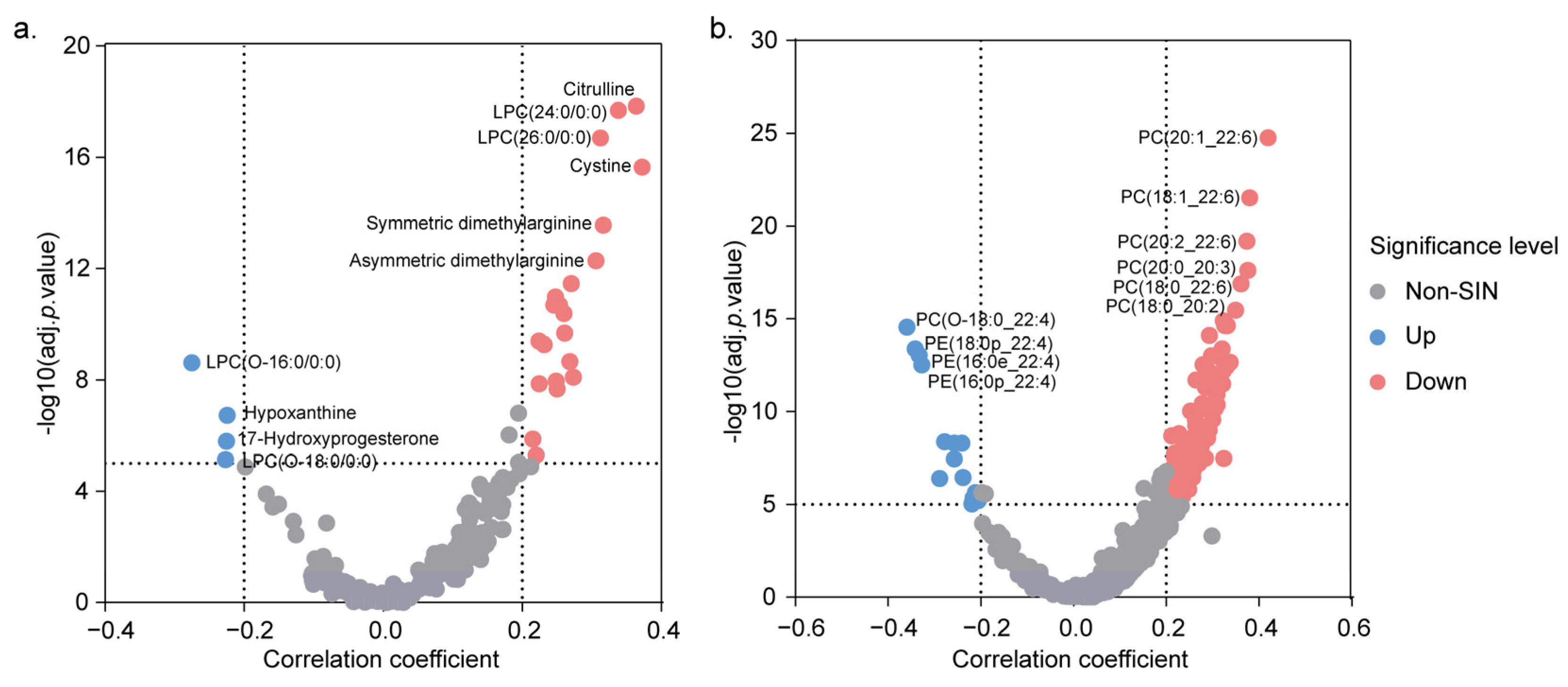
3.3. Effects of Sex on the Metabolome and Lipidome Levels
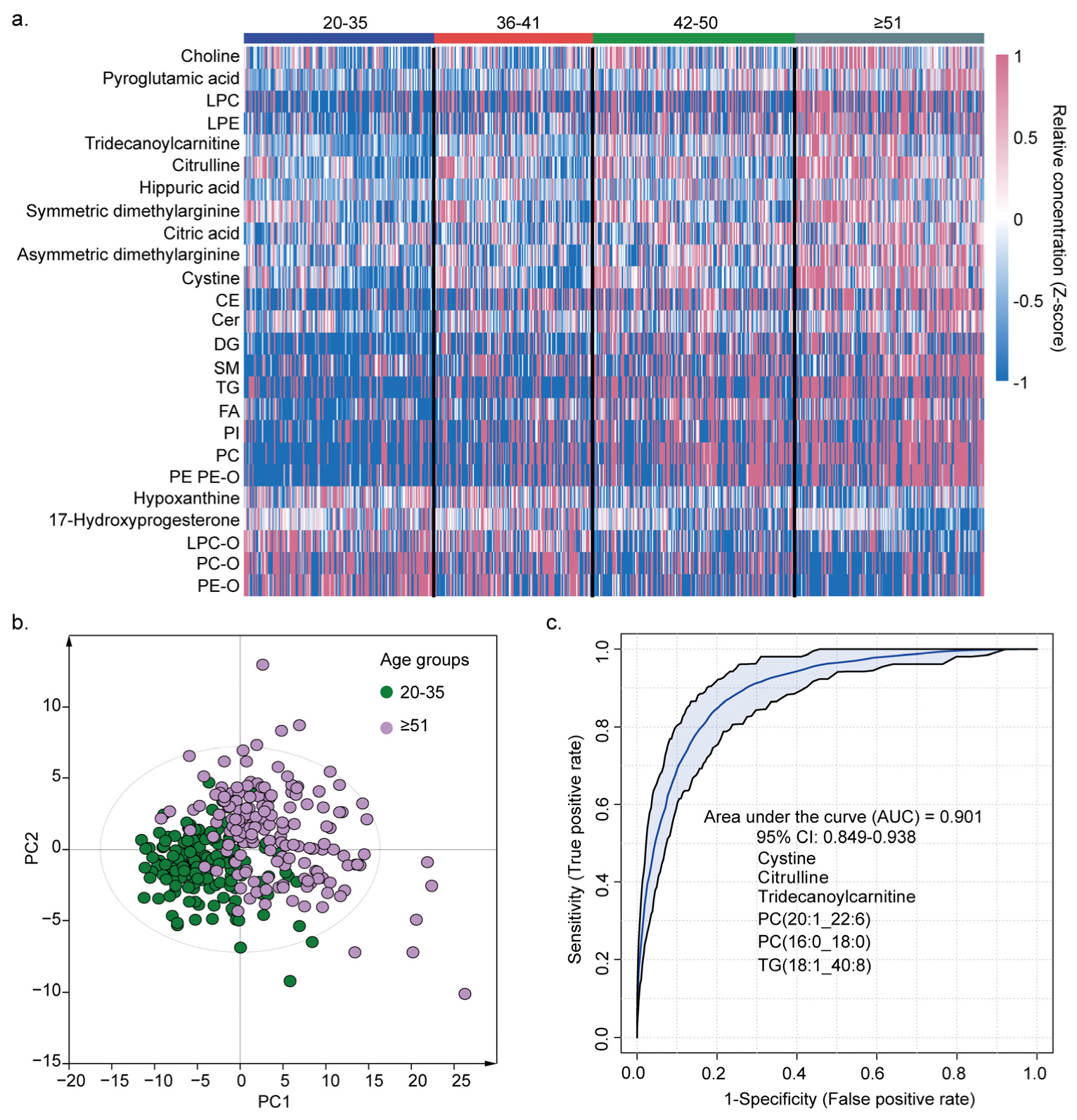
3.4. Effects of Age on the Metabolome and Lipidome Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serkova, N.J.; Standiford, T.J.; Stringer, K.A. The emerging field of quantitative blood metabolomics for biomarker discovery in critical illnesses. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, J.B.; Hammock, B.D.; Watkins, S.M. Metabolomics: Building on a century of biochemistry to guide human health. Metabolomics 2005, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebani, A.; Afonso, C.; Marret, S.; Bekri, S. Omics-based strategies in precision medicine: Toward a paradigm shift in inborn errors of metabolism investigations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Snyder, M.P. Integrative omics for health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, D.; Noureldein, M.; Bezdeková, D.; Schram, A.; Howard, R.; Powers, R. A reproducibility crisis for clinical metabolomics studies. Trends Analyt Chem. 2024, 180, 117918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstikov, V.; Moser, A.J.; Sarangarajan, R.; Narain, N.R.; Kiebish, M.A. Current status of metabolomic biomarker discovery: Impact of study design and demographic characteristics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozarda, Y. Reference intervals: Current status, recent developments and future considerations. Biochem. Med. 2016, 26, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeli, K.; Higgins, V.; Trajcevski, K.; White-Al Habeeb, N. The Canadian laboratory initiative on pediatric reference intervals: A CALIPER white paper. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2017, 54, 358–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Su, Z.; Zhao, M. Big data and reference intervals. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 527, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, P.S.; Pesce, A.J. Reference intervals: An update. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 334, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinu, F.R.; Goldansaz, S.A.; Jaine, J. Translational metabolomics: Current challenges and future opportunities. Metabolites 2019, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusparum, M.; Ertaylan, G.; Thas, O. Individual reference intervals for personalised interpretation of clinical and metabolomics measurements. J. Biomed. Inform. 2022, 131, 104111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, I.Y.; Wilson, A.R.; Delgado, J.C. Reference interval computation: Which method (not) to choose? Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratulic, S.; Limeta, A.; Maccari, F.; Galeotti, F.; Volpi, N.; Levin, M.; Nielsen, J.; Gatto, F. Analysis of normal levels of free glycosaminoglycans in urine and plasma in adults. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Pan, Y.; Cui, X.; Sun, J.; Zhao, F.; Cao, Y. Simultaneous determination of serum homocysteine, cysteine, and methionine in patients with schizophrenia by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustolin, S.; Giugliani, R.; Félix, T.M. Genetics of homocysteine metabolism and associated disorders. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Milburn, M.