Metabolomic Revelations into the Dynamic Transformations Across Various Developmental Stages of Coprinus comatus Through UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coprinus comatus Cultivation and Collection
2.2. Metabolomics
2.2.1. Sample Preparation and Extraction
2.2.2. UHPLC-HRMS Analysis
2.2.3. Metabolite Identification and Data Analysis
2.3. Determination of Total Phenols and DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
3. Results
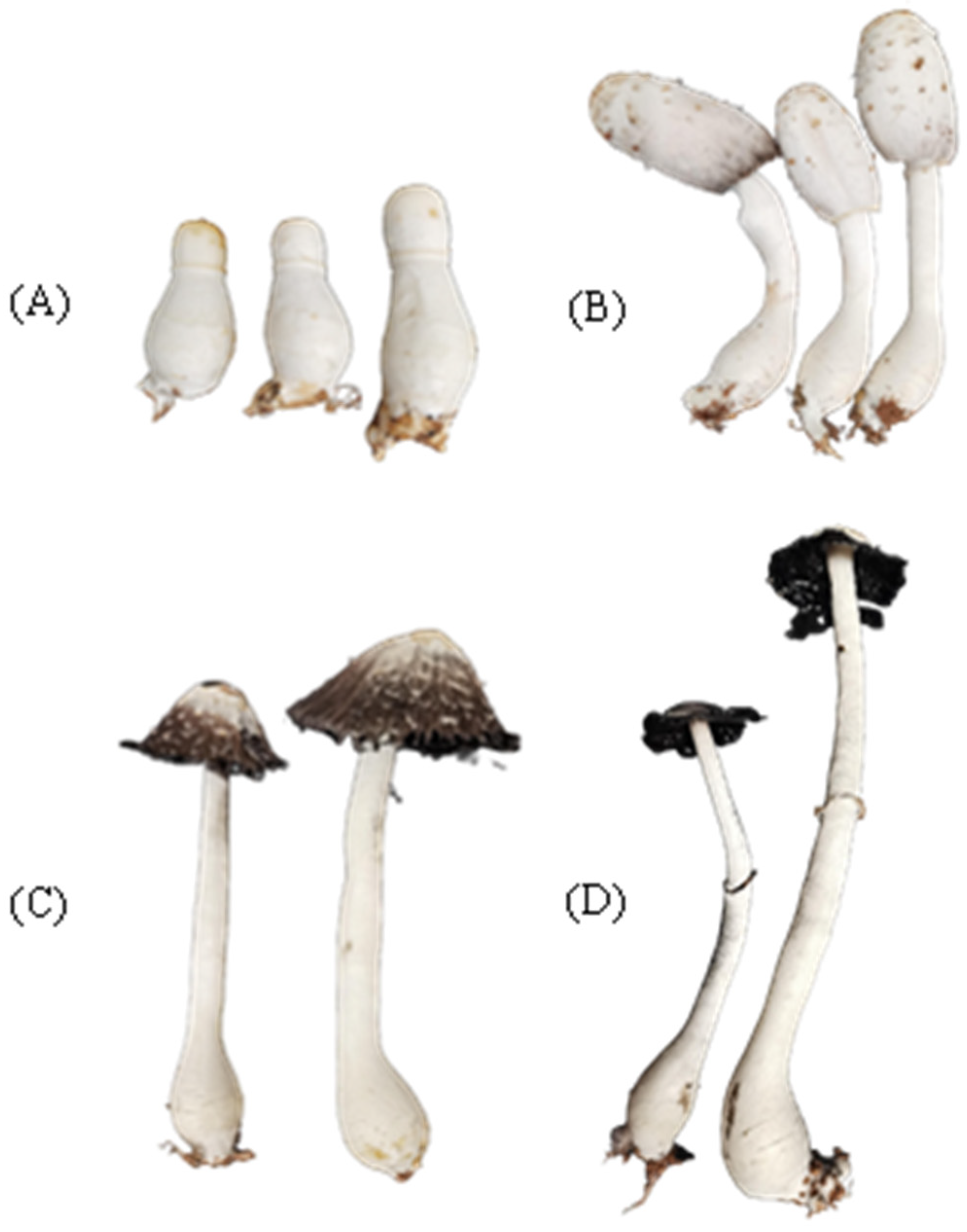
3.1. Coprinus comatus Cultivation and Collection
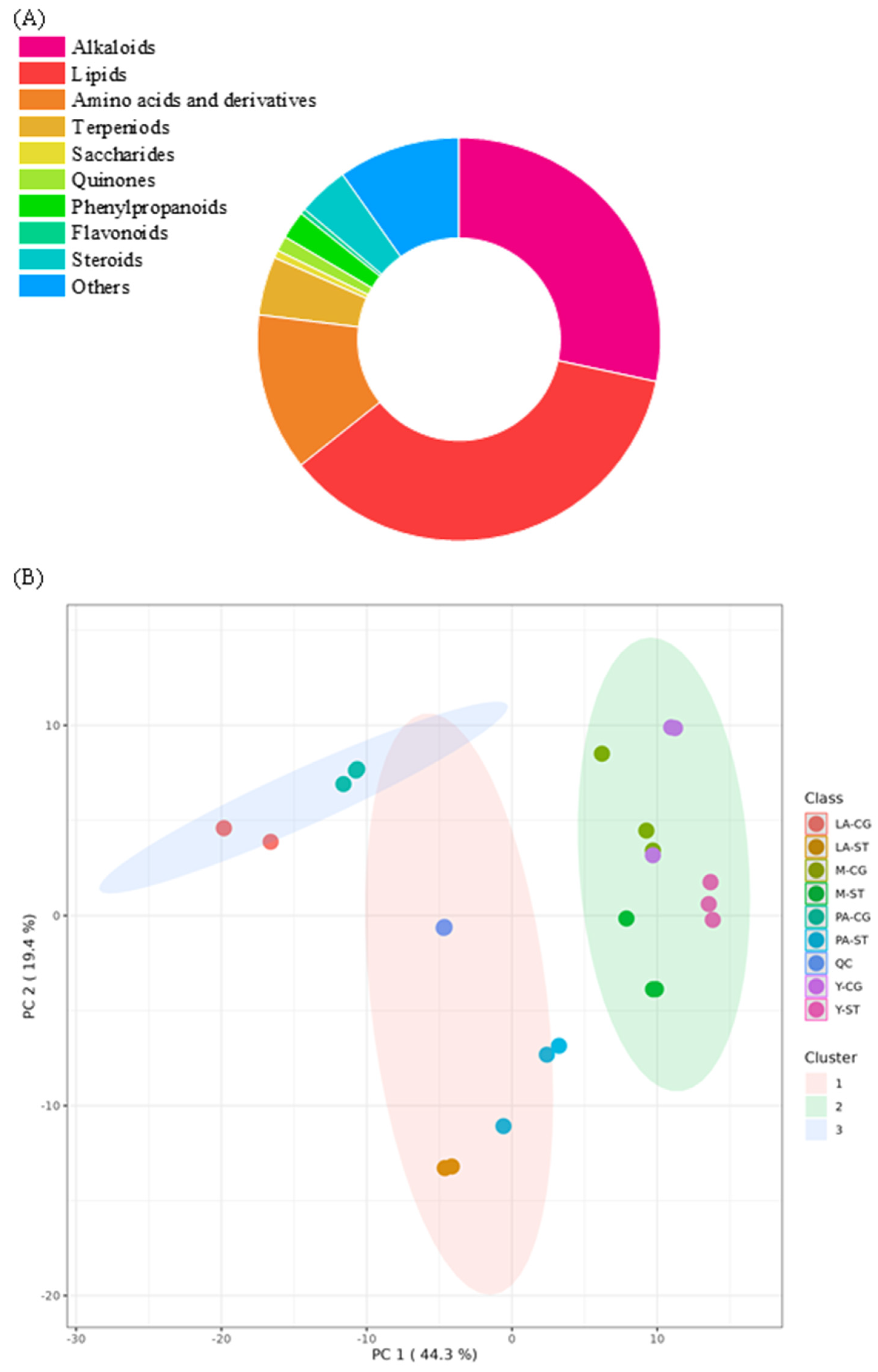
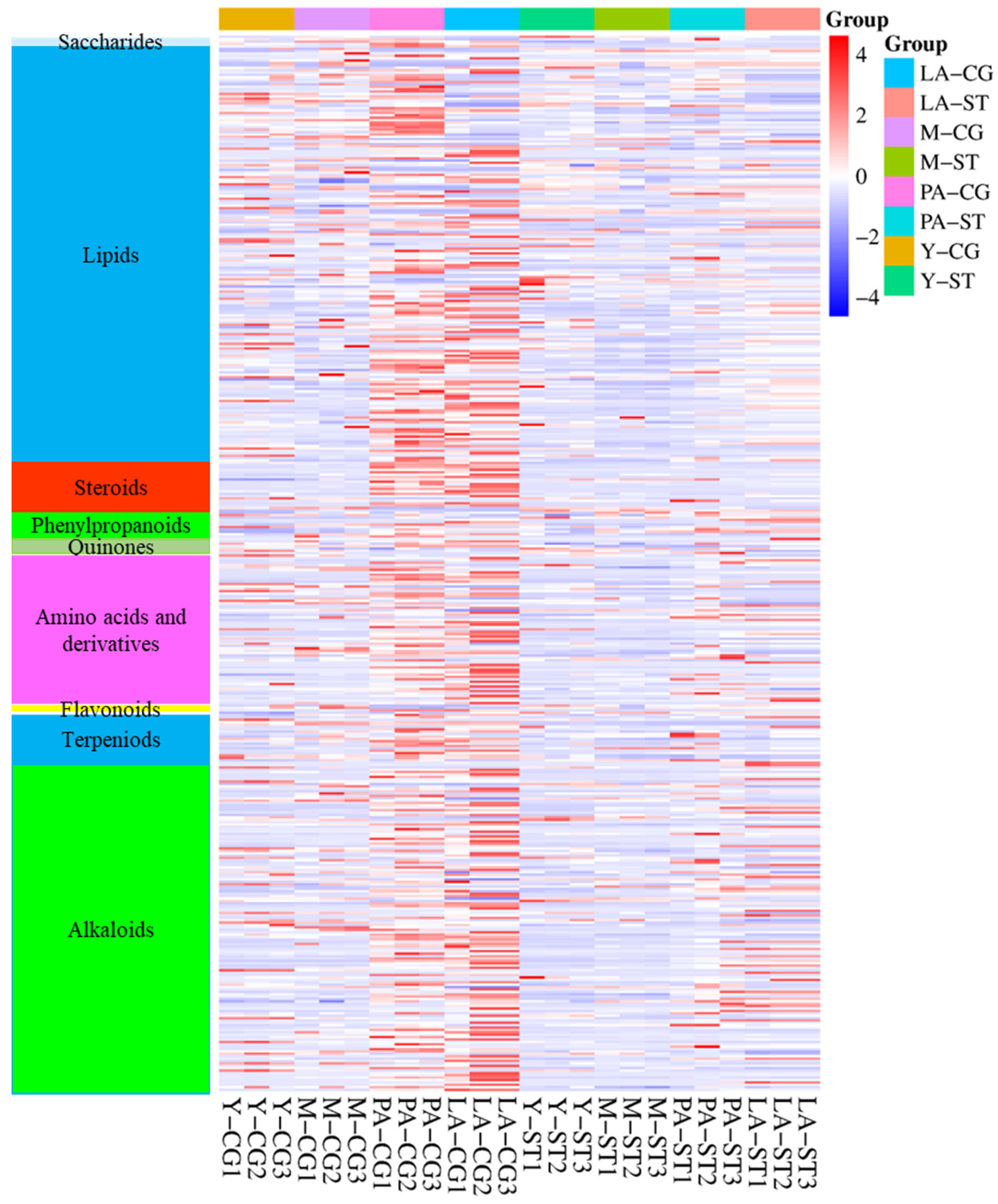
3.2. Analysis of Metabolite in the Four Stages of the Coprinus comatus Fruiting Body
3.3. Analysis of the Metabolite Differences Between CG and ST at the Same Stage and CG or ST Between Adjacent Stages
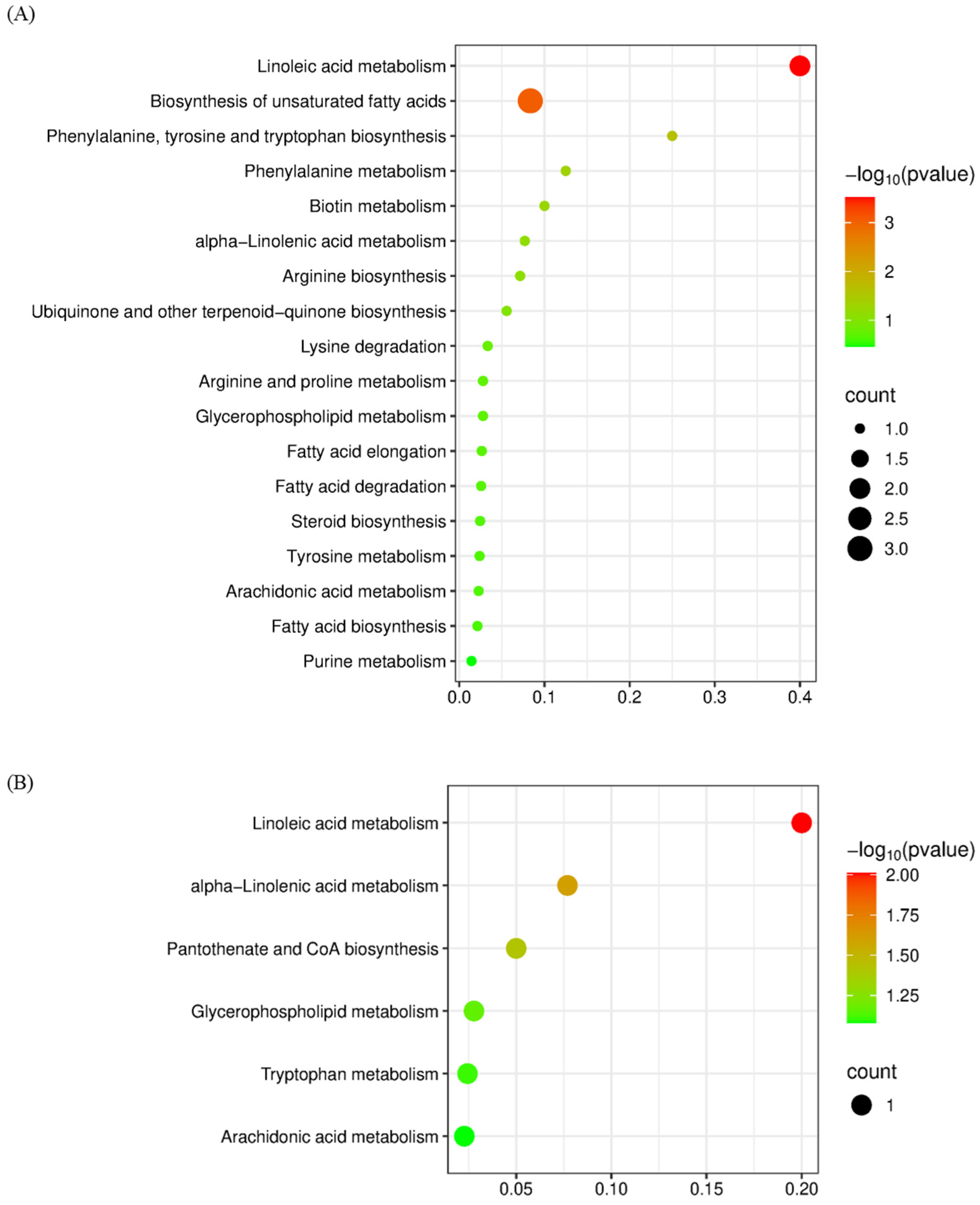
3.4. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DAMs Between Adjacent CG Samples
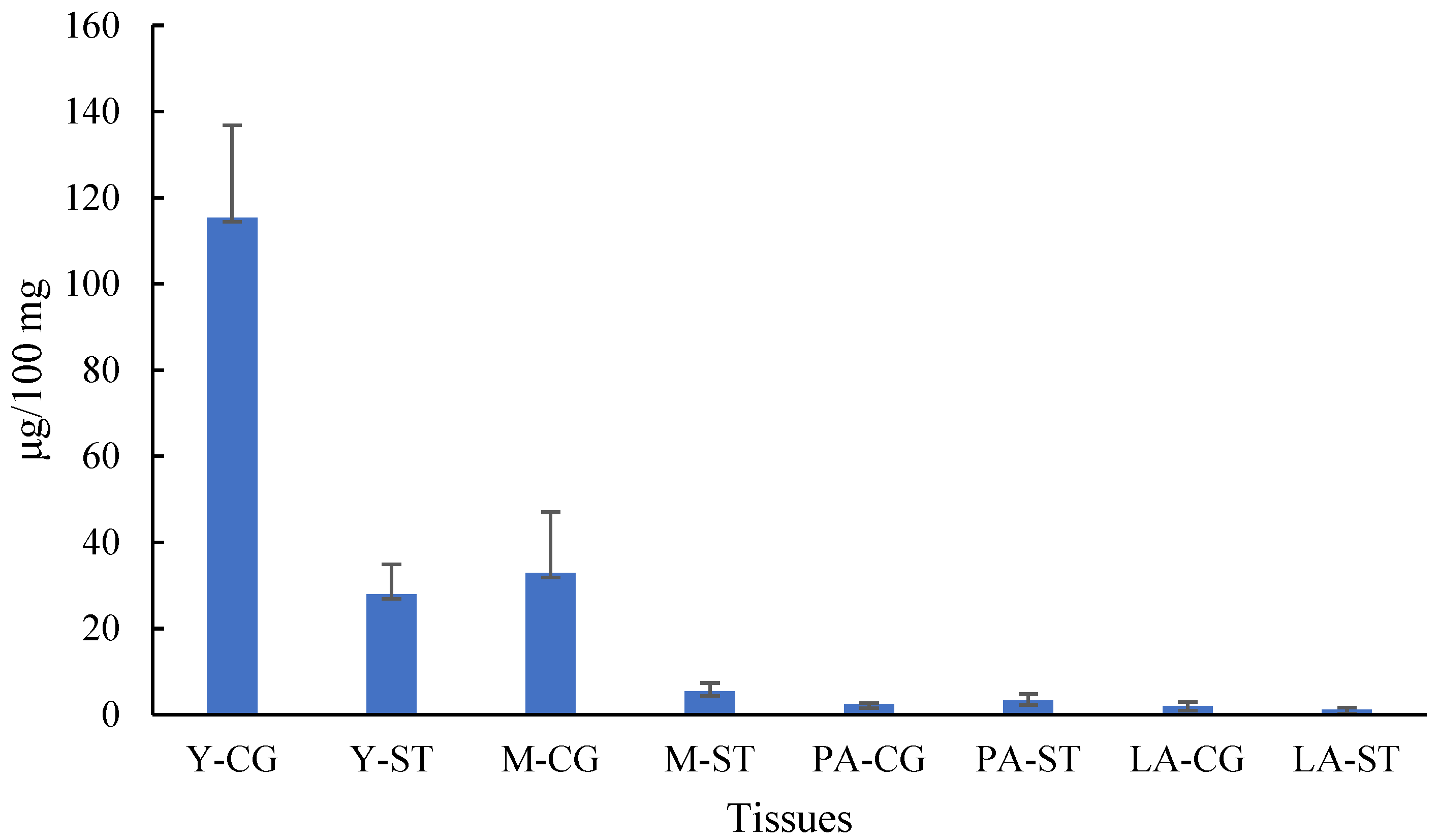
3.5. Determination of Total Phenols and DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CG | cap and gills tissues |
| ST | stipe tissues |
| DAM | differential accumulated metabolites |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| POD | peroxidase |
| CAT | catalase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| Y | the young mushroom stage |
| M | the maturation stage |
| PA | the pre-autolysis stage |
| LA | the late autolysis stage |
| QC | quality control |
| TIC | total ion current |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| dd-MS2 | MS–data-dependent product ion scan |
| ESI | electrospray ionization |
| AGC | automatic gain control |
| NCE | normalized collision energy |
| VIP | variable importance in projection |
| FC | fold change |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
References
- Stilinovic, N.; Capo, I.; Vukmirovic, S.; Raskovic, A.; Tomas, A.; Popovic, M.; Sabo, A. Chemical composition, nutritional profile and in vivo antioxidant properties of the cultivated mushroom Coprinus comatus. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J.; Li, H.P.; Lai, Q.Q.; Yang, Q.H.; Dong, Y.H.; Liu, X.C.; Wang, W.S.; Zhang, J.J.; Jia, L. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of modified polysaccharides from Coprinus comatus in mice with alcohol-induced liver injury. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Kong, D.Y.; Cai, W.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Jia, L. Characterization and anti-diabetic nephropathic ability of mycelium polysaccharides from Coprinus comatus. Carbohy. Polym. 2021, 251, 117081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabutaje, E.M.; Seki, K.; Kodama, M.; Arie, T.; Ueno, K.; Cruz, T.E.E.D.; Ishihara, A. Coprinolide, a novel antifungal tricyclic polyketide with a rare furanone-fused chromene skeleton isolated from the mushroom Coprinus comatus. J. Pestic. Sci. 2024, 49, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, M.; Tesanovic, K.; Novakovic, A.; Jakovljevic, D.; Janjusevic, L.; Sibul, F.; Pejin, B. Coprinus comatus filtrate extract, a novel neuroprotective agent of natural origin. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2346–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Mo, M.H.; Huang, X.W.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.Q. Coprinus comatus: A basidiomycete fungus forms novel spiny structures and infects nematode. Mycologia 2004, 96, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Shi, J.L.; Han, C.C.; Liu, Z.Q.; Guo, J.Y. Isolation and biological activity of triglycerides of the fermented mushroom of Coprinus comatus. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, P.; Markiewicz-Zukowska, R.; Gromkowska-Kepka, K.; Naliwajko, S.K.; Moskwa, J.; Bielecka, J.; Grabia, M.; Borawska, M.; Socha, K. Mushrooms as potential therapeutic agents in the treatment of cancer: Evaluation of anti-glioma effects of Coprinus comatus, Cantharellus cibarius, Lycoperdon perlatum and Lactarius deliciosus extracts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.W.; Chen, N.J.; Wang, C.; Feng, S.; Xu, H. Combined bioremediation of soil co-contaminated with cadmium and endosulfan by Pleurotus eryngii and Coprinus comatus. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2136–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.Y.; Teng, Z.; Ding, S.J. Heterologous expression and characterization of a novel laccase isoenzyme with dyes decolorization potential from Coprinus comatus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falandysz, J. Mercury bio-extraction by fungus Coprinus comatus: A possible bioindicator and mycoremediator of polluted soils? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7444–7451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Jing, Y.; Zheng, X.Q. Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel fibrinolytic enzyme from culture supernatant of Coprinus comatus. Foods 2024, 13, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, P.; Naliwajko, S.K.; Markiewicz-Zukowska, R.; Borawska, M.H.; Socha, K. The two faces of Coprinus comatus—Functional properties and potential hazards. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 2932–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhou, H.B.; Qu, H.; Gao, H.Y. Proteomics reveals the mechanism underlying the autolysis of postharvest Coprinus comatus fruiting bodies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, T.L.; Jiang, H.M.; Gu, Y.F.; Chen, Q.; Yang, C.R.; Qi, W.L.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, X.P. Postharvest biochemical characteristics and ultrastructure of Coprinus comatus. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.B.; Zhang, Z.F.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Xing, X.Y.; Qi, X.J.; Yu, X.D. Transcriptome analysis of genes associated with autolysis of Coprinus comatus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.R.; Zheng, E.P.; Zhou, H.B.; Qu, H.; Yang, H.L. Integration of transcriptomics and metabolomics to reveal the mechanism of allyl isothiocyanate delaying postharvest quality deterioration of Coprinus comatus. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 216, 113075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassen, C.; Kuballa, J.; Rohn, S. Metabolomics-based approach for the discrimination of potato varieties (Solanum tuberosum) using UPLC-IMS-QToF. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5700–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Wu, X.L.; Schaich, K. Standardized methods for the determination of antioxidant capacity and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4290–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free-radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, P.; Ivanovic, K.; Jovanovic, A.; Simovic, M.; Milutinovic, V.; Kozarski, M.; Petkovic, M.; Cvetkovic, A.; Klaus, A.; Bugarski, B. The impact of puffball autolysis on selected chemical and biological properties: Puffball extracts as potential ingredients of skin-care products. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2019, 71, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, I.K.; Halliwell, B. Ergothioneine; antioxidant potential, physiological function and role in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamichi, N.; Tsuzuku, S.; Shibagaki, F. Ergothioneine and central nervous systipe diseases. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodina, I.; Kenny, L.C.; McCarthy, C.M.; Paramasivan, K.; Pretorius, E.; Roberts, T.J.; van der Hoek, S.A.; Kell, D.B. The biology of ergothioneine, an antioxidant nutraceutical. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2020, 33, 190–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Xue, S.; Guo, H.; Dai, Y.; Ji, C.; Dong, L.; Zhang, S. Ergothioneine: New functional factor in fermented foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 7505–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahi, T.; Wu, X.; Shimoda, H.; Hisaka, S.; Harada, E.; Kanno, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kato, Y.; Osawa, T. A mushroom-derived amino acid; ergothioneine, is a potential inhibitor of inflammation-related DNA halogenation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L.; Chen, M.; Guo, Q.; Tong, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y. Comparative proteomics study on the postharvest senescence of Volvariella volvacea. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.; Cheung, M.K.; Clarke, A.; Golding, S.; Sagi, M.; Fluhr, R.; Rock, C.; Hancock, J.; Neill, S. Hydrogen peroxide is a common signal for darkness- and ABA-induced stomatal closure in Pisum sativum. Funct. Plant Biol. 2004, 31, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X. Effect