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Lonergan, S.C.; Mitchell, M.W.; Wulff, J.E.; Alexander, D.C.; Evans, A.M.; Bridgewater, B.; Miller, L.; et al. Plasma metabolomic profiles enhance precision medicine for volunteers of normal health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4901–E4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabado, S.; Al-Salameh, A.; Croixmarie, V.; Masson, P.; Corruble, E.; Fève, B.; Colle, R.; Ripoll, L.; Walther, B.; Boursier-Neyret, C.; et al. The human plasma-metabolome: Reference values in 800 French healthy volunteers; impact of cholesterol, gender and age. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, N.; Korem, T.; Weissbrod, O.; Zeevi, D.; Rothschild, D.; Leviatan, S.; Kosower, N.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Weinberger, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; et al. A reference map of potential determinants for the human serum metabolome. Nature 2020, 588, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbenstedt, A.; Ziarrusta, H.; Benskin, J.P. Development, characterization and comparisons of targeted and non-targeted metabolomics methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, O.I.; Sandberg, A.S.; Ross, A.B. A simultaneous metabolic profiling and quantitative multimetabolite metabolomic method for human plasma using gas-chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, G. Comprehensive metabolite quantitative assay based on alternate metabolomics and lipidomics analyses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1215, 339979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, C.Z.; Ragland, J.M.; Koelmel, J.P.; Heckert, A.; Jones, C.M.; Garrett, T.J.; Yost, R.A.; Bowden, J.A. LipidQC: Method validation tool for visual comparison to SRM 1950 using NIST interlaboratory comparison exercise lipid consensus mean estimate values. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13069–13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Balasubramanian, R.; Li, J.; Clish, B.C.; Paynter, P.N.; Albert, M.C.; Liu, S.; Rosal, C.M.; Nassir, R.; Rexrode, M.K. Abstract MP55: Racial Differences in Metabolomic Profiles Between African Americans and Whites in the Women’s Health Initiative. Circulation 2019, 139, MP55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Song, J.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, L.; Qiao, Y.; Li, B.; Xia, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Targeting the metabolic profile of amino acids to identify the key metabolic characteristics in cerebral palsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1237745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Brown, N.M.; McCoy, A.N.; Sandler, R.S.; Keku, T.O. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, gut microbiota, microbial metabolites, and risk of colorectal adenomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawua, S.A.; Ichihara, K.; Keatley, R.; Arko-Mensah, J.; Ayeh-Kumi, P.F.; Erasmus, R.; Fobil, J. Derivation of sex and age-specific reference intervals for clinical chemistry analytes in healthy Ghanaian adults. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2022, 60, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Bell, J.A.; Cadenas, J.G.; Volpi, E. Basal muscle intracellular amino acid kinetics in women and men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E77–E83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoppolo, M.; Campesi, I.; Scolamiero, E.; Pecce, R.; Caterino, M.; Cherchi, S.; Mercuro, G.; Tonolo, G.; Franconi, F. Serum metabolomic profiles suggest influence of sex and oral contraceptive use. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2014, 6, 614–624. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Han, X. Lipidomics: Techniques, applications, and outcomes related to biomedical sciences. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, H.B.; Olshansky, G.; Smith, A.A.T.; Giles, C.; Huynh, K.; Cinel, M.; Mellett, N.A.; Cadby, G.; Hung, J.; Hui, J.; et al. High-coverage plasma lipidomics reveals novel sex-specific lipidomic fingerprints of age and BMI: Evidence from two large population cohort studies. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000870. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Wang, E.; Innis, W.S.; Mullins, R. Increases in serum sphingomyelin by 17 beta-estradiol. Lipids 1985, 20, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.C.; Martens, C.R.; Santos-Parker, J.R.; Bassett, C.J.; Strahler, T.R.; Cruickshank-Quinn, C.; Reisdorph, N.; McQueen, M.B.; Seals, D.R. Amino acid and lipid associated plasma metabolomic patterns are related to healthspan indicators with ageing. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Ni, Z.; Lam, S.M.; Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Shui, G. Precise metabolomics reveals a diversity of aging-associated metabolic features. Small Methods 2022, 6, e2200130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davignon, J.; Ganz, P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 109, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedhelm, E.; Böger, R.H. The role of asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginines in renal disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seals, D.R.; Jablonski, K.L.; Donato, A.J. Aging and vascular endothelial function in humans. Clin. Sci. 2011, 120, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T. The metabolic regulation of aging. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Otin, C.; Galluzzi, L.; Freije, J.M.P.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. Metabolic control of longevity. Cell 2016, 166, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaarhorst, A.A.; Beekman, M.; Suchiman, E.H.; van Heemst, D.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Westendorp, R.G.; Slagboom, P.E.; Heijmans, B.T.; Leiden Longevity Study (LLS) Group. Lipid metabolism in long-lived families: The Leiden Longevity Study. Age 2011, 33, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.C.; Parker, K.; Aguirre, B.F.; Nemkov, T.G.; D’Alessandro, A.; Johnson, S.A.; Seals, D.R.; Martens, C.R. The plasma metabolome as a predictor of biological aging in humans. Geroscience 2019, 41, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornburg, D.; Wu, S.; Moqri, M.; Zhou, X.; Contrepois, K.; Bararpour, N.; Traber, M.G.; Su, B.; Metwally, A.A.; Avina, M.; et al. Dynamic lipidome alterations associated with human health, disease and ageing. Nat. Metabolism. 2023, 5, 1578–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.M.; Lodhi, I.J. Structural and functional roles of ether lipids. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, P.L.; Mankidy, R.; Ritchie, S.; Heath, D.; Wood, J.A.; Flax, J.; Goodenowe, D.B. Circulating plasma logen levels and alzheimer disease assessment scale-cognitive scores in alzheimer patients. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2010, 35, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 615 | 286 | 329 |