of 60Co-irradiation on postharvest quality and selected enzyme activities of Hypsizygus marmoreus fruit bodies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8126–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classification | Y-CG/Y-ST | M-CG/M-ST | PA-CG/PA-ST | LA-CG/LA-ST | Y-CG/M-CG | M-CG/PA-CG | PA-CG/LA-CG | Y-ST/M-ST | M-ST/PA-ST | PA-ST/LA-ST | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | |
| Alkaloids | 8 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 35 | 26 | 50 | 9 | 4 | 65 | 7 | 14 | 8 | 14 | 2 | |||||
| Lipids | 1 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 58 | 20 | 44 | 6 | 9 | 74 | 12 | 11 | 18 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 6 | 1 | |
| Amino acids derivatives | 4 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 19 | 8 | 24 | 5 | 1 | 30 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 10 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Terpeniods | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 5 | 2 | |||||||||||
| Saccharide | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Quinones | 3 | 3 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Flavonoids | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Phenylpropanoids | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Steroids | 4 | 2 | 14 | 11 | 1 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Others | 3 | 1 | 2 | 13 | 6 | 14 | 7 | 2 | 14 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Sum | 4 | 24 | 13 | 34 | 40 | 145 | 74 | 153 | 21 | 18 | 202 | 33 | 36 | 34 | 26 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 4 |
| Samples | Y-CG | M-CG | PA-CG | LA-CG | Y-ST | M-ST | PA-ST | LA-ST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total phenols (mg/g) | 9.33 ± 0.08 | 8.09 ± 0.13 | 8.12 ± 0.35 | 4.46 ± 0.47 | 10.10 ± 0.02 | 12.48 ± 0.22 | 13.03 ± 0.17 | 7.87 ± 0.27 |