| Age (years) (SD) | 43.5 ± 11.3 | 44.5 ± 12.3 | 42.5 ± 10.3 |
| Waistline (cm) (SD) | 78.3 ± 8.1 | 82.9 ± 6.8 | 74.3 ± 6.8 |
| Body mass index (Kg/m2) (SD) | 22.5 ± 2.4 | 23.2 ± 2.3 | 21.8 ± 2.3 |
| Systematic blood pressure (mmHg) (SD) | 118.4 ± 10.8 | 120.9 ± 10.1 | 116.2 ± 10.9 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) (SD) | 72 ± 8.1 | 74 ± 7.4 | 70.2 ± 8.2 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) (SD) | 67.1 ± 14.1 | 79 ± 9.7 | 56.7 ± 7.6 |
| Uric acid (µmol/L) (SD) | 308.7 ± 62.2 | 352.8 ± 45.4 | 270.5 ± 47.9 |
| Blood glucose (mmol/L) (SD) | 5.3 ± 0.3 | 5.4 ± 0.3 | 5.2 ± 0.3 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) (SD) | 4.7 ± 0.7 | 4.6 ± 0.7 | 4.7 ± 0.7 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) (SD) | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mmol/L) (SD) | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.3 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mmol/L) (SD) | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.4 ± 0.6 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) (SD) | 142.1 ± 15.4 | 154.2 ± 9.2 | 131.7 ± 11.5 |
| Erythrocyte count (1012/L) (SD) | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 4.5 ± 0.3 |
| Leukocyte count (109/L) (SD) | 5.5 ± 1.3 | 5.7 ± 1.4 | 5.4 ± 1.2 |
| Absolute neutrophil count (109/L) (SD) | 3.3 ± 1.0 | 3.3 ± 1.0 | 3.3 ± 1.0 |
| Absolute lymphocyte count (109/L) (SD) | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 |
| Platelet count (109/L) (SD) | 236 ± 52.3 | 222.4 ± 46.2 | 247.8 ± 54.5 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) (SD) | 18.9 ± 8.4 | 21.5 ± 9.1 | 16.7 ± 7.1 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (U/L) (SD) | 20.6 ± 5.2 | 21.4 ± 4.9 | 20 ± 5.4 |
| γ-Glutamyl transferase (U/L) (SD) | 16.2 ± 9.1 | 19.6 ± 10.2 | 13.2 ± 6.9 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) (SD) | 56.3 ± 14.4 | 60.3 ± 15.0 | 52.9 ± 13.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, X.; Jia, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, G. Reference Intervals of Serum Metabolites and Lipids of a Healthy Chinese Population Determined by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2025, 15, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020106
Zhang Y, Zhao J, Zhao H, Lu X, Jia X, Zhao X, Xu G. Reference Intervals of Serum Metabolites and Lipids of a Healthy Chinese Population Determined by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites. 2025; 15(2):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuqing, Jinhui Zhao, Hui Zhao, Xin Lu, Xueni Jia, Xinjie Zhao, and Guowang Xu. 2025. "Reference Intervals of Serum Metabolites and Lipids of a Healthy Chinese Population Determined by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry" Metabolites 15, no. 2: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020106
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhao, J., Zhao, H., Lu, X., Jia, X., Zhao, X., & Xu, G. (2025). Reference Intervals of Serum Metabolites and Lipids of a Healthy Chinese Population Determined by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites, 15(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020106