| DPPH∙scavenging activity (%) | 71.8 ± 2.2 | 65.0 ± 8.1 | 88.8 ± 2.4 | 93.7 ± 0.9 | 51.2 ± 3.8 | 52.9 ± 6.9 | 61.1 ± 8.7 | 56.8 ± 3.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ding, G.; Xu, P.; Cheng, Y.; Liang, X.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Y. Metabolomic Revelations into the Dynamic Transformations Across Various Developmental Stages of Coprinus comatus Through UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS Analysis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110703
Wang Y, Ding G, Xu P, Cheng Y, Liang X, Wu C, Yang Z, Ma Y. Metabolomic Revelations into the Dynamic Transformations Across Various Developmental Stages of Coprinus comatus Through UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS Analysis. Metabolites. 2025; 15(11):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110703
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Guangsheng Ding, Peng Xu, Yun Cheng, Xuan Liang, Chunying Wu, Zhi Yang, and Yatuan Ma. 2025. "Metabolomic Revelations into the Dynamic Transformations Across Various Developmental Stages of Coprinus comatus Through UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS Analysis" Metabolites 15, no. 11: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110703
APA StyleWang, Y., Ding, G., Xu, P., Cheng, Y., Liang, X., Wu, C., Yang, Z., & Ma, Y. (2025). Metabolomic Revelations into the Dynamic Transformations Across Various Developmental Stages of Coprinus comatus Through UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS Analysis. Metabolites, 15(11), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15110703







